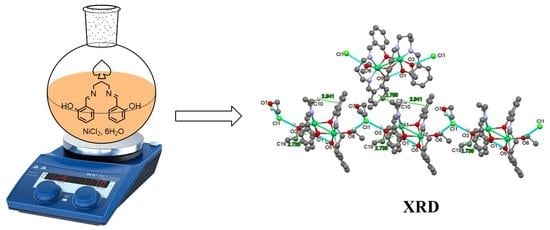
New Bi-Nuclear Nickel(II) Complex-Based Salen Schiff Base: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Electrical Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
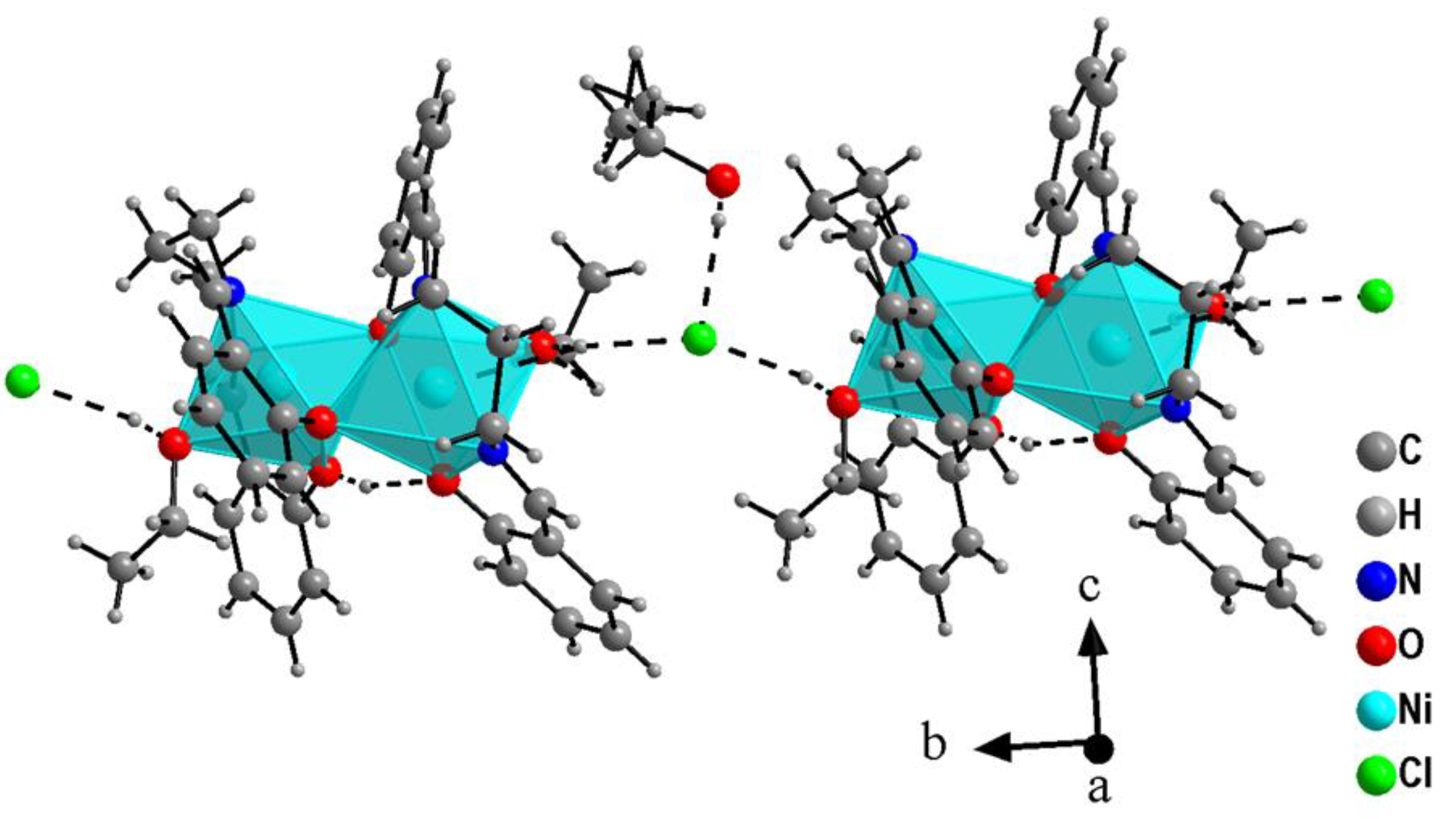
2.1. Crystal Structure Description
2.2. Spectroscopic Studies
2.3. Electronic Spectra
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.5. Dielectric Studies
2.6. Electrical Studies
2.6.1. Dc Electrical Conductivity
2.6.2. Ac electrical Conductivity
- If the frequency exponent (s) is independent of temperature, the mechanism is the quantum mechanical tunnel model (QMT);
- If (s) decreases to a minimum and then increases with a further increase in temperature, the mechanism is the large polaron tunnel model (LPT);
- If (s) increases with increasing temperature, the mechanism corresponds to the small polaron tunnel model (SPT);
- If (s) decreases with increasing temperature, the conductivity origin is described by the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Section
3.1.1. Preparation of Ligand H2L
3.1.2. Synthesis and Crystallization of Nickel Complex [Ni2HL2(EtOH)2](Cl)(EtOH)
3.1.3. X-Ray Data Collection and Crystal Structure Determination
3.1.4. Electrical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Ismail, N.M.; Ismael, M.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Ahmed, E.A.-H. Synthesis, Characterization, DFT Calculations and Biological Studies of Mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II) and Cd(II) Complexes Based on a Tetradentate ONNO Donor Schiff Base Ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1134, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, H.; Fallah-Mehrjardi, M.; Behjatmanesh-Ardakani, R.; Bahadori, M.; Moghadam, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Munawar, K.S.; Tahir, M.N. Pd(II) and Ni(II) Complexes Containing ONNO Tetradentate Schiff Base Ligand: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectral Characterization, Theoretical Studies, and Use of PdL as an Efficient Homogeneous Catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction. Polyhedron 2022, 213, 115622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaji, F.E.; Belghiti, M.E.; Drissi, M.; Fahim, M.; Salim, R.; Hammouti, B.; Taleb, M.; Nahle, A. Electrochemical, Quantum Calculations and Monte Carlo Simulation Studies of N1, N2-Bis (1-Phenylethylidene) Ethane-1, 2-Diamine as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Carbon Steel in a 1.0 M Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 37, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahron, H.; Ahmad, S.N.; Tajuddin, A.M. Substituent Effect on Catalytic Activity of Palladium(II) Schiff Base Complexes for Sonogashira Reaction. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zoubi, W.; Ko, Y.G. Schiff Base Complexes and Their Versatile Applications as Catalysts in Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Part I. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, A.; Fuentealba, M.; Carrillo, D.; Manzur, C.; Ledoux-Rak, I.; Hamon, J.-R.; Saillard, J.-Y. Synthesis, Spectral, Structural, Second-Order Nonlinear Optical Properties and Theoretical Studies On New Organometallic Donor−Acceptor Substituted Nickel(II) and Copper(II) Unsymmetrical Schiff-Base Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2750–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesley Jeevadason, A.; Kalidasa Murugavel, K.; Neelakantan, M.A. Review on Schiff Bases and Their Metal Complexes as Organic Photovoltaic Materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Moustafa, M.G. Spectroscopic, Morphology and Electrical Conductivity Studies on Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Mn(II)-Oxaloyldihydrazone Complexes. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Biswas, S.; Liao, M.-S.; Kar, T.; Aydogdu, Y.; Dagdelen, F.; Mostafa, G.; Chattopadhyay, A.P.; Yap, G.P.A.; Xie, R.-H.; et al. An Attempt towards Coordination Supramolecularity from Mn(II), Ni(II) and Cd(II) with a New Hexadentate [N4O2] Symmetrical Schiff Base Ligand: Syntheses, Crystal Structures, Electrical Conductivity and Optical Properties. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 3359–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.-L.; Yang, P.-P. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetic Properties of a Series of Binuclear Lanthanide Compounds Derived from the 4-Bromo-2-((Quinolin-8-Ylimino)Methyl)Phenol Ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Drew, M.G.B.; Lu, C.-Z.; Tercero, J.; Diaz, C.; Ghosh, A. Dinuclear Complexes of MII Thiocyanate (M = Ni and Cu) Containing a Tridentate Schiff-Base Ligand: Synthesis, Structural Diversity and Magnetic Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 2005, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunadevi, A.; Raman, N. Biological Response of Schiff Base Metal Complexes Incorporating Amino Acids—A Short Review. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Ahmed, S.S.; Alam, S.M.R. REVIEW: Biomedical Applications of Schiff Base Metal Complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 3109–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.I.; Ayad, M.M. Electrical Properties of Ga(III), In(III), Zr(IV) and Sn(IV) Complexes with Schiff Bases Derived from 2-Hydroxynaphthaldehyde and Phenylenediamines. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1993, 4, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, F.; Hameed, A.; Sayqal, A.; Bayazeed, A.A.; Alzahrani, S.; Al-Ahmed, Z.A.; Althagafi, I.; Zaky, R.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Green-Synthesis and Characterization for New Schiff-Base Complexes; Spectroscopy, Conductometry, Hirshfeld Properties and Biological Assay Enhanced by in-Silico Study. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6327–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domingo, E.; Folcia, C.L.; Ortega, J.; Etxebarria, J.; Termine, R.; Golemme, A.; Coco, S.; Espinet, P. Striking Increase in Hole Mobility upon Metal Coordination to Triphenylene Schiff Base Semiconducting Multicolumnar Mesophases. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 10482–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, M. Synthesis, Spectral and Magnetic Studies of Mono- and Bi-Nuclear Metal Complexes of a New Bis(Tridentate NO2) Schiff Base Ligand Derived from 4,6-Diacetylresorcinol and Ethanolamine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Singha, S.; Saha, R.; Singha Roy, A.; Islam, M.; Kumar, S. A Bi-Nuclear Cu(II)-Complex for Selective Epoxidation of Alkenes: Crystal Structure, Thermal, Photoluminescence and Cyclic Voltammetry. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 486, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, P.; Brandão, P.; Benmansour, S.; García, C.J.G.; Saha, A. Azido and Thiocyanato Bridged Dinuclear Ni(II) Complexes Involving 8-Aminoquinoline Based Schiff Base as Blocking Ligands: Crystal Structures, Ferromagnetic Properties and Magneto-Structural Correlations. Polyhedron 2020, 188, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, P.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Drew, M.G.B.; Diaz, C.; Ghosh, A. Synthesis, Structure and Magnetic Properties of Mono- and Di-Nuclear Nickel(II) Thiocyanate Complexes with Tridentate N3 Donor Schiff Bases. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Shibasaki, M. Recent Advances in Cooperative Bimetallic Asymmetric Catalysis: Dinuclear Schiff Base Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsunuma, H.; Matsunaga, S. Dinuclear Ni 2—Schiff Base Complex-Catalyzed Asymmetric 1,4-Addition of β-Keto Esters to Nitroethylene toward γ 2,2 -Amino Acid Synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z. Structurally Simple Dinuclear Nickel Catalyzed Olefin Copolymerization with Polar Monomers. J. Catal. 2018, 368, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, D. Olefin Polymerization and Copolymerization Catalyzed by Dinuclear Catalysts Having Macrocyclic Ligands. J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2019, 77, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, S.; Kandaswamy, M.; Varghese, B. Structural, Electrochemical, Phosphate-Hydrolysis, DNA Binding and Cleavage Studies of New Macrocyclic Binuclear Nickel(II) Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 3823–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Kai, K.; Ando, I.; Kawano, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Sakai, K. A Dinuclear Nickel Catalyst Based on Metal–Metal Cooperation for Electrochemical Hydrogen Production. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 119498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, M.; Qiao, L.; Xie, J. Recent Advances of Dinuclear Nickel- and Palladium-Complexes in Homogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8524–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Soliman, S.M.; Trzesowska-Kruszynska, A.; Kruszynski, R.; Khan, Z. A (Salicylaldiminato)Pt(II) Complex with Dimethylpropylene Linkage: Synthesis, Structural Characterization and Antineoplastic Activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 176, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I. Phenoxy-Bridged Binuclear Zn(II) Complex Holding Salen Ligand: Synthesis and Structural Characterization. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1107, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelar, M.D.; Quadri, S.; Pathan, M.A.A.K.; Kamble, S.; Farooqui, M.; Nuzaat, D.A.; Shaikh, J.D.; Syed, F.M. Pharmaceutically Fine Synthesis and Their Study of Antimicrobial Activity of Metal Complexes with Some Schiff’s Bases. Der Pharma Chem. 2011, 3, 486–490. [Google Scholar]
- Corden, J.P.; Errington, W.; Moore, P.; Wallbridge, M.G.H. N,N’-Bis(2-Hydroxybenzylidene)-2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Propanediamine. Acta Cryst. C 1996, 52, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An Update. J. Appl. Cryst. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A.L. PLATON SQUEEZE: A Tool for the Calculation of the Disordered Solvent Contribution to the Calculated Structure Factors. Acta Cryst C 2015, 71, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.-L.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Xian, D.-M.; Zhang, M. Unprecedented Preparation of Dinuclear Nickel(II) and Zinc(II) Complexes with Schiff Base Ligands Transformation Under Solvolthermal Conditions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2012, 26, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondo, M.; Doejo, J.; Garcia-Deibe, A.M.; Ocampo, N.; Sanmartin, J. Carboxylic Decorated Schiff Base Complexes as Metallotectons for Hydrogen Bonded 3D Networks. Polyhedron 2015, 101, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, P.; Bauza, A.; Frontera, A.; Drew, M.G.B.; Ghosh, A. Syntheses of Four New Asymmetric Schiff Bases and Their Cu(II) Complexes: Theoretical calculations to rationalize the packing of molecules in the crystals. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Muriel, A.; Reyes-Márquez, V.; Cañavera-Buelvas, F.; Parra-Unda, J.R.; Cuenú-Cabezas, F.; Polo-Cerón, D.; Colorado-Peralta, R.; Suárez-Moreno, G.V.; Aguilar-Castillo, B.A.; Morales-Morales, D. Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals. Inorganics 2022, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, A.; Nagasubramanian, S.; Thamilarasan, V.; Ojwach, S.O.; Gopu, G.; Sengottuvelan, N. In-Situ Nickel(II) Complexes of 3-(Dimethylamino)-1-Propylamine Based Schiff Base Ligands: Structural, Electrochemical, Biomolecular Interaction and Antimicrobial Properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadavi, S.K.; Rajput, J.D.; Bagul, S.D.; Hosamani, A.A.; Sangshetti, J.N.; Bendre, R.S. Synthesis, Crystal Structures, Biological Screening and Electrochemical Analysis of Some Salen-Based Transition Metal Complexes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 4863–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, A.; Sethupathi, M.; Ojwach, S.O.; Sengottuvelan, N. Investigation on Biomolecular Interactions of Nickel(II) Complexes with Monoanionic Bidentate Ligands. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1151, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.M.; El-Ghamaz, N.A.; Diab, M.A. Effect of the Type of Metal on the Electrical Conductivity and Thermal Properties of Metal Complexes: The Relation between Ionic Radius of Metal Complexes and Electrical Conductivity. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1160, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassib, H.; Abdel Razik, A. Dielectric Properties and AC Conduction Mechanism for 5,7-Dihydroxy-6-Formyl-2-Methylbenzo-Pyran-4-One Bis-Schiff Base. Solid State Commun. 2008, 147, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laajimi, M.; Jebnouni, A.; Chemli, M.; Majdoub, M.; Ben Chaabane, R. Optical, Dielectric and Oxygen Sensing Properties of an Anthracene and Carbazole Based π-Conjugated Schiff Base. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 228, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghamaz, N.A.; El-Sonbati, A.Z.; Diab, M.A.; El-Bindary, A.A.; Awad, M.K.; Morgan, S.M. Dielectrical, Conduction Mechanism and Thermal Properties of Rhodanine Azodyes. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 19, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Dielectric Relaxation in Solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, R57–R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghamaz, N.A.; El-Bindary, A.A.; Diab, M.A.; El-Sonbati, A.Z.; Nozha, S.G. Dielectrical Properties and Conduction Mechanism of Quinoline Schiff Base and Its Complexes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 2501–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker. APEX3 (Version 5.054), SAINT+ (Version 6.36A), SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of Silver and Molybdenum Microfocus X-Ray Sources for Single-Crystal Structure Determination. J. Appl. Cryst. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.; Flack, H.D.; Wagner, T. Use of Intensity Quotients and Differences in Absolute Structure Refinement. Acta Cryst. B 2013, 69, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



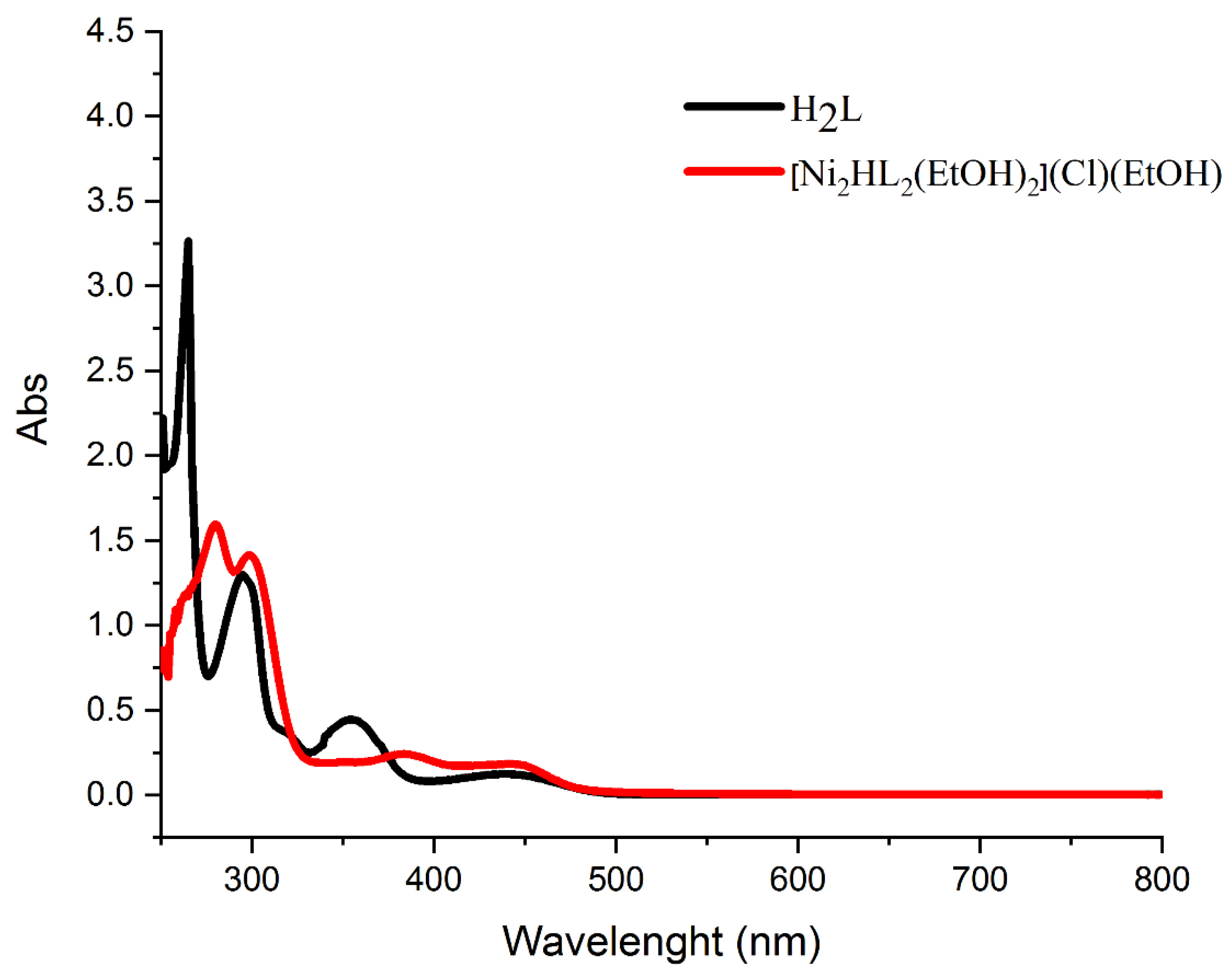




| Entry | Wave Lengths (nm) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| H2L | 264, 295 | π→π* (phenolic chromophore) |
| 354 | n→π* | |
| 440 | π→π* (C=N) | |
| [Ni2HL2(EtOH)2](Cl)(EtOH) | 279, 298 | π→π* |
| 384 | n→π* | |
| 447 | d→ π* charge transfer (CT) |
| Entry | εr | Tan δ | σdc × 10−10(S·cm−1) | σac × 10−8(S·cm−1) | Ea (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2L | 2.8 | 0.07 | 7.05 | 1.44 | 0.81 |
| [Ni2HL2(EtOH)2](Cl)(EtOH) | 0.9 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.37 |
| Crystal data | Chemical formula | C38H45N4Ni2O6·C2H6O·Cl |
| Mr | 852.71 | |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, Pca21 | |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | |
| a, b, c (Å) | 17.5795 (12), 11.8562 (9), 20.2065 (13) | |
| V (Å3) | 4211.6 (5) | |
| Z | 4 | |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.01 | |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.36 × 0.25 × 0.18 | |
| Data collection | Diffractometer | Bruker D8 VENTURE Super DUO [48] |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan [49] | |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.638, 0.746 | |
| No. of measured, independent, and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 108,380, 10,452, 8643 | |
| Rint | 0.047 | |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.667 | |
| Refinement | R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.029, 0.069, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 10,452 | |
| No. of parameters | 517 | |
| No. of restraints | 59 | |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | |
| Δ〉max, Δ〉min (e Å−3) | 0.22, −0.22 | |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 3701 quotients [(I+) − (I−)]/[(I+) + (I−)] [51] | |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.002 (4) |
| D–H…A | D−H | H…A | D…A | D−H…A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5–H50…O1 | 0.82 | 1.66 | 2.401 (3) | 148 |
| O7–H7A…Cl1 | 0.82 | 2.28 | 3.060 (7) | 160 |
| O3–H3O…Cl1 | 0.86 (4) | 2.24 (5) | 3.082 (3) | 165 (4) |
| O6−H6O…Cl1 i | 0.86 (5) | 2.25 (5) | 3.102 (3) | 171 (5) |
| C8−H8A…Cg11 ii | 0.97 | 2.78 | 3.722 (4) | 163 |
| C10−H10A…Cg10 | 0.97 | 2.94 | 3.825 (4) | 152 |
| C19−H19A…Cg9 | 0.96 | 2.74 | 3.616 (5) | 152 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Es-Sounni, B.; Haily, E.M.; Nakkabi, A.; Bakhouch, M.; Bejaoui, L.; Kaya, S.; El Yazidi, M.; Bih, L.; Saadi, M.; El Ammari, L.; et al. New Bi-Nuclear Nickel(II) Complex-Based Salen Schiff Base: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Electrical Investigations. Chemistry 2022, 4, 1193-1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040080
Es-Sounni B, Haily EM, Nakkabi A, Bakhouch M, Bejaoui L, Kaya S, El Yazidi M, Bih L, Saadi M, El Ammari L, et al. New Bi-Nuclear Nickel(II) Complex-Based Salen Schiff Base: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Electrical Investigations. Chemistry. 2022; 4(4):1193-1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleEs-Sounni, Bouchra, El Mehdi Haily, Asmae Nakkabi, Mohamed Bakhouch, Linda Bejaoui, Savaş Kaya, Mohamed El Yazidi, Lahcen Bih, Mohamed Saadi, Lahcen El Ammari, and et al. 2022. "New Bi-Nuclear Nickel(II) Complex-Based Salen Schiff Base: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Electrical Investigations" Chemistry 4, no. 4: 1193-1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040080
APA StyleEs-Sounni, B., Haily, E. M., Nakkabi, A., Bakhouch, M., Bejaoui, L., Kaya, S., El Yazidi, M., Bih, L., Saadi, M., El Ammari, L., & Fahim, M. (2022). New Bi-Nuclear Nickel(II) Complex-Based Salen Schiff Base: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Electrical Investigations. Chemistry, 4(4), 1193-1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040080