Marine Geohazards of the Bay of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A Review Integrating Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
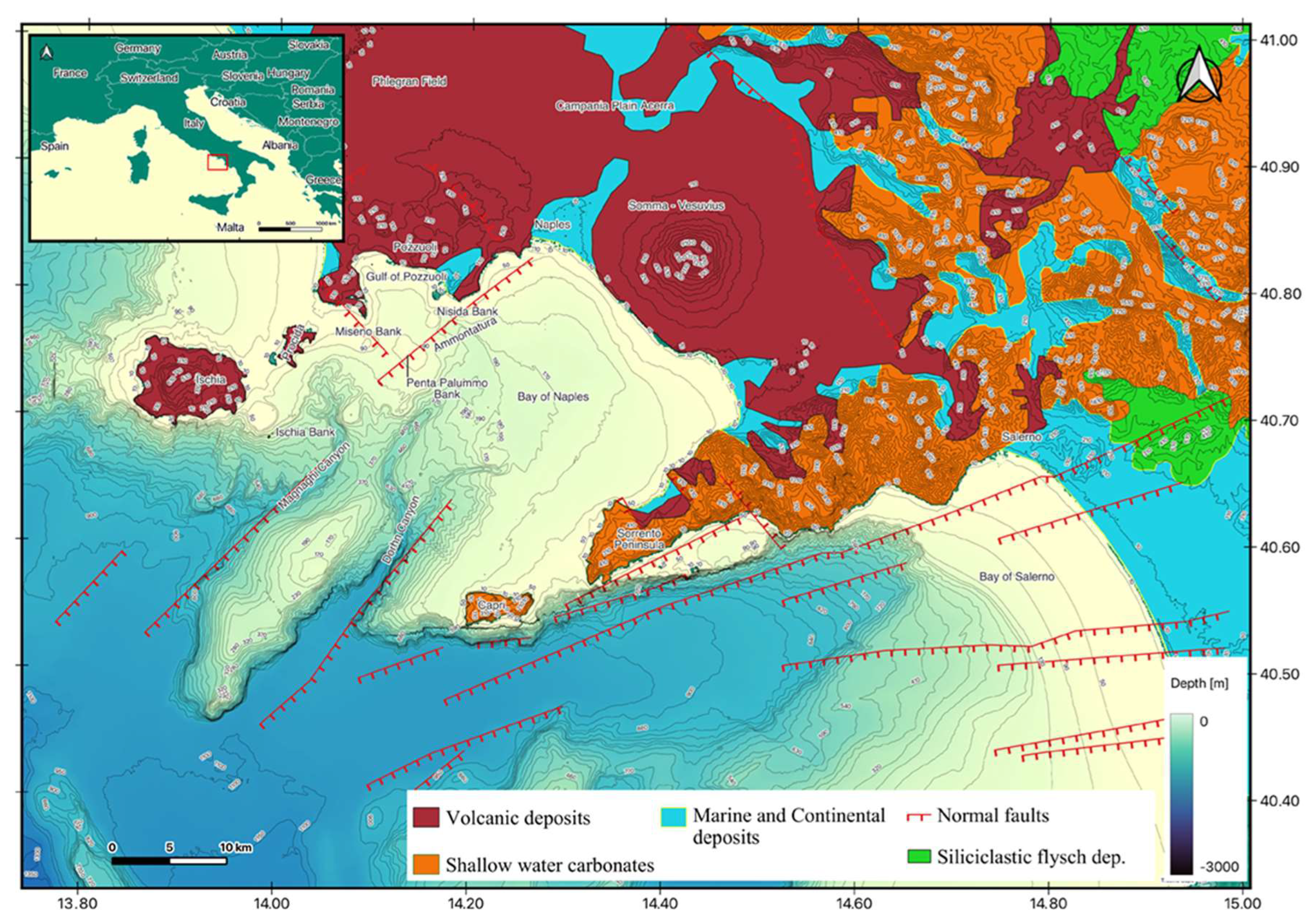
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Literature Review
4.1.1. Earthquakes
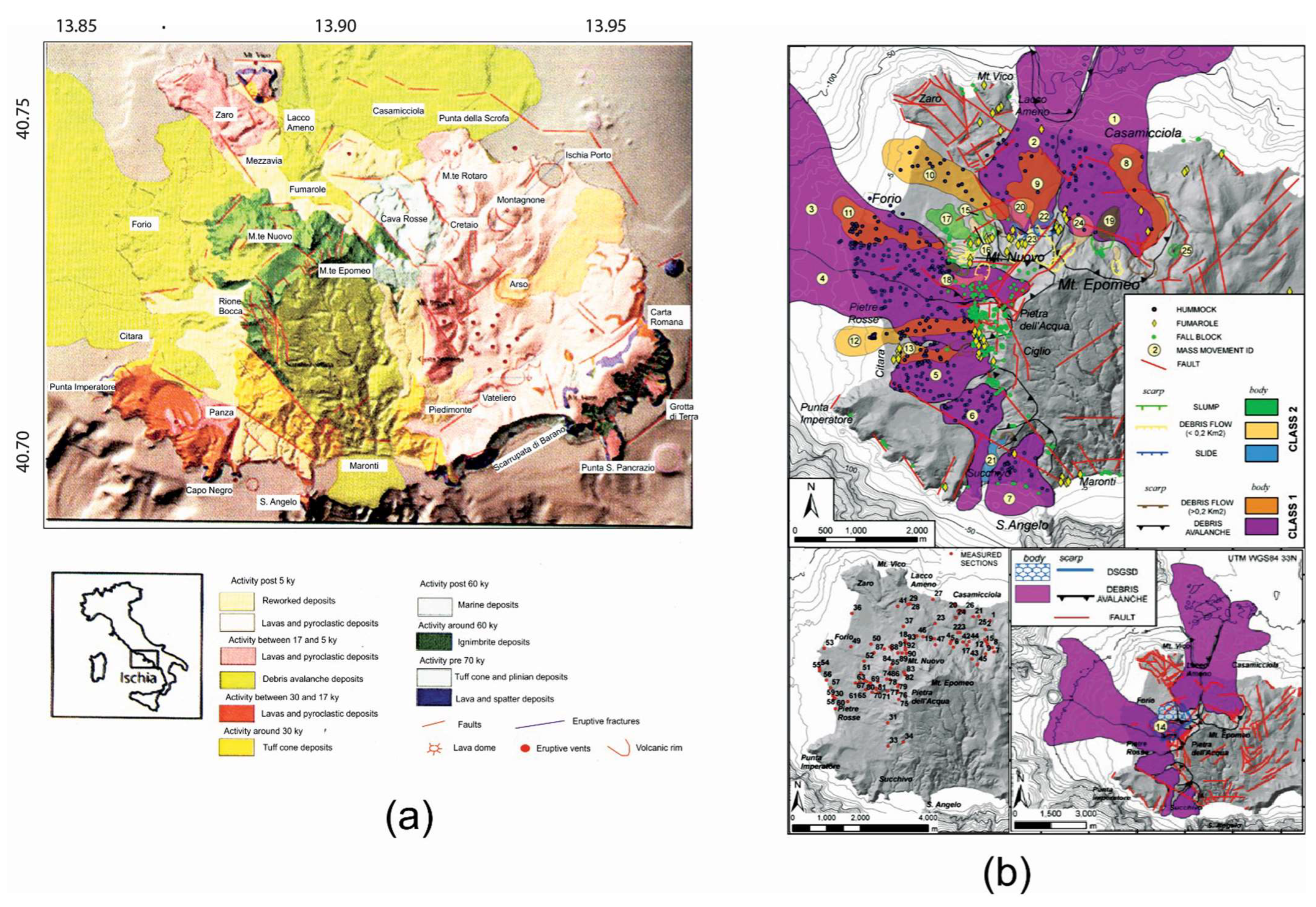
4.1.2. Submarine Landslides
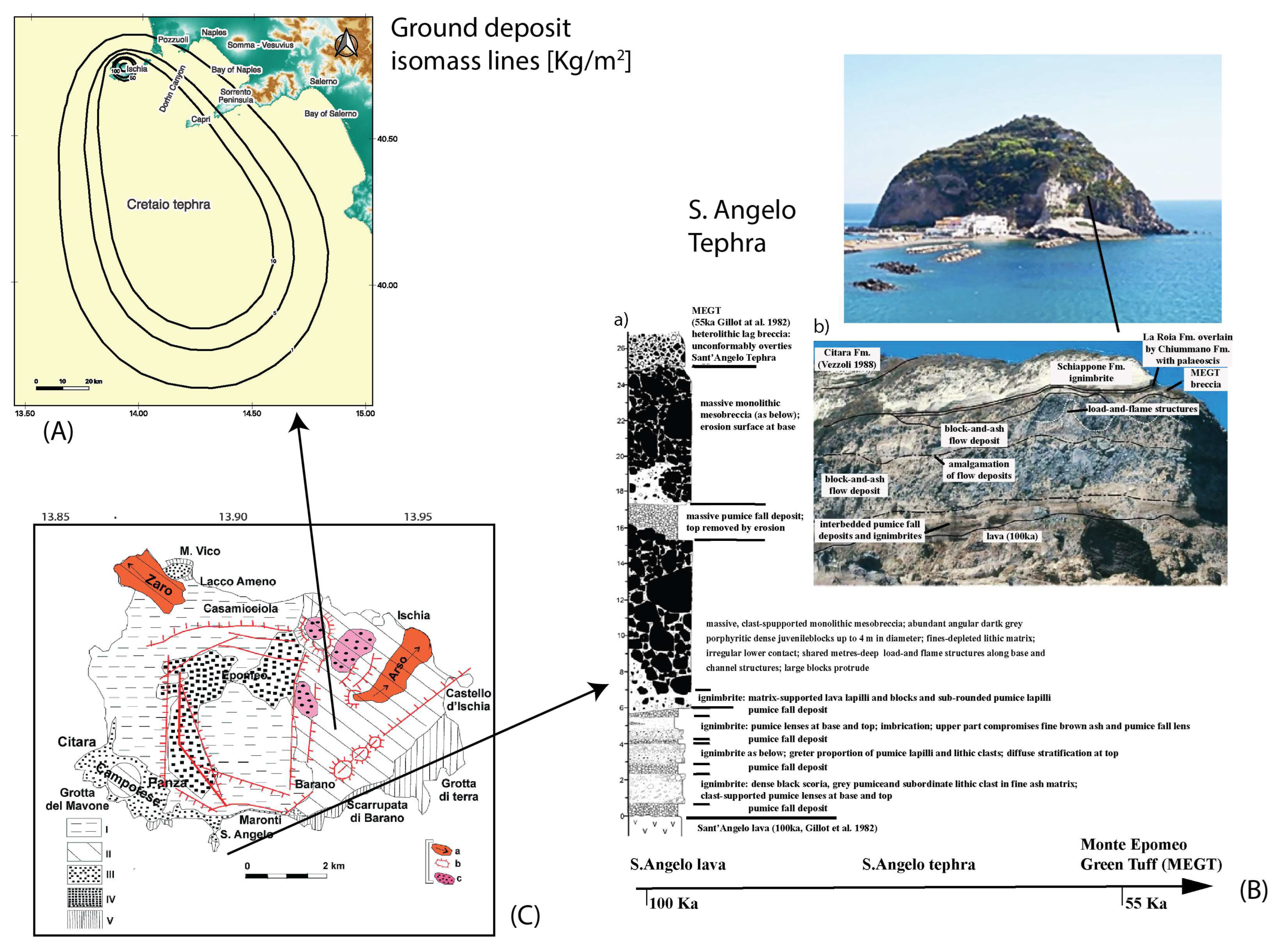
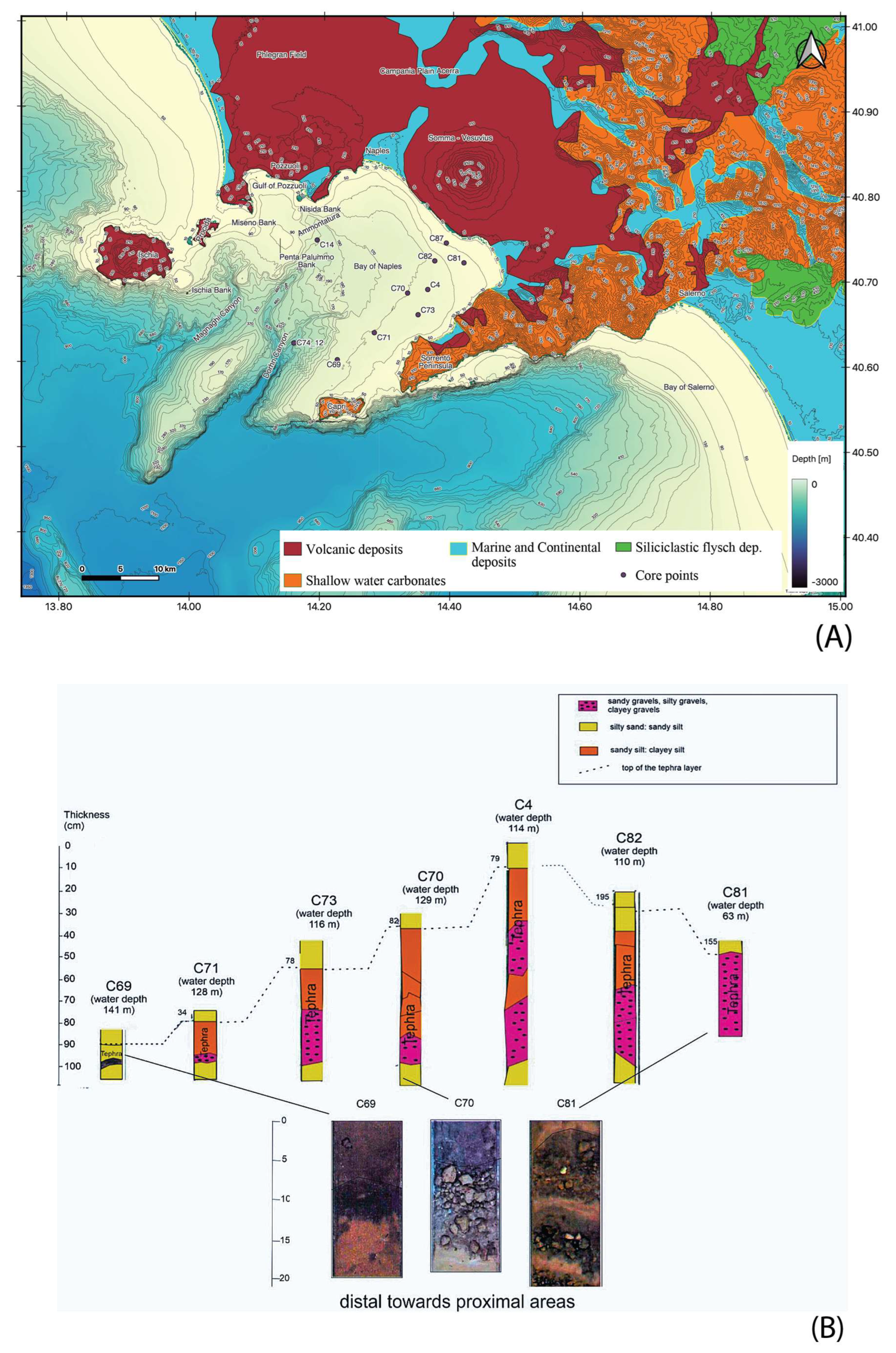
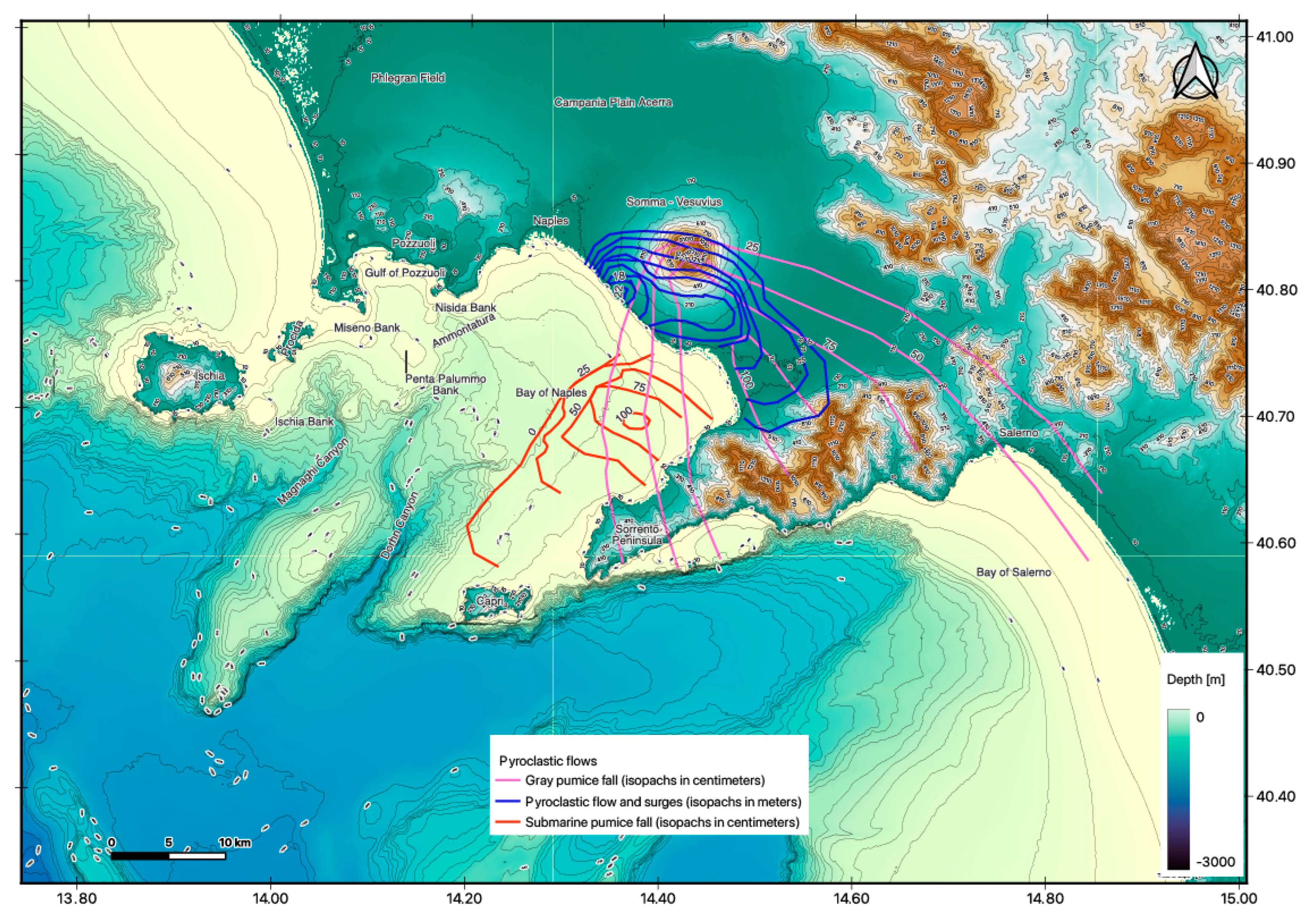
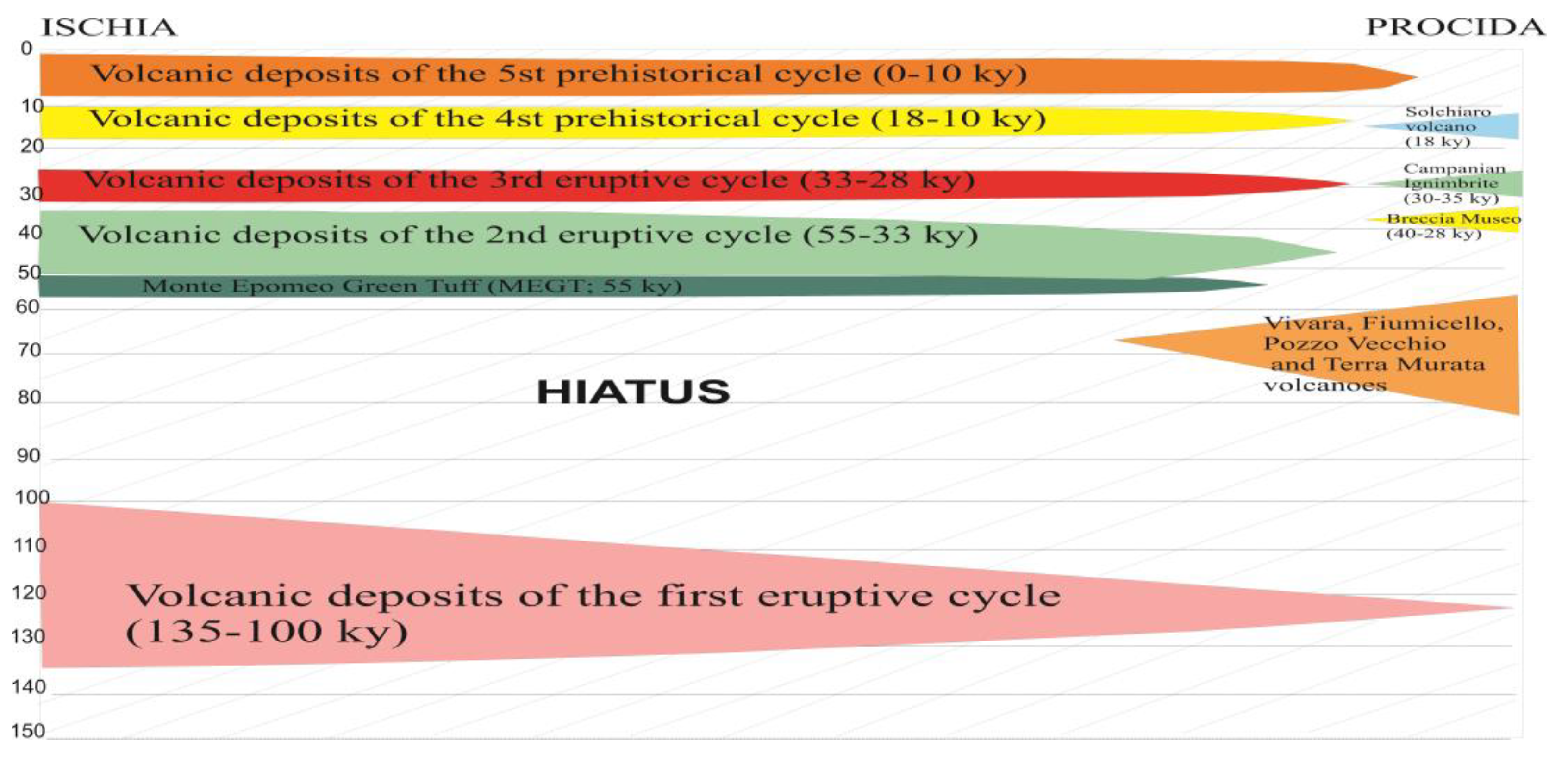
4.1.3. Marine Tephra
4.1.4. Pyroclastic Density Currents
4.1.5. Tsunamis
4.2. Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis
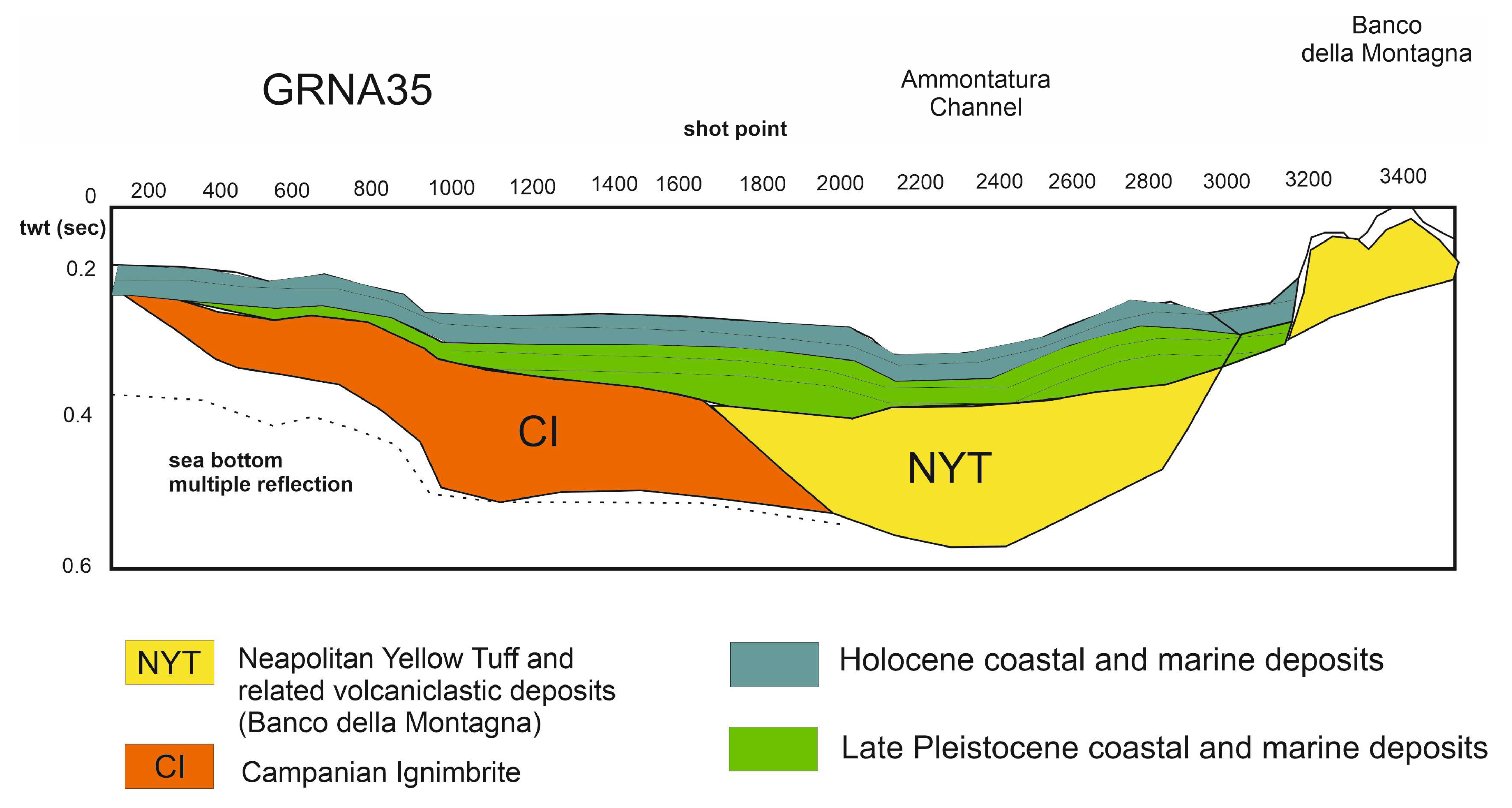
4.2.1. Ammontatura Slope Basin
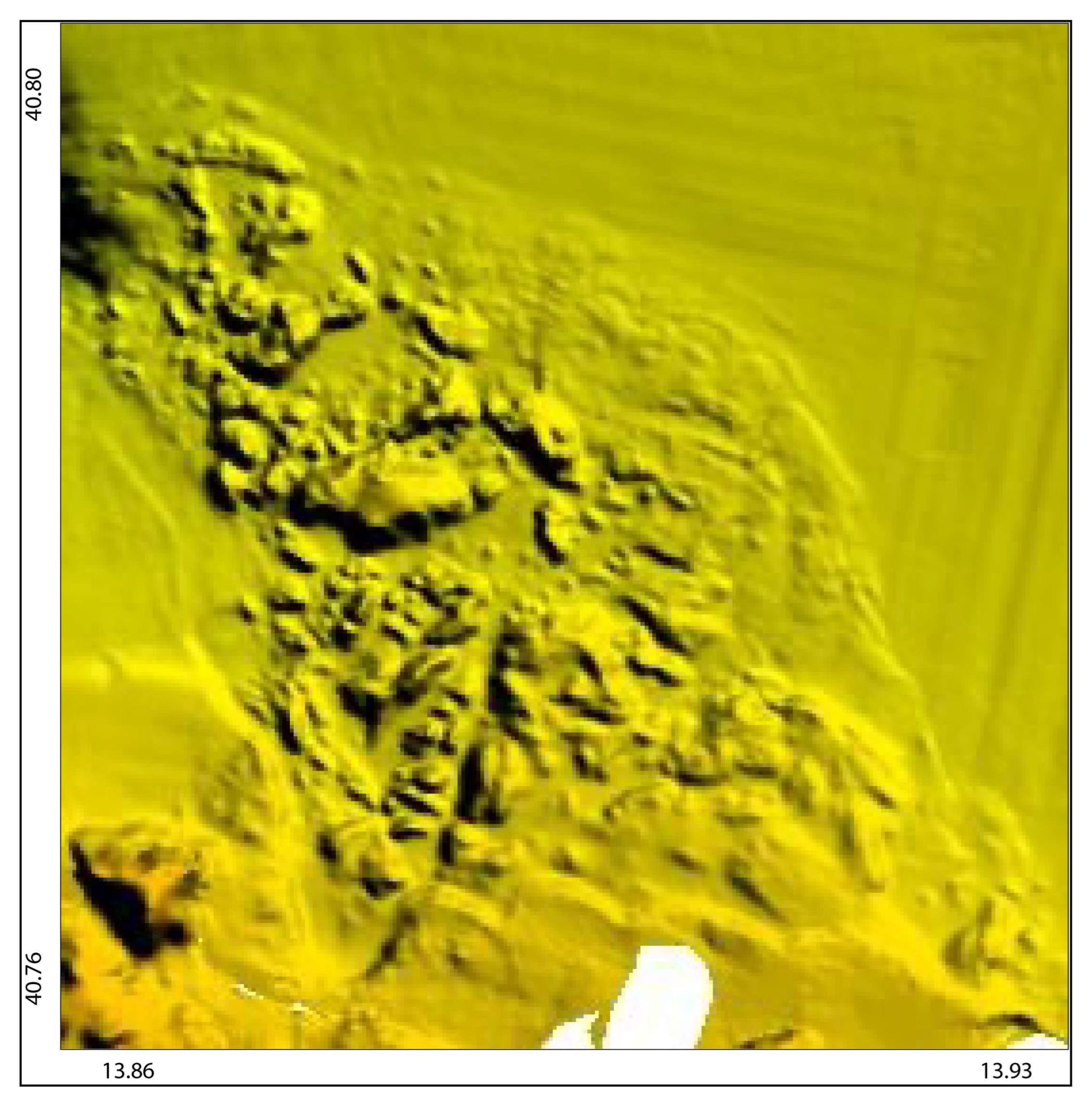
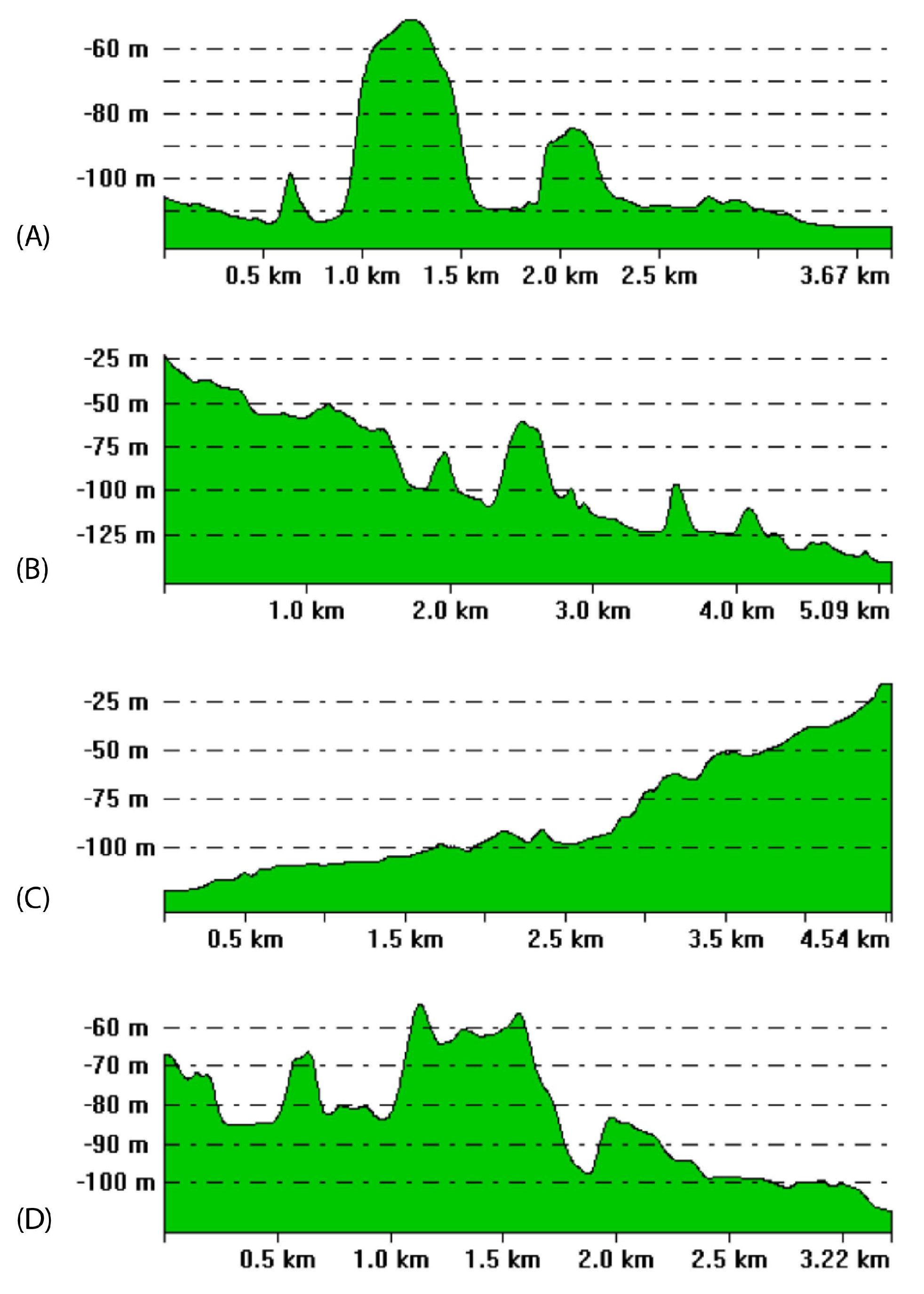
4.2.2. Northern Ischia Debris Avalanche Deposits
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopp, H.; Chiocci, F.L.; Berndt, C.; Çağatay, M.N.; Ferreira, T.; Fortes, C.J.E.M.; Gràcia, E.; González Vega, A.; Kopf, A.; Sørensen, J.; et al. Marine Geohazards: Safeguarding Society and the Blue Economy from a Hidden Threat; Position Paper 26 of the European Marine Board; European Marine Board IVZW: Ostend, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–100. ISBN 9789464206111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Centre for Geohazard. Offshore Geohazards. 2003. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/4725434/offshore-geohazards-ngi (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- CIESM. Marine Geo-Hazards in the Mediterranean; CIESM Workshop Monographs; CIESM: Monte Carlo, Monaco, 2011; Volume 42, pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Urgeles, R.; Camerlenghi, A. Submarine landslides of the Mediterranean Sea: Trigger mechanisms, dynamics, and frequency-magnitude distribution. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 2600–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceramicola, S.; Praeg, D.; Coste, M.; Forlin, E.; Cova, A.; Colizza, E.; Critelli, S. Submarine Mass-Movements along the Slopes of the Active Ionian Continental Margins and Their Consequences for Marine Geohazards (Mediterranean Sea). In Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences, 1st ed.; Krastel, S., Behrmann, J., Volker, G., Urgeles, R., Chaytor, J., Huhn, K., Strasser, N., Harbitz, C., Eds.; Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 37, pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.M.R.; Silva, M.; Ferreira, A.; Araujio, T. Marine Geohazards: A Bibliometric-Based Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivata Cardenas, I.; Flage, R.; Aven, T. Marine geohazards exposed: Uncertainties involved. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2023, 41, 589–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Heidarzadeh, M.; Satake, K.; Mulia, I.E.; Yamada, M. A tsunami warning system based on offshore bottom pressure gauges and data assimilation for Crete Island in the Eastern Mediterranean Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB020293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Gusman, A.R.; Mulya, I.R. The landslide source of the eastern Mediterranean tsunami on 6 February 2023 following the MW 7.8 Kahramanmaraş (Türkiye) inland earthquake. Geosci. Lett. 2023, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, N.; Mirabile, L.; Camerlenghi, A.; Ranieri, G. Marine geophysical survey of the Gulf of Naples (Italy): Relationship between submarine volcanic activity and sedimentation. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1991, 47, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Milia, A.; Torrente, M.; Russo, M.; Zuppetta, A. Tectonics and crustal structure of the Campania continental margin: Relationships with volcanism. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 79, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insinga, D.; Molisso, F.; Lubritto, C.; Sacchi, M.; Passariello, I.; Morra, V. The proximal marine record of Somma–Vesuvius volcanic activity in the Naples and Salerno bays, Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea, during the last 3 kyrs. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2008, 177, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Pepe, F.; Corradino, M.; Insinga, D.D.; Molisso, F.; Lubritto, C. The Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera offshore the Campi Flegrei: Stratal architecture and kinematic reconstruction during the last 15 ky. Mar. Geol. 2014, 354, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; De Natale, G.; Spiess, V.; Steinmann, L.; Acocella, V.; Corradino, M.; de Silva, S.; Fedele, A.; Fedele, L.; Geshi, N.; et al. A roadmap for amphibious drilling at the Campi Flegrei caldera: Insights from a MagellanPlus workshop. Sci. Drill. 2019, 26, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocci, F.L.; De Alteriis, G. The Ischia debris avalanche: First clear submarine evidence in the Mediterranean of a volcanic island prehistorical collapse. Terra Nova 2006, 18, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alteriis, G.; Scotto di Santolo, A.; Chiocci, F.L.; Ramondini, M.; Violante, C. The Case of Ischia Underwater Debris Avalanche (Italy, Tyrrhenian Sea) and Its High Mobility. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory; Lollino, G., Manconi, A., Locat, J., Huang, Y., Canals Artigas, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A. The Dohrn canyon: A response to the eustatic fall and tectonic uplift of the outer shelf along the eastern Tyrrhenian sea margin, Italy. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2000, 20, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Iorio, M.; Molisso, F.; Sacchi, M. Integrated Morpho-Bathymetric, Seismic-Stratigraphic, and Sedimentological Data on the Dohrn Canyon (Naples Bay, Southern Tyrrhenian Sea): Relationships with Volcanism and Tectonics. Geosciences 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinti, S.; Pagnoni, G.; Piatanesi, A. Simulation of tsunamis induced by volcanic activity in the Gulf of Naples (Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinti, S.; Chiocci, F.L.; Zaniboni, F.; Pagnoni, G.; de Alteriis, G. Numerical simulation of the tsunami generated by a past catastrophic landslide on the volcanic island of Ischia, Italy. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2011, 32, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, J.; Acocella, V.; Bisson, M.; Caliro, S.; Costa, A.; Della Seta, M.; De Martino, P.; de Vita, S.; Giordano, G.; Martino, S.; et al. Multiple natural hazards at volcanic islands: A review for the Ischia volcano (Italy). J. Appl. Volcanol. 2019, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grezio, A.; Cinti, F.R.; Costa, A.; Faenza, L.; Perfetti, P.; Pierdominici, S.; Grezio, A.; Cinti, F.R.; Costa, A.; Faenza, L.; et al. Multisource Bayesian probabilistic tsunami hazard analysis for the Gulf of Naples (Italy). J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2019JC015373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Caccavale, M. Quaternary Evolution of Ischia: A Review of Volcanology and Geology. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Sacchi, M. New morpho-bathymetric data on marine hazard in the offshore of Gulf of Naples (Southern Italy). Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 2881–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacca, E.; Scandone, P. Geology of Southern Apennines. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2007, 75–119. [Google Scholar]
- Milia, A.; Torrente, M.M. Tectonics and stratigraphic architecture of a peri-Tyrrhenian half-graben (Gulf of Naples, Italy). Tectonophysics 1999, 315, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Bigi, S.; Cuffaro, M.; Doglioni, C.; Scrocca, D.; Muccini, F.; Cocchi, L.; Ligi, M.; Bortoluzzi, G. Transfer zones in an oblique back-arc basin setting: Insights from the Latium-Campania segmented margin (Tyrrhenian Sea). Tectonics 2017, 36, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, A. Evolution of the Tyrrhenian Sea-Calabrian Arc system: The past and the present. Rend Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2012, 21, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bigi, G.; Coli, M.; Cosentino, D.; Dal Piaz, G.V.; Parotto, M.; Sartori, R.; Scandone, P. Structural Model of Italy—Scale 1: 500.000; CNR 1983-SELCA 1992; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, S.; Ciarcia, S. Tectono-stratigraphic setting of the Campania region (Southern Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, A.; Merola, D.; Perrone, V.; Amato, A.; Cinque, A.; Santacroce, R.; Sbrana, A.; Sulpizio, R.; Zanchetta, G.; Budillon, F.; et al. Note Illustrative della Carta Geologica d’Italia alla Scala 1: 50.000—Fogli 466—485 “Sorrento-Termini”; ISPRA, Servizio Geologico d’Italia: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–201. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/Media/carg/note_illustrative/466_485_Sorrento_Termini.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Gurioli, L.; Sulpizio, R.; Cioni, R.; Sbrana, A.; Santacroce, R.; Luperini, W.; Andronico, D. Pyroclastic flow hazard assessment at Somma–Vesuvius based on the geological record. Bull. Volcanol. 2010, 72, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P.; de Alteriis, G.; Florio, G. The western undersea section of the Ischia volcanic complex (Italy, Tyrrhenian sea) inferred by marine geophysical data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, S.; Sansivero, F.; Orsi, G.; Marotta, E. Cyclical slope instability andvolcanism related to volcano-tectonism in resurgent calderas: The Ischia island (Italy) case study. Eng. Geol. 2006, 86, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alteriis, G.; Violante, C. Catastrophic landslides off Ischia volcanic island (Italy) during prehistory. In Geohazard in Rocky Coastal Areas; Violante, C., Ed.; The Geological Society: London, UK, 2009; Volume 322, pp. 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbrana, A.; Toccaceli, R.M.; Biagio, G.; Cubellis, E.; Faccenna, C.; Fedi, M.; Florio, G.; Fulignati, P.; Giordano, F.; Giudetti, G.; et al. Geologic Map of Ischia, Scale 1:10.000—Maps and Explanatory Notes; Campania Region, Sector of Soil Defence, Geothermics and Geotechnics: Naples, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sbrana, A.; Marianelli, P.; Pasquini, G. Volcanology of Ischia (Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Seta, M.; Marotta, E.; Orsi, G.; De Vita, S.; Sansivero, F.; Fredi, P. Slope instability induced by volcano-tectonics as an additional source of hazard in active volcanic areas: The case of Ischia island (Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2012, 74, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, C.R.J.; Carlino, S.; Danesi, S.; Pino, N.A. Potential for rupture before eruption at Campi Flegrei caldera, Southern Italy. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Novellis, V.; Carlino, S.; Castaldo, R.; Tramelli, A.; De Luca, C.; Pino, N.A.; Pepe, S.; Convertito, V.; Zinno, I.; De Martino, P.; et al. The 21 August 2017 Ischia (Italy) earthquake source model inferred from seismological, GPS, and DInSAR measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, V.; Aiello, G.; D’Argenio, B. Gravity instabilities in the Dohrn Canyon (Bay of Naples, Southern Tyrrhenian Sea): Potential wave and run-up (tsunami) reconstruction from a fossil submarine landslide. Geol. Carpathica 2011, 62, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratson, L.F.; Coakley, B.J. A model for the headward erosion of submarine canyons induced by downslope-eroding sediment flows. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1996, 108, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Caccavale, M. The Coastal Areas of the Bay of Naples: The Sedimentary Dynamics and Geological Evolution of the Naples Canyons. Geosciences 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satow, C.; Watt, S.; Cassidy, M.; Pyle, D.; Deng, Y.N. The Contributions of Marine Sediment Cores to Volcanic Hazard Assessments: Present Examples and Future Perspectives. Geosciences 2023, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.; Orsi, G.; De Vita, S. New insights into Late Pleistocene explosive volcanic activity and caldera formation on Ischia (southern Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2008, 70, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alteriis, G.; Insinga, D.D.; Morabito, S.; Morra, V.; Chiocci, F.L.; Terrasi, F.; Lubritto, C.; Di Benedetto, C.; Pazzanese, M. Age of submarine debris avalanches and tephrostratigraphy offshore Ischia Island, Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy. Mar. Geol. 2010, 278, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vita, S.; Di Vito, M.A.; Gialanella, C.; Sansivero, F. The impact of the Ischia Porto Tephra eruption (Italy) on the Greek colony of Pithekoussai. Quat. Int. 2013, 303, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, E.; Albert, P.G.; Wulf, S.; Brown, R.J.; Smith, V.C.; Keller, J.; Orsi, G.; Bourne, A.J.; Menzies, M.A. Age and geochemistry of tephra layers from Ischia, Italy: Constraints from proximal-distal correlations with Lago Grande di Monticchio. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2014, 287, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, M.; Arienzo, I.; Brown, R.J.; Petrosino, P.; Pelullo, C.; Giaccio, B. Petrography and Mineral Chemistry of Monte Epomeo Green Tuff, Ischia Island, South Italy: Constraints for Identification of the Y-7 Tephrostratigraphic Marker in Distal Sequences of the Central Mediterranean. Minerals 2021, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primerano, P.; Giordano, G.; Costa, A.; de Vita, S.; Di Vito, M.A. Reconstructing fallout features and dispersal of Cretaio Tephra (Ischia Island, Italy) through field data analysis and numerical modelling: Implications for hazard assessment. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2021, 415, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Insinga, D.; Milia, A.; Molisso, F.; Raspini, A.; Torrente, M.M.; Conforti, A. Stratigraphic signature of the Vesuvius 79 AD event off the Sarno prodelta system, Naples Bay. Mar. Geol. 2005, 222–223, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insinga, D.D.; Petrosino, P.; Alberico, I.; de Lange, G.J.; Lubritto, C.; Molisso, F.; Sacchi, M.; Sulpizio, R.; Wu, J.; Lirer, F. The Late Holocene tephra record of the central Mediterranean Sea: Mapping occurrences and new potential isochrons for the 4.4–2.0 ka time interval. J. Quat. Sci. 2020, 35, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Passaro, S.; Molisso, F.; Matano, F.; Steinmann, L.; Spiess, V.; Pepe, F.; Corradino, M.; Caccavale, M.; Tamburrino, S.; et al. The Holocene marine record of unrest, volcanism, and hydrothermal activity of Campi Flegrei and Somma Vesuvius. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H.E., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 435–469. [Google Scholar]
- de Vita, S.; Sansivero, F.; Orsi, G.; Marotta, E.; Piochi, M. Volcanological and structural evolution of the Ischia resurgent caldera (Italy) over the past 10 k.y. In Stratigraphy and Geology of Volcanic Areas; Groppelli, G., Viereck, L., Eds.; GSA Book Series, Special Paper; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010; Volume 464, pp. 193–239. [Google Scholar]
- Alberico, I.; Lirer, L.; Petrosino, P.; Scandone, R. Volcanic hazard and risk assessment from pyroclastic flows at Ischia Island (southern Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm Res. 2008, 171, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurioli, L.; Cioni, R.; Sbrana, A.; Zanella, E. Transport and deposition of pyroclastic density currents over an inhabited area: The deposits of the AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius at Herculaneum (Italy). Sedimentology 2002, 49, 929–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, R.; Gurioli, L.; Lanza, R.; Zanella, E. Temperatures of the A.D. 79 pyroclastic density current deposits (Vesuvius, Italy). J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, B02207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurioli, L.; Zanella, E.; Pareschi, M.T.; Lanza, R. Influences of urban fabric on pyroclastic density currents at Pompeii (Italy) I: Flow direction and deposition. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B05213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, T.; Gurioli, L.; Houghton, B.F.; Cioni, R.; Cashman, K.V. Column collapse and generation of pyroclastic density currents during the A.D. 79 eruption of Vesuvius: The role of pyroclastic density. Geology 2011, 39, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, R.; Tadini, A.; Gurioli, L.; Bertagnini, A.; Mulas, M.; Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A. Estimating eruptive parameters and related uncertainties for pyroclastic density current deposits: Worked examples from Somma-Vesuvius (Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2020, 82, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadini, A.; Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A.; Cioni, R.; Biagioli, G.; Vitturi, M.; Esposti Ongaro, T. Reproducing pyroclastic density current deposits of the 79 CE eruption of the Somma-Vesuvius volcano using the box-model approach. Solid Earth 2021, 12, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G. Submarine Stratigraphy of the Eastern Bay of Naples: New Seismo-Stratigraphic Data and Implications for the Somma-Vesuvius and Campi Flegrei Volcanic Activity. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A.; Molisso, F.; Raspini, A.; Sacchi, M.; Torrente, M.M. Syneruptive features and sedimentary processes associated with pyroclastic currents entering the sea: The AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius, Bay of Naples, Italy. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2008, 165, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.S.J.; Sigurdsson, H.; Carey, S.N. The entrance of pyroclastic flows into the sea, II. Theoretical considerations on subaqueous emplacement and welding. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 1980, 7, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimovs, J.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Talling, P.J. Anatomy of a submarine pyroclastic flow and associated turbidity current: July 2003 dome collapse, Soufrière Hills volcano, Montserrat, West Indies. Sedimentology 2008, 55, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, A.; Groppelli, G. Emplacement of pyroclastic density currents (PDCs) in a deep-sea environment: The Val d’Aveto Formation case (Northern Apennines, Italy). J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2016, 328, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, M.A.; Yeo, I.A.; Watson, S.; Wysoczanski, R.; Seabrook, S.; Mackay, K.; Hunt, J.E.; Lane, E.; Talling, P.J.; Pope, E.; et al. Fast and destructive density currents created by ocean-entering volcanic eruptions. Science 2023, 381, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeno, F.; Imamura, F. Tsunami generation by a rapid entrance of pyroclastic flow into the sea during the 1883 Krakatau eruption, Indonesia. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B09205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberico, I.; Di Fiore, V.; Iavarone, R.; Petrosino, P.; Piemontese, L.; Tarallo, D.; Punzo, M.; Marsella, E. The Tsunami Vulnerability Assessment of Urban Environments through Freely Available Datasets: The Case Study of Napoli City (Southern Italy). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 981–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Ulvrova, M.; Selva, J.; Brizuela, B.; Costa, A.; Grezio, A.; Lorito, S.; Tonini, R. Probabilistic hazard analysis for tsunamis generated by subaqueous volcanic explosions in the Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 379, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Levi, S.T.; Pistolesi, M.; Bertagnini, A.; Brunelli, D.; Cannavò, V.; Di Renzoni, A.; Ferranti, F.; Renzulli, A.; Yoon, D. Geoarchaeological Evidence of Middle-Age Tsunamis at Stromboli and Consequences for the Tsunami Hazard in the Southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maramai, A.; Graziani, L.; Brizuela, B. Italian Tsunami Effects Database (ITED): The First Database of Tsunami Effects Observed Along the Italian Coasts. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 596044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateo, F. Horribile dictu: Environmental catastrophes and writing in the late Middle Ages. In Le Calamità Ambientali nel Tardo Medioevo Europeo: Realtà, Percezioni, Reazioni, Proceedings of the Atti del XII Convegno del Centro Studi Sulla Civiltà del Tardo Medioevo, San Miniato, Italy, 31 May–2 June 2008; Centro Studi Sulla Civiltà del Tardo Med; Mattheus, M., Ed.; Firenze University Press: Firenze, Italy, 2010; Volume 12, p. 111. ISBN 978-88-8453-499-6. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]







| Time | Magnitude (Mw) | Location | Depth | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 September 2023 | 4.2 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°82′ | 14°16′ |
| 2 October 2023 | 4.0 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°83′ | 14°15′ |
| 21 August 2017 | 3.9 | Casamicciola (Ischia) | 2 km | 40°74′ | 13°90′ |
| 7 September 2023 | 3.8 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°83′ | 14°15′ |
| 16 October 2023 | 3.6 | Campi Flegrei | 2 km | 40°8′ | 14°14′ |
| 11 June 2023 | 3.6 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°83′ | 14°11′ |
| 18 August 2023 | 3.6 | Campi Flegrei | 2 km | 40°83′ | 14°14′ |
| 8 May 2023 | 3.4 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°83′ | 14°14′ |
| 22 September 2023 | 3.0 | Campi Flegrei | 1 km | 40°83′ | 14°14′ |
| 23 November 2023 | 3.1 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°83′ | 14°14′ |
| 17 February 2024 | 3.0 | Campi Flegrei | 3 km | 40°84′ | 14°12′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aiello, G.; Caccavale, M. Marine Geohazards of the Bay of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A Review Integrating Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis. GeoHazards 2024, 5, 393-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020021
Aiello G, Caccavale M. Marine Geohazards of the Bay of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A Review Integrating Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis. GeoHazards. 2024; 5(2):393-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiello, Gemma, and Mauro Caccavale. 2024. "Marine Geohazards of the Bay of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A Review Integrating Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis" GeoHazards 5, no. 2: 393-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020021
APA StyleAiello, G., & Caccavale, M. (2024). Marine Geohazards of the Bay of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): A Review Integrating Morpho-Bathymetric and Seismo-Stratigraphic Analysis. GeoHazards, 5(2), 393-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5020021







