Effect of Different Air Oven Temperatures on Chemical, Physical, and Microbial Properties of Dried Bio-Yoghurt Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Yoghurt Production
2.2.1. Yoghurt Analysis
Chemical Composition
Physiochemical Tests
Starter Bacteria Count
2.3. Yoghurt Drying
2.4. Reconstitution of Dried Yoghurt
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bio-Yoghurt Properties
3.2. Dried Yoghurt Properties
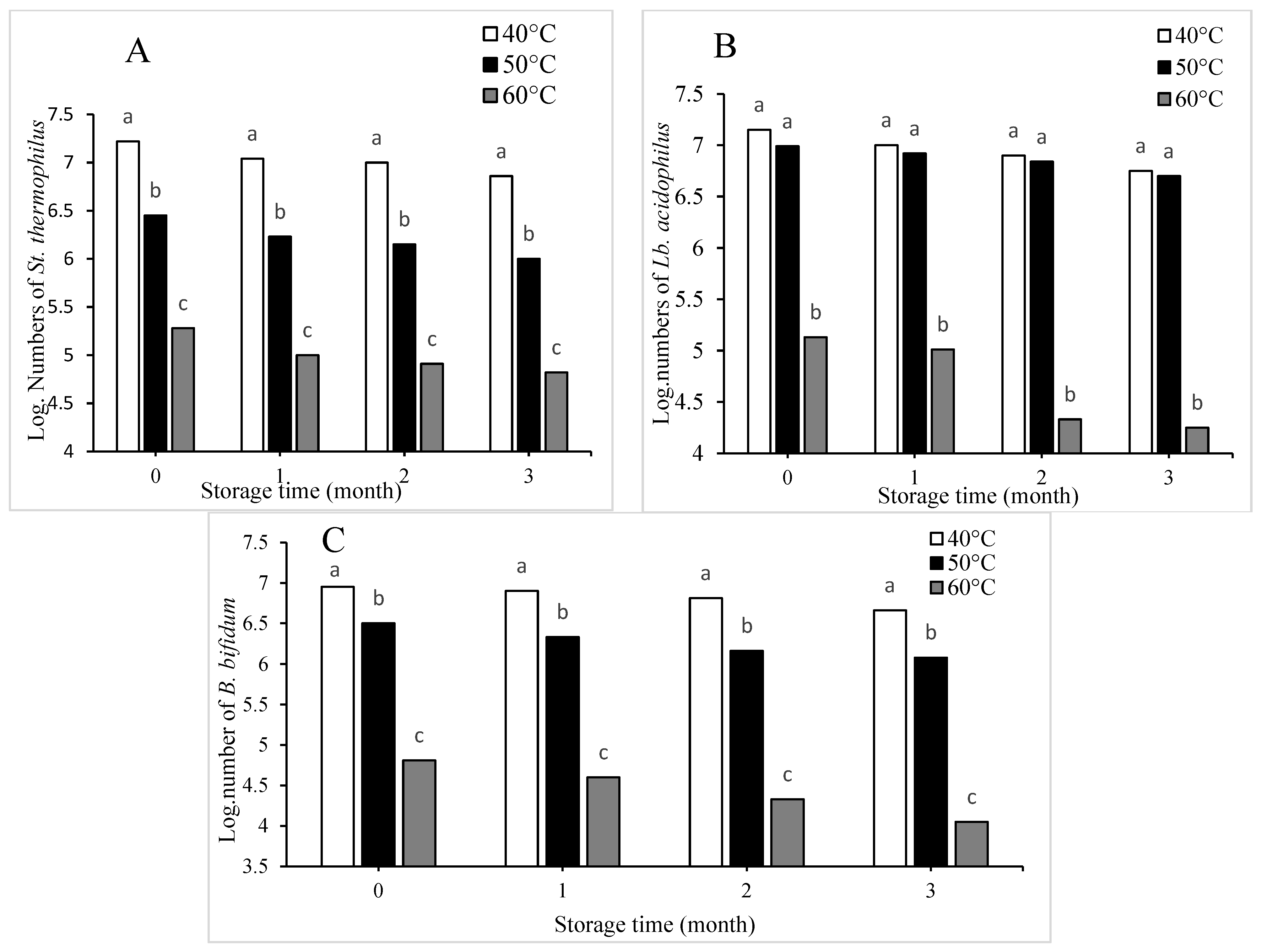
3.3. Bacteria Starter Count
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kok, C.R.; Hutkins, R. Yogurt and Other Fermented Foods as Sources of Health-Promoting Bacteria. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjimbei, E.; Botsaris, G.; Chrysostomou, S. Beneficial Effects of Yoghurts and Probiotic Fermented Milks and Their Functional Food Potential. Foods 2022, 11, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kadamany, E.; Khattar, M.; Haddad, T.; Toufeili, I. Estimation of Shelf-Life of Concentrated Yogurt by Monitoring Selected Microbiological and Physicochemical Changes during Storage. LWT 2003, 36, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, N.; James, S.; Blessing, O.O. Development and Comparative Evaluation of Storage Changes in Probiotic Soy-Yoghurt. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 9, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mishra, H.N. Yoghurt Powder—A Review of Process Technology, Storage and Utilization. Food Bioprod. Process. 2004, 82, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasaekoopt, W.; Bhatia, S. Production of Yogurt Powder Using Foam-Mat Drying. AU J. Technol. 2012, 15, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Myllärinen, P.; Crittenden, R.; Mogensen, G.; Fond, R.; Saarela, M. Technological Challenges for Future Probiotic Foods. Int. Dairy J. 2002, 12, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysona Ar, Ö.; Ocak, E. Storage of Yoghurt Powder Obtained by Different Drying Methods and Its Use in Reconstituted Ayran Production. Yuz. Yil Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 32, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Khassaf, W.H.; Niamah, A.K.; Al-Manhel, A.J. Date Juice Addition to Bio-Yogurt: The Effects on Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties during Storage, as Well as Blood Parameters in Vivo. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2023, 22, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K. Physicochemical and Microbial Characteristics of Yogurt with Added Saccharomyces boulardii. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 5, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-fekaiki, D.F.; Thyab Gddoa Al-Sahlany, S.; Verma, D.K.; Patel, A.R.; Singh, S. Investigating the Effect of Addition of Probiotic Microorganisms (Bacteria or Yeast) to Yoghurt on the Viability and Volatile Aromatic Profiles. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5463–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S. Yogurt Production. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 1887, pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. International A: Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC International, 17th ed.; The Association: Arlington County, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bensoltane, A.; Fadela, C.; Abderrahim, C.; Ahmed, B. Physico-chemical and rheological properties of yoghurt manufactured with ewe’s milk and skim milk. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Niamah, A.K.; Thyab, S.; Al-Sahlany, G.; Al-Manhel, A.J. Gum Arabic Uses as Prebiotic in Yogurt Production and Study Effects on Physical, Chemical Properties and Survivability of Probiotic Bacteria During Cold Storage. World Appl. Sci. J. 2016, 34, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K. Ultrasound Treatment (Low Frequency) Effects on Probiotic Bacteria Growth in Fermented Milk. Future Food J. Food Agric. Soc. 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontul, İ.; Ergin, F.; Eroğlu, E.; Küçükçetin, A.; Topuz, A. Physical and Microbiological Properties of Yoghurt Powder Produced by Refractance Window Drying. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 85, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S. Suzanne. In Food Analysis; Aspen Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; ISBN 083421203X. [Google Scholar]
- Özaslan, M.S.; Demir, Y.; Aksoy, M.; Küfrevioğlu, Ö.I.; Beydemir, Ş. Inhibition Effects of Pesticides on Glutathione-S-Transferase Enzyme Activity of Van Lake Fish Liver. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetachukwu, A.S.; Thongraung, C.; Yupanqui, C.T. Development of Reduced-Fat Coconut Yoghurt: Physicochemical, Rheological, Microstructural and Sensory Properties. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosry Abdel Halim, E.; El-Essawy, H.; Abdel Nasser Awad, A.; El-Kutry, M.S.; Ibrahim Ahmed, L. Estimating the Microbial Safety and Sensory Characteristics of Some Imported Dairy Products Retailed in the Egyptian Markets. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2022, 10, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybodi, N.M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Arab, M.; Nematollahi, A. Probiotic Viability in Yoghurt: A Review of Influential Factors. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.P.; Mota, M.J.; Sousa, S.; Gomes, A.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Saraiva, J.A. Combined Effect of Pressure and Temperature for Yogurt Production. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatloo, N.V.; Mehdizadeh, T.; Aliakbarlu, J.; Tahmasebi, R. Physicochemical, Sensory and Microbiological Characteristics of Coriander Seed Powder Yogurt. AMB Express 2023, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüksel, A.N. Development of Yoghurt Powder Using Microwave-Assisted Foam-Mat Drying. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2834–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koc, B.; Yilmazer, M.S.; Balkir, P.; Ertekin, F.K. Spray Drying of Yogurt: Optimization of Process Conditions for Improving Viability and Other Quality Attributes. Dry. Technol. 2010, 28, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronoiu, D.-G.; Nistor, O.-V.; Mocanu, G.-D.; Barbu, V.; Botez, E.; Petroiu, M. Quality characteristics of yoghurt powder obtained by hybrid drying methods. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2019, 29, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, G.D.; Nunes, T.P.; Silva, M.A.A.P.; Rosenthal, A.; Pagani, A.A.C. Development and Acceptance of Freeze-Dried Yogurt “Powder Yogurt”. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Tereshchenko, A.G. Dynamic Method for the Determination of Hygroscopicity of Water-Soluble Solids. J Solut. Chem. 2020, 49, 1029–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.İ. The Effect of Different Lyophilisation Pressures on the Microbiological Stability, Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Sensorial Properties of Yoghurt Powders. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 129, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornuk, F.; Ozturk, I.; Karaman, S.; Sagdic, O.; Yetim, H. Rheological and Some Physicochemical Properties of Probiotic Boza Beverage Fermented with Lactobacillus Casei Shirota: Application of Principal Component Analysis for the Characterisation. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2014, 6, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, Y.H. Importance of glass transition and water activity to spray drying and stability of dairy powders. Le Lait 2002, 82, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya, S. Microstructure analysis of dried yogurt: Effect of different drying methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirjantoro, T.I.; Phianmongkhol, A. The viability of lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacterium bifidum in yoghurt powder during storage. J. Nat. Sci. 2009, 8, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Niamah, A.K.; Gddoa Al-Sahlany, S.T.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Singh, S.; Patel, A.R.; Aguilar, C.N.; Utama, G.L. Electro-Hydrodynamic Processing for Encapsulation of Probiotics: A Review on Recent Trends, Technological Development, Challenges and Future Prospect. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiepś, J.; Dembczyński, R. Current Trends in the Production of Probiotic Formulations. Foods 2022, 11, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, H.S.; Salama, H.H.; Edris, A.E. Survival of Lactobacillus Helveticus CNRZ32 in Spray Dried Functional Yogurt Powder during Processing and Storage. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tests | Value * | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Protein (N × 6.38) % | 5.17 ± 0.13 |
| Carbohydrates (lactose)% | 5.02 ± 0.09 | |
| Ash (%) | 1.10 ± 0.01 | |
| Moisture (%) | 88.45 ± 5.06 | |
| Fat (%) | 0.26 ± 0.00 | |
| Physical | pH | 4.33 ± 0.11 |
| Total acidity (%) | 1.12 ± 0.03 | |
| Viscosity (cp) | 1645 ± 35.19 | |
| Syneresis (%) | 29.14 ± 2.15 | |
| Water-holding capacity (%) | 55.79 ± 3.36 | |
| Microbial | St. thermophilus (log CFU/g) | 8.86 ± 0.29 |
| Lb. acidophilus (log CFU/g) | 8.72 ± 0.41 | |
| B. bifidium (log CFU/g) | 8.71 ± 0.25 | |
| Chemical Ingredients | Treatments (°C) | Storage Periods (Months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Protein (N × 6.38) % | 40 | 37.51 c ± 2.13 | 37.58 b ± 2.63 | 37.70 ab ± 1.84 | 37.78 ab ± 2.31 |
| 50 | 38.49 b ± 1.11 | 38.43 b ± 1.90 | 38.28 a ± 1.55 | 38.61 a ± 1.34 | |
| 60 | 39.28 a ± 1.18 | 39.41 a ± 1.43 | 39.46 a ± 1.31 | 39.59 a ± 1.01 | |
| Carbohydrates (lactose) % | 40 | 50.16 a ± 2.95 | 50.11 a ± 3.15 | 50.09 a ± 3.11 | 50.07 a ± 2.97 |
| 50 | 49.29 a ± 2.61 | 49.37 a ± 2.10 | 49.56 a ± 2.01 | 49.22 a ± 2.41 | |
| 60 | 48.68 ab ± 1.99 | 48.64 ab ± 2.39 | 48.66 b ± 2.19 | 48.61 ab ± 2.59 | |
| Ash (%) | 40 | 6.37 a ± 0.12 | 6.38 a ± 0.31 | 6.38 a ± 0.22 | 6.40 a ± 0.19 |
| 50 | 6.37 a ± 0.10 | 6.40 a ± 0.22 | 6.38 a ± 0.09 | 6.44 a ± 0.11 | |
| 60 | 6.55 a ± 0.19 | 6.50 a ± 0.81 | 6.44 a ± 0.41 | 6.40 a ± 0.21 | |
| Moisture (%) | 40 | 4.55 a ± 0.06 | 4.52 a ± 0.10 | 4.42 a ± 0.11 | 4.33 a ± 0.09 |
| 50 | 4.42 a ± 0.01 | 4.40 a ± 0.12 | 4.38 a ± 0.15 | 4.33 a ± 0.18 | |
| 60 | 4.16 a ± 0.02 | 4.12 ba ± 0.09 | 4.08 a ± 0.08 | 4.00 a ± 0.05 | |
| Fat (%) | 40 | 1.41 a ± 0.01 | 1.41 a ± 0.02 | 1.41 a ± 0.01 | 1.42 a ± 0.01 |
| 50 | 1.43 a ± 0.03 | 1.40 a ± 0.05 | 1.40 a ± 0.05 | 1.40 a ± 0.02 | |
| 60 | 1.33 a ± 0.04 | 1.33 a ± 0.06 | 1.36 a ± 0.01 | 1.40 a ± 0.01 | |
| Physical Properties | Treatments (°C) | Storage Periods (Months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| pH | 40 | 4.60 a ± 0.17 | 4.55 a ± 0.12 | 4.50 a ± 0.16 | 4.31 a ± 0.09 |
| 50 | 4.32 a ± 0.14 | 4.30 a ± 0.11 | 4.29 a ± 0.10 | 4.25 a ± 0.13 | |
| 60 | 4.11 b ± 0.41 | 4.10 b ± 0.22 | 4.06 b ± 0.31 | 4.00 a ± 0.17 | |
| Total acidity (%) | 40 | 1.35 a ± 0.02 | 1.39 a ± 0.05 | 1.40 a ± 0.03 | 1.41 a ± 0.08 |
| 50 | 1.36 a ± 0.01 | 1.38 a ± 0.01 | 1.40 a ± 0.05 | 1.44 a ± 0.07 | |
| 60 | 1.36 a ± 0.01 | 1.37 a ± 0.08 | 1.40 a ± 0.01 | 1.41 a ± 0.02 | |
| Viscosity (cp) | 40 | 600.00 a ± 15.31 | 550.00 a ± 12.61 | 510.00 a ± 32.00 | 450.00 b ± 44.15 |
| 50 | 620.00 a ± 11.11 | 580.00 a ± 10.17 | 530.00 a ± 21.09 | 500.00 a ± 26.74 | |
| 60 | 550.00 b ± 19.28 | 525.00 a ± 10.73 | 510.00 a ± 17.71 | 500.00 a ± 21.19 | |
| WHC (%) | 40 | 36.11 a ± 1.25 | 36.23 a ± 1.39 | 36.29 b ± 1.11 | 37.01 b ± 1.95 |
| 50 | 37.00 a ± 1.09 | 37.23 a ± 1.13 | 37.50 a ± 1.34 | 37.73 a ± 1.35 | |
| 60 | 37.00 a ± 1.36 | 37.21 a ± 1.94 | 37.56 a ± 1.68 | 38.03 a ± 1.61 | |
| Hygroscopicity (%) | 40 | 9.69 a ± 0.42 | 9.55 a ± 0.64 | 9.42 a ± 0.55 | 9.21 a ± 0.91 |
| 50 | 9.55 a ± 0.16 | 9.50 a ± 0.27 | 9.40 a ± 0.31 | 9.16 a ± 0.63 | |
| 60 | 9.15 b ± 0.22 | 9.10 b ± 0.37 | 8.98 b ± 0.81 | 8.87 b ± 0.62 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaafar, F.E.; Rubaiy, H.H.M.A.; Niamah, A.K. Effect of Different Air Oven Temperatures on Chemical, Physical, and Microbial Properties of Dried Bio-Yoghurt Product. Dairy 2024, 5, 44-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy5010004
Jaafar FE, Rubaiy HHMA, Niamah AK. Effect of Different Air Oven Temperatures on Chemical, Physical, and Microbial Properties of Dried Bio-Yoghurt Product. Dairy. 2024; 5(1):44-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaafar, Fatimah Eesee, Hassan Hadi Mehdi Al Rubaiy, and Alaa Kareem Niamah. 2024. "Effect of Different Air Oven Temperatures on Chemical, Physical, and Microbial Properties of Dried Bio-Yoghurt Product" Dairy 5, no. 1: 44-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy5010004
APA StyleJaafar, F. E., Rubaiy, H. H. M. A., & Niamah, A. K. (2024). Effect of Different Air Oven Temperatures on Chemical, Physical, and Microbial Properties of Dried Bio-Yoghurt Product. Dairy, 5(1), 44-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy5010004







