1. Introduction
In the Refs. [
1,
2], the idea was conjectured that the neutron
n can be transformed into a sterile neutron
that belongs to a hypothetical parallel mirror sector. This mirror sector is an exact copy of the ordinary particle sector with identical fermion content and identical gauge forces, different in the respect that the strong and electroweak forces described by the Standard Model (SM)
act only between ordinary particles, and gauge forces of the mirror Standard Model (SM
)
act only between mirror particles (for a review, see e.g., Refs. [
3,
4,
5]). The particle physics of the two sectors are exactly the same due to a discrete symmetry
under exchange of all ordinary and mirror particles modulo the fermion chirality which symmetry can be considered as a generalization of parity, namely for our sector being left-handed, the mirror sector can be considered as right-handed. In fact, parity restoration was the initial motivation for introducing the mirror sector [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10] (for a hystorical overview see Ref. [
11]). However, in principle, this discrete symmetry can be simply
without the chirality change, in which case the parallel sector will have identical physics in left basis [
3,
4,
5]. Most physical applications do not depend on the type of this discrete symmetry, and we shall continue to call this parallel sector the “mirror sector” in both cases. If
or
is an exact symmetry, then each ordinary particle as the electron, photon, proton, neutron etc. must have a mirror twin, the electron
, photon
, proton
, neutron
etc. exactly degenerate in mass. Interactions between the two sectors are possible via the common gravitational force but, in principle, also via some very feeble interactions induced by new physics beyond the Standard Model. These new interactions, typically related to higher order effective operators, can arise at some a priori unknown energy scale which in principle might be not very far and can be even as small as few TeV. Any new interactions must respect gauge invariances of both sectors and can manifest itself in a mixing phenomena between the neutral particles of the two sectors, in particular as the photon-mirror photon kinetic mixing [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17], the mixing of (active) ordinary neutrinos and (sterile) mirror neutrinos [
18,
19,
20,
21], the above mentioned mixing of the neutron and mirror neutron [
1,
2], and similar mixings between other neutral particles such as pions and kaons induced e.g., by the common gauge flavor symmetry between the two sectors [
22,
23,
24]. Mirror matter is a viable candidate for light dark matter, a sort of asymmetric atomic dark matter consisting dominantly of mirror hydrogen and helium [
25]. Therefore, any transition of a neutral particle of the ordinary sector into a neutral particle of another sector can be considered as a conversion to dark matter. In fact, the underlying baryon or lepton number (and CP) violating particle processes in the early universe can be at the origin of the cogenesis of ordinary and dark baryon asymmetries [
26,
27]. However, in this paper we will not focus on the cosmological aspects of mirror matter (see Refs. [
25,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32] and reviews [
3,
4,
5] for corresponding discussions) and shall discuss essentially the features of a laboratory search for
transition.
This transition was suggested to occur via the mass mixing term
in Ref. [
1], and the masses of
n and
are exactly the same due to the initial assumption of mirror parity leading to the the degeneracy between the ordinary and mirror particles. Then, the phenomenon of free
oscillation is essentially described in the same way as free neutron–antineutron oscillation
due to the Majorana mass term
[
33,
34] (for a recent review see [
35,
36]). Namely, for free non-relativistic neutrons in vacuum but in the presence of magnetic fields, the time evolution of
and
systems are described respectively by the Hamiltonians:
where
and
are respectively the masses and magnetic moments of the neutron and mirror neutron,
and
are ordinary and mirror magnetic fields, and
stands for Pauli matrices.
However, between these two cases there are important differences:
- (i)
First of all,
transition changes the baryon number
B by two units,
, while
transition changes
B by one unit,
, but it changes also the mirror baryon number
by one unit,
. Therefore,
mixing conserves the combination of two baryon numbers
while
mixing violates
. From the theoretical side, the phenomena of neutron–mirror neutron and neutron–antineutron mixings can be intimately related, with
–conserving
mixing being a dominant effect and
mixing being subdominant effect emerging due to explicit [
1] or spontaneous [
37] violation of
.
- (ii)
Exact degeneracy between the neutron and antineutron masses (and also magnetic moments) is based on fundamental CPT invariance, which cannot be violated in the frames of local relativistic field theories. (However, environmental energy splitting can be induced by some long range fifth-forces related e.g., to very light
baryophotons [
38,
39], or in bi-gravity picture when ordinary and mirror components are coupled to different metric tensors [
40,
41,
42].) The degeneracy between the neutron and mirror neutron is related to mirror parity which in principle can be spontaneously broken [
43,
44,
45]. The order parameters of this breaking can be naturally small and the mass splitting between
n and
states can be rather tiny, say as small as
neV in which case it can have implications for the neutron lifetime problem [
46]. Both
and
oscillations are affected by the matter medium and magnetic fields. However, in the case of
oscillation, the presence of mirror matter and mirror magnetic field
will be manifested as uncontrollable background in experiments.
- (iii)
transition can be experimentally manifested [
35,
36] as the antineutron appearance in the beam of free neutrons, or as nuclear disintegration
’s due to
conversion of a neutron bound in nuclei and its subsequent annihilation with other nucleons producing multiple pions. As for
transition, it is kinematically suppressed for a bound neutron, simply because of energy conservation, and thus it has no influence on the stability of nuclei [
1]. However, free
transition is possible and it can be experimentally manifested as the neutron disappearance
or regeneration
[
1].
- (iv)
There are severe experimental limits on
mixing mass
, usually expressed as limits on the free oscillation time
. (Hereafter we use natural units,
,
.) Namely, the direct experimental limit on free
oscillation is
s [
47] while the limit from the nuclear stability [
48] yields
s. The latter corresponds to the upper bound
eV. As for
oscillation, it can be rather fast, even faster than the neutron decay itself [
1]. Several dedicated experiments were performed for testing the ultra-cold neutron (UCN) disappearance due to
transition [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54]. Assuming the absence of the mirror magnetic field at the Earth, the strongest limit was obtained in Ref. [
51] that implies
s which is equivalent to an upper limit
eV. This limit, however, becomes invalid if the Earth possesses a mirror magnetic field
[
2]. For non-zero
the limits on
are much weaker, and the present experimental situation is summarized in Ref. [
54]. In fact, for
G,
oscillation time as small as
s can be allowed. In addition, some of the experimental data show significant anomalies, the strongest one of
deviation from the null hypothesis [
55], which can be interpreted by
oscillation with
s (or
eV) in the presence of mirror magnetic field
G. Mirror magnetic field at the Earth could be induced by a tiny fraction of captured mirror matter via the electron drag mechanism [
56]. Let us also remark that fast
oscillation can have interesting implications for the propagation of ultra-high energy cosmic rays at cosmological distances [
57,
58] or for the neutrons from solar flares [
59]. These oscillations also can be tested via
regeneration experiments like those discussed in Refs. [
60,
61] and will be discussed also in this paper in relation to the possible existence of transition magnetic moment between
n and
states.
The neutron magnetic dipole moment
determines the Larmor precession of the neutron spin in an external magnetic field
. It is known with high precision,
[
62] where
is the nuclear magneton. It is convenient to use it as
eV/G. In principle, the neutron could have also an electric dipole moment which would violate P and CP-invariance; however, there are severe experimental limits on it [
62]. If the mirror sector exists, the same limits on an electric dipole moment should apply to the mirror neutron.
However, the transformation
can be also due the existence of a transition magnetic moment (TMM) between the neutron and mirror neutron. Notice that the existence of a TMM between the neutron and antineutron is forbidden by Lorentz invariance while between the neutron and mirror neutron it is allowed [
63,
64]. In other terms, there can exist the following non-diagonal operators between
n and
states:
where
and
are respectively the ordinary and mirror electromagnetic fields. For the transition magnetic moments (TMM) we have
depending on the type of exchange symmetry between two sectors,
or
. Let us notice that the constants
in Equation (
2) can be generically complex, and besides the TMM there can exist also transition electric dipole moment (TEDM) between
n and
states which potentially would introduce CP violating effects in
conversion.
In this paper we are interested in exploring possible experimental manifestations of the neutron TMM. We do not discuss the particular mechanisms of its generation. Most generically, if a mechanism exists that causes the
mixing, it will involve the charges of the constituent quarks of
n and
and the corresponding interactions of these charges either with the photons or with mirror photon will induce also the transitional moments between
n and
. Moreover, the neutron TMM can be induced by loops involving hypothetical charged particles, in an analogous way as the transition magnetic moment between neutrinos (for some possible models one can address Ref. [
65]). In principle, such loops should induce both the TMM and TEDM with the comparable magnitudes. However, here for brevity we concentrate on the case of transition magnetic moment only.
2. Neutron TMM and System
For describing the time evolution of the mixed
system in the background of uniform magnetic fields
and
and the possible presence of ordinary and/or mirror matter, the Hamiltonian
of Equation (
1) should be modified to the following form:
where we neglected the terms describing the decay, incoherent scattering and absorption of
n and
states assuming that the densities of both ordinary and mirror matter are low. However, we kept the optical potentials due to the coherent zero-angle scattering.
Hamiltonian (
3) is in fact a
Hermitian matrix that includes two spin-polarizations of
n and
states. Here
V and
stand for
n and
Fermi potentials induced respectively by ordinary and mirror matter,
is a set of Pauli matrices,
is a mass mixing of Equation (
1) and
and
, are the TMM’s between
n and
of Equation (
2) related respectively to ordinary and mirror magnetic fields. In the following, in view of
or
parities, we take
eV/G for normal magnetic moments of
n and
while for the TMM’s we consider two possibilities,
.
The magnitude of
nTMM
is unknown; it can be either positive or negative. (Let us remind that for simplicity we do not discuss transitional electric dipole moments.) We can measure the TMM in units of the neutron magnetic moment itself,
with
being dimensionless parameter. Therefore, Equation (
3) can be conveniently rewritten as:
where
,
and
(one can drop the equal additive diagonal terms since they will not affect the evolution of the system, and the
–term which can be positive or negative comprises the difference of the Fermi potentials as well as the possible mass difference between the ordinary and mirror neutrons as discussed in Ref. [
46]). The sign ± in the non-diagonal terms takes into account that the unknown parity of the mirror photon (
) can be the same (+) or opposite (−) to that of the ordinary photon. For simplicity, we coin these two cases as “+ parity” and “−parity”.
Let us consider first the case when mirror magnetic field is negligibly small,
(e.g., mirror galactic magnetic fields of few
G can be the case here) but ordinary magnetic field is rather large and it cannot be neglected. In
approximation (or
)] the time evolution described by the Hamiltonian (
4) is very simple since the spin quantization axis can be taken in the direction of magnetic field
thus reducing the evolution Hamiltonian (
matrix) to two independent
matrices for two polarization states:
where signs
and
stand for the cases of the neutron spin parallel/antiparallel to the magnetic field direction
, and since
eV/G we have numerically
. Therefore, generically the probabilities of
transition after time
t depend on the neutron spin-polarizations:
In particular, if , one can tune the applied magnetic field B (i.e., ) so that . The conversion probability can be resonantly enhanced for one polarization state (+ or −, depending on the sign of and also on once the nTMM effects are included).
Let us consider the case when
which corresponds to the minimal hypothesis assuming that
n and
are exactly degenerate in mass, there are no effects of mirror matter at the Earth, and the ordinary gas density is properly suppressed as is usually done in the experiments using the UCN for the neutron lifetime measurements of for search of
effects. Then oscillation probabilities (
6) become:
where we consider that
and
. In the general case, when both
and
are present, these probabilities are different. However, if
(or
),
and
must be equal.
For unpolarized neutrons one can consider an average probability between two polarisations:
In this case contributions of
mass mixing and magnetic moment mixing are disentangled, and they contribute independently as
and
. Obviously, this is not the case when
as one can see directly from Equation (
6).
The typical time for free neutron propagation in experiments is
s or so (e.g., for ultra-cold neutrons (UCN) this is the time between bounces from the walls in the trap). Thus, provided that
, which means that
B is larger than few mG (which regime we call the case of non-zero field
), the oscillation probabilities can be averaged in time and we obtain:
However, in small magnetic field
mG or so, when
(which case we can call zero-field limit), oscillations cannot be averaged, and we have:
where
stands for the mean free-flight time square averaged over the neutron velocity spectrum. Therefore, the two cases can be distinguished by comparing the neutron losses in zero and non-zero field regimes. In the case of
mass mixing
, the non-zero field suppresses
transitions,
, and thus the neutron losses should be larger in smaller applied field. In the case of
TMM, the situation is just the opposite,
, so that in the limit of zero magnetic field
conversion probability due to
nTMM is suppressed while for large enough
B it becomes constant. Summarizing, in the generic case, both effects can contribute in
transitions and the average oscillation probability has a form
. Thus, if there is no mirror magnetic field at the Earth,
, for smaller applied field
B, the contribution of the first term should be larger, whereas for large enough magnetic field, when
, the second term induced by the
nTMM effect should become dominant.
However, in the presence of non-zero mirror magnetic field,
, the situation becomes different. Let us consider the case when the mirror magnetic field at the Earth is not negligible, i.e., it is at least larger than few mG and it perhaps can be
G, comparable with the normal magnetic field of the Earth [
2]. In the presence of
mass mixing but without the
nTMM terms, the exact general solution for
oscillation probability vs. time in a constant and uniform magnetic fields
and
was obtained in Refs. [
2,
55]. The probability of
conversion in this case has a resonance character at
and it depends on the spatial angle between vectors
and
. The direction and magnitude of the vector
is a priori unknown but it can be determined from scanning experiments, e.g., with the high-flux cold neutron beams as described in Refs. [
60,
61].
Let us now study a situation with
when also the
nTMM term is present in the Hamiltonian (
4) (but assuming again that
). Now the probability of
transition depends on the values of
as well as
. The exact expression for time dependent probability is difficult to extract in analytical form from the Hamiltonian represented by
matrix (
4). However, if we focus on non-resonant region assuming that
, which for the neutron mean flight times
s means that the difference of magnetic fields
is larger than several mG, then the mean oscillation probability
between two spin states, averaged over many oscillations, can be readily calculated following the techniques of Ref. [
2]. Interestingly, the interference terms between the two effects cancel out and one gets the average probability simply as a sum
.
Here
is the average
oscillation probability due to mass mixing:
where
, analogously
, and
is the angle between the directions of ordinary and mirror magnetic fields,
and
. In Refs. [
54,
55] this formula was given in somewhat different form
, where:
which expressions depend only on the modulus of the magnetic field
.
The second term instead describes the probability of transition only due to transition magnetic moment , and it depends on the choice of ± parity. Namely, in the case of parity, it does not depend on the values B and and angle , and one simply gets .
As for the case of
parity, the dependence on the magnetic field is non-trivial. Performing calculations similar to that of Ref. [
2], we get for the average
transition probability:
Obviously, these formulas for
as well as Equation (
11) for
cannot be used exactly at the resonance when
. However, in practical sense, they are valid also in proximities of the resonance as soon as
. Let us remark also that the separability of two effects,
, holds only if
is vanishing. For
, which is the case when ordinary or mirror matter densities are not negligible (or there is a mass difference between
n and
states) the effects of mass mixing and TMM cannot be separated and the oscillation probability has the form
where the “interference” term
non-trivially depends on all parameters, and generically two resonances can exist [
2].
Therefore, in the case
, the average probability in the background of mirror magnetic field
can be presented as:
where the terms
and
, with
and
given in Equation (
12) and
and
having the following form:
The values
and
can be conveniently measured in experiments by studying the dependence of the neutron losses on magnetic field. In particular, in a background of non-zero mirror field
the oscillation probabilities in the applied magnetic fields of opposite directions,
and
, are respectively
and
. Therefore, the average of these probabilities should not depend on the angle
but only on the magnetic field value
B. Namely, we have
, while their difference depends also on the angle
and we have
. Notice that Equations (
11) and (
15) are invariant under exchange
by mirror symmetry for both types of parity (+ or −).
In the limit
, when the ordinary magnetic field is screened, we see from Equation (
14) that
and so we get
, where:
These expressions are analogous to that of Equation (
9) when the roles of ordinary and mirror magnetic fields are reversed, i.e.,
.
Thus, if
, the probability
of
oscillation in vanishing magnetic field can be small, and it should be modified in larger magnetic fields. In particular, it can be resonantly enhanced when the applied magnetic field has the values comparable to
. From Equations (
10) and (
15) we obtain the modification factor simply as a function of
:
In principle, the scenarios of mass mixing and
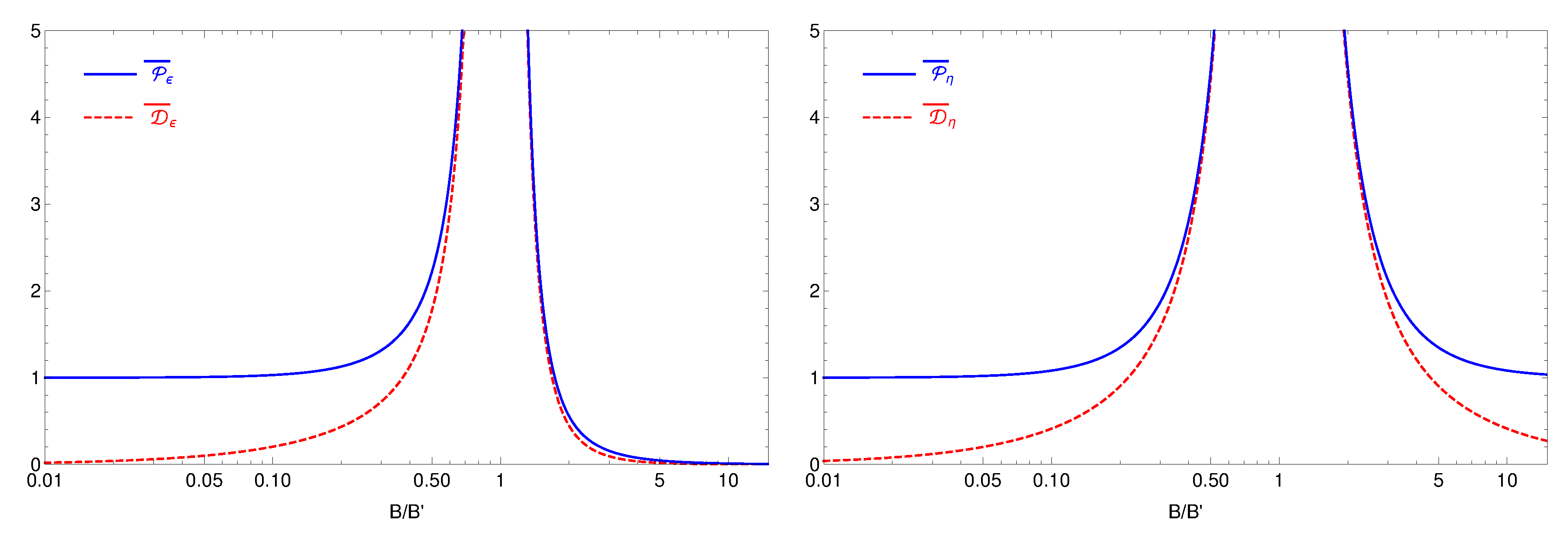
nTTM (in the case of + parity) can be distinguished by the shape of the oscillation probability in the neighbourhoods of the resonance (see
Figure 1), which can be studied by scanning over the magnetic field values. As for the case of − parity, there is no resonant behaviour, the averaged probabilities are practically independent of
B and thus, in this case the
nTTM effects will be more difficult to distinguish. As for + parity case, the effect is substantial only when
while in both limits
and
we have
. (Very close to the resonance
the probability will depend on the magnitude of magnetic field
B and its direction also for − parity case.) Thus, for large magnetic fields
probability will be constant independent on the parity sign as also can be seen directly from Equation (
13).
On the other hand, assuming that
, instead of applying non-zero magnetic field, one can introduce some matter potential for the ordinary component. In this case, taking
, the Hamiltonians (
5) should be changed to the form:
where now signs
and
indicate the neutron spin parallel/antiparallel respective to the mirror magnetic field direction
. Correspondingly the oscillation probabilities (
6) read:
Thus, at the resonance
, the probability
is resonantly enhanced to maximal value:
while for
the same occurs for
. Hence, by introducing some gas with positive or negative potential one could achieve a resonance amplification of
conversion probability for one polarization, for both parities.
Let us consider e.g., the case of cold neutrons propagating in air or in another gas described by the positive Fermi quasi-potential
[
66]. At the same time, the density of this gas can be low enough to neglect the incoherent scattering at a finite angles and the absorption of neutrons. e.g., for air at normal temperature and pressure (NTP) this Fermi potential is
neV. The probability of elastic scattering and absorption for cold neutrons in air at the NTP is ≈0.05 per meter of path. It is low enough to consider few meters of cold neutron beam propagation in air. In this way, if the polarization dependent losses will be observed, they can test the
nTTM-induced
conversions if the mirror magnetic field
at the Earth is up to few Gauss.
3. Experimental Limits from Direct Searches with UCN
The experiments with the UCN traps such as [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54] were performed for direct search of
transition under the hypothesis of non-zero mass mixing
. The above experiments study the dependence of the loss rate of the neutrons stored in the UCN traps on the strength and direction of the applied magnetic field
. Under the assumption of possible presence of mirror magnetic field
at the Earth, their results can be interpreted as upper limits on
(or lower limits on
oscillation time
) as a function of mirror field
. Below, we shall use the results of these experiments for obtaining the similar limits on
transitional moment
. In this section we consider more interesting case corresponding to
parity leaving the more simple case of negative
parity, particularly in the resonant region, for discussion elsewhere.
The experimental strategy described e.g., in Ref. [
54] is the following. In the absence of
transitions, the number of neutrons
surviving after effective storage time
inside a UCN trap should not depend on
, given that the usual UCN losses, such as neutron decay, wall absorption, or up-scattering, are magnetic field independent according to standard physics. But, when we consider oscillations, during the motion between two consecutive wall collisions the neutron can transform into a sterile state
, and so per each collision it has a certain probability to escape from the trap. Therefore the number of survived neutrons in the UCN trap with applied magnetic field
after a time
is given by
, where
is the amount of UCN that would have survived in the absence of
oscillation,
is the average probability of
conversion between the wall scatterings given in Equation (
14) and
is the mean number of wall scatterings for the neutrons survived after the time
. The oscillation probability depends on strengths
B and
of magnetic fields and the angle
between their directions,
. If the magnetic field direction is inverted,
, i.e.,
, we have
. Then one can define the “directional” asymmetry between
and
as
where
is the difference between the respective average oscillation probabilities which is proportional to
and the expression of
is given in Equation (
15). The common factor
cancels in the neutron count ratios, and
directly traces the difference of the average oscillation probabilities in magnetic fields of the opposite directions,
and
.
One can also compare the average between those two counts:
with the counts
acquired under zero magnetic field. We then obtain:
where
is the average of the oscillation probabilities between two opposite directions, see Equation (
15). Thus, the value
measuring the difference between the average probabilities at zero and non-zero magnetic fields should not depend on the magnetic field orientation but only on its modulus
.
The current experimental situation in the case of
mass mixing
is summarised in Ref. [
54]. These experiments, by measuring
for different values of
B, in fact determine the mass mixing parameter
while via measuring
they determine the combination
, i.e., the mass mixing corrected by the unknown angle
between the ordinary magnetic field
and background mirror field
. Namely, the results of all dedicated experiments [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54] were used to set lower limits on the oscillation time
and the combined value
as a function of mirror magnetic field
, see Figure 7 of Ref. [
54] (in the limit
, the upper limit corresponds to
s at 90 % C.L. [
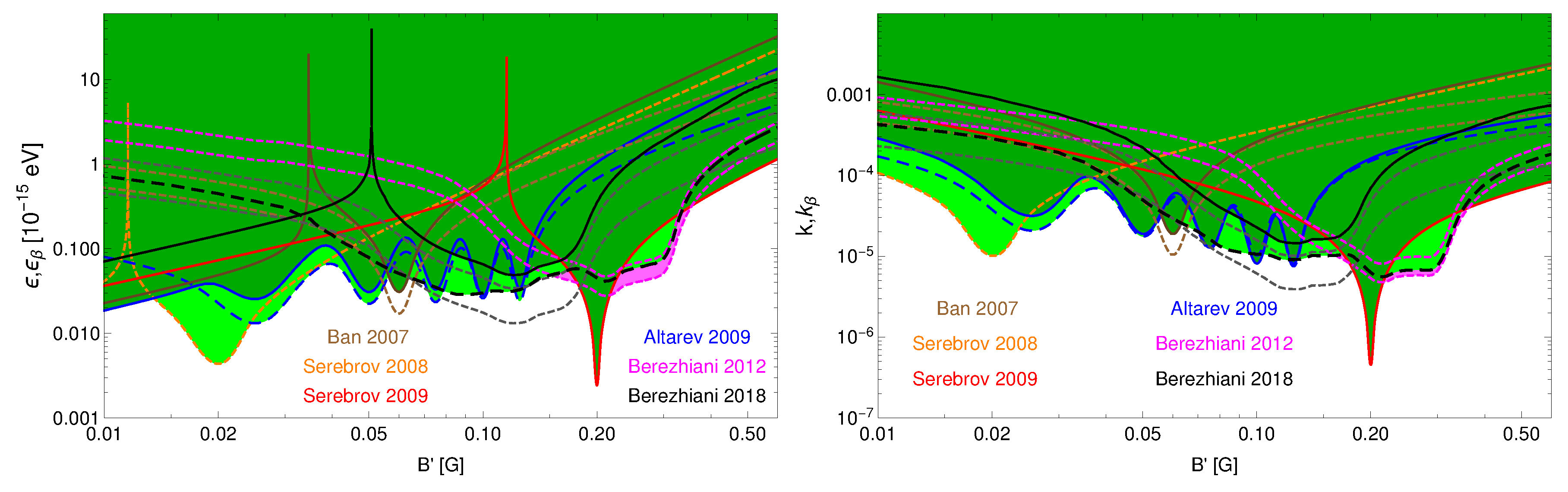
50]). For convenience, in this paper (see left panel of
Figure 2) we show the same limits directly in terms of physical parameters
and
as upper limits. (Clearly, in our generic context, these limits correspond to the case without
nTTM contribution, i.e.,
.)
The data of the same measurements can be used for setting the upper limits on
assuming in turn that
mass mixing is vanishing and
conversion occurs solely due to
nTTM effects. In the right panel of
Figure 2 we show upper limits on
and
in the case of
. We used the same Monte Carlo code developed in [
67] and used in [
54] to calculate the average oscillation probability
for the UCN inside the trap in non-homogeneous magnetic field but using the probabilities
instead of
. This will give us differences between the shapes of the exclusion regions for mass mixing and
nTTM cases which can be observed by comparing the left and right panels of
Figure 2. The magenta shaded areas in
Figure 2 correspond to parameter regions relevant for more than
deviation from null hypothesis in the measured asymmetry
[
55] which still is not excluded by the present experimental limits. Let us remind that this anomaly, as the variation of between the numbers of the survived UCN stored under the vertical magnetic field
G directed up and down, was obtained in Ref. [
55] via re-analysis of the experimental data of Ref. [
51]. This asymmetry can been interpreted as an effect of
oscillation in the presence of a mirror magnetic field on the order of 0.1 G at the Earth [
54,
55].
In this section we have not considered the effects of magnetic field gradients to be introduced in the following
Section 4 for the estimates of possible magnitude of
nTMM. In UCN experiments [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54] certain attempts were made to maintain the uniformity of magnetic fields, so the effects of collapse of
system in the trap volume between the wall collisions due to gradients might be not very significant besides the the fact that detailed field maps for most of these experiments are also not available. Thus, the limits shown on the right panel in
Figure 2 should be considered as orientative upper limits for
obtained in the assumption of the presence of mirror magnetic field
.
4. System in Non-uniform Magnetic Field
If at
the
system were in vacuum and in a constant magnetic field
(
), then for initial condition at
, the kinetic energies
are the same, as it is assumed in Equation (
3). The system will oscillate in time between two states
n and
which interact with ordinary matter differently. Two orthogonal eigenstates of the oscillating (
) system are formed corresponding to the different total energy eigenvalues. Namely, the Hamiltonian eigenstate
has interaction properties close to that of the ordinary neutron (
n) and the state
close to that of the mirror neutron (
) once the mixing angle
arising due to non-diagonal terms in Hamiltonian is small. In the medium is uniform and also constant in time, the eigenstates
and
do not oscillate between each other but just propagate independently. Let us remind however that in non-uniform medium the angle
is position dependent and thus the notion of the Hamiltonian eigenstates has only a local significance. However if the evolution of the system is adiabatic, then the Hamiltonian eigenstates adiabatically evolve from one position to another.
Let us assume that at
the system enters a region of non-uniform magnetic field which is a function of coordinates and has non-zero gradients. The gradient of potential energy
from a semi-classical point of view generates a force. In some UCN experiments, e.g., in the UCN
experiment with magnetic Hallbach array [
68], this force can exceed the Earth gravitational attraction force and cause vertical bouncing of neutrons (of a certain polarization) from the surface with an arranged strong magnetic field gradient. By virtue of the Mirror Model this gradient force mainly acts on the “almost" neutron component
of the system but very weakly on the “almost" mirror component
, while the gravity is the same for both components
and
. A similar situation occurs in the collision of neutrons with the wall in gravitational UCN traps, where the gradient is due to the Fermi potential of the trap walls. A positive Fermi potential
of the wall material will repulse neutrons with kinetic energy smaller than
at the characteristic distance of the neutron wave packet, ∼
for typical
neV. In this way, the gradient of potential in the interaction with wall can be estimated as ∼1 eV/m. In the UCN
experiment [
68] the gradient of the magnetic field is ∼1 T/cm near the bouncing surface that corresponds to the gradient of potential energy ∼
eV/m.
Integrated over time , this force provides a relative momentum between the two components. If it exceeds the width of the neutron wave packet , then that will lead to the “separation of components” or to decoherent collapse of system into either or states. If this force would be exerted only for time and then reduced to zero, then finite relative momentum will continue in time the separation of the components. The same conclusion can be formulated in a language more appropriate for quantum mechanics as a potential energy variation different for the two components of wave function in non-uniform magnetic field.
At some point the two components will be “pulled away” by gradient, and the entanglement of system moving in the non-uniform magnetic field will be broken. If “measured” at this moment the system will be found with probability P in the pure state of “mirror neutron” or with probability in the state of “neutron” . If not “measured,” each of the states will be subject to further oscillation with the reset of initial conditions at the time of “separation.”
The situation is similar in UCN traps with the material walls where entanglement will be broken with n component being reflected or absorbed by the wall with the probability and component escaping from the UCN trap through the wall with a small probability P.
More generally, the motion of the oscillating
system in the slowly (adiabatically) changing magnetic field can lead either to a change of the kinetic energy of the components of wavefunction and/or to their spin rotation. Both these effects can result in decoherence of the system. The decoherence problem expectedly can be properly treated by modern methods using the density matrix formalism [
69,
70]. One can consider master equation of the evolution of density matrix of
system in the environment of the external potential
, different for two components of the system (four components when spins are included). These techniques are not yet sufficiently developed and tested in respect to particle oscillations and therefore we will refrain from the construction and solution of the density matrix evolution equation. Instead we try to consider the decoherence problem qualitatively. For these qualitative arguments we will ignore the spin rotation in a non-uniform magnetic field and will consider one-dimensional motion in a field with a gradient. Let us first assume a hypothetical simple case of a constant gradient of the magnetic field along the direction of the motion. The magnitude of
B is linearly increasing with the distance
x, but the direction of vector
remains practically the same. For a neutron with a certain polarization propagating along axis
x from the initial condition
and for the observation time
, the kinetic energy width of the wave packet
of the
system is:
For a path
, passed by the neutron for the observation time
, the change of potential energy produced by the magnetic field gradient is
. If
is much smaller than
:
then the
system will remain entangled.
For sufficiently large
, the entanglement of the
system will be broken. T his means that the system will collapse to pure states of either
or
n with probabilities
P and
correspondingly. Assuming that the velocity will not change significantly by magnetic gradient for the time
(say, for the time of flight between two wall collisions in a UCN gravitational trap), then the gradient that should lead to the decoherence collapse of the system can be estimated in a following way:
Thus, for the entangled evolution of the system e.g., with velocity m/s in a UCN gravitational trap with a flight time s between wall collisions, the magnetic field gradient should be mG/m. Larger gradients can cause the collapse of the wavefunction at an earlier time and can cause the transformation of n to to occur in the volume of the trap rather than in collisions with the trap walls. Thus, the effect of a non-uniform magnetic field might result in the transformation in the trap volume with the same result as that which would be expected in collisions of the entangled system with the trap walls.
In the UCN gravitational trap experiments measuring the neutron lifetime the Earth magnetic field
G is usually considered as a non-essential factor. The number of wall collisions is experimentally extrapolated to the “zero number of collisions,” e.g., in [
71,
72,
73]. A magnetic field non-uniformity can produce a similar disappearance effect in the volume of UCN gravitational traps, but this effect is not removable by extrapolation to the zero number of wall collisions. Unfortunately, the UCN gravitational trap experiments do not use magnetic shielding of the trap, and the actual maps of magnetic fields in these experiments are unknown. For getting some idea of the possible non-uniformity of the Earth magnetic field in such conditions, we have measured some vertical gradients as high as 75 mG/m in an arbitrary general-purpose laboratory room of a typical university building. Therefore, we can advocate that the contribution of
nTMM (that outside the resonance does not depend on the magnitude of the magnetic field) to
transformation could be also essential as a source of the neutron loses.
In the proposed cold-neutron-beam disappearance/regeneration experiments [
60,
61], with average neutron velocity
m/s and flight path e.g., 16 m, for the entangled evolution of the
oscillating system the gradients ≪
mG/m would be required. Larger gradients can shorten the path of entangled evolution and effectively will lead to multiple shorter-in-time collapses which will increase the production of
states, since the probability in the fields larger than few mG and far from resonance due to
nTMM will remain constant
.
5. Possible Magnitude of Neutron TMM
It is a well known problem in UCN gravitational trap experiments that the measured wall losses are larger than these predicted from theoretical models using known scattering lengths of materials (see discussion in Refs. [
74,
75] and references therein). Lowering the temperature of the trap walls, although reducing the loss coefficient (per single collision), does not resolve the discrepancy between experiment and theoretical calculations. Only in one of a few experiments using fomblin-oil coated trap [
73] the measured (
) and expected (
) loss factors per wall collision were in good agreement. (In all other experiments the measured losses were significantly exceeding the theoretical predictions.) Hence, one can speculate that losses at least at the level of
per collision can be due to the losses in the trap volume caused by the neutron TMM in the non-uniform environmental magnetic field. The local Earth magnetic field in these experiments can be affected by magnetic constructional materials, platforms, etc., as well as by metal reinforced concrete walls of the industrial buildings. Let us assume that in a typical trap of the size ∼0.3 m the magnetic field uniformity is <5% from wall to wall such that the moving neutron can see a constant gradient of about 75 mG/m. We are not considering the effect of neutron spin rotation due to possible change of the direction of the magnetic field—this might result in additional decoherence effects that are not discussed here. For a typical UCN velocity 3 m/s, and assuming that the velocity will not essentially be changed by the gradient during the flight from wall to wall, from Equation (
25) we can find that the typical time for collapse to occur will be ∼
s. Thus, we can estimate that ∼5 volume collapse events will occur per one collision with the trap wall. Attributing this totally to the neutron TMM transformations with constant probability
, we can estimate that losses per collision of
correspond to a neutron TMM of
In the neutron lifetime measurement with large UCN gravitational trap [
72], assuming the same magnetic field gradients, the number of decoherence events per second occurring in the volume of the storage trap can be estimated as ∼50 s
. With the probability of
transformation per event as
, this can generate a neutron disappearance rate that can explain the difference [
76] between the result [
72] of the UCN disappearance lifetime experiment and the result of the beam appearance measurement [
77]. The required value of
nTMM in this case can be estimated again as (
26).
If magnetic field gradients in the gravitational trap are higher than we have assumed, then the magnitude of neutron TMM required to produce mentioned disappearance rate can be lower than in (
26). Also, if
is present it might increase the conversion probability thus reducing our estimate of
in (
26). Would the UCN lifetime experiment with gravitational trap be magnetically shielded with residual field magnitude
mG (that means assuming that both
B and
are vanishing) then
effect due to
nTMM will vanish and measured lifetime might be affected only by a smaller effect of
oscillations due to mixing mass
as was discussed earlier.
In experiments with “UCN magnetic field trap” [
68,
78], where neutrons are repulsed from the strong gradient of the magnetic field, the number of decoherence events can be greatly increased. For a rough estimate we have attempted to reproduce in a simplified one-dimensional way the vertical bouncing of UCN in the magnetic field with a strong gradient described in the papers [
68] up to the height of 50 cm and obtained with Equation (
25) approximately 3500 decoherence events per a second of the neutron motion. Thus, to produce a UCN disappearance rate ∼
per second in experiment [
68], using constant conversion probability
one can estimate the magnitude of
nTMM:
Simulations for neutron propagation in the trap with more details of magnetic field configuration (not available to us) will likely affect this estimate. Also, the potential reason for disappearance in [
68] can be a change of the spin precession phase due to the presence of
oscillations [
2] that can lead to unexpected depolarization effect in the magnetic trap.
We also can get another
nTMM estimate from the different interpretation of the limit on
obtained in [
51] at
and under assumption that
. We will assume for this result instead that mirror magnetic field
is present (although unknown) with magnitude larger than few mG and thus the measured limit on disappearance probability in [
51] should be taken as a limit determined by the magnitude of probability
due to
nTMM. From this we can obtain the following estimate:
We can conclude this section by noting that these estimates, although very rough, are suggesting the order of magnitude of the
nTMM
that doesn’t contradict the existing experimental observations and might be the parameter of the mechanism responsible for the neutron disappearance in the UCN trap lifetime experiments, such as [
68,
72,
78] and others. Such range of possible magnitudes for
is also allowed by the limits obtained from the direct
search discussed in
Section 3.
6. How nTMM can be Measured
Beyond the results obtained in
direct searches with UCN [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55] and summarized in [
54] the possible new searches with cold neutrons, described in [
60,
61], might bring more evidence whether
transformation exists. These new proposed measurements are based on the detection of cold neutrons in intense beam after coming through the “region A” of controlled uniform magnetic field (in disappearance mode) or on total absorption of the cold neutron beam after passing through the “region A”, allowing only produced mirror neutron to pass through an absorber and then regenerating them back to the detectable neutrons in the second “region B” with similar controlled uniform magnetic field (regeneration mode). Variation of the magnitude of uniform magnetic field
B in the range 0 to 0.5 G by small-steps scan (also with possible variation of direction of vector
) can reveal the resonance in the
n-counting rates corresponding to
with magnitude and width related to mass mixing parameter
in Equation (
4). The presence of
nTMM can enhance the resonance magnitude or, as follows from Equation (
15), can offer an alternative interpretation of the effect (if observed or excluded) in terms of magnitude of
nTMM.
We would like to discuss here other two new methods that can be used for the detection of nTMM effect in the magnetic fields stronger than the Earth magnetic field.
The first method is a variation of the regeneration method where “region A” and “region B” mentioned above, instead of uniform magnetic field, are implementing strongly non-uniform magnetic field. Since nTMM transition probability remains constant in any sufficiently large magnetic field, strong gradients of the field can generate large number of decoherent collapses of system into either n, or with a small probability to -states; the latter will lead to enreachment of in the “region A.” The absorber between “region A” and “region B” will remove all not-transformed neutrons from the beam allowing only the to pass through the absorber. Strong gradients of the magnetic field in the “region B” will similarly enhance the transformation of back to detectable n, the latter can be counted above the natural background e.g., by the He detector.
Strong magnetic field gradients in “region A” and “region B” can be implemented e.g., as a series of equally spaced coils around the neutron beam with alternating directions of constant current. Every coil will contribute opposite direction of magnetic field with zig-zag pattern and can provide practically constant strong
gradient along the beam axis. Simple estimates show that the gradient ∼100 G/m can be maintained along the vacuum tube that is e.g., 15 m long. For the cold neutron beam with average velocity ∼800 m/s using Equation (
25) we can estimate that the number of decoherent collapses in such “region A”- or “region B”- devices will be around 500.
The use of superconducting solenoidal magnet with a borehole along the beam axis and with maximum magnetic field of ∼10 T will be a more compact approach for reaching high gradients. The total length of the magnet can be of the order of 1 m. The magnet front field ramping-up side can serve as a “region A” and back side with ramping-down field as a “region B,” each with a decoherence collapse factor ∼700. A beam absorber should be installed in the middle of the magnet, thus transforming it into a regeneration device.
With cold neutron beams available e.g., at ILL and at HFIR/ORNL reactors, or at SNS/ORNL, or at the future ESS spallation neutron source [
79], where cold beam intensities are in the range
–
n/s, the effect of
nTMM in the whole range of
–
can be explored in rather short and not expensive experiments [
80].
The second method is based on the idea of compensation of Fermi quasi-potential of the gas media with a constant uniform magnetic field as discussed in the
Section 2 of this paper with oscillation probability given by Equations (
6) and (
20). In Equation (
6) both parameters of the resonance
and
are known and can be adjusted to compensate each other. Then, close to the resonance the probability of quasi-free oscillation can coherently grow as square of neutrons propagation time through the gas, e.g., through the air at NTP. This will work, according to Equation (
6), only for one of neutron polarizations. Regeneration scheme can be used here again with “region A” and “region B” represented by the air-filled tubes of length e.g.,
m in the solenoidal constant uniform field of
B∼10 G. Effects of the beam scattering and absorption in the gas will reduce the rate of regenerated neutrons by ≈20%. Probability of regeneration observation provided by this second method can be an order of magnitude higher than for the first method discussed above. If the resonance will be observed for the values
different from anticipated zero, that will indicate the presence of either mirror magnetic field
or small mirror Fermi-potential
. In this case, the same two-tubes layout can be used foe regeneration search with the magnetic field
B shielded below a ∼mG and the gas pressure in the tubes, i.e., parameter
varied in order to find the resonance condition described by Equation (
20) corresponding to the unknown mirror magnetic field
. The second method can be further optimized for the use with a beam of collimated UCN propagating in the gas with low absorption. In this case, due to slow UCN velocities the probability for
transformation potentially can grow approaching the maximum value.