Towards High Efficacy of Pd-Au/C Catalyst for Tetrachloromethane Hydrodechlorination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Supported Pd, Au, and Pd–Au Catalysts
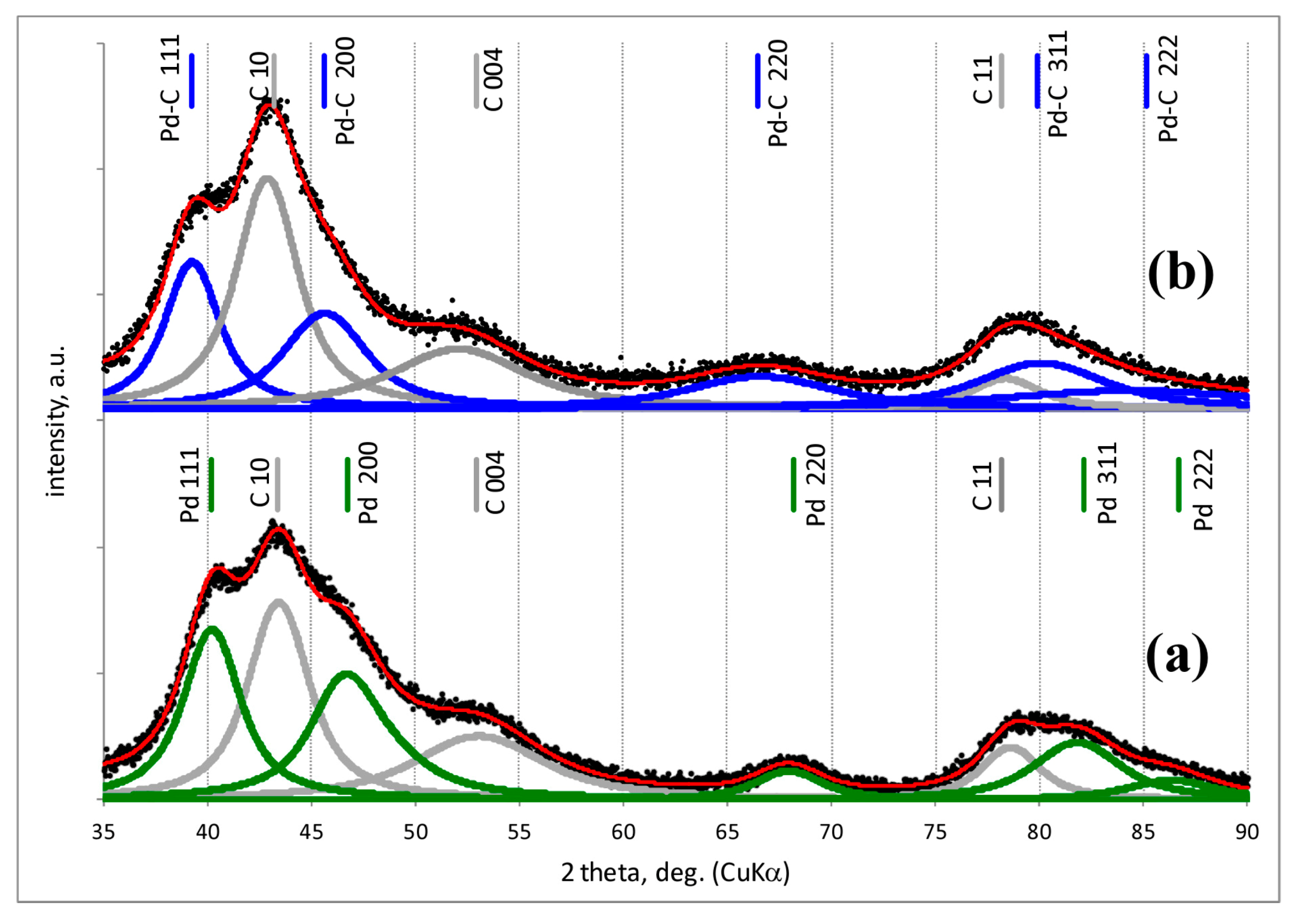
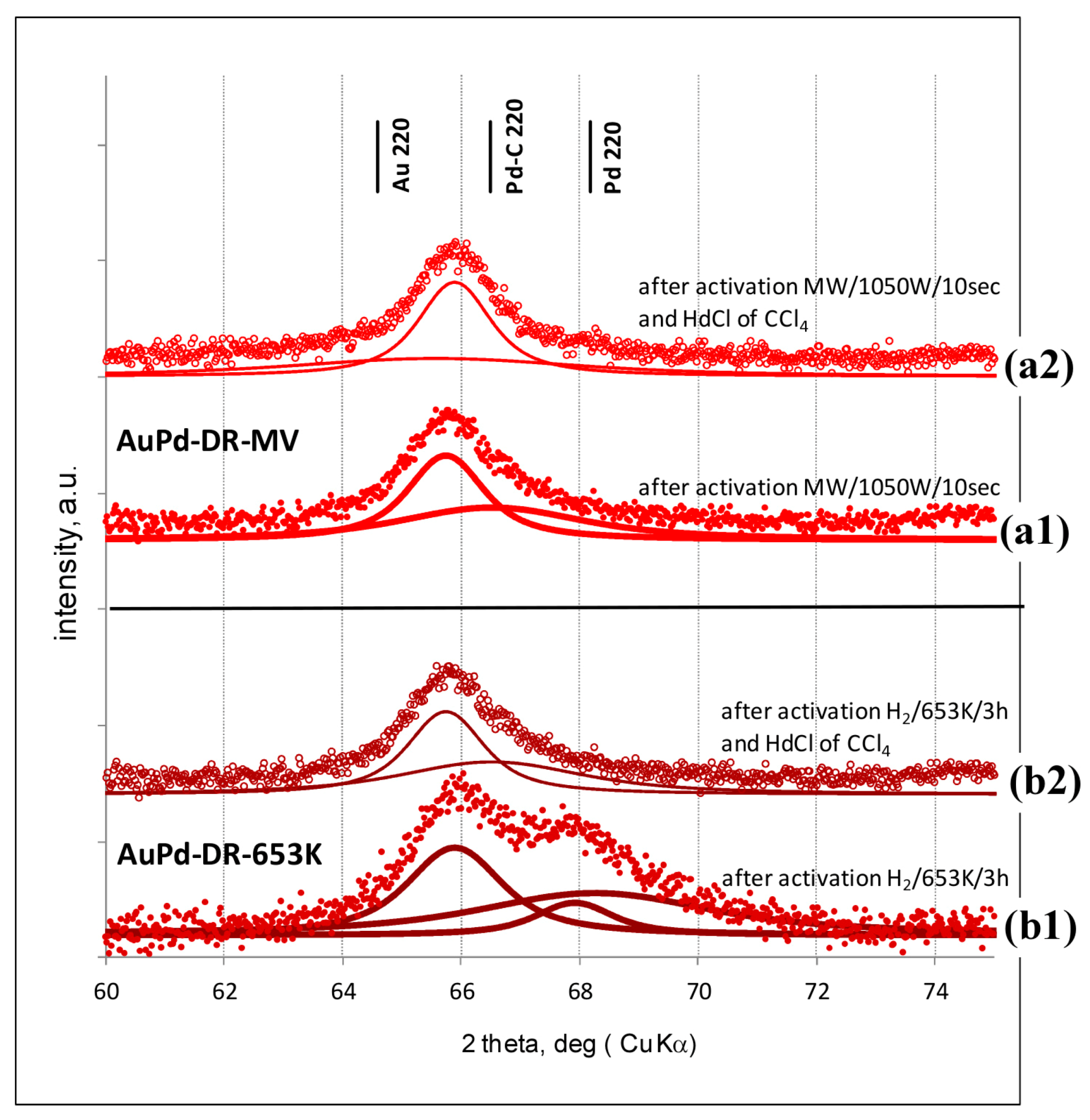
2.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3. CO-Chemisorption
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
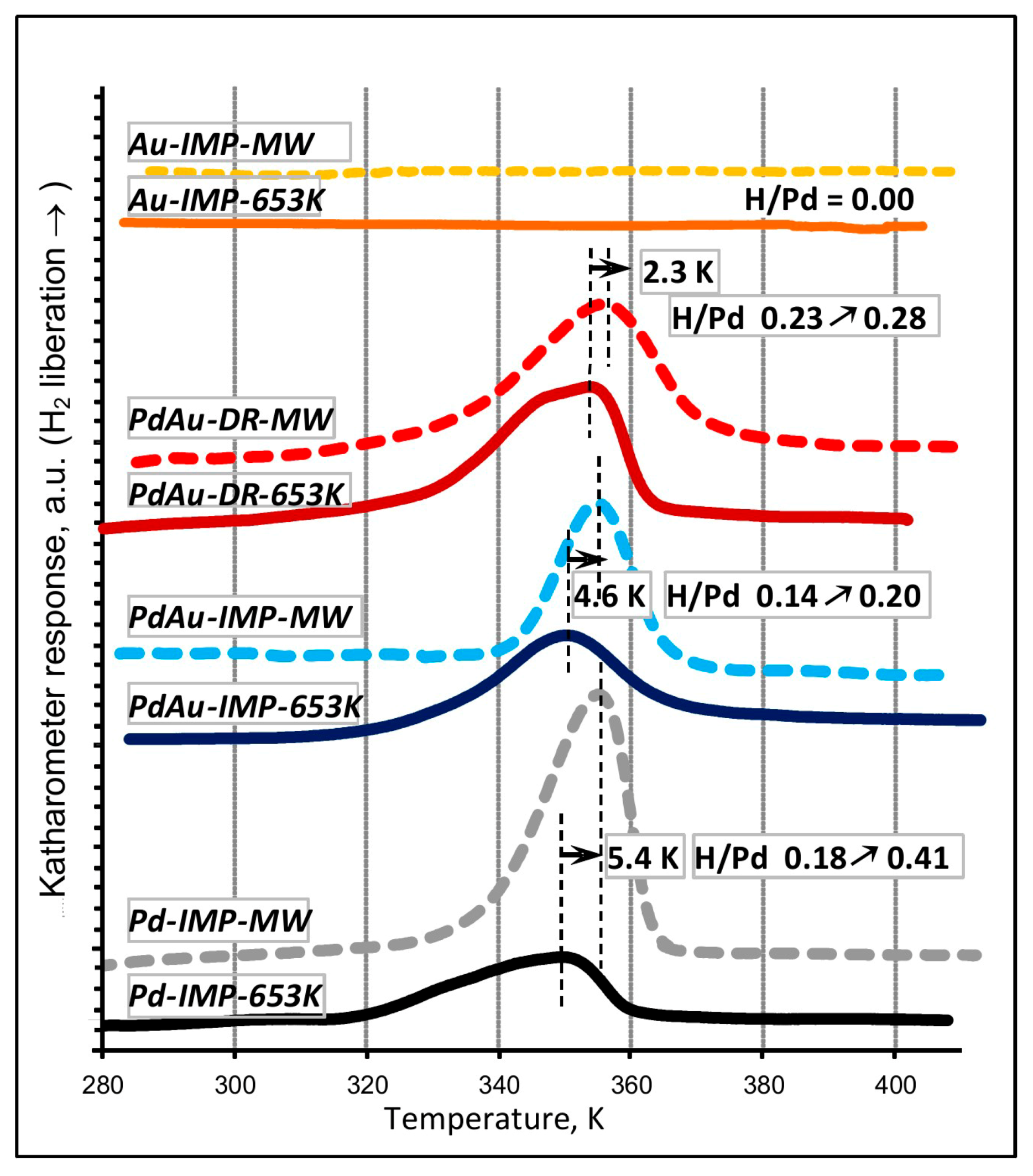
2.5. Temperature-Programmed β-Hydride Phase Decomposition (TPHD)
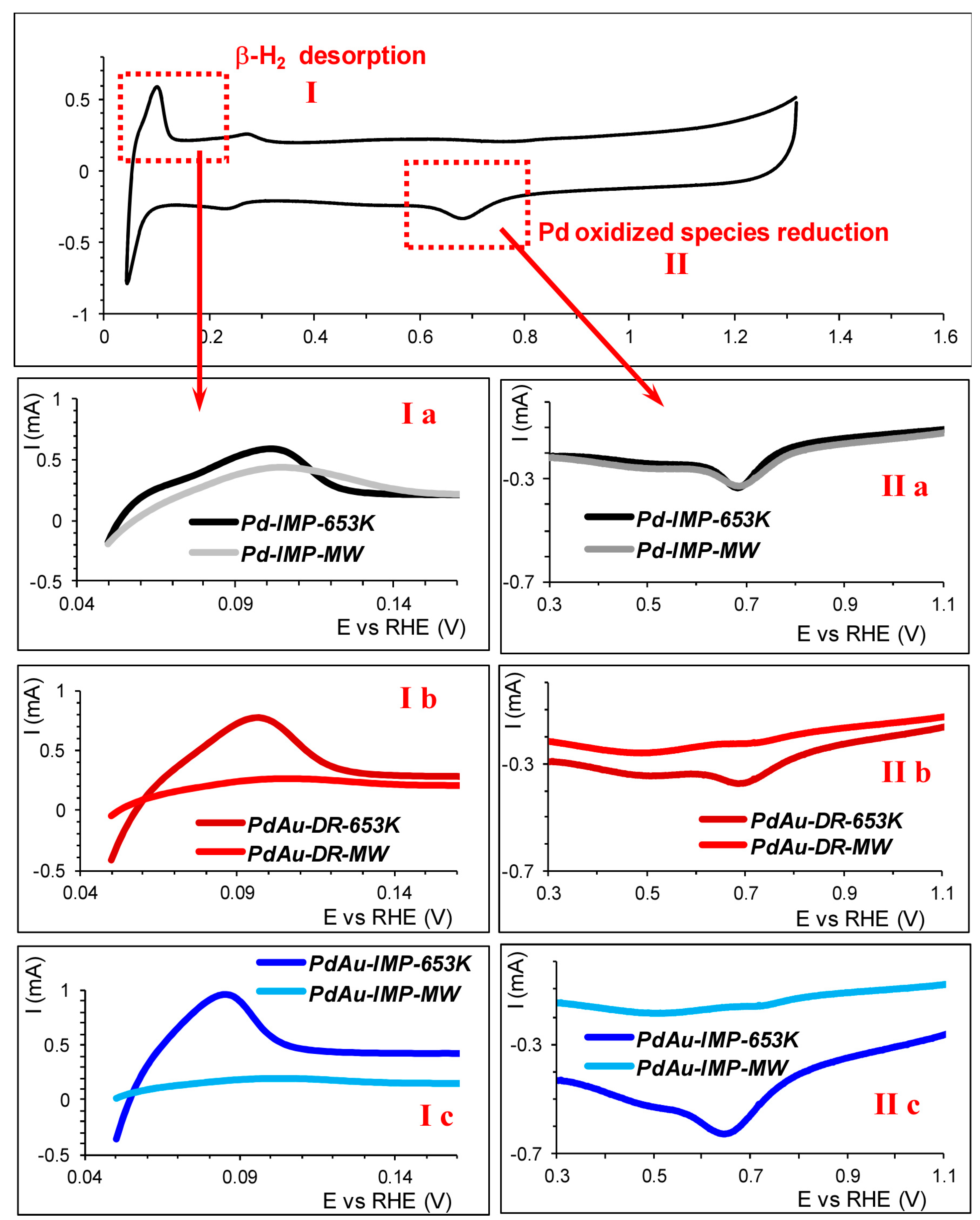
2.6. The Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
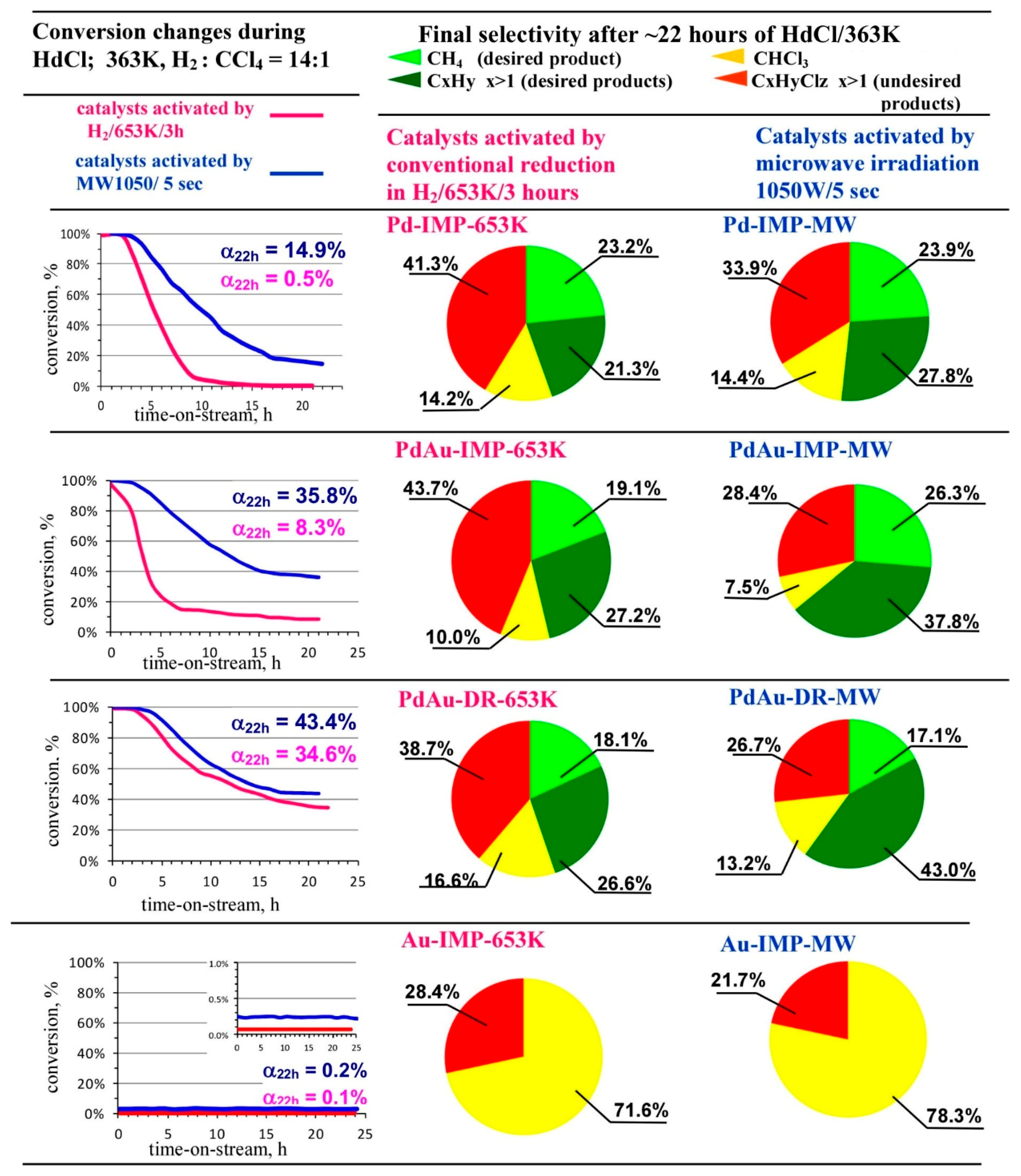
2.7. Catalytic Tests—Hydrodechlorination of Tetrachloromethane (HdCl of CCl4)
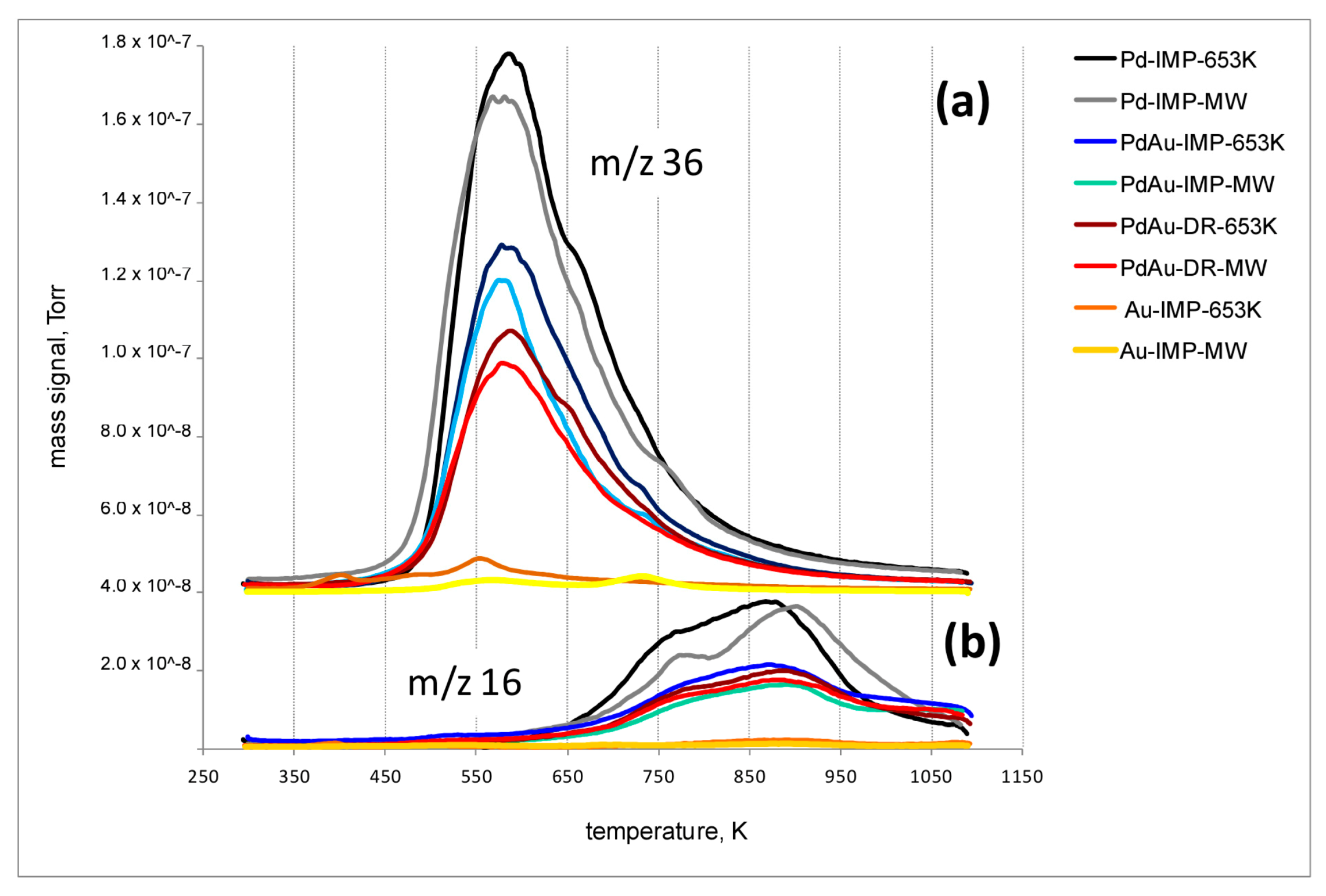
2.8. Temperature-Programmed Hydrogenation of Catalysts after HdCl of CCl4 (TPH-MS)
3. Results and Discussion
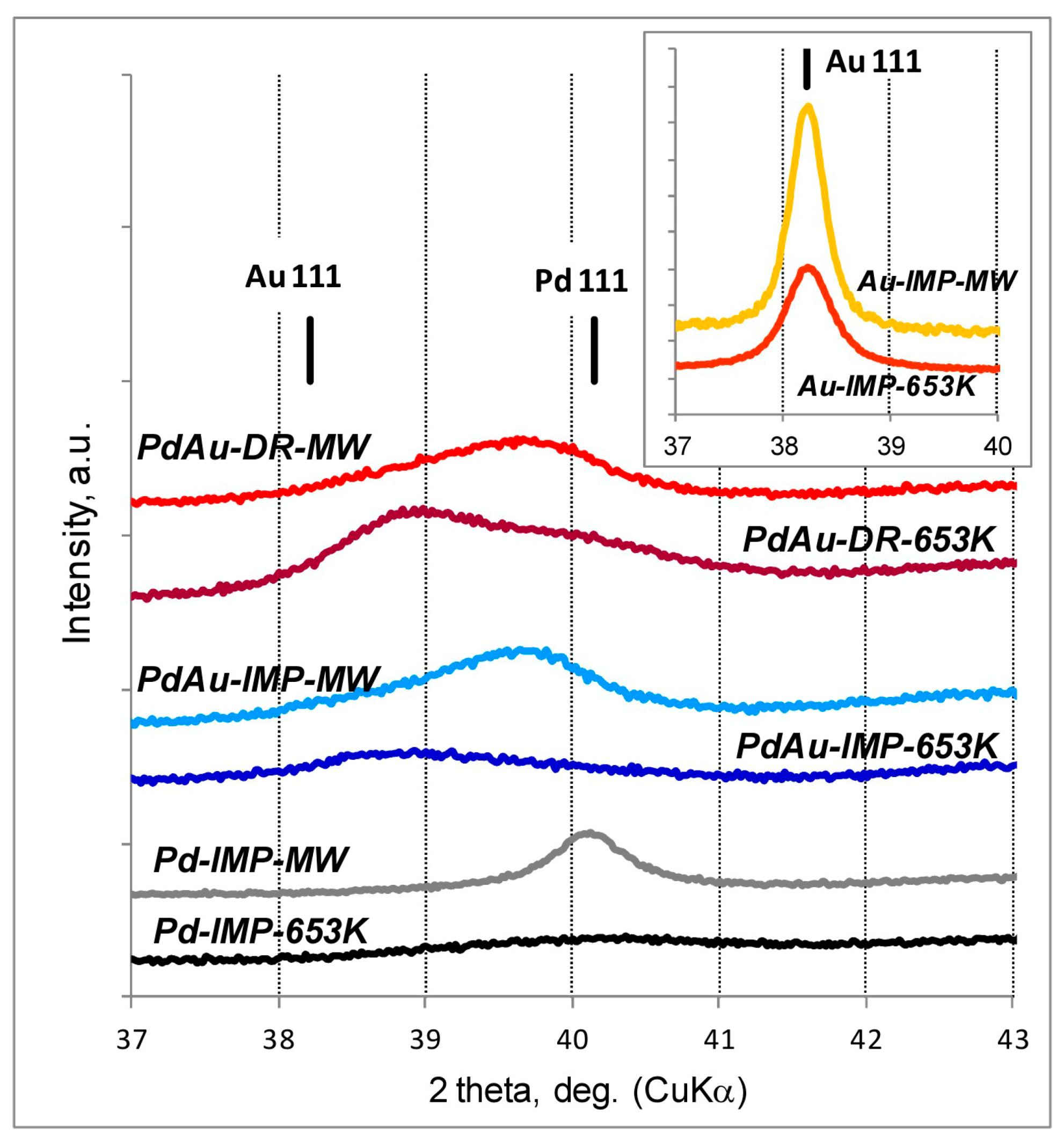
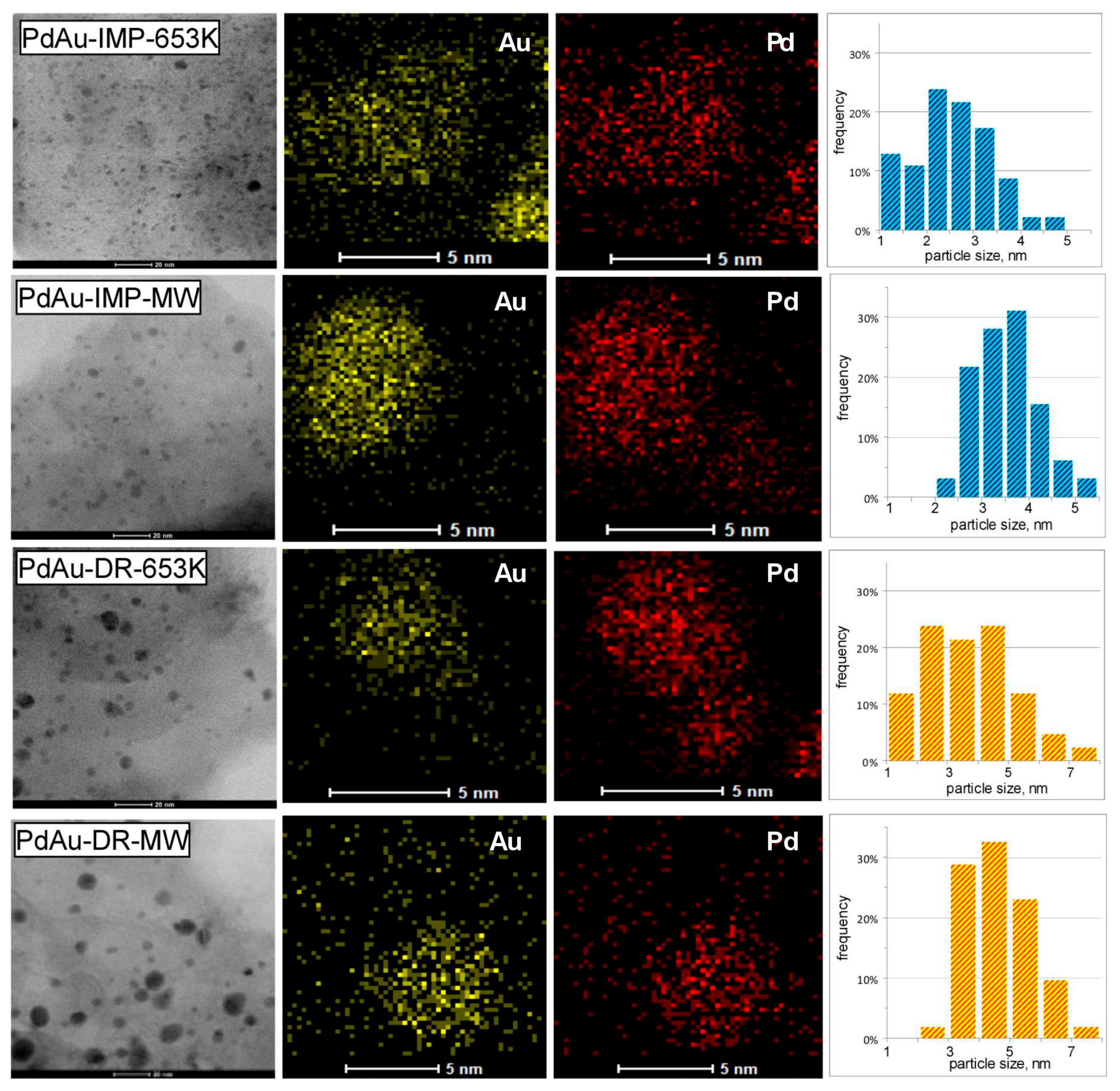
3.1. Characterisation of Pd–Au/Sibunit Catalysts
| Catalyst Designation 1,2 | Catalyst Composition 3 and Activation Method | CO Chemisorption 4 | TPHD 5 | XRD Analysis (Metal Dominant Phases) | TEM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE 6 | d, nm | H/Pd 6 | Tmax, K | ||||
| Pd-IMP-653 K | 2.64 wt% Pd/Csib reduction in H2/653 K/3 h | 0.40 | 2.8 | 0.18 | 349.0 | Pd 2.2 nm | not tested |
| Pd-IMP-MW | 2.64 wt% Pd/Csib MW irradiation/1050 W/5 s | 0.21 | 5.3 | 0.41 | 354.4 | Pd 4.4 nm | |
| PdAu-IMP-653 K | 2.64 wt% Pd85Au15/Csib reduction in H2/653 K/3 h | 0.23 | 5.2 | 0.14 | 350.2 | Pd 2.3 nm Pd42Au58 4.0 nm Pd13Au87 3.4 nm | davg = 2.6 nm 1.3–4.9 nm |
| PdAu-IMP-MW | 2.64 wt% Pd85Au15/Csib MW irradiation/1050 W/5 s | 0.12 | 9.5 | 0.20 | 354.8 | Pd72Au28 6.3 nm Pd25Au75 3.7 nm | davg = 3.9 nm 2.1–5.3 nm |
| PdAu-DR-653 K | 2.64 wt% Pd85Au15/Csib reduction in H2/653 K/3 h | 0.13 | 8.7 | 0.23 | 353.6 | Pd 4.1 nm Pd37Au63 6.4 nm Pd89Au11 5.8 nm | davg = 3.8 nm 1.8–7.9 nm |
| PdAu-DR-MW | 2.64 wt% Pd85Au15/Csib MW irradiation/1050 W/5 s | 0.09 | 12.3 | 0.28 | 355.9 | Pd77Au23 6.2 nm Pd26Au74 6.6 nm | davg = 5.1 nm 2.2–7.0 nm |
| Au-IMP-653 K | 2.64 wt% Au/Csib reduction in H2/653 K/3 h | no CO chemisorption | no H2 release | Au 15.0 nm | not tested | ||
| Au-IMP-MW | 2.64 wt% Au/Csib MW irradiation/1050 W/5 s | as above | as above | Au 17.0 nm | |||
3.2. Catalytic Behaviour of Pd–Au/Sibunit in CCl4 Hydrodechlorination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, L.; Montszka, S.A.; Miller, B.R.; Andrews, A.E.; Miller, J.B.; Lehman, S.J.; Sweeney, C.; Miller, S.M.; Thoning, K.; Siso, C.; et al. Continued emissions of carbon tetrachloride from the United States nearly two decades after its phaseout for dispersive uses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2880–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluid, M.R.; Kartashov, L.M.; Treger Yu, A. Understanding Hydrodechlorination of Chloromethanes. Past and Future of the Technology. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, P.J.; Dunse, B.L.; Manning, A.J.; Walsh, S.; Wang, R.H.J.; Krummel, P.B.; Steele, L.P.; Porter, L.W.; Allison, C.; O’Doherty, S.; et al. Australian carbon tetrachloride emissions in a global context. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, M.; Elbir, T.; Dumanoglu, Y.; Sofuoglu, S.C. Halogenated volatile organic compounds in chlorine-bleach-containing household products and implications for their use. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Kaszkur, Z.; Łomot, D.; Rawski, M.; Karpiński, Z. Effect of gold on catalytic behavior of palladium catalysts in hydrodechlorination of tetrachloromethane. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 162, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T. Fate of Chloromethanes in the Atmospheric Environment: Implications for Human Health, Ozone Formation and Depletion, and Global warming Impacts. Toxics 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafaïdeen, T.; Baranton, S.; Coutanceau, C. Pd-shaped nanoparticles modified by gold ad-atoms: Effects on surface structure and activity toward glucose electrooxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 243, 641–656. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Yoshida, H. Photocatalytic Ullmann coupling of aryl halides by a novel blended catalyst consisting of a TiO2 photocatalyst and an Al2O3 supported Pd-Au bimetallic catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 6196–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongli, S.; Kangjuan, Y.; Cuihua, A.; Zihui, X. Design of a difunctional Zn-Ti LDHs supported PdAu catalyst for selective hydrogenation of phenylacetylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.W.; Chiang, M.H.; Lee, C.L. Tuning saw-toothed morphology on Pd/Pt nanocubes as oxygen reduction catalysts by co-surfactant synthesis method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 467, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilburna, M.S.; Epling, W.S. SO2 adsorption and desorption characteristics of bimetallic Pd-Pt catalysts: Pd:Pt ratio dependency. Catal. Today 2019, 320, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironenko, R.M.; Belskaya, O.B.; Lavrenov, A.V.; Likholobov, V.A. Palladium–Ruthenium Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural to Cyclopentanol. Kinet. Catal. 2018, 59, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloag, L.; Benedetti, T.M.; Cheong, S.; Marjo, C.E.; Gooding, J.J.; Tilley, R.D. Cubic-Core Hexagonal-Branch Mechanism To Synthesize Bimetallic Branched and Faceted Pd–Ru Nanoparticles for Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12760–12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asset, T.; Serov, A.; Padilla, M.; Roy, A.J.; Matanovic, I.; Chatenet, M.; Maillard, F.; Atanassov, P. Design of Pd-Pb Catalysts for Glycerol and Ethylene Glycol Electrooxidation in Alkaline Medium. Electrocatalysis 2018, 9, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coq, B.; Hub, S.; Figueras, F.; Tournigant, D. Conversion under hydrogen of dichlorodifluoromethane over bimetallic palladium catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1993, 101, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yan, B.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Li, S.M.; Wang, C.Q.; Du, Y.K.; Yang, P. Sub-5nm monodispersed PdCu nanosphere with enhanced catalytic activity towards ethylene glycol electrooxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 261, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Moran, C.; Nie, X.; Gong, Y.; Guo, X.; Walton, K.S.; Song, C. CO2 hydrogenation to methanol on PdCu bimetallic catalysts with lower metal loadings. Catalysis Comm. 2019, 118, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coq, B.; Cognion, J.M.; Figuéras, F.; Tournigant, D. Conversion under hydrogen of dichlorodifluoromethane over supported palladium catalysts. J. Catal. 1993, 141, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersma, A.; van de Sandt, E.J.A.X.; den Hollander, M.A.; van Bekkum, H.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Comparison of the Performance of Activated Carbon-Supported Noble Metal Catalysts in the Hydrogenolysis of CCl2F2. J. Catal. 1998, 177, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkee, M.; Wiersma, A.; van de Sandt, E.J.A.X.; van Bekkum, H.; Moulijn, J.A. Development of a palladium on activated carbon for a conceptual process in the selective hydrogenolysis of CCl2F2 (CFC-12) into CH2F2 (HFC-32). Catal. Today 2000, 55, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.L.; Schmal, M.G.; Aranda, D.A.; Somorjai, G.A. Hydrodechlorination of dichlorodifluoromethane over palladium model catalysts and a comparison with the hydrodechlorination of 1,1-dichlorotetrafluoroethane. J. Catal. 2000, 192, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, Z.; d’Itri, J.L. Hydrodechlorination of 1,1-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane on Supported Palladium Catalysts. A Static-Circulation Reactor Study. Catal. Lett. 2001, 77, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.C.; Jiang, X.Z.; Song, W.H.; Bai, Z.Q.; Fang, X.Q. Hydrodechlorination of CFC-12 over Novel Supported Palladium Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2001, 76, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Goodman, D.W. Pd-Au bimetallic catalysts: Understanding alloy effects from planar models and (supported) nanoparticle. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8009–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, M.O.; Hughes, J.B.; Wong, M.S. Designing Pd-on-Au bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for trichloroethene hydrodechlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzer, L.A.; Song, H.J.; Fang, Y.-L.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, N.; Wuc, T.; Arslan, I.; Miller, J.T.; Wong, M.S. Hydrodechlorination catalysis of Pd-on-Au nanoparticles varies with particle size. J. Catal. 2013, 298, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Pielaszek, J.; Semikolenov, V.A.; Karpiński, Z. Pd-Au/sibunit carbon catalysts: Characterization and catalytic activity in hydrodechlorination of dichlorodifluoromethane (CFC-12). J. Catal. 2002, 209, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Watanabe, T.; Okumura, M.; Haruta, M.; Toshima, N. Catalytically highly active top gold atom on palladium nanocluster. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Mou, C.Y.; Zhang, T. Understanding the synergistic effects of gold bimetallic catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 308, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Kumar, D.; Yi, C.W.; Goodman, D.W. The Promotional Effect of Gold in Catalysis by Palladium-Gold. Science 2005, 310, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, A.; Juszczyk, W.; Pielaszek, J.; Bonarowska, M.; Wojciechowska, M.; Karpiński, Z. Magnesium fluoride as a catalytic support in hydrodechlorination of CCl2F2 (CFC-12). Chem. Commun. 1999, 8, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, A.; Juszczyk, W.; Pielaszek, J.; Bonarowska, M.; Wojciechowska, M.; Karpiński, Z. Hydrodechlorination of CCl2F2 (CFC-12) by carbon- and MgF2-supported palladium and palladium-gold catalysts. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 130, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bonarowska, M.; Rarog-Pilecka, W.; Karpiński, Z. The use of active carbon pretreated at 2173 K as a support for palladium catalysts for hydrodechlorination reactions. Catal. Today 2011, 169, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Barba, D.; Cortese, M.; Martino, M.; Renda, S.; Meloni, E. Microwaves and Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Reviewon Selected Catalytic Processes. Catalysts 2020, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, F.J.; Smart, L.E.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Lingaiah, N.; Kanta Rao, P. Microwave heating during catalyst preparation: Influence on the hydrodechlorination activity of alumina-supported palladium–iron bimetallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2000, 204, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahsepar, M.; Kim, H. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of bimetallic PtRu alloy nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 649, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Matus, K.; Śrębowata, A.; Sá, J. Application of silica-supported Ir and Ir-M (M = Pt, Pd, Au) catalysts for low-temperature hydrodechlorination of tetrachloromethane. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, A.R.M.; Antonetti, C.; Venezia, A.M.; Giambastiani, G. An easy microwave-assisted process for the synthesis of nanostructured palladium catalysts and their use in the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyd. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 386, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenelonov, V.B.; Likholobov, V.A.; Derevyankin, A.Y.; Mel’gunov, M.S. Porous carbon materials prepared from C1–C3 hydrocarbons. Catal. Today 1998, 42, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Pielaszek, J.; Juszczyk, W.; Karpiński, Z. Characterization of Pd–Au/SiO2 Catalysts by X-ray Diffraction, Temperature-Programmed Hydride Decomposition, and Catalytic Probes. J. Catal. 2000, 195, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheaud, C.; Guerin, M.; Marecot, P.; Geron, C.; Barbier, J. Preparation and characterization of Pd-Pt/Al2O3 catalysts. J. Chim. Phys. 1996, 93, 1394–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyr, M. Fityk: A general-purpose peak fitting program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2010, 43, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Karpiński, Z. Application of the β-PdH decomposition for characterization of supported palladium catalysts. Pol. J. Chem. 2008, 82, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Juszczyk, W.; Malinowski, A.; Karpiński, Z. Hydrodechlorination of CCl2F2 (CFC-12) over γ-alumina supported palladium catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 1998, 166, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, S.; Poppa, H.; Boudart, M. Disproportionation of CO on small particles of silica-supported palladium. J. Catal. 1985, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnankutty, N.; Vannice, M.A. The Effect of Pretreatment on Pd/C Catalysts: I. Adsorption and Absorption Properties. J. Catal. 1995, 155, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrath, M.; Kuretzky, T.; Boehm, H.P.; Okhlopkov, L.B.; Lisitsyn, A.S.; Likholobov, V.A. Palladium catalysts on activated carbon supports: Influence of reduction temperature, origin of the support and pretreatments of the carbon surface. Carbon 2000, 38, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Zieliński, M.; Matus, K.; Sá, J.; Śrębowata, A. Influence of microwave activation on the catalytic behavior of Pd-Au/C catalysts employed in the hydrodechlorination of tetrachloromethane. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2018, 124, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Martra, G. New gold catalysts for liquid phase oxidation. Gold Bull. 1999, 32, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Dai, S. Development of novel supported gold catalysts: A materials perspective. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Ilieva, L.; Ivanov, I.; Zanellab, R.; Sobczak, J.W.; Lisowski, W.; Kaszkur, Z.; Andreeva, D. Influence of the preparation method and dopants nature on the WGS activity of gold catalysts supported on doped by transition metals ceria. Appl. Catal. Environ. 2013, 136–137, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, G.; Davoglio, R.A.; Hartl, F.W.; Marco, J.F.; Pereira, E.C.; Biaggio, S.R.; Varela, H.; Cuesta, A. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Pt-Au Nanoparticles with Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity for the Oxidation of Formic Acid. Electrochim Acta 2017, 224, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudart, M.; Hwang, H.S. Solubility of hydrogen in small particles of palladium. J. Catal. 1975, 39, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbatt, P.H.; Sermon, P.A.; Luengo, M.A.M. Rate of Hydrogen Sorption by Well-Dispersed Palladium. Z. Phys. Chem. 1986, 147, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, D.; Flanagan, T.B. Thermodynamics of Hydrogen in fcc Pd–Au Alloys. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 6117–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemecki, S.B.; Michel, J.B.; Jones, G.A. Hydride formation as a measure of alloying in bimetallic systems containing palladium. React. Solids 1986, 2, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumełda, T.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Lalik, E.; Kosydar, R.; Duraczyńska, D.; Gurgul, J. Carbon-supported Pd100-X AuX alloy nanoparticles for the electrocatalytic oxidation of formic acid: Influence of metal particles composition on activity enhancement. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 221, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumełda, T.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Kosydar, R.; Gurgul, J.; Duraczyńska, D.; Gurgul, J. Synthesis of carbon-supported bimetallic palladium-iridium catalysts by microemulsion; characterization and electrocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 392–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankiang, S.; Chiwata, M.; Baranton, S.; Uchida, H.; Coutanceau, C. Oxygen reduction reaction at binary and ternary nanocatalysts based on Pt, Pd and Au. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewski, M.; Czerwiński, A. Selected electrochemical properties of Pd-Au alloys: Hydrogen absorption and surface oxidation. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2008, 12, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Simoes, M.; Baranton, S.; Coutanceau, C. Electrooxidation of sodium Borohydride at Pd, Au and PdAu Carbon-Supported nanocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 13369–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, R. Enhanced formic aid electro-oxidation on PdIr nanoparticles prepared by ethylene glycol-assisted NaBH4 reduction process. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 7008–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewski, M.; Żurowski, A.; Grdeń, M.; Czerwiński, A. Correlations between hydrogen electrosorption properties and composition of Pd-noble metal alloys. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewski, M.; Kuśmierczyk, K.; Kotowski, J.; Siwek, H.; Czerwinski, A. Electrosorption of hydrogen into palladium-gold alloys. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2003, 7, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ha, S.; Scudiero, L. Temperature dependence study of Pd–Cu supported bimetallic films by photoelectron spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 105, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.A.I.; Woods, R. Determination of the surface composition of smooth noble metal alloys by cyclic voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1972, 36, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A.; Gómez-Quero, S.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Shen, W.Q. Alumina-supported Ni-Au: Surface synergistic effects in catalytic hydrodechlorination. ChemCatChem 2009, 1, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Santo, V.; Dossi, C.; Recchia, S.; Colavita, P.E.; Vlaic, G.; Psaro, R. Carbon tetrachloride hydrodechlorination with organometallics-based platinum and palladium catalysts on MgO. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 182–183, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubina, E.V.; Lokteva, E.S.; Lunin, V.V.; Turakulova, A.O.; Simagina, V.I.; Stoyanova, I.V. Modification of the supported palladium catalysts surface during hydrodechlorination of carbon tetrachloride. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 241, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öcal, M.; Maciejewski, M.; Baiker, A. Conversion of CCl2F2 (CFC-12) in the presence and absence of H2 on sol–gel derived Pd/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 1999, 21, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, A.; Alonso, C.; Medina, F.; Garreta, J.L.; Sueiras, J.E.; Cesteras, Y.; Salagre, P.; Tichit, D.; Coq, B. KMg1−xPdxF3 with Perovskite-Like Structures as Precursors for the Catalytic Hydroconversion of CCl2F2 and CHClF2. Catal. Lett. 2001, 77, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarowska, M.; Malinowski, A.; Juszczyk, W.; Karpiński, Z.; Karpiński, Z. Hydrodechlorination of CCl2F2 (CFC-12) over silica-supported palladium–gold catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 30, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachurski, J.; Frąckiewicz, A. A new phase in the Pd-C system formed during the catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene. J. Less-Common Met. 1985, 108, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemecki, S.B.; Jones, G.A.; Swartzfager, D.G.; Harlow, R.L.; Faber, J. Formation of interstitial palladium-carbon phase by interaction of ethylene, acetylene, and carbon monoxide with palladium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 4547–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszkur, Z.; Stachurski, J.; Pielaszek, J. X-ray diffraction study of the palladium-carbon system. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1986, 47, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, 3rd ed.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.N.; Rioux, M.M.; Barbosa, L.A.M.; Ribeiro, F.H. Kinetic and Theoretical Study of the Hydrodechlorination of CH4−xClx (x = 1–4) Compounds on Palladium. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16615–16624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method of Preparation and Activation Method | Prepared from Aqueous Solutions [48] | Prepared from Acetone Solutions (Current Work) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant Metal Phases | Size of Crystallites, nm | Dominant Metal Phases | Size of Crystallites, nm | |
| Coimpregnation H2, 653 K, 3 h | Pd Pd30Au70 Au | 4.5 2.0 35.0 | Pd Pd42Au58 Pd13Au87 | 2.3 4.0 3.4 |
| Coimpregnation MW, 1050 W, 5 s | Pd Pd30Au70 Au | 3.6 9.0 29.0 | Pd72Au28 Pd25Au75 | 6.3 3.7 |
| direct redox method H2, 653 K, 3 h | Pd28Au72 Pd83Au17 Pd94Au6 | 6.4 3.0 13.7 | Pd Pd37Au63 Pd89Au11 | 4.1 6.4 5.8 |
| direct redox method MW, 1050 W, 5 s | Pd37Au63 Pd75Au25 Pd | 7.3 3.4 11.0 | Pd77Au23 Pd26Au74 | 6.2 6.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonarowska, M.; Kaszkur, Z.; Matus, K.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Szumełda, T.; Kubas, A. Towards High Efficacy of Pd-Au/C Catalyst for Tetrachloromethane Hydrodechlorination. Chemistry 2021, 3, 338-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010025
Bonarowska M, Kaszkur Z, Matus K, Drelinkiewicz A, Szumełda T, Kubas A. Towards High Efficacy of Pd-Au/C Catalyst for Tetrachloromethane Hydrodechlorination. Chemistry. 2021; 3(1):338-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonarowska, Magdalena, Zbigniew Kaszkur, Krzysztof Matus, Alicja Drelinkiewicz, Tomasz Szumełda, and Adam Kubas. 2021. "Towards High Efficacy of Pd-Au/C Catalyst for Tetrachloromethane Hydrodechlorination" Chemistry 3, no. 1: 338-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010025
APA StyleBonarowska, M., Kaszkur, Z., Matus, K., Drelinkiewicz, A., Szumełda, T., & Kubas, A. (2021). Towards High Efficacy of Pd-Au/C Catalyst for Tetrachloromethane Hydrodechlorination. Chemistry, 3(1), 338-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3010025