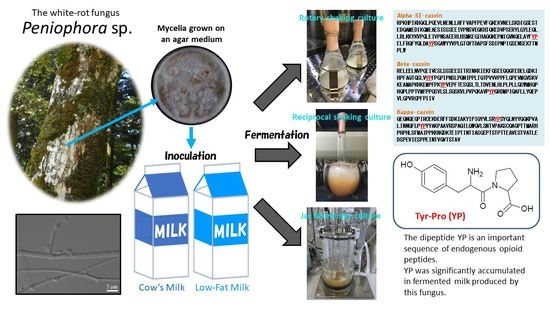
Production of the Antihypertensive Peptide Tyr-Pro from Milk Using the White-Rot Fungus Peniophora sp. in Submerged Fermentation and a Jar Fermentor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Analysis of YP and Aromatic Amino Acids in Fermented Milk
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.4. Assay of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Activity
3. Results and Discussion
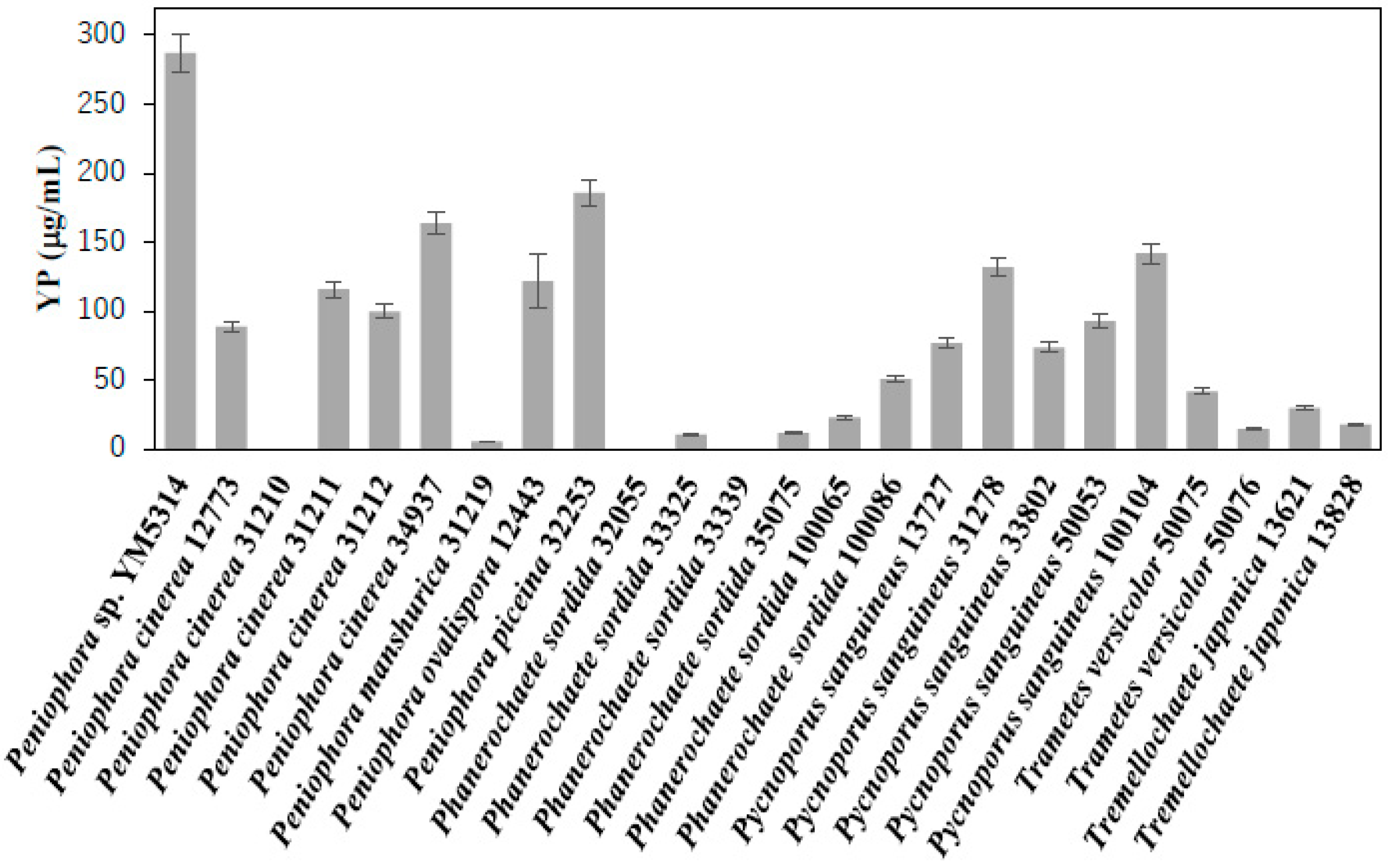
3.1. Screening of a Basidiomycete Fungus Suitable for YP Production
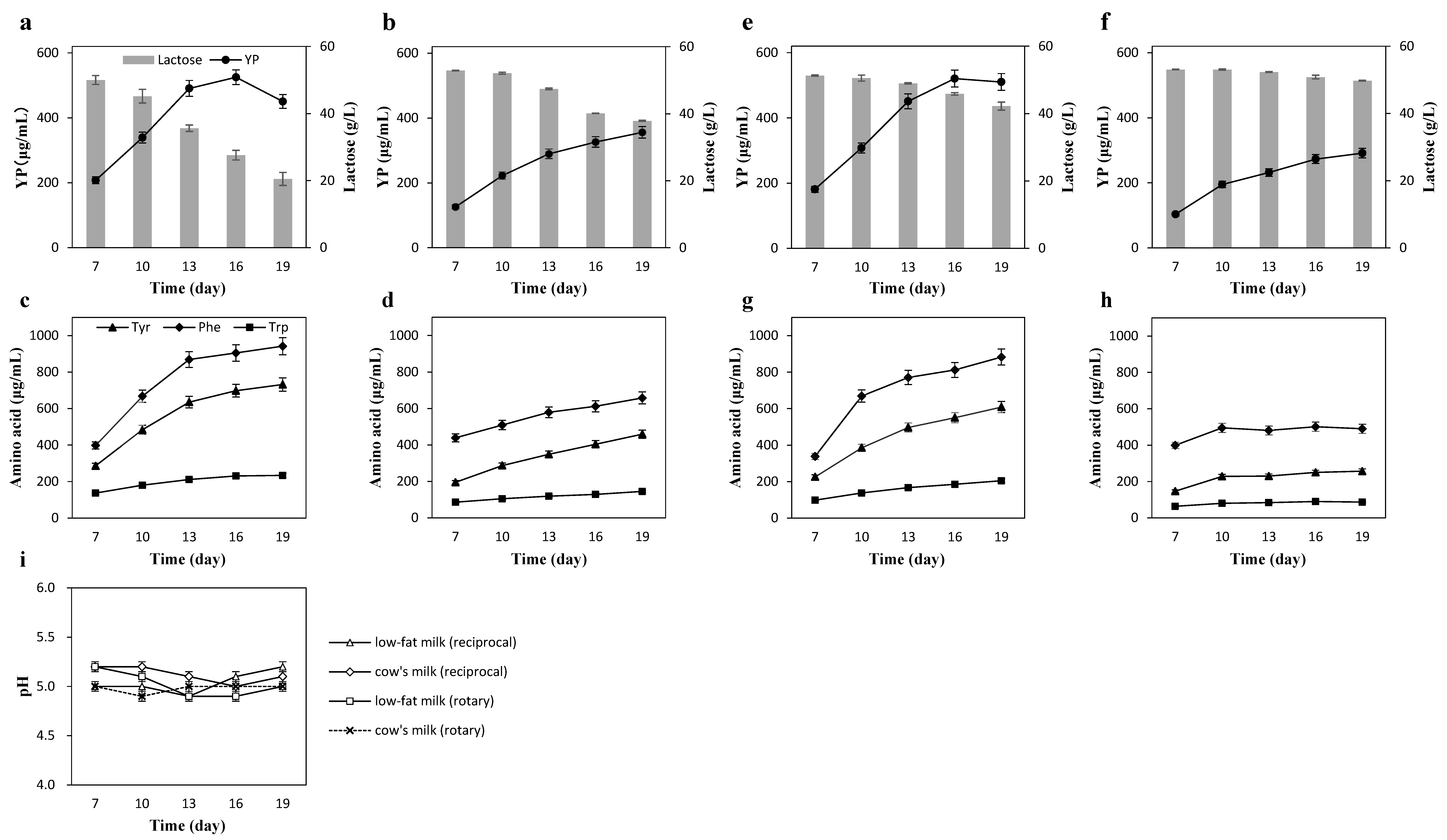
3.2. Effects of Shaking Conditions on YP Production
3.3. Transcriptome Analysis
3.4. YP Production and ACE-Inhibitory Activity in a Jar Fermentor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: Challenges and opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, R.J.; Murray, B.A. Bioactive peptides and lactic fermentations. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hengst, C.D.; Curley, P.; Larsen, R.; Buist, G.; Nauta, A.; van Sinderen, D.; Kuipers, O.P.; Kok, J. Probing direct interactions between CodY and the oppD promoter of Lactococcus lactis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakai, T.; Yamamoto, N. A novel branched chain amino acids responsive transcriptional regulator, BCARR, negatively acts on the proteolytic system in Lactobacillus helveticus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holton, T.A.; Vijayakumar, V.; Khaldi, N. Bioinformatics: Current perspectives and future directions for food and nutritional research facilitated by a Food-Wiki database. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokozeki, K.; Hara, S. A novel and efficient enzymatic method for the production of peptides from unprotected starting materials. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 115, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Arimura, Y.; Ishikura, S.; Kino, K. l-Amino acid ligase from Pseudomonas syringae producing tabtoxin can be used for enzymatic synthesis of various functional peptides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5023–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.S.; Cho, H.Y.; Yang, H.C.; Ra, K.S.; Suh, H.J. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from Grifola frondosa. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the edible mushroom Tricholoma giganteum. Peptides 2004, 25, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.C.; Lee, D.H.; Yu, H.E.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.S. Production and characterization of antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from Pholiota adiposa. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 16, 757–763. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.H.; Jeong, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Ju, Y.C.; Lee, J.S. Characterisation of a new antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Pleurotus cornucopiae. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from an edible mushroom, Pleurotus cystidiosus O.K. Miller identified by LC-MS/MS. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Bolormaa, Z.; Kim, M.K.; Seo, G.S.; Lee, J.S. Characterization of an antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from the edible mushroom Hypsizygus marmoreus. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 283964. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S.; Aminudin, N. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (J. E. Lange) Imbach identified by LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ansor, N.M.; Abdullah, N.; Aminudin, N. Anti-angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) proteins from mycelia of Ganoderma lucidum (Curtis) P. Karst. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ryu, M.; Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. Isolation of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory protein with antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats from the edible wild mushroom Leucopaxillus tricolor. Molecules 2015, 20, 10141–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. A Tricholoma matsutake peptide with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidative activities and antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Kanawaku, R.; Kawamura, S. Ethanol production from cheese whey and expired milk by the brown rot fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Fermentation 2019, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, N.; Maeno, M.; Takano, T. Purification and characterization of antihypertensive peptide from a yogurt-like product fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus CPN4. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Kawamura, S.; Tagawa, M.; Mizuta, T.; Zahid, H.M.; Nabika, T. Production of an antihypertensive peptide from milk by the brown rot fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Yoneda, M.; Fumioka, T. Isolation of a Peniophora strain capable of producing ethanol from starch and kitchen waste. Ferment. Technol. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, D.W.; Cheung, H.S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1970, 20, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Liao, J.H.; Li, F.G.; Wang, H.C. Studies on the genetic basis of esterase isozyme loci Est A, B and C in Agaricus bisporus. Mushroom Sci. 1991, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, P. The isozyme pattern of esterase and fuzzy clustering analysis of Lentinus edodes strains. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2000, 15, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.S.; Ko, H.C. Glucose stimulates production of the alkaline-thermostable lipase of the edible Basidiomycete Antrodia cinnamomea. Enz. Microb. Technol. 2005, 37, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.H.; Xu, C.J.; Lin, G.C. Purification and partial characterization of a lipase from Antrodia cinnamomea. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krügener, S.; Zelena, K.; Zorn, H.; Nimtz, M.; Berger, R.G. Heterologous expression of an extracellular lipase from the basidiomycete Pleurotus sapidus. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 57, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelena, K.; Krügener, S.; Lunkenbein, S.; Zorn, H.; Berger, R.G. Functional expression of the lipase gene Lip2 of Pleurotus sapidus in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett. 2009, 31, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Singh, J.; Kumar, M.; Thakur, I.S. Novel lipase from basidiomycetes Schizophyllum commune ISTL04, produced by solid state fermentation of Leucaena leucocephala seeds. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 110, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, A.; Tarallo, V.; Guarino, L.; Sannia, G.; Birolo, L.; Pezzella, C. New lipases by mining of Pleurotus ostreatus genome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure-activity relationship study of di- and tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiyama, M.; Itoh, Y. Polyphenol oxidase production in a jar fermentor by Coriolus versicolor. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1994, 78, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, O.V.; Stepanova, E.V.; Gavrilova, V.P.; Yakovleva, N.S.; Landesman, E.O.; Yavmetdinov, I.S.; Yaropolov, A.I. Laccase and Mn-peroxidase production by Coriolus hirsutus strain 075 in a jar fermentor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 93, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berovic, M.; Podgornik, B.B. Engineering aspects of Lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum (Agaricomycetes) biomass submerged cultivation in bioreactors: A Review. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berovic, M.; Podgornik, B.B. Engineering aspects in production of various medicinal mushrooms biomass in submerged bioreactors. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónai, A.Z.; Szemenyei, E.; Kató, E.; Kocsis, L.; Orosz, G.; Al-Khrasani, M.; Tóth, G. Endomorphin synthesis in rat brain from intracerebroventricularly injected [3H]-Tyr-Pro: A possible biosynthetic route for endomorphins. Regul. Pept. 2006, 134, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzevatykh, L.S.; Voronina, T.A.; Emel’yanova, T.G.; Andreeva, L.A.; Alfeeva, L.Y.; Seredenin, S.B.; Myasoedov, N.F. Analgesic activity of dipeptide Tyr–Pro. Biol. Bull. 2008, 35, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Dohgu, S.; Komabayashi, G.; Kiyohara, H.; Takata, F.; Kataoka, Y.; Nirasawa, T.; Maebuchi, M.; Matsui, T. Brain-transportable dipeptides across the blood-brain barrier in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Contig Length | Putative Proteolytic Enzymes | FPKM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (bp) | 3 Days | 7 Days | |
| 2288 | Acid protease | 0 | 3.62 |
| 2737 | Metalloprotease | 0 | 0.11 |
| 227 | Zn-dependent exopeptidase | 0 | 1.08 |
| 2037 | Aspartic endopeptidase Pep2 | 1.04 | 5.43 |
| 373 | Aspartic peptidase A1 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 701 | Aspartyl aminopeptidase | 0 | 2.77 |
| 3133 | AAP1-alanine/arginine aminopeptidase | 0.48 | 1.88 |
| 250 | Cytosol aminopeptidase | 0 | 0.95 |
| 1425 | Leucine aminopeptidase | 18.74 | 31.5 |
| 2068 | Methionine aminopeptidase | 0 | 9.69 |
| 483 | Peptidase M14 | 1.5 | 2.2 |
| 324 | Peptidase M17 | 0.48 | 2.44 |
| 2194 | Peptidase M20 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 952 | Peptidase M24A | 0 | 4.43 |
| 241 | Peptidase M28 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 1294 | Peptidase M36 | 0 | 0.45 |
| 2337 | Peptidase M48 | 0 | 4.01 |
| 702 | Peptidase M50B | 3.54 | 16.83 |
| 1910 | Peptidase S10 | 20.17 | 30.78 |
| 371 | Peptidase S28 | 0 | 3.56 |
| 776 | Peptidase S41 | 0 | 0.78 |
| 236 | Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase | 0 | 2.05 |
| 5975 | Xaa-Pro dipeptidase | 0.94 | 2.64 |
| 1261 | Proline iminopeptidase | 2.02 | 7.18 |
| 213 | Proline-specific peptidase | 0 | 1.76 |
| 1370 | Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase BIII | 14.02 | 31.89 |
| 701 | Tripeptidyl peptidase A | 0 | 1.95 |
| 224 | Tripeptidyl peptidase sed2 | 0 | 1.1 |
| 2178 | Tripeptidyl peptidase sed3 | 0 | 1.59 |
| 530 | Carboxypeptidase S | 0 | 2.58 |
| 1828 | Carboxypeptidase Y | 0 | 3.78 |
| 2724 | Serine carboxypeptidase | 0 | 6.43 |
| 516 | Family S53 protease | 0 | 1.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okamoto, K.; Ito, R.; Hayashi, J.; Tagawa, M. Production of the Antihypertensive Peptide Tyr-Pro from Milk Using the White-Rot Fungus Peniophora sp. in Submerged Fermentation and a Jar Fermentor. Dairy 2021, 2, 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy2030036
Okamoto K, Ito R, Hayashi J, Tagawa M. Production of the Antihypertensive Peptide Tyr-Pro from Milk Using the White-Rot Fungus Peniophora sp. in Submerged Fermentation and a Jar Fermentor. Dairy. 2021; 2(3):452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy2030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkamoto, Kenji, Ryosuke Ito, June Hayashi, and Mizuki Tagawa. 2021. "Production of the Antihypertensive Peptide Tyr-Pro from Milk Using the White-Rot Fungus Peniophora sp. in Submerged Fermentation and a Jar Fermentor" Dairy 2, no. 3: 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy2030036
APA StyleOkamoto, K., Ito, R., Hayashi, J., & Tagawa, M. (2021). Production of the Antihypertensive Peptide Tyr-Pro from Milk Using the White-Rot Fungus Peniophora sp. in Submerged Fermentation and a Jar Fermentor. Dairy, 2(3), 452-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy2030036