Abstract
Reinhard Schlickeiser has made groundbreaking contributions to various aspects of blazar physics, including diffusive shock acceleration, the theory of synchrotron radiation, the production of gamma-rays through Compton scattering in various astrophysical sources, etc. This paper, describing the development of a self-consistent shock-in-jet model for blazars with a synchrotron mirror feature, is therefore an appropriate contribution to a Special Issue in honor of Reinhard Schlickeiser’s 70th birthday. The model is based on our previous development of a self-consistent shock-in-jet model with relativistic thermal and non-thermal particle distributions evaluated via Monte-Carlo simulations of diffusive shock acceleration, and time-dependent radiative transport. This model has been very successful in modeling spectral variability patterns of several blazars, but has difficulties describing orphan flares, i.e., high-energy flares without a significant counterpart in the low-frequency (synchrotron) radiation component. As a solution, this paper investigates the possibility of a synchrotron mirror component within the shock-in-jet model. It is demonstrated that orphan flares result naturally in this scenario. The model’s applicability to a recently observed orphan gamma-ray flare in the blazar 3C279 is discussed and it is found that only orphan flares with mild (≲ a factor of 2–3) enhancements of the Compton dominance can be reproduced in a synchrotron-mirror scenario, if no additional parameter changes are invoked.
1. Introduction
Blazars are a class of jet-dominated active galactic nuclei. As most convincingly argued by Reinhard Schlickeiser (RS) in 1996 [1], their broad-band non-thermal emission, ranging from radio to gamma-rays, must be strongly Doppler boosted due to relativistic motion of an emission region along the jet, oriented close to our line of sight. The spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of blazars are dominated by two broad, non-thermal radiation components. The low-frequency component, from radio to optical/UV/X-ray frequencies, is generally attributed to synchrotron radiation by relativistic electrons. Most notably, Crusius and Schlickeiser [2,3] have evaluated the angle-averaged synchrotron emission from isotropically distributed electrons in random magnetic fields, including plasma effects, which are now frequently used as the standard expressions for the low-frequency emission from blazars. However, note also an alternative suggestion by RS in 2003 [4] that the low-frequency emission may be produced as electrostatic bremsstrahlung, i.e., the scattering of electrostatic Langmuir waves excited by two-stream instabilities, as expected in the jet-inter-stellar-medium interaction scenario of Schlickeiser et al. (2002) [5].
Motivated by early -ray observations by the SAS-2 and COS-B satellites, already in 1979–1980, RS had considered inverse-Compton scattering as the dominant mechanism to produce high-energy -rays in astrophysical sources, pointing out the importance of Klein-Nishina effects in the calculation of -ray spectra [6,7,8]. Also in leptonic models for blazars, inverse-Compton scattering by relativistic electrons in the jet is considered the dominant high-energy emission mechanism. Target photons for Compton scattering can be the co-spatially produced synchrotron (or electrostatic bremsstrahlung) radiation, in which case it is termed synchrotron self-Compton (SSC) emission (e.g., [9,10]). The first suggestion of target photon fields from outside the jet involved RS in two seminal papers suggesting the photon field of the accretion disk as the dominant target photon field [11,12]. Alternative sources of external target photons may be the broad-line region (BLR) (e.g., [13]), a dusty, infra-red emitting torus (e.g., [14]), or other regions of the jet (e.g., [15,16]). The relativistic motion of the high-energy emission region in a blazar jet through these generally anisotropic external radiation fields leads to complicated transformation properties from the active galactic nucleus (AGN) rest frame into the emission-region frame, which were studied in detail by Dermer and Schlickeiser in 2002 [17]. Which of these potential radiation fields might dominate, depends critically on the location of the emission region, which can be constrained by the absence of obvious signatures of absorption of high-energy and very-high-energy -rays by the nuclear radiation fields of the central AGN, with one of the first detailed discussions of such constraints published by Dermer and Schlickeiser in 1994 [18].
The generation of the non-thermal broadband emission from blazars requires the efficient acceleration of electrons to ultra-relativistic energies. One of the plausible mechanisms of particle acceleration acting in the relativistic jets of blazars is diffusive shock acceleration (DSA), which was studied in the context of a general derivation of the kinetic equation of test particles in turbulent plasmas by RS in two seminal papers in 1989 [19,20] for non-relativistic shock speeds, while particle acceleration by magnetic turbulence, specifically in relativistic jets was studied by Schlickeiser and Dermer in 2000 [21]. Particle acceleration at relativistic shocks has been considered by several authors, using both analytical methods (e.g., [22,23,24]) and Monte-Carlo techniques (e.g., [25,26,27,28,29]). The simulations by Niemiec and Ostrowski [28] and Summerlin and Baring [29] indicate that diffusive shock acceleration at oblique, mildly relativistic shocks is able to produce relativistic, non-thermal particle spectra with a wide range of spectral indices, including as hard as , where p is the particle’s momentum.
In two recent papers [30,31], we had coupled Monte-Carlo simulations of diffusive shock acceleration (DSA), using the code of Summerlin and Baring [29], with time-dependent radiation transfer, based on radiation modules originally developed by Böttcher, Mause and Schlickeiser in 1997 [32] and further developed as detailed in [33,34]. In those studies, we found that the particles’ mean free path for pitch-angle scattering, , which mediates the first-order Fermi process in DSA, must have a strong dependence on particle momentum, with an index for a parameterization of . This likely indicates a decaying level of magneto-hydrodynamic turbulence with increasing distance from the shock front. Higher-energy particles, with their larger gyro radii, then probe more distant regions from the shock front, experiencing less efficient pitch-angle scattering. Time-dependent simulations of DSA plus radiation transfer were used to fit the multi-wavelength variability of the blazars 3C279 and Mrk 501 in [31] and the X-ray variability of 1ES 1959 + 650 in [35]. Multi-wavelength flares with approximately equal flare amplitude in the low-frequency (synchrotron) and high-frequency (Compton) components of the SED were naturally produced by an increase of the power injected into shock-accelerated particles, without the need for significant changes of the plasma parameters determining .
However, an orphan -ray flare on 20 December 2013, with no significant counterpart in the synchrotron emission component, reported as Flare B in [36], presented a severe challenge to this as well as any other single-zone emission model for blazars. A fit to the observed -ray flare was possible with a significant hardening of the DSA-generated particle spectrum as the result of a reduction of the pitch-angle-scattering mean-free path, both in overall normalization and index . However, keeping the optical (synchrotron) flux approximately constant, as observed, required a reduction of the magnetic field by a factor of 8.7, followed by a gradual recovery to the quiescent-state value with a fine-tuned time dependence. While the authors argue that such magnetic-field reductions and subsequent gradual recoveries after the passage of a shock have indeed been observed in interplanetary shocks (e.g., [37]), it is worth exploring alternative ways to explain orphan -ray flares in blazars within the framework of the shock-in-jet model developed in [30,31].
One plausible way of producing orphan -ray flares in the framework of a leptonic single-zone blazar model is the temporary enhancement of an external radiation field that serves as target for inverse-Compton scattering. This is the basis of a class of models termed synchrotron mirror models, where the synchrotron radiation of the high-energy emission region traveling along the jet, is reflected by a cloud to re-enter the emission region at a later time. Such models were first considered by Ghisellini and Madau [38], however without proper consideration of light-travel time effects, and by Böttcher and Dermer [39] and Bednarek [40], properly treating light-travel time effects, but considering primarily the time-dependence of the target-photon energy density without detailed calculations of the emerging -ray spectra. The synchrotron mirror model was more recently re-visited by Vittorini et al. [41], with a fully time-dependent leptonic synchrotron mirror model applied to the spectral variability of 3C454.3 in 2010 November, and Tavani et al. [42], considering also moving mirrors and applying the model to the light curve of the same flare B of 3C279 considered by [31]. Note a similar model termed the “ring of fire” model by MacDonald et al. [43,44], where the emission region passes a static synchrotron-emitting region of an outer sheath of the jet (the “ring of fire”), which produces very similar variability features as the synchrotron mirror model.
In the present paper, the time-dependent shock-in-jet model of Böttcher and Baring [31] is extended to include self-consistently a synchrotron-mirror component. Section 2 describes the additions to the model. Section 3 presents the resulting spectral variability features from an attempt to apply this model to the orphan -ray flare B of 3C279. Section 4 summarizes and discusses the results.
2. Model Description
The model developed here is a further development of the time-dependent shock-in-jet model of Böttcher and Baring [31]. In addition to the radiation components already included in [31] , we now introduce synchrotron emission reflected by a spherical cloud of radius at a distance from the central engine, assumed for simplicity to be located close to the path of the jet, however, not hydrodynamically interacting with it, as considered, e.g., by the jet-star interaction model [45,46] or the cloud ablation model [47,48]. A mildly relativistic, oblique shock is propagating along the jet, thus accelerating particles in the local environment of the shock which constitutes our moving emission region of radius . The emission region is starting out at time (in the AGN rest frame) at a height above the black-hole—accretion-disk system powering the jet, and is propagating with a bulk Lorentz factor , corresponding to a speed of . Thus, at any given time , the emission region is located at .
Synchrotron radiation emitted by the emission region at is reflected back by the cloud to re-enter the emission region at a distance from the central engine, given by
at a time (in the AGN rest frame) given by
Equation (2) may be inverted to find the time at which reflected synchrotron radiation received at time has been emitted:
implying that reflected synchrotron emission will be received starting at a time (corresponding to ) given by
Reflected synchrotron radiation will be received by the emission region until it passes the cloud at .
The code writes out the observed synchrotron emission spectra, for every time step (with times in the observer’s frame) as the shock propagates along the jet. Therefore, at any time , one can use Equation (3) to find the time (in the AGN frame) at which synchrotron radiation reflected back into the emission region, has been emitted. The synchrotorn flux irradiating the cloud, , is then found as
where is the luminosity distance to the source.
Assuming, for simplicity, that the cloud re-radiates a fraction of the impinging synchroton radiation isotropically, it will emit a spectral luminosity of . The emission region will thus receive a flux of Reflected Synchrotron (RS—happy coincidence) radiation, in the comoving frame, of
where is the photon frequency in the co-moving frame.
The code evaluates a time-evolving reflected-synchrotron photon field in the emission region, , where is the dimensionless photon energy in the emission-region frame by the interplay of RS emission entering the emission region at a rate , where is the volume of the emission region, and escape on an escape time scale , over a simulation time step as
In the above expressions, h is the Planck constant, the electron mass, and .
The time-dependent RS photon field resulting from Equation (7) acts target for inverse-Compton scattering to produce the synchrotron-mirror Compton emission, and synchrotron-mirror Compton cooling is included self-consistently. For the evaluation of the synchrotron-mirror Compton emission, it is assumed, for simplicity, that the target photons enter the jet directly from the front, and the head-on approximation (e.g., [49]) for the Compton cross section is used. Hence, photons scattered along the viewing direction, making an angle with respect to the jet axis in the co-moving frame of the emission region, with , have been scattered by a scattering angle . The rate density at which Reflected Synchrotron Compton (RSC) emission is produced, is calculated as
where
with , and [49].
3. Results: Spectral Variability Features
As detailed in the introduction, the study of the synchrotron mirror model developed here was motivated by the difficulties in modeling the orphan -ray flare B of 3C279 in December 2013 reported by Hayashida et al. [36]. We therefore start with the quiescent-state parameters of the shock-in-jet model for 3C279 used in [31]. The emission region is set to start out at pc, and the cloud acting as the mirror is assumed to be located at pc. The bulk Lorentz factor is , as used in [31]. The cloud radius is assumed to be cm and its reflective fraction is . The complete list of model parameters can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Relevant model parameters for the case study motivated by the December 2013 flare of 3C279.
The resulting sequence of snap-shot SEDs (starting right before the onset of the synchrotron-mirror Compton emission) is illustrated in Figure 1. It is clear that the model does produce a significant orphan -ray flare, accompanied by a slight reduction of the synchrotron emission due to the increased Compton cooling of relativistic electrons. The latter is consistent with the observed evolution of the SED. However, the amplitude of the orphan -ray flare amounts only to an enhancement of the -ray flux by a factor of ∼2, in contrast to the observed dramatic increase by a factor of ≳10. Even increasing the synchrotron-mirror efficiency (e.g., by increasing or ; see Equation (6)), does not increase the -ray flare amplitude substantially. The reason for this is that the -ray flux is limited by the available power injected into shock-accelerated electrons, which are already in the fast-cooling regime, thus radiating very efficiently. Any further enhancement of the reflected-synchrotron energy density will only suppress the synchrotron emission further, but not lead to a significant increase of the -ray flare amplitude. We therefore conclude that a pure shock-in-jet synchrotron mirror scenario is not able to produce the observed large-amplitude orphan -ray flare in 3C279 in December 2013. In order to achieve this, additional power would need to be injected into shock-accelerated electrons, leaving us with the same difficulties encountered in [31], i.e., requiring a fine-tuned reduction and gradual recovery of the magnetic field.
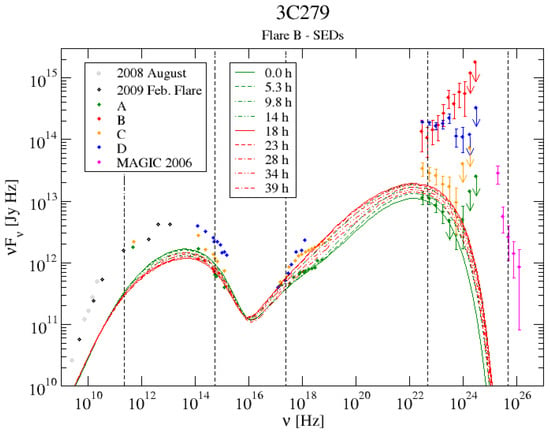
Figure 1.
Spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of 3C279 in 2013–2014, from [36], along with snap-shot model SEDs from the shock-in-jet synchrotron-mirror model. The dashed vertical lines indicate the frequencies at which light curves and hardness-intensity relations were extracted. The legend follows the nomenclature of different periods from Hayashida et al. (2015) [36].
Nevertheless, in spite of its inapplicability to this particular orphan flare, it is worthwhile considering this simulation for a generic study of the expected spectral variability patterns in the shock-in-jet synchrotron mirror model. The multi-wavelength light curves at 5 representative frequencies (high-frequency radio, optical, X-rays, high-energy [HE, 200 MeV], and very-high-energy [VHE, 200 GeV] -rays) are shown in Figure 2. All light curves in the Compton SED component (X-rays to VHE -rays) show a flare due to the synchrotron-mirror Compton emission. Note that the VHE -ray light curve had to be scaled up by a factor of to be visible on this plot. Thus, the apparently large VHE flare is actually at undetectably low flux levels for the parameters chosen here. In contrast, the 230 GHz radio and optical light curves show a dip due to increased radiative cooling during the synchrotron mirror action. The radio dip is significantly delayed compared to the optical due to the longer cooling time scales of electrons emitting in the radio band.
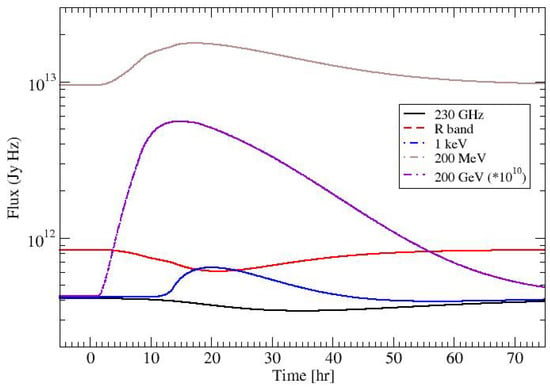
Figure 2.
Model light curves in various frequency/energy bands resulting from the synchrotron mirror simulation illustrated in Figure 1 at the 5 representative frequencies/energies marked by the vertical dashed lines. Note that the very-high-energy (VHE, 200 GeV) -ray flux is scaled up by a factor of in order to be visible on the plot.
Cross-correlation functions between the various light curves from Figure 2 are shown in Figure 3. As expected from inspection of the light curves, significant positive correlations between X-rays and the 2 -ray bands with only small time lags (-rays leading X-rays by a few hours) and between the radio and optical band, with optical leading the radio by ∼15 h, are seen. The synchrotron (radio and optical) light curves are anti-correlated with the Compton (X-rays and -rays) ones, again with a significant lag of the radio emission by ∼15 h.
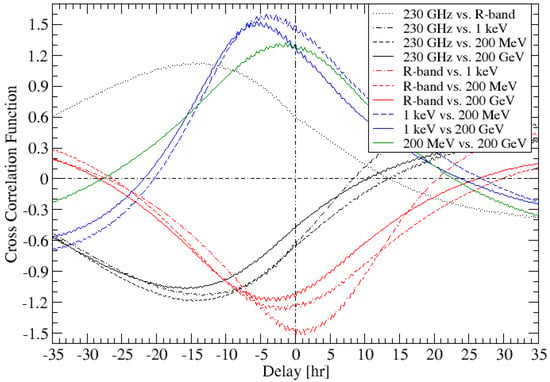
Figure 3.
Cross-correlation functions between the model light curves in various energy/frequency bands.
Figure 4 shows the hardness-intensity diagrams for the 5 selected frequencies/energies, i.e., the evolution of the local spectral index (a, defined by ) vs. differential flux. Generally, all bands, except the optical, exhibit the frequently observed harder-when-brighter trend. Only the radio and X-ray bands show very moderate spectral hysteresis. The dip in the optical R-band) light curve is accompanied by a very slight redder-when-brighter trend, likely as the consequence of the increased radiative cooling during the synchrotron-mirror action.
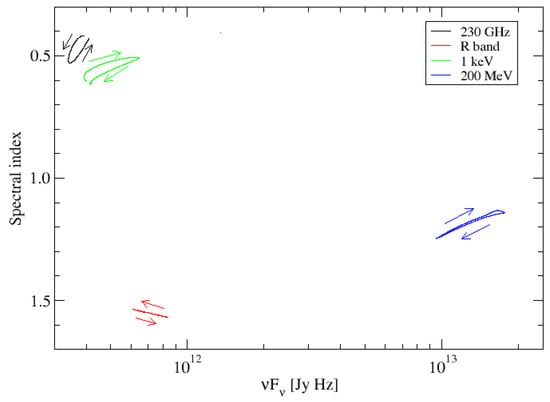
Figure 4.
Model hardness-intensity diagrams at the selected frequencies/energies. The spectral index a is defined by , so that a smaller value indicates a harder spectrum. The VHE band has been omitted here due to its unobservably low flux level and very steep local spectral index. Arrow indicate the evolution in time.
4. Summary, Discussion, and Conclusions
In this paper, the leptonic shock-in-jet blazar model of [31] is extended with the addition of a self-consistent synchrotron mirror component. This was motivated by the difficulty in modeling orphan -ray flares with such an effectively single-zone model. A particularly high-amplitude (factor of ∼10) orphan -ray flare of the blazar 3C279 from December 2013 was chosen as a case study. However, the attempt to model this flare with the shock-in-jet synchrotron mirror model developed here, failed because the maximum -ray flux was limited by the (fixed) amount of power injected into shock-accelerated electrons, allowing for orphan flares with amplitudes of at most ∼2–3. Higher-amplitude flares would require an enhanced energy injection into relativistic electrons, in addition to more efficient pitch-angle scattering, leading to a harder electron spectrum. However, this would cause the same difficulties of having to decrease the magnetic field, followed by a fine-tuned recovery to its quiescent state, as were encountered in [31].
More successful model representations of this particular flare of 3C279 were presented by several authors. Hayashida et al. [36] use the model of Nalewajko et al. [50] to reproduce this orphan -ray flare by introducing an extreme hardening of the electron spectrum, along with a location of the emission region much closer to the BH and accretion disk. A hard electron spectrum up to a cut-off energy of a few 1000 is invoked, which may be difficult, but not impossible, to achieve with standard particle acceleration mechanisms. Asano and Hayashida [51] employ a time-dependent one-zone model with second-order Fermi acceleration, where an enhanced acceleration efficiency leads to a hardening of the electron spectrum, and a significant reduction of the magnetic field is required to suppress a simultaneous optical flare. While their model represents the -ray spectrum during the flare well, it does predict a non-negligible optical synchrotron flare accompanying the -ray flare. A similar strategy, based on an analytical solution to the steady-state electron distribution, was adopted by Lewis et al. [52], also requiring a significant reduction of the magnetic field to suppress a simultaneous optical synchrotron flare. Yan et al. [53] modelled the orphan-flare SED using a time-dependent single-zone model with rapid electron cooling. However, it is unclear whether a transition from the quiescent to this flaring state may be produced in a natural way. Lepto-hadronic models naturally de-couple the (proton-initiated) high-energy emission from the (electron-initiated) synchrotron radiation and therefore offer an alternative way of reproducing orphan -ray flares. Paliya et al. [54] used the time-dependent lepto-hadronic model of Diltz et al. [55] to model the December 2013 orphan -ray flare of 3C279. They also considered the possibility of a two-zone model, with a small emission region emitting an SED with very large Compton dominance, emerging during the time of the orphan -ray flare.
A representative simulation of the shock-in-jet synchrotron mirror scenario was then used for a generic study of the expected spectral variability patterns. X-ray and -ray light curves as well as radio and optical light curves are significantly correlated with each other, while radio and optical light curves are significantly anti-correlated, with radio and optical (synchrotron) dips accompanying the high-energy flare resulting from more efficient radiative cooling of the electrons. The response in the radio light curves is found to be delayed by ∼15 h with respect to other bands. In the scenario investigated here, where no changes to the diffusive shock acceleration process along the entire evolution of the flare are assumed, significant spectral hysteresis is not expected, but a mild harder-when-brighter trend in most wavebands is found.
While it is found that the specific December 2013 orphan -ray flare of 3C279 can not be successfully reproduced with this scenario, it may be applicable to other, more moderate orphan -ray flares. Especially the expected anti-correlation between Compton and synchrotron wavebands may serve as a smoking-gun signature of this scenario. The failure of the shock-in-jet synchrotron mirror model for the December 2013 flare of 3C279 was primarily caused by the fact that the shock-accelerated, relativistic electrons were already in the fast-cooling regime and radiating very efficiently, as was required by the fit to the quiescent state of 3C279. If the quiescent emission of a blazar can be produced by a less radiatively efficient configuration, then the increase in radiative efficiency in the synchrotron mirror scenario may lead to substantially higher-amplitude flares. A systematic study of different scenarios and applications to other sources will be presented in a forthcoming publication.
Funding
The work of M.B. is supported by the South African Researc Chairs Initiative of the National Research Foundation (any opinion, finding, and conclusion or recommendation expressed in this material is that of the authors, and the NRF does not accept any liability in this regard) and the Department of Science and Innovation of South Africa through SARChI grant no. 64789.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Schlickeiser, R. Models of high-energy emission from active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1996, 120, 481–489. Available online: https://adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1996A%26AS..120C.481S (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Crusius, A.; Schlickeiser, R. Synchrotron radiation in random magnetic fields. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 164, L16–L18. Available online: https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1986A%26A...164L..16C (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Crusius, A.; Schlickeiser, R. Synchrotron radiation in a thermal plasma with large-scale random magnetic fields. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 196, 327–337. Available online: https://adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1988A%26A...196..327C (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Schlickeiser, R. Nonthermal radiation from jets of active galactic nuclei: Electrostatic bremsstrahlung as alternative to synchrotron radiation. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 419, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Vainio, R.; Böttcher, M.; Lerche, I.; Pohl, M.; Schuster, C. Conversion of relativistic pair energy into radiation in the jets of active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 393, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R. Astrophysical gamma-ray production by inverse Compton interactions of relativistic electrons. Astrophys. J. 1979, 233, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R. Astrophysical gamma-ray production by inverse Compton interactions of relativistic electrons.II. Constraints on Compton emission models for NGC 4151, NP 0532, and PSR 0833-45 from gamma-ray data. Astrophys. J. 1980, 236, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R. Astrophysical gamma-ray production by inverse Compton interactions of relativistic electrons. III. Cutoff effect for inverse Compton spectra applied to the case of the hard X-ray and gamma-ray emission of NGC 4151. Astrophys. J. 1980, 240, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A jet model for the gamma-ray-emitting blazar 3C279. Astrophys. J. 1992, 397, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.D.; Marscher, A.P. An analysis of the synchrotron self-Compton model for the multi-wave band spectra of blazars. Astrophys. J. 1996, 461, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R.; Mastichiadis, A. High-energy gamma radiation from extragalactic radio sources. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 256, L21–L30. [Google Scholar]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R. Model for the high-energy emission from blazars. Astrophys. J. 1993, 416, 458–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Begelmann, M.C.; Rees, M.J. Comptonization of diffuse ambient radiation by a relativistic jet: The source of gamma rays from blazars? Astrophys. J. 1994, 421, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blażejowski, M.; Sikora, M.; Moderski, R.; Madejski, G.M. Comptonization of infrared radiation from hot dust by relativistic jets in quasars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganopoulos, M.; Kazanas, D. Decelerating flows in TeV blazars: A resolution to the BL Lacertae–FR I unification problem. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G. Spine-sheath layer radiative interplay in subparsec-scale jets and the TeV emission from M87. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 385, L98–L102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R. Transformation properties of external radiation fields, energy-loss rates, scattered spectra, and a model for blazar variability. Astrophys. J. 2002, 575, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R. On the location of the acceleration and emission sites in gamma-ray blazars. In International Astronomical Union Colloquium; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 142, pp. 945–948. [Google Scholar]
- Schlickeiser, R. Cosmic-ray transport and acceleration. I. Derivation of the kinetic equation and application to cosmic rays in static cold media. Astrophys. J. 1989, 336, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R. Cosmic-ray transport and acceleration. II. Cosmic rays in moving cold media with application to diffusive shock wave acceleration. Astrophys. J. 1989, 336, 264–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Dermer, C.D. Proton and electron acceleration through magnetic turbulence in relativistic outflows. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 360, 789–794. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, J.A. Fermi acceleration by relativistic shock waves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 196, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kirk, J.G.; Heavens, A.F. Particle acceleration at oblique shock fronts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1989, 239, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.G.; Guthmann, A.W.; Gallant, Y.A.; Achterberg, A. Particle acceleration at ultrarelativistic shocks: An eigenfunction method. Astrophys. J. 2000, 542, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.C.; Jones, F.C.; Reynolds, S.P. First-order Fermi particle acceleration by relativistic shocks. Astrophys. J. 1990, 360, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, J.; Ostrowski, M. Energy spectra of cosmic rays accelerated at ultrarelativistic shock waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3911–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.C.; Double, G.P. Diffusive shock acceleration in unmodified relativistic, oblique shocks. Astropart. Phys. 2004, 22, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, J.; Ostrowski, M. Cosmic-ray acceleration at relativistic shock waves with a “realistic” magnetic field structure. Astrophys. J. 2004, 610, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Summerlin, E.J.; Baring, M.G. Diffusive acceleration of particles at oblique, relativistic magnetohydrodynamic shocks. Astrophys. J. 2012, 745, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baring, M.G.; Böttcher, M.; Summerlin, E.J. Probing acceleration and turbulence at relativistic shocks in blazar jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 4875–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Baring, M.G. Multi-wavelength variability signatures of relativistic shocks in blazar jets. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Mause, H.; Schlickeiser, R. γ-ray emission and spectral evolution of pair plasmas in AGN jets. I. General theory and a prediction for the GeV–TeV emission from ultrarelativistic jets. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 324, 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher, M.; Chiang, J. X-ray Spectral Variability Signatures of Flares in BL Lacertae Objects. Astrophys. J. 2002, 581, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Reimer, A.; Sweeney, K.; Prakash, A. Leptonic and hadronic modeling of Fermi-detected blazars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chra, S.; Böttcher, M.; Goswami, P.; Singh, K.P.; Zacharias, M.; Kaur, N.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Ganesh, S.; Chandra, D. X-ray observations of 1ES 1959 + 650 in its high activity state in 2016–2017 with AstroSat and Swift. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.08119. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida, M.; Nalewajko, K.; Madejski, G.M.; Sikora, M.; Itoh, R.; Ajello, M.; Blandford, R.D.; Buson, S.; Chiang, J.; Fukazawa, Y.; et al. Rapid variability of blazar 3C279 during flaring states in 2013–2014 with joint Fermi-LAT, NuSTAR, Swift, and ground-based multiwavelength observations. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baring, M.G.; Ogilvie, W.; Ellison, C.; Forsyth, R.J. Acceleration of solar wind ions by nearby interplanetary shocks: Comparison of Monte Carlo simulations with Ulysses observations. Astrophys. J. 1997, 476, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghisellini, G.; Madau, P. On the origin of the γ-ray emission in blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 280, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Dermer, C.D. On Comptonscattering scenarios for blazar flares. Astrophys. J. 1998, 501, L51–L54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedmarek, W. On the application of the mirror model for the gamma-ray flare in 3C279. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 336, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Vittorini, V.; Tavani, M.; Cavaliere, A.; Striani, E.; Vercellone, S. The blob crashes into the mirror: Modeling the exceptional γ-ray flaring activity of 3C454.3 in 2010 November. Astrophys. J. 2014, 793, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tavani, M.; Vittorini, V.; Cavaliere, A. An emerging class of gamma-ray flares from blazars: Beyond one-zone models. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Marscher, A.P.; Jorstad, S.G.; Joshi, M. Through the ring of fire: γ-ray variabilit in blazars by a moving plasmoid passing a local source of seed photons. Astrophys. J. 2015, 804, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Jorstad, S.G.; Marscher, A.P. “Orphan” γ-ray flares and stationary sheaths of blazar jets. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkov, M.V.; Aharonian, F.A.; Bogovalov, S.V.; Kelner, S.R.; Khangulyan, D. Rapid TeV variability in blazars as a result of jet-star interaction. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araudo, A.T.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Romero, G.E. Gamma-ray emission from massive stars interacting with active galactic nuclei jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 3626–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, M.; Böttcher, M.; Jankowsky, F.; Lenain, J.-P.; Wagner, S.J.; Wierzcholska, A. Cloud ablation by a relativistic jet and the extended flare in CTA 102 in 2016 and 2017. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, M.; Böttcher, M.; Jankowsky, F.; Lenain, J.-P.; Wagner, S.J.; Wierzcholska, A. The extended flare in CTA 102 in 2016 and 2017 within a hadronic model through cloud ablation by the relativistic jet. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Menon, G. High Energy Radiation from Black Holes: Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays, and Neutrinos; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nalewajko, K.; Begelman, M.C.; Sikora, M. Constraining the location of gamma-ray flares in luminous blazars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Hayashida, M. The most intensive gamma-ray flare of quasar 3C 279 with the second-order Fermi acceleration. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 808, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.R.; Finke, J.D.; Becker, P.A. Electron Acceleration in Blazars: Application to the 3C 279 Flare on 2013 December 20. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.-N. Formation of very hard electron and gamma-ray spectra of flat-spectrum radio quasars in the fast-cooling regime. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3175–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paliya, V.S.; Diltz, C.D.; Böttcher, M.; Stalin, C.S.; Buckley, D.A.H. A hard gamma-ray flare from 3C 279 in 2013 December. Astrophys. J. 2016, 817, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diltz, C.S.; Böttcher, M.; Fossati, G. Time dependent hadronic modeling of flat spectrum radio quasars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).