First Insight into the Variation of the Milk Serum Proteome within and between Individual Cows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
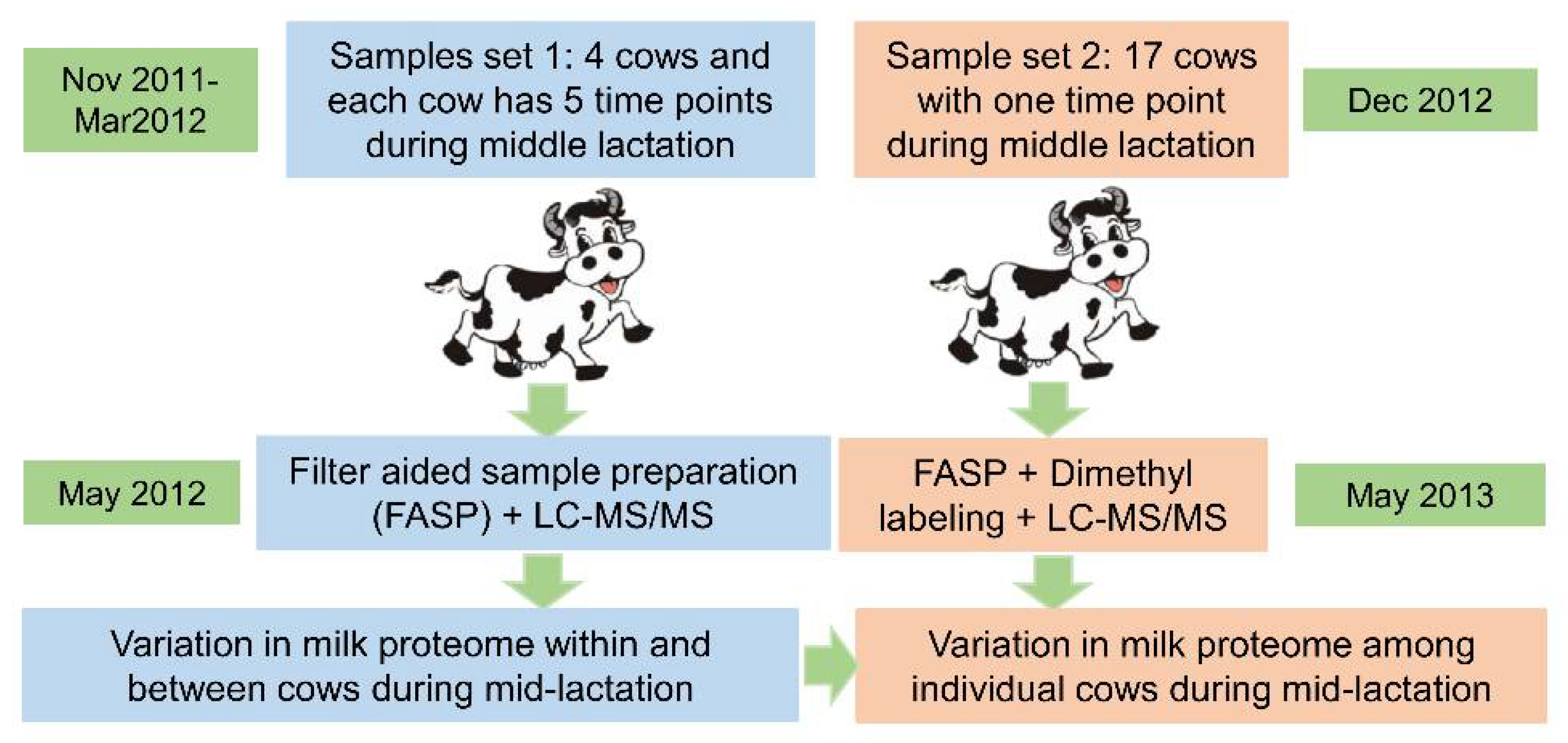
2.1. Samples
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Milk Serum Separation
2.2.2. Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Assay
2.2.3. Filter-Aided Sampled Preparation (FASP)
2.2.4. Dimethyl Labeling
2.2.5. LC-MS/MS
2.2.6. Data Analyses
3. Results
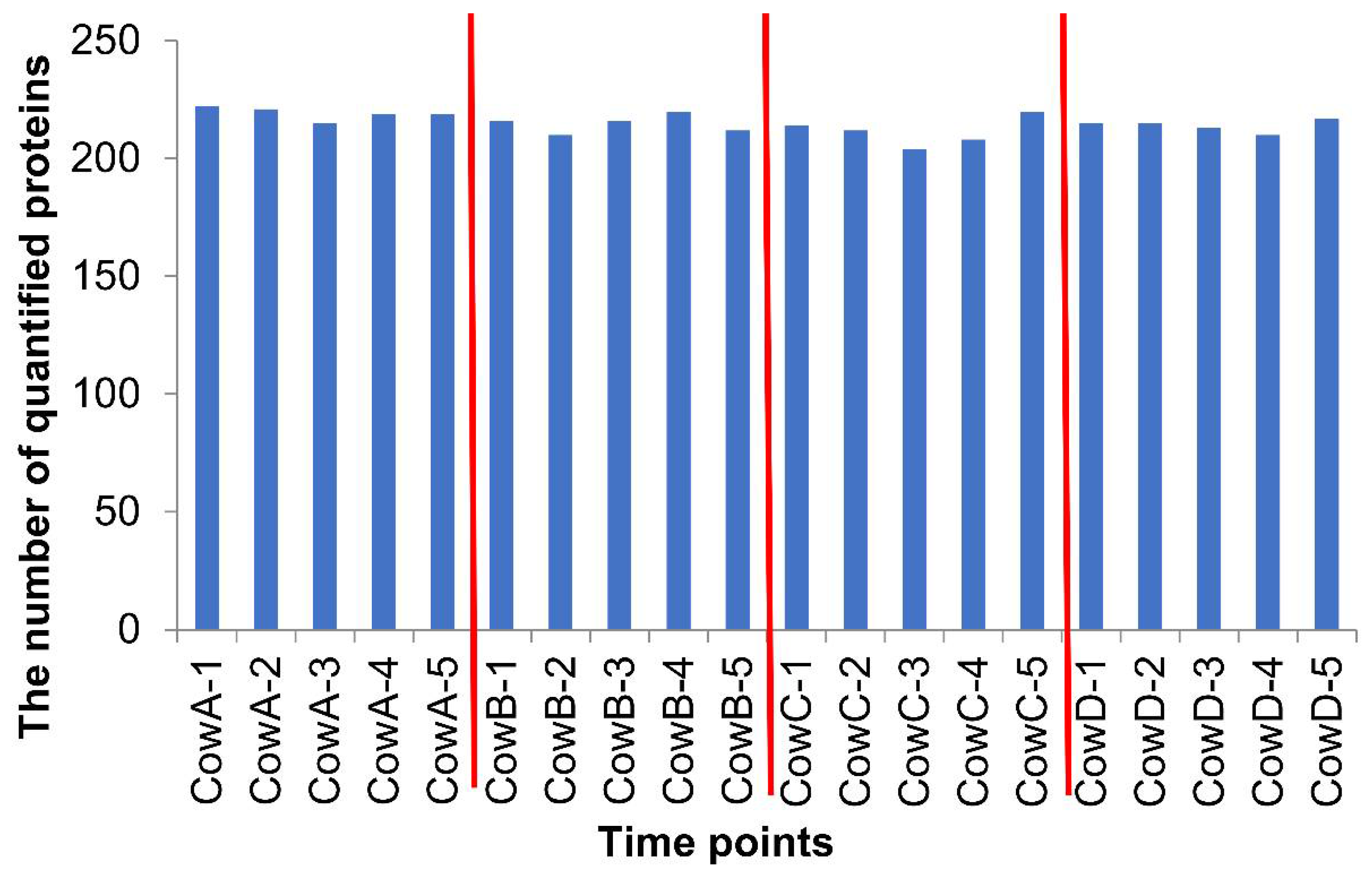
3.1. The Identified and Quantified Proteome in Sample Set 1
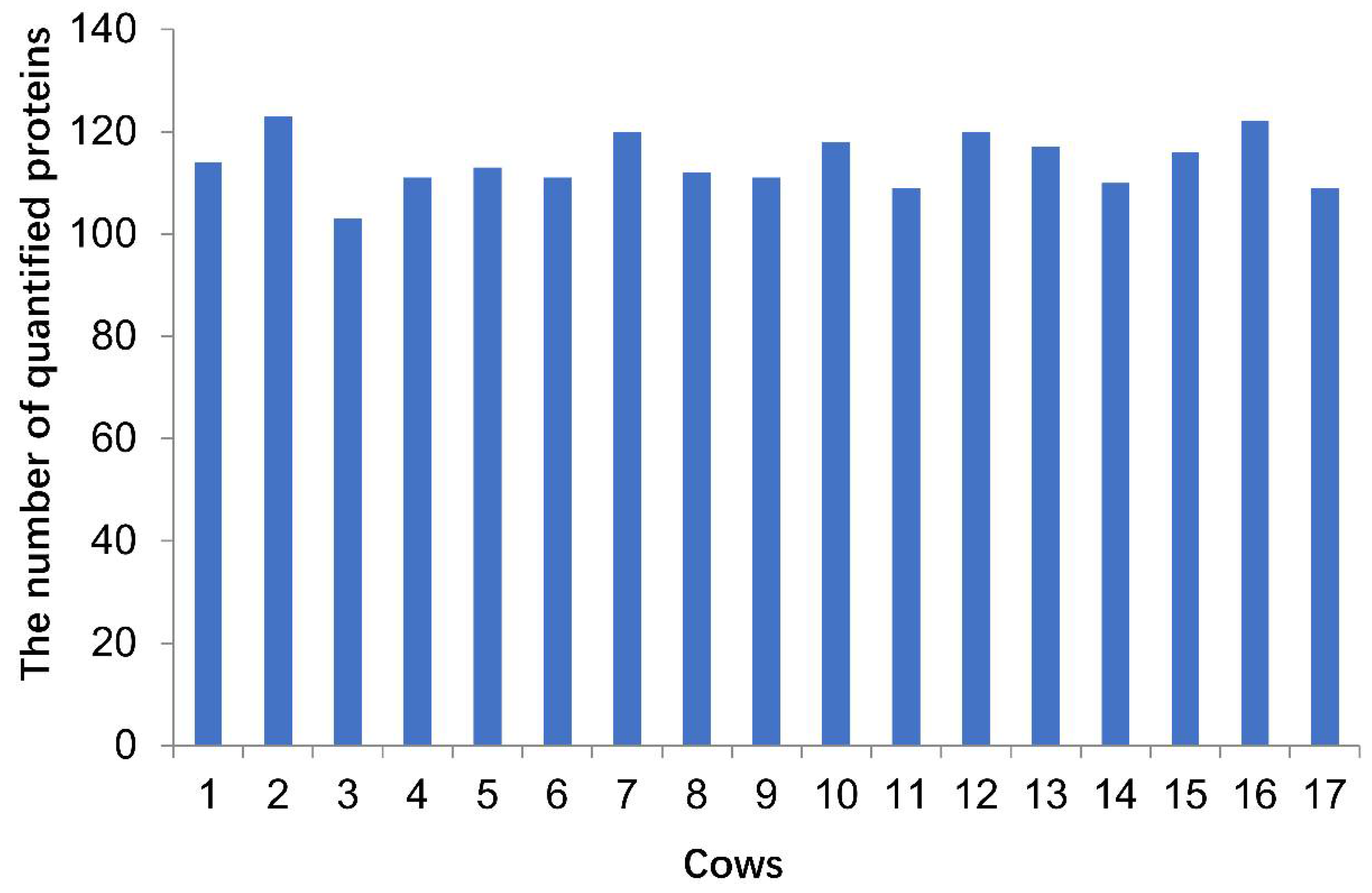
3.2. The Identified and Quantified Proteome in Sample Set 2
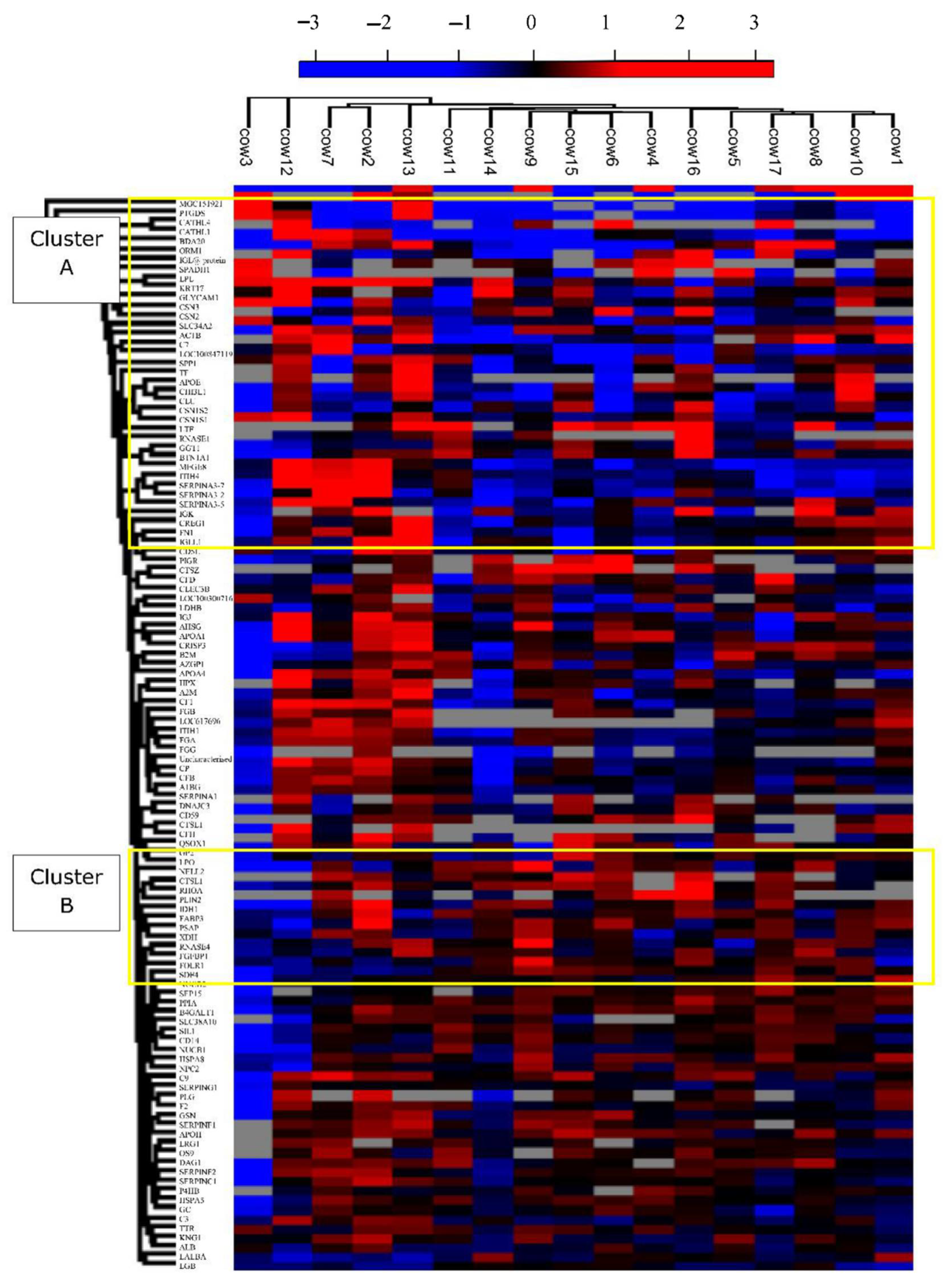
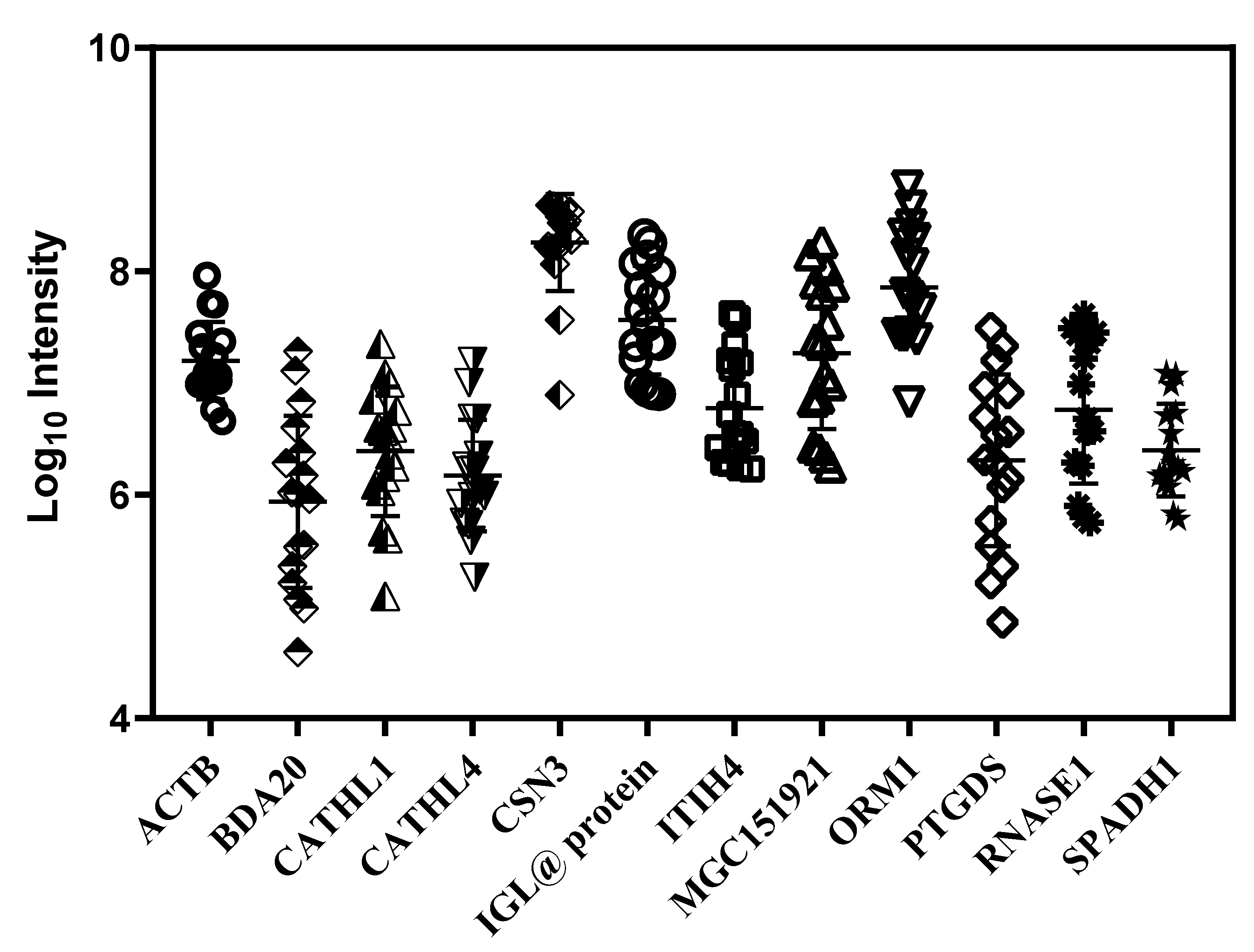
3.3. Quantitative Variation in Milk Serum Proteome between Individuals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Dingess, K.A. The Functional Power of the Human Milk Proteome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeds, P.J.; Burrin, D.G.; Davis, T.A.; Fiorotto, M.L.; Stoll, B.; van Goudoever, J.B. Protein nutrition of the neonate. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maity, S.; Bhat, A.H.; Giri, K.; Ambatipudi, K. BoMiProt: A database of bovine milk proteins. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurmayr, A.; Pegolo, S.; Malchiodi, F.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A. Milk protein composition in purebred Holsteins and in first/second-generation crossbred cows from Swedish Red, Montbeliarde and Brown Swiss bulls. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2018, 12, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, R.; Rošić, N.; Kuleš, J.; Horvatić, A.; Gelemanovic, A.; Galen, A.; Ljubić, B.B.; Benić, M.; Stevanović, V.; Mrljak, V.; et al. Milk and serum proteomes in subclinical and clinical mastitis in Simmental cows. J. Proteom. 2021, 244, 104277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Boeren, S.; Hageman, J.A.; van Hooijdonk, T.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Bovine milk proteome in the first 9 days: Protein interactions in maturation of the immune and digestive system of the newborn. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Boeren, S.; Hageman, J.A.; van Hooijdonk, T.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Perspective on calf and mammary gland development through changes in the bovine milk proteome over a complete lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5362–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, P. Changes in milk fat globule membrane proteome after pasteurization in human, bovine and caprine species. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Boeren, S.; De Vries, S.; van Valenberg, H.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Filter-aided sample preparation with dimethyl labeling to identify and quantify milk fat globule membrane proteins. J. Proteom. 2011, 75, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersema, P.J.; Raijmakers, R.; Lemeer, S.; Mohammed, S.; Heck, A.J. Multiplex peptide stable isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwanhäusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, G., Jr.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Harten, R.M.; van Woudenbergh, E.; van Dijk, A. Cathelicidins: Immunomodulatory Antimicrobials. Vaccines 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soler, L.; Dąbrowski, R.; García, N.; Alava, M.A.; Lampreave, F.; Piñeiro, M.; Wawron, W.; Szczubiał, M.; Bochniarz, M. Acute-phase inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 (ITIH4) levels in serum and milk of cows with subclinical mastitis caused by Streptococcus species and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hettinga, K.A.; Reina, F.M.; Boeren, S.; Zhang, L.; Koppelman, G.H.; Postma, D.S.; Vervoort, J.J.; Wijga, A.H. Difference in the breast milk proteome between allergic and non-allergic mothers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oetjen, L.K.; Kim, B.S. Interactions of the immune and sensory nervous systems in atopy. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3138–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blalock, J.E. The immune system as a sensory organ. J. Immunol. 1984, 132, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Jankovic, M.; Petrovic, B.; Novakovic, I. Genetic Aspects of Inflammation and Immune Response in Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson-Crispi, K.A.; Sargolzaei, M.; Ventura, R.; Abo-Ismail, M.; Miglior, F.; Schenkel, F.; Mallard, B.A. A genome-wide association study of immune response traits in Canadian Holstein cattle. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordero-Solorzano, J.; Parmentier, H.K.; Arts, J.A.J.; van der Poel, J.; de Koning, D.J.; Bovenhuis, H. Genome-wide association study identifies loci influencing natural antibody titers in milk of Dutch Holstein-Friesian cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11092–11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, S.C.; Graham, D.A.; Sayers, R.G.; Byrne, N.; Kelleher, M.M.; Doherty, M.L.; Berry, D.P. Genetic variability in the humoral immune response to bovine herpesvirus-1 infection in dairy cattle and genetic correlations with performance traits. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6190–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Schlitzer, A.; Placek, K.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Schultze, J.L. Innate and Adaptive Immune Memory: An Evolutionary Continuum in the Host’s Response to Pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, X. Epigenetic regulation of the innate immune response to infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; van Hooijdonk, T.; Boeren, S.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Identification of lipid synthesis and secretion proteins in bovine milk. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren-Babol, L.; Jägerstad, M. Folate-binding protein in milk: A review of biochemistry, physiology, and analytical methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Schuit, F.; Antonio, L.; Rastinejad, F. Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, S. Amino Acid Metabolism in Dairy Cows and their Regulation in Milk Synthesis. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wei, J.; Hao, L.; Shan, Q.; Li, H.; Gao, D.; Jin, Y.; Sun, P. Bioactive Proteins and their Physiological Functions in Milk. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.A.; Yada, R.Y.; Rousseau, D. Interactions of vitamin D3 with bovine beta-lactoglobulin A and beta-casein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8003–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cow | Parity | SCC (×1000 Cells/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Cow A | 5 | 148 |
| 55 | ||
| 184 | ||
| 131 | ||
| 128 | ||
| Cow B | 3 | 192 |
| 58 | ||
| 29 | ||
| 38 | ||
| 28 | ||
| Cow C | 3 | 133 |
| 17 | ||
| 22 | ||
| 39 | ||
| 34 | ||
| Cow D | 2 | 27 |
| 34 | ||
| 31 | ||
| 27 | ||
| 25 |
| Cow | Lactation Stage | SCC (103) | Parity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 174 | 205 | 3 |
| 2 | 162 | 197 | 2 |
| 3 | 136 | 185 | 3 |
| 4 | 245 | 270 | 4 |
| 5 | 203 | 234 | 3 |
| 6 | 226 | 261 | 2 |
| 7 | 247 | 268 | 2 |
| 8 | 186 | 217 | 3 |
| 9 | 202 | 237 | 2 |
| 10 | 120 | 165 | 5 |
| 11 | 222 | 243 | 2 |
| 12 | 222 | 247 | 4 |
| 13 | 190 | 221 | 3 |
| 14 | 204 | 239 | 2 |
| 15 | 112 | 151 | 2 |
| 16 | 162 | 207 | 3 |
| 17 | 151 | 200 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Boeren, S.; Heck, J.; Vervoort, J.; Zhou, P.; Hettinga, K. First Insight into the Variation of the Milk Serum Proteome within and between Individual Cows. Dairy 2022, 3, 47-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3010004
Zhang L, Boeren S, Heck J, Vervoort J, Zhou P, Hettinga K. First Insight into the Variation of the Milk Serum Proteome within and between Individual Cows. Dairy. 2022; 3(1):47-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lina, Sjef Boeren, Jeroen Heck, Jacques Vervoort, Peng Zhou, and Kasper Hettinga. 2022. "First Insight into the Variation of the Milk Serum Proteome within and between Individual Cows" Dairy 3, no. 1: 47-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3010004
APA StyleZhang, L., Boeren, S., Heck, J., Vervoort, J., Zhou, P., & Hettinga, K. (2022). First Insight into the Variation of the Milk Serum Proteome within and between Individual Cows. Dairy, 3(1), 47-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy3010004






