Abstract
Cobalt–zeolite composite catalysts (Co–zeolite) and their heterogeneous catalytic systems have garnered significant research attention owing to their superior catalytic activity and cost-effectiveness. The speciation of cobalt within these catalysts—either through impregnation onto the zeolite framework or structural incorporation within the aluminosilicate matrix—is critically governed by the employed synthesis methodology, which subsequently dictates their distinct catalytic advantages in targeted reaction systems. Compared to homogeneous catalytic systems, heterogeneous Co–zeolite configurations demonstrate enhanced structural integrity that effectively mitigates cobalt leaching, thereby improving catalyst recyclability while minimizing environmental contamination. This review systematically examines recent advancements in Co–zeolite fabrication techniques and their catalytic performance across diverse applications, including Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, nitrogen oxide abatement, hydrogenation processes, and oxidative transformations. Particular emphasis is placed on elucidating the metal-framework interactions, with analysis of synergistic effects arising from multi-valent cobalt speciation and bimetallic cooperativity between cobalt and secondary transition metals. This work critically evaluates current challenges in Co–zeolite catalyst design. Finally, we propose future research directions focusing on a precise identification of active species and mechanistic elucidation, innovative synthesis strategies for cobalt speciation control, machine learning-guided catalyst optimization, and the advancement of eco-friendly catalysts.
1. Introduction
The superior efficacy of noble metal catalysts is widely acknowledged. However, their exorbitant cost has substantially constrained their extensive application in industrial production. In this context, cobalt-based catalysts emerge as a viable alternative due to their comparatively lower cost and exceptional catalytic ability. This ability is either on par with or even exceeds that of noble metals in certain reactions [1,2,3,4,5].
In general, cobalt catalysts can exist in various morphologies. These morphologies not only enable the formation of complexes with ligands for homogeneous catalysis [6] but also facilitate their loading onto other supports such as various oxides and carbon-derived materials [7]. However, both the dimerization and/or oligomerization of complexes in homogeneous systems [8,9], as well as the aggregation of cobalt species or the deposition of coke in heterogeneous systems, may impede the further application of cobalt catalysts [10,11,12].
Cobalt–zeolite composite catalysts may offer an optimal solution. Zeolites, characterized by their ordered porous structure, possess several desirable attributes that make them an ideal support. These include a large surface area, adjustable pore size and acidity, high hydrothermal stability, and ion exchangeable sites [13,14,15]. Furthermore, zeolites themselves serve as significant catalysts in large-scale industrial production and scientific research, with applications in areas such as the catalytic cracking of petroleum, sewage treatment, and medicine. Their unique nanostructure, which features ubiquitous active sites, not only enables the cobalt species to be highly dispersed on the pore walls and/or framework, thereby preventing aggregation, but also enhances product selectivity [16]. This may also induce a “constraint effect”, which regulates catalytic side reactions that are prone to occur [17].
This review endeavors to present a comprehensive summary of cobalt–zeolite composite catalysts. We focused on the synthesis of catalysts and the morphology of cobalt and the synergistic effect of metal–framework interaction and bimetallic/multi-metallic in cobalt–zeolite composite catalysts. Next, the practical applications and catalytic performance study of cobalt–zeolite are reviewed (Figure 1). Following a summary of the advancements and challenges in potential applications, we offer a perspective on the future of cobalt–zeolite.
Figure 1.
Catalytic performance study of cobalt–zeolite composite catalysts.
2. Synthesis of Cobalt–Zeolite Composite Catalysts
2.1. Synthesis Method
Typically, cobalt–zeolite can be synthesized through various approaches. These methods can be broadly categorized into two main groups based on whether the incorporation of cobalt occurs during the synthesis process of the zeolite (in situ synthesis) or post-synthesis (Figure 2). One of the most representative methods from the former category is one-pot hydrothermal synthesis, which integrates the crystal framework around the Co2+ precursor via hydrothermal self-assembly [18,19]. The latter category mainly uses impregnation and ion exchange methods. In the impregnation method, synthesized zeolites are immersed in a solution of active Co species, and the suspension is heated and stirred until the Co species are anchored on the external surface or in the zeolite channels, followed by drying and calcination [20,21]. Conventional solution ion-exchange is similar to impregnation but involves the substitution of active cobalt species, such as cobalt ions, with cation sites on zeolites [22], while solid-state ion-exchange is achieved by ion exchange between a solid cobalt source and zeolite at high temperature [23].
The performance of cobalt–zeolite catalysts is primarily influenced by the type and morphology of Co species, which serve as the active component. These Co species typically manifest in the form of oxides, ions, or a metallic state on the inner/outer surfaces, within the framework, or within the supercages of the zeolite support [24,25,26,27] (Figure 2). A variety of Co species can be anchored onto zeolite supports through specific synthetic methods. For example, Zhang et al. loaded Co3O4 directly on the MWW zeolite and achieved high-efficiency oxidation of toluene and propane [28]. Xu et al. investigated three methods, including ion exchange, incipient-wetness impregnation, and solid-phase grinding, to establish a correlation between the chemical states of Co species and the C–H and C–C bond scissions during ethane dehydrogenation. The incipient-wetness impregnation method successfully produced stable, unreducible, and isolated exchanged Co sites that were anchored on the zeolite framework [29,30]. Sadek et al. synthesized catalysts that facilitated the incorporation of cobalt into SiBEA zeolite, resulting in isolated framework pseudo-tetrahedral Co(II) species. They observed a significant correlation between the presence and content of Co(II) in both the zeolite frame and extra-framework [31]. Cobalt oxides within zeolites tend to aggregate and grow, a process that not only obstructs the interconnections in zeolites, thereby inhibiting the mass transfer process, but also reduces the active surface area. A potential alternative solution could involve confining cobalt oxides within the zeolite cages. Lee et al. synthesized hollow ZSM-5 by selectively dissolving the ZSM-5 core using an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. Subsequently, they prepared CoOx/hollow ZSM-5, which contained uniformly sized CoOx nanoparticles within the zeolite through incipient wetness impregnation. The confined space effectively inhibited the sintering of active cobalt particles during Fischer–Tropsch synthesis [32]. Thermodynamic studies indicate that CoO readily transforms into Co3O4, with the latter demonstrating greater thermodynamic stability [33]. Recently, Zhang et al. have reported a hydrothermal method for synthesizing zeolite Beta containing ultra-small CoO particles. These particles exhibit high stability and dispersion, and demonstrate superior catalytic performance compared to other Co-containing zeolite Beta catalysts [34].
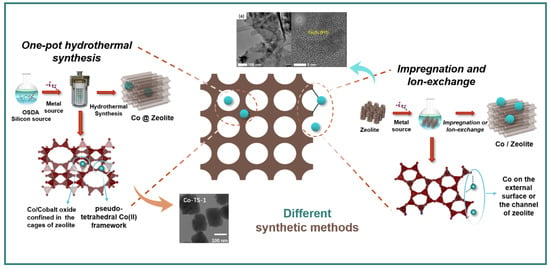
Figure 2.
Different kinds of Co species can be anchored on zeolite supports using specific synthetic methods. The symbol @ denotes core-shell structures, encapsulation configurations, or heterointerface composite systems. The brown arrow (One-pot hydrothermal synthesis) connects the structural model of the in-situ synthesized catalyst to its corresponding TEM image, while the blue arrow (Impregnation and Ion-exchange) links the structural model of the post-synthesized catalyst to its TEM image. TEM images adapted with permission from Refs. [25,28]. Copyright 2021, ACS Publications; 2024, Elsevier.
Co dispersion is critically influenced by synthesis methods: although high dispersion enhances activity, the associated high cost and intricate procedures hinder industrial scalability. Thus, industrial applications require balancing energy consumption, process intensification, and reproducibility metrics. Hydrothermal synthesis achieves atomic-level Co dispersion via controlled pH, temperature, and templating. Hellgardt’s team embedded Co atoms at specific Y-zeolite sites using in situ hydrothermal methods, with in situ characterization confirming high dispersion and exceptional semi-hydrogenation efficiency [35]. However, this method necessitates expensive structure-directing agents to prevent Co aggregation under alkaline conditions and prolonged synthesis times. Xiao’s group addressed this by introducing urea as a hard template, significantly reducing hydrothermal duration. The resulting CoS-1 catalyst matched Pt-based systems in propane dehydrogenation and enabled regeneration via air calcination, outperforming industrial CrOx/Al2O3 and PtSn/Al2O3 [36]. Post-synthetic methods (impregnation and ion exchange) offer industrial compatibility but often suffer from Co agglomeration and inhomogeneous distribution. Conventional impregnation may compromise hydrothermal stability due to exposed active sites, while random Co placement on microporous surfaces accelerates deactivation. Chelation-assisted strategies have emerged as solutions: Zurita et al. replaced aqueous solutions with ethylenediamine during impregnation, where ligand-induced steric hindrance enhanced Co dispersion [37]. This approach provides a cost-effective route to high-performance Co–zeolite catalysts.
2.2. Multiple Valence States of Co
Cobalt-based catalysts typically exhibit multiple valence states (Co2+, Co3+, and metallic Co0), and their exceptional catalytic performance stems from the dynamic synergy among these multivalent species and their rich redox properties. The ground-state electronic configuration of cobalt ([Ar]3d74s2) leads to significant variations in d-orbital electron counts and unpaired electrons depending on oxidation states (Co0: 3d74s2, Co2+: 3d7, Co3+: 3d6), endowing it with flexible electron transfer capabilities and adaptability to diverse reaction pathways. Metallic Co0 positions the d-band center near the Fermi level, enabling strong adsorption and activation of molecules such as H2 and CO. For instance, in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, Co0 nanoparticles dissociatively adsorb CO and regulate chain propagation pathways to optimize hydrocarbon selectivity. Additionally, the 4s orbital electrons weaken interactions with π-bonded molecules via antibonding orbital filling, thereby suppressing over-hydrogenation. Co2+ acts as a Lewis acid site to specifically interact with oxygen-containing functional groups, promoting substrate polarization. In selective oxidation reactions, Co2+ stabilizes radical intermediates through single-electron transfer mechanisms. Highly oxidized Co3+ exhibits strong electrophilicity, activating lattice oxygen to generate reactive oxygen species (O− or O2−), which serve as critical active sites in catalytic oxidation of VOCs and water splitting. The synergistic effects of multivalent cobalt species are often mediated by carrier interfaces or confinement structures, and advanced characterization techniques enable qualitative/quantitative analysis of these cooperative mechanisms. For example, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) quantifies the relative surface concentrations of Co2+, Co3+, and Co0, while depth profiling via Ar+ sputtering reveals bulk composition. X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) distinguishes oxidation states through Co K-edge absorption shifts. In situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM) monitors structural evolution of Co nanoparticles during reactions, and in situ Raman spectroscopy tracks dynamic changes in Co–O vibrational modes to probe redox transitions. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations elucidate electronic mechanisms of multivalent synergy by simulating d-band center positions, oxygen vacancy formation energies, and adsorption energy trends. For instance, in the Co0/CoO/Co3O4@K,N,O-doped carbon composite developed by Duan et al., XPS and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) analyses demonstrated that low-valent Co species dominate radical generation, while Co0 accelerates the initiation and cycling of Co-based redox pairs [38]. Peng’s team further validated via DFT calculations that the rapid Co3+/Co2+ redox cycling underpins the high catalytic activity in Fenton-like reactions [39].
2.3. Bimetallic Synergy
Furthermore, the introduction of bimetallic synergy can significantly enhance the catalytic activity of cobalt–zeolite systems by modulating the electronic structure or dispersion of cobalt species. Bimetallic systems typically exhibit synergistic, geometric, or electronic coupling effects, demonstrating superior catalytic performance compared to monometallic counterparts while reducing noble metal consumption and cost. The selection of secondary metals must align with zeolite topology and target reaction mechanisms: small-pore zeolites (CHA, AEI) preferentially accommodate redox-active metals with smaller dimensions (Cu, Ni) within their confined cages to stabilize isolated Co2+-Mn+ ion pairs, whereas large-pore zeolites (FAU, BEA) host bulkier noble metals (Pd, Pt) to form surface-confined Co-M nanoclusters for hydrocarbon upgrading. Metal pairing strategies also vary significantly depending on reaction mechanisms: radical-mediated processes (Fenton-like VOC oxidation) require coupling Co with oxygen-activating metals (Pd, Mn) to generate •OH/•OOH radicals, while thermally demanding reactions (Fischer–Tropsch synthesis) necessitate refractory metals (W, Re) to form Co alloys with enhanced sintering resistance. In environmental catalysis, non-noble metals (Fe, Ni) are favored due to cost efficiency and green chemistry compatibility. Notably, noble metals (Pd, Pt, Ag) play decisive roles in noble/transition metal pairs: Pd facilitates efficient H2 dissociation through its high hydrogen adsorption capacity and low H–H bond dissociation barrier, enabling hydrogen spillover to adjacent Co sites to enhance hydrogenation activity while suppressing Co aggregation; Pt’s high work function promotes electron transfer to Co, optimizing reducibility in hydrogenation; Ag’s low oxophilicity suppresses over-oxidation to improve partial oxidation selectivity. Current studies systematically explore how bimetallic synergy strengthens metal–framework interactions, focusing on precise control of active metal size/dispersion and optimization of reactant adsorption/dissociation. For instance, Zhu et al. developed a confined NiCo@silicalite-1 catalyst via grinding-crystallization, demonstrating exceptional sintering resistance and reduced carbon deposition [40]; Zhang’s team revealed that metallic Co dominates HMF conversion in Co/Sn-Beta composites, while framework Sn species regulate DMF selectivity through acid sites [41]; Wei’s PdCo/β-zeolite catalyst exhibited outstanding dehydrogenation performance for dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole via intermetallic electron transfer and strong metal-framework interactions [42]; Shi’s group found that Ag incorporation enhanced both the activity and hydrothermal stability of Co-ZSM-5 in CH4-SCR of NO [43]; Savost’yanov’s work highlighted Pt’s superior ability to modulate Co nanocluster electronic structures [44]. Subsequent sections will delve into the structure-activity relationships among cobalt species morphology, metal–framework interactions, and catalytic performance in specific reactions.
3. Application of Cobalt–Zeolite
3.1. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis
Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) offers an effective method to convert syngas, derived from natural gas, coal, and biomass, into clean hydrocarbon fuel and chemicals. This process has attracted significant research interest due to the ongoing depletion of conventional fossil resources and the increasing global demand for liquid fuel [45,46,47]. Currently, a range of metals, including Fe, Ru, Ni, and Co, have been identified as possessing catalytic activity for FTS. Among these, Co-based FTS catalysts are particularly notable due to their moderate cost, low water–gas shift reactivity, and slow deactivation rate. Despite the significant importance of the FTS process in both industrial applications and scientific research, it is still limited by two primary constraints [48]. The distribution of FTS products typically adheres to the Anderson–Schulz–Flory distribution. Consequently, the theoretical selectivity for gasoline-range hydrocarbons (generally, C5–C12) and diesel-range hydrocarbons (typically, C13–C20) is constrained to approximately 45% and 30%, respectively [49]. In addition, n-paraffins, as the predominant FTS products, degrade the quality of the synthetic gasoline by reducing its octane rating.
To enhance the selectivity towards the desired product, iso-paraffins, some scholars have proposed the assembly of active metals with zeolites to create a bifunctional catalyst. This approach allows for the hydrocracking/isomerization of primary heavy hydrocarbons formed on metal sites, which subsequently occur on zeolite surface acid sites. The result is the production of high-quality liquid hydrocarbons [50]. This method, while preserving the functionality of traditional catalysts, judiciously leverages the unique characteristics of zeolites, such as acidity, shape selectivity, and stability under FTS conditions [51]. For instance, cobalt nanoparticles anchored on ZSM-5 zeolite, a prevalent industrial catalyst, demonstrate superior CO hydrogenation efficacy and elevated C5+ hydrocarbon selectivity in the FTS [52]. Similarly, incorporating cobalt nanoparticles into zeolite crystals can also augment the selectivity of isoparaffins. This enhancement is attributed to the synergistic effect between the confined reaction environment and the optimal acidic properties [53].
As delineated in Section 2.1, numerous methods exist for the preparation of cobalt-containing zeolite, with the properties of the resultant catalyst being predominantly influenced by the chosen preparation technique [54,55]. Liu et al. have found that the catalyst, synthesized via the ultrasound-assisted impregnation method, exhibits superior selectivity for gasoline-range products and displays enhanced stability in CO conversion compared to its counterpart prepared by the incipient wetness impregnation method [56]. The study posits that an augmented dispersion of cobalt species amplifies its interaction with the zeolite surface, thereby promoting the hydrocracking of heavy hydrocarbons. Gorshkov et al. undertook additional investigations to elucidate the relationship between the efficacy of a cobalt catalyst embedded in zeolite and the agglomeration of cobalt clusters, as well as carbon deposition on the catalyst’s surface [11]. The use of suitable synthesis and regeneration methods is the key to maintaining the high activity of the catalyst. Ren et al. ground the MCM-22 with nanosized Co3O4 prefabricated by the thermal decomposition of the Co(II)-glycine complex to improve the mass-specific activity of Co supported on zeolite catalysts [57]. The study reveals that this innovative strategy significantly enhances the catalyst-specific activity of Co in FTS compared to the conventional impregnation method. Qi et al. developed ZSM-5 encapsulated cobalt particles, enhancing the thermal conductivity of the SiC matrix through a solvent-free synthesis method. The Co2C phase is readily produced during FTS, serving as a catalyst center for olefin synthesis [58].
To improve the catalytic performance of cobalt–zeolite catalysts in FTS, various innovative approaches have been developed and applied to conventional methods. For example, the shape selectivity of zeolites is derived from their unique pore structure. However, numerous acid and/or metal sites remain on the external surface, which can also participate in catalytic processes to form intermediates, potentially compromising product selectivity. Carvalho et al. engineered a nanocomposite wherein cobalt nanoparticles are exclusively confined within the zeolite pores. This was accomplished by employing heteropolyacid molecules, which are incapable of penetrating the zeolite pores, to selectively extract the metal oxide nanoparticles from the external zeolite surface (Figure 3) [59]. As expected, the modified catalyst showed obviously higher selectivity toward C5–12 branched hydrocarbons, and the maximum iso/n-paraffins ratio reached 5.8. The use of conventional synthesis methods always caused the zeolite pores to be filled with metal clusters, which would hinder the mass transfer process. Hierarchical porous systems have become a prevalent method to overcome the diffusion limitation of conventional zeolites. Khatrin et al. synthesized cobalt oxide-impregnated ZSM-5 zeolite samples with both intra- and inter-crystalline mesopores, employing two distinct synthesis strategies [60]. The researchers employed methane partial oxidation as a model reaction, discovering that the Co-oxide/ZSM-5 material, configured with inter-crystalline mesopores, exhibited greater activity in the methane partial oxidation reaction compared to its intracrystalline mesopore counterpart.
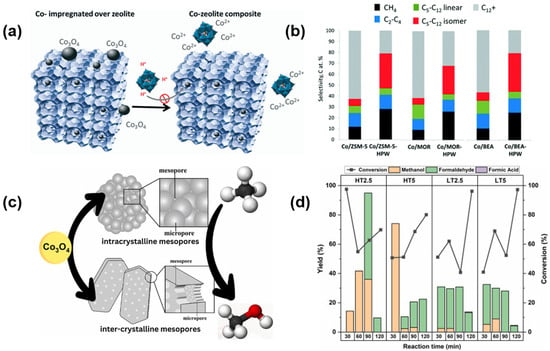
Figure 3.
(a) HPA extraction procedure for the synthesis of metal–zeolite composite material containing metal species only in the zeolite pores. (b) Selectivity (%) to hydrocarbons during FTS over cobalt–zeolite catalysts. Reproduced from Ref. [59]. Copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry. (c) Synthesis of hierarchical Co3O4/ZSM-5. (d) Catalytic activity (%) in methane partial oxidation of –3O4/ZSM-5. Reproduced from Ref. [60]. Copyright 2024, Elsevier.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the impact of bimetallic synergies on FTS. The incorporation of additional metals not only enhances the hydrogenation activity of the catalyst but also influences the particle size and cobalt reduction conditions. Yakovenko et al. pioneered the development of novel bifunctional Pt-Co/ZSM-5 catalysts [44]. The introduction of Pt intensified the hydrogenation processes, leading to the production of isomeric products and a reduction in unsaturated hydrocarbons. The study demonstrates that the activity of catalysts, as well as the distribution of products, is determined by the method of introducing a hydrogenating metal through the adjustment of the nano-sized spatial structure of the catalyst. Zhang et al. conducted an investigation into the impact of nickel incorporation on the catalytic efficacy of cobalt-based micro- and mesoporous Beta zeolite [61]. The introduction of Ni leads to a reduction in the temperature required for cobalt oxide reduction. The exceptional stability of Ni-Co/Beta catalysts is likely due to the hydrogen spillover mechanism, wherein metallic nickel particles aid in the transfer of hydrogen to cobalt oxides. This process effectively reduces re-oxidation of the active phase, sintering phenomena, and carbon deposition on the catalyst surface. The catalytic performance of the Co–zeolite catalyst in FTS is summarized in Table 1.
On the whole, the product distribution of FTS mainly depends on the following two points [32,62,63,64]. (a) The size and dispersion of cobalt nanoparticles, which can affect the active surface area as well as intensity of the interaction between metal sites and supports and in turn affect its own reducibility; (b) the acidity of zeolites and the shape/size of its channels that account for the hydrocracking and isomerizing capacity of the heavy hydrocarbons formed on metal sites and the shape selectivity. Furthermore, it is able to change the size and dispersion of cobalt nanoparticles to some extent, too.

Table 1.
Summary of catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis.
Table 1.
Summary of catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis.
| Catalyst | T (K) | Experimental Parameters | CO Conv. (%) | Product Selectivity (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PtCoAl2O3/SiO2 | 423 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 1000 h−1 | 87.2 | C5+: 70.6 | [44] |
| Co/HZSM-5 | 513 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 0.5 h−1 | 87 | C5+: 40 | [52] |
| Co3O4/Beta | 503 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 1705–1852 h−1 | 12.6 | C5+: 88.2 | [54] |
| Co/NaBEA | 523 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 40–65 L·h−1·gCo−1 | 68 | C5+: 71.9 | [55] |
| Co/H-ZSM-5 | 503 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 8 SL·g−1·h−1 | 14.3 | C5–12: 67.8 | [56] |
| Co-MCM-22 | 523 | H2/CO=2; W/F = 5.0 g·h·mol−1 | 60 | CH4: 33.3 | [57] |
| Co@ZSM-5/SiC | 673 | H2/CO=2; W/F = 10 g·h·mol−1 | 100 | C5–12: 60 | [58] |
| Co/BEA | 523 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 1.7–5 L·g−1·h−1 | 22 | Ciso(5–12): 35 | [59] |
| NiCoAlBeta | 533 | H2/CO=2; P = 30 atm | 100 | C5+: 100 | [60] |
| Co/SBA-15 | 463 | H2/CO=2; P = 1 atm | 4 | C5+: 71.8 | [64] |
| Co/MOR | 523 | H2/CO=2; GHSV 34 L·h−1·gCo−1 | 40.1 | C12+: 60.9 | [65] |
3.2. Catalytic Conversion of Nitrogen Oxides
Nitrogen oxides, including NO, NO2, and N2O, are significant greenhouse pollutants that contribute to a range of environmental issues, such as acid deposition and ozone layer destruction. These problems are becoming increasingly severe [65,66]. Therefore, it is crucial to identify effective methods for controlling nitrogen oxide emissions in order to protect the environment. The pioneering work of Iwamoto et al. [67], who used a catalytic conversion method to remove NO and N2O, has sparked interest in this area among many research groups. Subsequent studies have made substantial progress in understanding the reaction performance and mechanism involved in the catalytic removal of nitrogen oxides.
3.2.1. Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Decomposition
Transition and precious metal cation-exchanged zeolites are frequently employed in the decomposition of nitrous oxide [68,69]. Among the transition metal-exchanged zeolites, cobalt and copper zeolites exhibit the highest activity [70]. This study reports that, under severe reaction conditions, Co-ZSM-5 demonstrated significantly higher hydrothermal stability compared to other forms of metal–ZSM-5 [71]. Cruz et al. conducted a comparative analysis of the catalytic properties of cobalt-containing ZSM-5 zeolites, synthesized using various methods. They discovered that catalysts prepared through a single-step cation exchange method exhibited significantly higher activity and stability for N2O decomposition in the presence of O2 or H2O. This was particularly true when the reaction system contained both O2 and H2O. The enhanced performance could potentially be attributed to the rehydration of the isolated octahedral Co2+ ions within the zeolitic matrix [72]. In alignment with the aforementioned results, studies conducted by Ghahri et al. and Smeets et al. suggested that the isolated Co2+ ions occupying the ion exchange positions were instrumental in the high activity of the cobalt–zeolites catalysts [73,74]. Furthermore, after a detailed examination of the relationship between N2O decomposition activity and zeolite structure/active sites, Hao et al. identified that the most active sites in Co-ZSM-5 are α-type Co ions, which are weakly coordinated to framework oxygens within the straight channel. In contrast, in Co-BEA and Co-MOR, the most active sites are β-type Co ions, which are coordinated to the framework oxygens of the elongated six-membered ring of BEA and the interconnected small channel of MOR, respectively [75,76].
Contrary to prevailing assumptions, Abu-Zieds’ team suggests that the activity of N2O decomposition is associated with the relative decrease in conductivity upon introducing N2O over metal-exchanged ZSM-5 zeolites [77]. Catalysts exhibiting higher activity than their parent counterparts tend to experience a sharp decline in conductivity within the initial 5 min, followed by a gradual decrease. In contrast, catalysts with lower activity display a consistent, mild reduction in conductivity over the entire timescale. The study also examined the self-oscillatory behavior during N2O decomposition on Co-ZSM-5 catalysts. It was found that reducing the N2O inlet concentration, as well as the weight of the catalyst and increasing milling time, would result in the quenching of the established oscillations [78]. These may elucidate the factors influencing N2O decomposition activity from various angles, thereby facilitating the optimization of catalyst design.
Building upon prior research, an increasing number of modified cobalt–zeolite catalysts have been developed and examined. These advancements have effectively addressed the existing gaps in the underlying mechanisms. Li et al. successfully synthesized cobalt-incorporated HZSM-5 catalysts, where multiple cobalt species were identified and demonstrated cooperative catalysis in N2O decomposition [79]. Co2+ ions in cobalt species are regarded as active sites in N2O decomposition. Kang et al. synthesized a series of ZSM-5 zeolites with diverse contents and locations of Al pairs, in which Co2+ ions were subsequently anchored at the Al pairs by wet ion-exchange with H protons [80]. They found that the dissociation performance of N2O improved as more Al pairs coordinated with either protons or cobalt ions. Furthermore, the energy barrier required to overcome for O2 desorption at the γ-site Co2+ of ZSM-5 zeolite was less than that at the β-site (Figure 4).
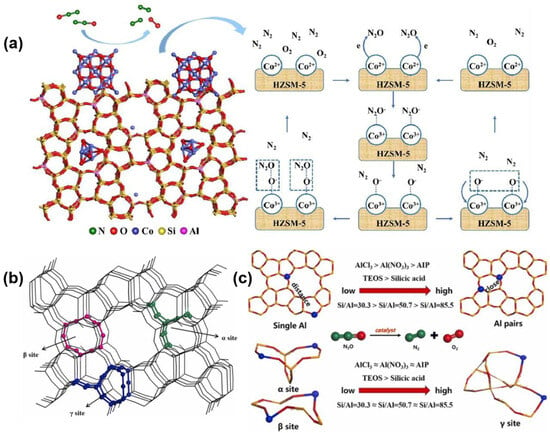
Figure 4.
Co2+ ions in cobalt species are regarded as active sites in N2O decomposition: (a) Schematic diagram of N2O adsorption on the Co/ZSM-5, Co2+ ions act as active sites for N2O decomposition, where dual-pathway oxygen release governs the cooperatively catalyzed reaction, with oxygen desorption identified as the rate-determining step. (b) Location of the α, β, and γ sites of Co2+ in ZSM-5 zeolite. (c) Al pairs coordinated with protons or cobalt ions. Reproduced from Refs. [79,80]. Copyright 2022,2024, Elsevier.
3.2.2. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NOx
Cobalt–zeolite catalysts have demonstrated activity in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx. They not only exhibit superior activity and selectivity compared to Cu catalysts due to their exceptional adsorption capacity for NO [81] but also outperform Fe-catalysts owing to their capability to form zero-valent metal clusters [82]. The study and development of SCR-NOx over cobalt–zeolite catalysts have gained momentum in recent decades, attributed to their unique properties. A variety of reductants, including NH3, ethanol, and hydrocarbons, can be employed in SCR-NOx. For the sake of clarity, a discussion on SCR-NOx over cobalt–zeolite catalysts is presented below, categorized by the type of reductants. The catalytic performance of the Co–zeolite catalyst in SCR is summarized in Table 2.
Cobalt–zeolite catalysts are effective for SCR-NOx, sustaining their high activity while enhancing stability and durability remains a challenge, particularly in the presence of water vapor. One solution is to prepare Co-Pd bimetallic catalysts by combining Co with Pd. The Pd species in Co-Pd-zeolite can enhance the reducibility of Co2+ at exchanged sites, promote methane activation, and significantly improve the water tolerance of the catalysts [83,84]. Conversely, some researchers posit that Pd2+ serves as the primary active species in the catalyst. They argue that the inclusion of Co enhances the dispersion of active Pd species and modifies the ion-exchange properties of isolated Pd2+. This results in a significantly higher stability compared to mono-metallic Pd-zeolite catalysts in terms of durability [85,86,87]. The synergistic effect between Co and Pd enhances the performance of the catalyst, given their individual activity in SCR-NOx. However, the cost issue remains a significant barrier to the large-scale application of Co-Pd-zeolite catalysts, irrespective of the amount of Pd added. Furthermore, PdO exhibits high methane-combustion activity, and the presence of O2 in the reaction system may pose a greater threat than water vapor [88,89].
SCR-NOx by NH3 is an attractive technology for removing NOx from stationary and mobile sources and has been successfully commercialized [90]. Bin et al. discovered that the ZSM-5 zeolite contains Brønsted acid sites, which facilitate the fine dispersion of cobalt species within the zeolite. These species can exist as either isolated cobalt ions anchored at exchanged sites or as amorphous cobalt oxides concentrated on the ZSM-5 surface. In contrast, SBA-15 zeolite lacks these features, leading to Co/ZSM-5 exhibiting greater activity than SBA-15 [91]. Research examining the impact of cobalt’s nature and environment on the catalytic activity of BEA zeolites suggests that NH3 can be oxidized by extra-framework Co (II) species. Additionally, NO is found to compete with NH3 molecules for identical adsorption sites during the SCR reaction. This competition influences both the conversion and selectivity of the SCR process [92,93]. Given that equipment can be corroded by NH3, the SCR of NOx using hydrocarbons, such as propane, has been proposed as an alternative technology [94]. To mitigate propane oxidation over Co/ZSM-5, Stakheev et al. incorporated alkaline-earth metal cations (Ba, Ca) into the catalysts, yielding the anticipated outcomes [95]. It is evident that the method of zeolite preparation and the environment in which Co and Al species are situated significantly impact its properties [96]. The ion-exchange method is one of the most suitable methods for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with propane [97,98]. Research has demonstrated that catalysts featuring medium-sized pores, a silicon to aluminum ratio of 8–30, and the absence of large cavities are more favorable for the reduction of NOx [99].
In recent years, the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by methane (CH4-SCR-NOx) has emerged as a focal point of research due to the advancements in natural gas and shale gas resources [29,74,100]. The primary active sites in the CH4-SCR reaction are highly dispersed metal ions. Prior studies have conducted an in-depth analysis of Co ion activity at various sites within zeolites. Among these, α-type Co ions, which are bound to the framework oxygens of the main channel wall in mordenite, exhibit the highest activity. Conversely, in ZSM-5, β-type Co ions, coordinated to the deformed six-membered ring at the intersection of straight and sinusoidal channels, demonstrate the highest activity (Figure 5) [101,102]. Additionally, the accessibility of Co species is crucial. For instance, most of the Co2+ in Co-LTA is located within cages formed by six rings, rendering them inaccessible to reactants and contributing to low activity [103].
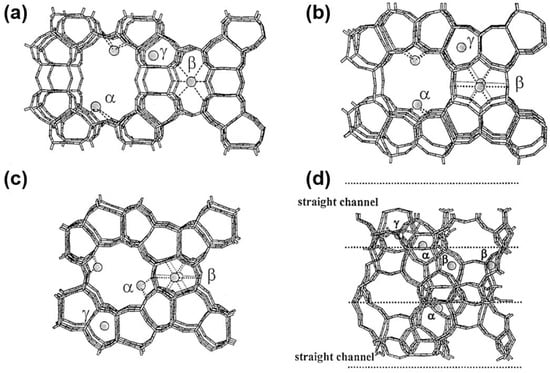
Figure 5.
Suggested cationic sites of the α-, β-, and γ -type Co ions in (a) MOR, (b) FER, and (c,d) MFI structures; (c) view through the straight channel and (d) view through the sinusoidal channel, straight channel indicated by dashed lines. Reproduced from Ref. [101]. Copyright 2000, Elsevier.
According to Lónyi and coworkers, the SCR reaction proceeded in consecutive steps via a bifunctional mechanism over active sites [104]. NO was oxidized by O2 to form NO2 first, and then the disproportionation and charge separation of NO2 happened on Co2+ to generate an activated surface intermediate NO3−/NO+ ion pair. The former was shown to proceed over Co-oxo species, and also over Brønsted acid sites, but at a significantly lower rate. Similarly, Sazama et al. dramatically increased the conversion of NOx to nitrogen in CH4-SCR-NOx by using Al-rich beta zeolite catalysts with a high concentration of transition metal counter-ions bearing an extra-framework oxygen ligand (M/M-oxo, where M = Cu, Co, Fe) [105]. Bellmann et al. proposed a slightly different perspective, suggesting that isocyanate species serve as intermediates and react with nitrato/nitrito (NOy) species and NO2 [106]. Nowadays, the general wisdom is that the formation of NO2 is the initial step of CH4–SCR–NOx. Oxygen participated in converting NO2 into NO3−, which subsequently reacted with CH4 to produce intermediate species CH3NO2. The interaction between CH3NO2 and NO+ ultimately resulted in N2 formation. Additionally, the aggregation of CH3NO2 could lead to CN/NCO formation, which also contributed to N2 generation [107,108,109]. Beyond the three predominant reductants, ethanol, ethylene, propylene, and butane have been effectively employed for NO reduction [110,111,112,113]. All studies consistently indicate that both the activity and selectivity of the process are primarily influenced by the structure of the zeolite and the positioning of Co species within it. Furthermore, variations in the reducibility of chosen reductants, as well as differences in intermediates, can significantly impact the reaction outcomes. Despite significant advancements in research on the catalytic conversion of nitrogen oxides using Co zeolite, challenges persist in achieving conversion in the presence of H2O and/or O2, necessitating further investigation.

Table 2.
Summary of catalysts for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx.
Table 2.
Summary of catalysts for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx.
| Catalyst | T (K) | Reaction Mixture a | Experimental Parameters | NO Conv. (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 wt% Pd/4.8 wt% Co-HMOR | 773 | 1000 ppm NO, 2700 ppm CH4, | GHSV 30,000 h−1 | 60% | [83] |
| 0.31 wt% Pd/5.35 wt% Co-FER | 773 | 6% O2, 8% H2O | GHSV 14,000 h−1 | ~80% | [84] |
| 0.4 wt% Pd/2.3 wt% Co-HZSM-5 | 723 | 1200 ppm NO, 2400 ppm CH4, | GHSV 20,000 h−1 | ~80–90% | [85] |
| 0.4 wt% Pd/3.3 wt% Co/HZSM-5 | 773 | 2.6% O2, 10% H2O | cat 0.1 g; flow rate | (first 30 h) | [86] |
| 9.4 wt% Co/SBA-15 | 873 | 500 ppm NO, 2500 ppm CH4, | 100 cm3 min−1 | ~60% * | [91] |
| 2.16 wt% CoSiBEA | 673 | 5% O2, 5% H2O | GHSV 15,000 h−1 | ~65% | [92] |
| 0.21 wt% Ba/1.28 wt% Co/ZSM-5 | 773 | 100 ppm NO, 2000 ppm CH4, | cat 0.2 g; flow rate | ~80% | [95] |
| 6.9 wt% CoO-IM5 | 723 | 700 ppm NO, 380 ppm C3H8, | cat 1.0 g; flow rate | ~79% | [97] |
| 1.13 wt% Co/BEA | 723 | 2% O2 | 650 cm3 min−1 | ~80% | [98] |
| Co-BEA | 723 | 1000 ppm NO, 1000 ppm C3H8, | GHSV 15,000 h−1 | ~90% | [99] |
| 2.87 wt% CoNH4-MFI | 698 | 850 ppm NO, 550 ppm C3H8, | 650 cm3 min−1 | ~90% * | [100] |
| CoNa-ZSM-5 (Co/Al 0.22) | 723 | 2.5% O2 | GHSV 30,000 h−1 | ~90% * | [102] |
| 3.3 wt% Co-CHA | 750 | 4000 ppm NO, 4000 ppm CH4, | GHSV 7500 h−1 | ~95% * | [103] |
| CoSiBEA | 650 | 2% O2 | GHSV 7500 h−1 | ~80% | [110] |
| Co-HZSM-5 | 573 | 900 ppm NO, 1200 ppm CH4, | GHSV 14,000 h−1 | ~90% | [111] |
a The ratio of O2 or H2O is relative to its mixture with an inert gas; * represents the conversion of NO to N2.
3.3. Catalytic Hydrogenation
Cobalt-modified zeolite is extensively employed in various catalytic hydrogenation processes, including hydrocracking, hydroisomerization, hydrodeoxidation, and hydroformylation.
In 1988, Suib et al. exploited the structure-sensitivity of Co particles within NaX zeolite to modulate the extent of secondary reactions, including ring opening, hydrogenolysis, and hydrogenation during the catalytic cracking of cyclopropane [114]. Similarly, the Co/HY catalyst demonstrated high catalytic activity and selectivity towards branched hydrocarbons in the hydroconversion of n-hexane. This was attributed to the synergistic effect of the hydrogenation activity of Co and the unique pore structure of HY zeolite [115].
To enhance the catalytic effect, cobalt is frequently utilized in combination with other transition metals or alkali metals. Although Co lacks selectivity for target products in a hydrogen atmosphere, it can augment the activity of hydrogenation and lead to superior performance of the CoMo/β catalyst compared to the Mo/β catalyst in the selective hydrocracking of tetralin into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [116]. In addition, the research results of Ahmed et al. indicated that the incorporation of Co would change the Brønsted and Lewis acidity and influence the hydrocracking activity of catalysts [117].
Hydrodeoxidation serves as an effective method for the catalytic upgrading of bio-oil, which is characterized by the presence of various oxygenated groups and fatty acids. The cobalt–zeolite catalyst has demonstrated superior performance in this reaction [22,118]. Olumide Bolarinwa Ayodele discovered that CoOx/ZSM-5 exhibited a significantly higher degree of active metal dispersion, smaller average particle sizes, and increased surface area, pore volume, and average pore size following oxalate ligand functionalization. This resulted in enhanced hydrodeoxidation and isomerization activities during the hydrodeoxygenation of oleic acid into hydrocarbon fuels [119]. Wu et al. engineered bifunctional Co/H-ZSM-5 zeolites using a surface organometallic chemistry grafting approach [120]. The exceptional hydrodeoxygenation performance of the bifunctional Co/H-ZSM-5 was attributed to the effective synergy between the uniformly distributed metallic cobalt clusters and the Bronsted acid sites present in H-ZSM-5.
Cobalt–zeolite can also be used for hydroformylation, which is one of the largest homogeneously metal-catalyzed reactions [121]. For instance, Qi et al. incorporated Rh into the nests of -SiO-Co-OH species that were synthesized within dealuminated BEA zeolite [122]. The activity of the Co-containing catalyst exceeds that of all previously reported Rh-containing bimetallic catalysts. The isolation of Rh atoms in bimetallic nanoparticles or by interaction with supported cobalt oxide species can produce active and selective sites for alkene hydroformylation. Fang et al. employed a NaBH4 in situ-reduced cobalt catalyst supported on zeolite A for 1-hexene hydroformylation [123]. The combination of the spatial limiting effect came from the unique topological structure of zeolite A, and the low-temperature in situ reduction significantly enhanced the selectivity to n-heptanal.
3.4. Selective Catalytic Oxidation and the Degradation of Contaminants
Oxidation plays a pivotal role in organic synthesis, enabling the production of various intermediates for pharmaceutical or cosmetic applications. However, achieving selective catalytic oxidation under mild conditions remains a challenging endeavor and has thus garnered significant attention [124,125]. In this context, cobalt–zeolite catalysts, representing a class of heterogeneous catalysts, have been the subject of extensive research. They offer advantages over homogeneous catalysts and some heterogeneous catalysts containing precious metals or having complex synthesis routes, including cost-effectiveness, ease of separation, superior recycling performance, and versatility. For example, Y-zeolite encapsulated ruthenium and cobalt Schiff base complexes demonstrated enhanced performance in the catalyzed allylic oxidation of α-pinene compared to bare metal complexes, with no observed leaching of metal complexes [126]. Furthermore, zeolite-encaged single-site cobalt ions efficiently catalyzed the model reaction of ethylbenzene aerobic oxidation to acetophenone, outperforming the industrial benchmark catalyst cobalt naphthenate under identical conditions [127].
Encapsulating active components within zeolites is a promising approach to enhance the stability and durability of catalysts [128]. Liu et al. achieved a styrene conversion rate of 96.8% with a benzaldehyde selectivity of 81.5% by preparing a catalyst with cobalt oxide particles encapsulated in ZSM-5 zeolites, thereby integrating a confined reaction environment with appropriate acidic properties [129]. Cobalt ions situated within the supercages of faujasite, which can be considered as a form of “encapsulation”, have been found to efficiently activate oxygen for the epoxidation of styrene [130]. Additionally, there has been research suggesting that zeolites with metal clusters encapsulated within their pore structure have garnered increased attention due to their unique properties, including high stability. However, diffusion resistance serves as a limiting factor in the utilization efficiency of these active centers. To address this issue, Wang et al. designed a cobalt-based hollow silicate-1 zeolite to enhance mass transport by reducing the wall thickness [131]. The existence of Lewis acid sites, coupled with the distinctive hollow structure, resulted in an elevated selectivity towards benzaldehyde during the styrene oxidation process.
Methane, a plentiful clean energy source, has garnered significant attention in recent years. The partial oxidation of methane to syngas, which can be utilized for FTS, hydroformylation, ammonia synthesis, and methanol synthesis, presents broad developmental prospects. Comparative experiments conducted by Khan et al. identified isolated Co2+ sites on ZSM-5 support as the active center for syngas formation [132]. To facilitate this reaction under more benign conditions, Hou et al. enhanced a zeolite-supported 3 wt% cobalt catalyst by incorporating a trace amount of mono-atomically dispersed rhodium (0.005 wt%) [133]. The study demonstrated that mono-atomically dispersed Rh facilitates the liberation of atomic H species via the dissociation of H2. This process subsequently transforms cobalt oxide into Co0 active species, thereby contributing to the superior performance of the catalyst, achieving 85–86% methane conversion with 90–91% CO selectivity. Furthermore, the researchers highlighted that the distinctive structure of the MOR support contributes to the high dispersion and excellent reducibility of Co species, which are crucial in preventing coking.
In addition to its passage through syngas-involved routes, methane can be directly oxidized to either methanol or formaldehyde [134]. Research conducted by Beznis et al. indicated that the type of Co species significantly impacts oxygenate selectivity [135,136]. A high degree of dispersion of Co2+ within zeolite channels favored the formation of formaldehyde, whereas Co oxide species resulted in a higher selectivity towards methanol. In essence, the product selectivity during the oxidation of methane can be manipulated simply by altering the preparation method or applying an alkaline/acid treatment.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), including Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene (BTEX), are significant air pollutants that have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health. These effects include urban grey haze, photochemical smog, teratogenicity, and carcinogenicity. Over the past few decades, extensive research has been conducted on the efficient catalytic combustion of VOCs using Co-containing zeolite. This includes studies on the catalytic oxidation of cyclohexane, isopropanol, and trichloroethylene [137,138,139]. A comparative study examining the influence of Co on two different supports, HAlBEA zeolite and aluminium-free SiBEA, in the combustion of toluene revealed that the presence of Lewis acid sites increased selectivity towards CO and benzene as by-products. The main active phase in the total oxidation of toluene was identified as Co3O4, with the catalyst containing a relatively high concentration of Co3O4 on the aluminium-free support proving to be the most effective [140]. Aziz et al. evaluated the adsorptive catalytic activities for the removal of VOCs from air using Co-ZSM-5 [141]. The superior performance of this catalyst is primarily attributed to its high content of the oxidation state (Co3+), large specific surface area, and high acidity.
3.5. Other Applications
Beyond the applications previously mentioned, cobalt–zeolite has potential uses in other areas. While some of these applications are related to catalysis, they do not involve typical reaction types such as the hydrodenitrogenation of nitrogen-containing compounds, catalytic synthesis of semi-linear higher-olefin, or direct methylation of benzene with methane [142,143,144]. Additionally, numerous cobalt–zeolites have been employed for the direct adsorption of pollutants like nitrosamines and hydrogen sulfide, rather than their catalytic transformation [145,146]. A cobalt-rich zeolite-modified sol-gel coating has also been developed for use in corrosion resistance on aluminum alloy, offering a novel approach to broadening the application of cobalt zeolite [147].
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Cobalt zeolite catalysts exhibit significant potential in scientific research, industrial manufacturing, and environmental purification. Their efficient catalytic performance is primarily attributed to the presence of various active Co species, including Co2+, Co0, Co3O4, and CoO. These species are incorporated into zeolite structures through diverse synthetic methods, thereby enhancing the catalyst’s activity, stability, and recyclability. Despite the remarkable advancements in cobalt–zeolite catalyst research, there remain several shortcomings and areas for improvement.
- (a)
- Precise identification of active species and mechanistic elucidation:
The primary active constituents within the reaction system have been identified in the present study. However, due to the coexistence of multiple Co forms within the zeolite and their intricate interactions, it remains challenging to ascertain whether single or multiple active substances are responsible for the observed reactions. Furthermore, understanding the reaction mechanism at the active site can facilitate the incorporation of auxiliaries during catalyst development. This can enhance the performance of the catalyst through the application of a multi-metal synergistic mechanism. To design and synthesize catalysts with enhanced efficiency in a more precise manner, further investigations are required to identify the specific active sites and elucidate their respective reaction mechanisms. Advanced in situ/operando characterization techniques (X-ray absorption spectroscopy, aberration-corrected STEM) combined with density functional theory (DFT) calculations are imperative to resolve the dynamic evolution of Co speciation under reaction conditions. Systematic investigations into structure-activity correlations will clarify whether mono- or multi-metallic centers dominate specific reaction pathways, enabling rational design of active sites through targeted ligand engineering or defect modulation.
- (b)
- The creation of innovative synthesis strategies and catalysts:
The advent of single-atom catalysis has underscored the importance of achieving the dispersion of single-atom cobalt in zeolite materials. Studies have demonstrated that single cobalt atoms display superior oxygen reduction properties on ordered porous materials akin to zeolite, such as nitrogen-doped porous carbon. The anchoring of the single atomic Co site via zeolite skeleton confinement is crucial for enhancing both the catalytic performance and the economic efficiency of the reaction. This necessitates the development of innovative synthesis methods and strategies to ensure uniform dispersion and stable fixation of cobalt species on zeolite. The development of dual-metal systems through topologically directed synthesis could exploit synergistic electronic effects, while hierarchical zeolite architectures with tailored mesoporosity may alleviate diffusion constraints in bulky molecule transformations.
- (c)
- Machine learning-guided catalyst optimization
Traditional trial-and-error approaches for designing Co–zeolite catalysts face significant bottlenecks due to the intricate interplay between synthesis parameters (Co precursor type, zeolite topology, calcination conditions) and catalytic performance. The multivariate nature of these systems, where subtle variations in Co coordination environments, Brønsted/Lewis acid site distribution, and pore architecture collectively dictate reactivity, renders manual optimization both time-intensive and prone to suboptimal outcomes.
To address these challenges, high-throughput combinatorial synthesis coupled with automated performance screening can generate robust datasets for training predictive models, enabling a priori selection of zeolite hosts and synthesis routes to achieve desired Co speciation. Furthermore, neural networks that integrate catalyst descriptors (Co coordination number, zeolite acidity, pore geometry) and reaction parameters (temperature, pressure) could accelerate the discovery of optimal Co–zeolite configurations for target reactions, particularly in multi-step catalytic cycles.
- (d)
- The advancement of eco-friendly catalysts:
As environmental awareness has increased, the development of eco-friendly catalysts has become a critical trend. In the realm of cobalt–zeolite catalyst research, it is essential to consider non-toxic, harmless, and renewable raw materials as well as synthesis methods that minimize environmental pollution during catalyst preparation. Concurrently, it is crucial to monitor the environmental impact of the catalyst in use to ensure that no harmful by-products are generated during the catalytic conversion process.
Beyond technical challenges, geopolitical risks in cobalt supply chains threaten the sustainable scaling of Co–zeolite catalysts. Over 70% of global cobalt production faces concentrated geopolitical and ethical concerns, compounded by rising competition from battery and energy storage markets. To mitigate supply volatility, strategies such as recycling cobalt from spent catalysts, developing cobalt-lean or cobalt-free alternatives, and advancing ethical sourcing policies are critical. Innovations in resource recovery technologies and cross-sector collaborations will be vital to ensure catalytic advancements align with resource sustainability. In conclusion, cobalt–zeolite catalysts necessitate further investigation and enhancement in numerous areas. By addressing the aforementioned issues and fostering continuous innovation, there is potential to develop a novel cobalt–zeolite catalyst that boasts superior efficiency, stability, environmental compatibility, and broad application prospects. Such advancements will pave the way for a more sustainable chemistry of tomorrow.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and G.X.; formal analysis, G.X.; investigation, W.L.; resources, G.X.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.L.; writing—review and editing, G.X.; visualization, W.L.; supervision, G.X.; project administration, G.X.; funding acquisition, G.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 21905266 (for G.X.), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number WK3530000013 (for G.X.), and the Ma’anshan City Science and Technology Innovation Tackling Project, grant number 2024CSJ001 (for G.X.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, C.; Si, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Xia, W.Q.; Liu, T.; Cao, X.; Guo, Z.Y.; Chen, J.J.; et al. Nanoconfinement steers nonradical pathway transition in single atom fenton-like catalysis for improving oxidant utilization. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.H.; Tian, S.N.; Liang, H.L.; Wang, H.; Gao, S.; Dai, W. Oxidative cleavage and ammoxidation of organosulfur compounds via synergistic Co-Nx sites and Co nanoparticles catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parastaev, A.; Muravev, V.; Osta, E.H.; Kimpel, T.F.; Simons, J.F.M.; van Hoof, A.J.F.; Uslamin, E.; Zhang, L.; Struijs, J.J.C.; Burueva, D.B.; et al. Breaking structure sensitivity in CO hydrogenation by tuning metal-oxide interfaces in supported cobalt nanoparticles. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharnagl, F.K.; Hertrich, M.F.; Ferretti, F.; Kreyenschulte, C.; Lund, H.; Jackstell, R.; Beller, M. Hydrogenation of terminal and internal olefins using a biowaste-derived heterogeneous cobalt catalyst. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Deng, K.J.; Lv, K.L.; Zhang, Z.H. High performance of a cobalt-nitrogen complex for the reduction and reductive coupling of nitro compounds into amines and their derivatives. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faculak, M.S.; Veatch, A.M.; Alexanian, E.J. Cobalt-catalyzed synthesis of amides from alkenes and amines promoted by light. Science 2024, 383, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, O.M.; Khan, W.U.; Hantoko, D.; Bakare, I.A.; Ali, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic activity of Co/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for decomposition of ammonia to produce hydrogen. Fuel 2024, 372, 132230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeletic, M.S.; Helm, M.L.; Hulley, E.B.; Mock, M.T.; Appel, A.M.; Linehan, J.C. A Cobalt Hydride Catalyst for the Hydrogenation of CO: Pathways for Catalysis and Deactivation. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3755–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Salmeia, K.A.; Vagin, S.I.; Rieger, B. Concerning the Deactivation of Cobalt(III)-Based Porphyrin and Salen Catalysts in Epoxide/CO Copolymerization. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4384–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschemann, T.O.; de Jong, K.P. Deactivation Behavior of Co/TiO2 Catalysts during Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.S.; Sineva, L.V.; Gryaznov, K.O.; Asalieva, E.Y.; Mordkovich, V.Z. Deactivation and Regeneration of a Zeolite-Containing Cobalt Catalyst in a Fisher-Tropsch Synthesis Reactor. Catal. Ind. 2023, 15, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, D.J.; van de Loosdrecht, J.; Saib, A.M.; Overett, M.J.; Datye, A.K.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Carbon deposition as a deactivation mechanism of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts under realistic conditions. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2009, 354, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.H. Emerging applications of zeolites in catalysis, separation and host-guest assembly. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, S.Q.; Yu, J.H. Metal Sites in Zeolites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 6039–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F.S. Metal@Zeolite Hybrid Materials for Catalysis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Hortiguela, L.; Perez-Pariente, J. Synthesis and Properties of Zeolite Materials Guided by Periodic Considerations. In Periodic Table II: Catalytic, Materials, Biological and Medical Applications; Mingos, D.M.P., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Janiak, C. Confinement Effects in Zeolite-Confined Noble Metals. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12340–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Zones, S.I.; Hong, Y.C.; Iglesia, E. Synthesis of highly dispersed cobalt oxide clusters encapsulated within LTA zeolites. J. Catal. 2017, 356, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Tang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Zheng, A.; Xiao, F.-S. Design of Cobalt-Amine Complex as an Efficient Structure-Directing Agent for One-Pot Synthesis of Co-SSZ-13 Zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 16343–16349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.M.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, D.-W. Ozone-induced lean methane oxidation over cobalt ion-exchanged BEA catalyst under dry reaction conditions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; He, H.; Miao, C.; Hua, W.; Yue, Y.; Gao, Z. Ethane conversion in the presence of CO2 over Co-based ZSM-5 zeolite: Co species controlling the reaction pathway. Mol. Catal. 2022, 519, 112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.M.; Smoljan, C.S.; Lucero, J.; Carreon, M.A. Deoxygenation of Stearic Acid over Cobalt-Based NaX Zeolite Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentys, A.; Lugstein, A.; Vinek, H. Co-containing zeolites prepared by solid-state ion exchange. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, J.; Bardez, I.; Bart, F.; Albouy, P.A.; Wallez, G.; Davidson, A. Dispersion of CoO nanoparticles within SBA-15 using alkane solvents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xu, G.; Fu, Y. Selective photocatalytic oxidation of furfural to C4 compounds with metal-TS-1 zeolite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 340, 123220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemthong, P.; Klysubun, W.; Prayoonpokarach, S.; Wittayakun, J. Reducibility of cobalt species impregnated on NaY and HY zeolites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bania, K.K.; Deka, R.C. Influence of Zeolite Framework on the Structure, Properties, and Reactivity of Cobalt Phenanthroline Complex: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9601–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shamzhy, M.; Molitorisova, S.; Opanasenko, M.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Total Oxidation of Toluene and Propane over Supported Co3O4 Catalysts: Effect of Structure/Acidity of MWW Zeolite and Cobalt Loading. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 15143–15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lónyi, F.; Solt, H.E.; Valyon, J.; Boix, A.; Gutierrez, L.B. The activation of NO and CH for NO-SCR reaction over In- and Co-containing H-ZSM-5 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2011, 345, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.B.; Yu, W.D.; Zhang, H.; Xin, J.; He, X.H.; Liu, B.; Jiang, F.; Liu, X.H. Suppressing C–C Bond Dissociation for Efficient Ethane Dehydrogenation over the Isolated Co(II) Sites in SAPO-34. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13001–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, R.; Chalupka-Spiewak, K.; Krafft, J.-M.; Millot, Y.; Valentin, L.; Casale, S.; Gurgul, J.; Dzwigaj, S. The Synthesis of Different Series of Cobalt BEA Zeolite Catalysts by Post-Synthesis Methods and Their Characterization. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bonte, W.; Corthals, S.; Krumeich, F.; Ruitenbeek, M.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Zeolite Nanoreactor for Investigating Sintering Effects of Cobalt-Catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5140–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wan, H.L. Characterizations of cobalt oxide nanoparticles within faujasite zeolites and the formation of metallic cobalt. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, D.G.; Feng, P.; Shi, S.; Wang, C.X.; Zheng, A.D.; Lu, G.; Tian, Z.J. Synthesis of zeolite Beta containing ultra-small CoO particles for ethylbenzene oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashmi, E.; Ebri, G.; Hellgardt, K. Highly Active and Stable Single-Atom Cobalt in Zeolite for Acetylene Semihydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2015, 15, 4121–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huan, L.; Wang, L.; Chu, S.; Liu, L.; Qi, J.; Ren, Z.; Cai, A.; Hui, Y.; Qin, Y.; et al. Cobaltosilicate zeolite beyond platinum catalysts for propane dehydrogenation. Nat. Catal. 2025, 8, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, E.; López, C.M.; Oropeza, F.; Bartolini, M.; Alvarez, J.; Goldwasser, M.; Linares, F.; Lamonier, J.; Zurita, M. HMS mesoporous silica as cobalt support for the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Pretreatment, cobalt loading and particle size effects. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 281, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Fu, L.; Gao, K.; Duan, X. Accelerating radical generation from peroxymonosulfate by confined variable Co species toward ciprofloxacin mineralization: ROS quantification and mechanisms elucidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 315, 121542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; Peng, W. Photo-accelerated Co3+/Co2+ transformation on cobalt and phosphorus co-doped g-C3N4 for Fenton-like reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 22399–22409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Di, J.; Liang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Gai, X. Embedded catalysts prepared by grinding crystallization and their catalytic performance in dry reforming of methane: Domain-limited nanostructures for high activity and stability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 73, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bo, S.; Liao, W.; Yang, K.; Su, T.; Lue, H.; Zhu, Z. Zeolitic framework Sn boosts the 2,5-dimethylfuran selectivity for the hydrodeoxygenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over Co/Sn-Beta catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Bai, X.; Maximov, A.L.; Wu, W. Ultrasound-assisted preparation of PdCo bimetallic nanoparticles loaded on beta zeolite for efficient catalytic hydrogen production from dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 103, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, A.; Shi, C. Enhanced Low-Temperature Activity of Ag-Promoted Co-ZSM-5 for the CH4-SCR of NO. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenko, R.E.; Zubkov, I.N.; Papeta, O.P.; Kataria, Y.V.; Bakun, V.G.; Svetogorov, R.D.; Savost’yanov, A.P. The Influence of Platinum on the Catalytic Properties of Bifunctional Cobalt Catalysts for the Synthesis of Hydrocarbons from CO and H2. Catalysts 2024, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telaar, P.; Diehl, P.; Muhler, M. Bridging Homogeneously and Heterogeneously Catalyzed Higher-Alcohol Synthesis via Cobalt-Based Catalysts. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2024, 9, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineva, L.; Mordkovich, V.; Asalieva, E.; Smirnova, V. Zeolite-Containing Co Catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis with Tailor-Made Molecular-Weight Distribution of Hydrocarbons. Reactions 2023, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurova, K.; Miyassarova, A.; Eliseev, O.; Stytsenko, V.; Glotov, A.; Stavitskaya, A. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Catalysts for Selective Production of Diesel Fraction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Rollán, J.; Arribas, M.A.; Cerqueira, H.S.; Costa, A.F.; Aguiar, E.F.S. A detailed study of the activity and deactivation of zeolites in hybrid Co/SiO2-zeolite Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 249, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Kang, J.C.; Wang, Y. Development of Novel Catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Tuning the Product Selectivity. Chemcatchem 2010, 2, 1030–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Research progress on the direct catalytic conversion of syngas to light olefins. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2022, 41, 4754–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xulu Martinez-Vargas, D.; Sandoval-Rangel, L.; Campuzano-Calderon, O.; Romero-Flores, M.; Lozano, F.J.; Nigam, K.D.P.; Mendoza, A.; Montesinos-Castellanos, A. Recent Advances in Bifunctional Catalysts for the Fischer-Tropsch Process: One-Stage Production of Liquid Hydrocarbons from Syngas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 15872–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalil, M.; Sohrabi, M.; Royaee, S.J. Application of nano-sized cobalt on ZSM-5 zeolite as an active catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Cobalt nanoparticles imbedded into zeolite crystals: A tailor-made catalyst for one-step synthesis of gasoline from syngas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21965–21978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Uddin, M.A.; Kato, Y.; Nishina, Y.; Hapipi, A.M. Effects of preparation method on the properties of cobalt supported β-zeolite catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2017, 291, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.; Batalha, N.; Marcilio, N.R.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Khodakov, A.Y. Influence of Impregnation and Ion Exchange Sequence on Metal Localization, Acidity and Catalytic Performance of Cobalt BEA Zeolite Catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Chemcatchem 2019, 11, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lyu, S.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Nano-ZSM-5-supported cobalt for the production of liquid fuel in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of preparation method and reaction temperature. Zurita 2020, 263, 116619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-P.; Xie, Z.-X.; Tian, S.-P.; Ding, S.-Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.-J.; Hao, Q.-Q. Physical Grinding of Prefabricated Co3O4 and MCM-22 Zeolite for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Impact of Pretreatment Procedure on the Dispersion and Catalytic Performance. Molecules 2024, 29, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Xing, C.; Huang, W.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, S. Design of a hierarchical Co@ZSM-5/SiC capsule catalyst for direct conversion of syngas to middle olefin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 343, 112134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Marinova, M.; Batalha, N.; Marcilio, N.R.; Khodakov, A.Y.; Ordomsky, V.V. Design of nanocomposites with cobalt encapsulated in the zeolite micropores for selective synthesis of isoparaffins in Fischer-Tropsch reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 5019–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatrin, I.; Abdullah, I.; McCue, A.J.; Krisnandi, Y.K. Mesoporous configuration effects on the physicochemical features of hierarchical ZSM-5 supported cobalt oxide as catalysts in methane partial oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 365, 112896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, R.; Chalupka, K.A.; Mierczynski, P.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Rynkowski, J.; Gurgul, J.; Lason-Rydel, M.; Casale, S.; Brouri, D.; Dzwigaj, S. The Catalytic Performance of Ni-Co/Beta Zeolite Catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Bechara, R.; Zholobenko, V.L. Pore size effects in Fischer Tropsch synthesis over cobalt-supported mesoporous silicas. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Bechara, R.; Griboval-Constant, A. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over silica supported cobalt catalysts: Mesoporous structure versus cobalt surface density. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2003, 254, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, V.; Zholobenko, V.L.; Cheng, K.; Lancelot, C.; Heyte, S.; Thuriot, J.; Paul, S.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Khodakov, A.Y. The Role of Steric Effects and Acidity in the Direct Synthesis of Paraffins from Syngas on Cobalt Zeolite Catalysts. Chemcatchem 2016, 8, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S.; Vazzana, F.; Marella, M.; Tomaselli, M.; Mantegazza, M. Novel catalysts and catalytic technologies for NO removal from industrial emissions containing O2, H2O and SO2. Adv. Environ. Res. 2000, 4, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Hegde, M.S.; Madras, G. Catalysis for NO abatement. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Hamada, H. Removal of Nitrogen Monoxide from Exhaust Gases through Novel Catalytic Processes. Catal. Today 1991, 10, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Armor, J.N. Catalytic Decomposition of Nitrous-Oxide on Metal Exchanged Zeolites. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1992, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Mccarty, J.G.; Wachsman, E.D.; Wong, V.L. Catalytic Decomposition of Nitrous-Oxide over Ru-Exchanged Zeolites. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1994, 4, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Correa, C.M.; Villa, A.L.; Zapata, M. Decomposition of nitrous oxide in excess oxygen over Co- and Cu-exchanged MFI zeolites. Catal. Lett. 1996, 38, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armor, J.N.; Farris, T.S. The Unusual Hydrothermal Stability of Co-Zsm-5. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1994, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, R.S.; Mascarenhas, A.J.S.; Andrade, H.M.C. Co-ZSM-5 catalysts for NO decomposition. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1998, 18, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahri, A.; Golbabaei, F.; Vafajoo, L.; Mireskandari, S.M.; Yaseri, M.; Shahtaheri, S.J. Removal of Greenhouse Gas (NO) by Catalytic Decomposition on Natural Clinoptilolite Zeolites Impregnated with Cobalt. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, P.J.; Meng, Q.G.; Corthals, S.; Leeman, H.; Schoonheydt, R.A. Co-ZSM-5 catalysts in the decomposition of NO and the SCR of NO with CH: Influence of preparation method and cobalt loading. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2008, 84, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Shen, Q.; He, C.; Wang, Y.F.; Cheng, J.; Hao, Z.P. CoMOR zeolite catalyst prepared by buffered ion exchange for effective decomposition of nitrous oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1756–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Shen, Q.; He, C.; Ma, C.Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Z.M.; Hao, Z.P. Decomposition of nitrous oxide over Cobalt-zeolite catalysts: Role of zeolite structure and active site. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zied, B.M.; Schwieger, W.; Unger, A. Nitrous oxide decomposition over transition metal exchanged ZSM-5 zeolites prepared by the solid-state ion-exchange method. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2008, 84, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zied, B.M.; Schwieger, W. Self oscillatory behaviour in NO decomposition over Co-ZSM-5 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2009, 85, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Shang, R.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, J. Multiple cobalt species on HZSM-5 cooperative catalyzing N2O decomposition. Mol. Catal. 2024, 552, 113706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Li, M.; Di, Z.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, R. Role of Al pairs on effective N2O decomposition over the ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst. Catal. Today 2022, 402, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Kokitsu, M.; Ohtsuka, H.; Okada, O.; Sabatino, L.M.F.; Bellussi, G. Study on catalysts of selective reduction of NOx using hydrocarbons for natural gas engines. Catal. Today 1996, 27, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Mechanism of the selective reduction of NO over Co/MFI: Comparison with Fe/MFI. J. Catal. 2001, 197, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, F.; Córdoba, F.; Yates, M.; de Correa, C.M. The promotion of cobalt mordenite by palladium for the lean CH-SCR of NO in moist streams. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2002, 234, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Nam, I.S.; Ham, S.W.; Baek, Y.S.; Shin, K.H. Effect of Pd on the water tolerance of Co-ferrierite catalyst for NO reduction-by CH. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2003, 41, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, J.A.Z.; van den Brink, R.W.; Booneveld, S.; de Bruijn, F.A. Influence of zeolite structure on the activity and durability of Co-Pd-zeolite catalysts in the reduction of NO with methane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2003, 46, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Kage, S.; Shimojo, T.; Oba, J.; Hayashi, M.; Matsukata, M.; Kikuchi, E. Co cation effects on activity and stability of isolated Pd(II) cations in zeolite matrices for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with methane. J. Catal. 2002, 211, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chen, J.; Giewont, K.; Mon, T.; Liu, C.-H.; Walker, E.A.; Kyriakidou, E.A. Effect of cobalt incorporation on the stability of ionic Pd in the presence of carbon monoxide over Pd/BEA passive NOx adsorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, J.A.Z.; van den Brink, R.W.; Booneveld, S.; de Bruijn, F.A. Durability of ZSM5-supported Co-Pd catalysts in the reduction of NO with methane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2002, 39, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Sugiura, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Kikuchi, E. Reduction of nitric oxide with methane on Pd/Co/H-ZSM-5 catalysts: Cooperative effects of Pd and Co. Catal. Lett. 1996, 42, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Li, Y.T.; Luo, Y.H.; Ye, D.Q.; Jiang, J.X.; Chen, P.R. Recent progress in novel zeolite catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides. Catal. Today 2023, 422, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, F.; Song, C.L.; Lv, G.; Song, J.O.; Cao, X.F.; Pang, H.T.; Wang, K.P. Structural Characterization and Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with Ammonia: A Comparison Between Co/ZSM-5 and Co/SBA-15. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 26262–26274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, R.; Krafft, J.M.; Onfroy, T.; Grzybek, T.; Dzwigaj, S. Influence of the nature and environment of cobalt on the catalytic activity of Co-BEA zeolites in selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 225, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boron, P.; Chmielarz, L.; Gil, B.; Marszalek, B.; Dzwigaj, S. Experimental evidence of NO SCR mechanism in the presence of the BEA zeolite with framework and extra-framework cobalt species. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 198, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, R.; Aissat, A.; Cousin, R.; Courcot, D.; Siffert, S. Catalysts for NO selective catalytic reduction by hydrocarbons (HC-SCR). Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2015, 504, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakheev, A.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Park, S.J.; Chong, P.J. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with propane over CoZSM-5 containing alkaline earth cations. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 1996, 9, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, H.; Tabata, T.; Okada, O.; Sabatino, L.M.F.; Bellussi, G. A study on the roles of cobalt species in NO reduction by propane on Co-Beta. Catal. Today 1998, 42, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, A.E.; Prato, J.G.; Corma, A. Co-exchanged IM5, a stable zeolite for the selective catalytic reduction of NO in the presence of water and SO. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Shen, S.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Kawi, S. Selective catalytic reduction of NO over Co/beta-zeolite: Effects of synthesis condition of beta-zeolites, Co precursor, Co loading method and reductant. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2004, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, A.E.; Franch, C.; Corma, A. Determining the characteristics of a Cobalt-zeolite to be active for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with hydrocarbons. Catal. Today 2011, 176, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resini, C.; Montanari, T.; Nappi, L.; Bagnasco, G.; Turco, M.; Busca, G.; Bregani, F.; Notaro, M.; Rocchini, G. Selective catalytic reduction of NO by methane over Co-H-MFI and Co-H-FER zeolite catalysts: Characterisation and catalytic activity. J. Catal. 2003, 214, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaucky, D.; Vondrová, A.; Dedecek, J.; Wichterlová, B. Activity of Co ion sites in ZSM-5, ferrierite, and mordenite in selective catalytic reduction of NO with methane. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedecek, J.; Kaucky, D.; Wichterlová, B. Does density of cationic sites affect catalytic activity of Co zeolites in selective catalytic reduction of NO with methane? Top. Catal. 2002, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.B.; Shin, J.; Ahn, N.H.; Heo, I.; Hong, S.B. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with CH over cobalt-exchanged cage-based, small-pore zeolites with different framework structures. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 267, 118710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lónyi, F.; Solt, H.E.; Pászti, Z.; Valyon, J. Mechanism of NO-SCR by methane over Co,H-ZSM-5 and Co,H-mordenite catalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2014, 150, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazama, P.; Pilar, R.; Mokrzycki, L.; Vondrova, A.; Kaucky, D.; Plsek, J.; Sklenak, S.; Stastny, P.; Klein, P. Remarkably enhanced density and specific activity of active sites in Al-rich Cu-, Fe- and Co-beta zeolites for selective catalytic reduction of NO. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 189, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, A.; Atia, H.; Bentrup, U.; Brückner, A. Mechanism of the selective reduction of NO by methane over Co-ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 230, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, B.J.; Beutel, T.; Lei, G.D.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Mechanistic cause of hydrocarbon specificity over Cu/ZSM-5 and Co/ZSM-5 catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of Nox. J. Catal. 1996, 158, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cant, N.W.; Liu, I.O.Y. The mechanism of the selective reduction of nitrogen oxides by hydrocarbons on zeolite catalysts. Catal. Today 2000, 63, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Qin, M.Y.; Li, Q.B. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with CH over zeolite catalysts: Research progress, challenges and perspectives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, J.; Machej, T.; Gurgul, J.; Socha, R.P.; Che, M.; Dzwigaj, S. Effect of Co content on the catalytic activity of CoSiBEA zeolite in the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ethanol: Nature of the cobalt species. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2007, 75, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.H.; Yang, X.F.; Zhu, A.M.; Shi, L.L.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; Shi, C. Plasma-assisted selective catalytic reduction of NO by CH over Co-HZSM-5 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praserthdam, P.; Chaisuk, C.; Panit, A.; Kraiwattanawong, K. Some aspects about the nature of surface species on Pt-based and MFI-based catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by propene under lean-burn condition. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2002, 38, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Catalytic reduction of NO by hydrocarbons over Co/ZSM-5 catalysts prepared with different methods. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2000, 26, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suib, S.L.; Zhang, Z.C. Structure-Sensitive Reactions of Cyclopropane with Cobalt and Iron Zeolite Catalysts. ACS Symp. Ser. 1988, 368, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, A.M.G.; Souza, M.J.B.; Melo, D.M.A.; Araujo, A.S. Cobalt and nickel supported on HY zeolite: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upare, D.P.; Park, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Chang, H.; Choi, W.; Choi, S.; Jeon, Y.P.; et al. Cobalt promoted Mo/beta zeolite for selective hydrocracking of tetralin and pyrolysis fuel oil into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Muraza, O.; Jamil, A.K.; Shafei, E.N.; Yamani, Z.H.; Choi, K.H. Steam Catalytic Cracking of -Dodecane over Ni and Ni/Co Bimetallic Catalyst Supported on Hierarchical BEA Zeolite. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 5482–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zula, M.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B. Hydrocracking, hydrogenation and hydro-deoxygenation of fatty acids, esters and glycerides: Mechanisms, kinetics and transport phenomena. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, O.B. Influence of oxalate ligand functionalization on Co/ZSM-5 activity in Fischer Tropsch synthesis and hydrodeoxygenation of oleic acid into hydrocarbon fuels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.J.; Zhang, N.; Dai, W.L.; Guan, N.J.; Li, L.D. Construction of Bifunctional Co/H-ZSM-5 Catalysts for the Hydrodeoxygenation of Stearic Acid to Diesel-Range Alkanes. Chemsuschem 2018, 11, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilbeer, C.; Selent, D.; Dyballa, K.M.; Franke, R.; Spannenberg, A.; Börner, A. Evaluation of Organoselenium Based Compounds as Co-Catalysts in Rhodium-Catalyzed Hydroformylation. Chemistryselect 2016, 1, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Das, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nozik, D.; Gates, B.C.; Bell, A.T. Ethene Hydroformylation Catalyzed by Rhodium Dispersed with Zinc or Cobalt in Silanol Nests of Dealuminated Zeolite Beta. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2911–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Guo, L.S.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, P.P.; Yoneyama, Y.; Yang, G.H.; Tsubaki, N. NaBH4 Reduced Cobalt Catalyst Supported on Zeolite A for 1-Hexene Hydroformylation. Chemistryselect 2019, 4, 10447–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Byun, S.W.; Kweon, S.; Shin, H.; Min, H.K.; Park, M.B.; Kang, S.B. Bi-functional two-dimensional cobalt silicate catalyst for selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2024, 340, 123264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chu, Q.; Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Jiang, P.; Li, T. Synthesis of Novel Catalytic Styrene Aerobic Oxidation Catalysts via Embedding Co and Ce. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 3787–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.; Sawant, D.P.; Gopinath, C.S.; Halligudi, S.B. Zeolite encapsulated ruthenium and cobalt schiff base complexes catalyzed allylic oxidation of α-pinene. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2002, 184, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Li, W.; Qin, B.; Chai, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, L. Self-adjusted reaction pathway enables efficient oxidation of aromatic C-H bonds over zeolite-encaged single-site cobalt catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2024, 57, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lv, H.; Liu, B. Encapsulation of Metal Nanoparticle Catalysts Within Mesoporous Zeolites and Their Enhanced Catalytic Performances: A Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Jian, P.M.; Jian, R.Q. Highly selective oxidation of styrene to benzaldehyde over a tailor-made cobalt oxide encapsulated zeolite catalyst. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wan, H.L. CO-Exchanged faujasite zeolites as efficient heterogeneous catalysts for epoxidation of styrene with molecular oxygen. Chem. Commun. 2004, 4, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M. Alkali metal ion assisted preparation of zeolite encapsulated small cobalt cluster CoOx for direct styrene oxidation to benzaldehyde. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 345, 112259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Kennedy, E.M.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Adesina, A.A.; Stockenhuber, M. Partial oxidation of methane with nitrous oxide forms synthesis gas over cobalt exchanged ZSM-5. Catal. Commun. 2014, 53, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.H.; Nagamatsu, S.; Asakura, K.; Fukuoka, A.; Kobayashi, H. Trace mono-atomically dispersed rhodium on zeolite-supported cobalt catalyst for the efficient methane oxidation. Commun. Chem. 2018, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, E.; Lemishka, M.; Sobalik, Z.; Mlekodaj, K.; Andrikopoulos, P.C.; Dedecek, J.; Sklenak, S. Low-temperature selective oxidation of methane over distant binuclear cationic centers in zeolites. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beznis, N.V.; van Laak, A.N.C.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Bitter, J.H. Oxidation of methane to methanol and formaldehyde over Co-ZSM-5 molecular sieves: Tuning the reactivity and selectivity by alkaline and acid treatments of the zeolite ZSM-5 agglomerates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 138, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beznis, N.V.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Bitter, J.H. Partial Oxidation of Methane Over Co-ZSM-5: Tuning the Oxygenate Selectivity by Altering the Preparation Route. Catal. Lett. 2010, 136, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoppen, D.L.; Devos, D.E.; Genet, M.J.; Rouxhet, P.G.; Jacobs, P.A. Cobalt-Containing Molecular-Sieves as Catalysts for the Low Conversion Autoxidation of Pure Cyclohexane. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.P.; Yan, Y. High efficiency of isopropanol combustion over cobalt oxides modified ZSM-5 zeolite membrane catalysts on paper-like stainless steel fibers. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 251, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch-Raga, N.; Palomares, A.E.; Martínez-Triguero, J.; Valencia, S. Cu and Co modified beta zeolite catalysts for the trichloroethylene oxidation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 187, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokicinska, A.; Drozdek, M.; Dudek, B.; Gil, B.; Michorczyk, P.; Brouri, D.; Dzwigaj, S.; Kustrowski, P. Cobalt-containing BEA zeolite for catalytic combustion of toluene. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 212, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Sajjad, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.S. An efficient Co-ZSM-5 catalyst for the abatement of volatile organics in air: Effect of the synthesis protocol. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, W.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, Y. In situ synthesis of Co modified SAPO-5 molecular sieves and the application in quinoline hydrodenitrogenation of their NiWS supported catalysts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 284, 119428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, J.; Kirschhock, C.E.A.; Mathys, G.M.; Martens, J.A. Design of a Cobalt-Zeolite Catalyst for Semi-Linear Higher-Olefin Synthesis. Chemcatchem 2012, 4, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, H.; Tsuji, E.; Moriwaki, Y.; Okumura, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakamura, K.; Suganuma, S.; Katada, N. Selective Formation of Active Cobalt Species for Direct Methylation of Benzene with Methane on MFI Zeolite by Co-presence of Secondary Elements. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhuang, T.T.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.D.; Huang, W.; Zhu, J.H. Promoting zeolite NaY as efficient nitrosamines trap by cobalt oxide modification. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.L.; Kuo, M.S.; Yang, W.D.; Huang, Y.C. Hydrogen sulfide adsorption by thermally treated cobalt (II)-exchanged NaX zeolite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zong, X.M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Luo, J. Corrosion Inhibition of a Sol-Gel Coating Modified with Cobalt-Enriched Zeolite on AA2024-T3 Aluminum Alloy. Int. J. Electrochem. Sc. 2019, 14, 10966–10982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).