Experimental Study on the Co-Combustion Characteristics of Brown Gas (HHO) and Bituminous Coal/Anthracite with Different Injection Modes in a One-Dimensional Furnace
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
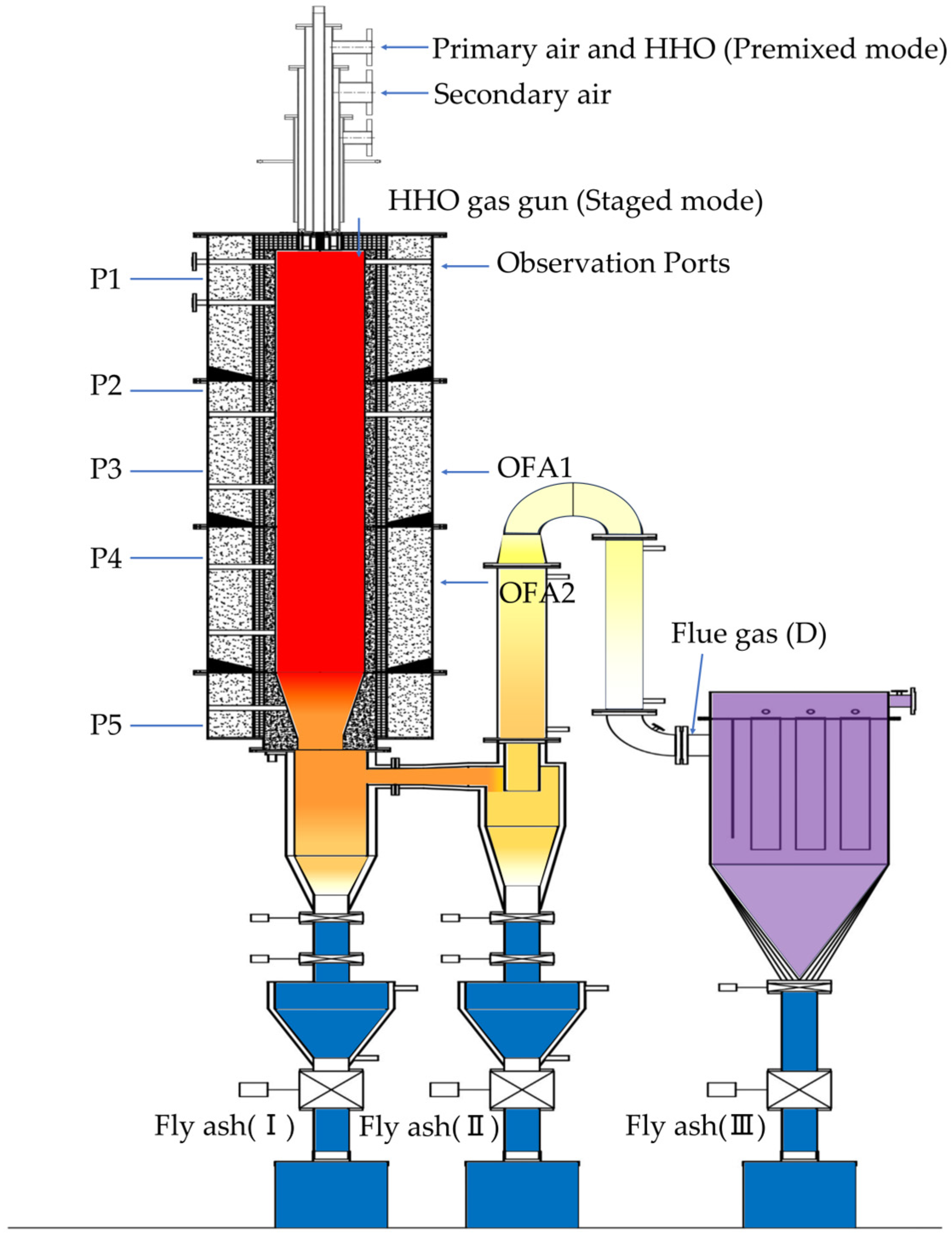
2.1. Experimental Equipment
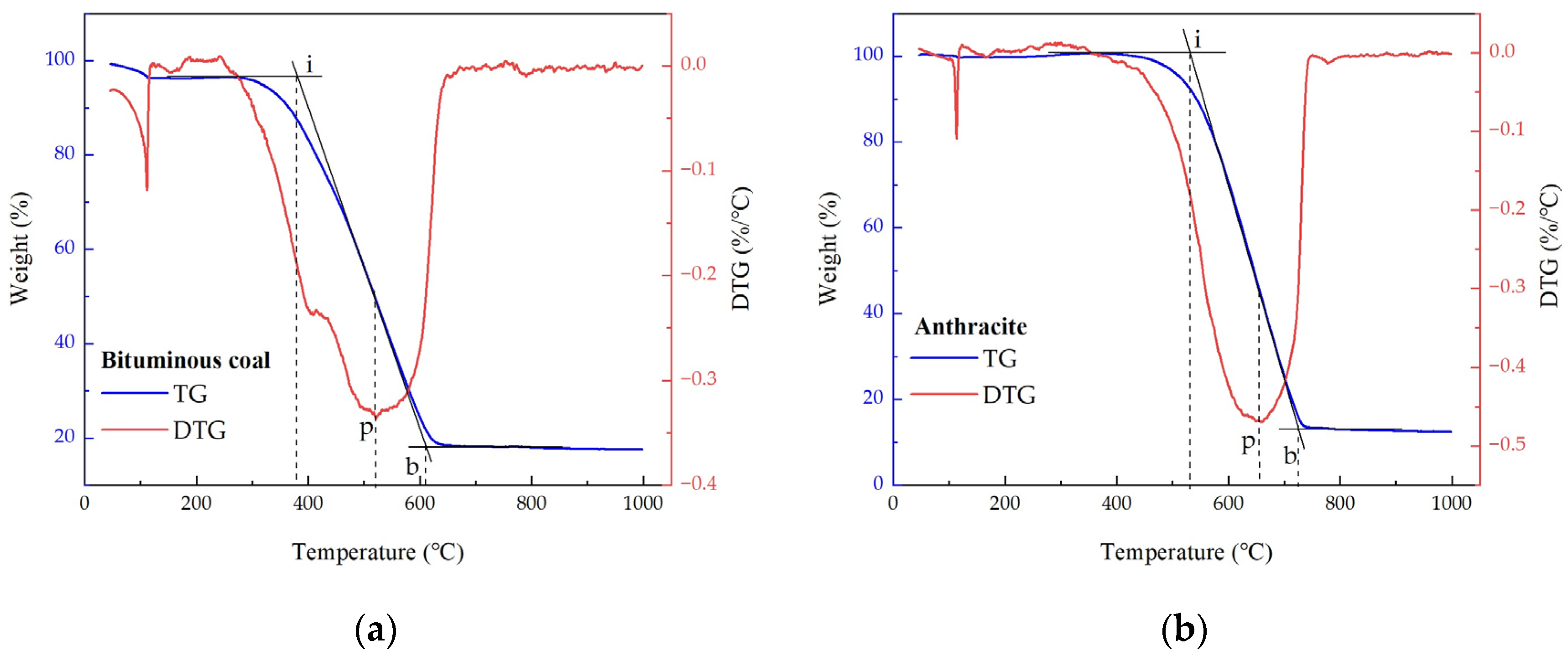
2.2. Fuel Properties
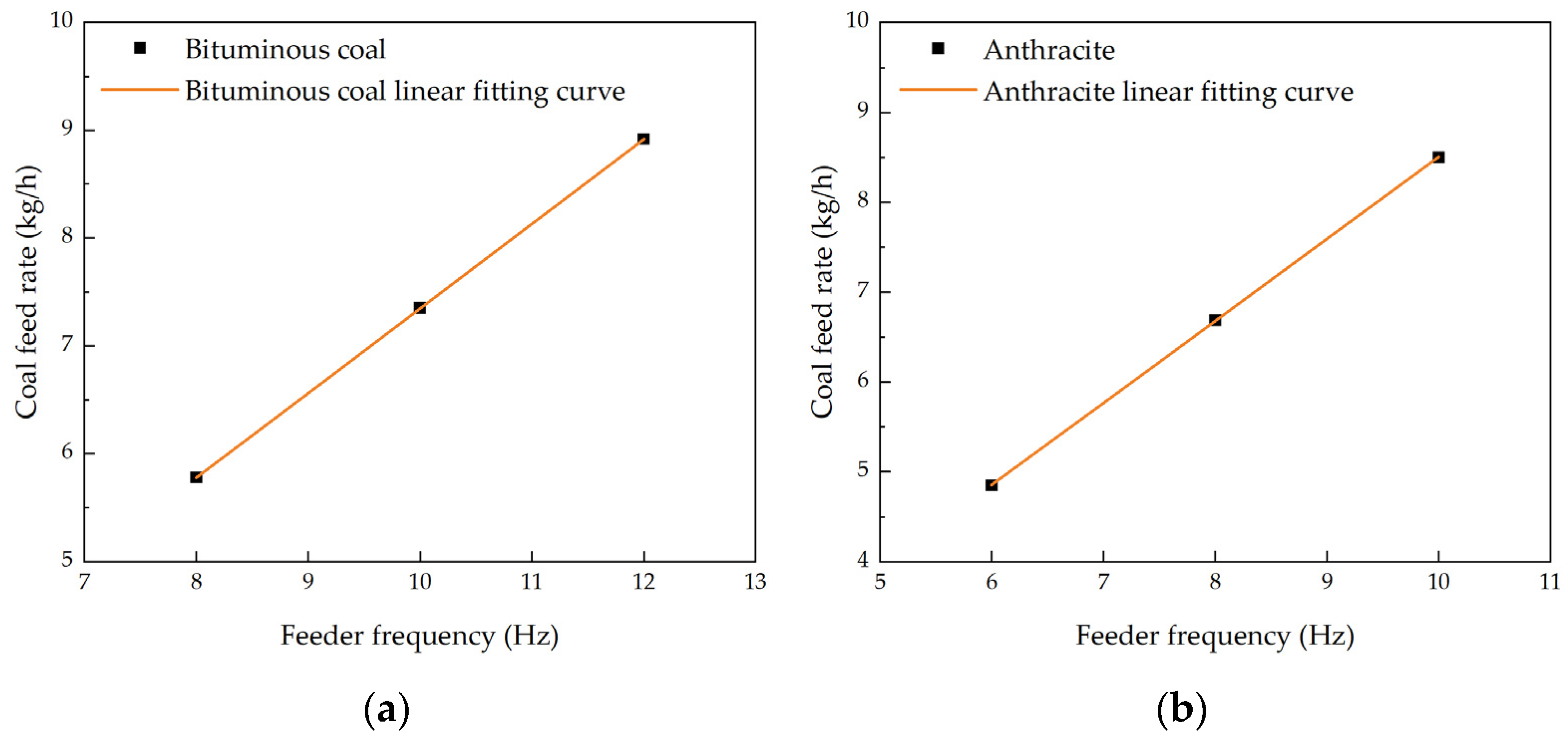
2.3. Experimental Conditions
2.4. Analytical and Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
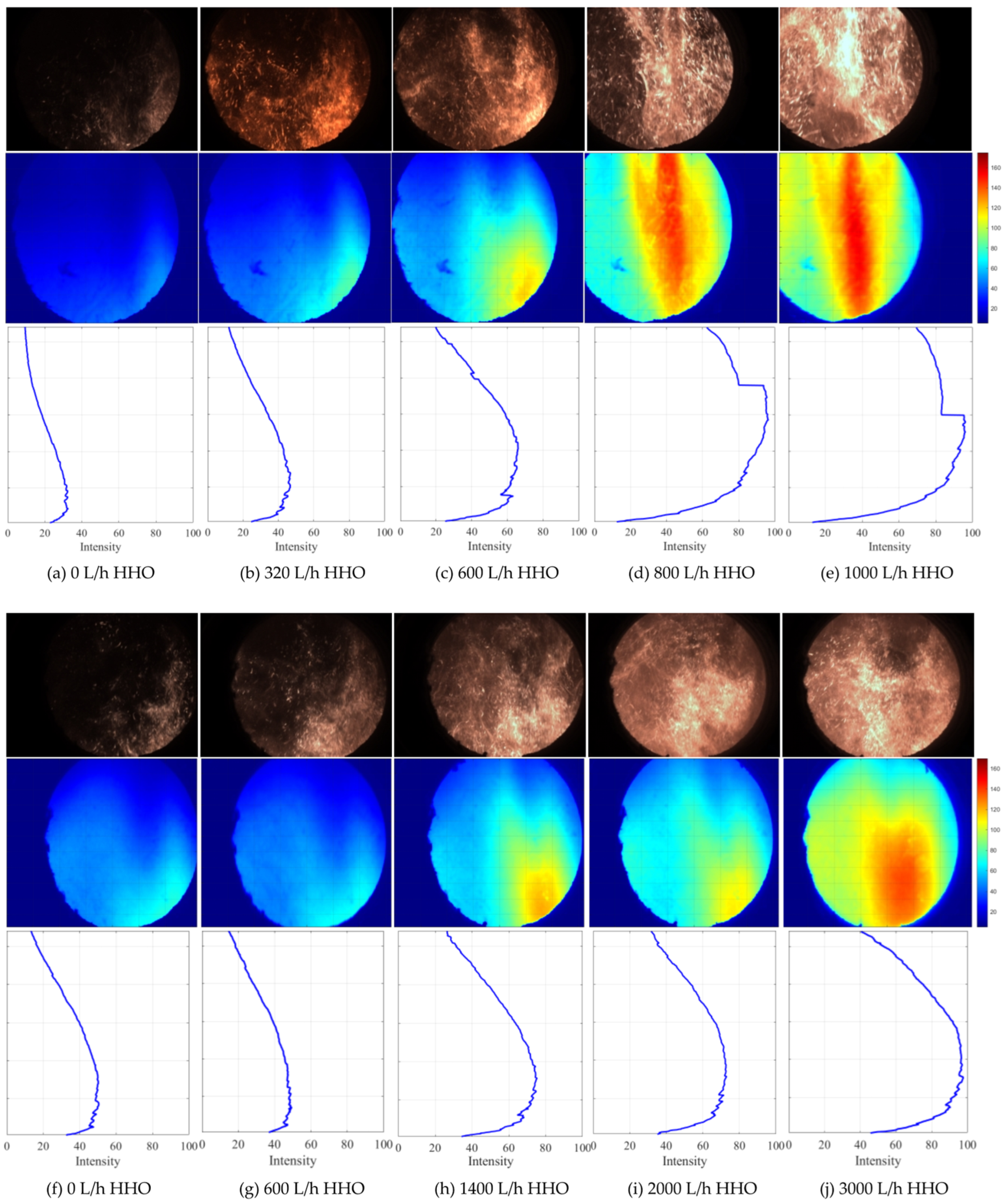
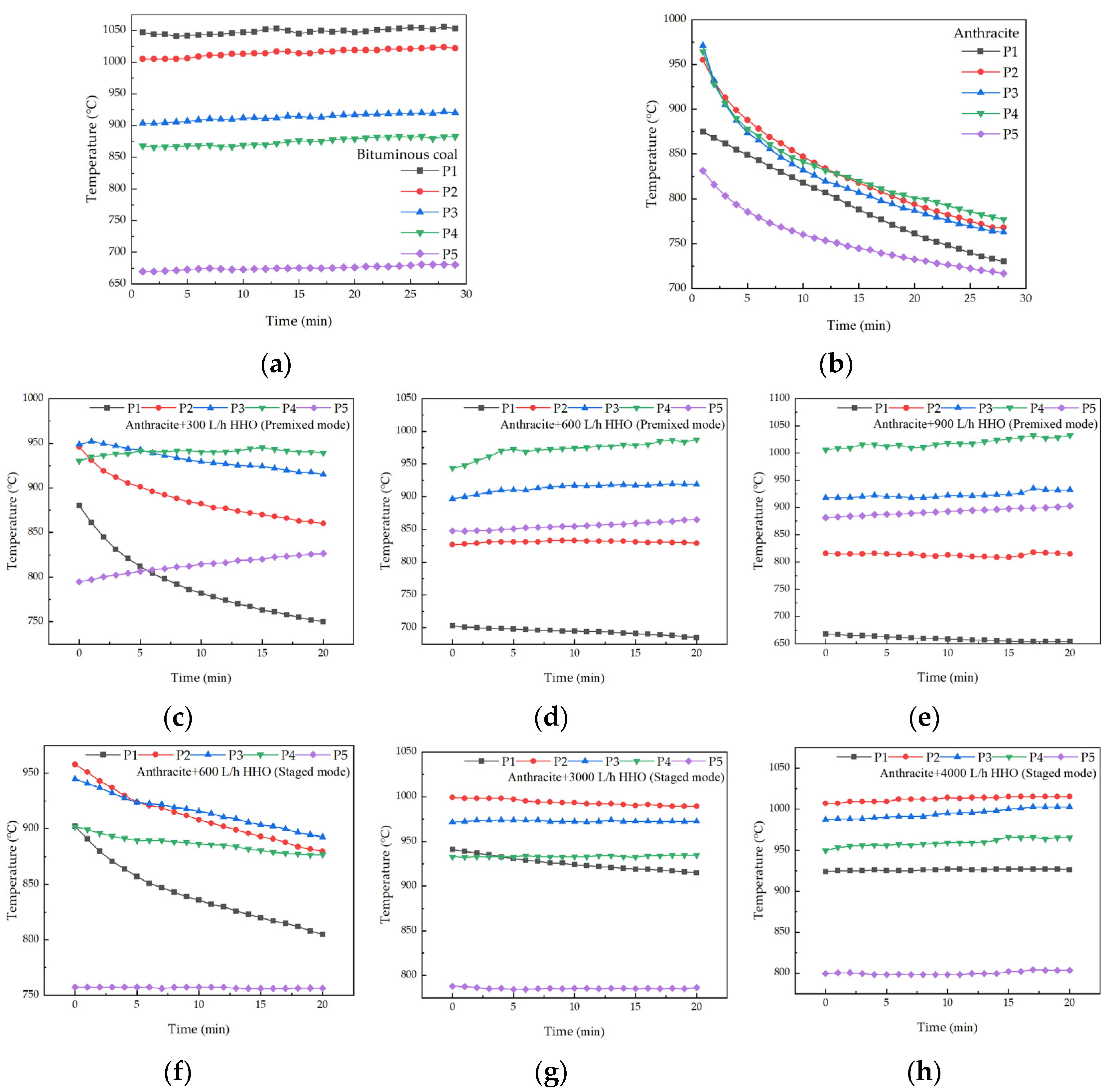
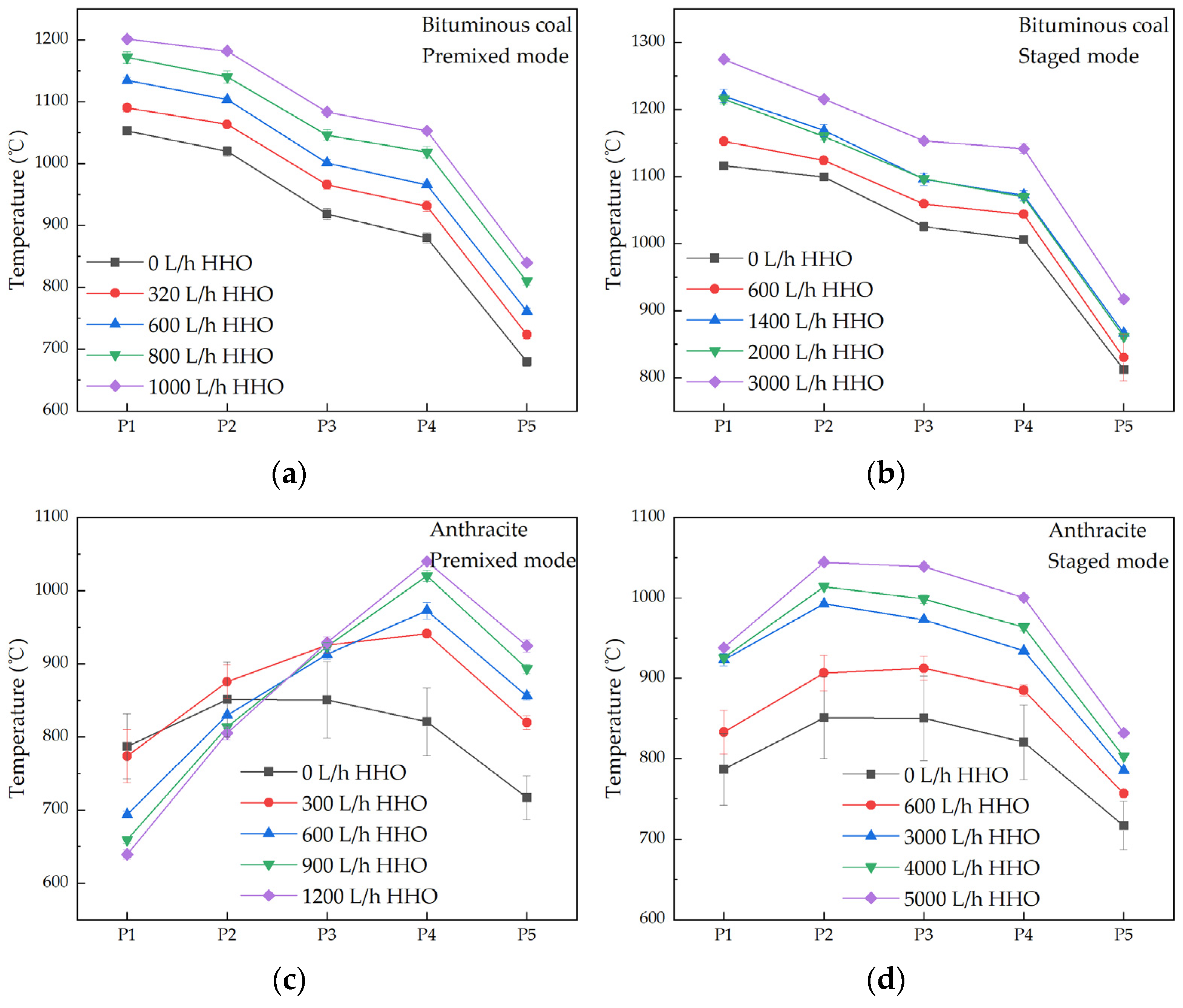
3.1. Effect of Co-Combustion on Ignition Position and Furnace Temperature
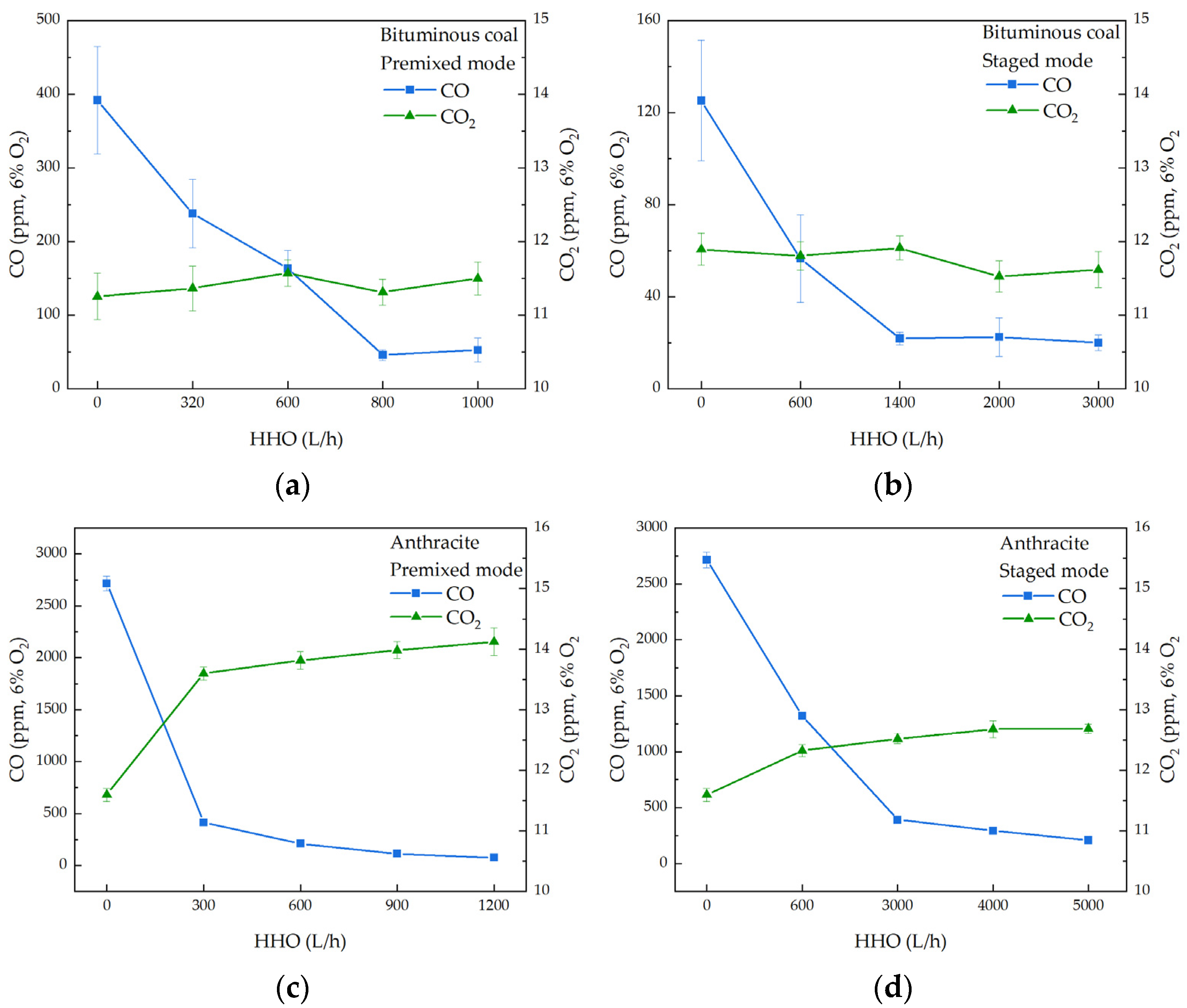
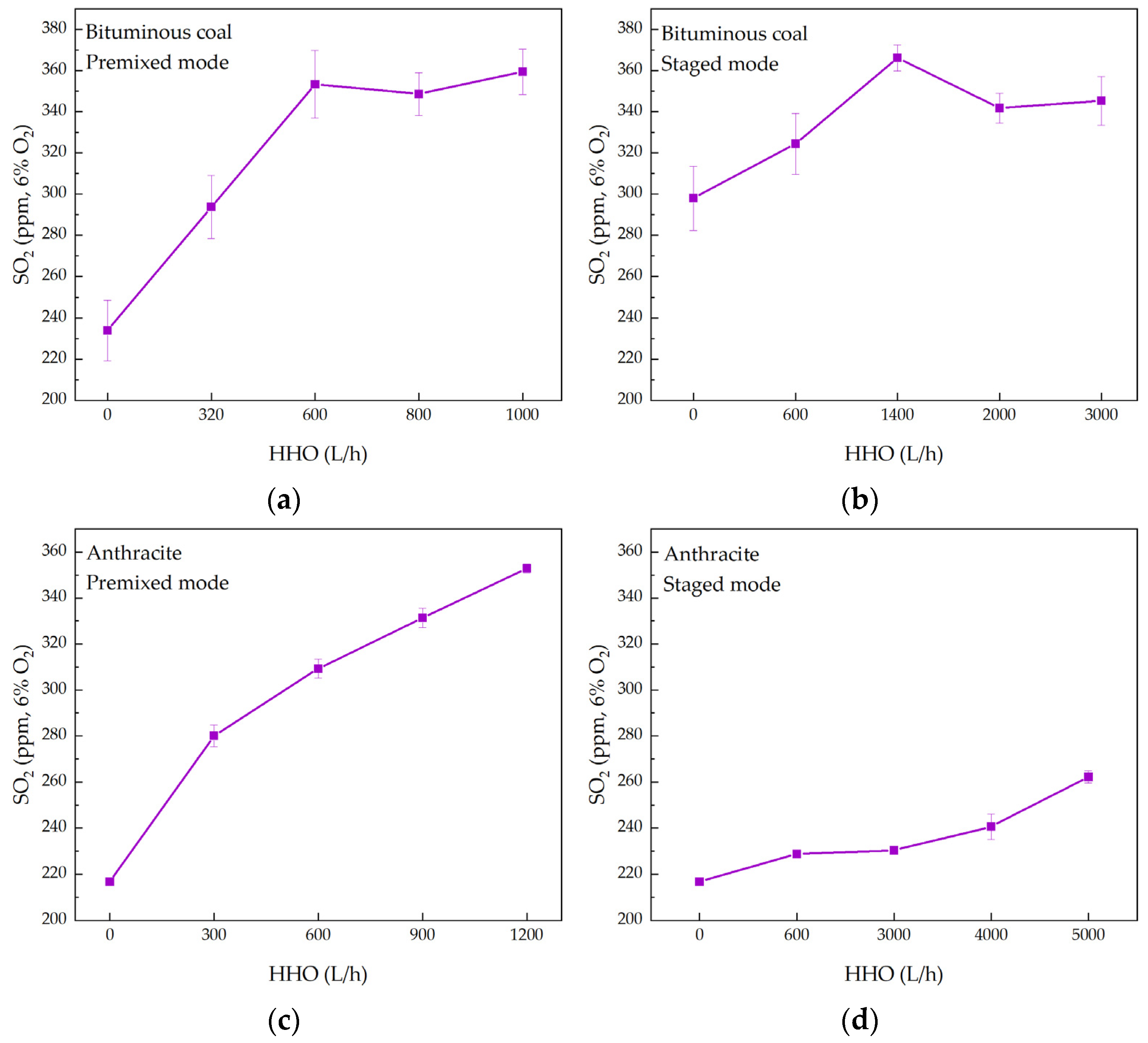
3.2. Effect of Co-Combustion on Emission Characteristics
3.2.1. CO2 and CO Emissions
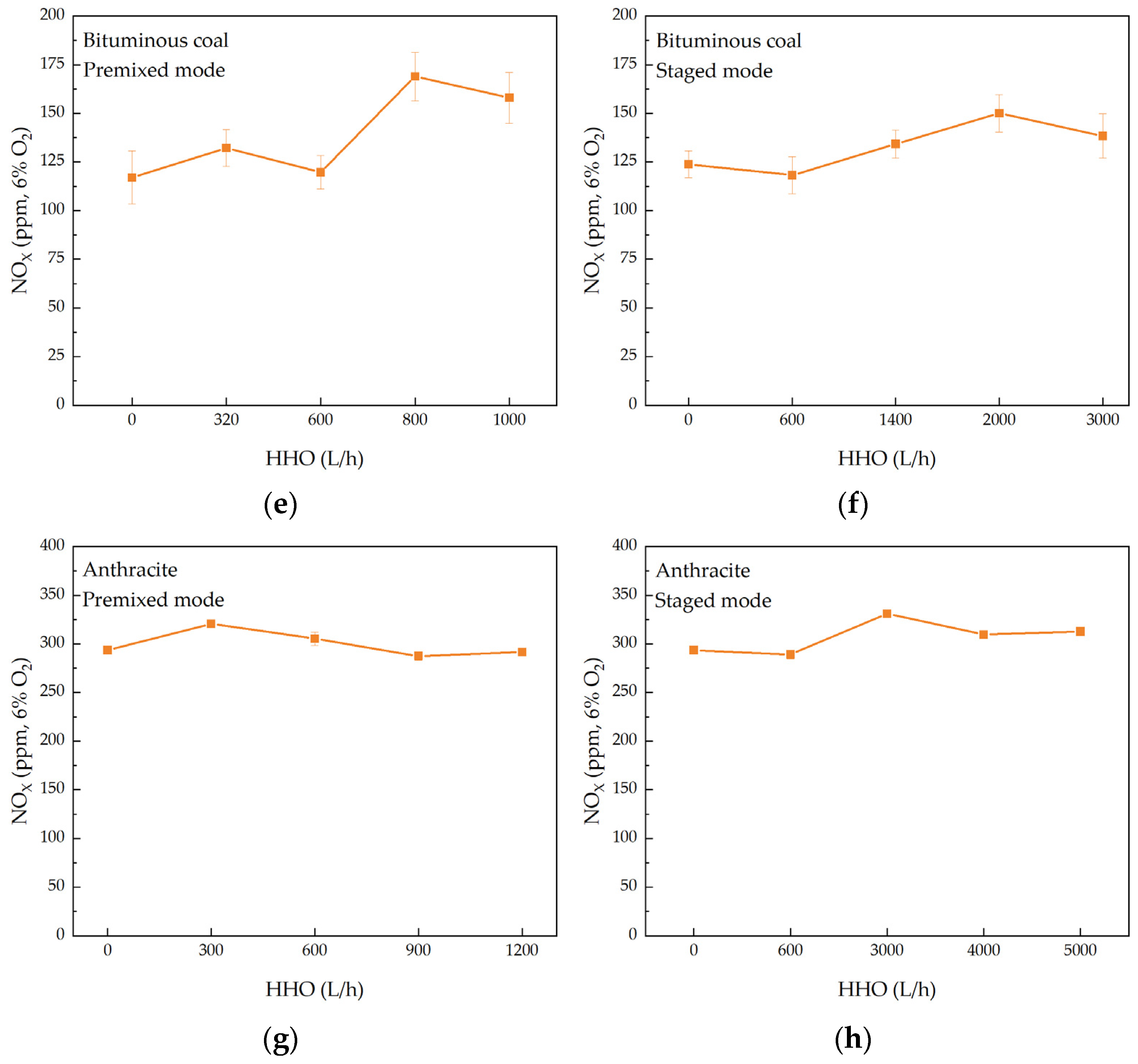
3.2.2. SO2 and NOX Emissions
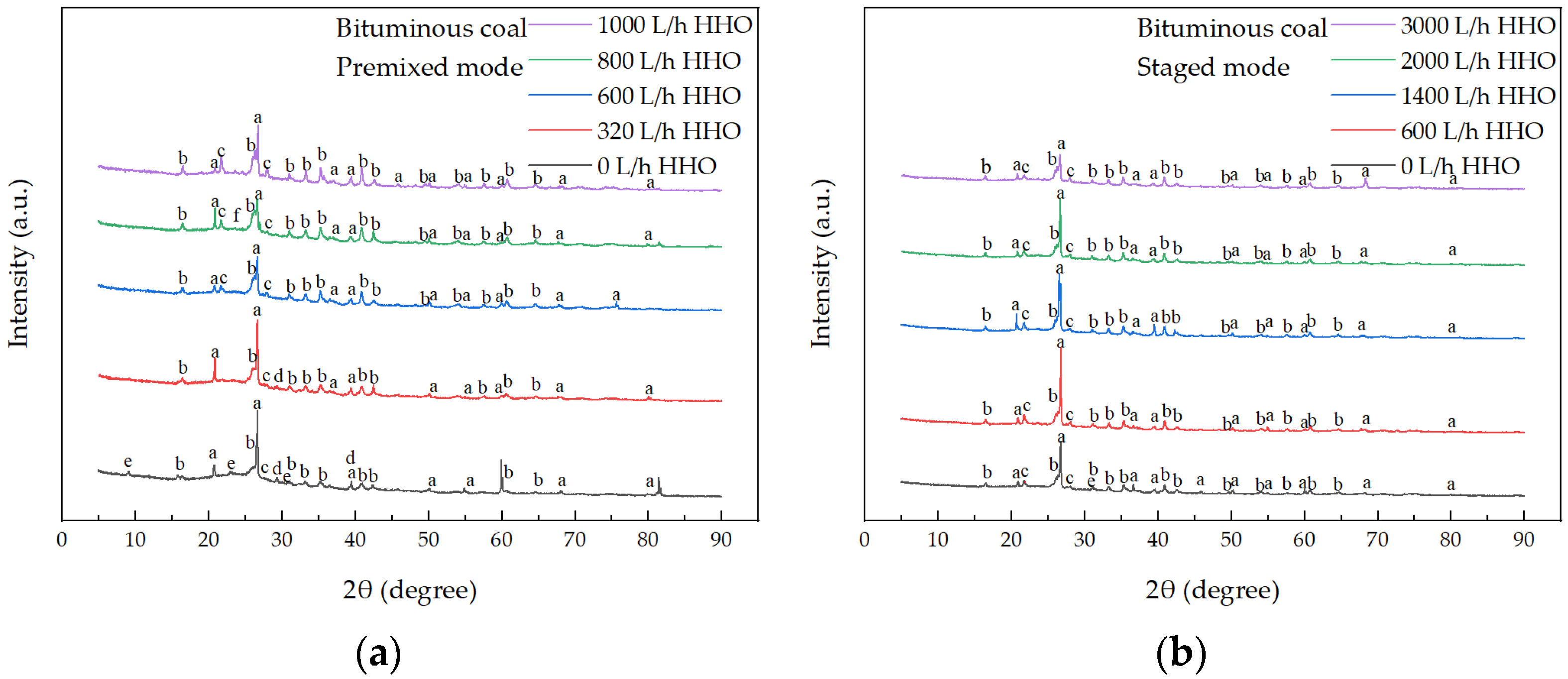
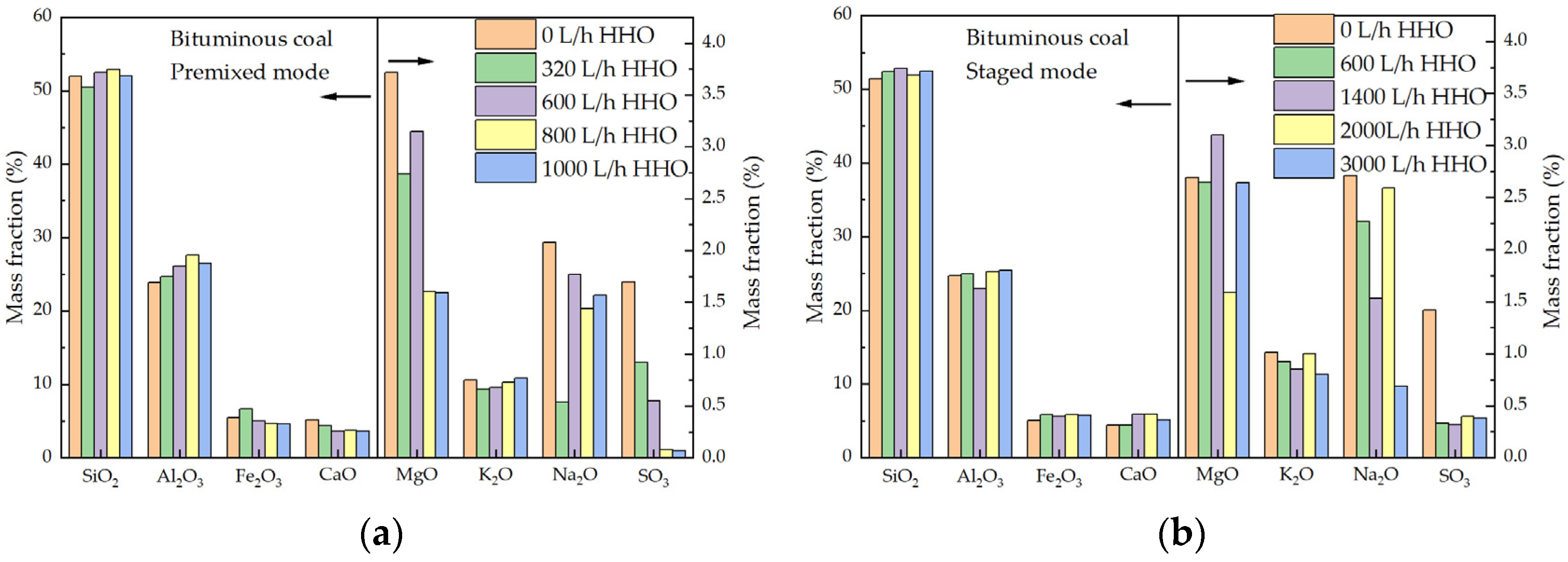
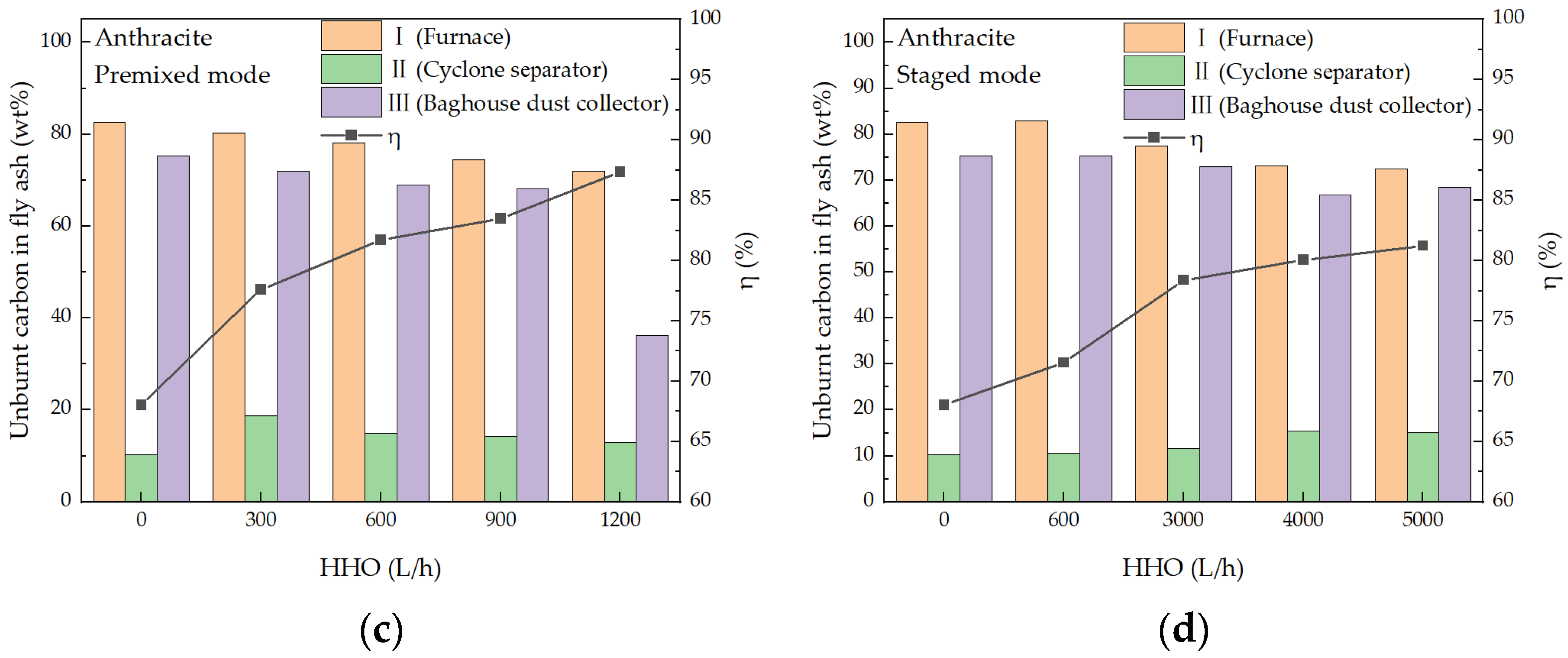
3.3. Effect of Co-Combustion on Fly Ash Characteristics in Furnace
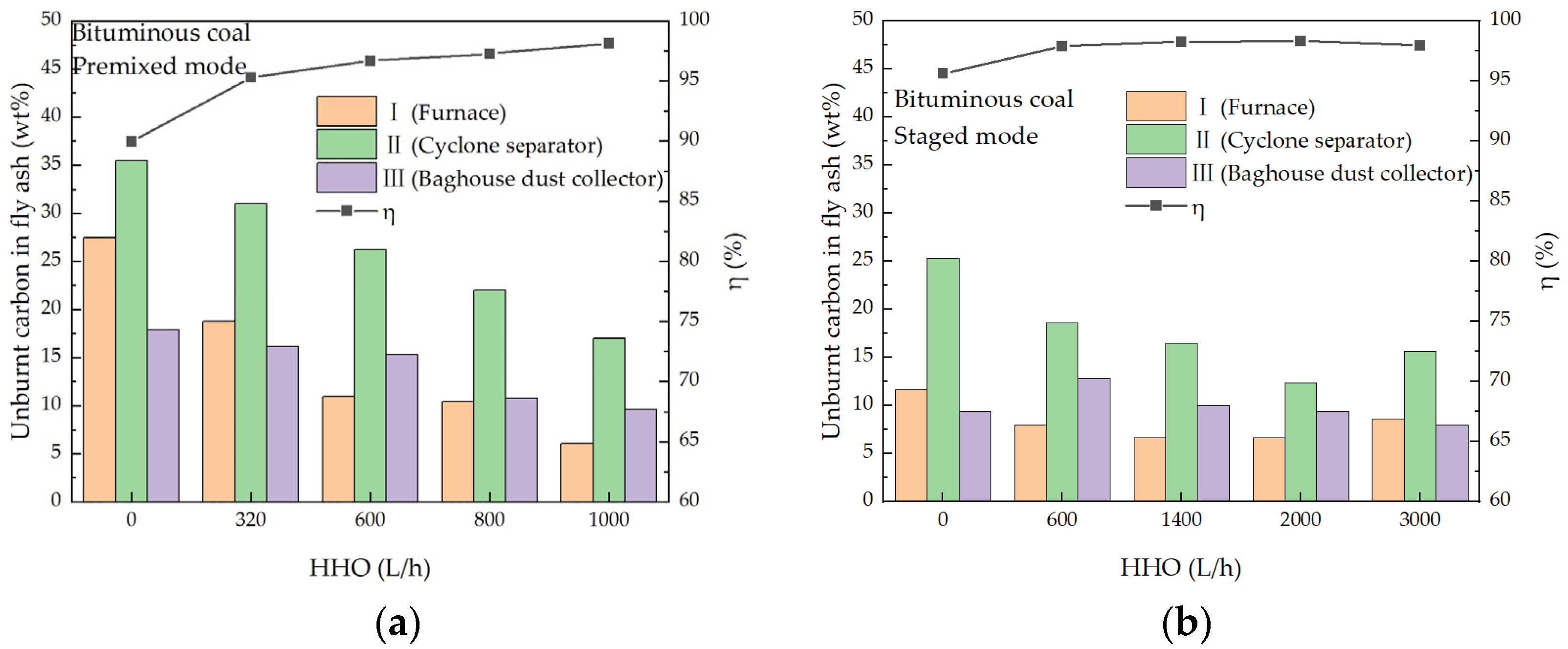
3.4. Effect of Co-Combustion on Combustion Efficiency
4. Conclusions
- HHO co-combustion improved combustion intensity and stability. The premixed mode advanced the ignition timing of bituminous coal, evidenced by an upstream shift of the flame front. For anthracite, stable combustion was achieved at HHO flow rates ≥ 600 L/h in the premixed mode, whereas the staged mode required ≥ 3000 L/h, effectively addressing the issue of unstable furnace temperatures that occurred when anthracite was burned alone.
- HHO co-combustion significantly increased the temperature in the main combustion zone. In the premixed mode, the maximum temperature rise for bituminous coal was 149 °C, while for anthracite, it reached 207 °C. In the staged mode, the maximum temperature rises for bituminous coal and anthracite were 158 °C and 191 °C, respectively. As the HHO flow rate increased, the CO emission concentrations from both bituminous coal and anthracite combustion were reduced by over 80%, indicating a substantial improvement in combustion completeness. HHO co-combustion significantly enhanced combustion efficiency: the efficiency of bituminous coal reached 98%, while that of anthracite increased by 19% in the premixed mode and 13% in the staged mode, confirming the superiority of the premixed mode in promoting the complete combustion of pulverized coal.
- HHO co-combustion promotes the release and oxidation of sulfur in coal, leading to increased SO2 emissions. The impact on NOX emissions is complex. This is primarily due to the competition between the reduction of NOX caused by HHO gas and the increased formation of NOX due to the higher combustion temperatures. Optimization is required based on specific combustion conditions.
- HHO co-combustion increases the melting point of fly ash and alters its chemical composition and micro-morphology. Compared with pure coal combustion, co-combustion with HHO gas increases the content of Al2O3 in fly ash while reducing the contents of Na2O, K2O, and MgO. These changes collectively reduce the risk of boiler slagging.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richter, M.; Oeljeklaus, G.; Görner, K. Improving the load flexibility of coal-fired power plants by the integration of a thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q. Overall review of peak shaving for coal-fired power units in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Z.; Song, J.; Fang, F.; Su, J.; et al. Industrial measurement of combustion and NOx formation characteristics on a low-grade coal-fired 600MWe FW down-fired boiler retrofitted with novel low-load stable combustion technology. Fuel 2022, 321, 123926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J. Energy consumption characteristics and energy saving potential of thermal power plants under ultra-low power load ratio conditions. Energy 2025, 330, 136946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jin, H.; Yang, Z.; Deng, S.; Wu, X.; An, J.; Sheng, R.; Ti, S. CFD modeling of flow, combustion and NOx emission in a wall-fired boiler at different low-load operating conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Zeng, L.; Li, Z. Achievement in ultra-low-load combustion stability for an anthracite- and down-fired boiler after applying novel swirl burners: From laboratory experiments to industrial applications. Energy 2020, 192, 116623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.; Moon, C.; Eom, S.; Choi, G.; Kim, D. Coal-particle size effects on NO reduction and burnout characteristics with air-staged combustion in a pulverized coal-fired furnace. Fuel 2016, 182, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Guo, X.; Hou, D.; Yao, W.; Yan, G.; Xin, Z.; Xiaoming, Z. Application of pure oxygen ignition technology in a 670 MW unit boiler firing inferior coal. Therm. Power Gener. 2013, 42, 103–106+128. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1111.TM.20131224.1700.021 (accessed on 29 December 2025).
- Ibrahimoglu, B.; Yilmazoglu, M.Z.; Cucen, A. Numerical modeling of repowering of a thermal power plant boiler using plasma combustion systems. Energy 2016, 103, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z. Influence of coal-feed rates on bituminous coal ignition in a full-scale tiny-oil ignition burner. Fuel 2010, 89, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; He, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Experimental study on co-firing characteristics of ammonia with pulverized coal in a staged combustion drop tube furnace. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Si, T.; Lv, Z.; Li, S. Comprehensive effect of the coal rank and particle size on ammonia/coal stream ignition. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2024, 40, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Experimental study on the effects of ammonia cofiring ratio and injection mode on the NOx emission characteristics of ammonia-coal cofiring. Fuel 2024, 363, 130996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Yin, Y. Study on Co-combustion Hydrogen in a 300 MW Coal-fired Boiler. Power Syst. Eng. 2016, 32, 37–38. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=Ow72tX7v2w20D5qJMxlWm2HgVU6MS8ta2TPjQQX9mNg6_Zsl36ytDS93IA6n5udM1wTPmGe1KIfFgIe8d579bbZST0imax9qsMN6PQ4ghlniGPAdCTDvzqapMDPRIvoSzf5z6FjTb8QnPNGp4xv7fZEhU86B-5WX6nG0ChVdYwNcimD3UTBmA42-iVZ5ktJ1&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 29 December 2025).
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, G.; Lin, S.; Fan, W. Experimental study on the influence of coal/hydrogen co-firing on combustion characteristics. Clean Coal Technol. 2024, 1–7. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3676.TD.20240730.0944.002 (accessed on 29 December 2025).
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, G.; Fan, W. Study on combustion technology of pulverized coal mixed with hydrogen. Ind. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 51, 104–108. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/42.1640.X.20241028.1120.016 (accessed on 29 December 2025).
- Ueki, Y.; Yoshiie, R.; Naruse, I.; Matsuzaki, S. Effect of hydrogen gas addition on combustion characteristics of pulverized coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 161, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lei, X.; Wang, C.; Jing, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, L.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H. Numerical Simulation Study of Hydrogen Blending Combustion in Swirl Pulverized Coal Burner. Energies 2024, 17, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Huang, S.; Qian, B.; Wang, K.; Gao, N.; Lin, X.; Shi, Z.; Lu, H. Numerical Simulation of Hydrogen–Coal Blending Combustion in a 660 MW Tangential Boiler. Processes 2024, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Z. Research progress of hydrogen energy and metal hydrogen storage materials. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momirlan, M.; Veziroglu, T.N. The properties of hydrogen as fuel tomorrow in sustainable energy system for a cleaner planet. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartys, V.A.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Linkov, V.; Pasupathi, S.; Davids, M.W.; Tolj, I.; Radica, G.; Denys, R.V.; Eriksen, J.; Taube, K.; et al. HYDRIDE4MOBILITY: An EU HORIZON 2020 project on hydrogen powered fuel cell utility vehicles using metal hydrides in hydrogen storage and refuelling systems. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 35896–35909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, R.M. A new gaseous and combustible form of water. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Feng, Z.; Guo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y. Catalytic Effect of Brown Gas on Low Oxygen Combustion of Pulverized Coal. J. Shenyang Inst. Eng. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 20, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Li, F.; Li, K. Numerical Simulation of Effect of Primary Air Mixed with Hydrogen and Oxygen on Furnace Temperature of Coal-fired Boiler. J. Eng. Therm. Energy Power 2023, 38, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, X.; Hou, B.; Zhou, H. Combustion stability and emission characteristics of a pulverized coal furnace operating at ultra-low loads assisted by clean gas (HHO) from water electrolysis. Fuel 2024, 370, 131811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, X.; Hou, B.; Zhou, H. Experimental study on the effects of co-firing mode and air staging on the ultra-low load combustion assisted by water electrolysis gas (HHO) in a pulverized coal furnace. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 117, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Kang, X.; Hou, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, H. Comparative experimental study on the co-firing characteristics of water electrolysis gas (HHO) and lean coal/lignite with different injection modes in a one-dimensional furnace. Fuel 2024, 378, 132968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 212-2008; Proximate Analysis of Coal. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 476-2001; Ultimate Analysis of Coal. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Wang, Z.; Costa, M.; He, Y.; Cen, K. Ignition and combustion of single pulverized biomass and coal particles in N2/O2 and CO2/O2 environments. Fuel 2021, 283, 118956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, N.A.; Gupta, M.M.; Joshi, S.S. Effect of oxy hydrogen gas addition on combustion, performance, and emissions of premixed charge compression ignition engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 227, 107098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y. Coal-nitrogen release and NOx evolution in the oxidant-staged combustion of coal. Energy 2017, 125, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigge, L.; Ströhle, J.; Epple, B. Release of sulfur and chlorine gas species during coal combustion and pyrolysis in an entrained flow reactor. Fuel 2017, 201, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, E.; Panahi, A.; Ren, X.; Levendis, Y.A. Curtailing the generation of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions by blending and oxy-combustion of coals. Fuel 2016, 181, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, K.; Ichimura, R.; Hashimoto, G.; Xia, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Fujita, O. Effect of fuel ratio of coal on the turbulent flame speed of ammonia/coal particle cloud co-combustion at atmospheric pressure. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 4131–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M. Flame Propagation Velocity for Co-combustion of Pulverized Coals and Gas Fuels. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6305–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Jia, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by H2 over Pd/TiO2 catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Lu, G.Q.; Rudolph, V. The kinetics of NO and N2O reduction over coal chars in fluidised-bed combustion. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1998, 53, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, B.; Wang, P.; Tan, H.; Sun, S. Effects of flue gases (CO/CO2/SO2/H2O/O2) on NO-Char interaction at high temperatures. Energy 2019, 174, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wei, B.; Zhang, L.; Tan, H.; Yang, T.; Mikulčić, H.; Duić, N. The ash deposition mechanism in boilers burning Zhundong coal with high contents of sodium and calcium: A study from ash evaporating to condensing. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 80, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.-Q.; Low, F.; De Girolamo, A.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L. Characteristics of Ash Deposits in a Pulverized Lignite Coal-Fired Boiler and the Mass Flow of Major Ash-Forming Inorganic Elements. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6198–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Yao, Q. Fine particulate formation and ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion of high-sodium lignite in a down-fired furnace. Fuel 2015, 143, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L.; Junker, H.; Baxter, L.L. Pilot-Scale Investigation of the Influence of Coal—Biomass Cofiring on Ash Deposition. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhiyanon, T.; Sathitruangsak, P.; Sungworagarn, S.; Pipatmanomai, S.; Tia, S. A pilot-scale investigation of ash and deposition formation during oil-palm empty-fruit-bunch (EFB) combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 96, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Pan, W. A review on release and transformation behavior of alkali metals during high-alkali coal combustion. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 70, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.-P.; Li, X.; Wei, B.; Tan, P.; Fang, Q.-Y.; Chen, G.; Xia, J. Release and transformation characteristics of Na/Ca/S compounds of Zhundong coal during combustion/CO2 gasification. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Fan, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Guo, M.; Fang, Y. The effects of Na2O/K2O flux on ash fusion characteristics for high silicon-aluminum coal in entrained-flow bed gasification. Energy 2023, 282, 128603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Baláš, M.; Lisý, M.; Lisá, H.; Milčák, P.; Elbl, P. An overview of slagging and fouling indicators and their applicability to biomass fuels. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 217, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Li, S.; Song, Q.; Yao, Q. The Electron Microscopy Study of PM1 in The Pulverized-Coal Flame. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2008, 871–875. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=Ow72tX7v2w1Gr6iTI97WlrapRZPaZobh1KJzamlcLRP4Q6EoAGMpcvNGggp_zicM-j1tTda7nqsUv3lkhCvndpCX6brrDII4Hk0a-M3V6t0iE3zUJdKl0wjs4ob1QqqvxLmDmr13l-lTLomBh2ChiqyJr0034rIKfpAoe7io5P0e0N_aGbP20A==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 29 December 2025).
- Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Tan, J.; He, Y.; Cen, K. Co-firing characteristics and fuel-N transformation of ammonia/pulverized coal binary fuel. Fuel 2023, 337, 126857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Guan, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Wollastonite addition stimulates soil organic carbon mineralization: Evidences from 12 land-use types in subtropical China. CATENA 2023, 225, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bituminous Coal | Anthracite | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Proximate analysis (wt.%, ad) | |||
| Moisture | 5.19 | 0.46 | |
| Ash | 18.64 | 12.25 | |
| Volatile | 32.3 | 6.71 | |
| Fixed carbon | 43.97 | 80.58 | |
| Ultimate analysis (wt.%, ad) | |||
| Carbon | 58.31 | 79.24 | |
| Hydrogen | 3.51 | 2.76 | |
| Nitrogen | 0.9 | 0.96 | |
| Sulfur | 0.67 | 0.71 | |
| Oxygen | 12.78 | 3.62 | |
| Heating value (kJ/kg) | Qb, ad | 23321 | 30475 |
| Ash composition (wt.%) | |||
| SiO2 | 46.10 | 46.86 | |
| Al2O3 | 27.95 | 26.24 | |
| Fe2O3 | 7.18 | 5.96 | |
| CaO | 4.57 | 5.78 | |
| MgO | 3.64 | 4.81 | |
| K2O | 0.70 | 0.71 | |
| Na2O | 6.06 | 2.12 | |
| SO3 | 2.81 | 2.75 | |
| Ignition temperature (°C) | Ti | 381.82 | 532.54 |
| Burnout temperature (°C) | Tb | 611.11 | 725.55 |
| Peak combustion temperature (°C) | Tp | 521.87 | 660.00 |
| Operation Parameters | Bituminous Coal | Anthracite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal input of coal (kW) | 37.44 | 41.10 | ||
| HHO injection mode | Premixed mode | Staged mode | Premixed mode | Staged mode |
| HHO flow (L/h) | 320/600/800/1000 | 600/1400/2000/3000 | 300/600/900/1200 | 600/3000/4000/5000 |
| Thermal input of HHO (kW) | 0.59/1.10/1.47/1.84 | 1.10/2.57/3.67/5.51 | 0.55/1.10/1.65/2.20 | 1.10/5.51/7.35/9.18 |
| Excess air ratio | 1.2 | 1.2 | ||
| Primary air (Nm3/h) | 12.84 | 13.86 | ||
| Secondary air (Nm3/h) | 16.62 | 21.58 | ||
| OFA (Nm3/h) | 10.71 | 10.28 | ||
| Total airflow (Nm3/h) | 40.18 | 45.72 | ||
| Primary air temperature (°C) | 110 | 130 | ||
| Secondary air temperature (°C) | 200 | 250 | ||
| OFA temperature (°C) | 200 | 250 | ||
| DT (°C) | ST (°C) | HT (°C) | FT (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premixed mode | ||||
| 0 L/h HHO | 1316 | 1486 | 1496 | >1500 |
| 320 L/h HHO | 1358 | 1490 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 600 L/h HHO | 1443 | >1500 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 800 L/h HHO | 1404 | >1500 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 1000 L/h HHO | 1479 | >1500 | >1500 | >1500 |
| Staged mode | ||||
| 0 L/h HHO | 1351 | 1490 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 600 L/h HHO | 1372 | 1498 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 1400 L/h HHO | 1357 | 1497 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 2000 L/h HHO | 1294 | >1500 | >1500 | >1500 |
| 3000 L/h HHO | 1300 | >1500 | >1500 | >1500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Huo, K.; Cai, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Weng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Experimental Study on the Co-Combustion Characteristics of Brown Gas (HHO) and Bituminous Coal/Anthracite with Different Injection Modes in a One-Dimensional Furnace. Reactions 2026, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions7010002
Huo K, Cai Y, He Y, Liu S, Xu C, Liu S, Weng W, Zhu Y, Wang Z. Experimental Study on the Co-Combustion Characteristics of Brown Gas (HHO) and Bituminous Coal/Anthracite with Different Injection Modes in a One-Dimensional Furnace. Reactions. 2026; 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions7010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Kaihong, Yunlong Cai, Yong He, Shiyan Liu, Chaoqun Xu, Siyu Liu, Wubin Weng, Yanqun Zhu, and Zhihua Wang. 2026. "Experimental Study on the Co-Combustion Characteristics of Brown Gas (HHO) and Bituminous Coal/Anthracite with Different Injection Modes in a One-Dimensional Furnace" Reactions 7, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions7010002
APA StyleHuo, K., Cai, Y., He, Y., Liu, S., Xu, C., Liu, S., Weng, W., Zhu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2026). Experimental Study on the Co-Combustion Characteristics of Brown Gas (HHO) and Bituminous Coal/Anthracite with Different Injection Modes in a One-Dimensional Furnace. Reactions, 7(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions7010002








