Abstract
Zinc-halogen batteries are usually based on two-electron transfer reactions from X− to X2. However, the halogen is capable of being further oxidized to higher valence states, thereby achieving the higher capacity of zinc- halogen batteries. Here, a six-electron reaction based on I−/I+ and Br−/Br0 is activated successfully by introducing KI into the electrolyte. ZIF-8-derived porous carbon (ZPC), serving as the host of halogen, effectively suppresses polybromide/polyiodide shuttle owing to the chemisorption/physical adsorption. Additionally, the adsorption of I− on the surface of the zinc anode effectively inhibits the growth of dendrites and the formation of by-products. Consequently, zinc-bromine batteries exhibit outstanding electrochemical performance, including a specific capacity of 345 mAh g−1 at 1 A g−1 and an excellent capacity retention of 80% after 3000 cycles at 2 A g−1. This strategy provides a novel way for enhancing the electrochemical performance of zinc-halogen batteries.
1. Introduction
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), with their advantages of light weight, high-energy density, and high specific power, have been widely used in many fields. However, LIBs still face challenges, such as the increasing depletion of lithium reserves, potential safety hazards, and environmental pollution caused by organic electrolytes, making it imperative to develop a new generation of safe, environmentally friendly, and low-cost secondary battery systems. As one of the most promising secondary batteries, aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) are promising alternatives for the next generation of energy storage systems due to their intrinsic economy, reliability, safety, and environmentally friendly and excellent electrochemical performance [1,2,3]. However, the theoretical capacity of AZIBs cathode is usually much lower than that of the zinc metal anode (820 mAh g−1) [4,5]. Therefore, increasing the energy density of AZIB cathodes is of great significance. In prior studies concerning the cathodes of aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AIBs), the focus was mainly on intercalation/de-intercalation cathode materials, which have relatively lower electrode potentials [6]. By contrast, cathode materials with a conversion mechanism manifest promising properties in terms of higher capacity and redox potential, especially for halogen-based cathodes [7,8]. The halogen-based cathodes possess high electrode potentials (I−/I0: 1.30 V vs. Zn/Zn2+; Br−/Br0: 1.85 V vs. Zn/Zn2+) and theoretical capacities (I−/I0: 211 mAh g−1, Br−/Br0: 335 mAh g−1) [9,10]. Notably, bromine stands out due to its remarkable electrochemical activity, redox potential, and high capacity [11,12].
Nevertheless, the commercialization of zinc-bromine batteries systems is impeded by several bottlenecks [13]. Firstly, the highly volatile Br2 produced on the cathode side during the charging process reacts with Br− in the electrolyte and is subsequently converted into the highly soluble polybromide Brn− (n = 3, 5) [14]. Meanwhile, zinc-bromine batteries involve a liquid–liquid conversion, which needs a specific conductive carrier because liquid bromine can hardly be confined by traditional conductive carriers for efficient redox [15]. The shuttle effect of polybromide species and liquid bromine migration during cycling results in severe capacity decay, thereby shortening the cycling life [16,17,18]. Secondly, side reactions of hydrogen evolution caused by aqueous electrolyte and the formation of Zn hydroxide sulfate decrease the cycling life [19]. Thirdly, the existing zinc-bromine batteries systems are based on two-electron transfer, thus exhibit relatively low capacity of usually no more than 150 mAh g−1 [20,21].
Herein, a six-electron redox reaction from I− to I+ and Br− to Br0 has been triggered and stabilized by an inter-halogen activation strategy for zinc-bromine batteries. Specifically, ZIF-8-derived porous carbon (ZPC) serves as the host material of the halogen cathode, preventing the volatilization/dissolution while suppressing the shuttle problems. Meanwhile, I− adsorbed onto the surface of Zn anode inhibits dendrite growth and the formation of by-products. With I− as the activator and ZPC as the cathode host, the aqueous rechargeable zinc-halogen batteries ensure both high potential and capacity, as well as excellent cycling performance. As a result, the zinc-bromine batteries achieved a capacity of 345 mAh g−1 at 1 A g−1, and demonstrated excellent stability of 3000 cycles at 2 A g−1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Section
C4H6N2 (98%) and ZnBr2 (98%) were purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). Zn(NO3)2 (99%) was purchased from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China), CH3OH (≥99.5%) and ZnSO4·7H2O (≥99.5%) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), KI (≥99.5%) was purchased from Shanghai Yindian Chemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), Zn-foil (99.99%, 100 µm) was purchased from Guangdong Canrd New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. (Dongguan, China), Glass fiber (GF/D, 90 mm in diameter, 675 μm in thickness, 2.7 μm in pore size) was purchased from Whatman, and carbon cloths (WOS 1011, CeTech, Taiwan) were purchased from Suzhou Zhengtairong Material Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) and denoted as CF.
A high-temperature calcined ZIF-8 was adopted to prepare ZPC. Firstly, 3.95 mmol of C4H6N2 and 0.987 mmol of Zn(NO3)2 were respectively dissolved into 100 mL of CH3OH. Then, the mixture was violently stirred for 10 min, and the mixed solution was aged for another 12 h. The white precipitate was collected after washing with CH3OH and dried at 60 °C. The ZPC was synthesized by calcining the ZIF-8 in Ar atmosphere at 900 °C for 4 h, with a heating rate of 5 °C min−1. The resulting porous carbon was designated as ZPC.
The ZPC, acetylene black, and polyvnylidene fluoride binder were mixed into a slurry with a mass ratio of 7:2:1. Then, the slurry was coated onto a carbon cloth and dried at 60 °C to obtain pristine ZPC electrode. After that, the ZPC electrode was electro-deposited at 2 V (versus Zn/Zn2+) for 30 min in 1 M ZnBr2 electrolyte to obtain ZPC-Br2. The adsorbed Br2 on the carbon cloth and carbon black was washed away using deionized water. Finally, the ZPC-Br2 electrode was obtained after drying in an oven. The mass loading of active materials was about 1.5 mg cm−2 (based on the mass of bromine).
2.2. Material Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku, Cu-Kα, Tokyo, Japan) was carried out to study the evolution of the phase composition. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S4800, Tokyo, Japan) was employed to characterize the morphology of the electrode materials. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo ESCALAB250Xi Waltham, MA, USA) was conducted to analyze the compositions and valance evolution. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Thermo Fisher iCAP 7400, Waltham, MA, USA) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS, EDAX ELECT PIUS, Mahwah, NJ, USA) were used to detected the existence of iodine species.
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
A CR2032 coin cell was assembled in the open-air environment by using a zinc metal plate as the anode, 85 µL 1 M ZnSO4 and 1 M ZnSO4 + 0.1 M KI as the electrolyte, glass fiber as the separator, and ZPC-Br2 electrode as the cathode.
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was performed on an electrochemical workstation CHI660E (Shanghai Chenhua Instrument, Shanghai, China). The galvanostatic charge–discharge (GCD), cycle performance and rate performance were tested on the battery measurement system (LAND CT2001A). and NEWARE Battery Test System (Shenzhen, China).
3. Results and Discussion
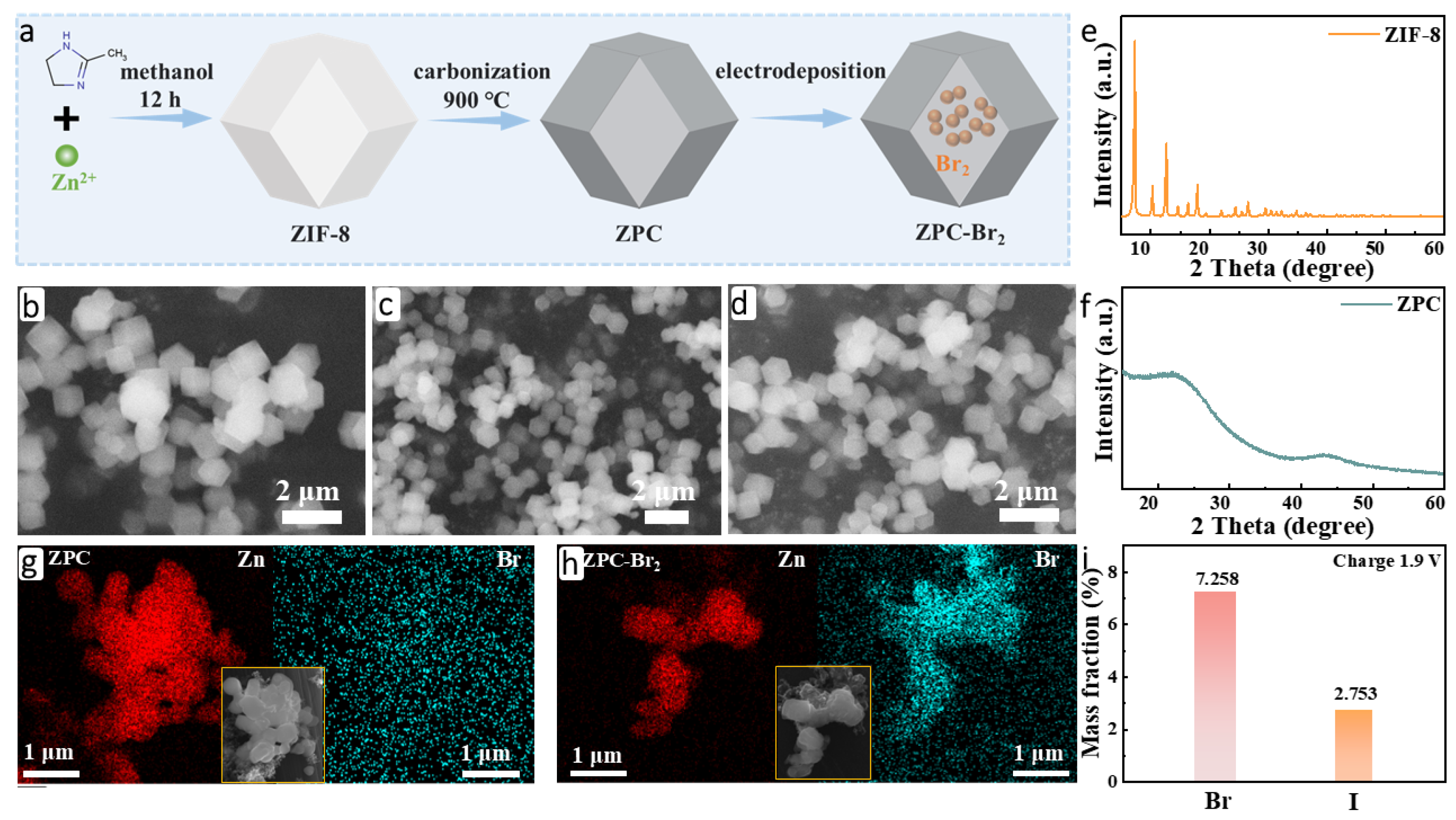
The ZIF-8-derived porous carbon (ZPC), serving as the host material of Br2, was synthesized successfully by pyrolysis of ZIF-8 at 900 °C under an argon atmosphere (denoted as ZPC in the following text), as illustrated in Figure 1a. SEM was conducted to analyze the morphology of the samples. As shown in Figure 1b, the typical rhombic dodecahedron structure of ZIF-8 is clearly observed, which is in accord with previous reports [22,23]. In Figure 1c, the morphology and structure are well preserved after calcination. Subsequently, ZPC was utilized as the electrode for the electrodeposition of Br2 to obtain ZPC-Br2. No alterations in the structure were observed after electrodeposition (Figure 1d), indicating that the ZPC exhibited favorable structural stability and efficient Br2 fixation. It is highly important for the long-life cycling performance of zinc-bromine batteries [24,25]. The crystal structure of the ZIF-8 was examined by XRD, as depicted in Figure 1e, and all the diffraction peaks can be attributed to the ZIF-8 (JCPDS 96-711-1974). Two weak crystallization diffraction peaks at about 24.0° and 44.0° are attributed to the low degree of graphitization of ZPC (Figure 1f). The images of EDS mapping also demonstrate that the bromine element effectively deposits onto the ZPC-Br2 electrode compared with the ZPC electrode, as shown in Figure 1g,h. Additionally, the results of ICP-MS indicate that the content of the Br-species in the ZPC-Br2 electrode is 7.258 wt.%, and the corresponding mass-loading is 1.441 mg cm−2. The iodine-species content of the ZPC-Br2 electrode is 2.753 wt.%, and the corresponding mass-loading is 0.544 mg cm−2. These results further demonstrate the existence of iodine species and Br species in the ZPC-Br2 electrode (Figure 1i).
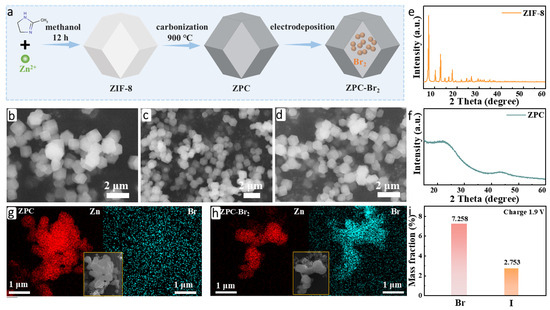
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process for ZPC-Br2. (b) SEM image of ZIF-8. (c) SEM image of ZPC. (d) SEM image of ZPC-Br2. (e) XRD pattern of ZIF-8. (f) XRD pattern of ZPC. (g) Element mapping of ZPC. (h) Element mapping of ZPC-Br2. (i) The concentration of Br and I elements in the ZPC-Br2 electrode after charging to 1.9 V.
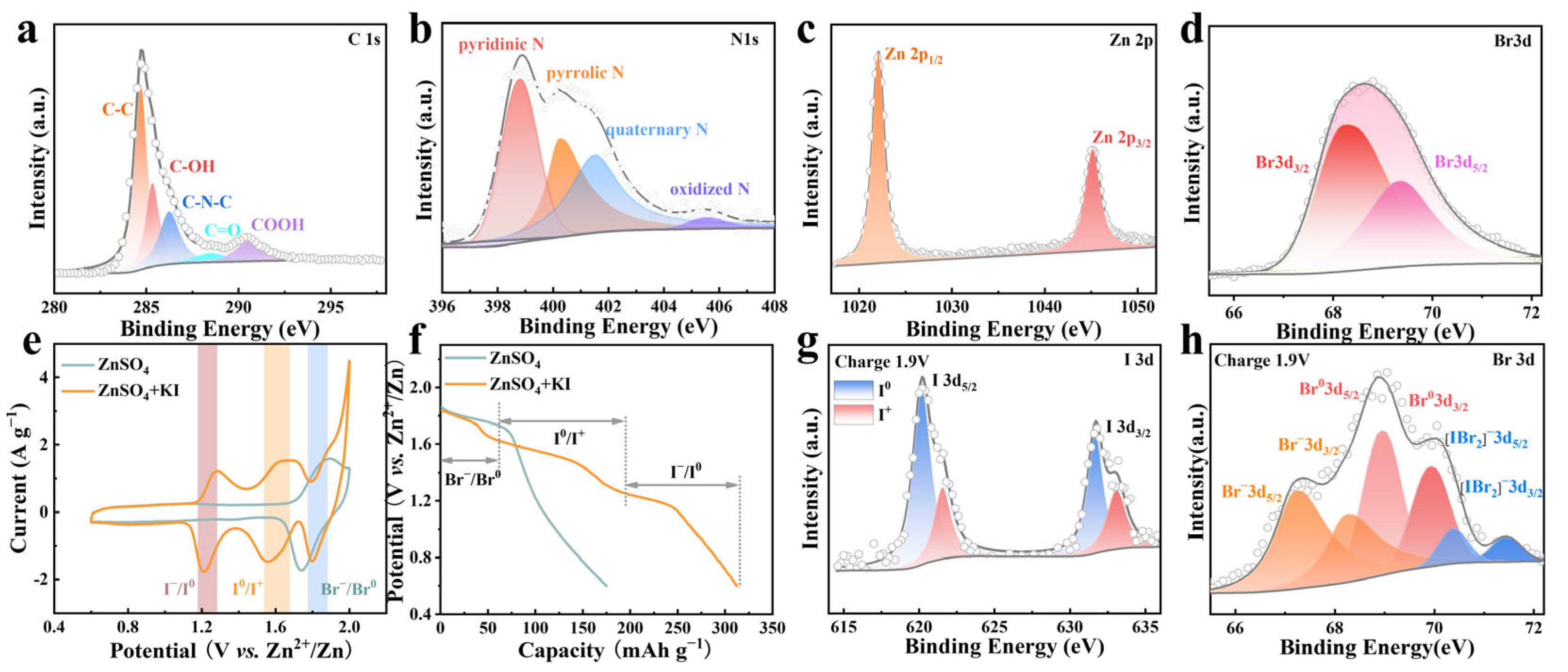
The element state in ZPC-Br2 cathode was characterized by XPS. As depicted in the survey spectrum of ZPC-Br2 cathode in Figure S1 (in the Supporting Information), the peaks of C, N, Zn, and Br elements are distinctly observed, revealing the existence of Br2 after electrodeposition. In the spectrum of C 1s, the peaks at 284.8 eV and 285.4 eV in Figure 2a can be indexed to C-C and C-OH, respectively, while the peaks located at 286.3 eV, 288.5 eV, and 290.5 eV are ascribed to C-N-C, C=O, and -COOH [26,27,28]. Furthermore, in the N 1s spectrum, the binding energies at 398.8 eV, 400.23 eV, 401.51 eV, and 405.53 eV (Figure 2b) are assigned to pyridinic N, pyrrolic N, quaternary N, and oxidized N. The N species serve as the active sites for anchoring the bromine species [29,30]. As shown in Figure 2c, the peaks located at 1022.1 eV and 1045.2 eV correspond to spin-orbit double peaks of Zn 2p3/2 and Zn 2p1/2 [31,32]. As for the Br 3d spectrum, the binding energy peaks at 68.3 and 69.4 eV correspond to Br 3d5/2 and Br 3d3/2 with an energy separation of 1.1 eV (Figure 2d) [32,33,34].
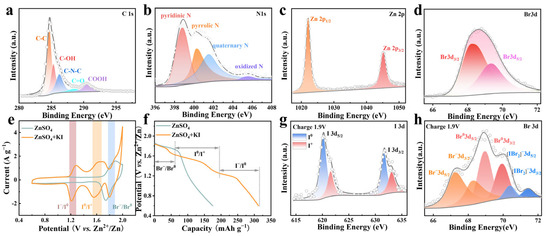
Figure 2.
(a) C 1s XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 cathode. (b) N 1s XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 cathode. (c) Zn 2p XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 cathode. (d) Br 3d XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 cathode. (e) CV curves of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 and ZnSO4 + KI electrolytes at 1 mV s−1. (f) The GCD curves at 2 A g−1 of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 and ZnSO4 + KI electrolytes. (g) I 3d XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 cathode at charge stage. (h) Br 3d XPS spectra of the ZPC-Br2 electrode at charge stage.
To evaluate the capacity of the ZPC-Br2 cathode, CV and GCD are tested. In the electrolyte containing ZnSO4 and KI, the peaks at 1.2/1.3 V are presumably attributed to the reactions of I− to I0, while the peaks around 1.6/1.7 V can be ascribed to the I0 to I+ (Figure 2e). In contrast, a single pair of redox peaks emerges at around 1.8/1.9 V, corresponding to the reactions involving the transformation of Br− to Br0 in pure ZnSO4 electrolyte. As shown in Figure 2f, the GCD profiles illustrated three pairs of discharge voltage platforms in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte, which stabilized at 1.2 V, 1.6 V, and 1.8 V, in alignment with the CV curves. The specific capacity reaches 320 mAh g−1 at 2 A g−1. It could be clearly observed that the GCD curve of ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte exhibits excellent symmetry, as shown in Figure S2, implying the high reversibility of this six-electron redox reaction. In contrast, a solitary voltage platform can be observed at 1.8 V in pure ZnSO4 electrolyte, which is associated with the Br−/Br0 redox reactions and exhibits a lower capacity of 170 mAh g−1. These results suggest that introducing I− into the electrolyte is a promising method to improve the capacity of zinc-bromine batteries.
The valence state changes of ZPC-Br2 cathode charged to 1.9 V (Supplementary Figure S3) are investigated by XPS [35]. In the I 3d spectrum, the binding energies at 620.2 eV and 631.7 eV correspond to I 3d5/2 and I 3d3/2 of I0, while the peaks located at 621.6 eV and 633.1 eV are assigned to I 3d5/2 and I 3d3/2 of I+ (Figure 2g) [36,37]. This indicates the iodine species are involved in the reactions from I− to I+. These results illustrate that the iodine species are involved in the reactions during charging to 1.9 V, leading to a four-electron reaction from I− to I+, which greatly enhanced the capacity. As shown in Figure 2h, binding energy peaks at 70.38 eV and 71.45 eV correspond to [IBr2]−, confirming that Br− stabilizes I+ by forming an interhalogen compound [38]. Meanwhile, the binding energy peaks at 69.01 eV and 70.01 eV and the binding energy peaks at 67.28 eV and 68.30 eV correspond to Br−, which further verifies the Br− is oxidized to Br2 when further charged to 1.90 V [39]. The introduction of I− into the electrolyte to trigger interhalogen interactions between I-species and Br− forms a stable interhalogen compound that stabilizes the Br species and suppresses the polybromide shuttle effect, significantly enhancing the reaction reversibility. Overall, a six-electron reaction is activated upon the addition of I− in the electrolyte. Initially, the I− is oxidized to I2 at about 1.2/1.3 V, involving a two-electron reaction. Subsequently, the I2 is further oxidized to I+ at about 1.6/1.7 V, and accompanied by two-electron transfer. Finally, with further charging to 1.9 V, Br− can be further oxidized to Br₂, releasing an additional two-electron capacity.
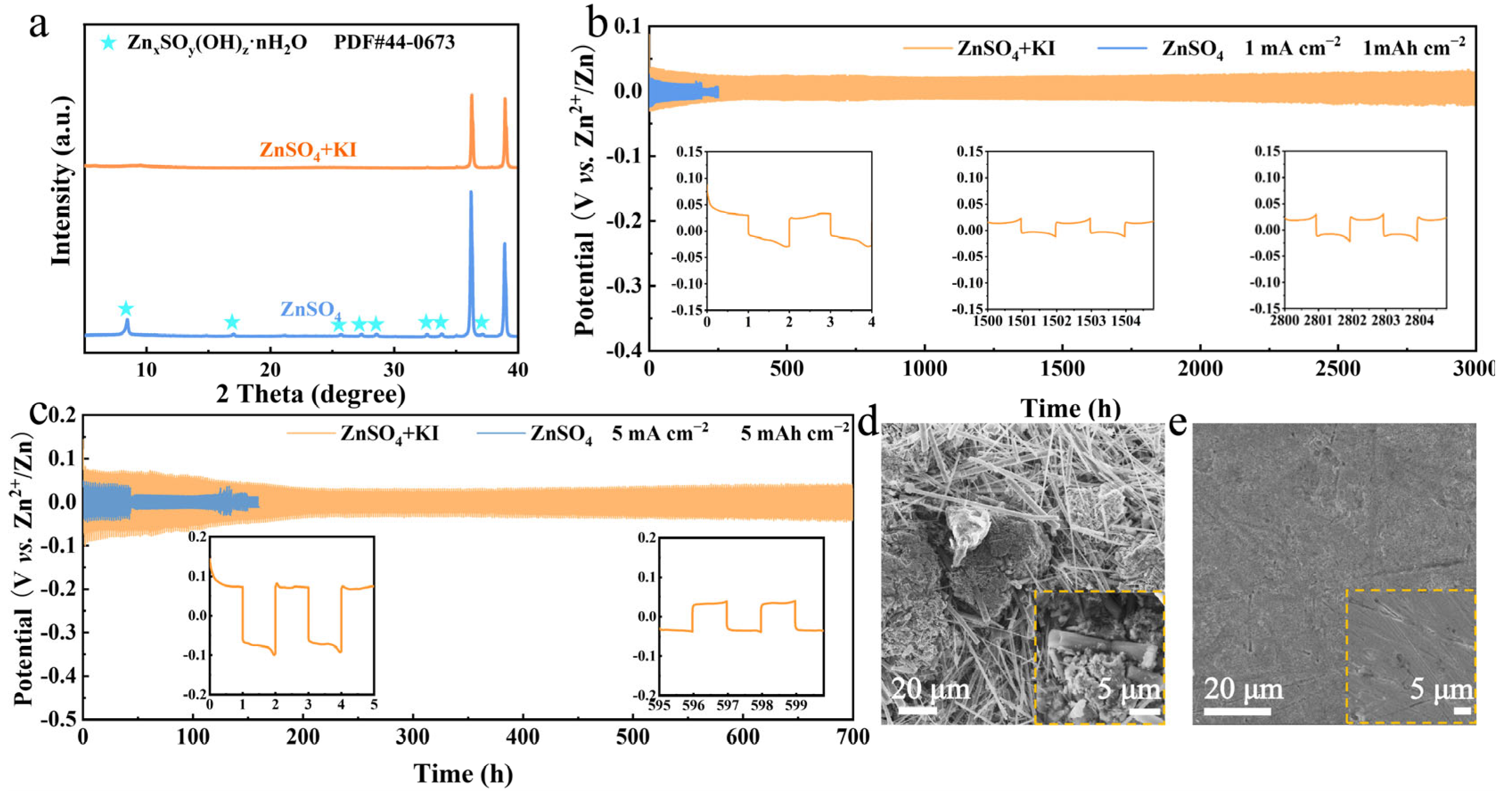
In addition to the cathode, the Zn anode also greatly affects the electrochemical performance of zinc-bromine batteries [40,41]. The effects of different KI concentrations on zinc anodes were investigated. As depicted in Supplementary Figure S4, the SEM images reveal that the corrosion of the zinc anode by KI intensifies with increasing concentration. Consequently, 0.1 M KI was introduced as an additive to the zinc-iodine battery electrolyte. It can provide sufficient I−/I+ redox activity (verified by cyclic voltammetry) and is cost-effective for scalable applications compared to higher concentrations. The electrolyte additive KI also inhibits the side reactions on the Zn anode, which is verified by the XRD patterns in Figure 3a, as no by-product peaks can be indexed after 20 cycles. The cycling lifespan of a Zn||Zn symmetric cell with I− additive, under the conditions of 1 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2, can reach 3000 h. In contrast, it is merely 250 h in pure ZnSO4 electrolyte (Figure 3b). Moreover, the lifespan of a Zn||Zn symmetric cell with I− additive is still much longer even at higher current density and areal capacity (5 mA cm−2 and 5 mAh cm−2), as shown in Figure 3c. It is probably because the I− accumulation on the Zn anode surface effectively inhibits the dendrite growth and by-product formation. As clearly presented in the SEM images (Figure 3d and Supplementary Figure S5), after 20 cycles, the surface of the Zn anode in pure ZnSO4 electrolyte is extensively covered by dendrites and by-products. Conversely, in the electrolyte containing I−, the Zn surface remains smooth and dense even after cycling, as can be confirmed in Figure 3e and Supplementary Figure S6.
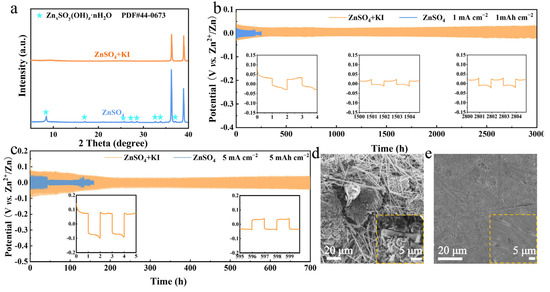
Figure 3.
(a) XRD patterns of Zn anode after 20 cycles in different electrolytes. (b) Cycling performance at 1 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2. (c) Cycling performance at 5 mA cm−2, 5 mAh cm−2. (d) SEM image of Zn anode after 20 cycles in ZnSO4 electrolyte at 5 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2. (e) SEM image of Zn anode after 20 cycles in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte at 5 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2.
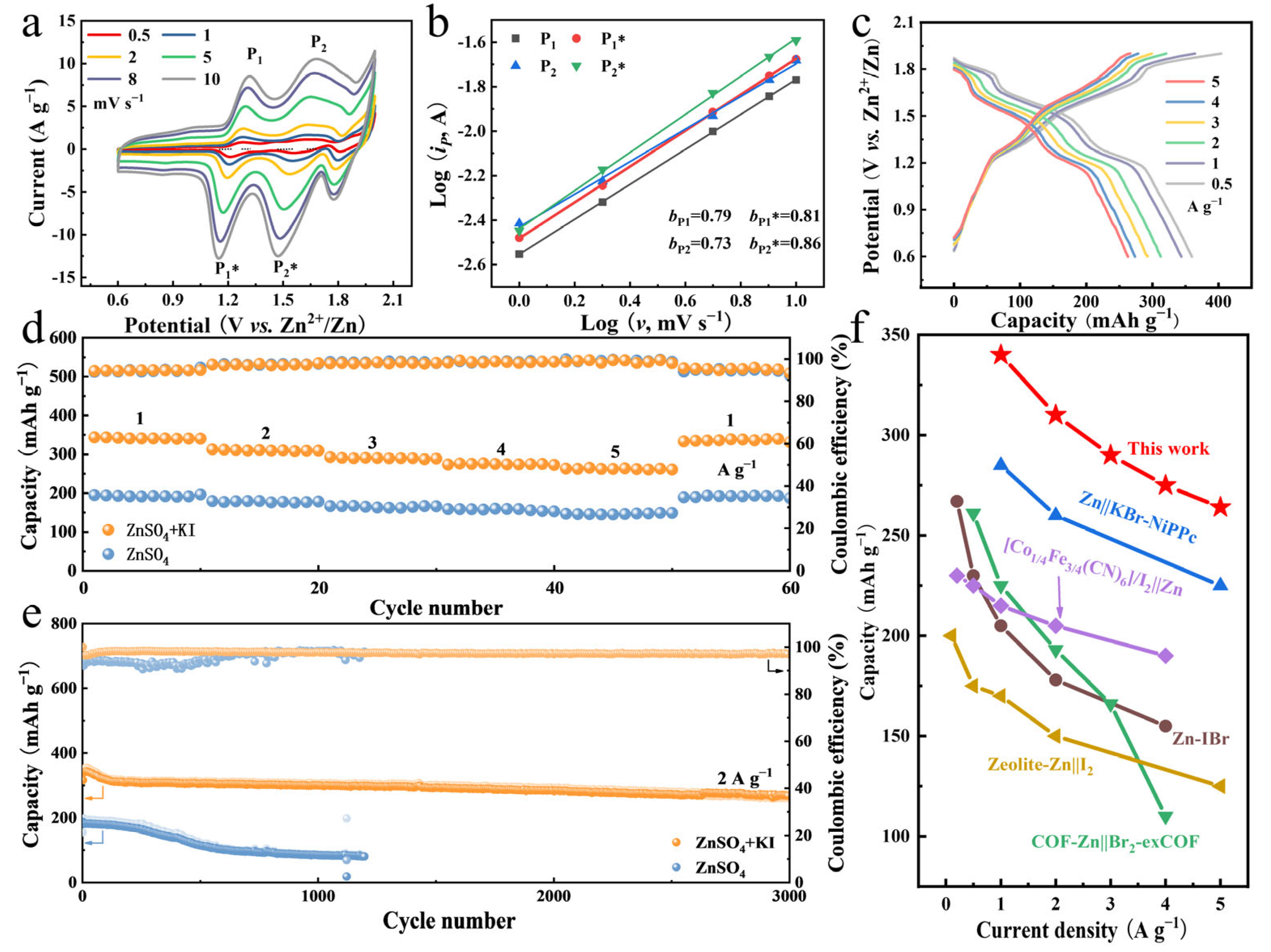
The effects of I− additive on the electrochemical performance of zinc-bromine batteries were further evaluated. The CV curves of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte at different scan rates display three pairs of reversible redox peaks at 1.2/1.3 V, 1.6/1.7 V, and 1.8/1.9 V (vs. Zn/Zn2+), which correspond to the I−/I0, I+/I0, and Br−/Br0 redox reactions, respectively (Figure 4a). Moreover, the shapes of the CV curves at different scan rates exhibit favorable symmetry. The slight shifts of the oxidation peaks in the positive direction and reduction peaks in the negative direction at high scan rates indicate the fast reaction kinetics. The plots of redox peak currents (ip) versus scan rates (ν) based on the CV curves are used to calculate the b values of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery. The b values are fitted to be 0.79/0.81 (P1/P1*) and 0.73/0.86 (P2/P2*), manifesting that these redox reactions are a combination of diffusion-controlled and capacitance-controlled behavior (Figure 4b) [42,43]. Furthermore, the GCD results in Figure 4c further demonstrate this, where the pairs of charging/discharging voltage plateaus at 1.2/1.3 V, 1.6/1.7 V, and 1.8/1.9 V (vs. Zn/Zn2+) align well with the results for the CV curves. Even at a high current density of 5 A g−1, the voltage plateau is well maintained with a much lower voltage drop, indicating the fast reaction kinetics.
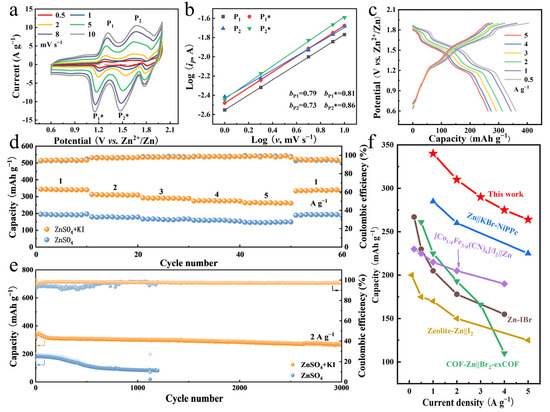
Figure 4.
(a) CV curves of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte at different scan rates. (b) Plots of log (ip, peak currents) versus log (v, scan rates) for ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte. (c) GCD plots of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte at different current densities. (d) Rate performance of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 electrolyte and ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte. (e) Long-cycle stability of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery at 2 A g−1. (f) The comparison of this work to previous reports on aqueous zinc-bromine batteries.
In addition, Figure 4d illustrates the rate performance of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in 1 M ZnSO4 + 0.1 M KI electrolyte. Specifically, a higher specific capacity of 345 mAh g−1 is achieved at 1 A g−1, which is much higher than 190 mAh g−1 in pure ZnSO4 electrolyte. The specific capacity of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery is retained at 265 mAh g−1 (capacity retention 82.8%) even at the high current density of 5 A g−1 and recovers to its initial capacity after returning to 1 A g−1, indicating excellent redox kinetics and reversibility. Furthermore, the cycling stability of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte, as depicted in Figure 4e, is still maintained as high as 80% after 3000 cycles, revealing the high reversible capacity retention. The performance is significantly better than that in ZnSO4 electrolyte (1000 cycles). This result is mainly due to the occurrence of the side reactions of hydrogen evolution reactions and the formation of the by-product Zn sulfate hydroxide in the ZnSO4 electrolyte, which ultimately leads to the corrosion of the Zn anode [44,45,46]. The long cycle stability indicates that the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery exhibits an excellent ability to fix bromine species with I− additive, thus effectively inhibiting the shuttle effect. As a result, the electrochemical performance of the ZPC-Br2||Zn battery is superior to that in many previous reports regarding zinc-bromine batteries (Figure 4f), such as KBr-NiPPc [47], Zn-IBr [48], Zeolite-Zn [49], and polysulfide-halogen ARFB systems [50].
4. Conclusions
In summary, a six-electron redox reaction involving I−/I+ and Br−/Br0 is achieved by introducing a small amount of KI into the electrolyte. Br− is capable of coupling with I− to form interhalogen compounds, which activates and stabilizes the highly reversible redox reactions of I0/I+. The ZPC serves as the host of the halogen, successfully suppressing the polybromide/polyiodide shuttle, which ensures the reversibility of the Br−/Br0 conversion, and finally boosts the highly reversible six-electron redox reaction from I−/I+ and Br−/Br0. Moreover, the I− accumulates on the Zn anode surface and effectively inhibits the dendrite growth and by-product formation. As a result, the zinc-bromine batteries exhibit high specific capacity of 345 mAh g−1 at a current density of 1 A g−1 and excellent capacity retention of 80% after 3000 cycles. These results highlight promising prospects for the future development of zinc-bromine batteries.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemistry7030075/s1, Figure S1: Survey spectrum of ZPC-Br2 cathode; Figure S2: The GCD curves at 2 A g−1 of ZPC-Br2||Zn battery in pure ZnSO4 or ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte. Figure S3: GCD plot with tagged voltage states.; Figure S4: SEM image of Zn anode after 20 cycles at 5 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2. Figure S5: SEM image of Zn anode after 20 cycles in ZnSO4 electrolyte at 5 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2; Figure S6: SEM image of Zn anode after 20 cycles in ZnSO4 + KI electrolyte at 5 mA cm−2, 1 mAh cm−2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and C.W.; Methodology, X.J. and X.X.; Software, J.Z. and N.L.; Validation, N.L. and M.K.; Formal analysis, J.Z., X.J. and Q.Y.; Investigation, J.Z. and X.Z.; Resources, C.L., C.W. and X.X.; Data curation, Q.Y. and D.L.; Writing—original draft, J.Z. and X.J.; Writing—review & editing, W.L., C.W. and X.X.; Visualization, X.Z., M.K. and W.L.; Supervision, C.L., D.L., C.W. and X.X.; Project administration, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U22A20140), Jinan City-School Integration Development Strategy Project (No. JNSX2023015), and the University of Jinan Disciplinary Cross-Convergence Construction Project 2023 (No. XKJC-202309). National Natural Science Foundation of China (22409071). Natural Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2024QB120) Youth Innovation Group Plan of Shandong Province (2024KJG046). Higher-Level Talent Initial Scientific Research and Discipline Construction Fund (511/1009530).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the contributions and assistance ofbattery measurement system (LAND CT2001A). and NEWARE Battery Test System (Shenzhen, China) in the electrochemical testing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Ma, Q.; Wan, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Luo, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T.; et al. A dual-functional organic electrolyte additive with regulating suitable overpotential for building highly reversible aqueous zinc ion batterie. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2214568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Kundu, D. A path forward for the translational development of aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Joule 2023, 7, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Bu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Kong, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Constructing a multifunctional SEI layer enhancing kinetics and stabilizing zinc metal anode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2415107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Jin, H.; Davey, K.; Liang, G.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z. Developing cathode materials for aqueous zinc ion batteries: Challenges and practical prospects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2301291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, F.; Jing, Z.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Anionic chemistry modulation enabled environmental self-charging aqueous zinc batteries: The case of carbonate ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202409774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, J. Corrosion as the origin of limited lifetime of vanadium oxide-based aqueous zinc ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, J.Z.X. Ternary chloride-free electrolyte design for highly efficient aqueous zinc–iodine batteries with four-electron conversion. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 5376–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ge, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. An iodine-chemisorption binder for high-loading and shuttle-free Zn-iodine batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 24, 2304110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liang, W.; Liu, X.; Yin, T.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, W.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.; et al. A bifunctional electrolyte additive features preferential coordination with iodine toward ultralong-life zinc-iodine batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2400110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Liang, B.; Chen, A.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiong, B.; et al. Development of rechargeable high-energy hybrid zinc-iodine aqueous batteries exploiting reversible chlorine-based redox reaction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Qu, G.; Shao, W.; Lin, C.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; et al. Activating and stabilizing a reversible four electron redox reaction of I−/I+ for aqueous Zn iodine battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202403187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Abdalla, K.; Xiong, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.M. High-energy and durable aqueous Zn batteries enabled by multi-electron transfer reactions. Energy Mater. 2024, 4, 400040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yun, D.; Jeon, J. Effect of a bromine complex agent on electrochemical performances of zinc electrodeposition and electrode dissolution in zinc-bromide flow battery. J. Power Sources 2019, 438, 227020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dong, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Ji, X.; Cheng, S. Achievement of efficient and stable non-flow zinc-bromine batteries assisted by rational decoration upon the two electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23278–23287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Byun, Y.; Jeong, G.H.; Choi, C.; Kwen, J.; Kim, R.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, S.O.; Kim, H. High-energy efficiency membraneless flowless Zn–Br battery: Utilizing the electrochemical–chemical growth of polybromides. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Q.; Wang, G.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Han, J. Visualizing and understanding the ionic liquid-mediated polybromide electrochemistry for aqueous zinc-bromine redox batteries. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 13796–13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dou, Q.; Deng, G.; Li, G.; Ma, Y.; Tang, P.; Cui, Y.; Yang, C.; Zang, L.; Yan, X. A hybrid-aqueous biphasic electrolyte for suppressed shuttle effects and self-discharge of zinc bromide batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 15658–15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, L.; Davey, K.; Qiao, S. Advanced cathodes for aqueous Zn batteries beyond Zn2+ intercalation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. Anode corrosion in aqueous Zn metal batteries. eScience 2023, 3, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wei, J.; Xue, L.; Luo, D.; Chen, G.; Chu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zong, K.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Regulating the electron structure of covalent organic frameworks to enable excellent cycle life and high rate toward advanced Zn−I2 Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lei, C.; Jiang, P.; Yang, W.; Ma, W.; He, X.; Liang, X. Practical high-energy aqueous zinc-bromine static batteries enabled by synergistic exclusion-complexation chemistry. Joule 2024, 8, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Kamali, A. ZIF-8 decorated on three-dimensional graphene as reusable magnetic adsorbent for efficient removal of malachite green from wastewater. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 1017, 179028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, R.; He, R.; Chen, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Mai, L.; Zhou, L. Encapsulating Si nanoparticles in ZIF-8-derived carbon through surface amination for stable lithium storage. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 216, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, J.; Xiao, P.; Nie, S.; Peng, S.; Chen, J.; Luo, F.; Janiak, C.; Chen, Y. Preparation of hierarchical porous ZIF-67 and its application in zinc battery separator. Chemistry 2024, 6, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Mao, L.; Qiao, S. Aqueous zinc-bromine battery with highly reversible bromine conversion chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202502386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Lei, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Liang, X. Recognition of the catalytic activities of graphitic N for zinc-iodine batteries. Energy Storage Matter. 2022, 53, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponrouch, A.; Dedryvère, R.; Monti, D.; Demet, A.E.; Mba, J.M.A.; Croguennec, L.; Masquelier, C.; Johanssoncf, P.; Palacín, M.R. Towards high energy density sodium ion batteries through electrolyte optimization. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; He, S.; Han, G.; Long, J.; Li, S.; Lau, C.; Zhang, S.; Shao, L. Aqueous one-step modulation for synthesizing monodispersed ZIF-8 nanocrystals for mixed-matrix membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11296–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qu, G.; Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Han, C.; Xu, X.; Zhi, C.; Li, H. Reversible solid-liquid conversion enabled by self-capture effect for stable non-flow zinc-bromine batteries. Green Energy Environ. 2024, 9, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, L.; Sun, J.; Ma, W.; Ren, M.; Cai, X.; Liu, W.; Yao, J. ZIF-8 derived porous carbon to mitigate shuttle effect for high performance aqueous zinc–iodine batteries. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2022, 610, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Kim, M.J.; Peng, L.; Lim, H.; Kaiser, R.; Ran, L.; Luo, B.; Han, Z.; Hossain, M.; Lu, X.; et al. Impact of micropores and dopants to mitigate lithium polysulfides shuttle over high surface area of ZIF-8 derived nanoporous carbons. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zheng, X.; Wei, C.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, K.; Sun, J.; Rümmeli, M.; Yang, R. Nitrogen-doped hollow carbon polyhedron derived from salt-encapsulated ZIF-8 for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 2021, 171, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Fang, T.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wei, C.; Zhou, D.; Tang, X.; Liu, X. A high-performance quasi-solid-state aqueous zinc−dual halogen battery. ACS Nano. 2022, 16, 10389–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Peng, C.; Zhu, D.; Zhi, C. Bifunctionally electrocatalytic bromine redox reaction by single-atom catalysts for high-performance zinc batteries. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2409810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, J. ZIF-8@CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals Formed by Conversion of Pb to CsPbBr3 in Bimetallic MOFs for Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2301508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, M.; Kim, J.; Peng, L.; Qiu, H.; Kaiser, R.; Qiu, L.H.; Kaiser, R.; Ran, L.; Hossain, M.A.; Luo, B.; et al. ZIF-8 derived hollow carbon to trap polysulfides for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 11086–11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ying, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Bai, S.; Zhi, C. Solid Interhalogen Compounds with Effective Br0 Fixing for Stable High-energy Zinc Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, N.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liang, G.; Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L.; Dong, B.; et al. Enhanced Redox Kinetics and Duration of Aqueous I2/I− Conversion Chemistry by MXene Confinement. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, J.; Liu, G.; Yan, J.; Qi, J.; Shi, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wen, Z.; et al. Reducing dead species by electrochemically-densified cathode-interface-reaction layer towards high-rate-endurable Zn||I-Br batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202416755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Du, G.; Zhao, S.; Qu, G.; Xing, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, H.; Xu, X. Stabilization of zinc anode by trace organic corrosion inhibitors for long lifespan. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 109531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Qu, G.; Zhao, S.; Qin, H.; Li, D.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Xu, X. Highly reversible Zn metal anode securing by functional electrolyte modulation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2400872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Song, X.; Wang, N.; Peng, H.; Su, J.; Zeng, S.; Xu, X.; Yang, J. Suppressed dissolution and enhanced desolvation in core–shell MoO3@TiO2 nanorods as a high-rate and long-life anode material for proton batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 202200157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Liang, G.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, A.; Cui, H.; Dong, B.; et al. Two-electron redox chemistry enabled high-performance iodide ion conversion battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, N.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, G.; Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Huang, Q.; Dong, B.; et al. Confining aqueous Zn-Br halide redox chemistry by Ti3C2TX Mxene. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Li, Q.; Jiang, F.; Huang, B.; Song, J.; Yun, S.; Liu, X.; Kimura, H.; Liu, J.; Kang, L. Boosting Zn||I2 battery’s performance by coating a zeolite-based cation-exchange protecting layer. Nano-Micro Letts. 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ying, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Zhi, C. Electrocatalytic iodine reduction reaction enabled by aqueous zinc-iodine battery with improved power and energy densities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3791–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Pi, Y.; Pang, H. Micro/nano metal–organic frameworks meet energy chemistry: A review of materials synthesis and applications. eScience 2023, 3, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Ren, K.; Wang, Q.; Lim, Y.; Ma, F.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lai, C. In situ construction of zinc-rich polymeric solid–electrolyte interface for high-performance zinc anode. eScience 2023, 3, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, X. Halogen Storage Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, 5, 1155–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ding, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, X. Cathode materials for halide-based aqueous redox flow batteries: Recent progress and future perspectives. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 4250–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).