Abstract
We suggest a new alternative model of positron origin in the Galaxy. It is shown in our model that interactions of the electromagnetic fields of colliding ions (ultraperipheral ion collisions) can contribute to the total production of Galactic positrons. The corresponding cross-section is estimated by using the Born approximation and the equivalent photon method. This process of ion collisions dominates in the range of subrelativistic energies and produces positrons with energies of several MeV. Despite its low efficiency, as it requires more than 0.1 erg to produce a single positron, this process may be an effective source of positrons in the Galactic medium.
1. Introduction
The positron puzzle of the 511 keV line emission is an enigma of the half-century, and its origin in the Galaxy has not been established yet, although several explanations have been suggested (see the recent reviews [1,2,3] and references therein). The most remarkable quasi-spherical feature of the 511 keV annihilation emission on the Galactic map is the so-called “bulge”, with the characteristic size of approximately – and the positrons annihilation rate of the order of .
One of the viable sources of Galactic positrons is electron–positron pair production in the collision of two real or virtual -ray photons. In particular, one can consider active [4] or extinct pulsars [5], jets of black holes (e.g., [6]) and binary systems. In Ref. [7], it was shown that low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs) can be responsible not only for the annihilating positrons in the Milky Way but also for the -ray excess observed from the inner part of the Galaxy. However, the amount of positrons that LMXBs can produce is uncertain.
Alternatively, positrons can be generated by the decay of unstable nuclei like 26Al, 56Co and 44Ti. The isotopes in question can be produced by cosmic ray interactions [8]; however, supernovae and novae are much more efficient sources of unstable nuclei [9]. In particular, it was shown that explosions of SNe Ia can produce enough 44Ti to supply enough positrons for the annihilation emission from the Galactic disk [10], yet it is not quite clear if emissions from the Galactic bulge can be explained in a similar way.
Another natural interpretation of the feature of positron annihilation could be the collisions of cosmic rays (CRs) in the Galactic center (GC) with the background gas proton-proton () collisions; see review [9]. These collisions of high-energy CRs produce pions (and therefore secondary -rays and positrons — see the estimates in Ref. [11]). The threshold of -collisions is above of about 290 MeV; therefore, secondary positrons are generated with energies above 30 MeV. If one accepts this interpretation of the positron origin in the GC, the positrons should be cooled down from the initial to thermal energy by Coulomb energy losses and produce a narrow line of 511 keV there.
Two complications of the positron model with a CR origin follow from the observations. One of the problems is an estimation of a -ray flux from the GC derived from the positron GC luminosity, which is two orders of magnitude higher than that observed in the GC (see [12]). The problem can be avoided, however, if periodic tidal disruptions produce the time-variable positron emission by the central black hole Sgr A* [13,14].
The second problem comes from the analyses in Refs. [15,16,17], where it is argued that the threshold of positron injection cannot exceed several MeV as otherwise, the in-flight annihilation flux of MeV positrons would exceed observations. Let us notice, however, that observations of the -ray spectrum in the MeV range are not reliable (see, e.g., [3]), so the question stays open.
Here, we suggest an alternative model of positron production by CRs less restricted by -ray production. We consider pair creation through the interaction of virtual photons of electric fields of colliding charged particles, i.e.,ultraperipheral collisions. Unlike strong collisions, the ultraperipheral collisions may involve subrelativistic nuclei, and those nuclei produce positrons of relatively low energies.
In what follows, we apply the concept of the ultraperipheral collision processes to high-energy astrophysics, where those processes have not been considered yet, and define the parameters of CR sources that may generate low-energy positrons.
2. Ultraperipheral Electron–Positron Pairs from Collisions
2.1. General Review
Previous reviews (see, e.g., [18,19]) have explored various mechanisms for the production of electron-positron () pairs in ultraperipheral collisions. Among the mechanisms considered, the free–free processes have the largest cross-sections at all energies, except for those at quite low energies. In these processes, both the electron and the positron are created by the collision of two virtual quanta in the electromagnetic fields of colliding protons and fly away freely from their production point. The cross-sections for the direct production of the electron and positron in their bound state, positronium, are relatively small. The bound-free processes, where the electron becomes bound to the proton and forms the hydrogen atom, have even much smaller cross-sections at all -collision energies and are further damped by an additional factor of the order of , where is the electromagnetic coupling contstant. At considerably low -collision energies, the dipole and quadrupole one-photon mechanisms of emissions can become more significant than the free–free processes, but the cross-sections corresponding to the emissions are negligible for further estimates. Therefore, the further discussion focuses on the free–free processes.
In the context of astrophysical applications, it is worth noting that protons with relatively low energies are the primary component of cosmic ray spectra. Therefore, it is crucial to estimate the corresponding -collision cross-sections over a wide energy interval including both nonrelativistic and relativistic energies. Two approaches are used here to address this problem: the Born approximation and the method of equivalent photons. Both approaches work well in an ultrarelativistic regime, while to obtain the cross-sections at lower energies, one must extrapolate the corresponding expressions. These extrapolations are shown in Figure 1 and are considered in the rest of this Section.
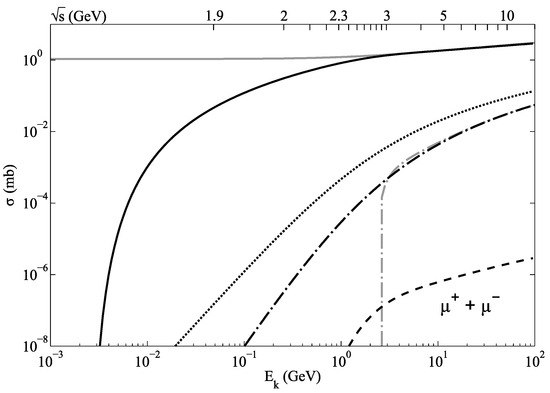
Figure 1.
The total cross-section of ultraperipheral proton–proton interactions interpolated from relativistic energies to the threshold of production as a function of the kinetic energy, , of the projectile proton in the target rest system and as a function of the proton–proton collision center-of-mass (c.m.) energy, , , where is a proton mass. The lines correspond to the calculations based on Refs. [20,21] (dotted line), [22] (black dashed-dotted), [23] (gray dashed-dotted), [24] (gray), our estimate (solid), and for muon pairs (dashed); see text for details. All of the lines tend to the same asymptotic () limit given by Equation (1). The projectile velocity is . The kinematic threshold of pair creation in the target rest system is considerably low, MeV (for the dimensionless threshold velocity, , of the leptons in their c.m.), where m is the lepton mass.
2.2. The Born Approximation
In 1934, Lev Landau and Evgeny Lifshitz applied [20,21] the Born approximation of quantum field theory to perturbatively treat the creation of free–free pairs by two virtual -quanta from the electromagnetic fields of colliding high-energy ions. It was discovered that the total ultraperipheral pair production cross-section is proportional to the squared Compton wavelength, , of electrons, where is the classical electron radius, and increases rapidly with increasing ion energy, as , where is the ion mass and represents the Lorentz factor of the projectile proton in the target rest system (see Equation (97.5) in Ref. [21]):
where the charge numbers of the projectile and target ions are denoted as and , respectively. Here and below, if not specified explicitly, is assumed, with ℏ the reduced Planck’s constant and c the speed of light, meaning that masses and frequencies are measured in energy units. The dependence (1) is shown in Figure 1 by the dotted line.
The asymptotic-energy dependence is more rapid than the limit imposed on the cross-sections of strongly interacting particles by the Froissart theorem [25]. The numerical factor, , in the total cross-section (1) compensates for the relatively small values for heavy ions with a large enough charge , where e denotes the elementary charge. Therefore, the ultraperipheral production of pairs (as well as muon , and other lepton pairs) in heavy ion collisions can become the dominant mechanism at considerably high energies and has already been extensively studied at colliders [26,27,28].
At low enough energies, the logarithmic corrections to Equation (1) become crucial. For instance, as calculated by Giulio Racah [23], in Equation (1) should be replaced by
where and is the Riemann zeta function; see Figure 1.
The Racah formula (2) displays significant cancellations, and the negative term can be combined [18,19] with the asymptotically leading term. As a result, the logarithmic term behaves like with a factor ; in some cases, this factor is estimated to be about 0.34 [29].
A straightforward interpolation of the Racah formulae (2) to lower energies is, however, not feasible, as it results in an abrupt fall off of the cross-section, as shown in Figure 1; for more details, see Figure 1 in Ref. [22].
The low-energy behavior of the cross-section was calculated in Refs. [22,30]. At low nonrelativistic velocities, , the cross-section behaves mainly as :
However, near the kinematic threshold of 2.05 MeV, the terms proportional to appear [30], while at the boundary of the nonrelativistic region, the -terms are found to present.
In Ref. [22], an attempt was made to interpolate between the nonrelativistic and relativistic regions through the sub-relativistic energies; the smoothed outcome of these calculations is shown in Figure 1.
It is worth noting that the logarithmic Racah terms in Equation (2) (and then the coefficient a) do not depend on the masses (Compton wavelengths) of the produced leptons. As an example, the cross-section of -pair production, which scales as the inverse lepton masses compared to -pairs, is displayed in Figure 1 by dashed line.
Let us note that we agree with the assessment of the authors of the earliest review [18] that the results obtained from the Born approximation can be considered as “lower-bound estimates” for the values of the ultraperipheral cross-sections.
2.3. The Equivalent Photon Approximation
The formula for the intensity of the electromagnetic field created by a moving charged object was derived by Enrico Fermi in 1924 [31,32]. In 1934, this formula was utilized by Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker [33] and Evan James Williams [34] to develop the method of equivalent photons, which today is commonly used in studies of ultraperipheral interactions. This method has been successfully applied to analyze experimental results from the ATLAS Collaboration on production at TeV-energies [26,27].
The distribution of equivalent photons generated by a moving nucleus with the charge is a key component of this method. These photons carry quite a small fraction x of the nucleon energy and, when integrated over the transverse momentum up to a certain value (see, e.g., [21,26]), lead to the flux given by
Equation (4) straightforwardly demonstrates that soft photons with relatively small fractions x of the nucleon energy dominate, with -factors in front of the ln-term and in its argument. The ultraperipherality parameter varies in different approaches and depends on the charges, sizes and impact parameters of the colliding objects (form factors and absorptive factors). The physical meaning of the u-parameter is the ratio of the maximum adoptable transverse momentum to the nucleon mass. The impact parameters cannot be measured directly but must exceed the sum of the radii of the colliding ions to avoid strong (quantum chromodynamics, QCD) interactions. This requirement can be restated as a bound on the exchanged transverse momenta, ensuring that the objects are not destroyed but only slightly deflected by the collision, and no excitations or nuclear transitions occur. The bound depends on the internal structure of the colliding objects, i.e., on the forces inside them. Protons can withstand larger transverse momenta compared to those in heavy ions due to the stronger forces inside the protons.
According to the equivalent photon approximation [21], the -cross-section can be expressed as the convolution of the densities, (4), of the photons carrying the shared -fraction of the proton energies with the cross-section of pair production, , as
The integration of Equation (5) with photon fluxes expressed as in Equation (4) gives the following expression for the differential cross-section of pair production (for more details, see, e.g., [28]):
where is the electron mass, s is the collision center-of-mass (c.m.) energy squared, and is the dimensionless velocity of leptons in their c.m.
Equation (6) contains a large ratio of proton and electron masses in the argument of the logarithmic term. It appears after integration over in Equation (5) with account of in logarithms of Equation (4). Physically, it corresponds to rather large phase space available for light lepton pairs even at comparatively low energies of protons. This large factor determines slower approach to asymptotics and larger cross sections at lower energies. Therefore, one can consider Equation (6) as an upper bound of the ultraperipheral cross section.
Let us remind that small prefactor a in Racah corrections (2) leads to severe problems at low energies. It is inessential for heavy lepton pairs because their masses are close to hadronic ones.
To obtain an upper-bound estimate of the total cross-section of the free–free ultraperipheral processes, Equation (6) has been integrated over all velocities from zero to the limiting velocities determined by the argument of the logarithm equal to 1. The resulting value [24] is presented in Figure 1 by the gray line. However, the interpolation of this relativistic result to lower energies shown in Figure 1 is invalid near the threshold energy where it must tend to zero.
To produce a more accurate expression for the cross-section, we use a slightly different formula for the photon flux, which accounts for the Sachs form factors [27]. This formula does not include the random parameter .
In addition, to consider energy conservation, which is of a particular importance at nonrelativistic energies, additional limits were imposed on the photon virtuality. It was assumed that the energy of a virtual photon cannot exceed the kinetic energy of the proton under whatever circumstances. Therefore, when calculating the spectrum of virtual photons by using Equation (1) from Ref. [27], we restricted the total photon energy, , via , where is the transverse component of a photon momentum and is the proton mass.
The corresponding cross-section is represented by the solid line in Figure 1. At high energies, the calculation is nearly identical to the results of Equation (6), but drops sharply at nonrelativistic energies due to the imposed virtuality dependence. This cross-section is used in the calculations in Section 3 below.
Using expressions from Ref. [27], we obtained differential cross-sections of positron production as a function of the kinetic energy, , of positrons in the laboratory frame. We took into account that the c.m. of the pair moves with the velocity relative to the c.m. of the colliding protons; here, . We also assumed that the distribution of positrons is isotropic in the c.m. of . Therefore,
where is the angle between the direction of the incoming proton and positron in the c.m. of the pair. In addition, to be expressed through , and .
The results of our calculations of the differential cross-section are presented in Figure 2 for various kinetic energies of the protons. As one can see, even for relativistic protons, positrons are mainly produced with energies of a few MeV. To date, there are still no direct measurements for ultraperipheral processes at low-energy accelerators.
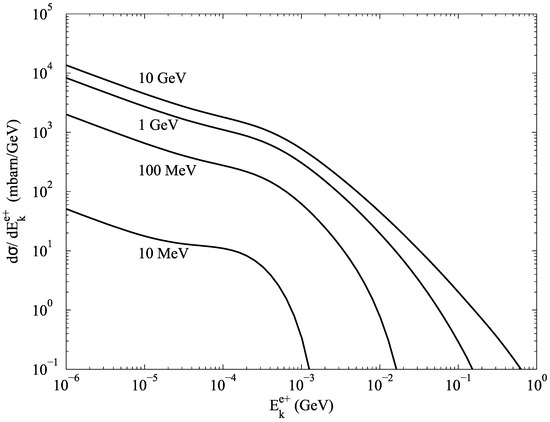
Figure 2.
Differential cross-section of positron production in ultraperipheral collisions of protons as function of kinetic energy, , of positrons in the laboratory frame. Different curves correspond to different kinetic energies of parent protons in the laboratory frame.
3. Positron Production in the Galaxy
In this Section, we apply the calculated cross-section of the ultraperipheral electron–positron production to processes in the Galaxy. In astrophysical environments, fast nonthermal particles are generally mixed with thermal ones and interact with each other. This interaction involves not only ultraperipheral processes and, hence, different byproducts are expected. The byproducts can set some additional restrictions on the process, as, e.g., byproduct of -ray emissions mentioned in Section 1 which can rule out strong interactions as sources of Galactic positrons.
Thus, to test the viability of the ultraperipheral process, one needs to answer the following questions:
- What power sources of fast particles need to be supplied in order to produce sufficient amounts of positrons?
- How does injecting this many fast particles affect the background gas?
- What spectrum of byproduct emission is expected?
To provide the estimations necessary to answer these questions, one needs to specify how many positrons should be produced. The Galactic 511-keV annihilation emission is primarily associated with the central source, Galactic bulge and Galactic disk. In Ref. [35], it is estimated that the annihilation rates in these regions to be approximately of the order of , and , respectively. Therefore, a positron production rate of is a suitable reference point for our model.
3.1. Power of Sources of Primary Particles
To identify the potential sources of the nonrelativistic particles responsible for positron production through the ultraperipheral processes, one must determine the total kinetic energy required for positron production. Let us assume here that quite a small amount of fast (nonrelativistic or mildly relativistic) ions interact with the background gas. Unlike in colliders, in astrophysical environments, the concentration of cosmic rays is often considerably smaller than the concentration of background particles; hence, the collision of two fast enough particles has exceptionally low probability.
Up to this point, only pair production was considered. However, charged particles propagating in the background medium also experience other types of interactions and may disperse energy more efficiently during these interactions as compared to pair production.
Nonrelativistic ions mainly lose energy through elastic collisions with ambient electrons (Coulomb losses) or through the ionization (ionization losses) of background neutral atoms. These two processes have a substantially larger cross-section as compared to that of the lepton pair production; therefore, before a single lepton pair is born, a number of elastic collisions happen.
To estimate the ratio between the energy losses and lepton pair production, it is necessary to specify a distribution function for protons. It is worth noting that the energy losses of nonrelativistic ions decrease as particle energy increases while the cross-section of positron production increases. Therefore, to maximize the positron production efficiency, it is necessary to concentrate particles at high energies, resulting in a harder particle spectrum. The hardest stationary energy spectrum possible is described by
where represents proton energy losses due to Coulomb collisions and is a cut-off energy parameter. The spectrum (8) corresponds to the case when ions are injected with energies of the order of while the rest of the spectrum is formed by the energy losses. Therefore, the spectrum (8) has the maximum concentration possible of particles with energy.
is the key parameter of the spectrum. This parameter allows us to restrict contributions from strong interactions between protons since strong interactions have a threshold energy. A cut-off in the spectrum can appear due to the following reasons. One can assume that the maximum energy in the spectrum is restricted by the acceleration time in the source of nonrelativistic particles. When the energy of protons reaches , the protons start escaping from the acceleration site, and, hence, an acceleration above becomes ineffective.
If the source is transient, one can assume that the lifetime of the source equals the protons’ acceleration time up to , and, therefore, the protons stop being accelerated beyond that energy. Or alternatively, one can assume that in some powerful event (such as tidal disruption), a bulk of protons is ejected with velocities of around . The upper velocity of the bulk restricts the cut-off energy.
If one assumes that the energy spectrum is described by Equation (8), the average energy lost by the charged particles per production of one positron can be estimated as
Since , where n is the ambient density, the energy value is proportional to the average charge of the background particles, , and is independent of both the ambient density and the charge of the fast particles. Figure 3 illustrates the dependence of W on in collisions. For comparison, we also show the estimates of the energy necessary to produce one positron via strong interactions by using the cross-sections from Ref. [36].
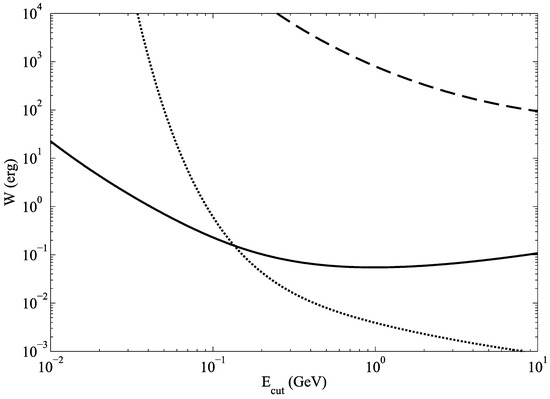
Figure 3.
Energy required to produce one positron by proton–proton collisions as function of cut-off energy in ultraperipheral process according to Born approximation (dashed line), equivalent photon method (solid line) and in strong interactions (dotted line). See text for details.
As one can see, if the extrapolated results of the Born approximation are valid, the ultraperipheral process is negligible in comparison to other sources of Galactic positrons for any value of .
Under equivalent photon approximation, however, ultraperipheral processes dominate if 100 MeV. And, to produce a single positron through the ultraperipheral collisions with background protons, fast protons should spend at least 0.1 erg on elastic collisions with electrons. Therefore, to produce positrons per second, one must assume that the source of the fast particles provides at least erg/s in the form of protons accelerated up to 100 MeV (or to a velocity of about 0.4).
How big is erg/s? Supernova explosions are one of the possible sources of fast particles. Assuming that one explosion occurs every 10 years within the Galaxy and produces about erg, the average energy production is approximately of , which is comparable with the estimates made here. However, it is unlikely that supernovae convert all of their kinetic energy into 100 MeV particles effectively. Other sources of fast particles, such as pulsar wind nebulae or active Galactic nuclei, may also be considered.
The tidal disruptions of stars by a central black hole can produce up to erg/s. However, the majority of fast particles produced during the disruption may have energy considerably lower than 100 MeV (see, e.g., [37]).
Injecting as much as erg/s in the form of fast protons can significantly affect the background medium. Indeed, as mentioned just above, most of the energy of nonrelativistic protons is spent on the ionization or Coulomb collisions. Therefore, the current ionization rate of molecular hydrogen in the central region of the Galaxy presents another limitation. Observations indicate that the ionization rate of molecular hydrogen reaches a value of ∼ [38]. If one assumes that the total mass of hydrogen in the region is of the order of solar masses [39] and that each ionization requires approximately 50 eV, we can estimate that the central region absorbs about erg/s. This suggests that the interaction of nonrelativistic Galactic cosmic rays with diffuse molecular gas can only contribute to about 10% of the total positrons production. Other sources of protons, such as those mentioned in this Section, may be required to account for the observed positron production rates in the Galaxy.
We also estimate how ultraperipheral processes affect the positrons production by Galactic cosmic rays if the spectrum of the cosmic rays is approximately the same through the Galaxy (and coincides with the local spectrum in the Solar System). To describe the spectrum, we use the corresponding expression from Ref. [40], where two cases are considered: case “L”, which reproduces Voyager 1 data [41], and case “H”, which sets the upper limit on the amount of nonrelativistic protons based on ionization data in the vicinity of the Solar System.
For local spectra of cosmic rays, we obtain the following production rates: for case “L”, the rate equals , and for case “H”, this rate equals . For comparison, the production rates for the same spectra via strong interactions are and , respectively. Therefore, the contribution of ultraperipheral processes to positron production by Galactic cosmic rays is quite small and one needs to consider additional powerful sources of nonrelativistic protons. These sources should be located at a large distance from the Solar System for their contribution to the local cosmic ray spectrum to be negligible.
In central bulge, the local cosmic ray spectrum can be produce about positrons per second via ultraperipheral processes. Therefore, to match the observations, the local spectrum of nonrelativistic cosmic rays in the GC should be enhanced by a factor of .
3.2. Byproduct -Ray Emission
As mentioned in Section 1, the production of positrons by cosmic rays is accompanied by -ray emission. Most of the emission comes from the decay of neutral pions born by strongly interacting protons and from the annihilation of nonthermal positrons.
To verify how restrictions on -ray emission affect our model, we calculated the expected spectrum of gamma-ray emission from the GC assuming that all annihilating positrons are produced by cosmic ray protons. Like in Section 3.1 let us assume that the spectrum of cosmic ray protons is described by Equation (8) with the cut-off energy, , being a free parameter.
The production rate of the positrons is estimated as
and the spectrum of the positrons can be estimated as
where the differential cross-sections, , of positron production via ultraperipheral processes are described by Equation (7) and the differential cross-sections, , of positron production via strong interactions are taken from Ref. [36]. The energy losses, , of positrons include ionization losses and bremsstrahlung losses in a neutral medium. If one assumes that the cooling of nonthermal positrons happens in an ionized medium, the byproduct -ray emission can be slightly reduced; see, e.g., [17].
To obtain the normalization of the proton spectrum, let us assume that all the positrons in the GC are born in proton collisions, i.e., that
Using the known proton spectrum and the spectrum of positrons, we estimate the expected -ray emission from the direct annihilation of nonthermal positrons [42] and from the decay of neutral pions [43]. The results are shown in Figure 4.
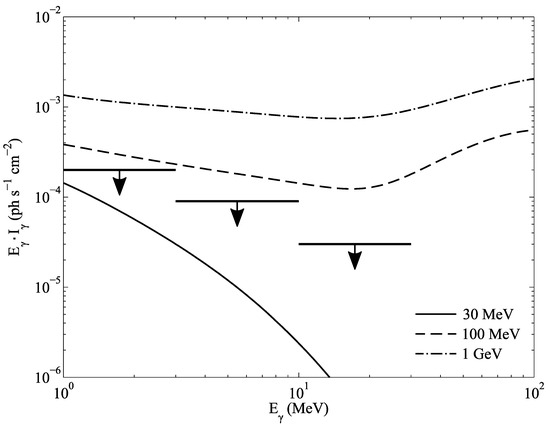
Figure 4.
Energy spectrum of -ray emission produced by particle interactions in the Galactic center assuming that positron production rate is for different proton cut-off energies, as indicated. The limits from the experimental data are shown by the horizontal lines and indicated by the arrows. denotes the energy spectrum of -ray emission here.
The Beacom–Yüksel criterion [16] assumes that the emission from charged particles cannot exceed statistical errors of the measurements of the diffuse -ray flux observed by COMPTEL experiment [44]. We indicate these restrictions with thick horizontal lines in Figure 4.
One can see that if the cut-off energy is 1 GeV and, hence, the production of positrons is dominated by strong interactions, -ray emission significantly exceeds the observation limits. This is consistent with the findings in Refs. [16,17]. However, by lowering the cut-off energy, one can reduce the -ray emission.
For a cut-off energy of the order of 100 MeV, the -ray emission exceeds the limits only by a factor of 2–3. And, the most significant contributor to the excess is the decay of neutral pions. That can be offset by assuming different shapes of the proton spectrum, e.g., with a sharper cut-off.
At a cut-off energy of 30 MeV, -ray emission falls under the experimental restrictions. For this spectrum contribution of strong interactions is negligible, and all positrons are born with low energies. However, this spectrum requires more energy for positron production see Figure 3.
4. Conclusions
The ultraperipheral process of -pair production is a promising contributor to the total positron production of the Galaxy. This mechanism involves the interaction of nonrelativistic nuclei with a background medium, resulting in the production of electron–positron pairs.
Most of the positrons produced in the ultraperipheral process are mildly relativistic, generally with energies of less or about several MeV. Therefore, they produce significantly less -ray emissions in the MeV energy range as compared to, e.g., positrons produced from the decay of charged pions.
Due to its quite low cross-section, the ultraperipheral process only dominates when the parent protons have kinetic energy less than the threshold of strong proton–proton interactions. A low value of the cross-section of the process results in significant energy necessary to produce a single positron (about 0.1–1 erg per one positron) since the energy of nonrelativistic protons is mostly spent on the ionization of the background medium. That sets stringent restrictions on the potential sources of the nonrelativistic protons as well as on the regions of the Galaxy, where the ultraperipheral production of positrons may take place.
Assuming that the spectrum of protons in the Galaxy does not differ much from their local spectrum, the ultraperipheral process can boost positron production by Galactic cosmic rays by only 20–25%. Therefore, for the process to be significant, we need to take into account additional powerful sources of nonrelativistic protons whose contribution to the local cosmic ray spectrum is quite small. The sources can either be located far from the Solar System or were active in the past and today are in a quiescent state.
Nonrelativistic particles do not travel far from their production sites. Therefore, the spatial morphology of the 511-keV annihilation emission should to some extent mimic the spatial distribution of sources of nonrelativistic protons. As the Galactic center shows the enhanced ionization of molecular hydrogen as compared to other parts of the Galaxy, the density of the nonrelativistic protons there should also be higher. That may explain why 511-keV emissions are significantly enhanced in the Galactic center.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.D.; methodology, V.D. and I.D.; validation, D.C., V.D. and I.D.; formal analysis, D.C.; data curation, D.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.C. and I.D.; writing—review and editing, D.C, V.D. and I.D.; visualization, D.C.; supervision, I.D.; project administration, I.D.; funding acquisition, I.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Russian Science Foundation (RSF) grant number 23-22-00068 (https://rscf.ru/en/project/23-22-00068/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Vladimir G. Terziev for help with the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Churazov, E.; Bouchet, L.; Jean, P.; Jourdain, E.; Knödlseder, J.; Krivonos, R.; Roques, J.P.; Sazonov, S.; Siegert, T.; Strong, A.; et al. INTEGRAL results on the electron-positron annihilation radiation and X-ray & Gamma-ray diffuse emission of the Milky Way. New Astron. Rev. 2020, 90, 101548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, F.; Virgilli, E.; Guidorzi, C.; Rosati, P.; Diehl, R.; Siegert, T.; Fryer, C.; Amati, L.; Auricchio, N.; Campana, R.; et al. Understanding the origin of the positron annihilation line and the physics of supernova explosions. Exp. Astron. 2021, 51, 1175–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, T. The Positron puzzle. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2023, 368, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pun, C.S.J.; Cheng, K.S. Could electron-positron annihilation lines in the Galactic center result from pulsar winds? Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 446, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomin, Y.N.; Chernyshov, D.O.; Sob’yanin, D.N. Extinct radio pulsars as a source of subrelativistic positrons. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.P.; Dermer, C.D. Interpretation of the gamma-ray bump from Cygnus X-1. Astrophys. J. 1988, 325, L39–L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.; Calore, F.; Storm, E.; Weniger, C. Galactic binaries can explain the Fermi Galactic centre excess and 511 keV emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3826–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pshirkov, M.S. Positron excess in the center of the Milky Way from short-lived β+ emitting isotopes. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantzos, N.; Boehm, C.; Bykov, A.M.; Diehl, R.; Ferrière, K.; Guessoum, N.; Jean, P.; Knoedlseder, J.; Marcowith, A.; Moskalenko, I.V.; et al. The 511 keV emission from positron annihilation in the Galaxy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 1001–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, R.M.; Ruiter, A.J.; Seitenzahl, I.R.; Panther, F.H.; Sim, S.; Baumgardt, H.; Möller, A.; Nataf, D.M.; Ferrario, L.; Eldridge, J.J.; et al. Diffuse Galactic antimatter from faint thermonuclear supernovae in old stellar populations. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 0135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoyan, A.M. Relativistic neutrons in active galactic nuclei. II. Gamma-rays of high and very high energies. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 257, 476–488. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.S.; Chernyshov, D.O.; Dogiel, V.A. Annihilation emission from the Galactic black hole. Astrophys. J. 2006, 645, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, K.S.; Chernyshov, D.O.; Dogiel, V.A. Diffuse gamma-ray emission from the Galactic center—A multiple energy injection model. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Totani, T. A RIAF Interpretation for the past higher activity of the Galactic center black hole and the 511 keV annihilation emission. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 58, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Atoyan, A.M. On the Origin of the Galactic Annihilation Radiation. Astron. Lett. 1981, 7, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Beacom, J.F.; Yüksel, H. Stringent constraint on Galactic positron production. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 071102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizun, P.; Cassé, M.; Schanne, S. Continuum γ-ray emission from light dark matter positrons and electrons. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnev, V.M.; Ginzburg, I.F.; Meledin, G.V.; Serbo, V.G. The two-photon particle production mechanism. Physical problems. Applications. Equivalent photon approximation. Phys. Rep. 1975, 15, 181–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremin, I.M. Ultraperipheral nuclear interactions. Phys. Uspekhi 2020, 63, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. On the production of electrons and positrons by a collision of two particles. Phys. Z. Sowjet. 1934, 6, 244–257, Reprinted in Perspectives in Theoretical Physics. The Collected Papers of E.M. Lifshitz; Pitaevskii, L.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berestetskii, V.B.; Lifshits, E.M.; Pitaevskii, L.P. Quantum Electrodynamics; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.N.; Mingulov, K.T. Total Born cross section of e+e−-pair production in relativistic ion collisions from differential equations. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 757, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racah, G. Sulla nascita di coppie per urti di particelle elettrizzate. Nuovo Cim. 1937, 14, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremin, I.M. Ultraperipheral production of lepton pairs (perturbative and nonperturbative effects). Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2022, 37, 2250098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froissart, M. Asymptotic behavior and subtractions in the Mandelstam representation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 123, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vysotsky, M.I.; Zhemchugov, E.V. Equivalent photons in proton-proton and ion-ion collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. Phys. Uspekhi 2019, 62, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godunov, S.I.; Karkaryan, E.K.; Novikov, V.A.; Rozanov, A.N.; Vysotsky, M.I.; Zhemchugov, E.V. pp scattering at the LHC with the lepton pair production and one proton tagging. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremin, I.M.; Gevorkyan, S.R.; Madigozhin, D.T. Enhancement of low-mass dileptons in ultraperipheral collisions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertulani, C.A.; Baur, G. Electromagnetic processes in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rep. 1988, 163, 299–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obraztsov, I.V.; Milstein, A.I. Quadrupole radiation and e+e- pair production in the collision of nonrelativistic nuclei. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 820, 136514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E. Sull’equilibrio termico di ionizzazione. Nuovo Cim. 1924, 1, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E. Über die Theorie des Stoßes zwischen Atomen und elektrisch geladenen Teilchen. Z. Phys. 1924, 29, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizsäcker, C.F.V. Ausstrahlung bei Stößen sehr schneller Elektronen. Z. Phys. 1934, 88, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J. Nature of the high energy particles of penetrating radiation and status of ionization and radiation formulae. Phys. Rev. 1934, 45, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, T.; Diehl, R.; Khachatryan, G.; Krause, M.G.H.; Guglielmetti, F.; Greiner, J.; Strong, A.W.; Zhang, X. Gamma-ray spectroscopy of positron annihilation in the Milky Way. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 586, A84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamae, T.; Karlsson, N.; Mizuno, T.; Abe, T.; Koi, T. Parameterization of γ, e±, and neutrino spectra produced by p-p interaction in astronomical environments. Astrophys. J. 2006, 647, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; McKinney, J.C.; Roth, N.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Miller, M.C. A Unified model for tidal disruption events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 859, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geballe, T.R.; McCall, B.J.; Hinkle, K.H.; Oka, T. Detection of in the diffuse interstellar medium: The Galactic center and Cygnus OB2 Number 12. Astrophys. J. 1999, 510, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrière, K.; Gillard, W.; Jean, P. Spatial distribution of interstellar gas in the innermost 3 kpc of our galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 467, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivlev, A.V.; Padovani, M.; Galli, D.; Caselli, P. Interstellar dust charging in dense molecular clouds: Cosmic ray effects. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.C.; Cummings, A.C.; McDonald, F.B.; Heikkila, B.C.; Lal, N.; Webber, W.R. Voyager 1 observes low-energy Galactic cosmic rays in a region depleted of heliospheric ions. Science 2013, 341, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirac, P.A.M. On the annihilation of electrons and protons. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1930, 26, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafexhiu, E.; Aharonian, F.; Taylor, A.M.; Vila, G.S. Parametrization of gamma-ray production cross sections for pp interactions in a broad proton energy range from the kinematic threshold to PeV energies. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 123014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.W.; Bloemen, H.; Diehl, R.; Hermsen, W.; Schönfelder, V. COMPTEL Skymapping: A new approach using parallel computing. Astrophys. Lett. Commun. 1999, 39, 209–212. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1999ApL%26C..39..209S%2F/ (accessed on 9 January 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).