Abstract
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) along with quantum dots (QDs) are independent structures that have garnered attention in the biomedical field due to their unique chemo-physical characteristics. MOFs are highly porous and tunable structures, while QDs are nanomaterials with excellent optical and fluorescent properties which make these potent diagnostic tools for sensing, detection, and therapeutics. Despite their potential, both materials have their shortcomings in terms of long-term stability and toxicity. However, the integration of these two materials to form QD–MOF hybrid systems has emerged to combine their strengths and overcome their limitations, introducing new possibilities for advanced therapeutic applications. In this mini review, we explore the evolution of the QD–MOF hybrid systems, focusing on their functional properties and applications in sensing, drug delivery and cancer therapy. Furthermore, we discuss the current implementation of this system and its future possibilities, exhibiting the novel impacts of the QD–MOF hybrids in biomedical research and clinical applications.
1. Introduction
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are crystalline materials that consists of metal ions in the center linked by ligands in a three-dimensional network [1,2]. These networks are porous and provides MOFs with a large surface area and tunable properties that make these a promising candidate for being used in drug-delivery systems [3,4,5]. MOFs were first introduced in 1995 by Omar Yaghi and Hailian Li by using copper nitrate, 4,4′-bipyridine, and 1,3,5-triazine as precursors. They were able to coordinate metals that formed open frameworks with properties like stability and porosity via a hydrothermal synthesis method [6]. Consequently, from its discovery to the present day, MOF studies have been on an exponential rise. According to PubMed, what started out as a single publication in the year 1995, as of April 2025, there have been 35,060 papers published with the keyword “Metal Organic Framework” in their title. This is a 3,506,000% increase in publications. Early MOF studies focused on the synthesis and characterization of MOFs using different metallic compounds as centers with different organic linkers [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Following studies have expanded to focus on the functionality of MOFs to deal with their application in catalysis, gas adsorption, and drug delivery. These studies have introduced numerous MOF structures with variable functionalities. In recent years, the studies on MOFs have been trending in the direction of integration of MOFs with other materials, such as zeolites, biopolymers and nanoparticles (quantum dots) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19], to develop hybrid structures that allow the best features of both components to be utilized in practical scenarios.
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor nanoparticles at the forefront of biomedicine due to their distinct optical and fluorescent properties that make them a promising diagnostic tool in drug delivery, imaging, and therapeutics. The first encounter with QDs dates back to 1981, when Alexey Ekimov and Alexei A. Onushchenko proclaimed the discovery of microscopic semiconductor crystals in a glass matrix that displayed quantum size effects [20]. Similarly, in 1983, Louis Brus further confirmed the size-dependent quantum effects (tunable optical properties) shown by semiconductor particles in a colloidal suspension [21,22]. After the initiation of a QD synthesis by molecular beam epitaxy by Leon et al., in 1995 [23], there was a surge in the colloidal synthesis of QDs [24,25,26,27], started by Radovanovic et al., to prepare ZnO QDs [28]. To this day, colloidal synthesis is the preferred method for synthesis—particularly, the hot injection method, where a cool preliminary solution is added into a heated reaction mixture to produce highly uniform QDs. Subsequent studies dealt with the development of core-shell QDs [29,30,31], followed by studies on the electron energy levels of QDs [32,33,34,35,36] and the exploration of the photoluminescent properties of QDs [37,38,39,40]. Having a grasp of the unique properties of QDs, their potential in biomedicine was explored primarily as fluorescent probes for cellular imaging, drug delivery, and diagnostics [41,42,43,44,45,46]. With extensive research being carried out on the biological applications of QDs, there have been significant concerns over the toxicity of QDs inside the human body, as well as in the environment [47,48,49]. To mitigate the potential hazardous impact caused by QDs, the research field has given more attention to the development of non-metal based QDs, such as carbon dots, a more environmentally friendly sustainable QD. At the same time, as a part of next generation nanotechnology, there has been rising interest in producing the QD–MOF hybrid composites to further enhance each individual component’s properties and effects. Most studies that have been carried out for the QD–MOFs hybrid structures focus largely on chemical and fluorescent sensing, detection, photocatalysis, and recently, therapeutics (Figure 1). In terms of cancer therapeutics, the recent literature mainly focuses on the examination of QDs and MOFs as individual components. Combining the structural and functional versatility of MOFs with the exceptional optical and electronic properties of QDs to develop a potent multifunctional theranostics tool highlights the appeal of merging these hybrid fields and showcases a new trend in therapeutics using QD–MOFs (Figure 1). Consequently, this mini-review explores the current advancements and challenges in the application of the QD–MOF hybrid system in cancer therapeutics, encouraging further research in this relatively new field to develop a well-rounded theranostics approach.
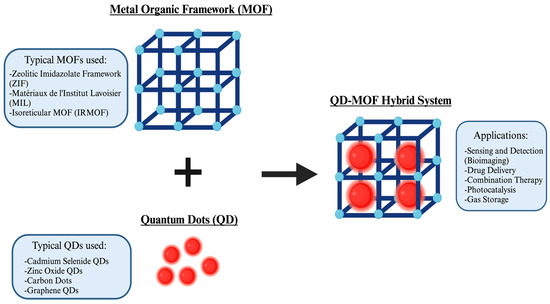
Figure 1.
Comprehensive representation of typical MOFs and QDs used and their applications as a hybrid system (Created in BioRender. Kim, K. (2025), https://BioRender.com/8w47vhy, accessed on 14 March 2025).
2. History of MOFs at the Nanoscale Level
The exploration of MOFs at the nanoscale level emerged as researchers speculated whether the miniature sizes of MOFs would ultimately enhance its properties in terms of surface area/volume ratio for faster diffusion rates and integration into the system [50,51]. The interest in the combined study of MOFs and nanoparticles (NPs) started as early as 2005 when Moon et al., utilized a redox-active MOF to generate silver nanoparticles from silver ions at room temperature [52]. The consequent studies focused on the synthesis of nanoscale MOFs (NMOFs) [53,54,55,56,57,58] along with the application of MOFs in gas-storage and catalysis [59,60,61,62,63]. Since then, the NP–MOF hybrid system has diversified, and focuses largely on making advancements in the biomedical field in terms of drug delivery, imaging, and theranostics.
In 2004, Bordiga et al. discovered that MOF-5, a type of MOF with zinc and oxygen (ZnO) clusters, exhibited behavior similar to ZnO QDs [64]. Correspondingly, Llabrés et al. also deduced that the ZnO clusters of MOF-5 were structurally stable QDs that enhanced the semiconductor properties of the MOF, making them promising tools to be utilized in photovoltaic cells, photocatalysis, and electroluminescence [65]. Next, in 2011, Buso et al. [66] made advances by studying the integration of MOFs and optically active semiconductor nanoparticles. They introduced highly luminescent QDs within MOF-5 to create a QD@MOF-5 composite [66]. In comparison to its alternatives, QDs exhibit superior optical properties in terms of quantum yield, stability, and precise emission wavelength control. Here, a major challenge lies in retaining this property of QDs as they are integrated into the MOF hybrid structures. On the other hand, QD–MOF integration may cause unwanted changes in the MOF lattice structure that may cause the framework to collapse and lose its porosity. With these challenges in mind, Buso et. al. characterized the QD@MOF-5 composite using X-ray fluorescence, confocal microscopy, and X-ray diffraction to showcase the preservation of QD optical properties and the MOF morphology [66].
As of 21 April 2025, there have been 473 papers published dealing with the QD–MOFs hybrid system. In 2024 alone, 103 papers were published, which is a 134.1% increase from 2020 (44 papers published). Therefore, there is an evident interest to integrate these structures to form a cohesive hybrid system with distinctive properties for applications in catalysis, sensing, detection, and biomedicine (Figure 2).
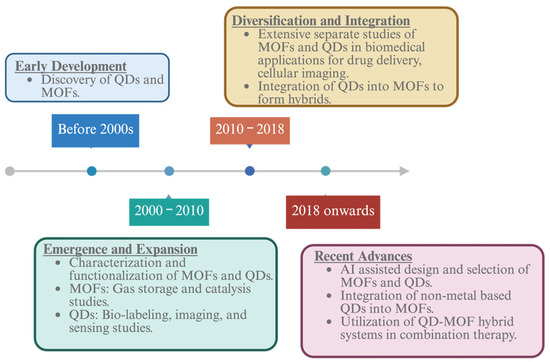
Figure 2.
Historical timeline QDs, MOFs, and their integration into the QD–MOF hybrids, highlighting evolution and key development in the field (Created in BioRender. Kim, K. (2025), https://BioRender.com/my54ifg, accessed on 21 April 2025).
3. Properties That Enhance the QD–MOF Hybrids Based Drug Delivery
As mentioned earlier, MOFs and QDs have emerged as promising candidates to be used as drug delivery vehicles due to their unique structural and functional properties. MOFs offer high tunability in terms of porosity and surface chemistry. The ability to fine tune the surface functionality of MOFs with numerous functional groups enhances drug loading capabilities onto MOFs, and it also improves their interaction with biological systems by attaching specific ligands onto its surface. In addition, the pore sizes can be adjusted to range from as small as 2 nm to over 50 nm [67] with the help of organic linkers in coordination with the metal nodes of the framework. These properties also help improve the drug shelf life and drug release capabilities by providing high thermal and hydrolytic stability [68,69]. Additionally, the lattice structure of MOFs also provides a competent environment for the encapsulation of QDs—that have excellent fluorescence for imaging and tracking—to combine and enhance their individual properties for a better drug delivery system.
In terms of drug delivery, controlled drug loading and release are crucial for treatment efficacy and safety in anticancer therapy. Nanocarriers have been highly sought after due to their versatility in biodistribution, solubility, stability, and release [70,71]. However, there remains a translational gap between laboratory experiments and clinical applications due to a low drug loading capacity, off-target toxicity, and lack of multi-functionality (theranostics). To address these issues, hybrid nanocarriers that alter the release pattern are studied, looking to provide enhanced therapeutic efficacy [72]. Having a high yet optimum drug loading capacity helps to maximize the therapeutic dosages reaching the tumors. Compared to other hybrid nanocarriers, the QD–MOF hybrid system helps improve drug loading because of the porosity of the MOF that results in a large surface area for enhanced encapsulation along with the stability provided by the QDs. During the encapsulation process, the MOF might lose its structural integrity due to the framework collapsing [73]. However, the addition of QDs into the pores of the MOF helps prevent the collapse, as the QDs provide structural support to the MOF [74], while simultaneously monitoring drug distribution. Likewise, controlled drug release by specific triggers like pH and temperature helps to minimize off-target toxicity by preventing drug leakage and reducing frequent drug administration.
Therefore, the QD–MOF hybrids offer a resilient theranostics platform for cancer therapy by enabling a controlled drug delivery mechanism and real time tracking, addressing the limitations presented by conventional nanocarriers.
4. The QD–MOF Hybrids as Biosensors for Sensing and Detection
The QD–MOF hybrid systems present an attractive foundation for sensing and detection applications due to the combination of their unique properties. This allows the hybrid structure to have a more enhanced signal response and be more sensitive over conventional methods such as colorimetric/electrochemical sensors and fluorescent dyes.
In 2013, a study carried out by Lin et al. utilized branched poly-(ethylenimine)-capped carbon quantum dots (BPEI-CQDs) encapsulated by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) MOFs to create the hybrid system BPEI-CQDs/ZIF-8 for enhanced chemical sensing of Copper (Cu2+) ions [75]. They found that the fluorescent intensity of BPEI-CQDs/ZIF-8 was significantly quenched compared to BPEI-CQDs upon Cu2+ ions treatment. In addition, even 0.002 µM of Cu2+ ions caused quenching of BPEI-CQDs/ZIF-8 composites. This further showcased the superior sensing ability of BPEI-CQDs/ZIF-8. Lin et al. [75], also examined the practicality of this hybrid sensor as they measured the concentration of Cu2+ ions (2.201 ± 0.084 μM) in environmental water samples and compared it to the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method (2.164 ± 0.052 μM Cu2+ ions). The ICP-MS method is a highly sensitive technique that analyzes the composition of a sample by measuring the concentration of its elements, but it is very expensive and requires significant expertise to operate. The consistent results among these methods have demonstrated the superior fluorescent activity and sensing of the MOF–QD hybrid sensor while also exhibiting robust and selective accumulation of the target analytes (Cu2+ ions).
In 2022, Zhou et al. [76] introduced a fluorescent biosensor that detected the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) N protein (Table 1). The biosensor was based on an entropy-driven DNA circuit, graphitic carbon nitrides quantum dots encapsulated in a Zn-based metal–organic framework (g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF), and a quenching group called Dabcyl. Here, the DNA circuit is used to recognize the SARS-CoV-2 N protein and amplify the signal. Upon recognition, signal strands are released and bind to molecular beacon strands labeled with g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF and Dabcyl. This binding separates g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF from Dabcyl and allows for the release of a strong fluorescence signal. They carried out a fluorescence assay where they treated the biosensor in the presence and absence of g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF with varying concentrations of N protein (5.0 pg/mL to 1000 pg/mL). The detection limit of the biosensor was enhanced by nearly 50-fold in the presence of g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF (1 pg/mL i.e., 8.77 × 10−9 µM) compared to in its absence (50 pg/mL i.e., 4.386 × 10−7 µM). Additionally, another fluorescence assay demonstrated that the biosensor released high fluorescent signals for N protein of SARS-CoV-2 compared to the N proteins of HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV due to the N-48 aptamer present in the DNA circuit [76]. These attributes of the biosensor help in sensitive and accurate detection, which address the limitations presented by conventional methods, like RT-PCR, which does not directly measure protein concentration, but via an indirect method reporting mRNA levels. Although the hybrid system is very promising, there is little to no research on its stability in different environmental conditions.

Table 1.
Comprehensive table showcasing different QD–MOF composites utilized in sensing and detection.
In a recent study carried out by in 2024, Zhang et al. [77] constructed a dual-potential ratio electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor based on perylene diimide (PDI)-isoreticular metal–organic framework-3 (IRMOF-3) and DNA nanoflowers (NFs)–Cadmium sulfide (CdS) QDs for detection of breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) (Table 1), which are both markers for breast cancer [79,80]. They carried out fluorescence studies to demonstrate the ECL responses of the biosensor at different concentrations of BRCA1 and CEA, where the results indicated the limit of detection to be 46.25 fM (4.625 × 10−8 µM) and 6.79 fg/mL (3.772 × 10−11 µM), respectively. Furthermore, the biosensor was used to the determine the amount of BRCA1 and CEA recovered when known concentrations were added to human serum samples by the standard addition method [77]. Here, the average recovery for BRCA1 and CEA in three different runs were 100.7% and 98.6%, respectively. These results highlight the biosensor’s potential for the early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Likewise, in 2025, Liu et al. [78] developed an ECL biosensor using CdS QDs encapsulated in IRMOF-3, CdS@IRMOF-3, as a signal probe and hollow silver (Ag), gold (Au), Ag@Au, nanotubes as a sensor substrate for detection of human epididymis protein 4 (HE4)—a biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer [81]. The hollow nanotubes helped to increase the biosensor’s sensitivity while the probe improved luminophore loading and reduced the energy loss [78]. ECL biosensors use light emission to detect biological analytes and can also detect cancer biomarkers in body fluids like urine, serum, and saliva [82]. In this study, the biosensor enhances ECL emission and efficiency due to its co-reaction accelerator functionality and non-radiative transitions. The biosensor also demonstrated a broad linear range (50 fg/mL to 50 ng/mL) and a low detection limit (9.89 fg/mL i.e., 3.956 × 10−10) for HE4 [78].
Overall, the QD–MOF hybrid structure provides a versatile system with enhanced sensing and detection due to the combination of their unique properties as evident by the studies mentioned above. However, a severe challenge for the usage of these biosensors in real-world applications lies in addressing its stability. Most QD–MOF hybrid biosensor studies are based on short term stability, about 1–2 weeks, in controlled environments with little to no research on long term stability over months or even years. Furthermore, the components of these hybrid structures are sensitive to varying environmental conditions, like temperature, humidity, light, and pH changes. This variation can degrade the hybrid system over time, so it is necessary to study the system in different conditions over an extended period. In biomedicine, future studies should also focus on testing the biosensor in complex environments that mimic the body’s physiological environment to prevent false results and signal distortion, and to ensure biocompatibility. Therefore, it is essential to carry out long term studies based on diverse environmental conditions to ensure the practical implementation of these QD–MOF based biosensors.
5. The QD–MOF Hybrids as Drug Delivery Vehicles with a Focus on Cancer Therapeutics
The development of the QD–MOF hybrid system provides a revolutionary platform for nanomedicine in cancer therapy and therapeutics in general with its ability to be a precise drug delivery carrier and to be used in combination therapy which makes treatment more effective.
Accordingly, the studies carried out by Tian et al. [83] and Pan et al. [84], in 2017 and 2022, respectively, dealt with the synergetic relationships between two different treatments and looked to increase the therapeutic efficacies to treat different diseases. In both studies the initial treatment was combined with photothermal therapy (PTT) to imply the more effective outcomes of multimodal therapy. Tian et al. [83] focused on the anti-cancer potential of Doxorubicin (DOX), whereas Pan et al. [84] loaded their system with polydopamine (PDA) due to its excellent photothermal conversion efficiency and biocompatibility for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment.
The study carried out by Tian et al. [83] used zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/graphene quantum dots (ZIF-8/GQDs) to test the therapeutic efficacy for synergistic chemotherapy and PTT rather than carrying them out separately (Table 2). ZIF-8 behaved as the drug carrier while PTT was successful due to the photothermal effects demonstrated by the GQDs. The hybrid system was loaded with 5 µg/mL DOX. The 4T1 cells—a breast cancer cell line derived from mouse mammary gland tissue—were then initially treated with DOX, ZIF-8/GQDs, or DOX-ZIF-8/GQDs, followed by near-infrared (NIR) irradiation. Then, they compared the effectiveness of the treatment by observing the cell viability before and after NIR irradiation (Figure 3). Here, the treatment with DOX only, both before and after NIR irradiation resulted in 75% cell viability; whereas ZIF-8/GQDs or DOX-ZIF-8/GQDs treatment after irradiation demonstrated significant decrease in cell viability compared to before irradiation. Overall, the synergistic treatment of DOX-ZIF-8/GQDs nanoparticles after irradiation demonstrated the best efficacies, with only 18% of the cells still viable compared to before irradiation (84% viability) [83].
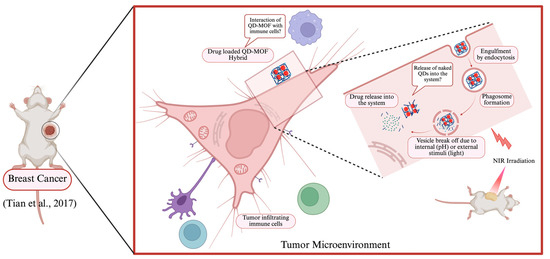
Figure 3.
A representative illustration of QD–MOF hybrid drug delivery in cancer therapeutics using the study by Tian et al., 2017 [83] (Created in BioRender. Kim, K. (2025), https://BioRender.com/cnsho97, accessed on 21 April 2025).
It is important to note that, while the ZIF-8/GQDs system utilizes the tumor’s acidic environment for drug release, the system is not specific for selecting tumor cells over normal functioning cells (Figure 3). As a response to the tumor microenvironment, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) penetrate and combat against tumor cells. The effect of the presence of this hybrid system on TILs was not considered in this paper. The specificity of the ZIF-8/GQDs system can be enhanced by attaching tumor-specific ligands, like in this case, with folic acid onto its surface. The 4T1 cells express the folate receptor [85] making them a suitable target for cancer therapy. The use of redox-sensitive linkers is also suitable as it can be modified to focus on controlled drug release only in the reducing environment of the tumor cells. This reducing environment is a result of having elevated levels of reducing agents like glutathione (GSH). At the same time, it is also crucial to carry out subsequent studies focusing on the interaction of this ZIF-8/GQDs system with the tumor microenvironment before and after drug release. Overall, this study provides a strong foundation to further work on the development of the QD–MOF hybrid structure for drug delivery and therapy.
In addition to cancer therapeutics, the QD–MOF hybrid can be utilized in the treatment of other inflammatory diseases as well. In 2022, Pan et al. [84] developed a multifunctional platinum (Pt)-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA system to treat RA in vitro and in vivo by reducing oxidative stress, as rheumatoid joints suffer from severe bone and cartilage degeneration due to oxidative stress. This is a novel and intriguing approach, as both MOF and QDs are photocatalysts capable of generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increasing oxidative stress. They used perovskite QDs, which is based on a class of minerals called perovskite [86,87,88] for fluorescence and loaded PDA for hydrogenothermal therapy. Hydrogenothermal therapy is the combination of hydrogen (H2) and PTT to treat tumors [89,90]. They utilized two different cell lines: human fibroblast-like synoviocytes-rheumatoid arthritis (HFLS-RA) cells and a mouse macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) and stained them with methylene blue (MB) to showcase H2 production when treated by Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA before and after NIR-visible (VIS) irradiation. Methylene blue is reduced to its colorless form in the presence of hydrogen. Here, the number of stained cells observed were comparatively low in the treatment with Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA after irradiation, which indicated a higher H2 production.
They carried out a cytotoxicity assay where they treated the HFLS-RA cells with varying concentrations (2.5 µg/mL to 12.5 µg/mL) of Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA. This assay revealed that more than 90% of the cells were viable after treatment with the Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA system, showcasing its promising biocompatibility. They also carried out another cytotoxic assay, where they treated the HFLS-RA cells with Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA and compared it to treatments with Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA with NIR and Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA with NIR-VIS irradiation. The results showed that Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA with NIR-VIS irradiation significantly reduced the cell viability in HFLS-RA cells compared to other treatments. Hence, they were able to establish a synergistic relationship between the H2 therapy and PTT in accordance with the treatment.
To provide a more accurate representation, they also carried out an in vivo study using the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model. Here, they carried out an efficacy study where they injected 10 µg/mL Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA in the tail vein of the mice. Treatment with Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA only was compared with Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA + NIR and Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA + NIR-VIS irradiation of the mice paws using images and CIA mice clinical index—a clinical index helps record the severity of the arthritis. The images showed that the Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA + NIR-VIS treatment group demonstrated significantly reduced swelling and flare ups. Similarly, the clinical index significantly decreased for the Pt-MOF@Au@QDs/PDA + NIR-VIS group after 15 days of treatment. Therefore, the in vivo study was in agreement with the in vitro results, i.e., the combined treatment of H2 and PTT was more effective compared to individual therapies. By using histopathology, they were also able to demonstrate improving joint health in the CIA mouse models [84].
In this study by Pan et al. [84], the multifunctionality of the system enables imaging, targeted delivery, and therapy. In addition, its biocompatibility is further evidence for its usage in biomedical applications. However, a major drawback is concerning the inclusion of perovskite QDs. These QDs have excellent optical properties but are very sensitive to environmental factors like light, heat, and oxygen. Also, the doses that they used in the cytotoxic studies ranged from 2.5 µg/mL to 12.5 µg/mL, so we do not know the effects of this hybrid system on the cells and the mice at relatively higher doses to assess safety and dose optimization for clinical viability. Additionally, the relative efficacy of this system is difficult to assess, as Pan et al. [84] did not provide any direct comparison to existing therapies.
One thing to consider is that the efficacy of the PTT treatment is dependent on light irradiation whose usage is limited in deep tissues or areas where light penetration is difficult. Although the range of doses (2.5 µg/mL to 12.5 µg/mL) of the hybrid system utilized by Pan et al. [84] was substantially low compared to Tian et al. [83] (0 µg/mL to 200 µg/mL), their study was more in-depth as they also used the in vivo mice model to show the efficacy of the treatment.

Table 2.
Comprehensive table showcasing different QD–MOF composites utilized in cancer therapeutics.
Table 2.
Comprehensive table showcasing different QD–MOF composites utilized in cancer therapeutics.
| QD–MOF Hybrid System | Author | Key Aspects | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8/GQD | Tian et al. | The hybrid system was loaded with DOX to investigate synergistic breast cancer therapy. | [83] |
| BQ-MIL@cat-MIL | Liu et al. | This system was utilized for synergistic PDT/PTT treatment against hypoxic tumor cells. | [91] |
| AS1411@PEGMA@GQD@γ-CD-MOF | Jia et al. | This system was also loaded with DOX for tumor treatment in vitro and in vivo. | [92] |
| MIL-53@CMC/GQDs | Pooresmaeil et al. | DOX loaded MIL-53@CMC/GQDs investigated the biocompatibility and therapeutic ability against human breast cancer. | [93] |
| GQDs@Bio-MOF | Hassanpouraghdam et al. | The hybrid system was loaded with 5-Fu to study colon-specific delivery. | [94] |
The studies by Tian et al. [83] and Pan et al. [84] demonstrated promising biosafety and biocompatibility of the QD–MOF hybrid system. However, a study carried out in 2022 by Liu et al. [95] explored how even non-cytotoxic doses of ZIF-8 NPs elicit unwanted effects on human health. They found that the uptake of ZIF-8 NPs by human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) increased the endothelial permeability coupled with actin rearrangement, increased gap formation, and disrupted cell junctions between neighboring HAECs at doses of 25 and 50 µg/mL. They also carried out similar experiments on RAW 264.7 macrophages and obtained results where the macrophages decreased in size and had an altered actin cytoskeleton. This alteration in the actin cytoskeleton was attributed to the increased production of ROS by the NPs in the cell [95]. Therefore, this study highlights the potential risks even at safe, regulatory approved standards, and challenges the limitations within the nanoparticle cytotoxicity approach. They also emphasize the necessity to use biophysical properties like actin as markers in addition to cytotoxic assays when it comes to evaluating its safety in regard to usage on human health. It is worth noting that, in the ZIF-8/GQD system used by Tian et al. [83], there was no cytotoxicity found, even at higher doses of 100–200 µg/mL; whereas, for the ZIF-8 NPs, the cell viability dropped significantly to 57% and 40% at doses of 75 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL, respectively.
As of April 2025, the most recent study on the QD–MOF hybrid and its application in cancer therapeutics was carried out by Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94] in 2022. Hassanpouraghdam et al. developed a novel hybrid system combining graphene quantum dots (GQDs) with a bio–metal–organic framework (Bio-MOF), GQDs@Bio-MOF, to enhance colon-specific drug delivery (Table 2). The hybrid system was further loaded with the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) and a starch polymer to form the composite, St@5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF. The addition of the starch polymer facilitated a more sustained release of 5-Fu from the delivery system. To evaluate the composite’s cytotoxicity and anti-cancer activity, they treated HT 29 cells, which is a human colon adenocarcinoma cell line, with different concentrate ions of 5-Fu, 5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF, and St@5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF ranging from 0 µg/mL to 70 µg/mL. At the 70 µg/mL treatment, 89.97% of the cells were dead when treated with 5-Fu alone compared to 67.8% and 44.82% when treated with 5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF and St@5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF, respectively [94]. The higher viability upon treatment with St@5-Fu@GQDs@Bio-MOF further showcased the release of 5-Fu in a sustained manner. While 5-Fu alone was able to kill HT 29 cells more rapidly, it is well known that 5-Fu is associated with cardiotoxic properties and is able to kill healthy cells as well [96,97].
Therefore, to assess the biocompatibility of their naked hybrid composite, they treated MCF 10A—a normal human breast cell line—with varying concentrations (0 µg/mL to 50 µg/mL) of GQDs@Bio-MOF and St@GQDs@Bio-MOF. At the 50 µg/mL treatment, the St@GQDs@Bio-MOF composite was proven less toxic to the cells (84% cell viability) compared to the GQDs@Bio-MOF (78% cell viability) [94]. However, the study lacked quantitative data and statistical analysis for the cytotoxic studies. Consequently, a more comprehensive assessment of the novel hybrid system’s cytotoxic effects and biocompatibility would have been possible if the concentration range for both cell lines had been the same.
Both Tian et al. [83] and Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94] shared similar study objectives as they investigated the use of graphene QDs and MOFs for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Yet, the two studies emphasized different therapeutic applications. Tian et al. [83] focused on enhancing breast cancer treatment efficiency by studying the synergistic relationship of chemo- and photothermal therapy using ZIF-8/GQDs loaded with doxorubicin. By contrast, Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94] focused on developing a colon-specific drug delivery system, St@GQDs@Bio-MOF, loaded with 5-Fu for colorectal cancer treatment.
Although both studies utilized GQDs in their hybrid system, they differ in terms of MOFs and drug release mechanisms.
In addition to the specific drug release triggers mentioned in Table 3, some other triggers could include redox-sensitive responses and enzymatic triggers. The addition of disulfide bonds to the QD–MOF hybrids results in a more stable system that is broken down only under reducing conditions, like in the tumor microenvironment. Likewise, a QD–MOF hybrid system could be developed such that the MOF coating is sensitive to specific enzymes, like matrix metalloproteinase-2 and phospholipase A2 [98], which are overexpressed in tumors, cleaving the coating to release the drug.

Table 3.
Comparative drug release triggers and mechanisms followed by the current QD–MOF hybrid systems.
As such, Tian et al. [83] incorporated ZIF-8 as their MOF to enable pH sensitive drug release. This hybrid system released only 12% of Dox at pH 7.4 but had a faster release of 80% under acidic conditions (pH 4.5). In terms of drug release, while this study addresses pH responsive drug release, it does not explore controlled drug release, nor does it analyze the drug release kinetics or provide comparative data on the drug loading capacity.
On the other hand, Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94] used a bio-MOF, which is based on biomaterials, like amino acids and, in this instance, phenylalanine, to make use of their availability and non-toxic nature. Their hybrid system observed a 62.3% drug release at pH 7.4 over 96 h. This demonstrated a sustained drug release which was facilitated by the starch biopolymer coating. Furthermore, they carried out a detailed study on the drug release mechanism which was found to follow the Higuchi model. As per this model, the drug release is controlled by diffusion. This study also reported a drug loading capacity of 42.04%, which is relatively low compared to other 5-Fu carriers, such as 5-Fluorouracil–Gemcitabine (GEM)@Materials Institute Lavoisier (MIL)-100 (78.5%) [99] and chitosan-coated magnetic iron oxide/graphene quantum dots (MGC) nanohybrid (90%) [100], but remains well within the acceptable range for drug delivery systems as most nanomedicine carriers still have a relatively low drug loading capacity of 5–25% [101,102].
Both these studies were centered on the cellular level, where they developed hybrid systems that showcased negligible cytotoxicity to normal cells but were effective against cancer cells. However, the synergistic treatment utilized by Tian et al. [83] proved to be more lethal. Despite this, they have not explored the long-term stability and biocompatibility of PTT in addition to chemotherapy. Also, these studies have not explored the role of ROS which treatments like PTT and chemotherapy often generate [103]. In terms of cancer treatment, ROS plays a complex role as it has both pro- and anti-tumorigenic effects, depending on its concentration and the type of cancer [104]. On the one hand, ROS can act as signaling molecules that promote tumor progression; while, on the other hand, elevated ROS levels can trigger cell death mechanisms, like apoptosis and ferroptosis [105]. Beyond cancer treatment, ROS generation could also help the QD–MOF hybrids become antimicrobial agents. ROS disrupts bacterial membranes and induces oxidative stress in bacterial cells [106]. However, once again, it is critical to understand the complex role of ROS in the host and bacteria before taking further steps in utilizing the QD–MOF hybrids in antibacterial treatments.
In addition to the cellular assessments by Tian et al. [83] and Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94], tissue-level examinations would have added another dimension to obtain a better understanding of the hybrid systems for targeted therapy. Overall, these studies provided novel approaches for cancer therapeutics using specific drug delivery systems. In the first case, DOX release can be triggered in an acidic environment (tumor microenvironment) to reduce any side effects to normal tissues. As mentioned earlier, the tumor microenvironment still consists of healthy cells that interact with each other to facilitate tumor growth and progression [107]. As a result, the drug, released along with the naked hybrid system, is able to interact with the healthy cells present in the microenvironment, and the side effects of the latter are unknown. Secondly, the 5-Fu release tested at pH 7.4 mimics the pH of the colon but the tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer is often acidic [108]. This raises concerns on the effectiveness of the system in tumor microenvironments as the drug release kinetics might differ. Also, further studies need to be carried out concerning the biodegradation and interaction between the hybrid system and the cells present in the microenvironment to assess its potential in colorectal cancer therapeutics. Therefore, both studies are indicative of the importance of further research, especially in vivo studies to further validate their safety and efficacy for clinical applications.
6. Conclusions
In the field of nanoparticles, studies based on NP–MOF drug delivery significantly outweigh QD–MOF based studies. The existing literature includes 882 studies on NP–MOF based drug delivery, compared to only 22 studies on QD–MOF—a staggering 190.3% difference. A major reason for this disparity may be the relative ease of synthesis of NPs without degrading the components themselves and the MOF during integration. Nanoparticles can be integrated into MOFs via in situ synthesis, a process that is relatively straightforward compared to the more rigorous conditions required by QDs. In addition, QDs are generally much smaller in size, which makes them more susceptible to aggregation and further complicates their incorporation with MOFs.
Within the QD–MOF hybrid system, most biological application studies have predominantly focused on sensing and detection with limited exploration on drug delivery. This disparity in the number of studies can be credited to the inherent properties of both the MOF and the QDs. Quantum dots are ideal for optical sensing as they exhibit a strong and bright intrinsic fluorescence. Additionally, MOFs can enhance detection limits by concentrating chemicals near the QDs as a result of their highly porous structure. While these properties can also be beneficial for drug delivery, concerns regarding the stability of the hybrid system in a physiological environment have hindered its application. Recent studies have seen the hybrid structures demonstrate good stability using the biocompatible polymers’ coating and low toxicity—the metal-based QDs’ toxicity was countered by using non-metal based QDs, like graphene. However, the number of studies carried out remains insufficient. Additionally, in the study carried out by Hassanpouraghdam et al. [94], the QD–MOF hybrid exhibited controlled and sustained colon-specific pH-based drug release. This is promising as it promotes controlled therapeutics with further possibilities in developing more tumor-specific stimuli-controlled drug release. Selectivity can also be increased by developing QD–MOF systems with specific ligand functionality that minimizes off target effects on healthy cells and tissues. A major question remains that, even after the successful delivery of the drug, what will happen to the naked hybrid system and how will it interact with its surrounding environment (Figure 3).
Furthermore, the regulatory challenges associated with drug delivery applications compared to the relatively fewer regulations for sensing applications may contribute to the slower translation of QD–MOF hybrids into practical drug delivery systems with the long-term effects on health and environment unknown. The regulatory status for the QD–MOF hybrids is ambiguous to begin with as the system itself does not fall under a distinct classification. The regulation of nanoparticles as separate entities is majorly influenced by the regulatory systems in the United States and Europe. These regulations are carried out by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, while the European Commission sets up the legal framework in Europe [109]. These guidelines are based on the intended use, safety, biodistribution, and quality control of nanoparticles for large-scale synthesis. As of now, these nanoparticles undergo extensive characterization, toxicology, and immunogenicity testing due to their unique properties, like quantum effects and high surface area. Some additional factors for assessment of nanoparticles are understanding and predicting the in vivo release mechanisms for clinical studies [110,111]. These conventional nanoparticle guidelines would be even stricter for the QD–MOF hybrids, due to their complexity and enhanced properties that result in dynamic behavior in vivo and batch variability, which causes concerns over the stability of and control over manufacturing reproducibility.
It is essential to carry out in vivo studies using animal models to bridge the gap between in vitro and clinical studies. In vitro replication of the physiological environment has limited reliability, and studies conducted in vivo can reveal unanticipated side effects or off-target interactions that would not be observed in vitro. Alternatively, organoid model systems, which mimic specific organs and functions, can be used to address limitations presented by in vivo studies that deal with high cost and ethical concerns. Although these organoid systems may lack the complete complexity of in vivo conditions, more studies are developing physiologically relevant systems in organoid models, for example, by integrating immune cells [112,113].
The potential of this system in cancer therapeutics has been severely undermined by the limited number of studies carried out. To deal with the challenges regarding design, optimization, and feasibility of this system within the cellular environment, further integrating this system with artificial intelligence (AI) would have the probability to revolutionize this field (Figure 2). The implementation of AI is usually disapproved of in scientific settings; however, using AI algorithms could prove pivotal in unlocking the full potential of the QD–MOF hybrid system in terms of functionality and sustainability. In 2024, Kang and Kim developed an AI system named “ChatMOF” that predicts and generates MOFs with desired properties by combining large language models with machine learning and an existing database [114]. Another study, by Menon and Fairen-Jimenez in 2022, utilized machine learning to screen the Cambridge Structural Database to identify biocompatible MOFs with low toxicity for drug delivery [115]. Likewise, a review by Munyebvu et al. discusses the potential of achieving quality control of QD production with automation and algorithm [116]. Therefore, combining AI with the QD–MOF hybrids could accelerate the development and implementation of an optimal drug delivery system. However, it is crucial to keep in mind that it is indispensable to carry out extensive experimental validations on the AI estimations for real world applications.
Even with its challenges, the QD–MOF hybrid system remains an attractive diagnostic tool in cancer therapeutics with its distinct properties that allows it to take a theranostics approach. In terms of cancer therapeutics, QD–MOF hybrids offer multi-functionality over other hybrid systems. This is due to the intrinsic optical properties of QDs that offer tunability and broad emission spectra which are ideal for bioimaging as well as PDT and PTT. On the other hand, MOFs possess high surface area, tunable porosity, and yield a structured framework for controlled drug delivery. The combination of these properties makes this hybrid system potent in terms of carrying out simultaneous imaging and drug release for accurate monitoring of therapeutic effects. Therefore, the QD–MOF hybrid system is a highly viable drug delivery nanocarrier with the potential for transformative applications in oncology due to its innovative approach.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, A.C.; writing—review and editing, A.C. and K.K.; visualization, A.C.; supervision, K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Missouri State University (MSU) Thesis Funding and The Roy D. Blunt Life Science Professorship awarded to Kyoungtae Kim. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of MSU and/or Roy D. Blunt.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to MSU and its Biology Department for the use of space and equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MOFs | Metal–organic frameworks |
| QDs | Quantum dots |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| NMOFs | Nanoscale metal–organic frameworks |
| BPEI | Branched poly-(ethylenimine)-capped carbon quantum dots |
| ZIF-8 | Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 |
| Cu2+ | Copper ions |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| g-CNQDs | Graphitic carbon nitrides quantum dots |
| Zn-MOF | Zinc-based metal–organic framework |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| HCoV-OC43 | Human coronavirus OC43 |
| HCoV-HKU1 | Human coronavirus HKU1 |
| MERS-CoV | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| ECL | Electrochemiluminescence |
| PDI | perylene diimide |
| IRMOF-3 | Isoreticular metal–organic framework-3 |
| NFs | Nanoflowers |
| CdS | Cadmium sulfide |
| BRCA1 | Breast cancer gene 1 |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen |
| Ag | Silver |
| Au | Gold |
| HE4 | Human epididymis protein 4 |
| PTT | Photothermal therapy |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| GQDs | Graphene quantum dots |
| NIR | Near infrared radiation |
| TILs | Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| Pt | Platinum |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| H2 | Hydrogen |
| HFLS-RA | Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes-rheumatoid arthritis |
| MB | Methylene blue |
| VIS | Visible |
| CIA | Collagen-induced arthritis |
| HAECs | Human aortic endothelial cells |
| 5-Fu | 5-Fluorouracil |
| GEM | Gemcitabine |
| MIL | Materials Institute Lavoisier |
| MGC | chitosan-coated magnetic iron oxide/graphene quantum dots |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
References
- Zhou, H.C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leus, K.; Muylaert, I.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Marin, G.B.; Van Der Voort, P. A coordinative saturated vanadium containing metal organic framework that shows a remarkable catalytic activity. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2010, 175, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Seow, J.Y.R.; Skinner, W.S.; Wang, Z.U.; Jiang, H.L. Metal–organic frameworks: Structures and functional applications. Mater. Today 2019, 27, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptopoulou, C.P. Metal-Organic Frameworks: Synthetic Methods and Potential Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, V.F.; Malek, N.I.; Kailasa, S.K. Review on Metal-Organic Framework Classification, Synthetic Approaches, and Influencing Factors: Applications in Energy, Drug Delivery, and Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 44507–44531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of a Metal-Organic Framework Containing Large Rectangular Channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10401–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, E.; Golub, V.; O’Connor, C.J.; Zubieta, J. Solid state coordination chemistry: One-, two-, and three-dimensional materials constructed from molybdophosphonate subunits linked through binuclear copper tetra-2-pyridylpyrazine groups. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 6729–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, O.R.; Lin, W. Pillared, 3D metal-organic frameworks with rectangular channels. Synthesis and characterization of coordination polymers based on tricadmium carboxylates. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Heo, J.; Whang, D.; Kim, K. A Two-Dimensional Polyrotaxane with Large Cavities and Channels: A Novel Approach to Metal-Organic Open-Frameworks by Using Supramolecular Building Blocks We gratefully acknowledge the Korean Ministry of Science and Technology (Creative Research Initiative Program) for support of this work and the Korean Ministry of Education (Brain Korea 21 program) for graduate studentships to E.L. and J.H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2001, 40, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chen, B.; Reineke, T.M.; Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; Moler, D.B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Assembly of metal-organic frameworks from large organic and inorganic secondary building units: New examples and simplifying principles for complex structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8239–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nieuwenhuyzen, M.; James, S.L. A nanoporous metal-organic framework based on bulky phosphane ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.K.; Pazzona, F.G.; Suffritti, G.B.; Demontis, P.; Masia, M. Estimation of Partial Charges in Small Zeolite Imidazolate Frameworks from Density Functional Theory Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.T.; Zuo, F.; Wu, T.; Irfanoglu, B.; Chou, C.; Nieto, R.A.; Feng, P.; Bu, X. Cooperative assembly of three-ring-based zeolite-type metal-organic frameworks and Johnson-type dodecahedra. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, F.; Brito, J.; Jeong, H.K. Rapid One-Pot Microwave Synthesis of Mixed-Linker Hybrid Zeolitic-Imidazolate Framework Membranes for Tunable Gas Separations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5586–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisser, D.; Wisser, F.M.; Raschke, S.; Klein, N.; Leistner, M.; Grothe, J.; Brunner, E.; Kaskel, S. Biological Chitin-MOF Composites with Hierarchical Pore Systems for Air-Filtration Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 12588–12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, E.; Hidalgo, T.; Lozano, M.V.; Guillevic, M.; Simón-Vázquez, R.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; González-Fernández, Á.; Serre, C.; Alonso, M.J.; Horcajada, P. Heparin-engineered mesoporous iron metal-organic framework nanoparticles: Toward stealth drug nanocarriers. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ge BDi Li, J.H.; Wang, G.M. Three-Shell Cu@Co@Ni Nanoparticles Stabilized with a Metal-Organic Framework for Enhanced Tandem Catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Paul, A.K.; Deep, A. Nanocomposite of europium organic framework and quantum dots for highly sensitive chemosensing of trinitrotoluene. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimov, A.I.; Onushchenko, A.A.; Ekimov, A.I.; Onushchenko, A.A. Quantum size effect in three-dimensional microscopic semiconductor crystals. JETPL 1981, 34, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, R.; Nakahara, S.; Brus, L.E. Quantum size effects in the redox potentials, resonance Raman spectra, and electronic spectra of CdS crystallites in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, L.E. A simple model for the ionization potential, electron affinity, and aqueous redox potentials of small semiconductor crystallites. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 5566–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, R.; Petroff, P.M.; Leonard, D.; Fafard, S. Spatially resolved visible luminescence of self-assembled semiconductor quantum dots. Science 1995, 267, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Norberg, N.S.; Nguyen, Q.P.; Parker, J.M.; Gamelin, D.R. Magnetic quantum dots: Synthesis, spectroscopy, and magnetism of Co2+- and Ni2+-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13205–13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack Li, J.; Tsay, J.M.; Michalet, X.; Weiss, S. Wavefunction engineering: From quantum wells to near-infrared type-II colloidal quantum dots synthesized by layer-by-layer colloidal epitaxy. Chem. Phys. 2005, 318, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norberg, N.S.; Kittilstved, K.R.; Amonette, J.E.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Schwartz, D.A.; Gamelin, D.R. Synthesis of colloidal Mn2+:ZnO quantum dots and high-TC ferromagnetic nanocrystalline thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9387–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietryga, J.M.; Schaller, R.D.; Werder, D.; Stewart, M.H.; Klimov, V.I.; Hollingsworth, J.A. Pushing the band gap envelope: Mid-infrared emitting colloidal PbSe quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11752–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, P.V.; Norberg, N.S.; McNally, K.E.; Gamelin, D.R. Colloidal transition-metal-doped ZnO quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 15192–15193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbousi, B.O.; Rodriguez-Viejo, J.; Mikulec, F.V.; Heine, J.R.; Mattoussi, H.; Ober, R.; Jensen, K.F.; Bawendi, M.G. (CdSe)ZnS Core−Shell Quantum Dots: Synthesis and Characterization of a Size Series of Highly Luminescent Nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 9463–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xiao, M. Modification of spontaneous emission from CdSe/CdS quantum dots in the presence of a semiconductor interface. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoto, A.; Maenosono, S.; Yamaguchi, Y. Oscillating fluorescence in an unstable colloidal dispersion of CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8916–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tablero, C. Energy levels in self-assembled quantum arbitrarily shaped dots. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 064701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, P.; Bleszynski, A.C.; Westervelt, R.M.; Huang, J.; Walls, J.D.; Heller, E.J.; Hanson, M.; Gossard, A.C. Imaging a single-electron quantum dot. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wuister, S.F.; Koole, R.; De Donegá, C.M.; Meijerink, A. Temperature-dependent energy transfer in cadmium telluride quantum dot solids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 5504–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarillo-Herrero, P.; Kong, J.; Van Der Zant, H.S.J.; Dekker, C.; Kouwenhoven, L.P.; De Franceschi, S. Electronic transport spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 156802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wei, S.H.; Wang, L.W. Stability of the DX- center in GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 185501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Han, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Q. In situ synthesis and photoluminescence of QD-CdS on silk fibroin fibers at room temperature. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 025601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, P.K.; Viswanatha, R.; Daniels, S.M.; Pickett, N.L.; Smith, J.M.; O’Brien, P.; Sarma, D.D. Investigation of the internal heterostructure of highly luminescent quantum dot-quantum well nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y. High photoluminescence quantum yield of TiO2 nanocrystals prepared using an alcohothermal method. Luminescence 2007, 22, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Shao, C.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Chu, X.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Zhang, B.X. Photoluminescence properties of highly dispersed ZnO quantum dots in polyvinylpyrrolidone nanotubes prepared by a single capillary electrospinning. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ge, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, S. Labeling of BSA and imaging of mouse T-lymphocyte as well as mouse spleen tissue by L-glutathione capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence 2010, 25, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakada, Y.; Cui, B. Real-time visualization of axonal transport in neurons. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 670, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, X.; Tan, M. Highly fluorescent carbon dots for visible sensing of doxorubicin release based on efficient nanosurface energy transfer. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, S.; Fujioka, K.; Futamura, Y.; Manabe, N.; Hoshino, A.; Yamamoto, K. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory drug-conjugated silicon quantum dots: Their cytotoxicity and biological effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.Y.; Shabani, F.; Dwek, M.V.; Seifalian, A.M. Conjugation of quantum dots on carbon nanotubes for medical diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, B.R.; Lee, H.J.; Shannon, K.B.; Winiarz, J.G.; Wang, T.C.; Chiang, H.-J.; Huang, Y.-W. Nona-arginine facilitates delivery of quantum dots into cells via multiple pathways. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 948543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paesano, L.; Perotti, A.; Buschini, A.; Carubbi, C.; Marmiroli, M.; Maestri, E.; Iannotta, S.; Marmiroli, N. Markers for toxicity to HepG2 exposed to cadmium sulphide quantum dots; damage to mitochondria. Toxicology 2016, 374, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.H.; Shiao, N.H.; Lu, P.Z. CdSe quantum dots induce apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells via mitochondrial-dependent pathways and inhibition of survival signals. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 167, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tang, M. Toxicity of quantum dots on target organs and immune system. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Metal−Organic Frameworks: Why Make Them Small? Small Struct. 2022, 3, 2100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Kong, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, N.; Bu, X.H. Recent Progress of Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks in Synthesis and Battery Applications. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Suh, M.P. Redox-active porous metal-organic framework producing silver nanoparticles from AgI ions at room temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieter, W.J.; Taylor, K.M.L.; Lin, W. Surface modification and functionalization of nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for controlled release and luminescence sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9852–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.G.; Su, C.Y.; Lu, T.B.; Jiang, L.; Chen, J.M. Two stable 3D metal-organic frameworks constructed by nanoscale cages via sharing the single-layer walls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Pashow, K.M.L.; Della Rocca, J.; Xie, Z.; Tran, S.; Lin, W. Postsynthetic modifications of iron-carboxylate nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for imaging and drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14261–14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieter, W.J.; Taylor, K.M.L.; An, H.; Lin, W.; Lin, W. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks as potential multimodal contrast enhancing agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9024–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houk, R.J.T.; Jacobs, B.W.; Gabaly FEl Chang, N.N.; Talin, A.A.; Graham, D.D.; House, S.D.; Robertson, I.M.; Allendorf, M.D. Silver cluster formation, dynamics, and chemistry in metal-organic frameworks. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3413–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.M.L.; Rieter, W.J.; Lin, W. Manganese-based nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14358–14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Furuta, T.; Li, J. Theoretical assessment of the elastic constants and hydrogen storage capacity of some metal-organic framework materials. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 084714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrusseng, D.; Daniel, C.; Gaudillère, C.; Ravon, U.; Schuurman, Y.; Mirodatos, C.; Dubbeldam, D.; Frost, H.; Snurr, R.Q. Heats of adsorption for seven gases in three metal-organic frameworks: Systematic comparison of experiment and simulation. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7383–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Grzywa, M.; Nayek, H.P.; Dehnen, S.; Senkovska, I.; Kaskel, S.; Volkmer, D. A cubic coordination framework constructed from benzobistriazolate ligands and zinc ions having selective gas sorption properties. Dalton Trans. 2009, 33, 6487–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, C. Electrostatic-field-induced enhancement of gas mixture separation in metal-organic frameworks: A computational study. Chemphyschem 2006, 7, 1417–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C.; Ricchiardi, G.; Regli, L.; Bonino, F.; Damin, A.; Lillerud, K.-P.; Bjorgen, M.; Zecchina, A. Electronic and vibrational properties of a MOF-5 metal–organic framework: ZnO quantum dot behaviour. Chem. Commun. 2004, 20, 2300–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llabrés i Xamena, F.X.; Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Applications for Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as quantum dot semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buso, D.; Jasieniak, J.; Lay, M.D.H.; Schiavuta, P.; Scopece, P.; Laird, J.; Amenitsch, H.; Hill, A.J.; Falcaro, P. Highly Luminescent Metal–Organic Frameworks Through Quantum Dot Doping. Small 2012, 8, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ebrahimnia, M.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Keçili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. Microporous metal–organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, D.; Liao, W.; Li, S.; Huang, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, R.; Xu, J. A hydrostable anionic zinc-organic framework carrier with a bcu topology for drug delivery. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5244–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Qin, L.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Luo, C.; Huang, H.; Ma, D.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. A hydroxyl-functionalized 3D porous gadolinium-organic framework platform for drug delivery, imaging and gas separation. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 289, 121544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal nanocarriers: A review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, F.U.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.R.; Gowtham, K.; Sheikh, A.; Parvez, S.; Dandela, R.; Kesharwani, P. Recent advances and future prospective of hybrid drug delivery systems. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials, Hybrid Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sivaram, N.; Nath, B.; Khan, N.A.; Singh, J.; Ramamurthy, P.C. Metal organic frameworks for wastewater treatment, renewable energy and circular economy contributions. Npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Nian, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, B.; Cheng, S.; Cao, C. Encapsulation of colloidal semiconductor quantum dots into metal-organic frameworks for enhanced antibacterial activity through interfacial electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Gao, G.; Zheng, L.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. Encapsulation of strongly fluorescent carbon quantum dots in metal-organic frameworks for enhancing chemical sensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Lin, C.; Hu, Y.; Zan, H.; Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Zou, H.; Li, Y. Sensitive fluorescence biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein detection in cold-chain food products based on DNA circuit and g-CNQDs@Zn-MOF. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2022, 169, 114032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, J.; Jie, G.; Zhou, H. Potential-Resolved Ratio Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor Based on Perylene Diimide-MOF and DNA Nanoflowers-CdS Quantum Dots for Detection of Dual Targets. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 13690–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, D.; Jiang, F.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Q. Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS QDs encapsulated in IRMOF-3 for sensitive detection of human epithelial protein 4. Talanta 2025, 282, 127052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrgou, A.; Akouchekian, M. The importance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes mutations in breast cancer development. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran. 2016, 30, 369. [Google Scholar]
- Khushk, M.; Khan, A.; Rehman, A.; Sheraz, S.; Tunio, Y.M.; Rehman, K.; Rehman, D.; Ahmed, M.; Abbas, K.; E Khan, M. The Role of Tumor Markers: Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Cancer Antigen 15-3 in Patients with Breast Cancer. Cureus 2021, 13, e16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, V.M.; Sundar, R.; Raman, D.; Ribeiro, J.R.; James, N.E.; Chichester, C. Beyond the Biomarker: Understanding the Diverse Roles of Human Epididymis Protein 4 in the Pathogenesis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Altintas, Z.; Devi, K.S.S.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemiluminescence biosensors for detection of cancer biomarkers in biofluids: Principles, opportunities, and challenges. Nano Today 2023, 50, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Yao, X.; Ma, K.; Niu, X.; Grothe, J.; Xu, Q.; Liu, L.; Kaskel, S.; Zhu, Y. Metal-Organic Framework/Graphene Quantum Dot Nanoparticles Used for Synergistic Chemo- and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Li, Z.; Qiu, S.; Dai, C.; Wu, S.; Zheng, X.; Guan, M.; Gao, F. Octahedral Pt-MOF with Au deposition for plasmonic effect and Schottky junction enhanced hydrogenothermal therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystofiak, E.S.; Matson, V.Z.; Steeber, D.A.; Oliver, J.A. Elimination of tumor cells using folate receptor targeting by antibody-conjugated, gold-coated magnetite nanoparticles in a murine breast cancer model. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 431012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, Q.A.; Manna, L. What Defines a Halide Perovskite? ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assirey, E.A.R. Perovskite synthesis, properties and their related biochemical and industrial application. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.A. Perovskite: Name Puzzle and German-Russian Odyssey of Discovery. Helv. Chim. Acta 2020, 103, e2000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, T.; Chen, D.; Meng, J.; Lu, X.; Gu, Z.; He, Q. Local generation of hydrogen for enhanced photothermal therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, D.W.; Li, C.X.; Zou, M.Z.; Yu, W.Y.; Liu, M.D.; Peng, S.-Y.; Zhong, Z.-L.; Zhang, X.-Z. Hydrogen gas improves photothermal therapy of tumor and restrains the relapse of distant dormant tumor. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Du, P.; Zhang, L.; Lei, J. Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) Hybrid as a Tandem Catalyst for Enhanced Therapy against Hypoxic Tumor Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7808–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, C.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Zhou, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Du, M. A γ-cyclodextrin-based metal-organic framework embedded with graphene quantum dots and modified with PEGMA via SI-ATRP for anticancer drug delivery and therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 20956–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooresmaeil, M.; Namazi, H.; Salehi, R. Simple method for fabrication of metal-organic framework within a carboxymethylcellulose/graphene quantum dots matrix as a carrier for anticancer drug. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanpouraghdam, Y.; Pooresmaeil, M.; Namazi, H. In-vitro evaluation of the 5-fluorouracil loaded GQDs@Bio-MOF capped with starch biopolymer for improved colon-specific delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rickel, A.; Smith, S.; Hong, Z.; Wang, C. “Non-cytotoxic” doses of metal-organic framework nanoparticles increase endothelial permeability by inducing actin reorganization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 634, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, C.; Papageorgiou, E.; Harstrick, A.; Bokemeyer, C.; Mugge, A.; Stahl, M.; Wilke, H.; Poliwoda, H.; Hiddemann, W.; Köhne-Wömpner, C.H.; et al. Cardiotoxicity of 5-Fluorouracil in Combination with Folinic Acid in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancer 1993, 72, 2242–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, J.D.; Kaur, J.; Khodadadi, R.; Rehman, M.; Lobo, R.; Chakrabarti, S.; Herrmann, J.; Lerman, A.; Grothey, A. 5-fluorouracil and cardiotoxicity: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918780140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Das, T.K. Zwitterionic, Stimuli-Responsive Liposomes for Curcumin Drug Delivery: Enhancing M2 Macrophage Polarization and Reducing Oxidative Stress through Enzyme-Specific and Hyperthermia-Triggered Release. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 8, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Gharehaghaji, N.; Divband, B. Chitosan-coated iron oxide/graphene quantum dots as a potential multifunctional nanohybrid for bimodal magnetic resonance/fluorescence imaging and 5-fluorouracil delivery. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resen, A.K.; Atiroğlu, A.; Atiroğlu, V.; Guney Eskiler, G.; Aziz, I.H.; Kaleli, S.; Özacar, M. Effectiveness of 5-Fluorouracil and gemcitabine hydrochloride loaded iron-based chitosan-coated MIL-100 composite as an advanced, biocompatible, pH-sensitive and smart drug delivery system on breast cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 198, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Jin, S.; Xu, L.; Zhao, C.-X. Title: Development of High-Drug-Loading Nanoparticles Front Piece Development of High-Drug-Loading Nanoparticles. Chempluschem 2020, 85, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. High drug-loading nanomedicines: Progress, current status, and prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, N.; Pathak, R.; Samanta, S.; Sen Sarma, N. A comprehensive analysis of photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for the treatment of cancer. Process Biochem. 2025, 148, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Villani, R.M.; Wang, H.; Simpson, M.J.; Roberts, M.S.; Tang, M.; Liang, X. The role of cellular reactive oxygen species in cancer chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ma, S.; Xu, R.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, T.; Wang, Z.; Deng, H.; Yang, N.; Shen, Q. Smart biomimetic metal organic frameworks based on ROS-ferroptosis-glycolysis regulation for enhanced tumor chemo-immunotherapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.L.; Wong, R.S.M.; Lam, K.H.; Hung, L.K.; Wong, M.M.; Yung, L.H.; Ho, Y.-W.; Wong, W.-Y.; Hau, D.K.-P.; Gambari, R.; et al. The role of reactive oxygen species in the biological activity of antimicrobial agents: An updated mini review. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 320, 109023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, K.E.; Louie, A.; Zhou, L.; Seyhan, A.A.; Maxwell, A.W.; El-Deiry, W.S. Colorectal cancer extracellular acidosis decreases immune cell killing and is partially ameliorated by pH-modulating agents that modify tumor cell cytokine profiles. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, F.D.; Monferrer, D.; Penon, O.; Rivera-Gil, P. Regulatory pathways and guidelines for nanotechnology-enabled health products: A comparative review of EU and US frameworks. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1544393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Nanotechnology Guidance Documents. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/science-research/nanotechnology-programs-fda/nanotechnology-guidance-documents (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Food and Drug Administration. Drug Products, Including Biological Products, That Contain Nanomaterials Guidance for Industry Contains Nonbinding Recommendations; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bouffi, C.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Sundaram, N.; Goddard, G.R.; Wunderlich, M.; Brown, N.E.; Staab, J.F.; Latanich, R.; Zachos, N.C.; et al. In vivo development of immune tissue in human intestinal organoids transplanted into humanized mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoslowski, A.; An, M.; Penninger, J.M. Incorporating Immune Cells into Organoid Models: Essential for Studying Human Disease. Organoids 2023, 2, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, J. ChatMOF: An artificial intelligence system for predicting and generating metal-organic frameworks using large language models. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, D.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. Guiding the rational design of biocompatible metal-organic frameworks for drug delivery. Matter 2025, 8, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyebvu, N.; Lane, E.; Grisan, E.; Howes, P.D. Accelerating colloidal quantum dot innovation with algorithms and automation. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 6950–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).