2D Numerical Simulation of Floods in Ebro River and Analysis of Boundary Conditions to Model the Mequinenza Reservoir Dam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations and Numerical Model
2.1. 2D Shallow Water Equations
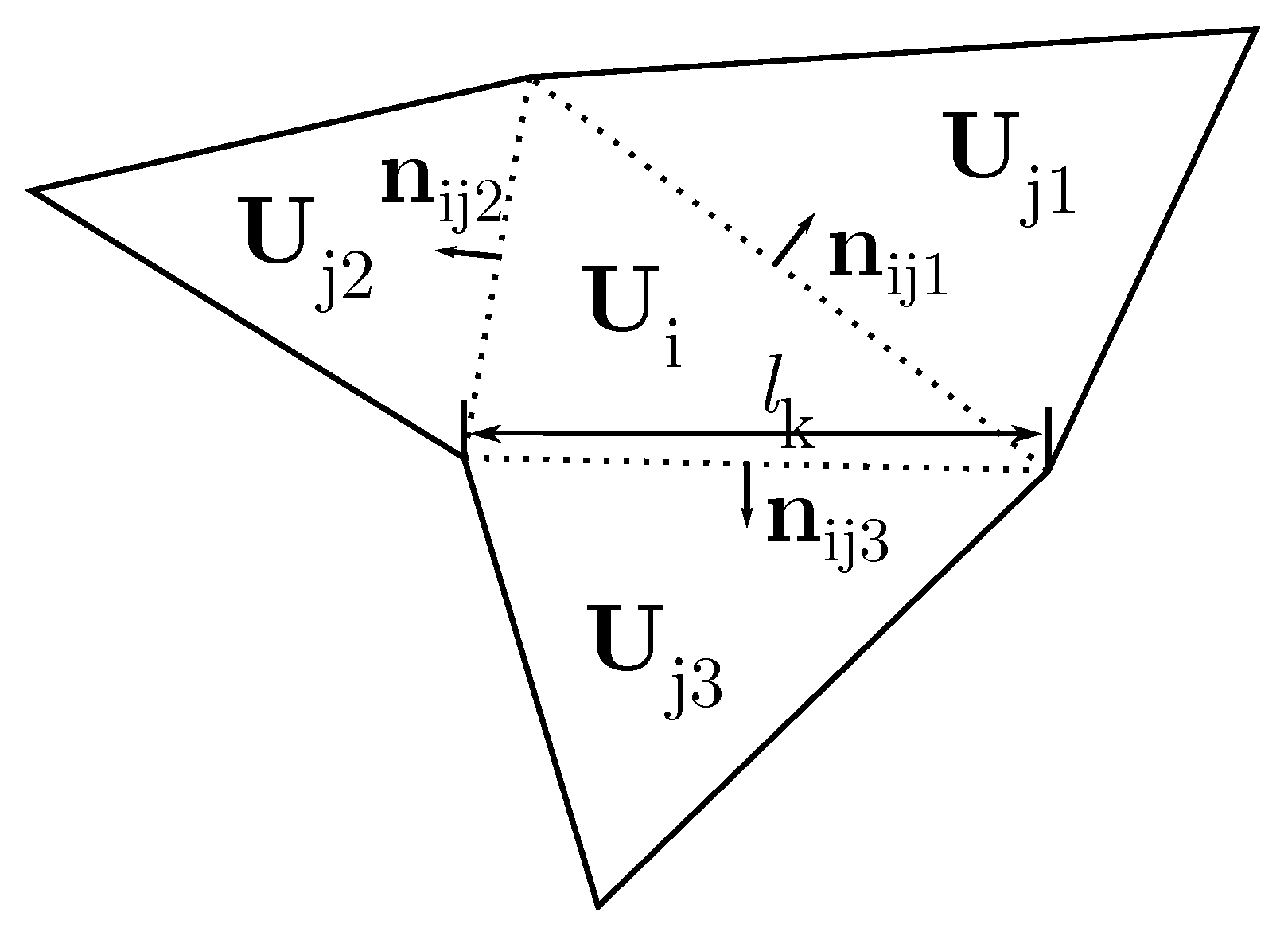
2.2. Numerical Scheme
3. Study Case and Model Setup
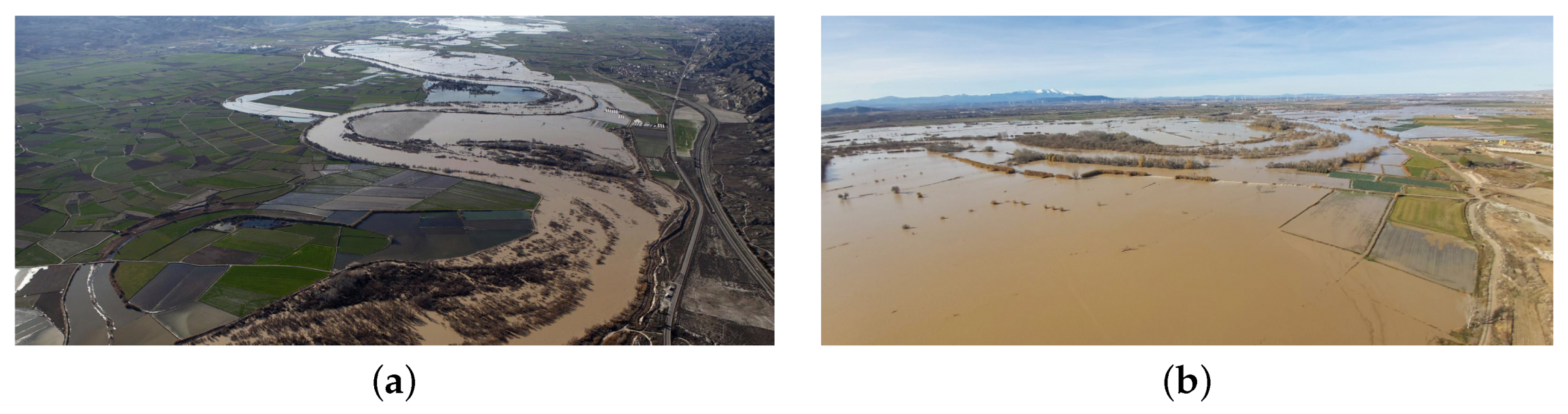
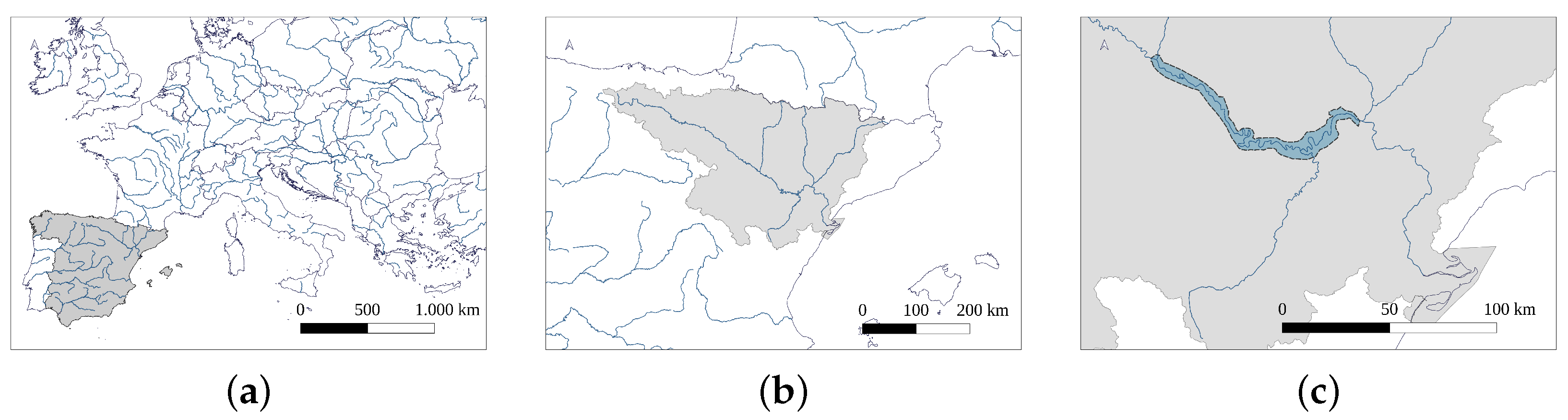
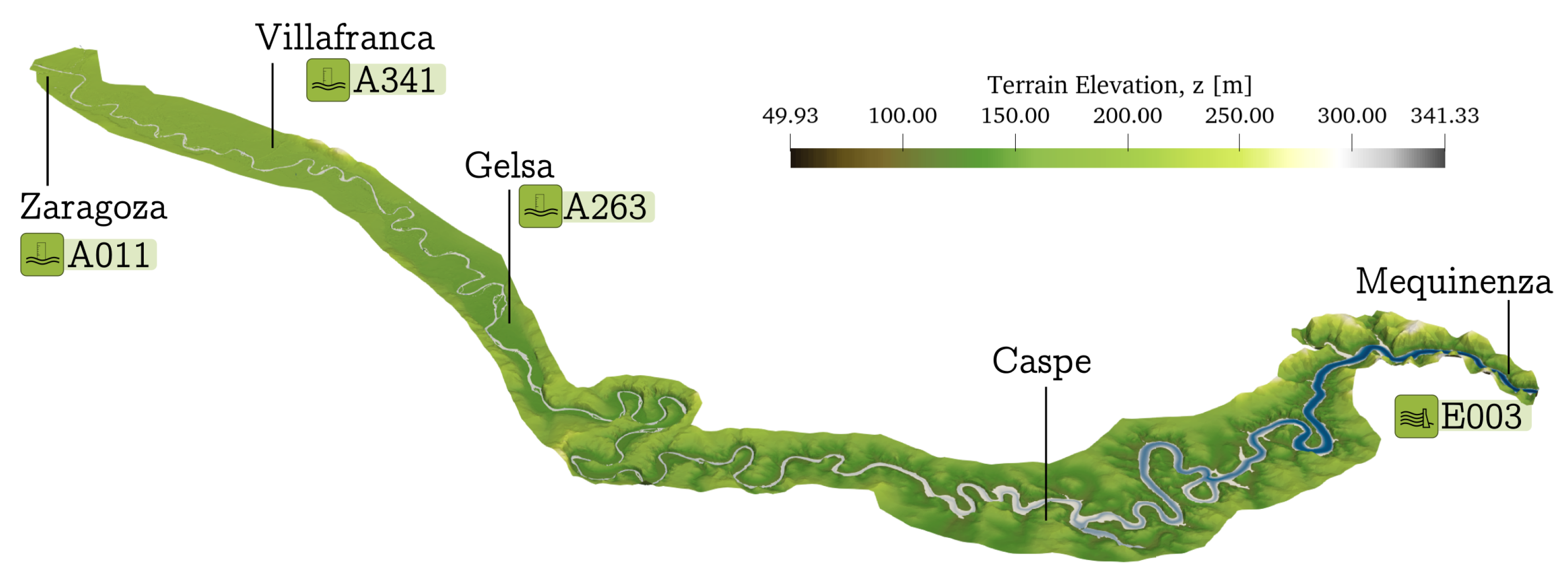
3.1. Study Case
3.2. Computational Model Setup
- 1.
- A digital terrain model (DTM);
- 2.
- a surface roughness map;
- 3.
- The creation of a triangular mesh;
- 4.
- Boundary conditions and initial conditions.
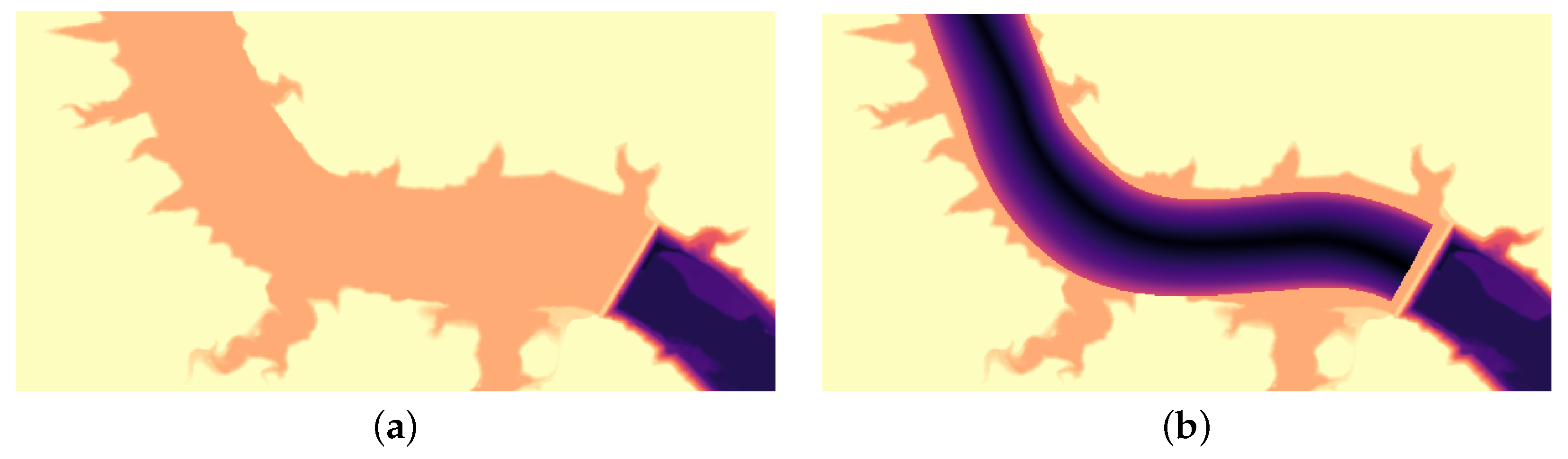
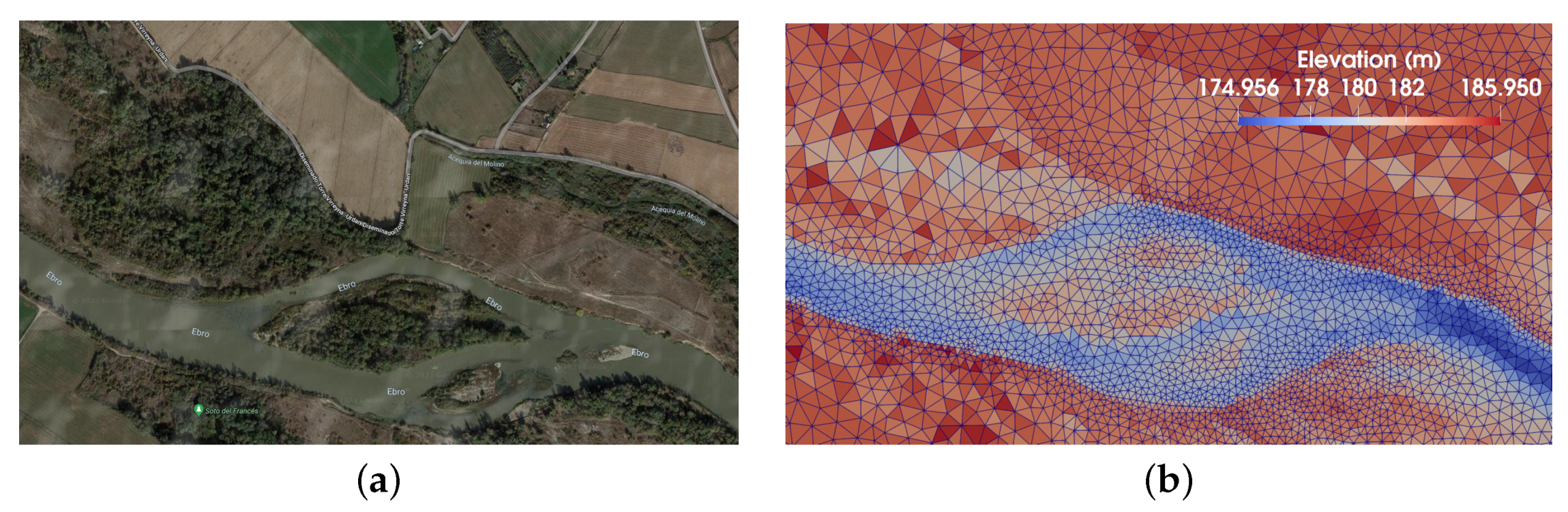
3.2.1. Topography: DTM
Reconstruction of the Riverbed from Sástago
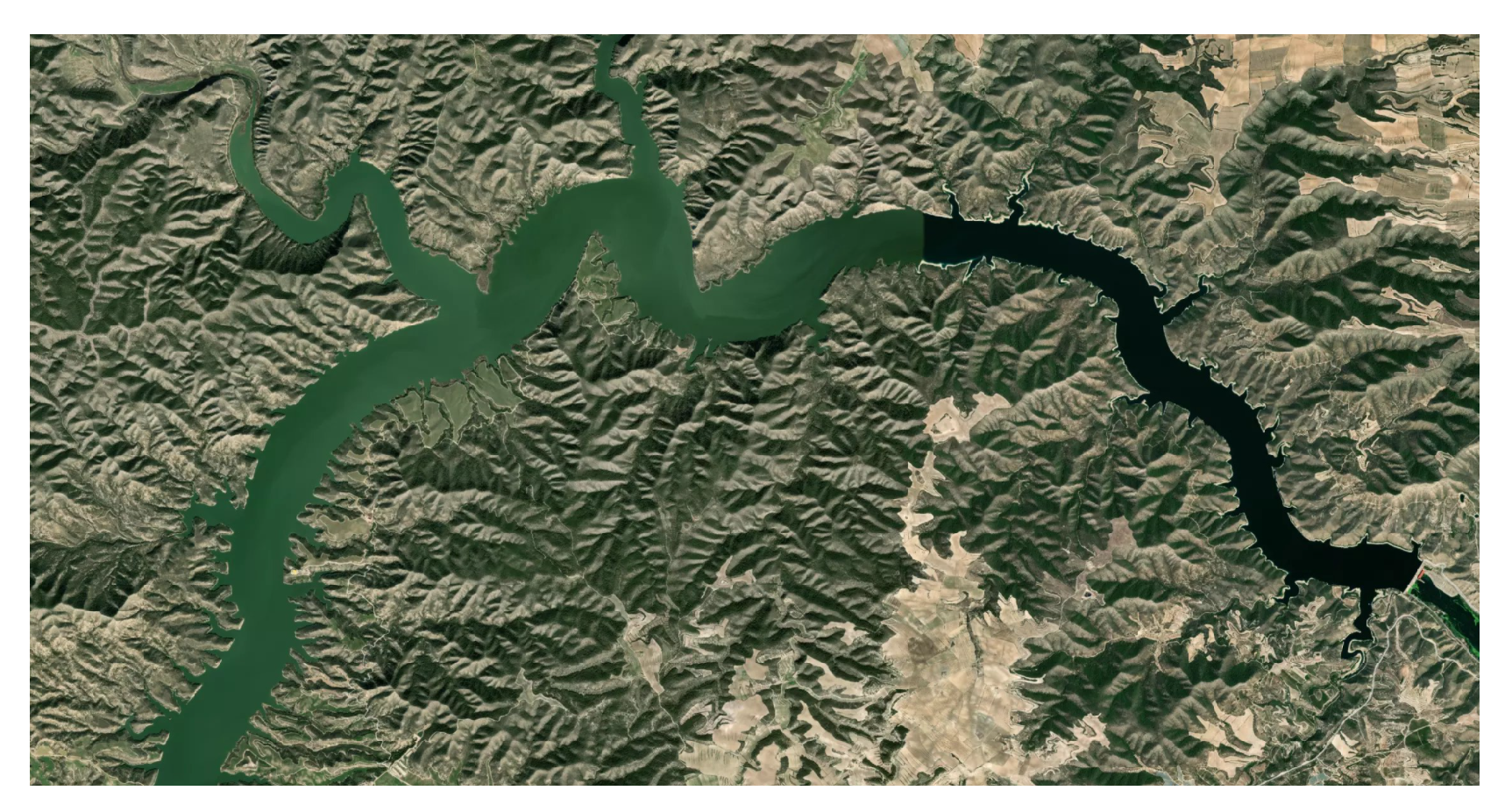
Reconstruction of the Reservoir
3.2.2. Surface Roughness Map
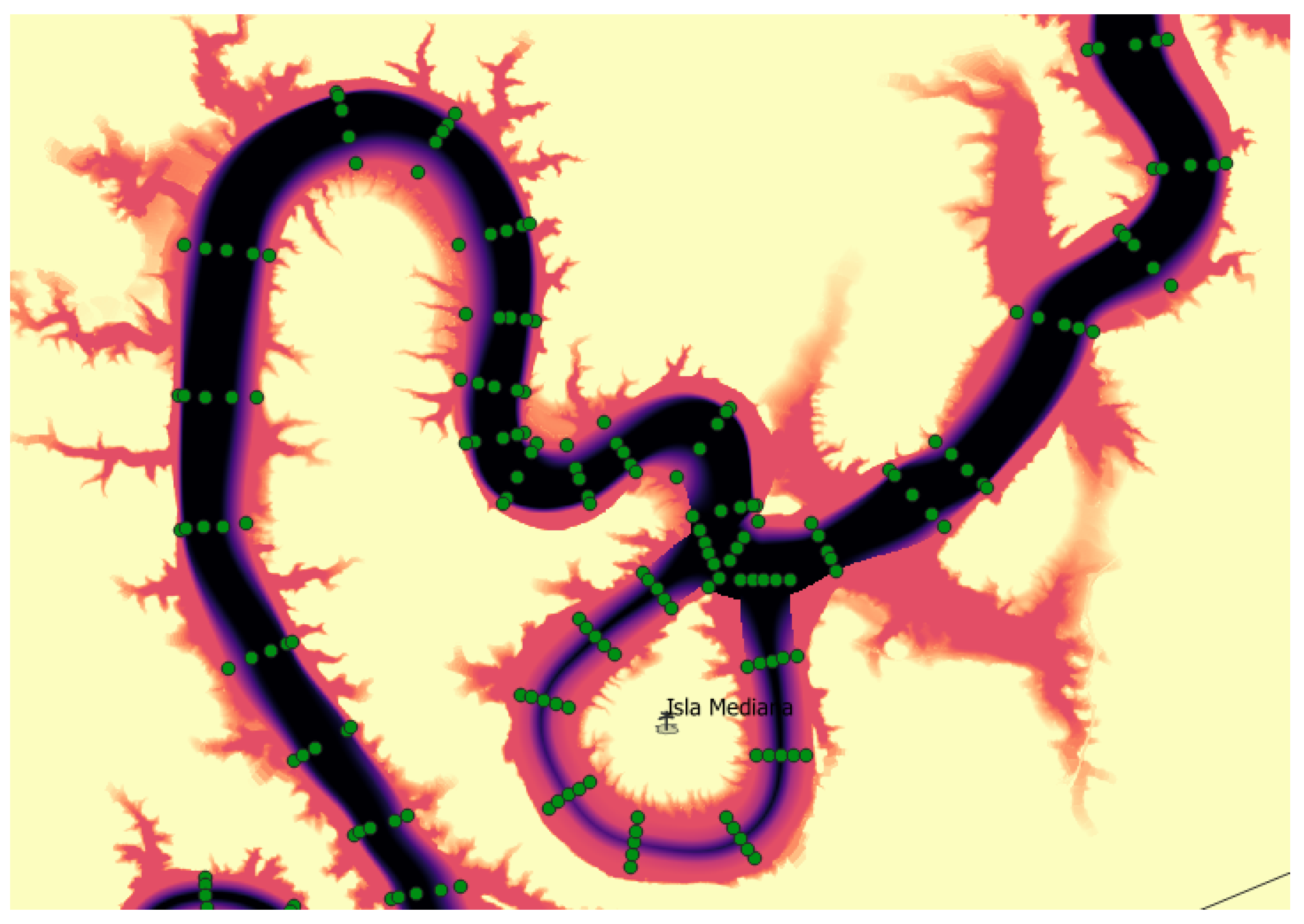
3.2.3. Meshing
3.2.4. Initial Condition
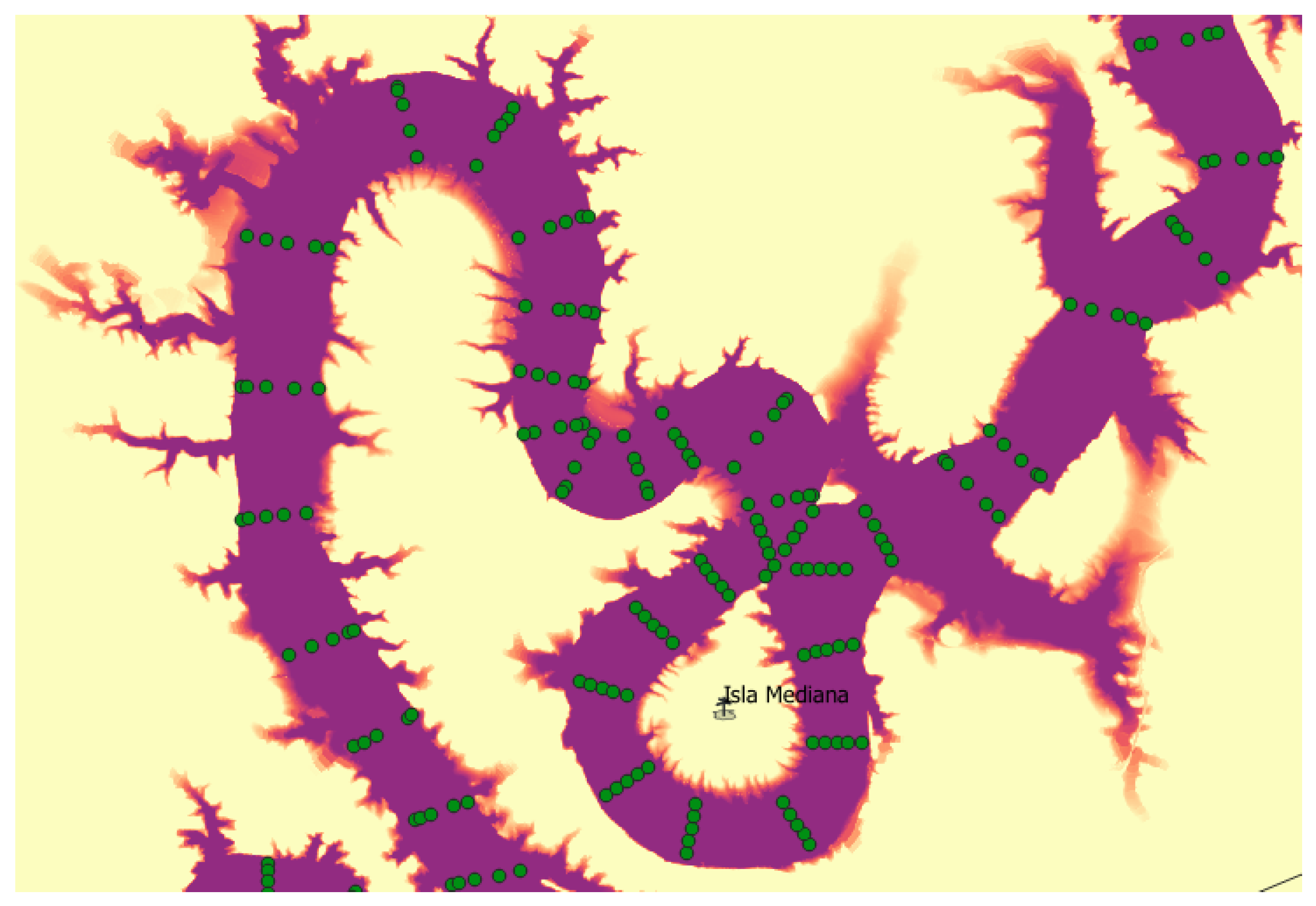
3.3. Boundary Conditions
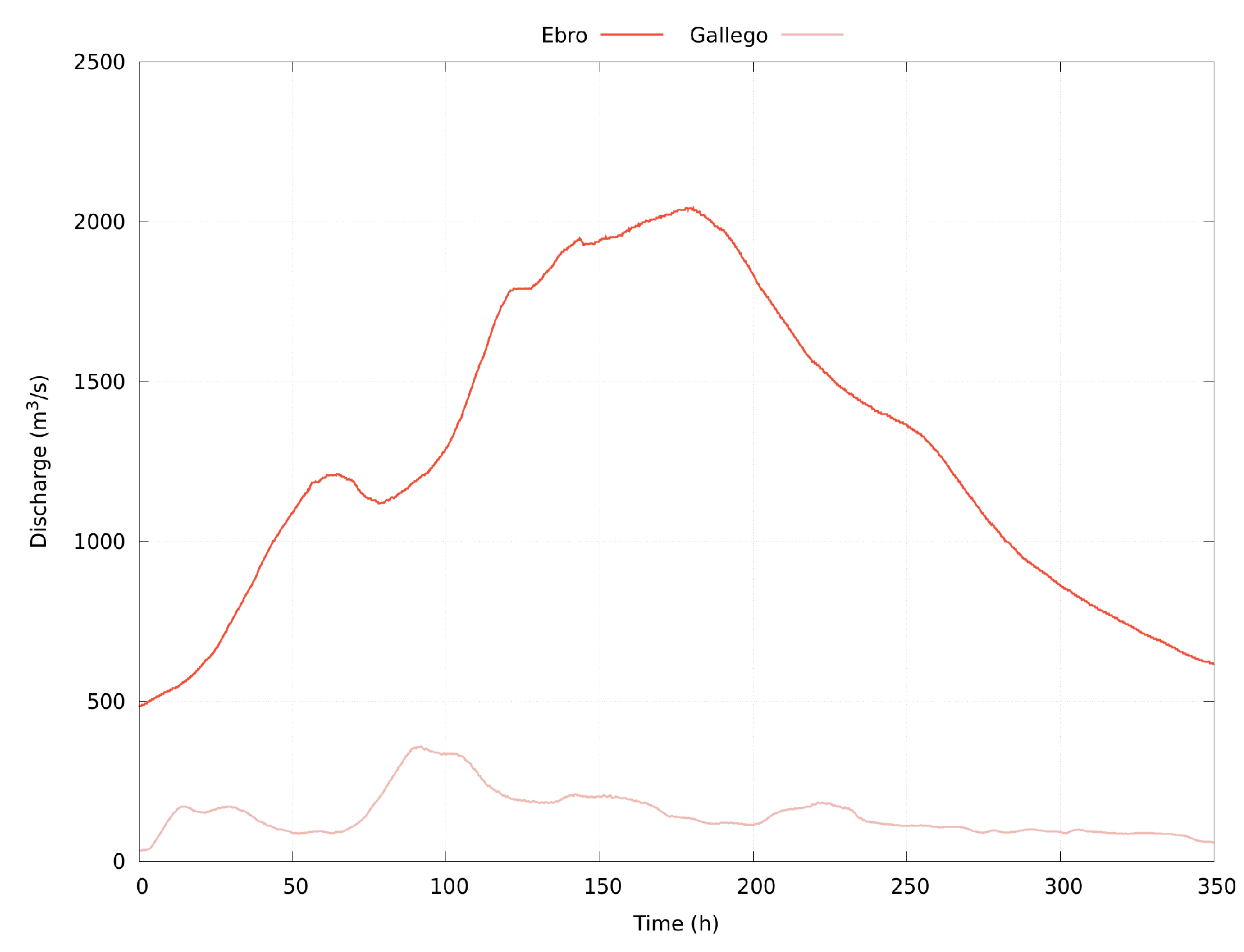
3.3.1. Upstream Boundary Conditions
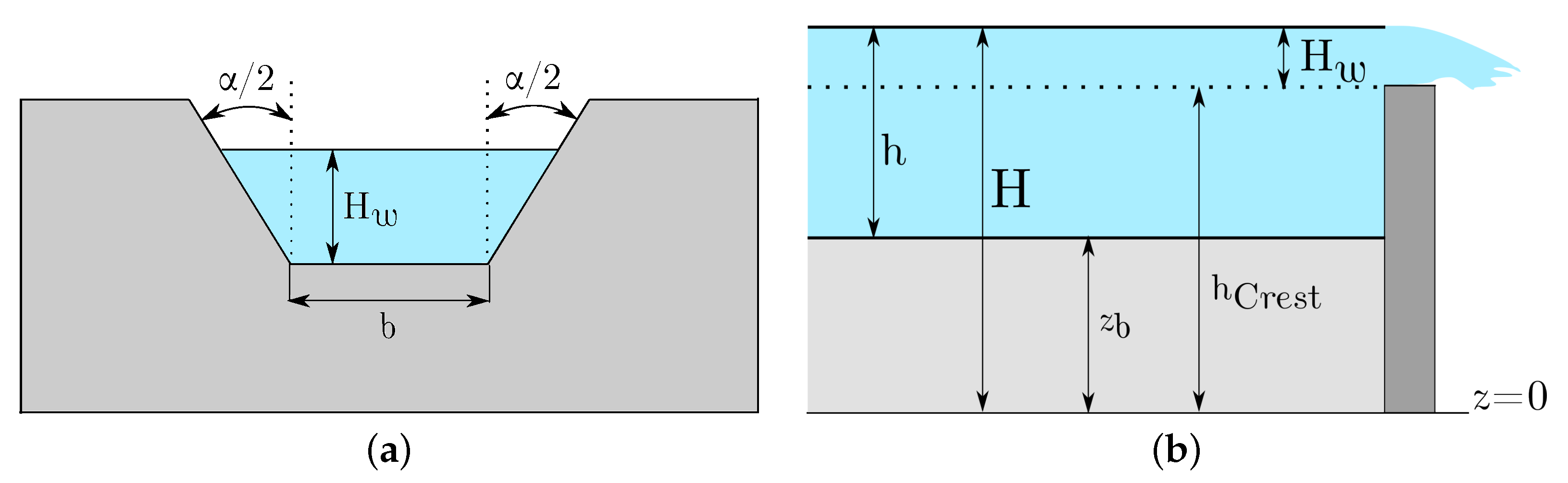
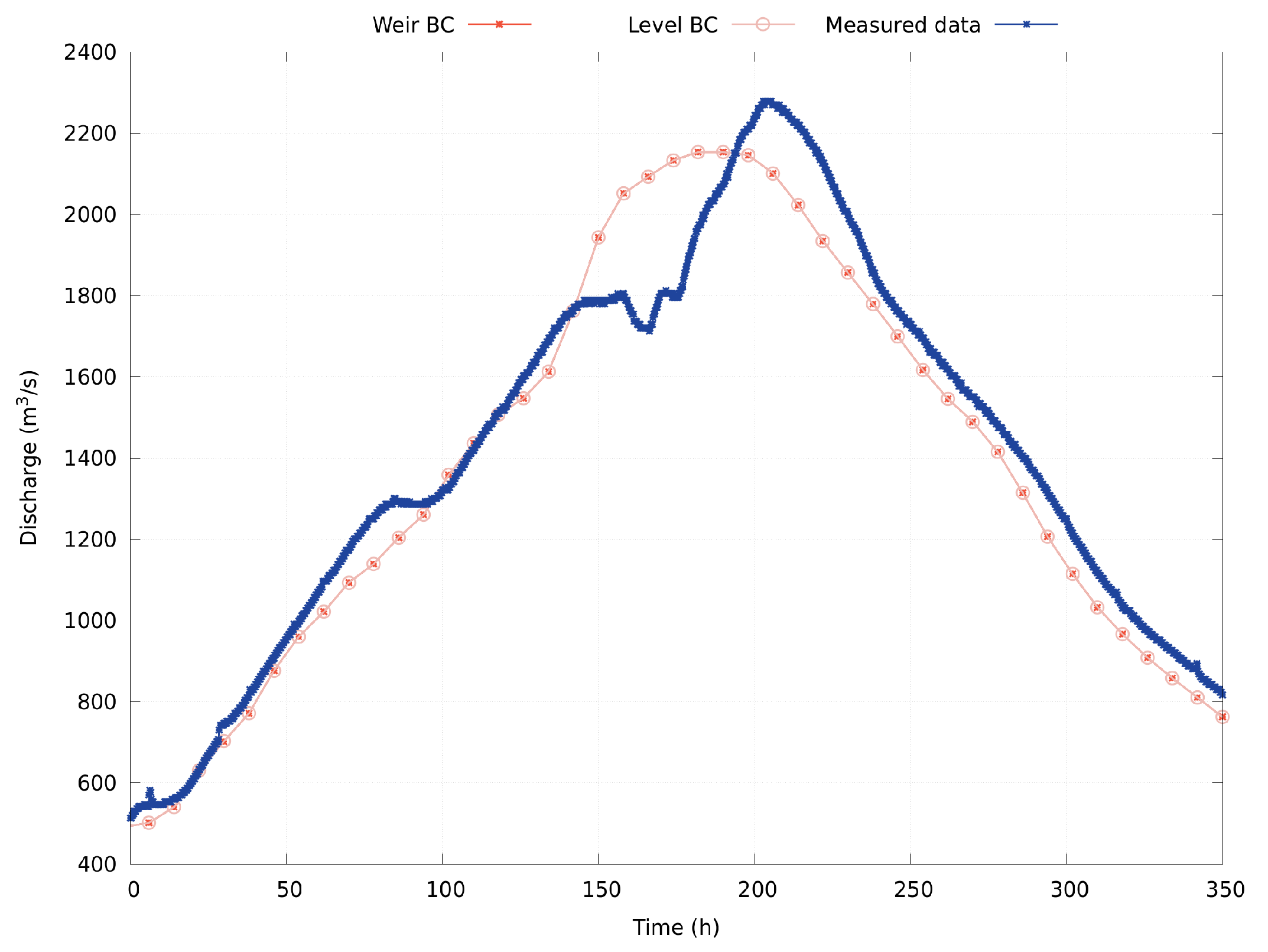
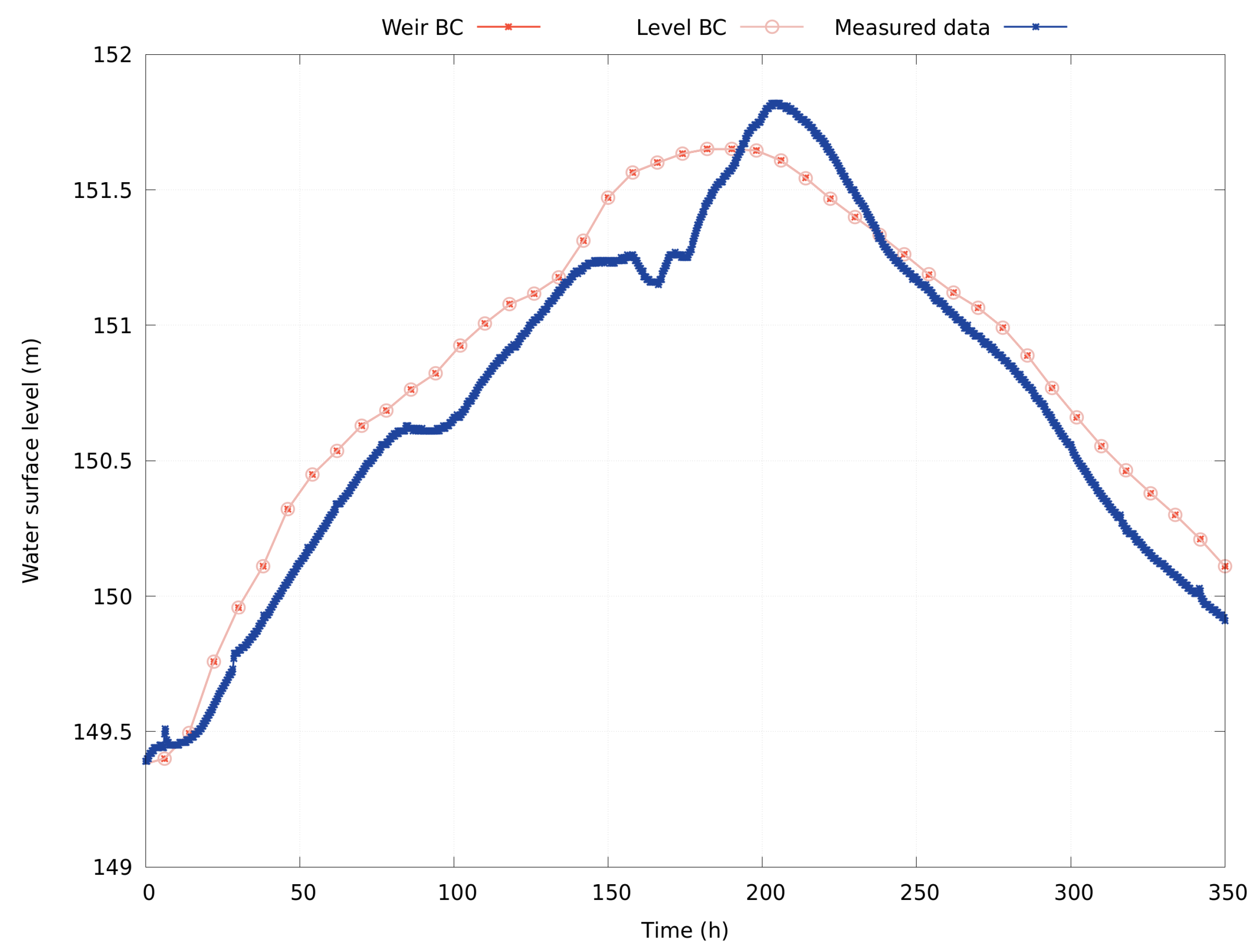
3.3.2. Downstream Boundary Conditions
Time-Dependent Level
Dam Spillway Condition
4. Calibration and Optimization of the Computational Mesh
4.1. Calibration of Mesh Refinement
4.2. Optimization
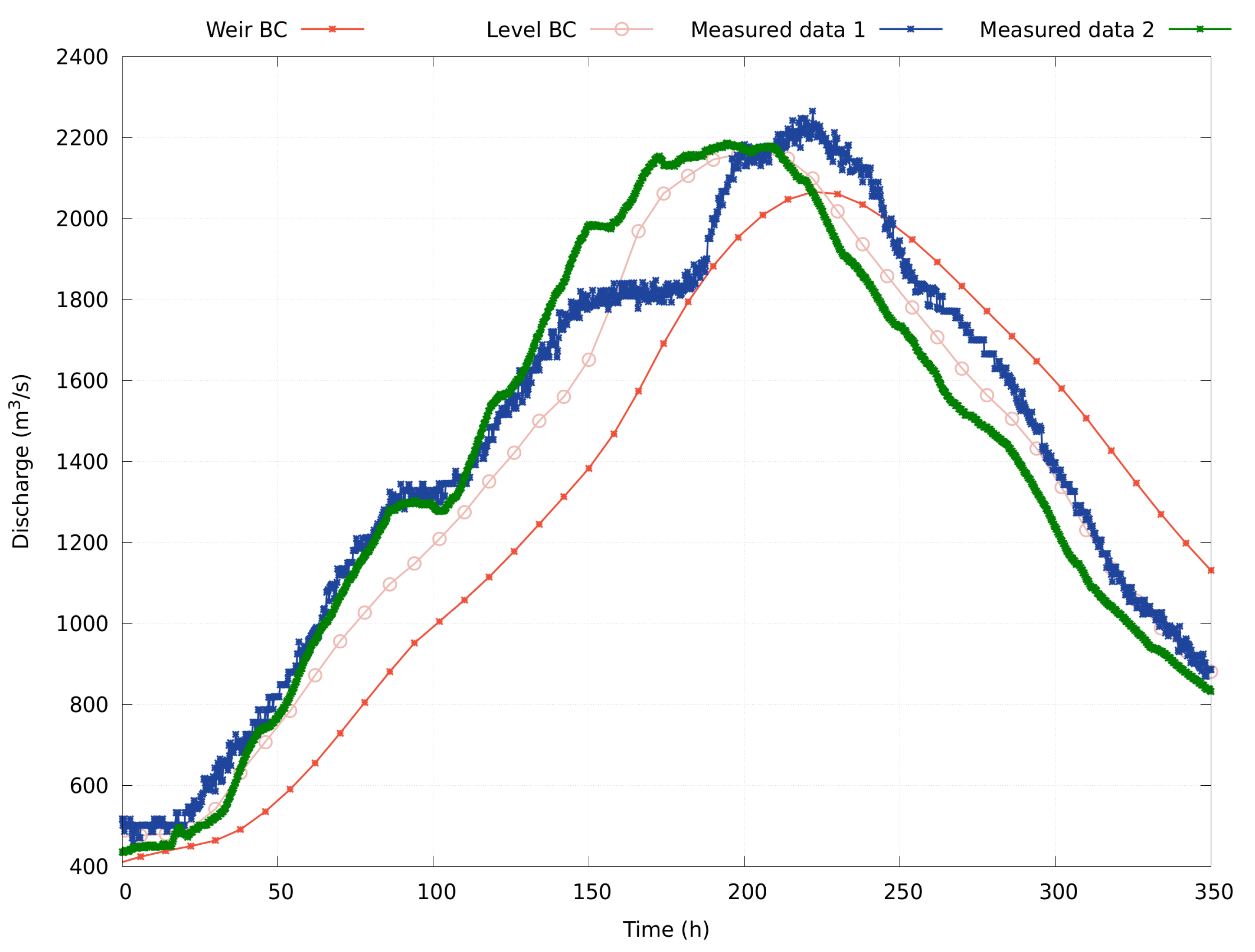
5. Numerical Results
2018 Event
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHE | Ebro River Authority (www.chebro.es, accessed on 1 February 2023) |
| DTM | Digital Terrain Model |
| IGN | National Geographic Institute (https://www.ign.es/web/ign/portal, accessed on |
| 1 February 2023) | |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Ripple, W.J.; Wolf, C.; Newsome, T.M.; Barnard, P.; Moomaw, W.R. World Scientists’ Warning of a Climate Emergency. BioScience 2020, 70, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallemacq, P.; Herden, C.; House, R. The Human Cost of Natural Disasters 2015: A Global Perspective; Technical Report; Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Subdirección General de Prevención, Planificación y Emergencias. Fallecidos por riesgos naturales en España en 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.proteccioncivil.es/documents/20121/64522/FALLECIMIENTOS+POR+RIESGOS+NATURALES+2019.pdf/ace258bb-e6f2-344b-d056-2fae84dc089c?t=1608632325113 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Hu, H.; Yang, H.; Wen, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y. An Integrated Model of Pluvial Flood Risk and Adaptation Measure Evaluation in Shanghai City. Water 2023, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Ramos, M.H.; de Roo, A. The European Flood Alert System—Part 1: Concept and development. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knijff, J.M.V.D.; Younis, J.; Roo, A.P.J.D. LISFLOOD: A GISbased distributed model for river basin scale water balance and flood simulation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GebreEgziabher, M.; Demissie, Y. Modeling Urban Flood Inundation and Recession Impacted by Manholes. Water 2020, 12, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hill, A.A.; Urbano, L.D. A GIS-based model for urban flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghansah, B.; Nyamekye, C.; Owusu, S.; Agyapong, E. Mapping flood prone and Hazards Areas in rural landscape using landsat images and random forest classification: Case study of Nasia watershed in Ghana. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2021, 8, 1923384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcina, J.; Sauri, D.; Hernández, M.; Ribas, A. Flood policy in Spain: A review for the period 1983–2013. Disaster Prevent. Manag. 2016, 25, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament 2007 Directive 2007/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2007 on the Assessment and Management of Flood Risks. EU Directive. 2007. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:32007L0060 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- European Environment Agency. The European Environment—State and Outlook 2020; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vacondio, R.; Aureli, F.; Ferrari, A.; Mignosa, P.; Palù, A. Simulation of the January 2014 flood on the Secchia River using a fast and high-resolution 2D parallel shallow-water numerical scheme. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M.S.; Bates, P.D. Evaluation of 1D and 2D numerical models for predicting river flood inundation. J. Hydrol 2002, 268, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, C.C.; Smith, A.M.; Bates, P.D.; Neall, J.C.; Alfieri, L.; Freer, J.E. A high-resolution global flood hazard model. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 7358–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasta, A.; Juez, C.; Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. An efficient solution for hazardous geophysical flows simulation using GPUs. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 78, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanapu, A.J.; Shankar, S.; Pardyjak, E.R.; Judi, D.R.; Burian, S.J. Assessment of GPU computational enhancement to a 2D flood model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, R.; Dodd, N. Shoreline motion in nonlinear shallow water coastal models. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, M.E.; Dodd, N. A 2D numerical model of wave run-up and overtopping. Coast. Eng. 2002, 47, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverribar, I.; Morales-Hernández, M.; Brufau, P.; García-Navarro, P. 2D numerical simulation of unsteady flows for large scale floods prediction in real time. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 134, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomers, A.; Schielen, R.M.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. The influence of grid shape and grid size on hydraulic river modelling performance. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 1273–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.; Schubert, J.; Detwiler, R. Parbrezo: A parallel, unstructured grid, Godunov type, shallow water code for high resolution flood inundation modeling at the regional scale. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoero, A.; Claps, P.; Asselman, N.E.M.; Mosselman, E.; Di Baldassarre, G. Reconstruction and analysis of the Po river inundation of 1951. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defina, A. Two-dimensional shallow flow equations for partially dry areas. Water Resourc. Res. 2000, 36, 3251–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C.; Macchione, F. Performances and limitations of the diffusive approximation of the 2-d shallow water equations for flood simulation in urban and rural areas. Appl. Numer. Math. 2017, 116, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Dittrich, A. 1D unsteady-state flow simulation of a section of the upper Rhine. J. Hydrol. 2002, 269, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.; Takeuchi, K. Assessment of flood hazard, vulnerability and risk of mid-eastern Dhaka using DEM and 1D hydrodynamic model. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fang, F.; Salinas, P.; Pain, C.C.; Sto.Domingo, N.D.; Mark, O. Numerical simulation of floods from multiple sources using an adaptive anisotropic unstructured mesh method. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 123, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kawaike, K.; Seo, D.J. Hyper-resolution 1D-2D urban flood modelling using LiDAR data and hybrid parallelization. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2018, 103, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, G.A.M.; Bates, P.; Freer, J.E.; Souvignet, M. Improving the stability of a simple formulation of the shallow water equations for 2-D flood modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W05528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Paquier, A.; Haider, S. Modeling floods in a dense urban area using 2D shallow water equations. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgen, I.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Hinkelmann, R. Urban flood modeling using shallow water equations with depth-dependent anisotropic porosity. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1165–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.F.; Schubert, J.E.; Gallegos, H.A. Integral formulation of shallow-water equations with anisotropic porosity for urban flood modeling. J. Hydrol. 2008, 362, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverribar, I.; Morales-Hernández, M.; Brufau, P.; García-Navarro, P. Use of internal boundary conditions for levees representation: Application to river flood management. Environ. Fluid. Mech. 2019, 19, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentini, M.; Orlandini, S. Robust numerical solution of the reservoir routing equation. Adv.Water Resour. 2013, 59, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, X. Development of a SWAT extension module to simulate riparian wetland hydrologic processes at a watershed scale. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 2901–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorchies, D.; Thirel, G.; Jay-Allemand, M.; Chauveau, M.; Dehay, F.; Bourgin, P.-Y.; Perrinb, C.; Joste, C.; Rizzolie, J.L.; Demerliac, S.; et al. Climate change impacts on multi-objective reservoir management: Case study on the Seine River basin, France. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Liechti, T.; Matos, J.P.; Ferràs Segura, D.; Boillat, J.-L.; Schleiss, A.J. Hydrological modelling of the Zambezi River Basin taking into account floodplain behaviour by a modified reservoir approach. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Issa, I.E.; Knutsson, S. Sediment in Mosul Dam reservoir using the HEC-RAS model. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2016, 21, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. Wave Riemann description of friction terms in unsteady shallow flows: Application to water and mud/debris floods. J. Comput. Phys. 2012, 231, 1963–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. Weak solutions for partial differential equations with source terms: Application to the shallow water equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 4237–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunge, J.; Holly, F.; Verwey, A. Practical Aspects of Computational River Hydraulics; Pitman: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Arcement, G.; Schneider, V. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains. In US Geological Survey. Water-Supply Paper; USGS Publications Warehouse: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; Volume 2339. [Google Scholar]
- Toro, E.F. The Riemann Solver of Roe. In Riemann Solvers and Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 313–343. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; Petaccia, G.; Brufau, P.; García-Navarro, P. Conservative 1D–2D coupled numerical strategies applied to river flooding: The Tiber (Rome). Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 2087–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, R. Numerical Methods for Conservation Laws Lectures in Mathematics; ETH: Zürich, Switzerland; Birkhuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, V.T. Open-Channel Hydraulics, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Palmeri, F.; Silván, F.; Prieto, I.; Balboni, M.; García-Mijangos, I. Manual de Técnicas de Ingeniería Naturalística en Ambito Fluvial; Departamento de Ordenación del Territorio y Medio Ambiente, País Vasco Government: Bilbao, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fread, D.; Hsu, K. Applicability of Two Simplified Flood Routing Methods: Level-Pool and Muskingum-Cunge. In Proceedings of the ASCE National Hydraulic Engineering Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 July 1993; pp. 1564–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo, G. Hidráulica General Vol. 1, 1st ed.; Limusa: Wellington, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, F.M. Open Channel Flow; Macmillan Series in Civil Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Pato, J.; Sánchez, A.; García-Navarro, P. Simulación de avenidas mediante un modelo hidráulico/hidrológico distribuido en un tramo urbano del río Ginel (Fuentes de Ebro). Ribagua 2019, 6, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; Murillo, J.; García-Navarro, P. The formulation of internal boundary conditions in unsteady 2D shallow water flows: Application to flood regulation. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 80, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Barnston, A.G. Correspondence among the Correlation, RMSE, and Heidke Forecast Verification Measures; Refinement of the Heidke Score. Wea. Forecast. 1992, 7, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






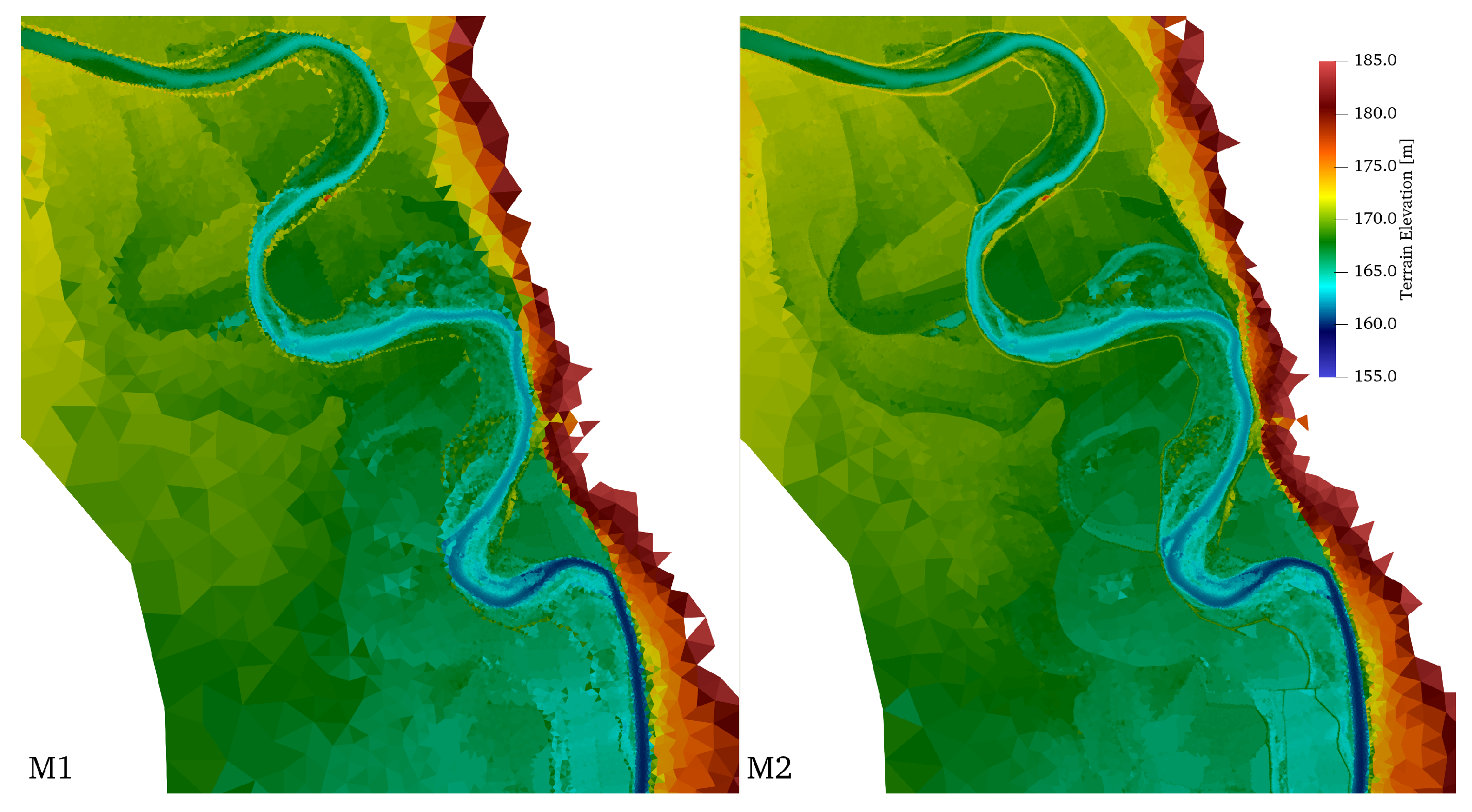
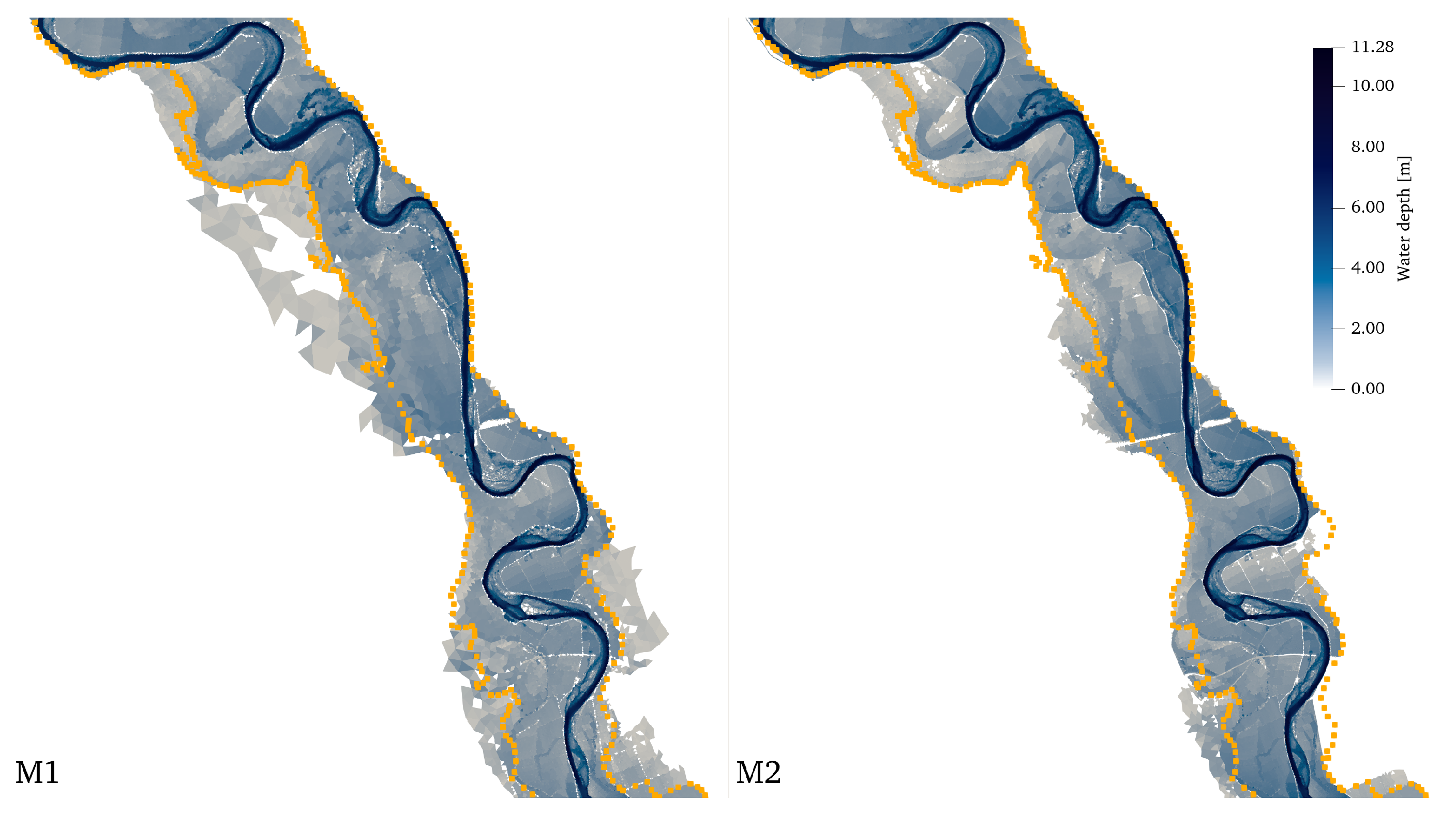
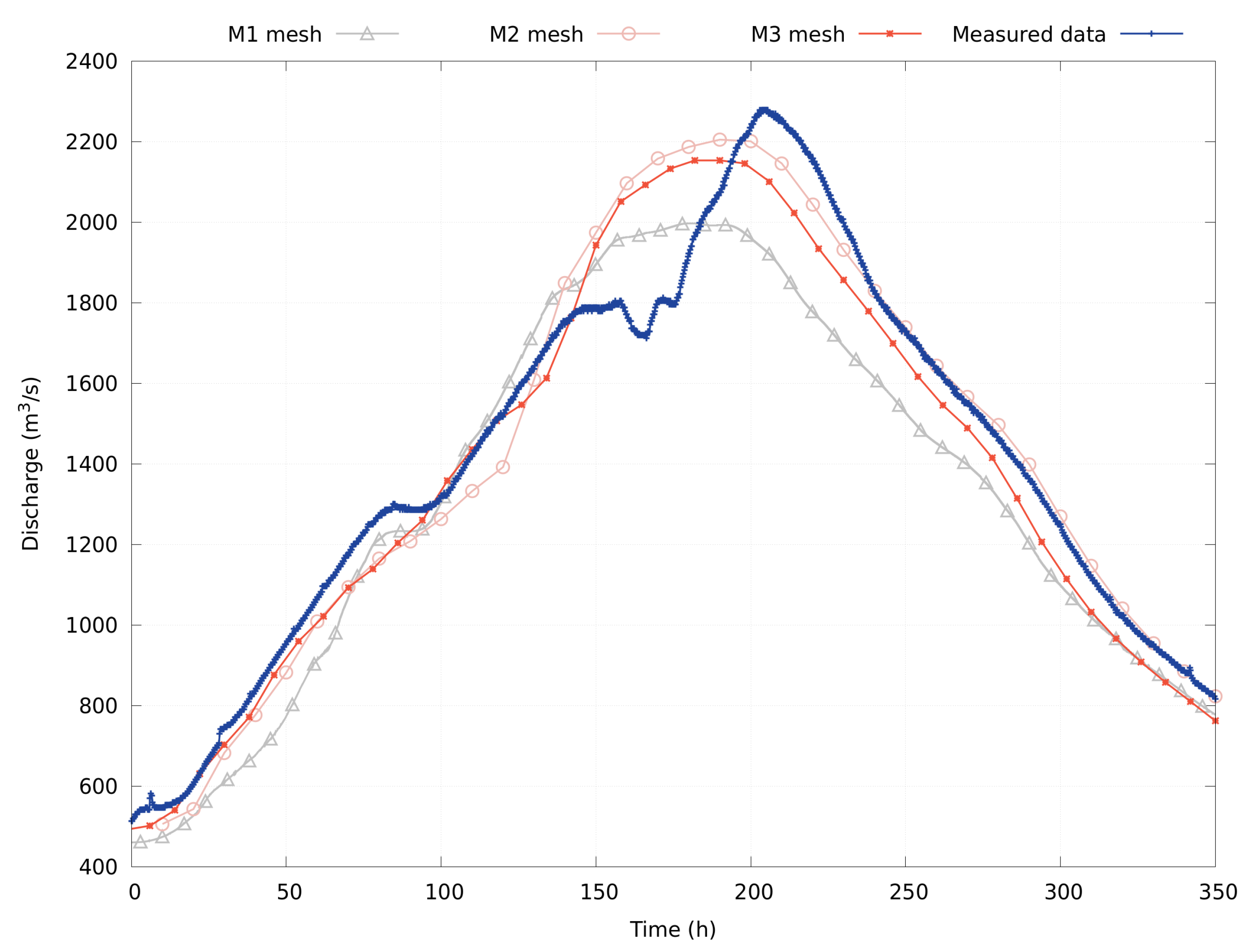

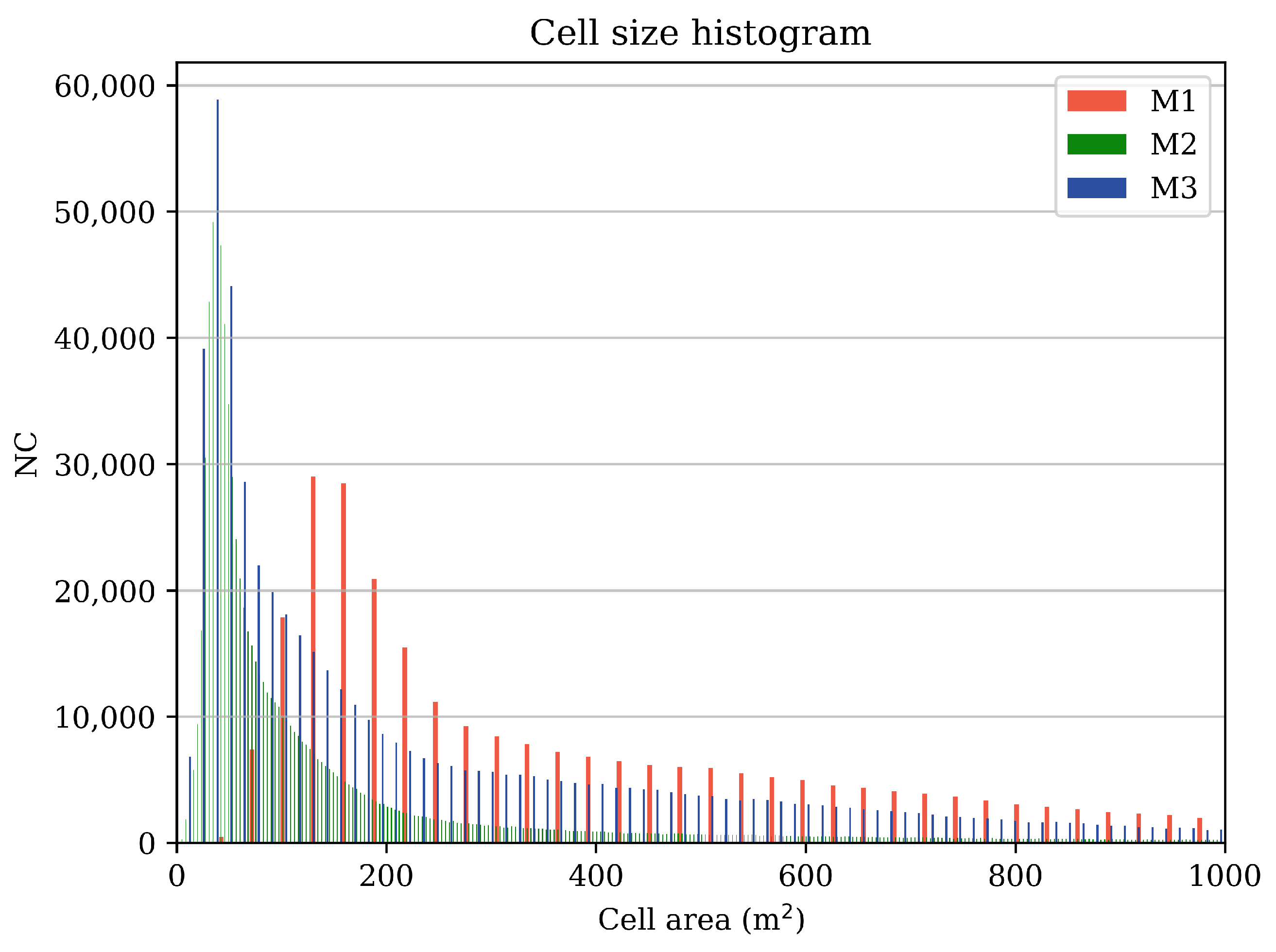

| Type of Soil | Manning’s Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Farm land | 0.028 |
| Riverbed | 0.035 |
| Urban area | 0.05 |
| River island | 0.06 |
| Mesh | Number of Cells | Computational Cost (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Preliminary mesh M1 | 351,799 | 9.52 |
| Refined mesh M2 | 949,445 | 23.80 |
| Mesh | Number of Cells | Computational Cost (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Refined mesh M2 | 949,445 | 23.80 |
| Optimized mesh M3 | 633,216 | 12.48 |
| Mesh | RMSE |
|---|---|
| Preliminary mesh M1 | 164.65 |
| Refined mesh M2 | 119.62 |
| Optimized mesh M3 | 120.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vallés, P.; Echeverribar, I.; Mairal, J.; Martínez-Aranda, S.; Fernández-Pato, J.; García-Navarro, P. 2D Numerical Simulation of Floods in Ebro River and Analysis of Boundary Conditions to Model the Mequinenza Reservoir Dam. GeoHazards 2023, 4, 136-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4020009
Vallés P, Echeverribar I, Mairal J, Martínez-Aranda S, Fernández-Pato J, García-Navarro P. 2D Numerical Simulation of Floods in Ebro River and Analysis of Boundary Conditions to Model the Mequinenza Reservoir Dam. GeoHazards. 2023; 4(2):136-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleVallés, Pablo, Isabel Echeverribar, Juan Mairal, Sergio Martínez-Aranda, Javier Fernández-Pato, and Pilar García-Navarro. 2023. "2D Numerical Simulation of Floods in Ebro River and Analysis of Boundary Conditions to Model the Mequinenza Reservoir Dam" GeoHazards 4, no. 2: 136-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4020009
APA StyleVallés, P., Echeverribar, I., Mairal, J., Martínez-Aranda, S., Fernández-Pato, J., & García-Navarro, P. (2023). 2D Numerical Simulation of Floods in Ebro River and Analysis of Boundary Conditions to Model the Mequinenza Reservoir Dam. GeoHazards, 4(2), 136-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4020009









