Hydroquinone-Based Anion Receptors for Redox-Switchable Chloride Binding
Abstract
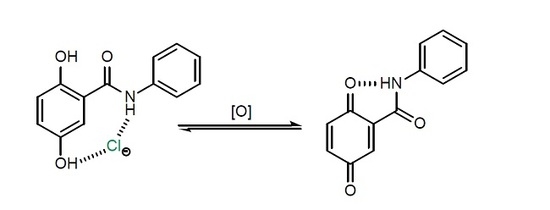
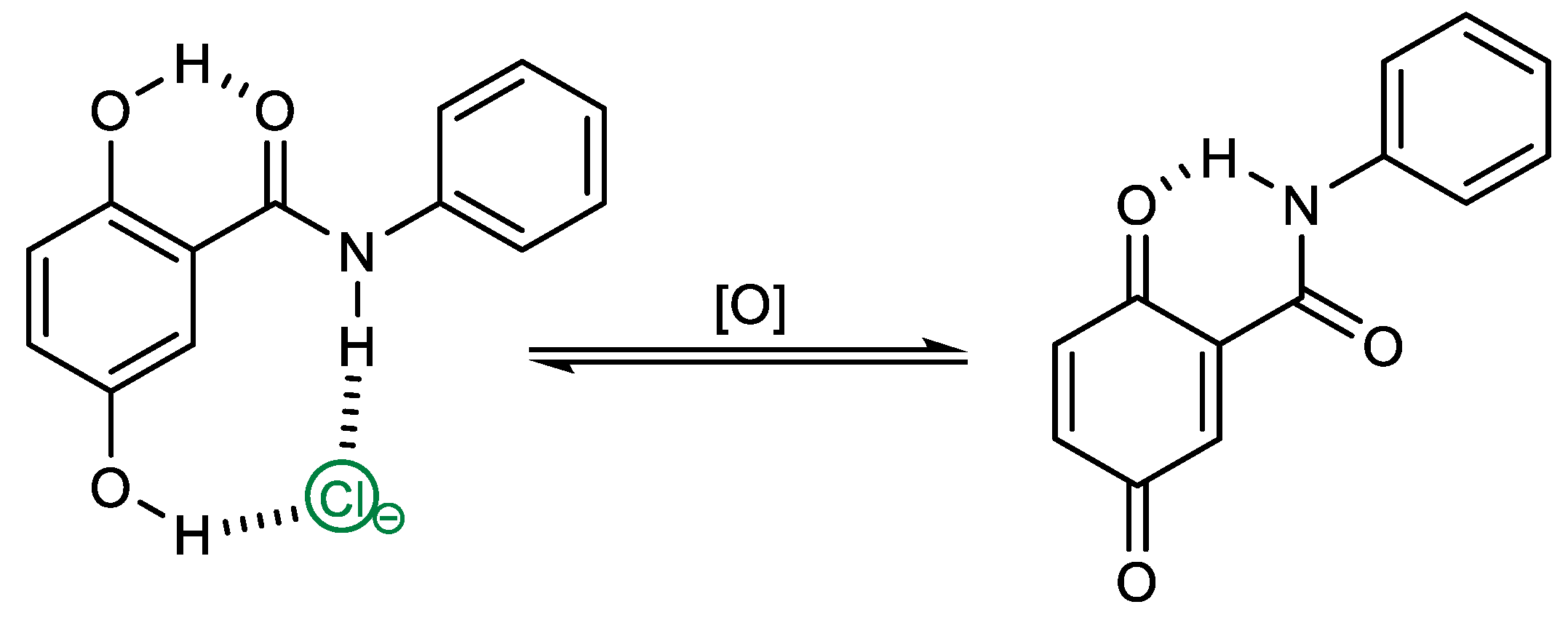
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
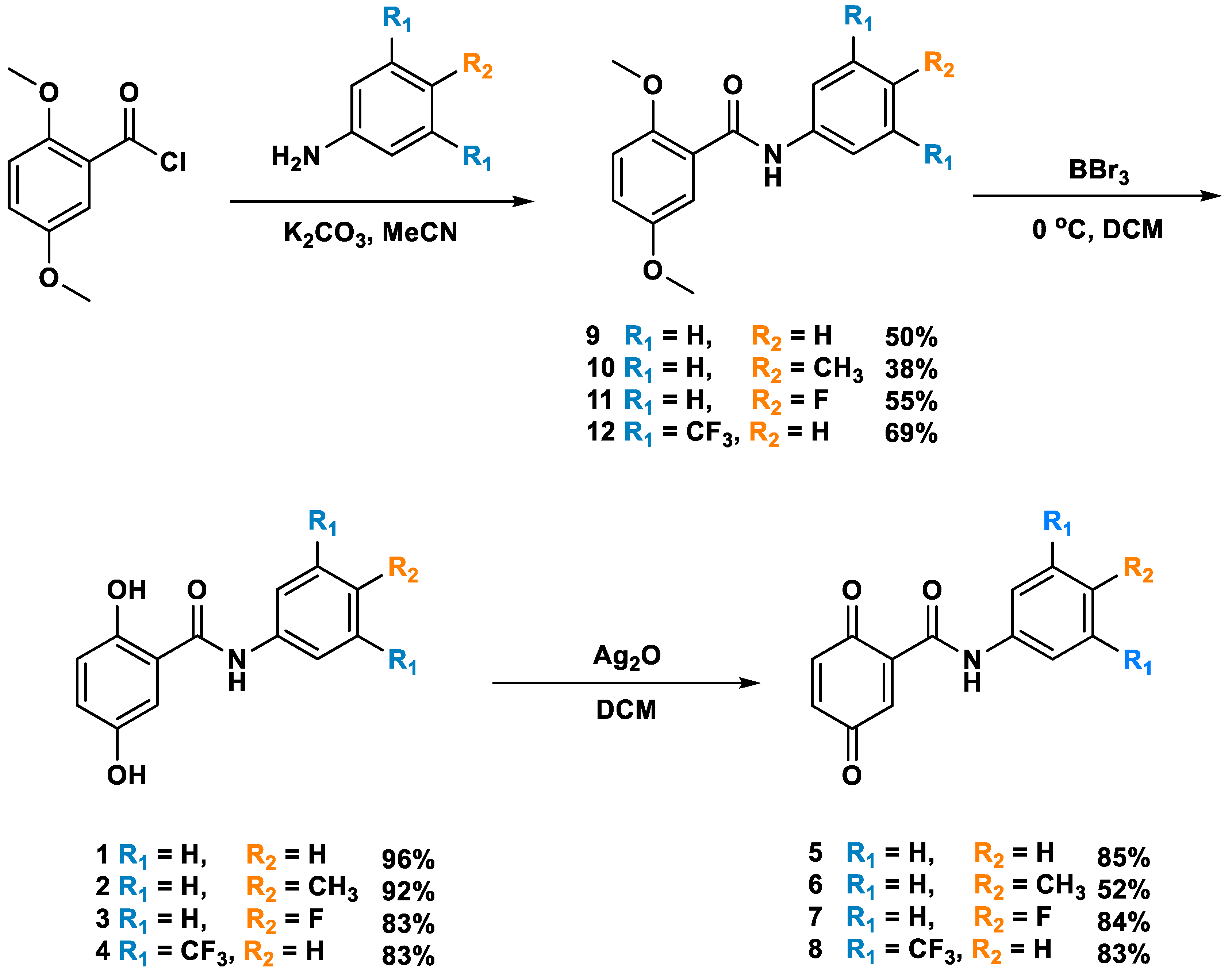
2.1. Synthesis
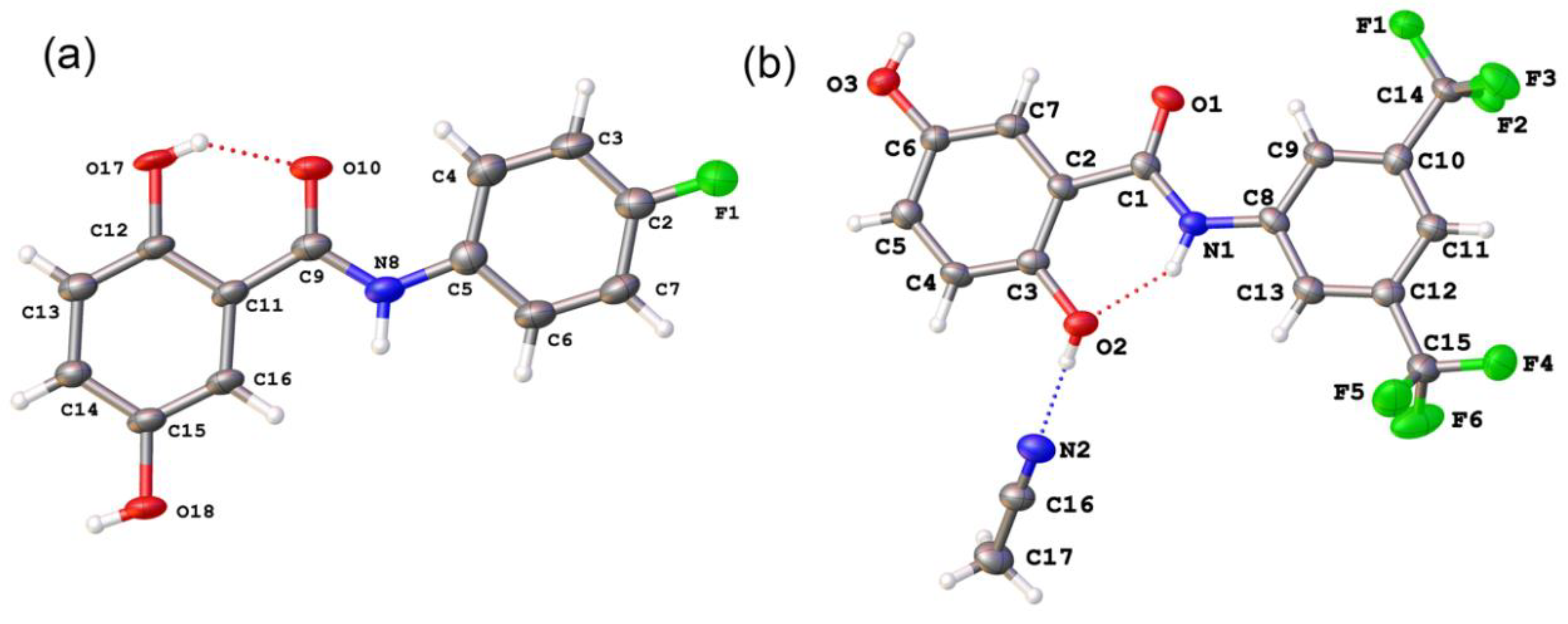
2.2. Anion Binding Studies
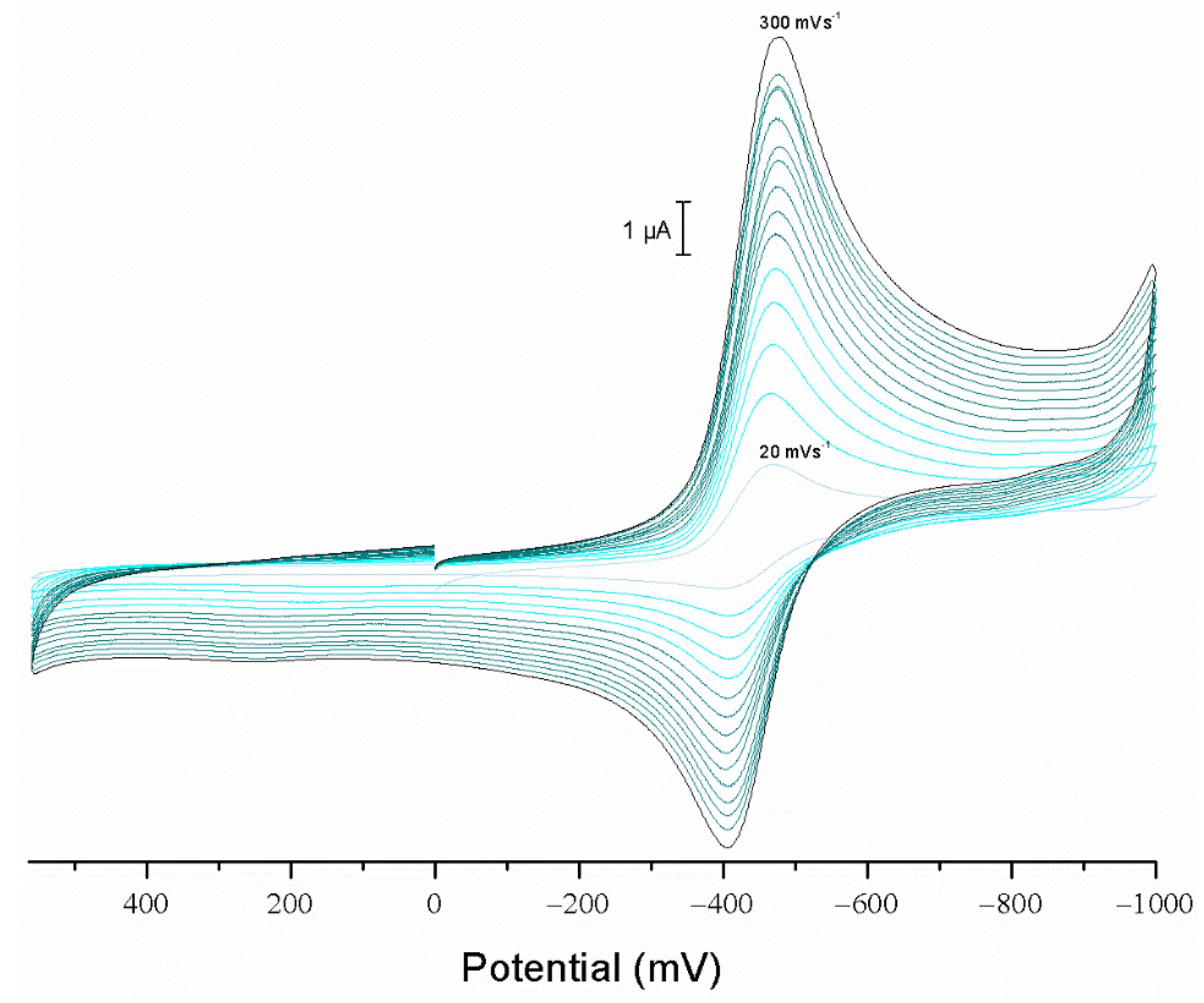
2.3. Electrochemical Studies
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balzani, V.; Credi, A.; Raymo, F.M.; Stoddart, J.F. Artificial molecular machines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3348–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roke, D.; Wezenberg, S.J.; Feringa, B.L. Molecular rotary motors: Unidirectional motion around double bonds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9423–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altieri, A.; Gatti, F.G.; Kay, E.R.; Leigh, D.A.; Martel, D.; Paolucci, F.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Wong, J.K.Y. Electrochemically switchable hydrogen-bonded molecular shuttles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8644–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, C.J.; Stoddart, J.F. Molecular machines muscle up. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamino, T.; Imada, K.; Namba, K. Molecular motors of the bacterial flagella. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008, 18, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, J.L. Variations on a molecular switch: Transport and sensory signalling by archaeal rhodopsins. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Campbell, E.B.; Hsiung, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of a Eukaryotic CLC transporter defines an intermediate state in the transport cycle. Science 2010, 330, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feringa, B.L.; Browne, W.R. Molecular Switches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Boelke, J.; Hecht, S. Designing molecular photoswitches for soft materials applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 1900404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, S.; Lee, A.T.L.; Leigh, D.A.; Markevicius, A.; Solà, J. Pick-up, transport and release of a molecular cargo using a small-molecule robotic arm. Nat. Chem. 2015, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kistemaker, J.C.M.; Štacko, P.; Roke, D.; Wolters, A.T.; Heideman, G.H.; Chang, M.C.; van der Meulen, P.; Visser, J.; Otten, E.; Feringa, B.L. Third-generation light-driven symmetric molecular motors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9650–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittel, M.; De, S.; Pramanik, S. Reversible ON/OFF nanoswitch for organocatalysis: Mimicking the locking and unlocking operation of CaMKII. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3832–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayev, E.A.; Kolesnikov, G.V.; Sessler, J.L. Molecular recognition of pertechnetate and perrhenate. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1572–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, B.A.; Bonnesen, P.V.; Custelcean, R.; Delmau, L.H.; Hay, B.P. Strategies for using host-guest chemistry in the extractive separations of ionic guests. Kem. Ind. 2005, 54, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, B.A.; Custelcean, R.; Hay, B.P.; Sessler, J.L.; Bowman-James, K.; Day, V.W.; Kang, S.O. A case for molecular recognition in nuclear separations: Sulfate separation from nuclear wastes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 3473–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busschaert, N.; Caltagirone, C.; Van Rossom, W.; Gale, P.A. Applications of supramolecular anion recognition. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8038–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Garrido, S.E.; Caltagirone, C.; Light, M.E.; Gale, P.A. Acridinone-based anion receptors and sensors. Chem. Commun. 2007, 14, 1450–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barendt, T.A.; Rašović, I.; Lebedeva, M.A.; Farrow, G.A.; Auty, A.; Chekulaev, D.; Sazanovich, I.V.; Weinstein, J.A.; Porfyrakis, K.; Beer, P.D. Anion-mediated photophysical behavior in a C60 fullerene [3] rotaxane shuttle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1924–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.; Naidu, V.R.; Liu, X.; Lah, M.S.; Jeong, K.S. A foldamer-based chiroptical molecular switch that displays complete inversion of the helical sense upon anion binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13938–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, I.M.; Hamilton, A.D. Anion-dependent switching: Dynamically controlling the conformation of hydrogen-bonded Diphenylacetylenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4597–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, E.N.W.; Busschaert, N.; Wu, X.; Berry, S.N.; Ho, J.; Light, M.E.; Czech, D.D.; Klein, H.A.; Kitchen, J.A.; Gale, P.A. pH-regulated nonelectrogenic anion transport by Phenylthiosemicarbazones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8301–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busschaert, N.; Elmes, R.B.P.; Czech, D.D.; Wu, X.; Kirby, I.L.; Peck, E.M.; Hendzel, K.D.; Shaw, S.K.; Chan, B.; Smith, B.D.; et al. Thiosquaramides: pH switchable anion transporters. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 3617–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, P.V.; Davis, J.T.; Light, M.E.; Gale, P.A.; Iglesias-Sánchez, J.C.; Prados, P.; Quesada, R. Conformational control of transmembrane Cl-transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1886–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasti, J.; Furukawa, H.; Gonzales, E.B.; Gouaux, E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 Å resolution and low pH. Nature 2007, 449, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessler, J.L.; Eller, L.R.; Cho, W.S.; Nicolaou, S.; Aguilar, A.; Lee, J.T.; Lynch, V.M.; Magda, D.J. Synthesis, Anion-binding properties, and in vitro anticancer activity of prodigiosin analogues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5989–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.K.; Kim, S.K.; Share, A.; Lynch, V.M.; Park, J.; Namkung, W.; Van Rossom, W.; Busschaert, N.; Gale, P.A.; Sessler, J.L.; et al. Synthetic ion transporters can induce apoptosis by facilitating chloride anion transport into cells. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Flood, A.H. Photoresponsive receptors for binding and releasing anions. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatković, M.; Feringa, B.L.; Wezenberg, S.J. Dynamic inversion of stereoselective phosphate binding to a bisurea receptor controlled by light and heat. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, S.H. Amide-and urea-functionalized dithienylethene: Synthesis, photochromism, and binding with halide anions. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6022–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimasaki, T.; Kato, S.; Ideta, K.; Goto, K.; Shinmyozu, T. Synthesis and structural and photoswitchable properties of novel chiral host molecules: Axis chiral 2, 2’-dihydroxy-1, 1’-binaphthyl-appended stiff-stilbene1. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohl, H.; Jordan, W.; Youngman, R.J. Quinones in biology: Functions in electron transfer and oxygen activation. Adv. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1986, 2, 211–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, T.J.; Hanzlik, R.P.; Cohen, G.M.; Ross, D.; Graham, D.G. Quinone chemistry and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 112, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüssel, C.; Janicke, W. Heterogeneous electron exchange of quinones in aprotic solvents: Part III. The second reduction step of p-benzoquinone and its dependence on the supporting electrolyte. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1986, 199, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggins, B.R.; Chambers, J.Q. Proton effects in the electrochemistry of the quinone hydroquinone system in aprotic solvents. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1970, 117, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.M.; Dryer, D.A.; Jacobson, D.D.; Foss, M.G.; Flynn, N.T. pH dependent redox couple: An illustration of the Nernst equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstanley, K.J.; Sayer, A.M.; Smith, D.K. Anion binding by catechols—an NMR, optical and electrochemical study. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachter, V. Chemical Synthesis of Small Molecule Libraries Around the p-Benzoquinone Scaffold. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis, L.; Granick, S. Molecular compounds of the quinhydrone type in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.A.; Zamorano, C.; González, M.F.; Prina, E.; Fournet, A. Studies on quinones. Part 39: Synthesis and leishmanicidal activity of acylchloroquinones and hydroquinones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 4153–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindfit. Available online: http://app.supramolecular.org/bindfit/ (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Thordarson, P. Determining association constants from titration experiments in supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, K.S.; Hester, D.K.; Golbeck, J.H. A relationship between amide hydrogen bond strength and quinone reduction potential: Implications for photosystem I and bacterial reaction center quinone function. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4891–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faulkner, L.R.; Bard, A.J. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
| Hydroquinone Receptor | K21a | K11a | α b | Quinone Receptor | Kaa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 c | 679.5 | 112.96 | 24.06 | 5 c | 12.57 |
| 5 d | 11.2 | ||||
| 2 c | 665.6 | 191.36 | 13.91 | 6 d | 11.39 |
| 3 c | 517.76 | 30.76 | 67.33 | 7 d | 19.64 |
| 4 c | 336.49 | 54.44 | 24.72 | 8 d | 67.72 |
| Compound | E1/2 (mV) a |
|---|---|
| 5 | −544 |
| 6 | −552 |
| 7 | −539 |
| 8 | −449 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McNaughton, D.A.; Fu, X.; Lewis, W.; D’Alessandro, D.M.; Gale, P.A. Hydroquinone-Based Anion Receptors for Redox-Switchable Chloride Binding. Chemistry 2019, 1, 80-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry1010007
McNaughton DA, Fu X, Lewis W, D’Alessandro DM, Gale PA. Hydroquinone-Based Anion Receptors for Redox-Switchable Chloride Binding. Chemistry. 2019; 1(1):80-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry1010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcNaughton, Daniel A., Xiaochen Fu, William Lewis, Deanna M. D’Alessandro, and Philip A. Gale. 2019. "Hydroquinone-Based Anion Receptors for Redox-Switchable Chloride Binding" Chemistry 1, no. 1: 80-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry1010007
APA StyleMcNaughton, D. A., Fu, X., Lewis, W., D’Alessandro, D. M., & Gale, P. A. (2019). Hydroquinone-Based Anion Receptors for Redox-Switchable Chloride Binding. Chemistry, 1(1), 80-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry1010007