Abstract
Obesity is a chronic disorder associated with serious comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Conventional pharmacological treatments often suffer from limited efficacy, poor selectivity, and undesirable side effects, highlighting the need for more effective alternatives. Nanomedicine offers a promising approach by overcoming these limitations through targeted drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic precision. This review examines key nanotechnological strategies in obesity management, including targeting white adipose tissue (WAT) and the vascular marker prohibitin, promoting WAT browning, and utilizing photothermal therapy and magnetic hyperthermia as nanotheranostic tools. We discuss major nanomedicine platforms—such as liposomes, nanoemulsions, and polymeric nanoparticles—alongside emerging applications in gene nanotherapy and herbal formulations. Potential toxicity concerns are also addressed. In summary, nanomedicine holds substantial potential to revolutionize obesity treatment through targeted, effective, and multifunctional therapeutic strategies.
1. Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), overweight and obesity are conditions characterized by abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. Overweight is typically defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 25 or higher, while obesity is defined as a BMI of 30 or above. Currently, approximately 40% of the global population is affected by overweight, and this number continues to rise steadily [1]. Obesity has a negative effect on almost all body functions and poses an important public health risk [2]. Since 1975, there has been a clear difference in obesity rates between adult males and females (≥18 years), with women exhibiting a greater susceptibility for obesity [3]. The aetiology of obesity is multifaceted and involves a combination of factors. Behavioural and genetic factors are considered to be the primary contributors to obesity [4]. Sustained energy imbalance, caused by excessive caloric intake and insufficient energy expenditure, results in overweight and obesity, which, in turn, trigger the development of serious health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), certain types of cancers, and metabolic disorders [3].
1.1. Obesity and the Impaired Role of Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue is traditionally classified into two types: white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT). WAT plays a major role in energy storage, regulating hormone communication, and maintaining insulin sensitivity. It constitutes the major volume of adipose tissue of mammals, including the human species. In contrast, BAT consumes energy to produce heat, which helps regulate the body temperature, participates in the oxidation of body fat, and activates thermogenesis after food intake [5]. This highlights the critical function of this type of adipose tissue [6]. Adipose tissues have two pathways for accumulating lipids: (a) under regular feeding conditions, the adipocytes uptake dietary lipids in the form of free fatty acids (FFAs), which are liberated from circulating triglycerides (TAGs) through the action of lipoprotein lipase (LPL); and (b) adipocytes undergo de novo lipogenesis (DNL), occurring within the adipocytes themselves [5]. De novo lipogenesis can be observed during both fasting and feeding time, although it is particularly active following the consumption of a carbohydrate-rich meal. The extra glucose is oxidized, leading to the accumulation of acetyl-CoA, which serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The enzymes acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) catalyse the conversion of acetyl-CoA into palmitate through DNL, which can subsequently produce several other types of fatty acids [7].
WAT secretes adipokines and cytokines into the bloodstream. Adipokines play a crucial role in multiple metabolic and physiological signalling pathways, including the regulation of insulin signalling, as well as glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation [8]. Obesity activates a phenotypic transformation of WAT that is characterized by the presence of inflamed and impaired function adipocytes, accompanied by the infiltration of immune cells into the stromal vascular fraction of WAT. These inflamed adipocytes release pro-inflammatory cytokines, which subsequently disrupt the regular functioning of adipose tissue and influence the functioning of organs in other parts of the body [9]. Obesity causes the expansion of WAT through the recruitment and differentiation of adipose precursor cells. Disturbances in precursor cell commitment and the process of subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) adipogenesis are linked to metabolic conditions that arise from obesity. Additionally, visceral adipose tissue (VAT) comprises a higher percentage of larger adipocytes and demonstrates higher metabolic and lipolytic activity compared to SAT. Increased VAT leads to the accumulation of more ectopic fat, which then releases free fatty acids into the portal circulation, impacting both the liver and peripheral tissues. Numerous studies have provided important evidence that the excessive accumulation of lipids in ectopic tissues is associated with the induction of local inflammation [10,11]. Furthermore, lipid accumulation leads to cellular stress and activates pathways such as JNK and NF-κB. The activation of these inflammatory signalling pathways is associated with the phosphorylation of proteins and numerous transcriptional changes. As a result, there is increased production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as TNF-α, IL-6, leptin, and resistin. Moreover, they also stimulate the synthesis of chemokines, such as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) [12].
1.2. Complications of Obesity
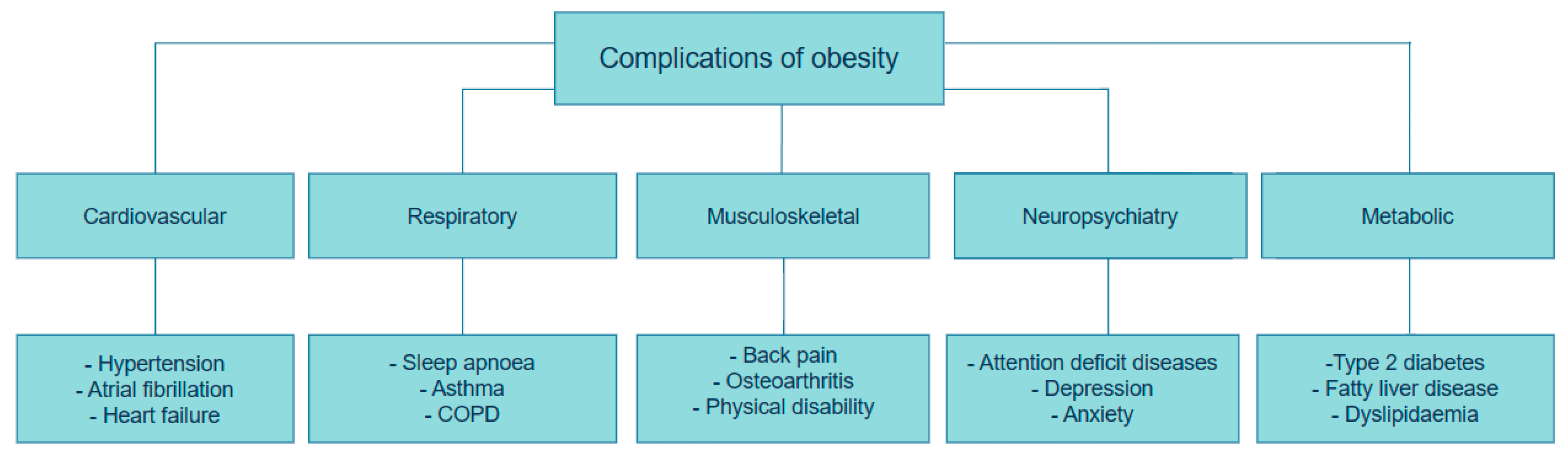
Adipose tissue is considered as both an active endocrine and immune organ, playing a critical role in maintaining optimal metabolic health [13]. As mentioned above, overabundant body fat serves a crucial role in the generation of adipocytokines and inflammatory substances that disrupt glucose and fat metabolism, ultimately diminishing adipogenesis. This, in turn, leads to adipocyte hypertrophy, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), fatty liver disease, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, as described in Figure 1 [14,15].
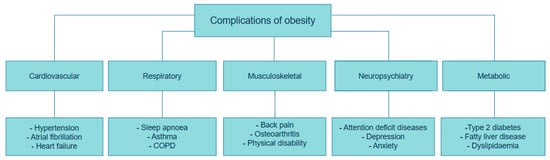
Figure 1.
Complications of Obesity. This figure was adapted and modified from Müller et al. [13]. The figure was created using draw.io diagram software (V28.0.7).
Obesity causes significant changes in lipid metabolism. Those with excess weight often demonstrate heightened serum cholesterol levels, including increases in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, as well as elevated triglycerides and apolipoprotein B. On the other hand, the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol are typically decreased in these individuals [16]. Furthermore, obesity is associated with T2DM through the accumulation of visceral fat in the liver and pancreas. Excessive triglycerides in the liver are carried by lipoproteins to different tissues that involve the beta-cells present in the pancreas. This causes a decline in the differentiation of pancreatic beta-cells, ultimately resulting in the development of diabetes [17]. Obesity can lead to a distinct type of cardiomyopathy due to persistent volume pressure. This typically involves the expansion of the left ventricle, elevated stress on the walls of the ventricle, and hypertrophy of the heart muscle [16].
Genetic factors and obesogenic environments, such as poverty and societies with insufficient resources, including limited access to healthy food, safe recreational spaces, and healthcare, contribute to a higher incidence of obesity in children and adolescents, especially if at least one parent suffers from obesity. Adolescents with obesity are predisposed to 32% greater risk of having or developing depression compared to adolescents of a healthy weight. Unfortunately, many commonly prescribed anti-depressant and antipsychotic drugs have weight gain side effects, which could entrap patients with obesity into a cycle of worsening mental health and medicine-related weight gain [18].
Obesity and Cancer
The rising cancer rates related to obesity have been the focus of several epidemiological studies in the past 40 years. At least 13 distinct cancer types—including breast, colorectal, endometrial, oesophageal, gallbladder, gastric, ovarian, pancreatic, liver, multiple myeloma, and thyroid—are associated with excess body weight. While the precise mechanisms linking obesity to elevated cancer risk are not yet fully understood, numerous possible pathways and mechanisms have been proposed. Disruptions to sex hormone levels induced by body weight are considered to constitute a key mechanism underlying the heightened susceptibility to breast and ovarian carcinogenesis [14]. Moreover, the endocrine function of adipose tissue, including the secretion of adipokines, such as leptin and adiponectin, has been recognized for its link to cancer development. Leptin is a possible contributor to cancer associated with obesity. It activates cancer development by stimulating cellular process pathways such as PI3K, MAPK, and STAT. Increased body fat is related to higher levels of inflammatory markers, such as IL-2, IL-10, IL-8, TNF-α, and prostaglandin E2 [15]. NF-κB activation may provide a pathway for inflammation to promote cancer progression [19]. Studies have shown that individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of cancer mortality, possibly related to hyperinsulinemia and increased levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1). High levels of IGF-1 are linked to a greater risk of various cancers. Insulin and IGF-1 trigger the Akt/PI3K/mTOR pathway to enhance cell growth and proliferation. This pathway also plays a crucial role in signalling factors associated with obesity and is considered the most commonly mutated pathway in human cancers [20].
1.3. The Cost of Obesity for Health Services
The growing rates of obesity in recent years constitute serious risks to public health that create a significant challenge for healthcare systems [21]. Research has demonstrated that a higher body mass index and greater obesity classification are linked to rising healthcare costs related to obesity. Tsai et al. calculated that the direct medical costs for obesity per person were over six times greater than those for individuals classified as overweight, with the total cost assessed to be around USD 114 billion [22]. Another study conducted in 2004, in a group of individuals aged 54 to 69 years, documented that individuals with a BMI exceeding 40 kg/m2 had costs that were double those of adults with normal weight [23]. For example, in 2009, the estimated direct and indirect costs of overweight and obesity were EUR 1.13 billion for the Republic of Ireland, while Northern Ireland faced estimated expenses of EUR 510 million. These conditions were estimated to represent 2.7% of total health costs in the Republic of Ireland and 2.8% in Northern Ireland. These results align with data reported across several European countries over the previous decade. The key factors influencing direct costs associated with medications and hospital care are type 2 diabetes, colon cancer, cardiovascular diseases, strokes, and gallbladder disorders [24]. A recent systematic review conducted in 2024 by Nagi et al. showed that obesity and its complications might consume up to 17.8% of overall healthcare costs [25]. On the other hand, in Saudi Arabia, the direct medical costs related to overweight and obesity are estimated at USD 3.8 billion each year, accounting for 4.3% of the overall healthcare expenditures. Additionally, the growing prevalence of overweight and obesity are likely to result in a 12.7% rise in annual healthcare spending in Saudi Arabia from 2020 to 2050 [26].
Researchers indicate that the reported costs are likely underestimated for several reasons, as noted by Nagi et al.: (a) while the WHO classifies obesity as a complex chronic disease that needs medical intervention, it is often inadequately diagnosed and treated, which may result in an underestimation of its effects; and (b) in the majority of studies, the costs were evaluated using the national health insurance claims database, which reflected only the medical costs covered by the system. This approach excluded direct non-medical costs, additional co-payments, and out-of-pocket payments for services not covered by insurance [25].
1.4. Current Treatments
Most guidelines in Europe and North America base the routine screening and diagnosis of obesity on body mass index (BMI) [27]. The primary goal of obesity treatment is the reduction of excessive body weight. According to international guidelines, adults are advised to aim for a weight loss of 5–10% of their initial weight over 6 to 12 months, typically achieved through a daily energy deficit of at least 500 calories [27,28]. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and physical activity, remain the first-line approach. When these are insufficient, pharmacotherapy and bariatric surgery may be considered. Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for individuals with BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 or ≥35 kg/m2, with obesity-related comorbidities. It has been shown to provide sustained weight loss and improve conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [29]. Candidates for bariatric procedures must undergo a thorough evaluation to assess surgical risks, including cardiovascular and pulmonary assessments [30].
In the United States, the distribution of primary bariatric surgeries has changed in the past few years. According to estimates of the approximately 252,000 procedures that were performed, 61% are now sleeve gastrectomies, and 17% are Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) procedures [31]. In the case of sleeve gastrectomies, the procedure entails the resection of approximately 80% of the stomach, without connection or anastomosis between the gastrointestinal tract and the small intestine. On the other hand, the RYGB procedure consists of multiple steps, such as balloon sizing of the upper stomach, using a hook cautery to create a tract for lesser curvature dissection, and finalizing the procedure by dividing the stomach with the aid of an endoscopic stapler [32].
In the United States and the European Union, there are currently five medications approved for the management of chronic weight in adults: orlistat, phentermine/topiramate extended-release, bupropion, naltrexone, along with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists liraglutide and semaglutide [13]. Due to its powerful incretin properties, GLP-1 is a promising therapeutic option for obesity and diabetes. GLP-1 is produced and released after eating, and it can successfully lower blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon release. Additionally, GLP-1 has the ability to slow gastric emptying and suppress appetite [33].
Nevertheless, the efficacy of anti-obesity medications in promoting weight loss is often undermined by the presence of negative side effects. As a result, many of these drugs were subsequently discontinued from the market [3]. Pharmaceutical drugs are specifically prescribed for overweight persons who do not show significant improvement through lifestyle modifications within the initial 6 months. Furthermore, they should be experiencing at least one of the health conditions associated with obesity [34]. Progress in obesity research has reached a stage where rational, targeted drug discovery for obesity treatment is both feasible and actively underway. These medications include ibutramine, fenfluramine, and dexfenfluramine, and the cause of failure is mostly related to adverse cardiovascular side effects. Other medications include an elevated risk of suicidal behaviour (rimonabant) or an increased susceptibility to drug dependence and abuse (methamphetamine) [3,35]. The disadvantages of current weight-loss treatments are summarised in Table 1.

Table 1.
Review of weight-loss treatments for obesity.
More recently, the challenge has been to achieve long-term pharmacotherapy to normalize body weight [13]. To overcome these challenges, nanomedicine offers promising approaches to enhance drug encapsulation, thus preserving its integrity from degradation, improve the dissolution and solubility properties, and enable targeted drug delivery to precise sites. Progress and innovations in nanomedicine have resulted in the development of methods that enhance compatibility, extend drug half-life, and decrease toxicity and adverse effects by manipulating the characteristics of nanoparticles [4].
Despite promising preclinical results, the clinical translation of nanomedicine for obesity treatment remains limited. Key barriers include insufficient long-term safety data, challenges in targeting adipose tissue selectively, and regulatory and manufacturing complexities. These gaps highlight the need for a more critical synthesis of existing nanomedicine strategies and their translational potential.
2. Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine presents a potentially promising approach for the creation of advanced drugs to combat obesity successfully. One key benefit of nanosized materials is their ability to efficiently encapsulate therapeutic and diagnostic agents, thus improving their stability in the presence of the body natural defence systems [50]. The field of nanomedicine is growing rapidly, motivated by the introduction of innovative delivery techniques, novel treatment approaches, the approval of new medications, as well as limitations of current treatments in clinical settings [51]. Nanotechnology deals with objects at the nanometre scale. Nanotechnology is expected to undergo expansion across various levels, including materials, instruments, and entire systems [52]. The formation of nanoparticles (NPs) is not limited to recent scientific research or synthetic materials; natural nanoparticles consist of both organic components, such as proteins, polysaccharides, and viruses, and inorganic compounds, including iron oxyhydroxides, aluminosilicates, and metals, which are also used in various applications [53]. Nanotechnology has led to more remarkable advancements in the field of cancer inhibition compared to obesity, due to various reasons, such as the limited development in discovering biomarkers for obesity and diabetes, the complex and diverse pathways, and the demand for the precise control of drug release. Additionally, there are difficulties related to targeting specific locations within the body. However, recent studies have highlighted the promising potential of nanoparticles for precise and efficient targeting of specific sites within the body [50].
2.1. Effective Strategies in the Fight Against Obesity Through Nanomedicine
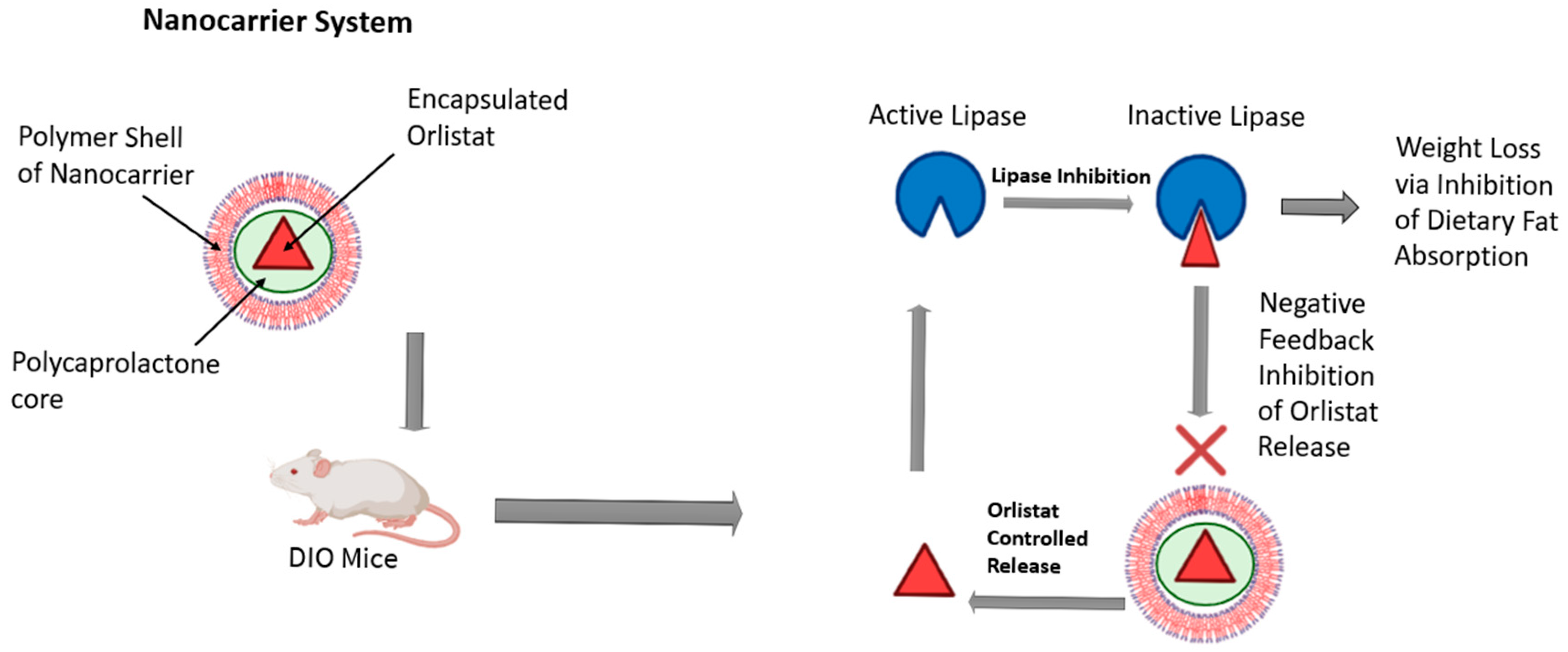
The growing interest in nanotechnology for obesity management has captured the attention of numerous research groups. Recent advancements in this field offer significant benefits, including the potential to minimize side effects and enhance the efficacy of conventional therapies [54]. NPs have shown promise in targeting angiogenic vessels in adipose tissues, and peptide-coated NPs have been designed to specifically target white adipose tissue and the adipose vascular marker prohibitin [50,55]. Hossen et al. showed that the conjugation of prohibitin-targeting ligand (AHP) with a KLA peptide (AHP-KLA) promoted cell death in the vascular system of WAT in obese mice, which led to the resorption of fat and a decrease in WAT mass. As a result, total body weight and obesity were reduced. Using a nanoparticle delivery system led to a threefold increase in treatment efficiency [56]. Moreover, liposomes, micelles, and nanoemulsions can be used to effectively transport drugs that target obesity and its subsequent metabolic syndrome effects. As an example, orlistat, a long-term obesity treatment, works as a pancreatic and gastro-intestinal lipase inhibitor, an enzyme that breaks down fatty acids and glycerol for intestinal absorption. The poor bioavailability of orlistat due to poor water solubility can be overcome by nanoemulsions that mask its hydrophobic characteristics and increase its efficacy [57]. Additionally, Chen et al. created an advanced system to control lipase activity through the regulation of negative feedback in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice, as illustrated in Figure 2. They used a lipase-sensitive conjugated polymer nanocarrier that encapsulates orlistat. The presence of active lipase in the digestive tract causes the degradation of the nanocarrier, resulting in the release of the encapsulated orlistat. Inhibiting lipase activity reduces the gastrointestinal absorption of fats, which promotes weight loss. This suppression of the enzyme activity causes the nanocarrier to degrade more slowly, triggering a feedback mechanism that regulates the release of orlistat and, consequently, the incidence of adverse effects. The results indicated that following a single dose of the nanocarrier, mice lost weight over eight days compared to the control group. Furthermore, the histological findings of the liver, spleen, and kidney revealed no signs of toxicity [58].
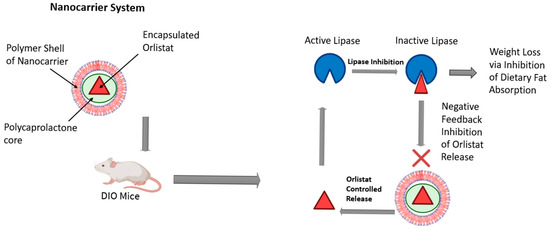
Figure 2.
A conjugated polymer nanocarrier was used to facilitate the controlled release of orlistat in diet-induced obese mice. This figure was adapted and modified from Chen et al. [58] and created in BioRender (Alanazi, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/drdbb7d).
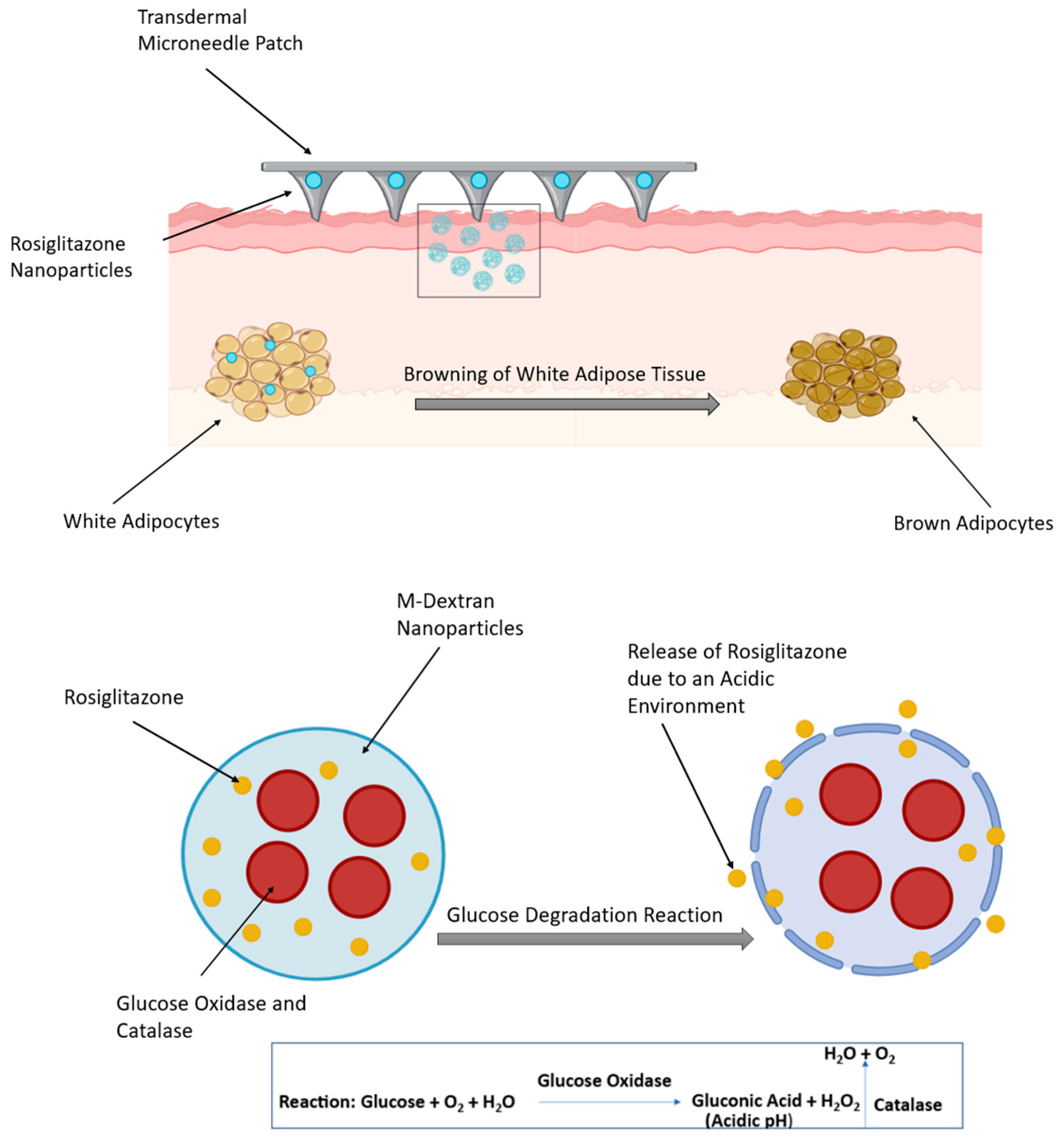
Rosiglitazone (Rosi), a member of the thiazolidinediones class of drugs, is a highly effective medication for the treatment of diabetes. It has been reported that Rosi has additional anti-obesity effects due to its ability to stimulate the browning of WAT, which, through various mechanisms, consequently leads to weight loss in rodents [3]. It inhibits the effects of TNF-α in WAT, enhancing adipocyte differentiation and suppressing the liberation of free fatty acids from adipocytes [59]. Upon oral administration, Rosi is rapidly absorbed through the body. However, a large percentage of the medication binds to proteins in the blood, leading to a decrease in its effectiveness [3]. In a mouse model, Xue et al. examined the conjugation of NPs with iRGD and P3, two peptides that have been designed to target the angiogenic blood vessels in adipose tissues. This allowed the effective delivery of Rosi which, in turn, permitted the accumulation of more NPs into adipose tissue and enhanced the browning process in WAT [60]. Another approach involved a transdermal delivery system in the form of a micro-needle patch to deliver Rosi-NPs to the subcutaneous WAT. It consisted of Rosi, glucose oxidase, and catalase encapsulated within dextran NPs, which have biodegradable acid-sensitive properties. Glucose oxidase catalyses the conversion of host glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), creating an acidic environment that promotes the release of the drug (Figure 3). Rosi-NPs stimulated subcutaneous WAT browning; this was confirmed by the increased expression of BAT markers, such as Cox8b, Dio2, Elovl3, and UCP1 [3].
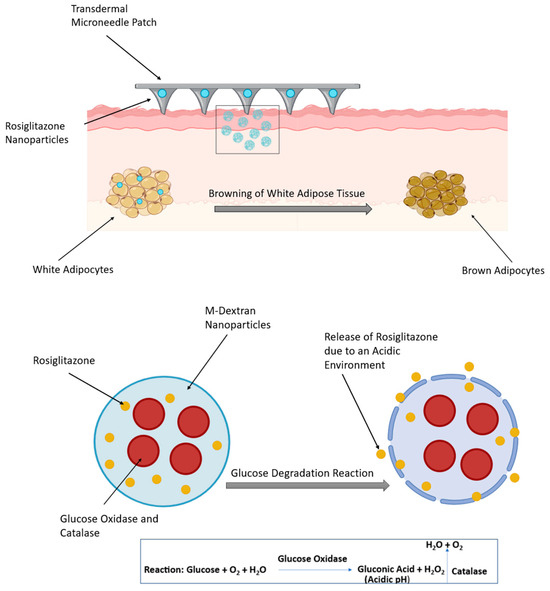
Figure 3.
Transdermal delivery of rosiglitazone nanoparticles via a microneedle patch in diet-induced obese mice (top panel). The bottom panel illustrates the glucose degradation reaction. The figure was created in BioRender. (Gobbo, O. (2025) https://BioRender.com/bboettd) and adapted from Zhang et al. [61].
2.1.1. Photothermal Lipolysis
Photothermal therapy (PTT) uses a laser-activated photothermal agent to induce heat, which effectively destroys cancer cells and eliminates tumours. Metallic NPs work as highly efficient photothermal mediators by converting near-infrared light (NIR) into heat upon laser excitation, enabling the targeted destruction of specified cells [3]. In recent years, gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) have become prominent in cancer research due to their easy manufacturing process, significantly improved optical features, and favourable biocompatibility. PTT using gold nanospheres (AuNS) is effective for superficial cancers, such as skin cancer, as it induces the photothermolysis of cancer cells [62]. Nanotheranostic strategy was utilized to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents for cancer treatment. This approach involves using photothermal NPs for cancer imaging and combining nano-chemotherapy with phototherapy [63].
PTT has also been explored as a potential approach for treating obesity. While techniques such as laser-assisted liposuction and laser irradiation are used to reduce white adipose tissue (WAT) mass by targeting and removing excess fat from both subcutaneous and visceral fat depots. Wanner et al. studied the effect of 1210 nm laser radiation on the abdomen of humans. Biopsies taken during the first three days and between four and seven weeks showed that the laser treatment resulted in tissue damage. This provided evidence for the possible application of laser-based lipolysis in reducing fat within WAT and the treatment of obesity [64]. In 2015, Sheng et al. used photothermal heating to target adipose tissue, employing polymer-coated gold nanorods (AuNRs) that were exposed to external NIR light at a wavelength of 800 nm to enhance fat removal. This method removes a greater amount of fat, with a shorter suction duration compared to suction-assisted lipectomy [65]. Lee et al. developed hyaluronate hollow gold nanospheres and adipocyte-targeting peptide (HA-HAuNS-ATP) photothermal lipolysis. HA acted as an effective transdermal delivery system, improving the biocompatibility of the formulation, while the addition of ATP enhanced the binding of HA-HAuNS-ATP to prohibitin proteins. The transdermal HA−HAuNS−ATP conjugate facilitated successful photothermal destruction of mouse adipose tissues when illuminated with a near-infrared laser. This was confirmed by photoacoustic imaging, which indicated the effective transdermal delivery of these NPs and successfully facilitated photothermal lipolysis [66,67]. In addition, body weight can be decreased by leptin, as it enhances insulin sensitivity in adipocytes and inhibits lipid accumulation. Methylcellulose (MC–gold NPs) hydrogels were designed to overcome the insufficient therapeutic effects of leptin and its negative side effects. Leptin was incorporated into MC-gold NP hydrogels and subsequently released efficiently upon exposure to light [68].
2.1.2. Gene Nanotherapy for Obesity Treatment
According to the genetic profile, obesity can be categorized into three main types: (a) monogenic cases, resulting from a single gene mutation, which is characterized by severe early-onset obesity, with a main impact on the leptin–melanocortin pathway; (b) syndromic obesity, such as the Prader–Willi syndrome, which is accompanied by neuro-developmental disorders and organ abnormalities; and (c) polygenic obesity, which is the most prevalent type and results from the effect of numerous genes [69]. FTO and TMEM18 are genes linked to a higher risk of obesity, while the sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) plays a role in activating genes related to cholesterol production, and fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) enhance the uptake and storage of fatty acids [70].
Nanotechnology techniques have the capability to encapsulate DNA, permitting its therapeutic delivery, while avoiding the immune system’s response. The application of nanotechnology in delivering DNA has attracted significantly more interest in cancer treatment than in obesity [50]. Park et al. developed gene therapy of IAPP and LEP that involved the insertion of these two genes into a single plasmid designed to treat obese mice. The plasmid DNA was administered using a non-viral polymeric carrier, and its once-weekly administrations showed a synergistic effect on body weight, resulting in reductions in fat mass, blood glucose, and lipid levels [71]. Moreover, modifying the genetic expression of GLP-1-FcmIgG-Leptin (polypeptide containing GLP-1 and leptin) and using nanotechnology methods to transport a grafted DNA sequence that raises GLP-1-FcmIgG-Leptin expression may provide a promising future strategy for managing metabolic syndrome [50].
In addition to their capability for delivering DNA, nanoemulsions, liposomes, and micelles can also effectively transport RNA. This functionality highlights a crucial use of these nanotechnology techniques in the management of metabolic syndrome [50]. Adipose-targeting sequence-9-arginine (ATS-9R) can specifically bind prohibitin receptors on adipocytes and undergo internalization. Researchers developed short-hairpin RNA (shFABP4) and ATS-9R to create an oligopeptide complex that reduces the storage of lipid droplets and, consequently, decreases fat accumulation and prevents weight gain [35].
2.1.3. Magnetic Hyperthermia Treatment for Obesity
Hyperthermia treatment (HT) is generally defined as the elevation of cell temperature to 43 °C for a prolonged period in order to achieve cell necrosis. HT is classified into three main categories: whole-body, regional, and local hyperthermia. Whole-body hyperthermia involves subjecting the entire body to high temperatures using an external heat source; however, this approach has negative side effects related to the non-specific heating. Regional hyperthermia focuses on heating a particular area of cells. Local hyperthermia is usually employed for targeting cancer cells in a specific small area, by administering heat-generating agents, including metallic nanoparticles and their oxides (e.g., Fe, Co, and Ni) [72].
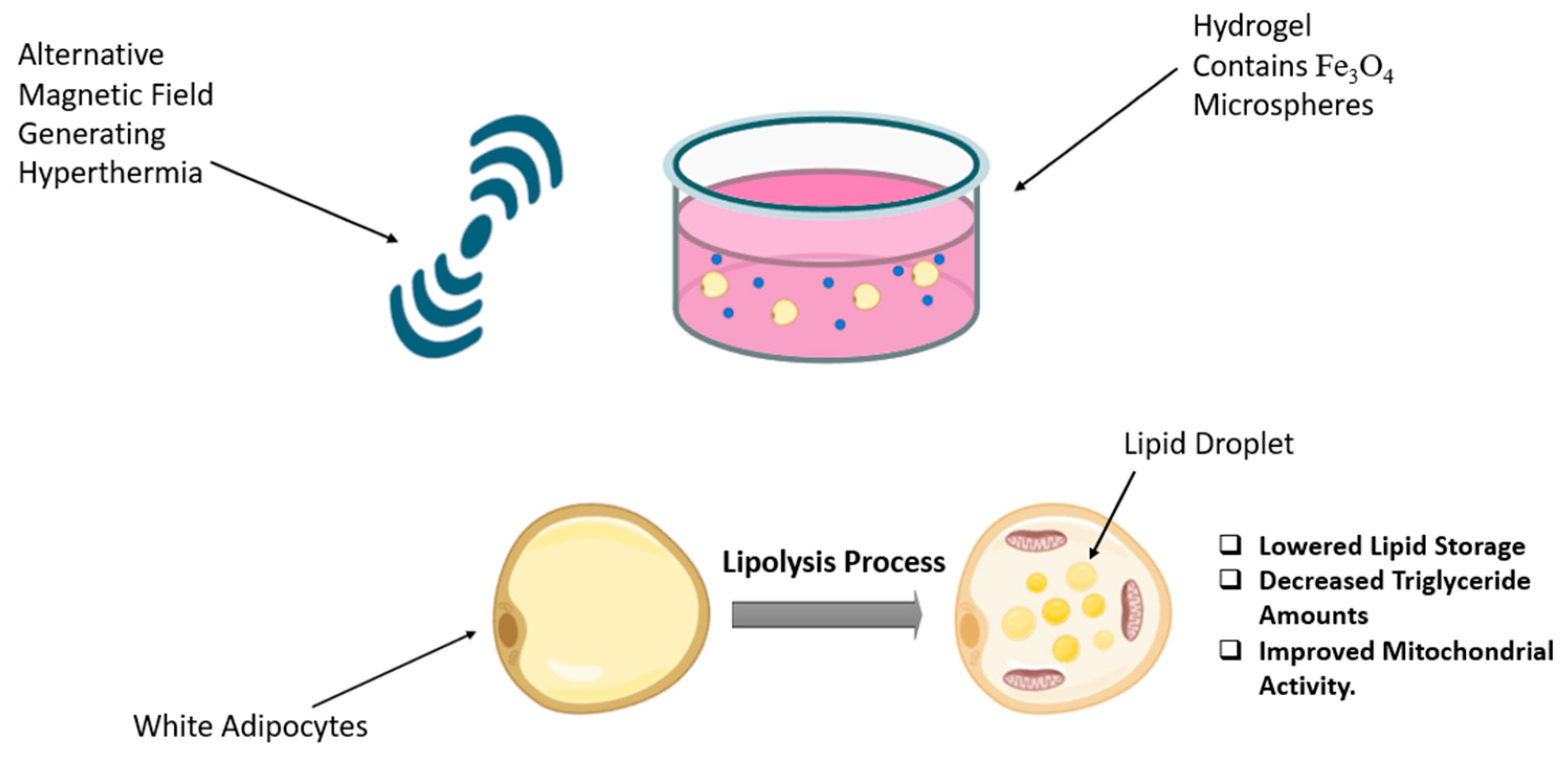
Magnetic hyperthermia uses magnetic nanoparticles delivered to the tumour site, followed by the application of an external magnetic field, resulting in the generation of heat localized within the tumour region. This technique is considered a highly promising tumour nanotheranostic strategy due to its non-invasive features and its capacity to effectively reach deep tissue areas [73]. In the field of obesity, Marinozzi et al. employed an alternating magnetic field on the 3T3 adipocyte cell line using polyhedral iron oxide nanoparticles that mediated hyperthermia treatment. The results indicated significant delipidation, observed by Oil Red O-staining, and no signs of damage or mutations [74]. In a recent in vitro study conducted in 2024 by Su et al., a novel composite hydrogel named Fe3O4@Gel was developed (Figure 4). This hydrogel consists of Fe3O4@CS/β-GP/collagen, where CS/β-GP serves as a thermo-sensitive hydrogel that remains in liquid form at room temperature and transitions into a gel at body temperature. Collagen was incorporated into the formulation to enhance biocompatibility and improve the gelation properties of the CS/β-GP-based hydrogel. Fe3O4@Gel was employed as a magnetocaloric agent for magnetic hyperthermia, with the primary goal of promoting lipolysis in white adipose tissue (WAT). The results indicate that Fe3O4@Gel exhibits several characteristics, including a high level of compatibility and exceptional magneto-thermal properties. Subjecting Fe3O4@Gel to an alternating magnetic field results in decreased lipid accumulation and reduced triglyceride content in adipocytes [75].
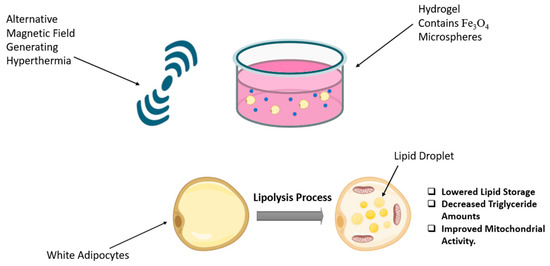
Figure 4.
Magnetic hyperthermia and Fe3O4 microsphere-infused hydrogel promote lipolysis in white adipocytes. The figure was created in BioRender (Alanazi, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/zqv5939) and adapted from Su et al. [75].
2.1.4. Herbal Anti-Obesity Nanomedicine
Increasing the intake of fruits and vegetables supports weight management, due to the anti-obesity action of phytochemicals. Phytochemicals play an important role in combating obesity through different mechanisms, including inhibiting adipocyte proliferation and preadipocyte differentiation, blocking lipogenesis and inflammation while facilitating adipocyte apoptosis [76]. Unfortunately, the high lipophilicity, poor bioavailability, and low target specificity of many therapeutic phytochemicals have hindered their clinical applications. Combining nanotechnology with herbal medicine provides several advantages, including enhancing the stability and therapeutic effectiveness of herbal products, as well as facilitating targeted delivery. These benefits make it particularly useful in addressing various health concerns, such as cancer, diabetes, and hypertension [77]. Examples of nanomedicine enhancement of anti-obesity phytochemicals are discussed in Table 2.
For instance, Zu et al. developed trans-resveratrol (R) in the form of R-encapsulated lipid nanocarriers (R-nano) and R-encapsulated liposomes (R-lipo) to protect trans-resveratrol from degradation while enhancing its intestinal permeability, bioactivity, biocompatibility, and solubility in water. At the same time, nanoencapsulation of R enhances browning efficacy, with reduced toxic effects [78]. Ahmad et al. created functional snacks through the addition of nano-encapsulated resveratrol. Starch from water chestnut, lotus stem, and horse chestnut was used to produce starch nanoparticles in order to overcome the poor physiochemical properties of resveratrol. These nano-encapsulated resveratrol snacks had 43–53% resveratrol content present after formulation compared to snacks containing free resveratrol (5.24%). Additionally, these snacks exhibited greater antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-obesity effects than those containing free resveratrol [79]. These approaches highlight the potential of nano-encapsulation to enhance the efficacy of resveratrol while minimizing its toxic effects.

Table 2.
Examples of herbal anti-obesity nanomedicine in animal studies.
Table 2.
Examples of herbal anti-obesity nanomedicine in animal studies.
| Bioactive Compound | Anti-Obesity Effect | Benefits of Nanomedicine | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin (Flavonol found in onions, citrus fruits, and tea) | Increases fatty acid β-oxidation and lipolysis by stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP), and hormone-sensitive lipase. | Insoluble in both hot and cold water; however, improved water solubility in nano-encapsulation and increased dissolution rate of nanoparticles due to their large surface area. | [50,76] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (Polyphenolic molecule abundantly found in green tea) | Promotes adipocyte apoptosis, lipolysis, and insulin sensitivity and inhibits adipocyte proliferation and differentiation. | Improved rapid oral metabolism is achieved through nanoencapsulation, which provides protection from degradation and addresses toxicity concerns. | [50,76] |
| Curcumin (Polyphenolic molecule found in turmeric) | Disrupts leptin signalling and increases adiponectin expression for decreased preadipocyte differentiation, increased lipolysis, and increased insulin sensitivity. | Low aqueous solubility and poor bioavailability enhanced by nano-formulations of curcumin for improved anti-obesity effects. | [70,76] |
| Resveratrol (Phytoalexin in red grapes, wine, and nuts) | Increases lipolysis, mitochondrial biogenesis (uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1) and CD137 expression for WAT browning), and fatty acid β-oxidation and regulates adipocyte differentiation (suppresses insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3)). | Photosensitive degradation, low thermal resistance, and negligible bioavailability after first-pass metabolism improved through nanoencapsulation in nanocarriers. | [3,67,76,80] |
2.2. Toxicity of Nanomedicine
Although nanomedicine offers several benefits, it is important to recognize its limitations. One such limitation is related to the characteristics of NPs, specifically their large surface-area-to-volume ratio, which lead to settling and caking. Settling describes the process by which NPs settle down in the formulation medium based on their density relative to that of the medium, while caking refers to the clumping of particles into hard aggregates, resulting in alterations the size and the formation of NPs [50]. Once NPs enter the body, they rapidly interact with the surrounding biological environment, leading to the formation of a coating on the NP surface, known as the protein corona. This protein has the potential to cause prominent changes in NP properties, including shape, size, and charge, resulting in a more anionic zeta potential. Studies have demonstrated that specific NPs can lead to structural changes in proteins such as cytochrome c, albumin, and ribonuclease A [81].
Furthermore, the use of NPs can lead to significant side effects due to oxidative stress. NPs produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can lead to a range of genetic damage, including DNA mutations and cross-linking. Additionally, these particles have the potential to activate neutrophil inflammatory cells [82].
In 2019, Hou et al. found that zinc oxide NPs exhibited inhibitory effects on the normal growth and development of zebrafish by disrupting the cell cycle. This disruption was confirmed by the failure of mini chromosome maintenance, resulting in a disorder in DNA replication during different phases: G1, M, and G2 [83]. In another mouse study, polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles (PVP-AgNPs) were administered orally, causing genetic alterations and DNA damage in various tissues [84]. Silica NPs can stimulate autophagy, which can be identified by assessing the conversion of LC3-I protein to LC3-II, directly observed using histological analysis. Furthermore, silica NPs have been demonstrated to induce prolonged inflammation, which may lead to fibrosis, as evidenced by increased collagen production [85]. While iron oxide NPs are employed in numerous fields of biomedicine, there have been multiple reports documenting their toxicity on normal healthy cells. Superparamagnetic iron oxide NPs cause cytotoxicity through cellular disruptions, including the alteration of gene expression profiles, the imbalance in iron regulation, DNA damage, and the generation of oxidative stress [86].
Dose is a crucial factor in NP toxicity. Researchers should evaluate the toxicity of nanoparticles using doses that are realistic and representative of real-life conditions, rather than using excessively high doses, in order to obtain a biological effect. The primary health concerns associated with nanoparticles (NPs) stem from prolonged, low-dose exposure over a lifetime, which has been linked to an increased risk of various degenerative disorders. In traditional toxicology, dose is usually associated with mass; however, the toxicological effects of nanoparticles do not correspond to these traditional principles. Due to their particulate nature, the most appropriate dosing metric for nanoparticles should relate to the number of particles reaching each cell. Mass alone does not accurately represent surface area; however, quantifying the number of nanoparticles within a specific size and shape range can effectively estimate surface area. Therefore, this metric may provide a more accurate indication of potential risk than mass alone [87].
2.3. Challenges Associated with Nanomedicines Restrict Their Translation into Clinical Use
Despite their promising therapeutic potential, nanomedicines have demonstrated limited clinical success compared to conventional pharmaceutical formulations, primarily due to a range of technological, manufacturing, and financial challenges [88]. One significant technical barrier is the stringent storage requirements associated with many nanomedicines, which often exceed the logistical and economic capacities of low-income regions [89]. Additionally, systemic administration of nanoformulations poses considerable hurdles. Nanoparticles frequently exhibit aggregation and interact with serum proteins, leading to opsonization, immune recognition, and subsequent rapid clearance from circulation, thereby diminishing therapeutic efficacy [90]. To mitigate these issues, localized delivery via direct injection into the affected tissue has been explored. However, this approach typically involves more invasive procedures than systemic administration, limiting its broad applicability. Another critical challenge involves the complexities of nanoparticle characterization, manufacturing, and quality control [91]. Nanomedicines often comprise multiple components with specific spatial configurations, necessitating a thorough understanding of their structural and functional properties. Comprehensive characterization of these elements and their interactions is essential for defining critical quality attributes and ensuring product consistency and safety [90].
The in vivo behaviour of nanomedicines distinguishes them from conventional drug products. Key factors, such as targeting a specific site, biodistribution, and drug availability in both healthy and diseased tissues, are essential for their safety and efficacy. These factors are primarily determined by the physicochemical characteristics of the nanoparticles that encapsulate the drug. Quality control is crucial for all medicinal products, including nanomedicines; however, additional quality control assessments are required beyond the typical standards due to the importance of factors such as particle size, surface structure, active ingredient loading and release mechanisms when using nanoproducts [91,92]. The production of nanoparticles includes a range of methods, such as homogenization, sonication, and lyophilization, often incorporating organic solvents. In the initial phases of development, it is crucial to evaluate how these processes can be efficiently enhanced, and important factors to be observed include the ratios of polymers and drugs, mixing methods, temperature regulation, and pH levels. These factors can greatly affect the chemical stability of the components and may lead to the introduction of impurities, denaturation, and degradation. Thus, ensuring the structural stability and physicochemical characteristics of nanoparticles during the formulation process is vital for achieving success [90]. Significant progress in the field of nanomedicine and the numerous industrial challenges, such as rising manufacturing costs and increased investment risks, have led to a notable rise in market charges for these nanomedicine products. Moreover, some manufacturers have discontinued the production of nanopharmaceuticals, driven by the challenge of elevated production expenses and limited affordability among consumers [88]. Specifically for adipocytes, the ability of nanomedicines to target fat tissue and their distribution in that area can be variable; therefore, it is essential to identify the key factors influencing their targeting ability, such as the type of nanocarrier used and the size of the particles. Furthermore, the variability in genetic backgrounds and the different causes of obesity among patients create significant hurdles in the creation of nanomedicines aimed at adipose tissue [93].
3. Conclusions
Obesity remains a global health crisis [94] and a major contributor to chronic conditions such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers [95]. While current anti-obesity drugs have shown effectiveness, many have been withdrawn due to adverse side effects. Newer agents, including GLP-1 receptor agonists such as Ozempic, represent significant pharmacological advances; however, additional strategies are needed to overcome limitations in efficacy and safety.
Nanomedicine offers innovative solutions to enhance obesity treatment by improving drug delivery, bioavailability, and targeting while reducing systemic toxicity [96]. Among the most promising nanomedicine modalities are liposomes, which enable targeted delivery and protect therapeutic agents from degradation; nanoemulsions, which increase solubility and absorption of lipophilic drugs; magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia, offering localized heating to enhance treatment efficacy; herbal nanotherapy [97], which can potentiate the effects of natural compounds; and nanotheranostics, which combine diagnostic and therapeutic functions to personalize treatment.
Despite the therapeutic promise of nanomedicine, several translational barriers persist, including concerns regarding long-term safety, complex manufacturing processes, and evolving regulatory requirements [98,99]. To facilitate clinical translation, future research must emphasize comprehensive preclinical and clinical evaluations, particularly long-term toxicity and immunogenicity assessments. Standardized protocols for nanoparticle characterization and quality control are also essential to ensure consistency and meet regulatory standards.
In parallel, the development of personalized nanomedicine strategies tailored to individual genetic backgrounds and metabolic profiles may enhance therapeutic efficacy. Well-designed clinical trials are necessary not only to assess therapeutic outcomes but also to elucidate pharmacokinetics, determine optimal dosing regimens, and evaluate patient adherence. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks must be adapted to address the specific challenges associated with nanomedicines, enabling innovation while maintaining rigorous safety standards [100]. Achieving these goals will require coordinated efforts across disciplines, including collaboration among researchers, clinicians, regulatory agencies, and industry stakeholders.
Although still in its nascent stages, as illustrated in Figure 5, nanomedicine represents a promising and innovative approach to obesity treatment [101,102]. The realization of its full clinical potential will require sustained investment in translational research, comprehensive clinical validation, and the development of an adaptive regulatory framework to ensure the safe and effective integration of nanotechnologies into routine medical practice.
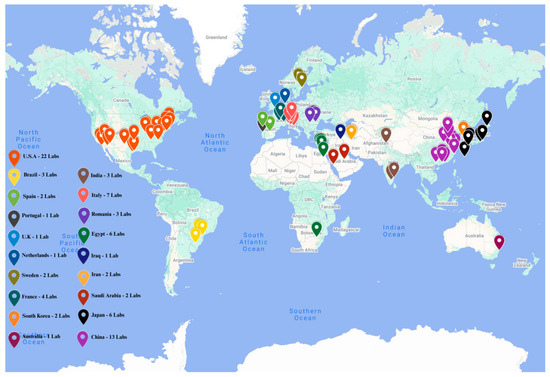
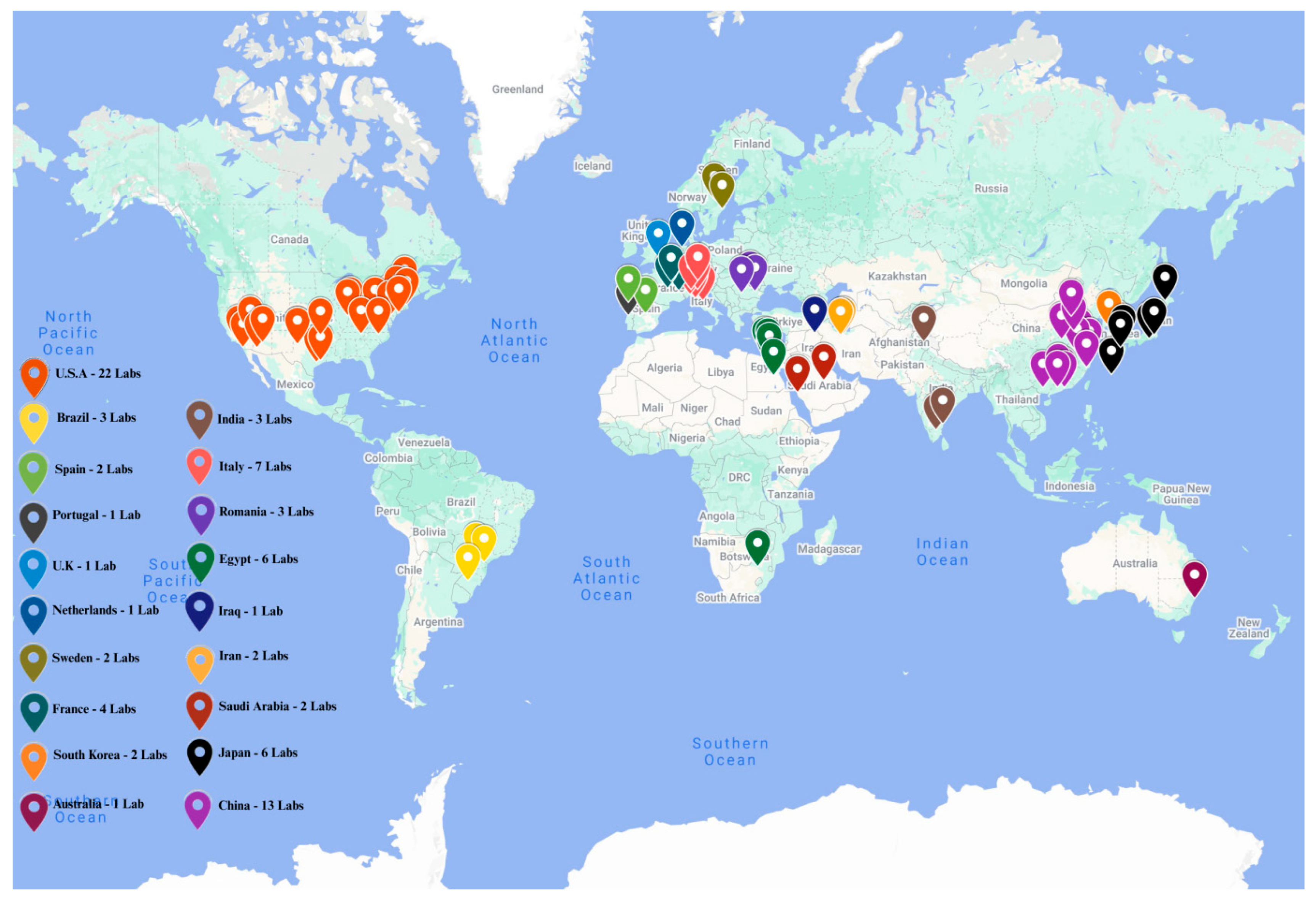
Figure 5.
Global distribution of research laboratories focused on obesity-related nanomedicine. This map was created by Mr. Sai Chitraksh Amram, Trinity College Dublin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A., A.C. and O.L.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A. and A.C.; writing—review and editing, O.L.G., M.J.S.-M., C.M. and S.V.S.; supervision, O.L.G., M.J.S.-M. and C.M.; funding acquisition, O.L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Research Boost Programme, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, and King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sai Chitraksh Amram of Trinity College Dublin for creating Figure 5, based on a concept proposed by Oliviero Gobbo.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| DNL | novo lipogenesis |
| ACC1 | acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
| SAT | subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| MCP-1 | chemoattractant protein 1 |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| VLDL | very low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor |
| BMI | body mass index |
| RYGB | Roux-en-Y gastric bypass |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| NP | nanoparticles |
| AHP | prohibitin-targeting ligand |
| AHP-KLA | prohibitin-targeting ligand with a KLA peptide |
| Rosi | Rosiglitazone |
| PTT | Photothermal therapy |
| NIR | near-infrared light |
| Au NP | gold nanoparticles |
| AuNS | gold nanospheres |
| H-AuNS | Hollow gold nanospheres |
| HA-HAuNS-ATP | adipocyte-targeting peptide |
| FABP | fatty acid-binding proteins |
| ATS-9R | Adipose-targeting sequence-9-arginine |
| PVP-AgNPs | polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles |
References
- Pandeya, P.R.; Lamichhane, R.; Lee, K.H.; Lamichhane, G.; Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.J. Efficacy of a Novel Herbal Formulation (F2) on the Management of Obesity: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8854915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The Epidemiology of Obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Moabelo, K.L.; Meyer, M.; Onani, M.O.; Dube, A.; Madiehe, A.M. Nanotechnology Advances towards Development of Targeted-Treatment for Obesity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, Y.H.; Wang, B.; Ho, W.; Hu, B.; Tang, P.; Sweet, S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Nanotechnology-Mediated Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Obesity and Its Related Comorbidities. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 18011184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.R.; Ursula, W. Adipose Tissue: Physiology to Metabolic Dysfunction. In Endotext; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32255578/ (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Hibi, M.; Oishi, S.; Matsushita, M.; Yoneshiro, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Usui, C.; Yasunaga, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kubota, K.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Brown Adipose Tissue Is Involved in Diet-Induced Thermogenesis and Whole-Body Fat Utilization in Healthy Humans. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xiaoli, A.M.; Yang, F. Regulation and Metabolic Significance of De Novo Lipogenesis in Adipose Tissues. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, Metaflammation and Immunometabolic Disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, P.; Wang, G.; Zhou, S. Features, Functions, and Associated Diseases of Visceral and Ectopic Fat: A Comprehensive Review. Obesity 2025, 33, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Hernández, A.; Beneit, N.; Díaz-Castroverde, S.; Escribano, Ó. Differential Role of Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Related Metabolic and Vascular Complications. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 16, 1216783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-Obesity Drug Discovery: Advances and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colditz, G.A.; Lindsay, L. Obesity and Cancer: Evidence, Impact, and Future Directions. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Stains, J.P. Obesity and Cancer Risk: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Recommendations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1271, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnick, S.D.H.; Knobler, H. The Medical Complications of Obesity. QJM Int. J. Med. 2006, 99, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Haboubi, H.; Haboubi, N. Adult Obesity Complications: Challenges and Clinical Impact. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampl, S.E.; Hassink, S.G.; Skinner, A.C.; Armstrong, S.C.; Barlow, S.E.; Bolling, C.F.; Avila Edwards, K.C.; Eneli, I.; Hamre, R.; Joseph, M.M.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.E.; Lashinger, L.M.; Hursting, S.D. The Growing Challenge of Obesity and Cancer: An Inflammatory Issue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1229, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Multiple Signal Pathways in Obesity-Associated Skin Cancer. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 247, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, A.; Callinan, A.; Doherty, E.; O’Neill, C.; McVeigh, T.; Sweeney, M.R.; Staines, A.; Kearns, K.; Fitzgerald, S.; Sharp, L.; et al. Overweight and Obesity on the Island of Ireland: An Estimation of Costs. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.G.; Williamson, D.F.; Glick, H.A. Direct Medical Cost of Overweight and Obesity in the USA: A Quantitative Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyeva, T.; Sturm, R.; Ringel, J.S. Moderate and Severe Obesity Have Large Differences in Health Care Costs. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, A.P.; Perry, I.J.; O’Neill, C.; Doherty, E.; Callan, A.; Kearns, K.; O’Dwyer, V.; Staines, A.; McVeigh, T.; Sweeney, M.R.; et al. The Cost of Overweight and Obesity on the Island of Ireland. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, M.A.; Ahmed, H.; Rezq, M.A.A.; Sangroongruangsri, S.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Almalki, Z.; Thavorncharoensap, M. Economic Costs of Obesity: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldubikhi, A. Obesity Management in the Saudi Population. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, B.; Mohini, A.; Louis, J. New Insights into the Treatment of Obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2058–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Semlitsch, T.; Stigler, F.L.; Jeitler, K.; Horvath, K.; Siebenhofer, A. Management of Overweight and Obesity in Primary Care—A Systematic Overview of International Evidence-Based Guidelines. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, C.; O’connell, J.; Geoghegan, J.; O’shea, D.; Birney, S.; Tully, L.; Gaynor, K.; O’kelly, M.; O’malley, G.; O’donovan, C.; et al. Obesity in Adults: A 2022 Adapted Clinical Practice Guideline for Ireland. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, B.M.; Kvach, E.; Eckel, R.H. Treatment of Obesity. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery in Adults: A Review. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinto, N.; Olatunji, G.; Kokori, E.; Olaniyi, P.; Isarinade, T.; Yusuf, I.A. Recent Advances in Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review of Weight Loss Procedures. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 6091–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lyu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhu, H.; Pan, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Gong, F. The Antiobesity Effect and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist in Overweight/Obese Patients Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2022, 54, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Qiang, L.; Gu, Z. Nanomedicine for Obesity Treatment. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesi, L.; El Ghoch, M.; Brodosi, L.; Calugi, S.; Marchesini, G.; Grave, R.D. Long-Term Weight Loss Maintenance for Obesity: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2016, 9, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.S.; Bloom, S.R. The Pharmacological Treatment and Management of Obesity. Postgrad. Med. 2011, 123, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Kahan, S. Maintenance of Lost Weight and Long-Term Management of Obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Who European Regional Obesity Report 2022. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/353747/9789289057738-eng.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- dos Santos Moraes, A.; da Costa Padovani, R.; La Scala Teixeira, C.V.; Cuesta, M.G.S.; dos Santos Gil, S.; de Paula, B.; dos Santos, G.M.; Gonçalves, R.T.; Dâmaso, A.R.; Oyama, L.M.; et al. Cognitive Behavioral Approach to Treat Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 611217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelnuovo, G.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manzoni, G.M.; Cattivelli, R.; Rossi, A.; Novelli, M.; Varallo, G.; Molinari, E. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy to Aid Weight Loss in Obese Patients: Current Perspectives. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2017, 10, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswami, V.; Dwoskin, L.P. Obesity: Current and Potential Pharmacotherapeutics and Targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 116–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. Xenical 120 mg Hard Capsules Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet 2017. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2592/smpc#gref (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Tchang, B.G. Pharmacologic Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. In Endotext; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279038/ (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Almeanazel, O.; Alanazi, F.; Alsarra, I.; Alshora, D.; Shakeel, F.; Almnaizel, A.; Alahmed, M.; Fouad, E. Nanotechnology as a Tool to Overcome the Bariatric Surgery Malabsorption. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and Cancer Risk: Emerging Biological Mechanisms and Perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Medical Devices for Weight Loss and Weight Management: What to Know. Available online: https://Www.Fda.Gov/Consumers/Consumer-Updates/Medical-Devices-Weight-Loss-and-Weight-Management-What-Know (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Dayyeh, B.K. Intragastric Balloons for Obesity Management. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 13, 737–739. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29339949/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Lari, E.; Burhamah, W.; Lari, A.; Alsaeed, T.; Al-Yaqout, K.; Al-Sabah, S. Intra-Gastric Balloons—The Past, Present and Future. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 63, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, G.I.; Kim, D.; Choudhury, M. Promises of Nanotherapeutics in Obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the Clinic: An Update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2019, 4, 10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, O.V. Applications of Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2004, 2, 3. Available online: http://www.jnanobiotechnology.com/content/2/1/3 (accessed on 12 April 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiligtag, F.J.; Niederberger, M. The Fascinating World of Nanoparticle Research. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafir, L.M.; Dodi, G.; Frasinariu, O.; Luca, A.C.; Butnariu, L.I.; Tarca, E.; Moisa, S.M. Tackling Dyslipidemia in Obesity from a Nanotechnology Perspective. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Onani, M.O.; Skepu, A.; Madiehe, A.M. Vascular Targeted Nanotherapeutic Approach for Obesity Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7915–7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.N.; Kajimoto, K.; Akita, H.; Hyodo, M.; Harashima, H. A Comparative Study between Nanoparticle-Targeted Therapeutics and Bioconjugates as Obesity Medication. J. Control. Release 2013, 171, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwai, M.; Sardar, S.; Vavia, P. Nanoemulsified Orlistat-Embedded Multi-Unit Pellet System (MUPS) with Improved Dissolution and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L.; Feng, P.J.; Yao, X.K.; Qian, C.G.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X.Q.; Shen, Q.D. Smart Conjugated Polymer Nanocarrier for Healthy Weight Loss by Negative Feedback Regulation of Lipase Activity. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3368–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Trasino, S.E.; Ferrante, A.W.; Vasselli, J.R. Prolonged Decrease of Adipocyte Size after Rosiglitazone Treatment in High- and Low-Fat-Fed Rats. Obesity 2007, 15, 2653–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Preventing Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Adipose Tissue Transformation and Angiogenesis Using Targeted Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5552–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Qiang, L.; Gu, Z. Locally Induced Adipose Tissue Browning by Microneedle Patch for Obesity Treatment. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9223–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles: Optical Properties and Implementations in Cancer Diagnosis and Photothermal Therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zheng, G.; Fan, L.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, K.; Guo, Y.; Shao, J.W. Carrier-Free Nanodrug by Co-Assembly of Chemotherapeutic Agent and Photosensitizer for Cancer Imaging and Chemo-Photo Combination Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, M.; Avram, M.; Gagnon, D.; Mihm, M.C.; Zurakowski, D.; Watanabe, K.; Tannous, Z.; Anderson, R.R.; Manstein, D. Effects of Non-Invasive, 1,210 Nm Laser Exposure on Adipose Tissue: Results of a Human Pilot Study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Alhasan, A.H.; DiBernardo, G.; Almutairi, K.M.; Rubin, J.P.; DiBernardo, B.E.; Almutairi, A. Gold Nanoparticle-Assisted Selective Photothermolysis of Adipose Tissue (NanoLipo). Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2014, 2, e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Beack, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, G.H.; Park, W.C.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.S.; Hahn, S.K. Targeted Hyaluronate-Hollow Gold Nanosphere Conjugate for Anti-Obesity Photothermal Lipolysis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cha, R.; Luo, H.; Hao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Nanomaterials for the Theranostics of Obesity. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.X.; Liu, M.C.; Kempson, I.M.; Fa, Y.C.; Huang, K.Y. Light-Triggered Methylcellulose Gold Nanoparticle Hydrogels for Leptin Release to Inhibit Fat Stores in Adipocytes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7603–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Belanger, M.J.; Kokkinos, A.; Koliaki, C.C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Novel Noninvasive Approaches to the Treatment of Obesity: From Pharmacotherapy to Gene Therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 507–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adetunji, C.O.; Michael, O.S.; Rathee, S.; Singh, K.R.; Ajayi, O.O.; Adetunji, J.B.; Ojha, A.; Singh, J.; Singh, R.P. Potentialities of Nanomaterials for the Management and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome: A New Insight. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 13, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Cho, S.; Han, Y.H.; Janat-Amsbury, M.M.; Boudina, S.; Bae, Y.H. Combinatorial Gene Construct and Non-Viral Delivery for Anti-Obesity in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, H.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Kim, K.S. Fundamentals to Apply Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Therapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chaverra, M.J.; Restrepo-Parra, E.; Acosta-Medina, C.D.; Mello, A.; Ospina, R. Synthesis of Oxide Iron Nanoparticles Using Laser Ablation for Possible Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinozzi, M.R.; Pandolfi, L.; Malatesta, M.; Colombo, M.; Collico, V.; Lievens, P.M.J.; Tambalo, S.; Lasconi, C.; Vurro, F.; Boschi, F.; et al. Innovative Approach to Safely Induce Controlled Lipolysis by Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Mediated Hyperthermic Treatment. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Jin, M.; Chen, F.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z. Promote Lipolysis in White Adipocytes by Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy with Fe3O4 Microsphere-Doped Hydrogel. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktas, Z.; Zu, Y.; Abbasi, M.; Galyean, S.; Wu, D.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S. Recent Advances in Nanoencapsulation of Phytochemicals to Combat Obesity and Its Comorbidities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8119–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, P.; Narvenker, R. Herbal Nanotherapy: A New Paradigm over Conventional Obesity Treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Overby, H.; Ren, G.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S. Resveratrol Liposomes and Lipid Nanocarriers: Comparison of Characteristics and Inducing Browning of White Adipocytes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Gani, A. Development of Novel Functional Snacks Containing Nano-Encapsulated Resveratrol with Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Obesity and Antioxidant Properties. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongioì, L.M.; La Vignera, S.; Cannarella, R.; Cimino, L.; Compagnone, M.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E. The role of resveratrol administration in human obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gentile, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Nie, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Safety of Nanoparticles in Medicine. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuna, C.; Parmar, V.K.; Jeevanandam, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Adetunji, C.O.; Khan, J.; Onyeike, E.N.; Uche, C.Z.; Akram, M.; et al. Toxicity of Nanoparticles in Biomedical Application: Nanotoxicology. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 9954443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Wang, X. Mechanism of Toxic Effects of Nano-ZnO on Cell Cycle of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Chemosphere 2019, 229, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.S.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Prasad, T. In Vitro Studies on Oxidative Stress-Independent, Ag Nanoparticles-Induced Cell Toxicity of Candida Albicans, an Opportunistic Pathogen. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Sayes, C.M. A Toxicological Profile of Silica Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 11, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Asadi, R.; Doak, S.H. Potential Toxicity of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaesser, A.; Howard, C.V. Toxicology of Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.A.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A.; Harashima, H. Clinical Translation of Nanomedicines: Challenges, Opportunities, and Keys. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 181, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Feng, S.S. Pharmaceutical Stability Aspects of Nanomedicines. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N. Challenges in Development of Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutics. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, J.M.; Lammers, T. Challenges in Nanomedicine Clinical Translation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragelle, H.; Danhier, F.; Préat, V.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems: A Commercial and Regulatory Outlook as the Field Matures. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Adipose Tissue-Targeting Nanomedicines for Obesity Pharmacotherapy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, T.; McGranahan, M.; Stewart, D.; Oyebode, O.; Shantikumar, S.; Proto, W.; Malik, B.; Yau, R.; Cobbin, M.; Sabouni, A.; et al. A systematic review of the burden of, access to services for and perceptions of patients with overweight and obesity, in humanitarian crisis settings. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Ryder-Burbidge, C.; McNeil, J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: Epidemiologic evidence and biologic mechanisms. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Lu, X.; He, X. Nanoparticle systems reduce systemic toxicity in cancer treatment. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Sun, D.S.; Wang, K.L.; Shang, D.Y. Nanomedicine of plant origin for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 811917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Banga, A.K. Advanced transdermal drug delivery system: A comprehensive review of microneedle technologies, novel designs, diverse applications, and critical challenges. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 670, 125118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaverdi, K.; Bakhshi, A.; Mozafari, M.R.; Naghib, S.M. A review of chitosan-based nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for brain diseases: Critical challenges, outlooks and promises. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, F.D.; Monferrer, D.; Penon, O.; Rivera-Gil, P. Regulatory pathways and guidelines for nanotechnology-enabled health products: A comparative review of EU and US frameworks. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1544393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusamy, S.R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Sundaravadivelu, S.; Huq, M.A.; Nag, S.; Mohanto, S.; Sukweenadhi, J.; Oh, D.H.; Perumalsamy, H. Nutraceuticals enhanced by nanotechnology: A new frontier for obesity treatment. Process Biochem. 2025, 156, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, O.L. Tackling Obesity from a Nanomedicine Perspective. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. Pharmacokinet. Int. Ed. 2024, 38, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).