Dietary Patterns and Depression: First Results in a Cross-Sectional Study from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
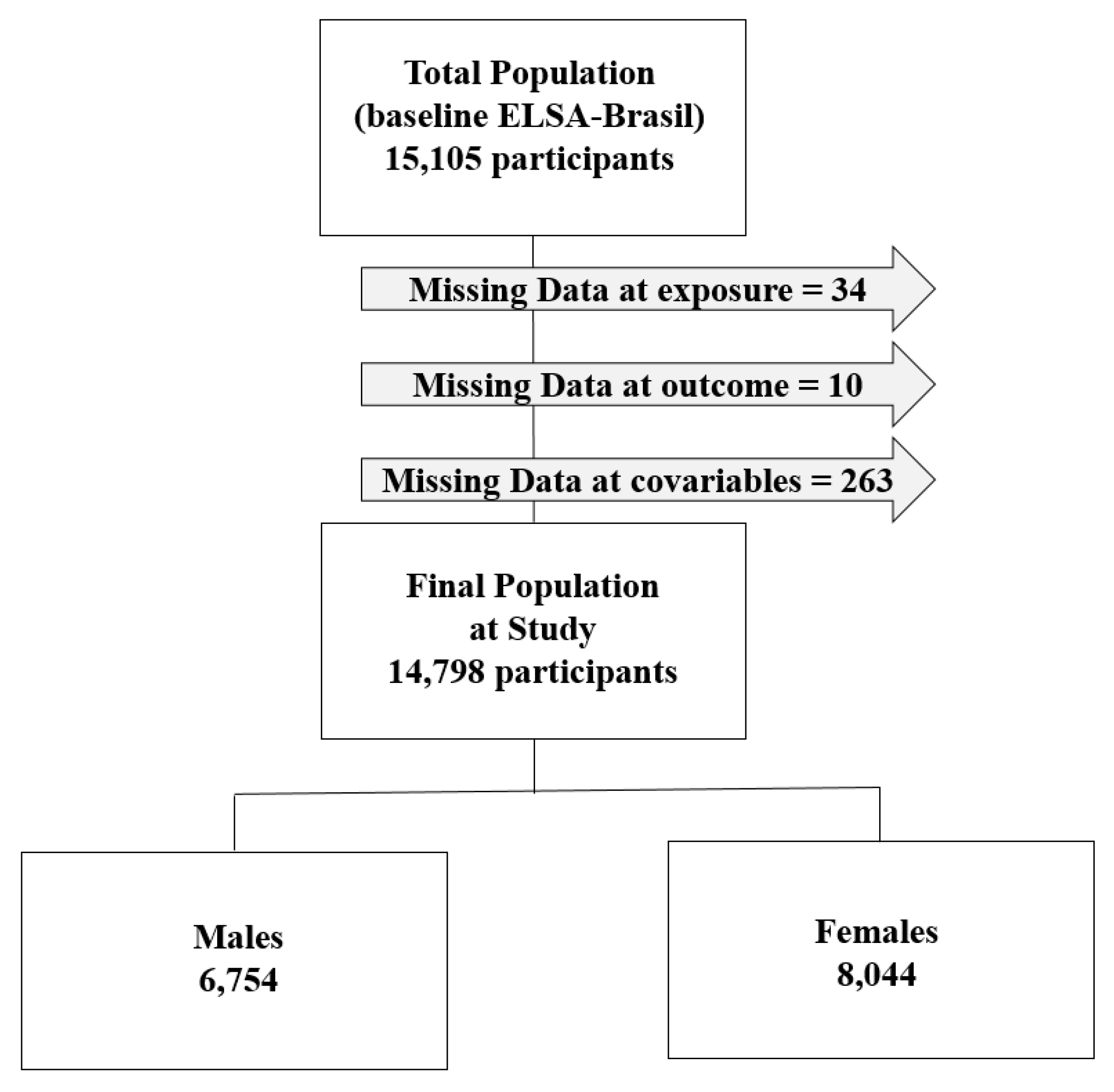
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diet Assessment and Dietary Patterns Estimation
2.3. Evaluation of Episodes of Depression
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
2.7. Conflict of Interest and Responsibility for the Manuscript
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- World Health Organization. WHO: The Global Burden of Disease, 2004; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Barber, R.M.; Foreman, K.J.; Abbasoglu Ozgoren, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.P.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990–2013: Quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet 2015, 386, 2145–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.F.; Mello, A.A.; Kohn, R. Epidemiologia da Saúde Mental no Brasil; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Melanson, K.J. Nutrition review: Relationships of nutrition with depression and anxiety. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2007, 1, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.E. Nutrition and late-life depression: Etiological considerations. Aging Health 2010, 6, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Port, A.; Gueguen, A.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Melchior, M.; Lemogne, C.; Nabi, H.; Goldberg, M.; Zins, M.; Czernichow, S. Association between dietary patterns and depressive symptoms over time: A 10-year follow-up study of the GAZEL cohort. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Martinez-Gonzales, M. Diet, a new target to prevent depression? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanhueza, C.; Ryan, L.; Foxcroft, D.R. Diet and the risk of unipolar depression in adults: Systematic review of cohort studies. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 26, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaraly, T.N.; Sabia, S.; Shipley, M.J.; Batty, G.D.; Kivimaki, M. Adherence to healthy dietary guidelines and future depressive symptoms: Evidence for sex differentials in the Whitehall II study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbody, S.; Lightfoot, T.; Sheldon, T. Is low folate a risk factor for depression? A meta-analysis and exploration of heterogeneity. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2007, 61, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Verberne, L.; De Irala, J.; Ruíz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Serra-Majem, L.; Martínez-González, M.A. Dietary fat intake and the risk of depression: The SUN Project. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Toledo, E.; de Irala, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Pla-Vidal, J.; Martínez-González, M.A. Fast-food and commercial baked goods consumption and the risk of depression. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oddy, W.H.; Robinson, M.; Ambrosini, G.L.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; de Klerk, N.H.; Beilin, L.J.; Silburn, S.R.; Zubrick, S.R.; Stanley, F.J. The association between dietary patterns and mental health in early adolescence. Prev. Med. 2009, 49, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanri, A.; Kimura, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Ohta, M.; Sato, M.; Mishima, N.; Sasaki, S.; Mizoue, T. Dietary patterns and depressive symptoms among Japanese men and women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popa, T.A.; Ladea, M. Nutrition and depression at the forefront of progress. J. Med. Life 2012, 5, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chocano-Bedoya, P.O.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Lucas, M.; Mirzaei, F.; Okereke, O.I.; Fung, T.T.; Hu, F.B.; Ascherio, A. Prospective study on long-term dietary patterns and incident depression in middle-aged and older women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rienks, J.; Dobson, A.J.; Mishra, G.D. Mediterranean dietary pattern and prevalence and incidence of depressive symptoms in mid-aged women: Results from a large community-based prospective study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, R.; Chan, D.; Woo, J. A prospective cohort study to examine the association between dietary patterns and depressive symptoms in older Chinese people in Hong Kong. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.S.; Hiles, S.; Bisquera, A.; Hure, A.J.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of dietary patterns and depression in community-dwelling adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahe, C.; Unrath, M.; Berger, K. Dietary patterns and the risk of depression in adults: A systematic review of observational studies. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 53, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruusunen, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Mursu, J.; Tolmunen, T.; Tuomainen, T.P.; Kauhanen, J.; Voutilainen, S. Dietary patterns are associated with the prevalence of elevated depressive symptoms and the risk of getting a hospital discharge diagnosis of depression in middle-aged or older Finnish men. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 159, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, A.A.; Farias, D.R.; Eshriqui, I.; Vaz Jdos, S.; Franco-Sena, A.B.; Castro, M.B.; Olinto, M.T.; Machado, S.P.; Moura da Silva, A.A.; Kac, G. Pre-pregnancy healthy dietary pattern is inversely associated with depressive symptoms among pregnant Brazilian women. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khosravi, M.; Sotoudeh, G.; Majdzadeh, R.; Nejati, S.; Darabi, S.; Raisi, F.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Sorayani, M. Healthy and unhealthy dietary patterns are related to depression: A case-control study. Psychiatry Investig. 2015, 12, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Park, Y. Associations between dietary pattern and depression in Korean adolescent girls. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2015, 28, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, T.; Kochi, T.; Kuwahara, K.; Eguchi, M.; Kurotani, K.; Tsuruoka, H.; Ito, R.; Kabe, I.; Kawakami, N.; Mizoue, T.; et al. Dietary patterns derived by reduced rank regression (RRR) and depressive symptoms in Japanese employees: The Furukawa nutrition and health study. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 229, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Alonso, A.; Schlatter, J.; Lahortiga, F.; Serra Majem, L.; Martínez-González, M.A. Association of the Mediterranean dietary pattern with the incidence of depression: The Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra/University of Navarra follow-up (SUN) cohort. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, H.J. The association between dietary pattern and depression in middle-aged Korean adults. Nutr. Res Pract. 2019, 13, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzada, M.L.C.; Martins, A.P.B.; Canella, D.S.; Baraldi, L.G.; Levy, R.B.; Claro, R.M.; Moubarac, J.C.; Cannon, G.; Monteiro, C.A. Ultra-processed foods and the nutritional dietary profile in Brazil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubarac, J.C. Ultra-processed Foods in Canada: Consumption, Impact on Diet Quality and Policy Implications; TRANSNUT, University of Montreal: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2017; Available online: https://mma.prnewswire.com/media/615057/Heart_and_Stroke_Foundation_Time_to_curb_our_appetite_for_ultra_.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Aquino, E.M.L.; Barreto, S.M.; Bensenor, I.M.; Carvalho, M.S.; Chor, D.; Duncan, B.B.; Lotufo, P.A.; Mill, J.G.; Molina, M.C.; Mota, E.L.; et al. Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil): Objectives and design. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B.; Mill, J.G.; Lotufo, P.A.; Chor, D.; Barreto, S.M.; Aquino, E.M.; Passos, V.M.; Matos, S.M.; Molina, M.C.; et al. Cohort profile: Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.I.; Schmidt, M.I.; Griep, R.H.; Passos, V.M.; Luft, V.C.; Goulart, A.C.; Menezes, G.M.S.; Molina, M.C.; Bisi, V.A.; Nunes, M.A. Strategies and development of quality assurance and control in the ELSA-Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2013, 47, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bensenor, I.M.; Griep, R.H.; Pinto, K.A.; Faria, C.P.; Felisbino-Mendes, M.; Caetano, E.I.; Albuquerque, L.S.; Schmidt, M.I. Routines of organization of clinical tests and interviews in the ELSA-Brasil investigation center. Rev. Saúde Pública 2013, 47 (Suppl. 2), 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chor, D.; Alves, M.G.; Giatti, L.; Cade, N.V.; Nunes, M.A.; Molina, M.C.; Benseñor, I.M.; Aquino, E.M.; Passos, V.; Santos, S.M.; et al. Questionnaire development in ELSA-Brasil: Challenges of a multidimensional instrument. Rev.Saúde Pública 2013, 47 (Suppl. 2), 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molina, M.C.B.; Benseñor, I.M.; Cardoso, L.O.; Velasquez-Melendez, G.; Drehmer, M.; Pereira, T.S.S.; Faria, C.P.; Melere, C.; Manato, L.; Gomes, A.L.C.; et al. Reprodutibilidade e validade relativa do Questionário de Frequência Alimentar do ELSA-Brasil. Cad. Saúde Pública 2013, 29, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F. Multivariate Data Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, L.O.; Carvalho, M.S.; Cruz, O.G.; Melere, C.; Luft, V.C.; Molina, M.C.; Faria, C.P.; Benseñor, I.M.; Matos, S.M.; Fonseca, M.J.; et al. Eating patterns in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil): An exploratory analysis. Cad. Saúde Pública 2016, 32, e00066215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, U.E.; Beglinger, C.; Schweinfurth, N.; Walter, M.; Borgwardt, S. Nutritional aspects of depression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schakel, S.F. Maintaining a nutrient database in a changing marketplace: Keeping pace with changing food products—A research perspective. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2001, 14, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.; Pelosi, A.J.; Araya, R.; Dunn, G. Measuring psychiatric disorder in the community: A standardized assessment for use by lay interviewers. Psychol. Med. 1992, 22, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.A.; Alves, M.G.M.; Chor, D.; Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B. Adaptação transcultural do CIS-R (Clinical Interview Schedule–Revised Version) para o português no estudo longitudinal de saúde do adulto (ELSA). Clin. Biomed. Res. 2011, 31, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Botega, N.J.; Pereira, W.A.; Bio, M.R.; Garcia Júnior, C.; Zomignani, M.A. Psychiatric morbidity among medical in patients: A standardized assessment (GHQ-12 and CIS-R) using lay interview in a Brazilian hospital. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 1995, 30, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, S.; Bebbington, P.; Jenkins, R.; Brugha, T. (Eds.) Mental Health and Wellbeing in England: Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey 2014; NHS Digital: Leeds, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, B.A.; Luft, V.C.; Schmidt, M.I.; Chambless, L.E.; Chor, D.; Barreto, S.M.; Duncan, B.B. Timing and Type of Alcohol Consumption and the Metabolic Syndrome—ELSA-Brasil. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.I.; Sadock, B.J.; Grebb, J.A. Compêndio de Psiquiatria. Ciências do Comportamento e Psiquiatria Clínica; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Quevedo, J.; Silva, A.G. Depressão Teoria e Clínica; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.A.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Bessel, M.; Brunoni, A.R.; Kemp, A.H.; Benseñor, I.M.; Chor, D.; Barreto, S.; Schmidt, M.I. Common mental disorders and sociodemographic characteristics: Baseline findings of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2016, 38, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.J.; Milte, C.M.; Torres, S.J.; Thorpe, M.G.; McNaughton, S.A. Dietary patterns are associated with depressive symptoms in older Australian women but not men. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R.C. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.S. R Studio: Integrated Development for R; R Studio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lv, M.R.; Wei, Y.J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, H.G.; Li, B. Dietary patterns and depression risk: A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 253, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Ruíz-Canela, M.; de la Fuente-Arrillaga, C.; Gea, A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Martínez-González, M.A. Dietary inflammatory index, cardiometabolic conditions and depression in the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Suzuki, K.; Ma, S.; Liu, C. Linking What We Eat to Our Mood: A Review of Diet, Dietary Antioxidants, and Depression. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brownell, K.D.; Gold, M.S. Food and Addiction. A Comprehensive Handbook; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, D.C. Theories of drug craving, ancient and modern. Addiction 2001, 96, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Andrade, J. The elaborated intrusion theory of desire: A 10-year retrospective and implications for addiction treatments. Addict. Behav. 2015, 44, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelchat, M.L. Of human bondage: Food craving, obsession, compulsion, and addiction. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 76, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, S.T.; Wray, J.M. The clinical significance of drug craving. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1248, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, R.J.; Wurtman, J.J. Brain Serotonin, Carbohydrate-Craving, Obesity and Depression. Obes. Res. 1995, 3 (Suppl. 4), 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knüppel, A.; Shipley, M.J.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Brunner, E.J. Sugar intake from sweet food and beverages, common mental disorder and depression: Prospective findings from the Whitehall II study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, D.P.; Williams, P.A. User’s Guide to the General Health Questionnaire; NFER-Nelson: Windsor, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. BDI-II: Beck Depression Inventory Manual; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, I.M.; Crawford, J.R.; Reid, I.C. Psychometric comparison of PHQ-9 and HADS for measuring depression severity in primary care. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2008, 58, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacka, F.N.; Cherbuin, N.; Anstey, K.J.; Butterworth, P. Dietary patterns and depressive symptoms over time: Examining the relationships with socioeconomic position, health behaviours and cardiovascular risk. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, P.F.; Tucker, K.L. Are dietary patterns useful for understanding the role of diet in chronic disease? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canale, A.; Furlan, M.M.D.P. Depressão. Arq. MUDI 2006, 10, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jacka, F.N.; Cherbuin, N.; Anstey, K.J.; Butterworth, P. Does reverse causality explain the relationship between diet and depression? J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 175, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Nunes, M.A.; Figueiredo, R.; Barreto, S.M.; da Fonseca, M.J.; Lotufo, P.A.; Benseñor, I.M. Patterns of benzodiazepine and antidepressant use among middle-aged adults. The Brazilian longitudinal study of adult health (ELSA-Brasil). J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 151, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Men (n = 6754) | Women (n = 8044) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Men | % | Depressive Episode | Prev. % | Total Women | % | Depressive Episode | Prev. % | |
| Dietary Pattern * | ||||||||
| Traditional | 3196 | 47.32 | 73 | 2.28 | 3549 | 44.12 | 190 | 5.35 |
| Fruit and Vegetables | 1304 | 19.31 | 25 | 1.92 | 2489 | 30.94 | 133 | 5.34 |
| Low-Sugar/Low-Fat | 175 | 2.59 | 3 | 1.71 | 465 | 5.78 | 15 | 3.23 |
| Bakery Products | 2079 | 30.78 | 56 | 2.69 | 1541 | 19.16 | 130 | 8.44 |
| Age—Years (SD) | ||||||||
| Mean Values | 52.24 (9.33) | 50.68 (9.46) | 52.05 (8.86) | 51.20 (8.23) | ||||
| Schooling * | ||||||||
| Never Attended School or Incomplete Elementary School (<5 Years of Schooling) | 555 | 8.22 | 15 | 2.70 | 321 | 3.99 | 25 | 7.79 |
| Complete Elementary School or Incomplete Secondary School (<12 Years of Schooling) | 567 | 8.40 | 22 | 3.88 | 440 | 5.47 | 37 | 8.41 |
| Complete Secondary School (12 Years of Schooling) | 2210 | 32.72 | 63 | 2.85 | 2901 | 36.06 | 222 | 7.65 |
| University Degree (>12 Years of Schooling) | 3422 | 50.67 | 57 | 1.67 | 4382 | 54.48 | 184 | 4.20 |
| Marital Status * | ||||||||
| Married/Cohabiting | 5528 | 81.85 | 108 | 1.95 | 4262 | 52.98 | 231 | 5.42 |
| Separated/Divorced | 794 | 11.76 | 33 | 4.16 | 2089 | 25.97 | 159 | 7.61 |
| Single | 352 | 5.21 | 11 | 3.13 | 1156 | 14.37 | 49 | 4.24 |
| Widowed | 80 | 1.18 | 5 | 6.25 | 537 | 6.68 | 29 | 5.40 |
| BMI * | ||||||||
| Underweight | 64 | 0.95 | 2 | 3.13 | 74 | 0.92 | 2 | 2.70 |
| Normal Weight | 2245 | 33.24 | 53 | 2.36 | 3063 | 38.08 | 133 | 4.34 |
| Overweight | 3051 | 45.17 | 59 | 1.93 | 2908 | 36.15 | 179 | 6.16 |
| Obese | 1394 | 20.64 | 43 | 3.08 | 1999 | 24.85 | 154 | 7.70 |
| MET-Minutes—Metabolic Equivalent Minutes (SD) | ||||||||
| Mean Values | 803.60 (1197.13) | 575.20 (1007.78) | 563.80 (955.61) | 294.20 (683.28) | ||||
| Dietary Pattern | All Participants | Men | Women | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 14,798) | (n = 6754) | (n = 8044) | |||||||
| OR | 95% CI | Pr (>|Z|) | OR | 95% CI | Pr (>|Z|) | OR | 95% CI | Pr (>|Z|) | |
| Crude Model | |||||||||
| Traditional | 1.00 | - | - | 1.00 | - | - | 1.00 | - | - |
| Low-Sugar/Low-Fat | 0.71 | (0.44–1.16) | 0.172 | 0.75 | (0.23–2.39) | 0.622 | 0.59 | (0.34–1.01) | 0.053 |
| Fruit and Vegetables | 1.07 | (0.87–1.31) | 0.503 | 0.84 | (0.53–1.32) | 0.445 | 1.00 | (0.79–1.25) | 0.986 |
| Bakery Products | 1.33 | (1.10–1.62) | 0.003 | 1.18 | (0.83–1.68) | 0.347 | 1.63 | (1.29–2.05) | 0.000 |
| Adjusted Model a | |||||||||
| Traditional | 1.00 | - | - | 1.00 | - | - | 1.00 | - | - |
| Low-Sugar/Low-Fat | 0.90 | (0.55–1.47) | 0.665 | 1.08 | (0.33–3.53) | 0.896 | 0.90 | (0.52–1.56) | 0.708 |
| Fruit and Vegetables | 1.09 | (0.88–1.34) | 0.435 | 0.93 | (0.58–1.50) | 0.784 | 1.15 | (0.91–1.46) | 0.246 |
| Bakery Products | 1.20 | (0.98–1.47) | 0.072 | 0.94 | (0.65–1.36) | 0.745 | 1.33 | (1.05–1.70) | 0.019 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno, A.B.; Chor, D.; Bensenor, I.M.; Nunes, M.A.; Griep, R.H.; Cardoso, L.O. Dietary Patterns and Depression: First Results in a Cross-Sectional Study from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Psych 2020, 2, 11-24. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2010002
Moreno AB, Chor D, Bensenor IM, Nunes MA, Griep RH, Cardoso LO. Dietary Patterns and Depression: First Results in a Cross-Sectional Study from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Psych. 2020; 2(1):11-24. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno, Arlinda B., Dóra Chor, Isabela M. Bensenor, Maria A. Nunes, Rosane H. Griep, and Leticia O. Cardoso. 2020. "Dietary Patterns and Depression: First Results in a Cross-Sectional Study from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil)" Psych 2, no. 1: 11-24. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2010002
APA StyleMoreno, A. B., Chor, D., Bensenor, I. M., Nunes, M. A., Griep, R. H., & Cardoso, L. O. (2020). Dietary Patterns and Depression: First Results in a Cross-Sectional Study from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Psych, 2(1), 11-24. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2010002





