Geospatial Analysis of Soil Quality Parameters and Soil Health in the Lower Mahanadi Basin, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
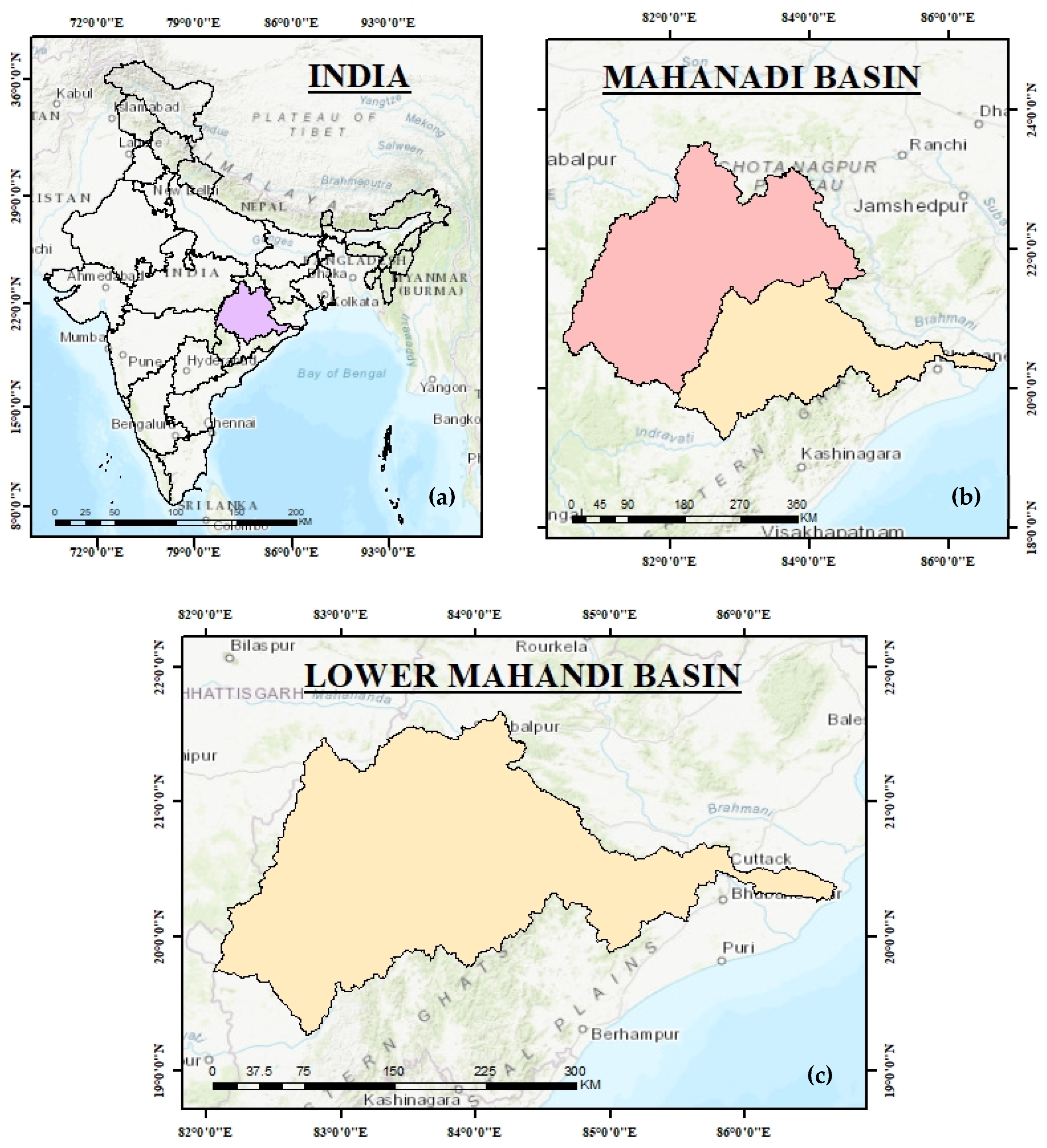
Study Area
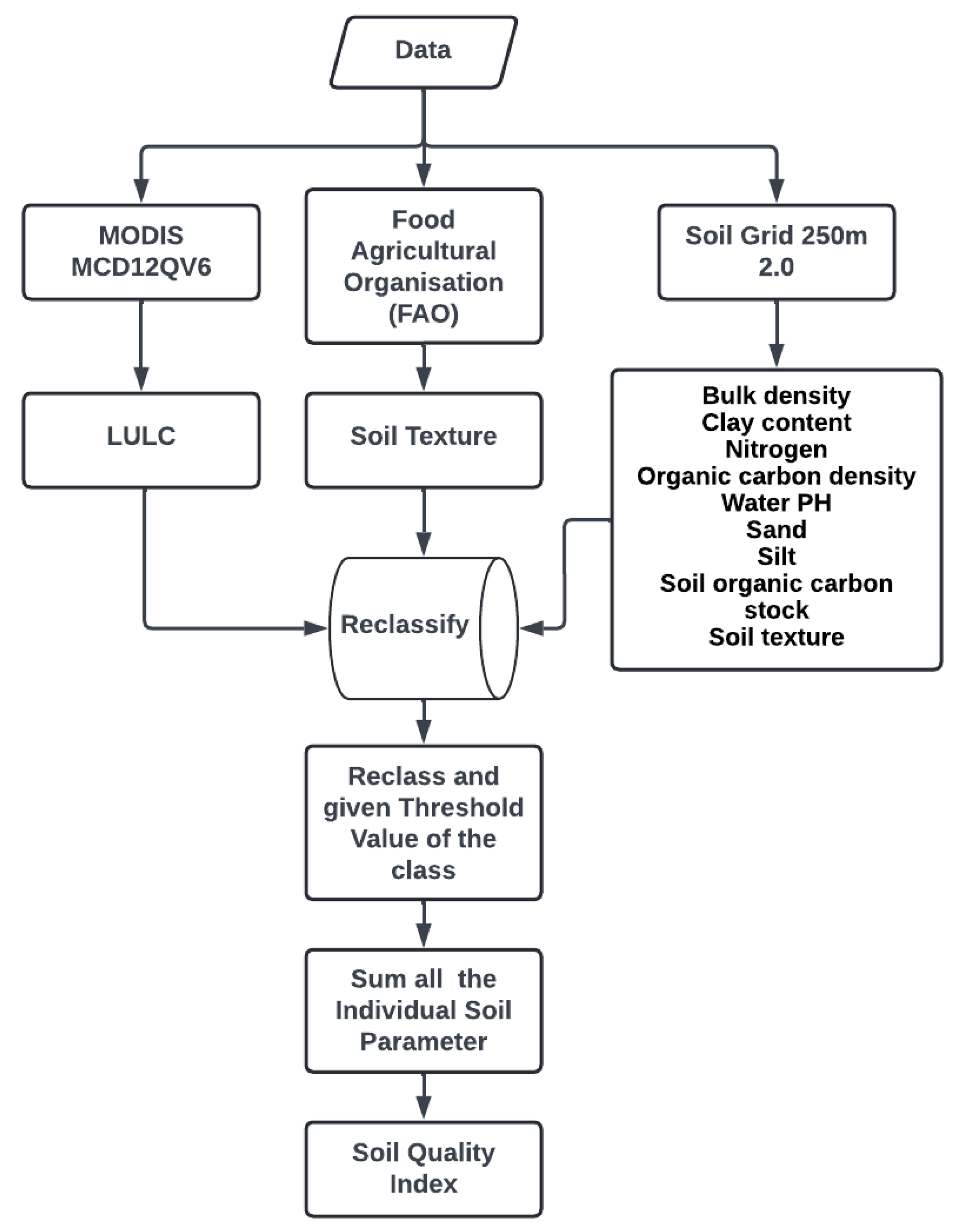
2. Materials and Methods
Soil Quality Assessment
| Data | Spatial Resolution | Year | Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCD12Q1 V6 | 500 m | 2011, 2020 | LULC map | LPDAAC [32] |
| Soil texture | 250 m | 2011 | Soil health | FAO [34] |
| Soil quality parameters (PH, Bulk density, SOC, Nitrogen) | 250 m | 2020 | Soil health | SoilGrid250m 2.0 [33] |
3. Results
3.1. Parameters Used in Soil Quality Assessment
3.1.1. Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Map
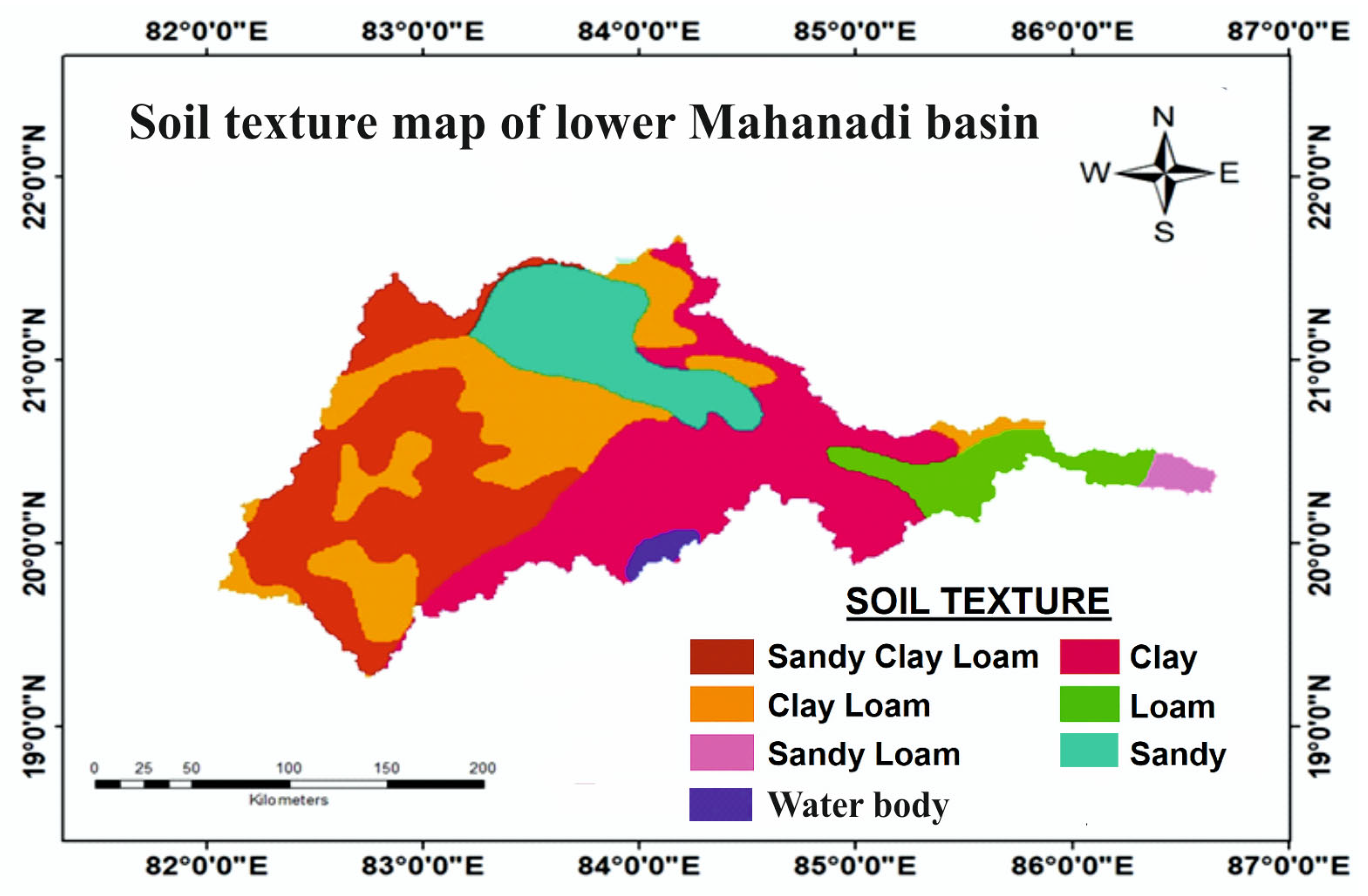
3.1.2. Soil Texture
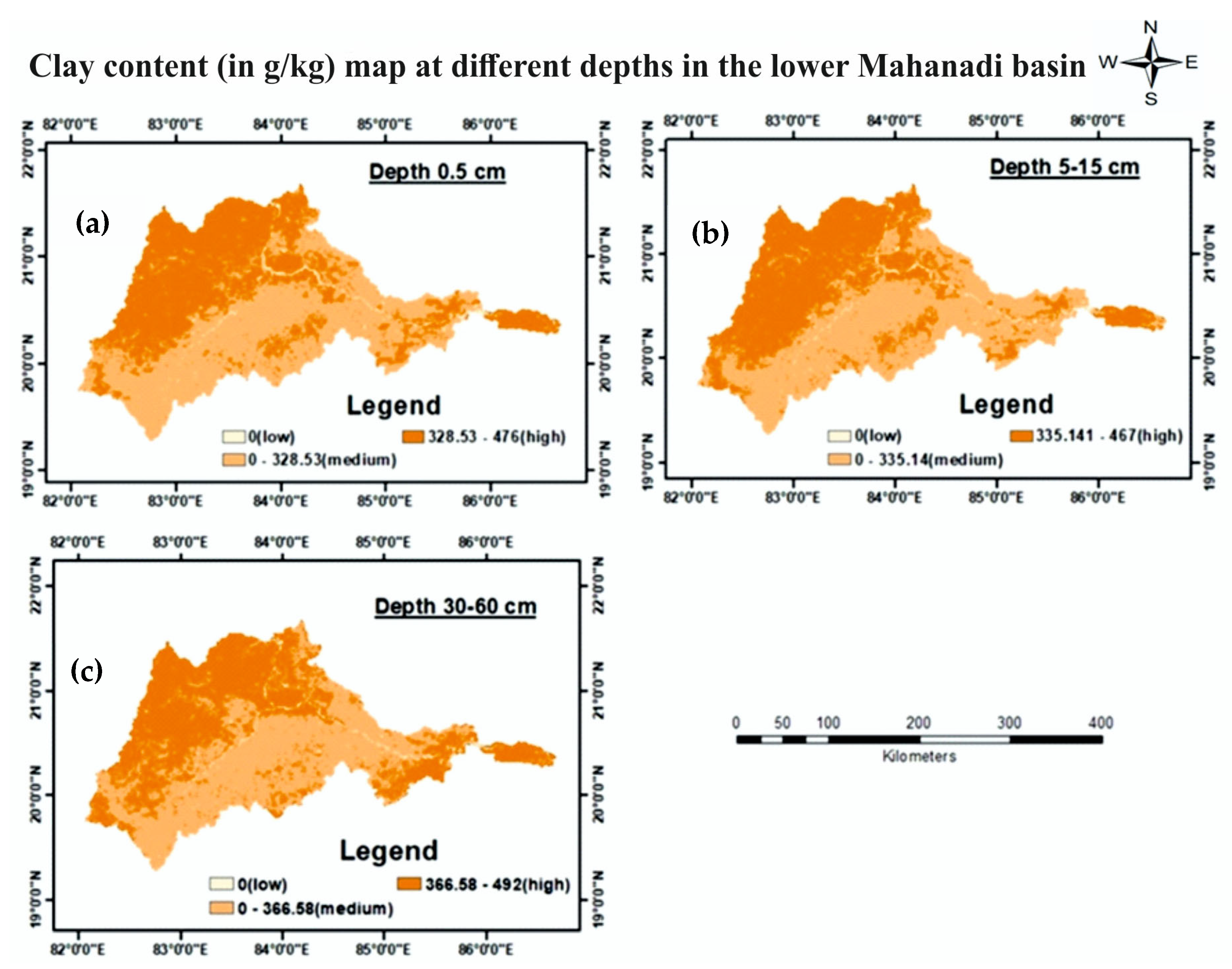
3.1.3. Clay Content
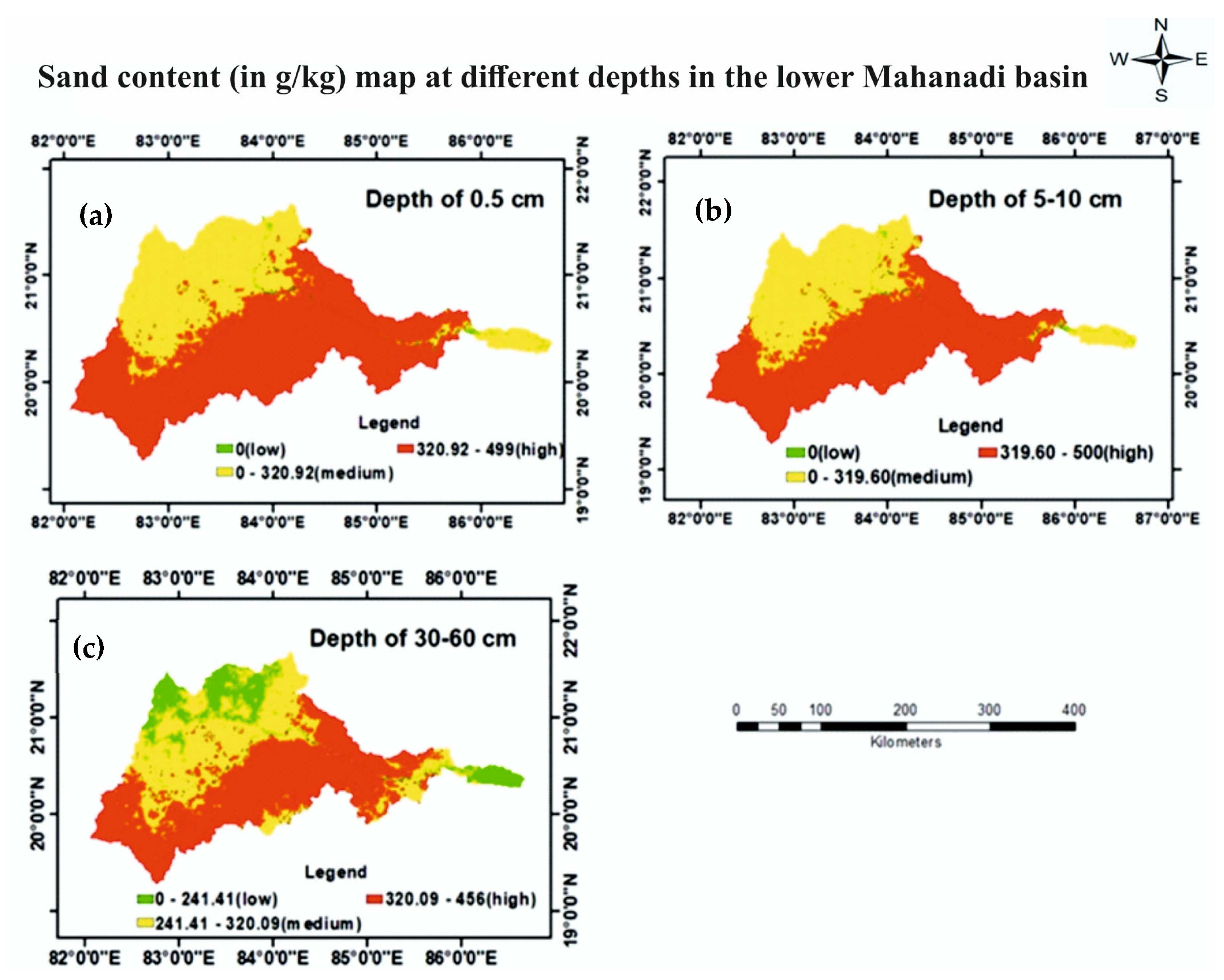
3.1.4. Sand Content
3.1.5. Silt Content
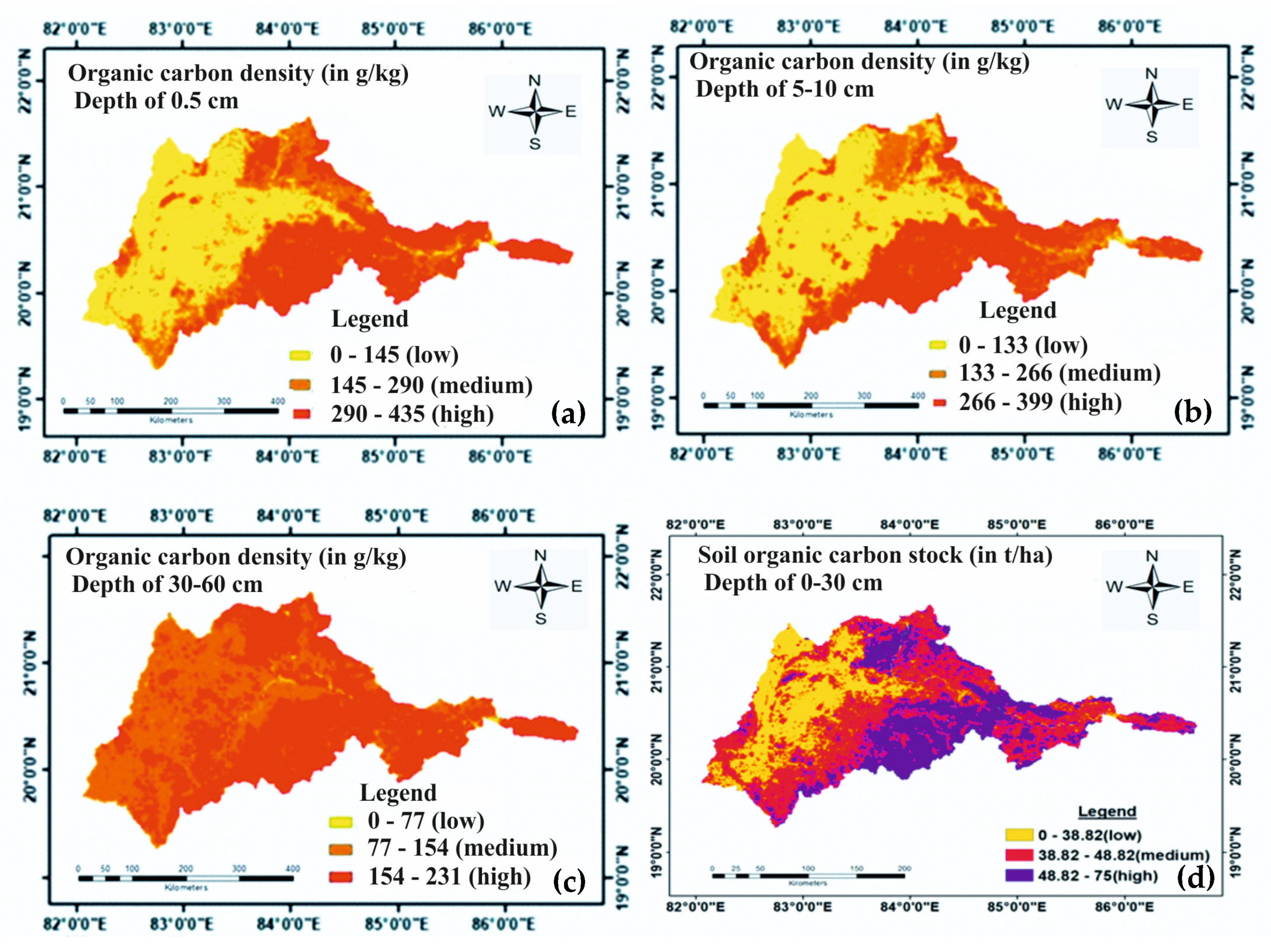
3.1.6. Organic Carbon Density and Soil Organic Carbon Stock
3.1.7. Nitrogen Content
3.1.8. Bulk Density
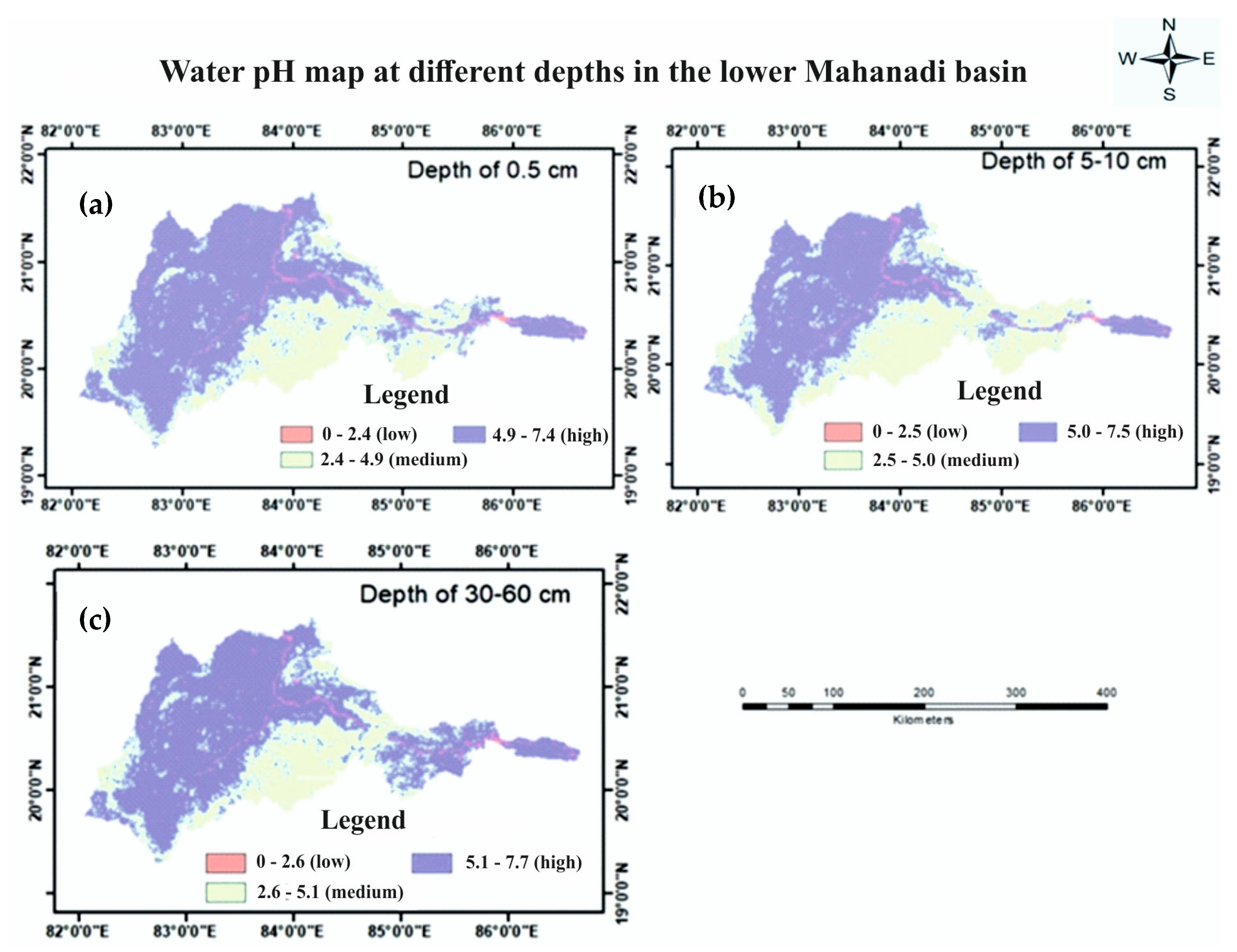
3.1.9. Water pH
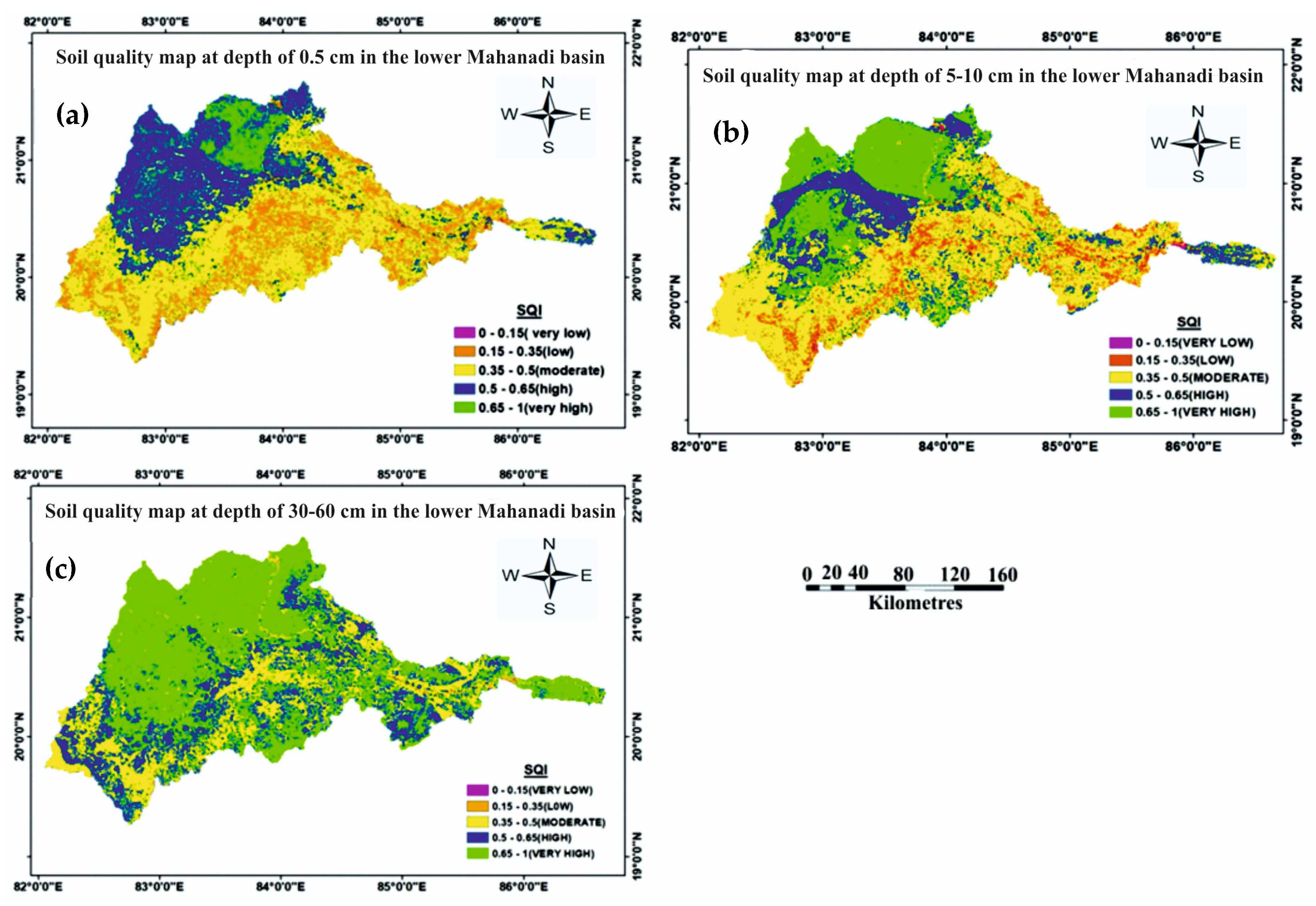
3.2. Soil Quality Map as Derived from SQI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The Causes of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: Moving beyond the Myths. Glob. Environ. Change 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.; Pradhan, B.; Huete, A.; Brennan, J. Assessing Soil Erosion Hazards Using Land-Use Change and Landslide Frequency Ratio Method: A Case Study of Sabaragamuwa Province, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltner, I.; Saeidi, S.; Grósz, J.; Centeri, C.; Laborczi, A.; Pásztor, L. Spatial Assessment of the Effects of Land Cover Change on Soil Erosion in Hungary from 1990 to 2018. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzha, A.C.; Rufino, M.C.; Okoth, S.; Jacobs, S.; Nóbrega, R.L.B. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Change on Surface Runoff, Discharge and Low Flows: Evidence from East Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, H.; Lal, R.; Reich, P.F. Land Degradation: An Overview. In Response to Land Degradation; Bridges, E.M., Hannam, I.D., Oldeman, L.R., De Vries, F.W.T.P., Scherr, S.J., Sombatpanit, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 20–35. ISBN 978-0-429-18795-7. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Jae Lim, K.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global Rainfall Erosivity Assessment Based on High-Temporal Resolution Rainfall Records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Soil Erosion in the Anthropocene: Research Needs. Earth Surf Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, A.A.; Cassalho, F.; Caldeira, T.L.; Oliveira, V.A.D.; Beskow, S.; Timm, L.C. Assessment of Soil Loss Vulnerability in Data-Scarce Watersheds in Southern Brazil. Ciênc. Agrotecnologia 2018, 42, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, C.S.; Dishant; Parida, B.R.; Pandey, A.C.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, N. Geoinformatics-Based Mapping of Environmental Sensitive Areas for Desertification over Satara and Sangli Districts of Maharashtra, India. GeoHazards 2024, 5, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Swain, S.K.; Parida, B.R.; Panda, A.; Dwivedi, C.S. Evaluating Impacts of Opencast Mining of Gondwana Coalfield (India) on Environment and Socioeconomic Using Multitemporal Satellite Data. Discov. Geosci. 2025, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, R. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment and Spatial Mapping Using LANDSAT-7 ETM+, RUSLE, and GIS—A Case Study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A. GIS Based Soil Erosion Estimation Using Rusle Model: A Case Study of Upper Kangsabati Watershed, West Bengal, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Res. 2018, 13, 555871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Koloa, C.; Pal, D.K.; Palsamanta, B. Estimation of Potential Soil Erosion Rate Using RUSLE and E30 Model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, M.; Soupios, P.; Vallianatos, F. Soil Erosion Prediction Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS Framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfahunegn, G.B. Soil Quality Assessment Strategies for Evaluating Soil Degradation in Northern Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 2014, 646502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, D.; Singh, S.K.; Ray, S.K.; Duraisami, V.P.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P.; Nimkar, A.M.; Anantwar, S.G. Soil Quality Index (SQI) as a Tool to Evaluate Crop Productivity in Semi-Arid Deccan Plateau, India. Geoderma 2016, 282, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the Intensification of Agriculture for Global Food Security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Tahoun, S. GIS Model-Builder Based on Comprehensive Geostatistical Approach to Assess Soil Quality. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A Comparison of Soil Quality Indexing Methods for Vegetable Production Systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, C.S.; Kumari, S.; Pandey, A.C.; Parida, B.R.; Sikka, G. Site Suitability Analysis of a Municipal Solid Waste Management System in Ranchi City Using AHP: A Multi-Criteria Decision Approach. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2024, 34, e22312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Rousseau, A.N.; Wang, L.; Yan, B. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Soil Organic Carbon and pH in Relation to Environmental Factors—A Case Study of the Black Soil Region of Northeastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 245, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Shen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, Z. Use of Bentonite to Control the Release of Copper from Contaminated Soils. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramady, H.; Alshaal, T.; Bakr, N.; Elbana, T.; Mohamed, E.; Belal, A.-A. (Eds.) The Soils of Egypt; World Soils Book Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-95515-5. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; Abdellatif, A.D.; Fadl, M.E. Modeling Soil Quality in Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt Using GIS Techniques. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.D.; Tripathi, P.; Das, P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Roy, P.S.; Joshi, C.; Behera, P.R.; Deka, J.; Kumar, P.; Khan, M.L.; et al. Remote Sensing Based Deforestation Analysis in Mahanadi and Brahmaputra River Basin in India since 1985. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Verma, M.K.; Prasad, A.D.; Mehta, D.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Muttil, N.; Rathnayake, U. Simulating the Hydrological Processes under Multiple Land Use/Land Cover and Climate Change Scenarios in the Mahanadi Reservoir Complex, Chhattisgarh, India. Water 2023, 15, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, B.; Paramjita, D.; Giri, M.A.; Paul, J.C. Frequency Analysis for Prediction of Maximum Flood Discharge in Mahanadi River Basin. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 3626–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, G.; Vidyarthi, V.K. Modeling Land Use/Land Cover Transformations in Mahanadi River Basin in Chhattisgarh, India: Trends and Future Projections. GeoJournal 2024, 89, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CWC. Water and Related Statistics; Central Water Commission, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IMD. Climate of India; India Meteorological Department, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- LPDAAC. MODIS Land Cover Type Product (MCD12Q1 Version 6); NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2021.
- ISRIC. SoilGrids250m Version 2.0: Global Gridded Soil Information at 250 m Resolution; ISRIC: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Harmonized World Soil Database (Version 1.2); FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lal, R. Comparison of Soil Quality Index Using Three Methods. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal Nasir, M.; Farooq Haider, M.; Ali, Z.; Akhtar, W.; Alam, S. Evaluation of Soil Quality through Simple Additive Soil Quality Index (SQI) of Tehsil Charsadda, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2024, 23, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Cichota, R.; Beare, M.; Müller, K.; Drewry, J.; Eger, A. Soil Structural Vulnerability: Critical Review and Conceptual Development. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Indicators | Depth Ranges | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 cm | 5–10 cm | 30–60 cm | ||
| LULC | Built-up | Built-up | Built-up | 0 |
| Forest | Forest | Forest | 2 | |
| Grassland | Grassland | Grassland | 1 | |
| Cropland | Cropland | Cropland | 2 | |
| Waste land | Waste land | Waste land | 0 | |
| waterbodies | waterbodies | waterbodies | 1 | |
| Soil texture | Sandy clay loam | Sandy clay loam | Sandy clay loam | 2 |
| Clay loam | Clay loam | Clay loam | 2 | |
| Sandy loam | Sandy loam | Sandy loam | 1 | |
| Clay | Clay | Clay | 2 | |
| Loam | Loam | Loam | 1 | |
| Sandy | Sandy | Sandy | 1 | |
| Clay content (g/kg) | 0–158.7 | 0–155.7 | 0–164.0 | 0 |
| 158.7–317.3 | 155.7–311.3 | 164.0–328.0 | 1 | |
| 317.3–476.0 | 311.3–467.0 | 328.0–492.0 | 2 | |
| Sand content (g/kg) | 0–166.3 | 0–166.7 | 0–152.0 | 2 |
| 166.3–332.7 | 166.7–333.3 | 152.0–304.0 | 1 | |
| 332.7–499.0 | 333.3–500.0 | 304.0–456.0 | 0 | |
| Silt content (g/kg) | 0–164.3 | 0–166.0 | 0–155.3 | 0 |
| 164.3–328.7 | 166.0–332.0 | 155.3–310.7 | 1 | |
| 328.7–493.0 | 332.0–498.0 | 310.66–466 | 2 | |
| Organic carbon density (g/kg) | 0–145 | 0–133 | 0–77 | 0 |
| 145–290 | 133–266 | 77–154 | 1 | |
| 290–435 | 266–399 | 154–231 | 2 | |
| Soil organic carbon stock (t/ha) | 0–25 | 0–25 | 0–25 | 0 |
| 25–50 | 25–50 | 25–50 | 1 | |
| 50–75 | 50–75 | 50–75 | 2 | |
| Nitrogen (g/kg) | 0–1.91 | 0–2.01 | 0–1.76 | 0 |
| 1.91–3.81 | 2.01–4.02 | 1.76–3.53 | 1 | |
| 3.81–5.72 | 4.02–6.03 | 3.53–5.29 | 2 | |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 0–0.55 | 0–0.56 | 0–0.59 | 2 |
| 0.55–1.11 | 0.56–1.12 | 0.59–1.19 | 1 | |
| 1.11–1.66 | 1.12–1.68 | 1.19–1.79 | 0 | |
| Water pH | 0–2.4 | 0–2.5 | 0–2.6 | 0 |
| 2.4–4.9 | 2.5–5.0 | 2.6–5.1 | 1 | |
| 4.9–7.4 | 5.0–7.5 | 5.1–7.7 | 2 | |
| LULC Classes | 2011 (km2) | 2020 (km2) |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 39,493.2 | 37,495.9 |
| Grassland | 4826.3 | 5432.1 |
| Forest | 12,401.2 | 13,822.2 |
| Built-up | 131.2 | 134.4 |
| Wasteland | 133.0 | 93.2 |
| Waterbody | 184.3 | 191.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swain, S.K.; Parida, B.R.; Mallick, A.; Dwivedi, C.S.; Kumar, M.; Pandey, A.C.; Kumar, N. Geospatial Analysis of Soil Quality Parameters and Soil Health in the Lower Mahanadi Basin, India. GeoHazards 2025, 6, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6040071
Swain SK, Parida BR, Mallick A, Dwivedi CS, Kumar M, Pandey AC, Kumar N. Geospatial Analysis of Soil Quality Parameters and Soil Health in the Lower Mahanadi Basin, India. GeoHazards. 2025; 6(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwain, Sagar Kumar, Bikash Ranjan Parida, Ananya Mallick, Chandra Shekhar Dwivedi, Manish Kumar, Arvind Chandra Pandey, and Navneet Kumar. 2025. "Geospatial Analysis of Soil Quality Parameters and Soil Health in the Lower Mahanadi Basin, India" GeoHazards 6, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6040071
APA StyleSwain, S. K., Parida, B. R., Mallick, A., Dwivedi, C. S., Kumar, M., Pandey, A. C., & Kumar, N. (2025). Geospatial Analysis of Soil Quality Parameters and Soil Health in the Lower Mahanadi Basin, India. GeoHazards, 6(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6040071









