Leveraging Sentinel-2 and Geographical Information Systems in Mapping Flooded Regions around the Sesia River, Piedmont, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
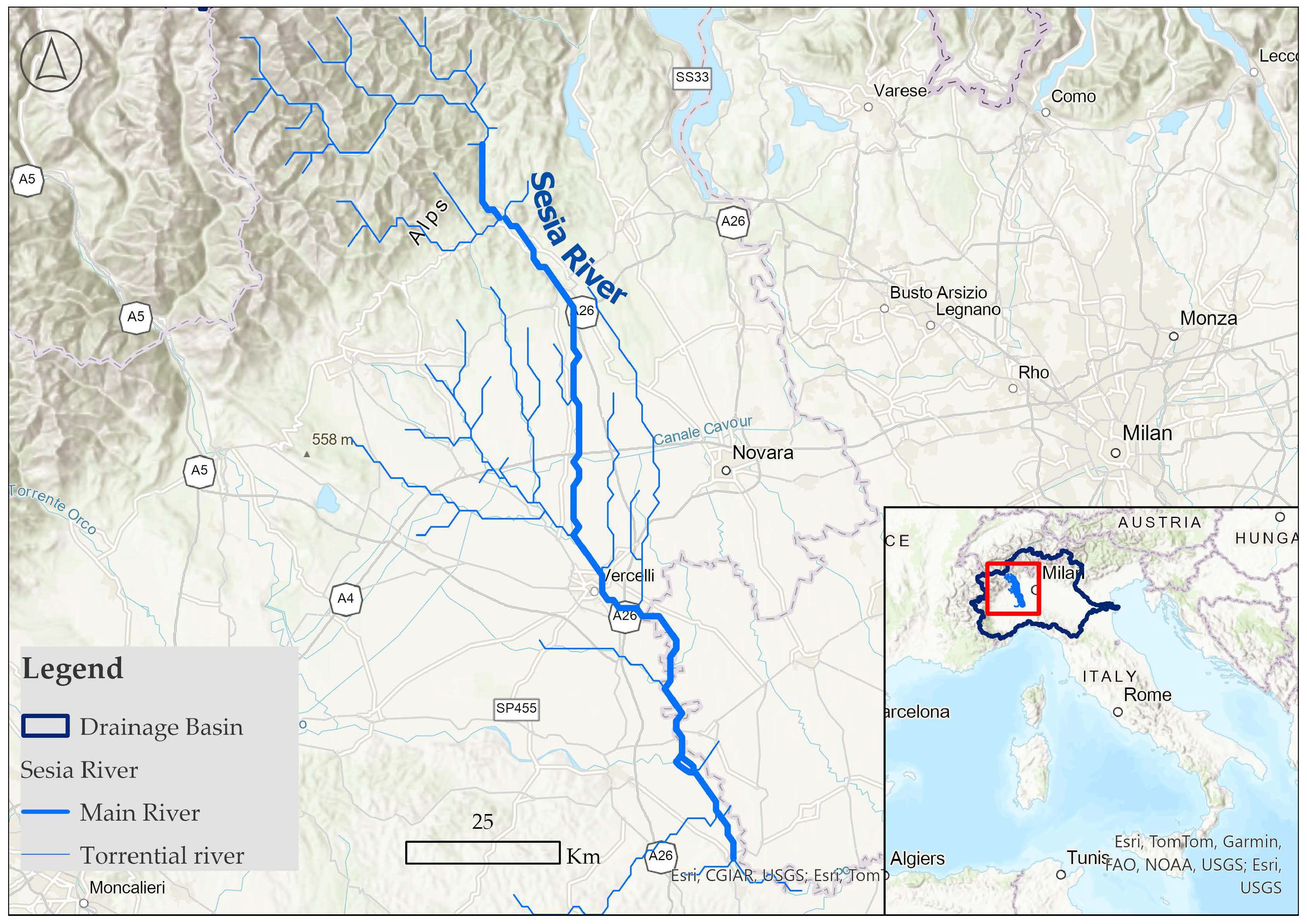
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
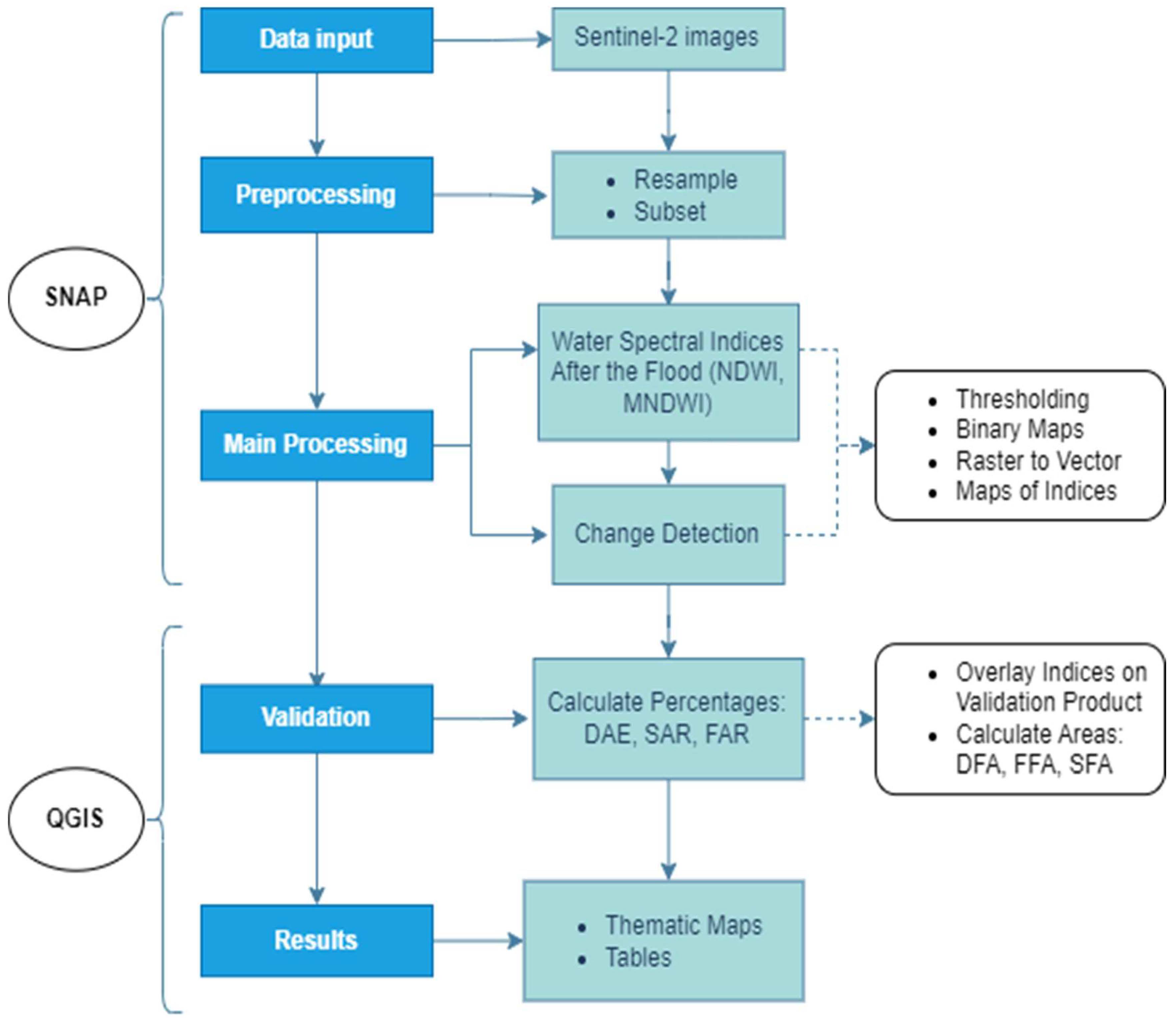
2.3. The Methodology
2.3.1. Data Pre-Processing
2.3.2. Main Processing
2.3.3. Validation
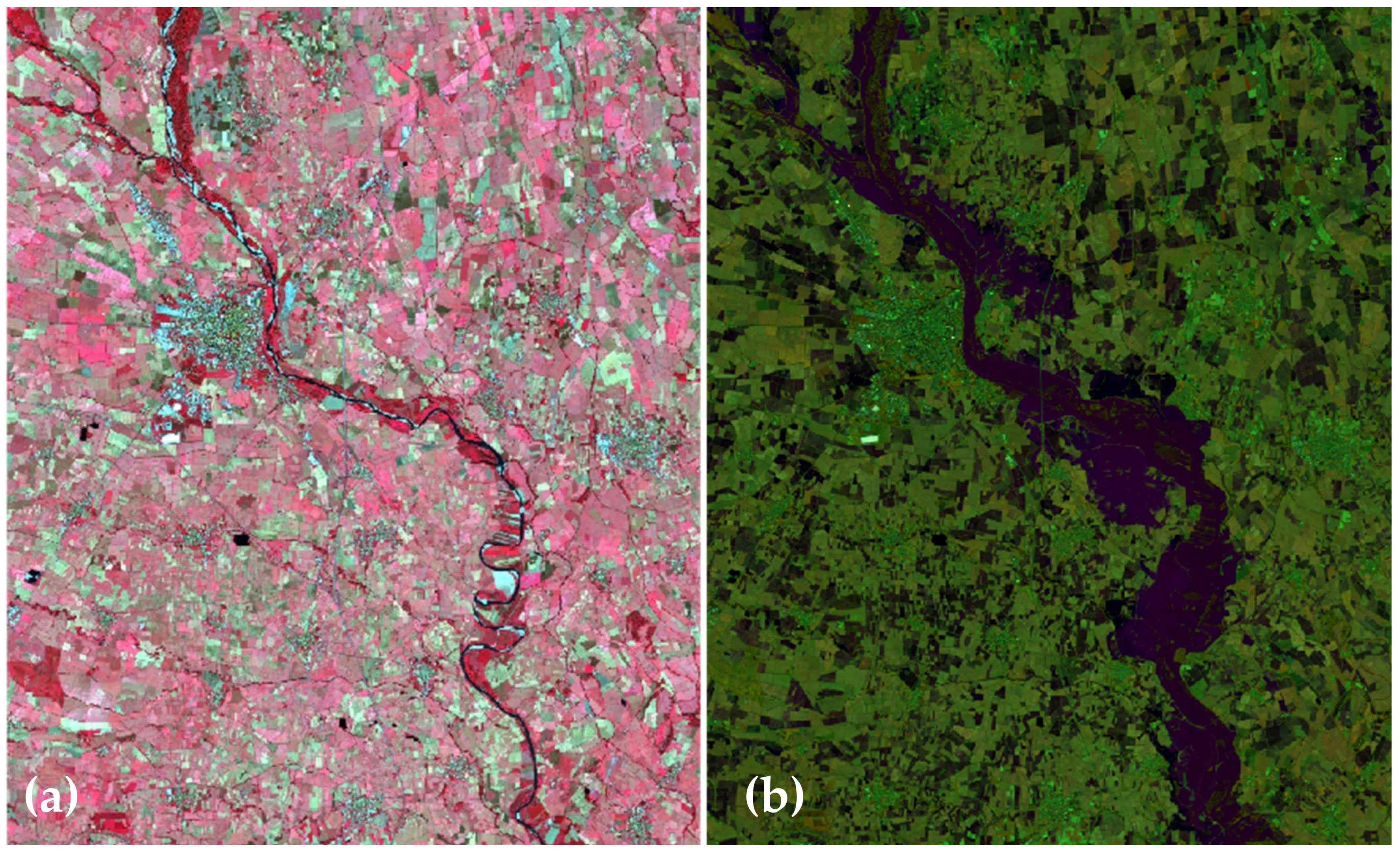
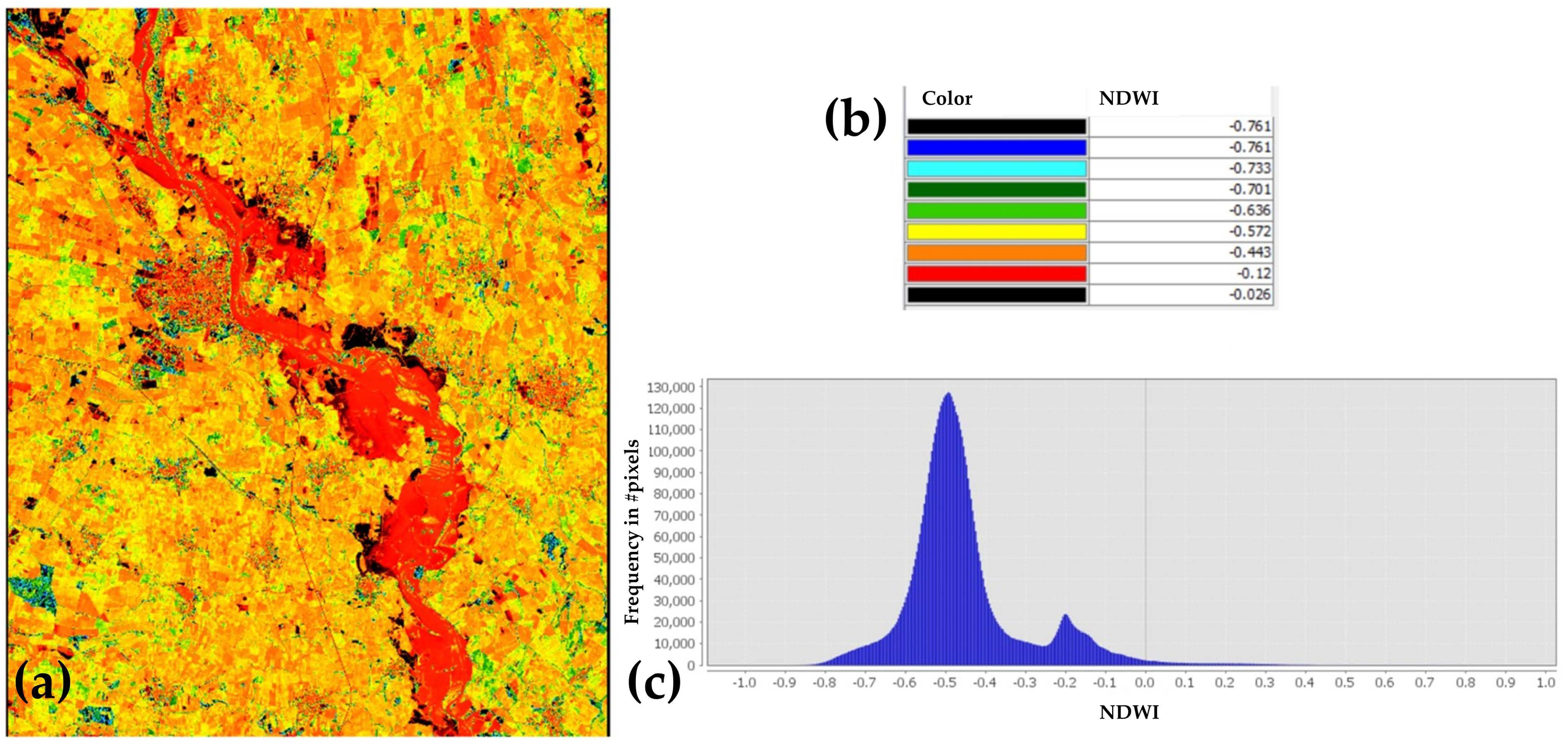
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Jasemizad, T.; Govarthanan, M.; Karmegam, N.; Wijesekara, H.; Amarasiri, D.; Hou, D.; Zhou, P.; Biswal, B.K.; et al. Impacts of Climate Change on the Fate of Contaminants through Extreme Weather Events. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, A.C.; Duarte, L. The Role of Satellite Remote Sensing in Natural Disaster Management. In Nanotechnology-Based Smart Remote Sensing Networks for Disaster Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 189–216. ISBN 978-0-323-91166-5. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S. Flood Inundation Modelling: A Review of Methods, Recent Advances and Uncertainty Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Martinis, S.; Plank, S.; Ludwig, R. An Automatic Change Detection Approach for Rapid Flood Mapping in Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Pan, B.; Ge, X.; Yang, H. Mapping Flood by the Object-Based Method Using Backscattering Coefficient and Interference Coherence of Sentinel-1 Time Series. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Tsatsaris, A.; Stathopoulos, N.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Psarogiannis, A.; Pissias, E. GIS & Remote Sensing for Local Development. Reservoirs Positioning. In GeoInformatics for Geosciences Advanced Geospatial Analysis using RS, GIS & Soft Computing; Stathopoulos, N., Tsatsaris, A., Kalogeropoulos, K., Eds.; Earth Observation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 978-0-323-98983-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Moller, D.K. Microwave Remote Sensing of Flood Inundation. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 83–84, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamellou, E.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Stathopoulos, N.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Louka, P.; Apostolidis, V.; Tsatsaris, A. A GIS-Cellular Automata-Based Model for Coupling Urban Sprawl and Flood Susceptibility Assessment. Hydrology 2021, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Capolongo, D. (Eds.) Flood Monitoring through Remote Sensing; Springer Remote Sensing/Photogrammetry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-63958-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Tsanakas, K.; Stathopoulos, N.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Tsatsaris, A. Cultural Heritage in the Light of Flood Hazard: The Case of the “Ancient” Olympia, Greece. Hydrology 2023, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulis, I.; Mavroulis, S. Flood Hazard Assessment in the Kladeos River Basin (Olympia—Western Peloponnese, Greece). In Proceedings of the AQUA 2008 3rd International Conference, Athens, Greece, 16–19 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cui, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Manandhar, B.; Nitivattananon, V.; Fang, X.; Huang, W. A Review of the Flood Management: From Flood Control to Flood Resilience. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T.; Thaheem, M.J.; Shrestha, A. An Integrated Approach for Post-Disaster Flood Management Via the Use of Cutting-Edge Technologies and UAVs: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T. Remote Sensing Methods for Flood Prediction: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Tripathi, J.N.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Kumar, P.; Singh, A.K.; Dakhore, K.K.; Ghosh, K.; Gupta, D.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; et al. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Investigation of Various Rainfall Intensities over Central India Using EO Datasets. Hydrology 2024, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, L.; Ruzza, G.; Guadagno, F.M.; Revellino, P. Flood Hazard Mapping Incorporating Multiple Probability Models. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JBA. Severe Storms Bring Flooding to Italy. 2018. Available online: https://www.jbarisk.com/products-services/event-response/italy-emilia-romagna-floods-may-2023/ (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T. A Review on Flood Management Technologies Related to Image Processing and Machine Learning. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Giordan, D.; Caló, F.; Pepe, A.; Zucca, F.; Galve, J. Potential and Limitations of Open Satellite Data for Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Flood Mapping Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis and Random Forest Classifier—The Case of Yuyao, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12539–12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, R.; Akhtar, Z.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. Integrating Remote Sensing and Social Sensing for Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 25, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazaj, F. SENTINEL-2 Imagery for Mapping and Monitoring Flooding in Buna River Area. J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci. 2019, 15, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, N.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Zoka, M.; Louka, P.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Tsatsaris, A. An Integrated Approach for a Flood Impact Assessment on Land Uses/Cover Based on SAR Images & Spatial Analytics. The Case of an Extreme Event in Sperchios River Basin, Greece. In GeoInformatics for Geosciences Advanced Geospatial Analysis Using RS, GIS & Soft Computing; Stathopoulos, N., Tsatsaris, A., Kalogeropoulos, K., Eds.; Earth Observation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 978-0-323-98983-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tedla, H.Z.; Bekele, T.W.; Nigussie, L.; Negash, E.D.; Walsh, C.L.; O’Donnell, G.; Haile, A.T. Threshold-Based Flood Early Warning in an Urbanizing Catchment through Multi-Source Data Integration: Satellite and Citizen Science Contribution. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstohy, R.; Ali, E.M. A Flash Flood Detected Area Using Classification-Based Image Processing for Sentinel-2 Satellites Data: A Case Study of Zafaraana Road at Red Sea. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Seo, M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.-M. Flash Flood Detection and Susceptibility Mapping in the Monsoon Period by Integration of Optical and Radar Satellite Imagery Using an Improvement of a Sequential Ensemble Algorithm. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2023, 41, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, A.C.; Duarte, L. The Synergy of Remote Sensing and Geographical Information Systems in the Management of Natural Disasters. In Nanotechnology-Based Smart Remote Sensing Networks for Disaster Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 217–230. ISBN 978-0-323-91166-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Chalkias, C. Modelling the Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Runoff in Small Mediterranean Catchments: Empirical Evidence from Greece. Water Environ. J. 2013, 27, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, K.; Stathopoulos, N.; Psarogiannis, A.; Penteris, D.; Tsiakos, C.; Karagiannopoulou, A.; Krikigianni, E.; Karymbalis, E.; Chalkias, C. A GIS-Based Method for Flood Risk Assessment. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016; Volume 18, p. 12788. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y.; Feng, M. An Adaptive Thresholding Approach toward Rapid Flood Coverage Extraction from Sentinel-1 SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigović, L.; Pamučar, D.; Bajić, Z.; Drobnjak, S. Application of GIS-Interval Rough AHP Methodology for Flood Hazard Mapping in Urban Areas. Water 2017, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liang, S.; He, X.; Ziegler, A.D.; Lin, P.; Pan, M.; Wang, D.; Zou, J.; Hao, D.; Mao, G.; et al. Rapid and Large-Scale Mapping of Flood Inundation via Integrating Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery with Unsupervised Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, K.; Beaulne, D.; Braun, A.; Fotopoulos, G. Fusion of SAR, Optical Imagery and Airborne LiDAR for Surface Water Detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.A.; Kilsby, C.G.; Moore, P. Multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Flood Mapping Using Change Detection. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Liu, G.; Parfitt, J.; Liu, X.; Van Herpen, E.; Stenmarck, Å.; O’Connor, C.; Östergren, K.; Cheng, S. Missing Food, Missing Data? A Critical Review of Global Food Losses and Food Waste Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6618–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konapala, G.; Kumar, S.V.; Khalique Ahmad, S. Exploring Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Diversity for Flood Inundation Mapping Using Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmand, S.; Abdullah, R.B.; Abustan, I.; Vosoogh, B. GIS-Based River Flood Hazard Mapping in Urban Area (a Case Study in Kayu Ara River Basin, Malaysia). Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2010, 2, 488–500. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z. Water Body Classification from High-Resolution Optical Remote Sensing Imagery: Achievements and Perspectives. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffi, A.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Bordogna, G.; Boschetti, M. Towards an Automated Approach to Map Flooded Areas from Sentinel-2 MSI Data and Soft Integration of Water Spectral Features. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jin, S. Rapid Flood Mapping and Evaluation with a Supervised Classifier and Change Detection in Shouguang Using Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-2 Optical Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangira, T.; Alfieri, S.M.; Menenti, M.; Van Niekerk, A. Comparing Thresholding with Machine Learning Classifiers for Mapping Complex Water. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, U.D.; Martori, A.N.; Hashim, M.A.; Chandio, A.I.; Sabri, S.; Balogun, A.L.; Abba, A.H. Geographic Information System and Remote Sensing Applications in Flood Hazards Management: A Review. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 3, 933–947. [Google Scholar]
- Tsatsaris, A.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Stathopoulos, N.; Louka, P.; Tsanakas, K.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Krassanakis, V.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Pappas, V.; Chalkias, C. Geoinformation Technologies in Support of Environmental Hazards Monitoring under Climate Change: An Extensive Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh Soltanian, F.; Abbasi, M.; Riyahi Bakhtyari, H.R. Flood Monitoring Using NDWI and MNDWI Spectral Indices: A Case Study of Aghqala Flood-2019, Golestan Province, Iran. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019; XLII-4/W18, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Setia, R.; Sahoo, S.; Prasad, A.; Pateriya, B. Evaluation of NDWI and MNDWI for Assessment of Waterlogging by Integrating Digital Elevation Model and Groundwater Level. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, G.; Lu, S.; Tong, Q. COmparison of MNDWI and DFI for Water Mapping in Flooding Season. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 2876–2879. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, D.; Cohen, S.; Huang, Y.; Tsang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Z. Intercomparison of Satellite Remote Sensing-Based Flood Inundation Mapping Techniques. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, C.; Gioia, A.; Iacobellis, V.; Manfreda, S. Detection of Surface Water and Floods with Multispectral Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanpillai, R.; Jacobs, K.M.; Mattilio, C.M.; Piskorski, E.V. Rapid Flood Inundation Mapping by Differencing Water Indices from Pre- and Post-Flood Landsat Images. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassardo, C.; Loglisci, N.; Paesano, G.; Rabuffetti, D.; Qian, M.W. The Hydrological Balance of the October 2000 Flood in Piedmont, Italy: Quantitative Analysis and Simulation. Phys. Geogr. 2006, 27, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Petrea, C.; Nigrelli, G. Uncorrected Land-Use Planning Highlighted by Flooding: The Alba Case Study (Piedmont, Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2329–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzini, F.; Fragkoulidis, G.; Pavan, V.; Antolini, G. The 1994 Piedmont Flood: An Archetype of Extreme Precipitation Events in Northern Italy. Bull. Atmos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzolan, E.; Brenna, A.; Surian, N.; Carbonneau, P.; Bizzi, S. Quantifying the Impact of Spatiotemporal Resolution on the Interpretation of Fluvial Geomorphic Feature Dynamics From Sentinel 2 Imagery: An Application on a Braided River Reach in Northern Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2023WR034699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolio, S.; Malguzzi, P.; Drofa, O.; Mastrangelo, D.; Buzzi, A. The Piedmont Flood of November 1994: A Testbed of Forecasting Capabilities of the CNR-ISAC Meteorological Model Suite. Bull. Atmos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, R.; Low-Nam, S.; Rotunno, R. Numerical Simulations of the Piedmont Flood of 4–6 November 1994. Tellus A 2000, 52, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, F.; Marconcini, M.; Ceccato, P.; Giupponi, C. Flood Depth Estimation by Means of High-Resolution SAR Images and Lidar Data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 3063–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, L.; Bollati, I.M.; Viani, C.; Zanoletti, E.; Caironi, V.; Pelfini, M.; Giardino, M. Fieldtrips and Virtual Tours as Geotourism Resources: Examples from the Sesia Val Grande UNESCO Global Geopark (NW Italy). Resources 2020, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrelli, G.; Audisio, C. The May 2008 Extreme Rain Event in the Germanasca Valley (Italian Western Alps): Processes and Effects Observed along the Hydrographic Network and Valley Slopes. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2009, 32, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nigrelli, G.; Audisio, C. Floods in Alpine River Bassins (Italy): An Interdisciplinary Study Combining Historical Information and Hydroclimatic Data. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2010, 33, 205–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sangati, M.; Borga, M.; Rabuffetti, D.; Bechini, R. Influence of Rainfall and Soil Properties Spatial Aggregation on Extreme Flash Flood Response Modelling: An Evaluation Based on the Sesia River Basin, North Western Italy. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampoulis, D.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Nikolopoulos, E.I. Assessment of High-Resolution Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates over the Mediterranean during Heavy Precipitation Events. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, V.; Piégay, H. Is Afforestation a Driver of Change in Italian Rivers within the Anthropocene Era? Catena 2021, 198, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, G.; Ferraris, L.; Pulvirenti, L.; Squicciarino, G.; Pierdicca, N.; Candela, L.; Pisani, A.R.; Zoffoli, S.; Onori, R.; Proietti, C.; et al. A Prototype System for Flood Monitoring Based on Flood Forecast Combined With COSMO-SkyMed and Sentinel-1 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuele, D.P.; Filippo, S.; Enrico, B.-M. Multi-Temporal Mapping of Flood Damage to Crops Using Sentinel-1 Imagery: A Case Study of the Sesia River (October 2020). Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 12, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, M.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Kanevski, M. Flooding Extent Cartography with Landsat TM Imagery and Regularized Kernel Fisher’s Discriminant Analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 57, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A New Technique for Surface Water Mapping Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.; Islam, A.K.M.S.; Mamoon, W.B.; Rahman, M.R. Random Forest Classifications for Landuse Mapping to Assess Rapid Flood Damage Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 30, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, F.; Mandery, N.; Wieland, M.; Groth, S.; Martinis, S.; Riedlinger, T. Time-Series Analysis of Sentinel-1/2 Data for Flood Detection Using a Discrete Global Grid System and Seasonal Decomposition. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 119, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhangumbe, M.; Nascetti, A.; Georganos, S.; Ban, Y. Supervised and Unsupervised Machine Learning Approaches Using Sentinel Data for Flood Mapping and Damage Assessment in Mozambique. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 32, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondízio, E.; Moran, E. Change Detection Techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Saha, S.; Saikh, N.I.; Sarkar, D.; Mondal, P. Application of Bivariate Approaches for Flood Susceptibility Mapping: A District Level Study in Eastern India. HydroResearch 2023, 6, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, F.D.C.; Mello, D.C.D.; Francelino, M.R.; Krause, M.B.; Soares, H.D.M.; Demattê, J.A.M. Mapping Deactivated Mine Areas in the Amazon Forest Impacted by Seasonal Flooding: Assessing Soil-Hydrological Processes and Quality Dynamics by Remote Sensing and Geophysical Techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 34, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Klobučar, D. Mapping Floods in Lowland Forest Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data and an Object-Based Approach. Forests 2021, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Mondini, A.C.; Camici, S. Effectiveness of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 for Flood Detection Assessment in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, L.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Van Coillie, F.M.B. Flood Mapping in Vegetated Areas Using an Unsupervised Clustering Approach on Sentinel-1 and -2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lin, N.; Liu, Z. Comparing Water Indices for Landsat Data for Automated Surface Water Body Extraction under Complex Ground Background: A Case Study in Jilin Province. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Sahebi, M.; Shokri, M. Modified optimization water index (MOWI) for Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017; XLII-4/W4, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Saleem, N. Rapid Riverine Flood Mapping with Different Water Indexes Using Flood Instances Landsat-8 Images. In Proceedings of the 5th International Electronic Conference on Water Sciences, Online, 16–30 November 2020; p. 8049. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gowda, P.H.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Kakani, V.G.; Wagle, P.; Chen, L.; Flynn, K.C.; Jiang, W. Application of the Water-Related Spectral Reflectance Indices: A Review. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenoğlu, R.C.; Arslan, E. Flood Analysis and Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Data: A Case Study from Tarsus Plain, Turkey. Lapseki Mesl. Yüksekokulu Uygulamalı Araştırmalar Derg. 2021, 2, 35–49. [Google Scholar]

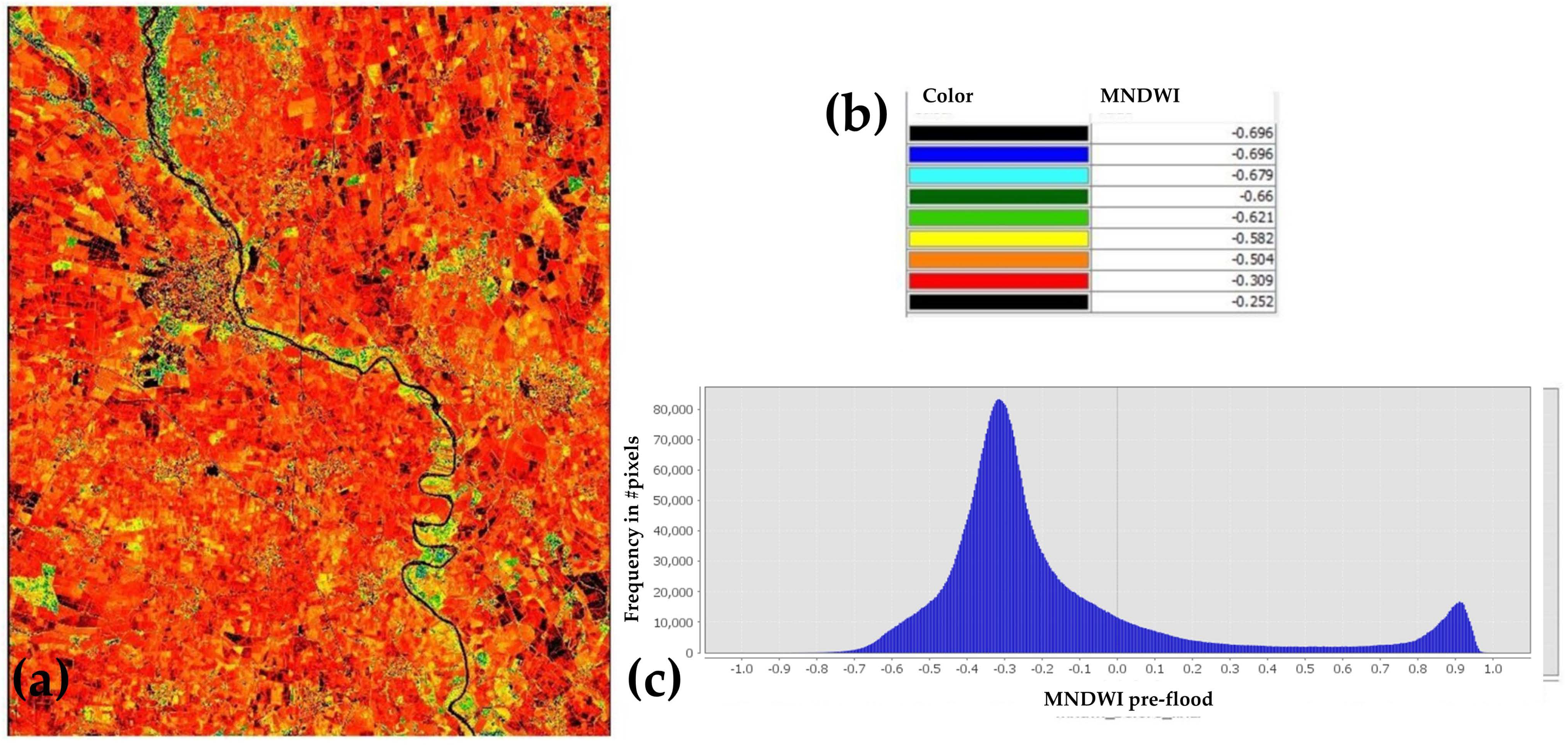


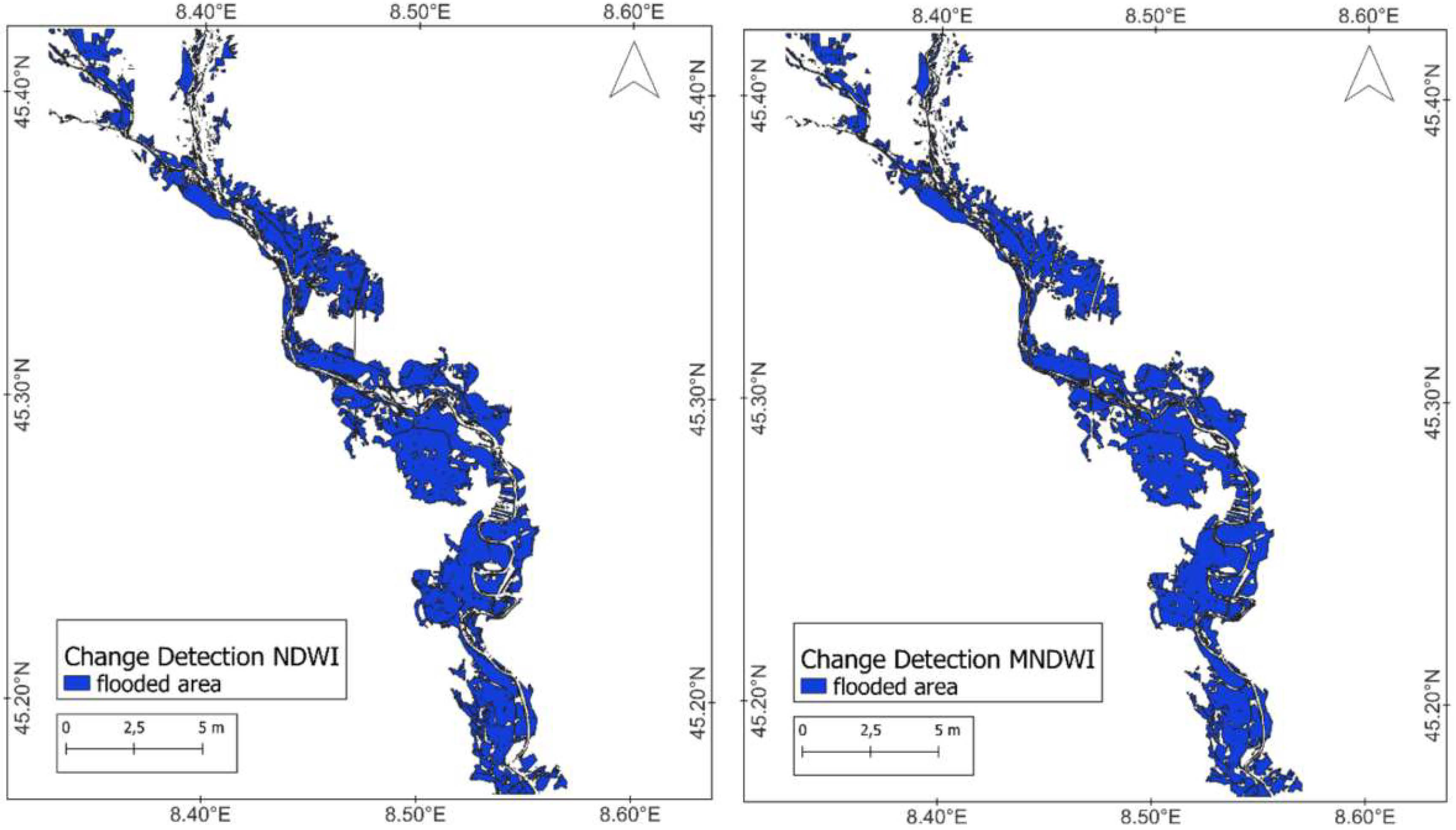
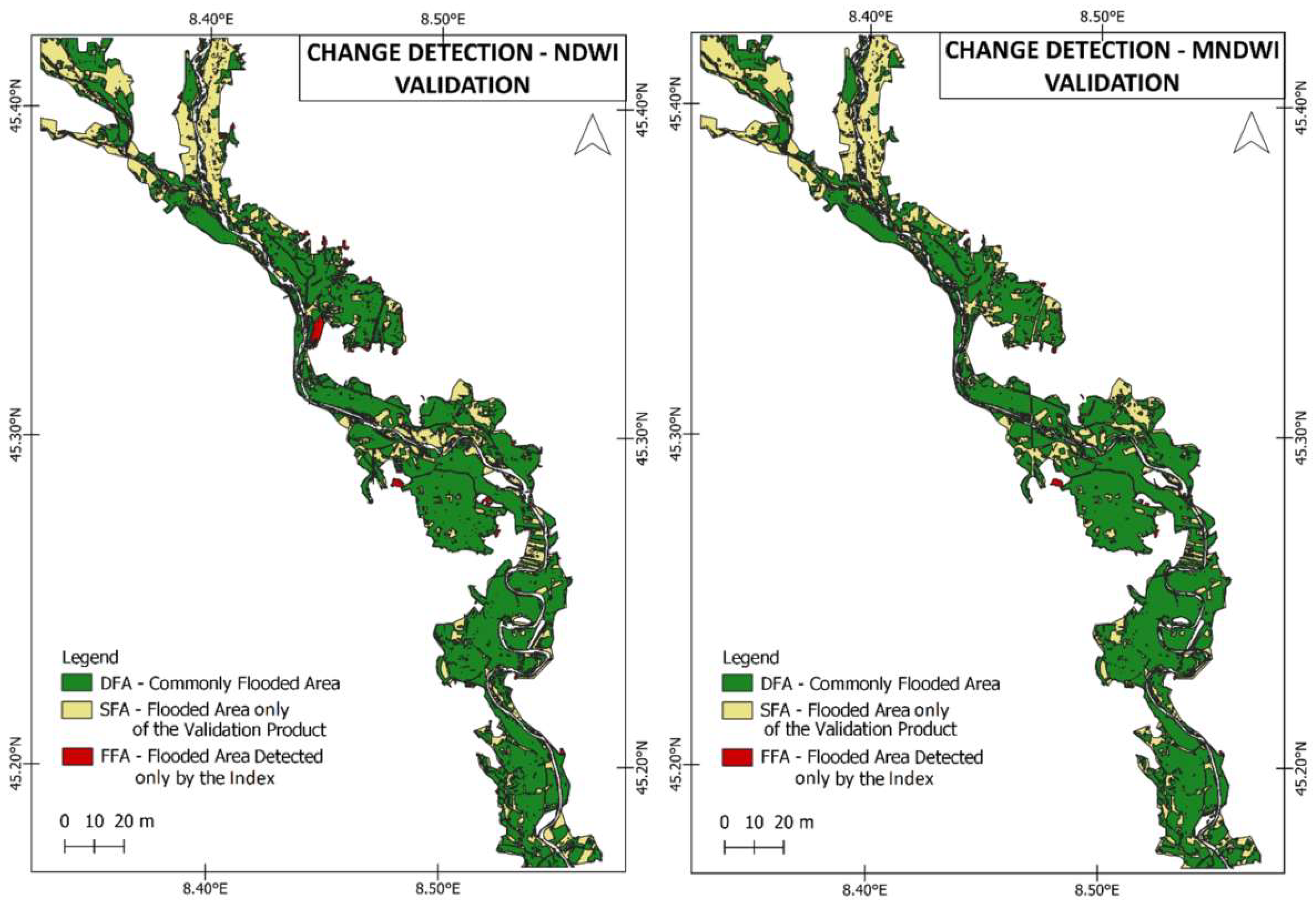
| Spectral Band | Band | Wavelength (μm) | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue (B) | B2 | 0.46–0.52 | 10 |
| Green (G) | B3 | 0.54–0.58 | 10 |
| Red (R) | B4 | 0.65–0.68 | 10 |
| Red edge (RE1) | B5 | 0.698–0.712 | 20 |
| Red edge (RE2) | B6 | 0.733–0.747 | 20 |
| Red edge (RE3) | B7 | 0.773–0.793 | 20 |
| Near-infrared (NIR) | B8 | 0.784–0.9 | 10 |
| Near-infrared (NIR) | B8A | 0.855–0.875 | 20 |
| Shortwave infrared (SWIR1) | B11 | 1.565–1.655 | 20 |
| Shortwave Infrared (SWIR2) | B12 | 2.1–2.28 | 20 |
| Date/hour (pre-flood) | 28 September 2020, 10:20:31 | ||
| Date/hour (post-flood) | 3 October 2020, 10:17:59 | ||
| Threshold | ||
|---|---|---|
| NDWI | MNDWI | |
| Pre-flood | if NDWI ≤ −0.252, then 1; otherwise, 0 | if MNDWI ≤ −0.253, then 1; otherwise, 0 |
| Water Spectral Indices with Change Detection | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change Detection | DFA (km2) | FFA (km2) | SFA (km2) | Detection Efficiency Rate (%) [DFA/(DFA + SFA)] | Commission Error (False Area Rate) (%) [FFA/(DFA + FFA)] | Omission Error (Skipped Area Rate) (%) [SFA/(DFA + SFA)] |
| NDWI | 52.91 | 1.59 | 24.15 | 0.687 | 0.029 | 0.313 |
| MNDWI | 52.48 | 0.75 | 24.76 | 0.679 | 0.014 | 0.321 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petropoulos, G.P.; Georgiadi, A.; Kalogeropoulos, K. Leveraging Sentinel-2 and Geographical Information Systems in Mapping Flooded Regions around the Sesia River, Piedmont, Italy. GeoHazards 2024, 5, 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020025
Petropoulos GP, Georgiadi A, Kalogeropoulos K. Leveraging Sentinel-2 and Geographical Information Systems in Mapping Flooded Regions around the Sesia River, Piedmont, Italy. GeoHazards. 2024; 5(2):485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020025
Chicago/Turabian StylePetropoulos, George P., Athina Georgiadi, and Kleomenis Kalogeropoulos. 2024. "Leveraging Sentinel-2 and Geographical Information Systems in Mapping Flooded Regions around the Sesia River, Piedmont, Italy" GeoHazards 5, no. 2: 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020025
APA StylePetropoulos, G. P., Georgiadi, A., & Kalogeropoulos, K. (2024). Leveraging Sentinel-2 and Geographical Information Systems in Mapping Flooded Regions around the Sesia River, Piedmont, Italy. GeoHazards, 5(2), 485-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020025








