Abstract
Enzymatic cross-linking by microbial transglutaminase is a prominent approach to modify the structure and techno-functional properties of food proteins such as casein. However, some of the factors that influence structure-function-interrelations are still unknown. In this study, the size of cross-linked sodium caseinate nanoparticles was modulated by varying the ionic milieu during incubation with the enzyme. As was revealed by size exclusion chromatography, cross-linking at higher ionic strength resulted in larger casein particles. These formed acid-induced gels with higher stiffness and lower susceptibility to forced syneresis compared to those where the same number of ions was added after the cross-linking process. The results show that variations of the ionic milieu during enzymatic cross-linking of casein can be helpful to obtain specific modifications of its molecular structure and certain techno-functional properties. Such knowledge is crucial for the design of protein ingredients with targeted structure and techno-functionality.
1. Introduction
Casein, the main protein fraction in milk from ruminants (e.g., ~80% in bovine milk), is the main contributor to structure formation in fermented dairy products such as cheese or yoghurt, but also the origin of casein-based ingredients with targeted functionality [1]. For instance, sodium caseinate (NaCn) is produced by acid precipitation of casein, washing, neutralisation of the precipitate with NaOH, and subsequent spray-drying [2]. In contrast to the casein micelles in milk, which are supramolecular, colloidal particles of ~200 nm in diameter, casein molecules in aqueous NaCn solutions were reported to associate to small, elliptical nanoparticles with a mean hydrodynamic radius of ~9.4 nm and a mean radius of gyration of ~21.4 nm [3].
NaCn possesses a wide range of techno-functional properties that are relevant for the food industry, such as gel formation, emulsification, foaming, as well as water and oil binding capacity, and exhibits a good stability against heating and ethanol, making it suitable as ingredient for a number of foods [1]. Prominent examples for the utilisation of NaCn in food products are yoghurt [4,5], cream liqueurs and other emulsions [6,7], as well as plant-based, fermented drinks [8].
For more than two decades, enzymatic cross-linking by microbial transglutaminase (mTGase; EC2.3.2.13) has been investigated as a possibility to modify techno-functional properties of casein in milk and thus to improve, e.g., texture and water holding capacity of yoghurt gels [9,10], or yield and firmness of cheese curd [11,12]. In contrast, the modification of casein-based ingredients such as NaCn by mTGase has been investigated to a much lesser extent, even though NaCn has previously served as model substrate for cross-linking and gelation experiments [13,14,15,16]. Kizzie-Hayford et al. [17] reported higher viscosity and lower syneresis of fermented, tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) based milk alternatives enriched with cross-linked NaCn compared to products that contained uncross-linked NaCn. Moreover, mTGase was used to produce functionalised skim milk powder and milk protein concentrate for the fortification of yoghurt milk [18,19,20], as well as to form emulsion gels from NaCn stabilised oil-in-water emulsions [21].
In a previous study, NaCn cross-linked by mTGase to different extents were spray-dried and applied as techno-functional ingredient in acid-induced skim milk gels [22]. It was shown that a lower amount of moderately cross-linked NaCn (~70% polymerisation) added to skim milk was sufficient to obtain gels with properties comparable to that with added uncross-linked NaCn. However, the amount of added NaCn could be decreased by only 25%, which is not sufficient for industrial application. Therefore, further modification of the structure of cross-linked NaCn by other means might be necessary for improved techno-functionality.
It was reported that the cross-linking of casein-bound glutamine and lysine residues by mTGase [23] occurs predominantly between casein molecules within the same NaCn nanoparticle, resulting in a change from elliptical to spherical shape [24,25] as well as in a transition from a soft particle character towards a hard sphere-like behaviour [26]. The size and aggregation number of native NaCn nanoparticles varied with casein concentration, temperature, pH and ionic strength due to modulation of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions [27,28]. Assuming predominantly intra-particle cross-linking, the alteration of these parameters during incubation with mTGase might result in different structure and functionality of the cross-linked NaCn nanoparticles.
A variation of the incubation temperature (10–40 °C), however, did not affect particle size and gelation properties of NaCn [29], and a change in incubation pH (5.9–7.3) affected the proteolytic activity of indigenous plasmin [30]. On the other hand, an increase in the ionic strength or the presence of bivalent Ca2+ ions resulted in larger cross-linked casein particles, as was shown by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) [31]. However, the gelation properties of the different samples could not be directly compared as the different ionic milieus affected the gelation behaviour.
The aim of the present study was thus to provide a more complete picture on how size modulation of NaCn nanoparticles by a variation in ionic strength affects the properties of acid-induced gels. To achieve this, NaCl or CaCl2 were dissolved in NaCn solutions either prior to or after cross-linking by mTGase to vary the particle size while ensuring identical ionic milieus during gelation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Acid casein powder from bovine milk, purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany), had a crude protein content of 868 g/kg as determined by Kjeldahl method using a conversion factor of N × 6.38 [32]. mTGase “Activa MP”, provided by Ajinomoto Foods Europe SAS (Hamburg, Germany), had an enzyme activity of 70 U per g as determined by the hydroxamate method [33,34]. Glucono-δ-lactone (GDL) was provided by Kampffmeyer Nachf. GmbH (Ratzeburg, Germany). All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
2.2. Sample Preparation
Table 1 provides an overview of the samples investigated in this study. NaCn and calcium caseinate (CaCn) solutions were prepared by dispersing acid casein powder in demineralised water and neutralising it with 1 M NaOH or 0.02 M Ca(OH)2, respectively. Sodium azide was added at a concentration of 0.3 g/kg to prevent microbial growth, and the suspensions were stirred overnight at room temperature (~23 °C) to ensure complete dissolution. Thereafter, pH was adjusted to 6.6 using 1 M NaOH or 0.02 M Ca(OH)2, and the protein content was finally set to 27 g/kg by adding demineralised water. The volume of base used for neutralisation was recorded. Additionally, acid casein powder was dissolved in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) containing 0.3 g/kg NaN3 at a concentration of 27 g/kg and stirred overnight at room temperature. The pH dropped to ~6.6 during dissolution of casein due to the release of H+. This sample is referred to as casein in phosphate buffer (Cn-PB).

Table 1.
Overview of the samples prepared in this study.
NaCn solution was divided into three parts prior to incubation with mTGase. One part was used without further treatment, one part was adjusted to a final concentration of 0.1 M NaCl, and one part was adjusted to 0.005 M CaCl2. If necessary, pH was readjusted to 6.6 using 0.1 M NaOH.
Cross-linking of caseins was achieved by adding mTGase at a concentration of 3 U per g protein. Incubation was carried out at 40 °C for 1–48 h or at 30 °C for 3 h–14 days (see Table 1). In the latter case, mTGase concentration was adjusted to compensate for the different enzyme activity at 30 °C (41.1 U/g [29]). After specific incubation times, the samples were heated for 15 min at 85 °C min for enzyme inactivation and subsequently cooled in ice water. Reference samples without enzyme addition were treated in the same way and referred to as 0 h.
NaCn solutions cross-linked at 40 °C without additional salts were adjusted to 0.05–0.15 M NaCl or 0.005–0.015 M CaCl2 after incubation (see Table 1). If necessary, the pH was readjusted to 6.6 using 0.1 M NaOH. All samples were stored at −18 °C until needed.
The approximate ionic strengths of the samples were calculated using the amount of NaOH, Ca(OH)2 or sodium phosphate buffer used for neutralisation of acid casein, the amount of NaN3 added for preservation, and the amount of added NaCl or CaCl2 (see Table 1). The ionic strength of the casein and the amount of NaOH used to readjust the pH were neglected in the calculations.
2.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography
A Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL and a Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL column (both GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB, Uppsala, Sweden) were coupled in series to a liquid chromatography system AZURA Assistant ASM 2.1 L (Knauer Wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH, Berlin, Germany). The elution buffer contained 6 M urea, 0.1 M NaCl, 0.1 M Na2HPO4 and 1 g/L 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulphonate (CHAPS) and was adjusted to pH 6.8 using 6 M HCl. The caseinate samples were diluted with elution buffer containing 100 mg/mL dithiothreitol to a protein concentration of 2 g/L and stored at 4 °C overnight to cleave disulphide bonds.
The samples were filtered through 0.45 µm regenerated cellulose syringe filters (Sartorius Stedim Biotech GmbH, Göttingen, Germany) prior to injecting a sample volume of 50 µL. The measurements were conducted at ambient temperature (~23 °C) and an isocratic flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The eluting protein was detected at 280 nm. Data were acquired and processed using ClarityChrom v3.0.7 (Knauer Wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH). The areas under the peaks corresponding to polymerised casein (APolymer) and casein monomers (AMonomer) were determined, and the polymerisation degree (PD) was calculated as follows:
2.4. Acid-Induced Gel Formation
All gelation experiments were carried out at 30 °C using glucono-δ-lactone (GDL) for acidification at a concentration of 40 mg/g, except for Cn-PB, which was acidified with 45 mg/g GDL to compensate the buffering capacity of the phosphate ions and to obtain comparable acidification profiles.
2.4.1. pH Monitoring during Acidification
The pH development during acidification was monitored using a six-channel data logger (MCC-SYSti-6b, EA Instruments Ltd., Wembley, UK) and the instrument-associated software (MCC-MON-6c, v2.3.1, EA Instruments Ltd.). The samples were blended with GDL and transferred to 15 mL centrifugation tubes, which were placed in a water bath at 30 °C. pH was recorded every 60 s. All samples were measured in duplicates. As it was previously reported that cross-linking by mTGase does not affect the acidification profile [31,35], the curves shown are averaged over all incubation times.
2.4.2. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear Rheometry
A strain-controlled ARES-G2 rheometer (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) equipped with a cup-and-bob geometry (di = 31.4 mm, do = 34 mm, h = 47.1 mm) was used for monitoring the acid-induced gelation of the caseinate samples. Samples were blended with GDL, and immediately transferred to the rheometer geometry. The development of storage modulus (G’) and loss factor (tan δ) over acidification time was obtained from time sweep measurements at constant strain (γ = 0.003) and frequency (ω = 1 rad/s). The temperature was kept constant at 30 °C by a Peltier element. Paraffin oil was added to the sample surface to prevent evaporation.
All measurements were carried out in duplicate; the half range was always smaller than 5% of the mean value.
2.4.3. Forced Syneresis
GDL was blended with 10 mL caseinate solution, transferred into 15 mL centrifugation tubes, and placed in a water bath at 30 °C until the maximum G’ in the rheological experiments was reached. The tubes were subsequently cooled in ice water for 10 min and centrifuged at 1000× g and 6 °C for 20 min (Sigma 3–30K, Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH, Osterode am Harz, Germany). The expelled supernatant was decanted, and syneresis was determined from the mass of the gel before (m0) and after centrifugation (m1):
Results are arithmetic means ± standard deviation from at least triplicate experiments.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Data were statistically evaluated with one-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s post hoc test using SigmaPlot v14.0.3.192 (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The statistical acceptance level was p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size Modulation of Cross-Linked Sodium Caseinate Nanoparticles
The SEC chromatograms (Figure 1) show a complete dissociation of the uncross-linked 0 h samples because of the denaturing elution buffer and the reducing agent, giving a single peak for monomeric casein at an elution volume (VE) of 25.75–29.75 mL. The different casein types co-eluted in this peak following the order β-casein < αS-caseins < κ-casein [36]. Therefore, the shift of the monomer peak to higher VE with ongoing incubation indicates increasing cross-linking velocities of the different casein types in the order β-casein > αS-caseins > κ-casein, which is in agreement with previous observations using gel electrophoresis [29,35,37].
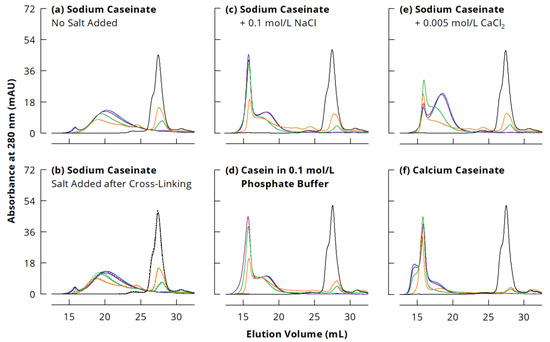
Figure 1.
Size exclusion chromatography of casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) in different ionic milieus (a,c–f) for 0 (black), 1 (orange), 3 (green), 24 (violet) or 48 h (blue). (b) shows the samples of (a) with 0.1 M NaCl (full lines) or 0.005 M CaCl2 (dotted lines) added after cross-linking was completed.
During incubation with mTGase, monomeric caseins were covalently cross-linked and could not be dissociated by denaturing agents anymore. Therefore, polymerised casein emerged in the chromatograms at 13.5–25.75 mL. Distinct peaks corresponding to casein dimers (23.5–25.75 mL) and trimers (22–23.5 mL) can be seen after incubation for 1 h. These were further cross-linked to larger species with ongoing mTGase treatment and thus disappeared from the chromatograms when samples were incubated for ≥3 h. It is important to note that, for all casein systems, the chromatograms of the 24 and 48 h incubated samples were very similar, indicating a maximum size for polymerised casein and thus underpinning the assumption of predominantly internal cross-linking of native NaCn nanoparticles.
In studies where only a Superdex 200 column was used for separation, just one peak was observed for polymerised caseins larger than trimers [38,39,40]. The combination of the Superdex 200 column with a Superose 6 column as used in the present study enabled to separate this peak into two fractions because of the much broader separation range of Superose 6 [36,41]. Appearance and intensity of these two peaks varied largely with the ionic milieu during incubation. In the case of NaCn without added salts, the polymerised casein eluted in one major fraction (16.5–25.75 mL) with a maximum at 20 mL, and a small peak at 13.5–16.5 mL (Figure 1a). The addition of 0.1 M NaCl or 0.005 M to NaCn after cross-linking did not change the appearance of the chromatograms (Figure 1b), indicating that the presence of these salts did not cause irreversible casein aggregation. When casein was cross-linked in the presence of 0.1 M NaCl, the peak at 13.5–16.5 mL was much more pronounced. The second fraction shifted to lower elution volumes (17–21.5 mL), showing a peak maximum at 18.5 mL (Figure 1c). This clearly indicates that larger cross-linked NaCn nanoparticles are obtained at higher ionic strength. Chromatograms of NaCn with 0.1 M NaCl were similar to those of Cn-PB (Figure 1d), which was used as substrate in many previous studies, e.g., [15,16,42,43], suggesting a similar effect of 0.1 M NaCl and 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer despite different ionic compositions.
Based on elution volumes, presumably the same species of polymerised casein were formed in the presence of 0.005 M CaCl2 as with 0.1 M NaCl, but at different ratios (Figure 1e). While after incubation for 3 h, the peak at 13.5–16.5 mL was most pronounced, its intensity decreased during further cross-linking and the smaller species eluting at 17–21.5 mL became dominant. Although CaCn and NaCn with 0.005 M CaCl2 had a similar ionic strength (see Table 1), the chromatograms were completely different (Figure 1f). The peak at 13.5–16.5 mL was already most prominent after 1 h incubation and increased slightly with further cross-linking. Additionally, two shoulders emerged at 13.5–15.25 mL and 17–21.5 mL, illustrating that the particle size was highest for cross-linked CaCn. It needs to be considered that the ionic strength of CaCn (0.03 M) derives mainly from the Ca2+ ions introduced during neutralisation of the acid casein powder with Ca(OH)2, whereas in NaCn with 0.005 M CaCl2, considerable amounts of Na+ and Cl− ions contribute to ionic strength. Therefore, the Ca2+/casein ratio was much larger in CaCn and certainly above the critical aggregation concentration, leading to the formation of large casein aggregates that were then cross-linked to large casein particles. Smialowska et al. [28] observed aggregation of 33 g/kg NaCn at 0.022 M CaCl2, whereas at 0.011 M CaCl2, the association of the casein molecules to slightly larger nanoparticles was promoted. From this point of view, the addition of 0.005 M CaCl2 or 0.1 M NaCl to NaCn had similar effects on the size of NaCn nanoparticles, but the ratio between the two observed species depended on the magnitude of the ionic strength.
The nature of the two polymeric species is not entirely clear yet and needs further investigation. However, some indications can be found in the literature. Smialowska et al. [28] applied cold acid precipitation to separate NaCn into a cold soluble and a cold insoluble casein fraction, which had the same casein composition but different calcium sensitivity. In some preliminary experiments, we replicated this procedure and incubated the resulting cold soluble and cold insoluble NaCn fractions with mTGase (see Appendix A.1). Subsequent sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE; see Appendix A.2) indicated a similar casein composition of the two fractions before cross-linking, but completely different cross-linking behaviour (Appendix B, Figure A1). Very large species unable to penetrate the separating gel were formed from the cold soluble fraction, whereas the majority of the polymerised casein in the cold insoluble fraction was small enough to enter the separating gel. With regard to the chromatograms (see Figure 1), this would mean that the larger, first eluting species (13.5–16.5 mL) corresponded to the cold soluble, and the second one (16.5–25.75 mL) to the cold insoluble NaCn fraction. This is also in agreement with the results of Smialowska et al. [28], who observed a slightly higher turbidity as well as slightly larger particle sizes in small-angle x-ray scattering for the cold soluble than for the cold insoluble NaCn fraction. However, their study does not clearly indicate if these two species would co-exist in NaCn solution, or rather form hybrid structures.
In this regard, non-denaturing SEC might provide useful insights. When using only a Superose 6 column for separation of Cn-PB under denaturing and reducing conditions, the two polymeric species eluted at ~7–9 mL and ~9–13 mL, and monomeric casein at ~15–17 mL [36]. Other researchers used the same column under non-denaturing and non-reducing conditions for characterising native, uncross-linked NaCn and observed three peaks at very similar elution volumes (Table 2) [25,44]. Based on multi-angle light scattering results, these research groups concluded that the last eluting fraction corresponded to small casein aggregates as well as some monomeric caseins at the end of the peak. Due to the low light scattering intensity provided by casein monomers, their molar mass is easily overestimated, especially at low concentrations [29]. The similar VE in denaturing and non-denaturing SEC therefore suggests that this fraction might rather be composed of mainly monomeric casein. It is, however, not clear, whether this fraction actually co-exists with casein nanoparticles in solution, or if its appearance in the chromatograms is rather due to measurement conditions causing some dissociation (i.e., dilution effects, shear forces during separation). No additional peak for casein monomers and/or small aggregates was observed in asymmetric flow field fractionation measurements of Cn-PB [24], or in SEC of NaCn in milk serum using a Sephacryl S-500 column [45]. With regard to the first peak in the chromatograms, Hannß et al. [25] reported that it contained only low amounts of protein, but also triglycerides and phospholipids, suggesting a co-elution of large casein particles and fat droplets. Nevertheless, the peak intensity and the protein content of this fraction increased with different, non-enzymatic cross-linking treatments [25], and the present study demonstrated a remarkable increase in this fraction with casein cross-linking by mTGase at increased ionic strength.

Table 2.
Elution volumes (mL) of different casein species in denaturing and reducing or native size exclusion chromatography using a Superose 6 column.
It seems therefore possible that the two particle species observed in denaturing and non-denaturing SEC correspond to the cold soluble and cold insoluble fractions of NaCn. In this regard, the chromatograms of cross-linked CaCn are particularly interesting, as the peak that presumably corresponded to the cold insoluble, more Ca2+-sensitive casein fraction [28] (17–21.5 mL) was rather small (Figure 1f). On the other hand, an additional shoulder was found at the beginning of the chromatogram (13.5–15.25 mL), which possibly refers to Ca2+-induced casein aggregates covalently cross-linked by mTGase. However, more research is necessary to characterise these two species of casein particles, prior to and after cross-linking, as well as to understand the effect of salts on their conformation. Further discussion in this study will therefore be limited to the observation that larger cross-linked casein particles were formed during mTGase treatment of NaCn in the presence of salts.
3.2. Quantitative Evaluation of Casein Polymerisation in Different Ionic Milieus
The PD calculated according to Equation (1) from the peak areas of polymerised casein (APolymer; VE = 13.5–25.75 mL) and monomeric casein (AMonomer; VE = 25.75–29.75 mL) increased rapidly to ~75% during the first hour of incubation for all samples (Figure 2). Further cross-linking took place between remaining monomers and polymerised casein, as well as within the already polymerised casein. Therefore, the PD increased only slightly although covalent cross-links were still formed to a large extent [30,31,46,47]. It is worth noting that NaCn without added salts had a distinctively lower PD than the other samples at all incubation times, which is in agreement with a previous study [31]. Typical SDS-PAGE patterns confirm that some uncross-linked κ-casein is still left in NaCn after mTGase treatment for 24 h, whereas this band is barely visible in 24 h cross-linked Cn-PB (Appendix B, Figure A2). It seems that due to the specific conformation of casein nanoparticles, κ-casein is less accessible for cross-linking by mTGase in NaCn than in other ionic milieus. The size exclusion chromatograms indicate that mainly the cold insoluble fraction was present and cross-linked in NaCn (see Figure 1a). This fraction was reported to be more Ca2+ sensitive, most likely because κ-casein is buried in the interior of the particles [28], which could explain the lower accessibility of κ-casein for mTGase in NaCn.
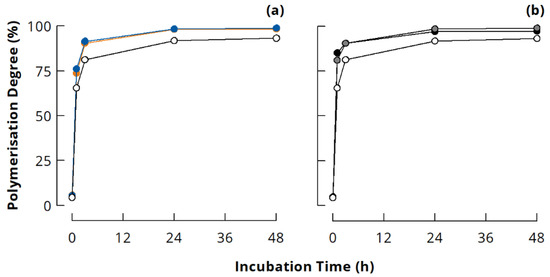
Figure 2.
Polymerisation degree of casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) in different ionic milieus: (a) sodium caseinate (open symbols), sodium caseinate in 0.1 M NaCl (blue), and sodium caseinate in 0.005 M CaCl2 (orange); (b) sodium caseinate (open symbols), casein in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (grey), and calcium caseinate (black).
3.3. Gels from Enzymatically Cross-Linked Sodium Caseinate Nanoparticles with Different Sizes
3.3.1. Small Deformation Rheology
Figure 3 depicts the maximum storage modulus (G’max) and the corresponding tan δ of acid-induced gels from the different casein systems as a function of mTGase incubation time. In line with previous results [29,31,39], G’max of NaCn gels without added salts increased continuously with increasing incubation time. The presence of 0.1 M NaCl or 0.005 M CaCl2 barely affected pH development during acidification with GDL, although slight differences could be noticed at the beginning of the acidification (see inserts to Figure 3). The addition of salts to cross-linked NaCn shifted the highest G’max to gels from 1 or 3 h incubated casein, which showed a higher G’max compared to the gels from the original NaCn. In contrast, the salts decreased G’max of gels from uncross-linked casein and casein cross-linked for ≥24 h (Figure 3a,b). A decrease in G’ of acid-induced gels from uncross-linked NaCn due to the addition of NaCl or CaCl2 was previously attributed to the screening of charged groups on the proteins, which decreases the strength of protein-protein interactions because of reduced electrostatic attraction [48,49]. The screening of charged groups seems, however, to enhance protein-protein interactions in case of NaCn cross-linked for 1 and 3 h, resulting in higher G’max of the gels. These samples also showed the lowest tan δ, underpinning their peculiar character and unique conformational properties, resulting from the partial cross-linking of the casein particles (see Figure 2), which leaves them as associates of monomers, dimers, trimers and/or loosely cross-linked polymers. When attractive electrostatic interactions are reduced due to screening of charged groups, other non-covalent interactions become more important, for instance hydrogen bonds or interactions between hydrophobic residues, which are mainly buried in the interior of the casein particles. Partial cross-linking of casein nanoparticles might facilitate the formation of casein clusters with a high number of such non-covalent bonds due to a more controlled reorganisation during acidification compared to uncross-linked casein particles. A previous study showed that a higher number of casein dimers and trimers is less favourable for the formation of gels with high G’max [50]. Therefore, the loosely cross-linked polymers might especially act as nuclei for a controlled network formation. On the other hand, if the casein particles are excessively cross-linked, their low flexibility may prevent the formation of a high number of non-covalent interactions, leading to lower G’max [31]. Figure 4 illustrates that G’max at a particular incubation time tends to decrease with increasing salt concentration, suggesting that electrostatic interactions were involved in gel network formation even at higher ionic strength, but that they became increasingly screened with increasing salt concentration.
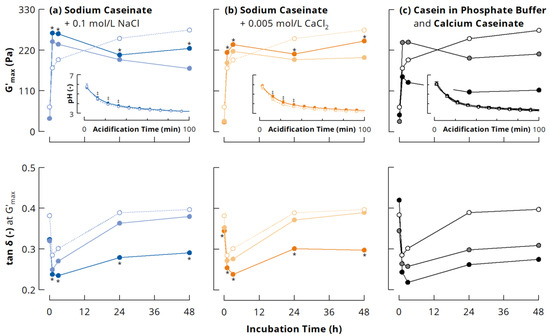
Figure 3.
Maximum storage modulus G’max (top) and loss factor tan δ at G’max (bottom) of acid-induced gels (30 °C) from casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) in different ionic milieus: (a) sodium caseinate (open symbols) with 0.1 M NaCl added before (dark blue) or after cross-linking (light blue); (b) sodium caseinate (open symbols) with 0.005 M CaCl2 added before (dark orange) or after cross-linking (light orange); (c) sodium caseinate (open symbols) compared to casein in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (grey) and calcium caseinate (black). Glucono-δ-lactone concentration was 40 mg/g (except grey symbols: 45 mg/g). Inserts show pH development of the samples during acidification. * indicates statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between sodium caseinate gels at a particular incubation time with salt added before and after incubation. ‡ indicates statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between the pH of sodium caseinate gels with and without salt at particular times during acidification.
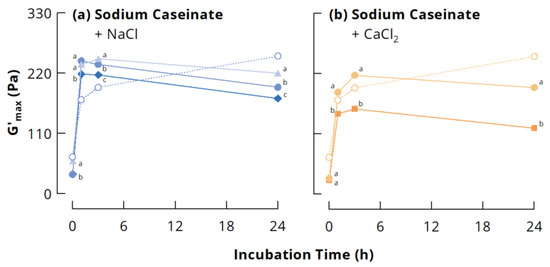
Figure 4.
Maximum storage modulus G’max top of acid-induced gels (30 °C, 40 mg/g glucono-δ-lactone) from casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C): (a) sodium caseinate (open symbols) with 0.05 (triangles), 0.1 (circles) or 0.15 M NaCl (diamonds) added after cross-linking; (b) sodium caseinate (open symbols) with 0.005 (circles) or 0.015 M CaCl2 (squares) added after cross-linking. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between sodium caseinate gels with different salt concentrations at a particular incubation time.
Enzymatic cross-linking of NaCn in the presence of salts consistently resulted in gels with significantly higher G’max and significantly lower tan δ compared to the corresponding samples where salts were added after incubation (Figure 3a,b). The properties of gels from Cn-PB and CaCn are in good agreement with previous results [31] and only shown for comparison (Figure 3c). Differences in the PD of the samples were not taken into account, as the number of covalent isopeptide bonds introduced by mTGase is more decisive for G’max [46,47,50], and this was shown to be comparable for NaCn and Cn-PB despite a different PD [31]. The results therefore demonstrate that larger cross-linked NaCn nanoparticles, which were formed in the presence of salts, are favourable to obtain gels with higher stiffness. Similar results were also reported for gel-like suspensions of jammed α-lactalbumin nanoparticles, which were generated by cross-linking with horseradish peroxidase [51]. These authors argued that the higher elastic response (higher G’, lower tan δ) of larger protein particles with lower internal density results from enhanced contact and stronger short-range interactions. As the number of cross-links is expected to be similar for all samples at a given incubation time [31], larger nanoparticles would have a lower internal density than smaller ones.
For almost all samples, G’max increased when mTGase treatment was continued after 24 h (see Figure 3), suggesting the formation of additional cross-links within the NaCn nanoparticles, which contributed to G’max of acid-induced gels while the molecular flexibility of the particles was already low and not further affected. To verify this assumption, NaCn and Cn-PB were incubated with mTGase for up to 14 days. For this, the incubation temperature was decreased to 30 °C to enhance the storage stability of mTGase without affecting casein cross-linking [29]. G’max of NaCn increased continuously with increasing incubation time (Figure 5), indicating an ongoing formation of isopeptide bonds. As is typical for gels from Cn-PB [16,35,46,47], G’max showed a maximum after 3 h of incubation. Further cross-linking resulted in a drop of G’max, which, however, increased, again from ~180 to ~230 Pa during further incubation. This demonstrates that the incorporation of additional isopeptide bonds into highly cross-linked casein nanoparticles further increases G’max, and underlines that there is a direct contribution of isopeptide bonds to the stiffness of acid-induced caseinate gels. G’max of both NaCn and Cn-PB reached a plateau after 7 days of incubation, which suggests that no further isopeptide bonds could be formed due to substrate limitation.
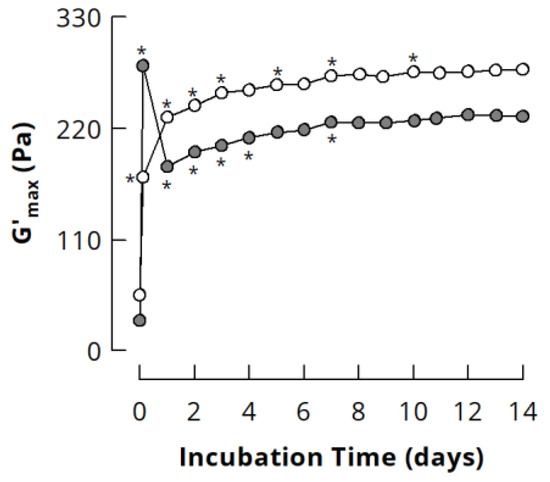
Figure 5.
Maximum storage modulus G’max of acid-induced gels (30 °C) from sodium caseinate (white; 35 mg/g glucono-δ-lactone) and casein in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (grey; 40 mg/g glucono-δ-lactone) cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 30 °C). * indicates a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) to the previous incubation time. Modified from [52], copyright by the author.
3.3.2. Forced Syneresis
Susceptibility of acid-induced gels from NaCn to syneresis is shown in Figure 6 as a function of incubation time with mTGase and for the different ionic conditions. Consistent with previous research [35,53], moderate cross-linking (1 and 3 h incubation) decreased the forced syneresis of the gels significantly, whereas excessive cross-linking (≥24 h) increased syneresis again. The addition of salts to cross-linked NaCn had no significant effect on susceptibility to syneresis, except for the 1 h sample where it was slightly reduced by the addition of NaCl. In contrast, syneresis of gels from uncross-linked NaCn was considerably decreased by the addition of 0.1 M NaCl and significantly increased by the addition of 0.005 M CaCl2.
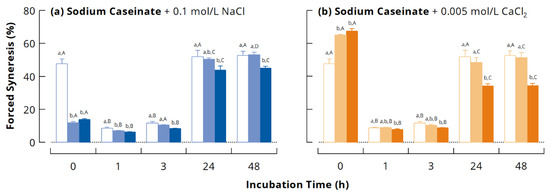
Figure 6.
Forced syneresis of acid-induced gels (30 °C, 40 mg/g glucono-δ-lactone) from casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) in different ionic milieus: (a) sodium caseinate (open bars) with 0.1 M NaCl added before (dark blue) or after cross-linking (light blue); (b) sodium caseinate (open bars) with 0.005 M CaCl2 added before (dark orange) or after cross-linking (light orange). Different lower-case letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between samples with the same incubation time; different capital letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between samples at the same ionic condition.
Lower syneresis, and, vice versa, a higher water holding capacity of the final gel are often related to a denser, more homogeneous microstructure with smaller pores. In fact, the microstructure rearranges from a dense and homogenous matrix shortly after gelation onset to a porous protein network around the isoelectric point [54]. Therefore, denser microstructures were previously interpreted as a prevention of these rearrangements by NaCl [55] as well as by covalent cross-linking of caseins by mTGase [56]. More recently, Hannß et al. [53] reported a comparable microstructure for acid-induced gels from uncross-linked Cn-PB and Cn-PB cross-linked by mTGase to a PD of ~60%, while forced syneresis was significantly decreased. This suggests that rearrangements of casein clusters might still be possible when casein is only partially cross-linked, while covalent isopeptide bonds contribute to the water holding capacity of the gel network. In case of excessively cross-linked NaCn (≥24 h), rearrangements are impaired on the molecular level due to the fixation of casein molecules. In combination with the increased internal density and higher sphericity of the casein particles [24,25,26], this might increase their mobility in the gel network, as was also indicated by the higher tan δ (see Figure 3). Thus, rearrangements of casein clusters on the microstructure level might be facilitated, leading to higher forced syneresis. Additionally, the higher cross-linking extent and thus the higher internal density might have decreased the water holding capacity of the individual casein particles.
Gels from NaCn cross-linked in the presence of ions showed lower susceptibility to syneresis than those with salts added after cross-linking, especially in the case of excessively cross-linked casein (≥24 h). This suggests that larger cross-linked casein nanoparticles with lower internal density possess a larger water holding capacity.
Figure 7a,b depict forced syneresis as a function of G’max and the corresponding tan δ, respectively. There was no clear relationship between the rheological parameters and forced syneresis. Instead, the samples could be grouped into three categories. (I) Gels from uncross-linked NaCn showed consistently rather low G’max (~25–65 Pa) and high tan δ (~0.32–0.38), but a broad range of forced syneresis (~12–67%), depending on the ionic milieu. (II) Gels from 1 and 3 h incubated NaCn showed high G’max ranging from ~170 to ~240 Pa, low tan δ (~0.25–0.30), and a consistently low forced syneresis (~6–12%). (III) Gels from 24 and 48 h incubated NaCn showed G’max in a similar range (~200–275 Pa) as those from moderately cross-linked NaCn, but higher tan δ (~0.23–0.40) and significantly higher forced syneresis (~34–50%). This indicates that susceptibility to syneresis is related to other gel parameters that were not investigated in this study, e.g., gel microstructure or fracture properties. However, it can be concluded that cross-linking of NaCn for 1–3 h in the presence of 0.1 M NaCl results in the highest G’max, lowest δ and lowest forced syneresis, which might be favourable for certain applications of NaCn as an ingredient.
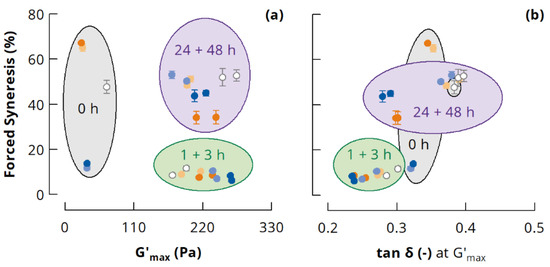
Figure 7.
Forced syneresis of acid-induced gels (30 °C, 40 mg/g glucono-δ-lactone) from casein cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) in different ionic milieus as a function of (a) G’max or (b) tan δ at G’max. Sodium caseinate (open symbols) with 0.1 M NaCl added before (dark blue) or after cross-linking (light blue); sodium caseinate with 0.005 M CaCl2 added before (dark orange) or after cross-linking (light orange). Numbers indicate incubation time with microbial transglutaminase.
4. Conclusions
Enzymatic cross-linking by mTGase has the potential to modify food proteins gently and specifically to alter their techno-functional properties and thus to design innovative food ingredients. However, it is still largely unknown how incubation parameters, such as ionic strength or pH during cross-linking, affect the structure of cross-linked proteins, and how the created structures affect the techno-functional properties of the modified proteins. In this study, the size of cross-linked NaCn nanoparticles was modulated by varying the ionic milieu. Cross-linking at higher ionic strength resulted in larger NaCn nanoparticles, which formed acid-induced gels with higher G’max and lower forced syneresis compared to those where the same number of ions was added after the cross-linking process. These results demonstrate the potential of varying certain solution parameters during enzymatic cross-linking of food proteins to modify their structure specifically to design protein ingredients with targeted structure. Additional research is necessary to describe the conformation of the created NaCn nanoparticles in more detail, and to evaluate their techno-functionality in relevant food systems, such as yoghurt or emulsions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.R. and L.L.; Methodology, N.R. and L.L.; Investigation, N.R. and L.L.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, N.R.; Writing—Review and Editing, L.L., H.R. and D.J.; Visualization, N.R.; Supervision, N.R., H.R. and D.J.; Project Administration, H.R. and D.J.; Funding Acquisition, N.R., H.R. and D.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; Bonn, Germany) under the grant number RO3454/5-1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Microbial transglutaminase was kindly provided by Ajinomoto Foods Europe SAS (Hamburg, Germany), and glucono-δ-lactone by Kampffmeyer Nachf. GmbH (Ratzeburg, Germany).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Additional Experiments
Appendix A.1. Preparation of Cold Soluble and Cold Insoluble Sodium Caseinate Fractions
The cold soluble and cold insoluble sodium caseinate fractions were prepared according to Smialowska et al. [28] with some modifications. Briefly, commercial NaCn (“Casein sodium salt”; Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Steinheim, Germany) was dissolved in demineralised water at a concentration of 80 g/kg, and 0.3 g/kg NaN3 was added for preservation. The casein was precipitated at pH 4.6 using 6 M HCl, and the slurry was stirred overnight at 4 °C to allow dissociation of cold soluble casein. After removal of the aqueous phase, the precipitate containing the cold insoluble fraction was dispersed in demineralised water again and the procedure was repeated. Afterwards, the aqueous phases from both steps were combined and heated to 60 °C to induce precipitation of the cold soluble casein. Both precipitates were washed, filtered and freeze-dried (Martin Christ GmbH, Osterode am Harz, Germany). After determination of the protein content using the Kjeldahl method (N × 6.38; [32]), the powders were redissolved in demineralised water at a concentration of 27 g/kg by neutralising to pH 6.6 with 1 M NaOH, and 0.3 g/kg NaN3 were added for preservation. Enzymatic cross-linking of the fractions was carried out at 40 °C using 3 U mTGase per g protein as described in Section 2.2.
Appendix A.2. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Linear sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis based on the method by Laemmli [57] was performed as described previously [36] using a vertical apparatus from CBS Scientific Co. Inc. (Del Mar, CA, USA). Separating and stacking gel contained 125 mg/mL and 40 mg/mL acrylamide, respectively. Casein samples were diluted with a 1:1 mixture of 8 M urea and sample buffer (0.8 M Tris, 2 mM EDTA, 4 M glycerine, 20 mg/mL SDS, 0.2 g/L Orange G; pH 8.0), treated with 150 mg/mL dithiothreitol, and boiled for 5 min to reduce disulphide bonds. The experiments were run at 120 V, and the protein fractions were subsequently stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. No molecular marker was used, as globular protein standards do not reflect the migration velocities of monomeric and polymerised caseins.
Appendix B. Supplementary Figures
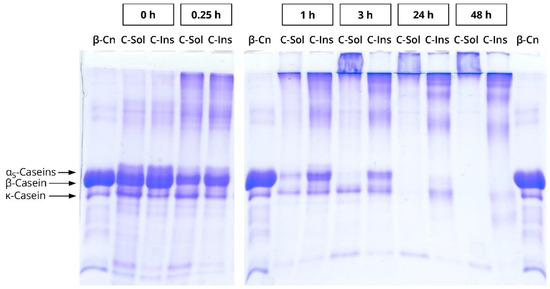
Figure A1.
Linear sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of the cold soluble (C-Sol) and the cold insoluble (C-Ins) fractions of sodium caseinate. The fractions were cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) for 0–48 h. Purified β-casein (β-Cn) served as standard. The preparation of the sodium caseinate fractions is described in Appendix A. Experimental details for SDS-PAGE can be found in Appendix A.2.

Figure A2.
Linear sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of sodium caseinate and casein in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, cross-linked by microbial transglutaminase (3 U per g protein, 40 °C) for 0–24 h. Unpublished results obtained in a previous study [31]. Experimental details for SDS-PAGE can be found in Appendix A.2.
References
- Carr, A.; Golding, M. Functional Milk Proteins Production and Utilization: Casein-Based Ingredients. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., O’Mahony, J.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1B: Proteins: Applied Aspects, pp. 35–66. ISBN 978-1-4939-2800-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, J.; Mulvihill, D.M. Caseins and Caseinates, Industrial Production, Compositional Standards, Specifications, and Regulatory Aspects. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 855–863. ISBN 978-0-12-374407-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Gazi, I.; Luyten, H.; Nieuwenhuijse, H.; Alting, A.; Schokker, E. Hydration of Casein Micelles and Caseinates: Implications for Casein Micelle Structure. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, H.; Schmid, W. Influence of Dry-Matter Fortification on Flow Properties of Yoghurt. 1. Evaluation of Flow Curves. Milchwiss. Milk Sci. Int. 1993, 48, 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Ünal, G.; Akalin, A.S. Influence of Fortification with Sodium-Calcium Caseinate and Whey Protein Concentrate on Microbiological, Textural and Sensory Properties of Set-Type Yoghurt. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2013, 66, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.G.; Mulvihill, D.M. Effect of Sodium Caseinate on the Stability of Cream Liqueurs. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1997, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. Aspects of Milk-Protein-Stabilised Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizzie-Hayford, N.; Jaros, D.; Zahn, S.; Rohm, H. Effects of Protein Enrichment on the Microbiological, Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Fermented Tiger Nut Milk. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Chronakis, I.S. Crosslinking of Milk Proteins by Microbial Transglutaminase: Utilization in Functional Yogurt Products. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeih, E.; Walker, G. Recent Advances on Microbial Transglutaminase and Dairy Application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Greiner, R.; George, S.; Roohinejad, S. Recent Advances in the Application of Microbial Transglutaminase Crosslinking in Cheese and Ice Cream Products: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raak, N.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Enzymatic Protein Cross-Linking in Dairy Science and Technology. In Agents of Change: Enzymes in Milk and Dairy Products; Kelly, A., Larsen, L.B., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 417–445. ISBN 978-3-030-55481-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, J.A.; Fazani Cavallieri, A.L.; Lopes da Cunha, R.; Sato, H.H. The Effect of Transglutaminase from Streptomyces sp. CBMAI 837 on the Gelation of Acidified Sodium Caseinate. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllärinen, P.; Buchert, J.; Autio, K. Effect of Transglutaminase on Rheological Properties and Microstructure of Chemically Acidified Sodium Caseinate Gels. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Enzymatic Cross-Linking of Casein Facilitates Gel Structure Weakening Induced by Overacidification. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, H.; Ullrich, F.; Schmidt, C.; Löbner, J.; Jaros, D. Gelation of Cross-Linked Casein under Small and Large Shear Strain. J. Texture Stud. 2014, 45, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizzie-Hayford, N.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Enrichment of Tiger Nut Milk with Microbial Transglutaminase Cross-Linked Protein Improves the Physico-Chemical Properties of the Fermented System. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Yuan, D.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, L. Influence of Transglutaminase-Induced Modification of Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC) on Yoghurt Texture. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 78, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, C.; Kulozik, U. Effect of Transglutaminase-Treated Milk Powders on the Properties of Skim Milk Yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeih, E.; Albadarin, A.B.; Olaleye, A.; Walker, G. Enzymatically Cross-Linked Skim Milk Powder: Enhanced Rheological and Functional Properties. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 113, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, B.; Beicht, J.; Eisele, T.; Gibis, M.; Fischer, L.; Weiss, J. Transglutaminase-Induced Crosslinking of Sodium Caseinate Stabilized Oil Droplets in Oil-In-Water Emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Enzymatically Cross-Linked Sodium Caseinate as Techno-Functional Ingredient in Acid-Induced Milk Gels. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2020, 13, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, D.; Partschefeld, C.; Henle, T.; Rohm, H. Transglutaminase in Dairy Products: Chemistry, Physics, Applications. J. Texture Stud. 2006, 37, 113–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, R.A.; Raak, N.; Boye, S.; Janke, A.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D.; Lederer, A. Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation for the Investigation of Caseins Cross-linked by Microbial Transglutaminase. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannß, M.; Abbate, R.A.; Mitzenheim, E.; Alkhalaf, M.; Boehm, W.; Lederer, A.; Henle, T. Association of Enzymatically and Non-Enzymatically Functionalized Caseins Analyzed by Size-Exclusion Chromatography and Light Scattering Techniques. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2773–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Abbate, R.A.; Alkhalaf, M.; Lederer, A.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Concentration-Triggered Liquid-To-Solid Transition of Sodium Caseinate Suspensions as a Function of Temperature and Enzymatic Cross-Linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HadjSadok, A.; Pitkowski, A.; Nicolai, T.; Benyahia, L.; Moulai-Mostefa, N. Characterisation of Sodium Caseinate as a Function of Ionic Strength, pH and Temperature Using Static and Dynamic Light Scattering. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smialowska, A.; Matia-Merino, L.; Ingham, B.; Carr, A.J. Effect of Calcium on the Aggregation Behaviour of Caseinates. Coll. Surf. A 2017, 522, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Brehm, L.; Abbate, R.A.; Henle, T.; Lederer, A.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Self-association of casein studied using enzymatic cross-linking at different temperatures. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Brehm, L.; Leidner, R.; Henle, T.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Hydrolysis by Indigenous Plasmin: Consequences for Enzymatic Cross-Linking and Acid-Induced Gel Formation of Non-Micellar Casein. Food Biophys. 2020, 15, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Schöne, C.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Acid-Induced Gelation of Enzymatically Cross-Linked Caseinate in Different Ionic Milieus. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Dairy Federation. Caseins and Caseinates—Determination of Protein Content (Reference Method); IDF Standard 92: Brussels, Belgium, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, J.E.; Cole, P.W. Structural Requirements of Specific Substrates for Guinea Pig Liver Transglutaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, J.E.; Cole, P.W. Mechanism of Action of Guinea Pig Liver Transglutaminase. I. Purification and Properties of the Enzyme: Identification of a Functional Cysteine Essential for Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 5518–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, D.; Jacob, M.; Otto, C.; Rohm, H. Excessive Cross-Linking of Caseins by Microbial Transglutaminase and Its Impact on Physical Properties of Acidified Milk Gels. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Abbate, R.A.; Lederer, A.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Size Separation Techniques for the Characterisation of Cross-Linked Casein: A Review of Methods and Their Applications. Separations 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macierzanka, A.; Bordron, F.; Rigby, N.M.; Mills, E.N.C.; Lille, M.; Poutanen, K.; Mackie, A.R. Transglutaminase Cross-Linking Kinetics of Sodium Caseinate is Changed after Emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bönisch, M.P.; Lauber, S.; Kulozik, U. Improvement of Enzymatic Cross-Linking of Casein Micelles with Transglutaminase by Glutathione Addition. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizzie-Hayford, N.; Raak, N.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Addition of Crude Tiger Nut Protein Extract Affects Stiffness of Enzymatically Cross-Linked Dairy Proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeckel, U.; Duerasch, A.; Weiz, A.; Ruck, M.; Henle, T. Glycation Reactions of Casein Micelles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagel, L. Gel Filtration: Size Exclusion Chromatography. In Protein Purification: Principles, High Resolution Methods, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Janson, J.-C., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 51–91. ISBN 978-0-470-93993-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, O.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Rohm, H.; Henle, T. Casein Gelation under Simultaneous Action of Transglutaminase and Glucono-δ-Lactone. Food Nahr. 2004, 48, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raak, N.; Gehrisch, S.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Rotational Thromboelastometry for Characterising Acid-Induced Gelation of Cross-Linked Casein. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A.; Srinivasan, M.; Singh, H.; Munro, P.A. Characterization of Commercial and Experimental Sodium Caseinates by Multiangle Laser Light Scattering and Size-Exclusion Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, E.A.; Donato, L.; Dalgleish, D.G. Effects of Added Sodium Caseinate on the Formation of Particles in Heated Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8265–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, D.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Raak, N.; Löbner, J.; Henle, T.; Rohm, H. Cross-Linking with Microbial Transglutaminase: Relationship between Polymerisation Degree and Stiffness of Acid Casein Gels. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 38, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, D.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Raak, N.; Löbner, J.; Henle, T.; Rohm, H. Corrigendum to “Cross-Linking with Microbial Transglutaminase: Relationship between Polymerisation Degree and Stiffness of Acid Casein Gels” [Int Dairy J 38 (2014) 174–178]. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 39, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A.; van Vliet, T.; Grolle, K.; Geurts, T.; Walstra, P. Properties of Acid Casein Gels Made by Acidification with Glucono-δ-Lactone. 1. Rheological Properties. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matia-Merino, L.; Lau, K.; Dickinson, E. Effects of Low-Methoxyl Amidated Pectin and Ionic Calcium on Rheology and Microstructure of Acid-Induced Sodium Caseinate Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Cross-linking with Microbial Transglutaminase: Isopeptide Bonds and Polymer Size as Drivers for Acid Casein Gel Stiffness. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 66, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saricay, Y.; Wierenga, P.A.; de Vries, R. Rheological Properties of Dispersions of Enzymatically Cross-Linked Apo-α-Lactalbumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N. Cross-Linking with Microbial Transglutaminase: Drivers of Structure-Function-Interrelations in Acid Caseinate Gels. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 8 July 2019. Available online: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-qucosa2-361633 (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Hannß, M.; Böhm, W.; Drichel, S.; Henle, T. Acid-Induced Gelation of Enzymatically and Nonenzymatically Cross-Linked Caseins—Texture Properties, and Microstructural Insights. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13970–13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschakis, T.; Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. On the Kinetics of Acid Sodium Caseinate Gelation Using Particle Tracking to Probe the Microrheology. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A.; van Vliet, T.; Grolle, K.; Geurts, T.; Walstra, P. Properties of Acid Casein Gels Made by Acidification with Glucono-δ-Lactone. 2. Syneresis, Permeability and Microstructural Properties. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercili-Cura, D.; Lille, M.; Legland, D.; Gaucel, S.; Poutanen, K.; Partanen, R.; Lantto, R. Structural Mechanisms Leading to Improved Water Retention in Acid Milk Gels by Use of Transglutaminase. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).