A New Pd-Based Catalytic System for the Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene to Form N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide Selectively in One Pot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
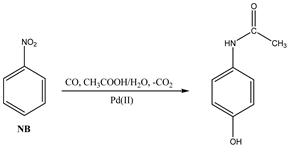
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Equipment and Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Reactions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Experiments
3.2. One-Pot Synthesis of Acetaminophen in H2O-Acetic Acid as a Solvent
3.3. Influence of Pressure and Temperature on Conversion and Selectivity
3.4. On the Reaction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellis, F. Paracetamol, a Curriculum Resource; Osborne, C., Pack, M., Eds.; RSC: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ogemdi, I.K. A Review on the Properties and Uses of Paracetamol. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. 2019, 5, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eynde, J.J.V. How Efficient Is My (Medicinal) Chemistry? Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saragiotto, B.T.; Shaheed, C.A.; Maher, C.G. Paracetamol for pain in adults. BMJ 2019, 367, l6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friderichs, E.; Christoph, T.; Buschmann, H. Analgesics and Antipyretics. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, P.N. p-acetamol from phenol via p-nitrophenol. Bull. Electrochem. 1985, 1, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, K.G.; Hilton, C.B. Process for Producing N-acyl-hydroxy Aromatic Amines. U.S. Patent 4,524,217, 18 June 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Fritch, J.R.; Fruchey, S.O.; Horlenko, T.; Aguilar, D.A.; Hilton, C.B.; Snyder, P.S.; Seeliger, W.J. Production of acetaminophen. U.S. Patent 5,155,273, 13 October 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, R.; Xu, N. Synthesis of p-aminophenol from p-nitrophenol over nano-sized nickel catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 277, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, C.V.; Vaidya, M.J.; Chaudhari, R.V. Synthesis of p-Aminophenol by Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 1999, 3, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Choi, J.; Chung, Y.; Ahn, W.; Ryoo, R.; Lim, P.K. p-Aminophenol synthesis in an organic/aqueous system using Pt supported on mesoporous carbons. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 337, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, F. Process for Synthesizing Paracetamol. CN Patent 1569819(A), 26 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki, M.; Motoyama, Y.; Higashi, K.; Yoon, S.-H.; Mochida, I.; Nagashima, H. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes with Carbon Nanofiber-Supported Platinum and Palladium Nanoparticles. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1601–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, L.; Cao, X.; Hong, H.; Lu, J.; Gu, H. Direct Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatics and One-Pot Amidation with Carboxylic Acids over Platinum Nanowires. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J. Convenient and Selective Hydrogenation of Nitro Aromatics with a Platinum Nanocatalyst under Ambient Pressure. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Berguerand, C.; Yuranov, I.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes: Boosting nanoparticle efficiency by confinement within highly porous polymeric framework. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. Peer Reviewed: Design Through the 12 Principles of Green Engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 94A–101A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.A.; Nguyen, N. Green engineering: Defining the principles”—Results from the Sandestin conference. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 4th ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 2, pp. 481–580. [Google Scholar]
- Juang, T.M.; Hwang, J.C.; Ho, H.O.; Chen, C.Y. Selectivity in the Phase Transfer Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene by Transition VIII Metals. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 1988, 35, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Williamson, T.C. (Eds.) Green Chemistry: Frontiers in Chemical Synthesis and Processes; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A. Industrial Environmental Chemistry; Sawyer, D.T., Martell,, A.E., Eds.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Busacca, C.A.; Fandrick, D.R.; Song, J.J.; Senanayake, C.H. The Growing Impact of Catalysis in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1825–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritch, J.R.; Fruchey, O.S.; Horlenko, T. Production of Acetaminophen. U.S. Patent 4,954,652, 4 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, E. Zur Kenntniss der Isonitrosoverbindungen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1886, 19, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaruma, L.G.; Heldt, W.Z. The Beckmann Rearrangement. Org. React. 1960, 11, 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Gawley, R.E. The Beckmann Reactions: Rearrangement, Elimination-Additions, Fragmentations, and Rearrangement-Cyclizations. Org. React. 1988, 35, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rode, C.V.; Vaidya, M.J.; Jaganathan, R.; Chaudhari, R.V. Hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol in a four-phase reactor: Reaction kinetics and mass transfer effects. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadgeri, J.M.; Biradar, N.S.; Patil, P.B.; Jadkar, S.T.; Garade, A.C.; Rode, C.V. Control of Competing Hydrogenation of Phenylhydroxylamine to Aniline in a Single-Step Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to p-Aminophenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, G.; Rancan, E.; Ronchin, L.; Vavasori, A. Beckmann rearrangement of acetophenone oximes to the corresponding amides organo-catalyzed by trifluoroacetic acid for sustainable NSAIDs synthesis. Appl. Cat. A Gen. 2014, 472, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.V.; Divekar, S.S.; Vaidya, M.J.; Rode, C.V. Single Step Process for the Preparation of P-aminophenol. U.S. Patent 6,028,227, 22 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, T.; Hirose, T. Gas phase synthesis of para-aminophenol from nitrobenzene on Pt/zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 276, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zhao, X. Synthesis of p-aminophenol from the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene over metal–solid acid bifunctional catalyst. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, Y.; Ni, M.; You, K.; Luo, H. Liquid Phase Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to Para-Aminophenol over Pt/ZrO2 Catalyst and SO4 2−/ZrO2–Al2O3 Solid Acid. Catal. Lett. 2010, 140, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X. Preparation of SAPO-5 and Its Catalytic Synthesis of p-Aminophenol. Chin. J. Catal. 2010, 311, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Figueras, F.; Kantam, M.L.; Ratnam, K.J.; Reddy, R.S.; Sekhar, N.S. Environmentally friendly hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol using heterogeneous catalysts. J. Catal. 2010, 275, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Synthesis of bifunctional Pt/MgAPO-5 catalysts and their catalytic performance in the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, F.; Quartarone, G.; Rancan, E.; Ronchin, L.; Tundo, P.; Vavasori, A. One-pot oximation–Beckmann rearrangement of ketones and aldehydes to amides of industrial interest: Acetanilide, caprolactam and acetaminophen. Cat. Commun. 2014, 49, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, E.; Aricò, F.; Quartarone, G.; Ronchin, L.; Tundo, P.; Vavasori, A. Self-catalyzed direct amidation of ketones: A sustainable procedure for acetaminophen synthesis. Cat. Commun. 2014, 54, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joncour, R.; Duguet, N.; Métay, E.; Ferreira, A.; Lemaire, M. Amidation of phenol derivatives: A direct synthesis of paracetamol (acetaminophen) from hydroquinone. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Purohit, V.C.; Suarez, V.; Tichkule, R.; Parmer, G.; Rinaldi, F. One-step reductive amidation of nitro arenes: Application in the synthesis of Acetaminophen™. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, P.N. Hydrogenation Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, F.D.; Liao, S.J.; Yu, D.R. Selective hydrogenation of nitrobenzene top-Aminophenol by the polymer-supported palladium-based mono- and bimetallic catalyst. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1998, 64, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; He, B.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, X.Q. MgAPO-5-supported Pt–Pb-based novel catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol. Catal. Commun. 2012, 24, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, G.; Ronchin, L.; Tosetto, A.; Vavasori, A. New insight on the mechanism of the catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to 4-aminophenol in CH3CN–H2O–CF3COOH as a reusable solvent system. Hydrogenation of nitrobenzene catalyzed by precious metals supported on carbon. Appl. Cat. A Gen. 2014, 475, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.Y.; Cui, Y.Y.; Dai, W.L. Highly Efficient Au/TiO2 Catalyst for One-pot Conversion of Nitrobenzene to p-Aminophenol in Water Media. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 32, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanielyan, S.K.; Nair, J.J.; Marin, N.; Alvez, G.; McNair, R.J.; Wang, D.; Augustine, R.L. Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to 4-Aminophenol over Supported Platinum Catalysts. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Alcobé, X.; Sort, J.; Nogués, J.; Vallés, E. Highly efficient electrochemical and chemical hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol using recyclable narrow mesoporous magnetic CoPt nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15676–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joncour, R.; Ferreira, A.; Duguet, N.; Lemaire, M. Preparation of para-Aminophenol from Nitrobenzene through Bamberger Rearrangement Using a Mixture of Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Acid Catalysts. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberger, E. Ueber das Phenylhydroxylamin. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1894, 27, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekha, V.R.; Manisha, J.V.; Chaudhari, R.V. Single Step Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to P-aminophenol. U.S. Patent 6,403,833 B1, 11 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Fonzo, N.; Quartarone, G.; Ronchin, L.; Tortato, C.; Vavasori, A. Kinetics and mechanistic study of the Bamberger rearrangement of N-phenylhydroxylamine to 4-aminophenol in acetonitrile-trifluoroacetic acid: A substrate acid complex as para selectivity driver. App. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 516, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olariu, T.; Suta, L.M.; Popoiu, C.; Ledeti, I.V.; Simu, G.M.; Balint, G.S. Fulias, Alternative Synthesis of Paracetamol and Aspirin Under Non-conventional Conditions. Rev. Chim. 2014, 65, 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Mane, S.N.; Gadalkar, S.M.; Rathod, V.K. Intensification of paracetamol (acetaminophen) synthesis from hydroquinone using ultrasound. Ultrasonics–Sonochemistry 2018, 49, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kawashima, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Imai, N. Synthesis of Acetaminophen Analogues Containing α-Amino Acids and Fatty Acids for Inhibiting Hepatotoxicity. Synthesis 2019, 51, 3683–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammin, M.; Iqbal, M.S. Solvent Free Synthesis of Acetaminophen. U.S. Patent 9,006,488 B1, 14 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Corma, A.; Concepción, P.; Serna, P. A Different Reaction Pathway for the Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds on Gold Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7266–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tan, C.; Xie, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y. One step synthesis of azo compounds from nitroaromatics and anilines. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3805–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehman, P.; Dol, G.C.; Moorman, E.R.; Kamer, P.C.J.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; Fraanje, J.; Goubitz, K. Ligand Effects in the Palladium-Catalyzed Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene. Organometallics 1994, 13, 4856–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehman, P.; Kaasjager, V.E.; de Lange, W.G.J.; Hartl, F.; Kamer, P.C.J.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; Fraanje, J.; Goubitz, K. Subtle Balance between Various Phenanthroline Ligands and Anions in the Palladium-Catalyzed Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene. Organometallics 1995, 14, 3751–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzacchini, E.; Lucini, R.; Meinardi, S.; Orlandi, M.; Rindone, B. Effect of a proximal substituent on the triruthenium dodecacarbonyl-catalyzed reductive carbonylation of nitroarenes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1996, 110, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macho, V.; Kralik, M.; Halmo, F. New catalytic system of N,N′-diphenylurea synthesis from nitrobenzene, carbon monoxide and water or aniline. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1996, 109, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehman, P.; Borst, L.; Kamer, P.C.J.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Influence of an aromatic carboxylic acid as cocatalyst in the palladium-catalysed reductive carbonylation of aromatic nitro compounds. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1996, 112, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehman, P.; Kamer, P.C.J.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Reductive carbonylation of aromatic dinitro compounds with a palladium(phenanthroline)2(triflate)2 catalyst and an aromatic carboxylic acid as cocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 1996, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, Y.; Lu, S. Selenium-catalyzed reductive carbonylation of nitrobenzene with amines as coreagents to give unsymmetric phenylureas. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4845–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaini, F.; Ghitti, A.; Cenini, S. Mechanistic Study of the Ru3(CO)12/Tetraalkylammonium Chloride Catalyzed Carbonylation Reactions of Nitroarenes to Carbamates and Ureas: A Completely Revised Picture. Organometallics 1999, 18, 4925–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaini, F.; Cenini, S. Mechanistic study of the Ru3(CO)12/chloride catalyzed carbonylation reactions of nitroarenes to carbamates and ureas; the role of the alkylammonium cation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 161, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G.; Chen, J.Z.; Lu, S.W. Selenium-catalyzed carbonylation of substituted nitrobenzenes with aminomethylpyrimidines as co-reagents to synthesize N-phenyl-N′-methylpyrimidylurea derivatives. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 202, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaini, F.; Gasperini, M.; Cenini, S.; Arnera, L.; Caselli, A.; Macchi, P.; Casati, N. Mechanistic Study of the Palladium–Phenanthroline Catalyzed Carbonylation of Nitroarenes and Amines: Palladium–Carbonyl Intermediates and Bifunctional Effects. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 8064–8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooibroek, T.J.; Schoon, L.; Bouwman, E.; Drent, E. Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene in Methanol with Palladium Bidentate Phosphane Complexes: An Unexpectedly Complex Network of Catalytic Reactions, Centred around a Pd–imido Intermediate. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 13318–13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Ronchin, L. Phosgene-free synthesis of 1,3-diphenylurea via catalyzed reductive carbonylation of nitrobenzene. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Capponi, M.; Ronchin, L. One-pot synthesis of paracetamol via the catalytic reductive carbonylation of nitrobenzene in acetic acid-water as a solvent. Chem. Listy 2012, 106, 1191. [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; Kamer, P.C.J.; Reek, J.N.H. The bite angle makes the catalyst. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, J.C.; McClelland, R.A. Halide ion trapping of nitrenium ions formed in the Bamberger rearrangement of N-arylhydroxylamines. Lifetime of the parent phenylnitrenium ion in water. Can. J. Chem. 1996, 74, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, H.E.; Hughes, E.D.; Ingold, C.K. A New View of the Arylhydroxylamine Rearrangement. Ingold Nat. 1951, 168, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, T.; Tokuda, Y.; Sakai, T.; Shinkai, S.; Manabe, O. Kinetics and mechanisms of the Bamberger rearrangement. Part 3. Rearrangement of phenylhydroxylamines to p-aminophenols in aqueous sulphuric acid solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1981, 2, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, T.; Hamamoto, K.; Seiji, Y.; Shinkai, S.; Manabe, O. Kinetics and mechanisms of the Bamberger rearrangement. Part 4. Rearrangement of sterically hindered phenylhydroxylamines to 4-aminophenols in aqueous sulphuric acid solution. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1981, 2, 1596–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnstam, G.; Petch, W.A.; Williams, D.L.H. Kinetic substituent and isotope effects in the acid-catalysed rearrangement of N-phenylhydroxylamines. Are nitrenium lons involved? J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1984, 2, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavasori, A.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Cavinato, G.; Toniolo, L. Influence of the operating conditions on the catalytic activity of [PdCl2(dapp)] in the CO–ethene copolymerization in the H2O–CH3COOH as a solvent (dapp = 1,3-bis(di(2-methoxyphenyl)phosphino)propane). J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 332, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zudin, V.N.; Ill’inich, G.N.; Likholobov, V.A.; Yermakow, Y.I. New catalyst for the synthesis of dialkyl ketones from olefins, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zudin, V.N.; Chinakov, V.D.; Nekipelov, V.M.; Rogov, V.A.; Likholobov, V.A.; Yermakow, Y.I. Determination of key intermediates for homogeneous water-gas shift reaction and hydrocarbonylation of ethylene to diethyl ketone catalyzed by the Pd(OAc)2-PPh3-CF3COOH/H2O system. J. Mol. Catal. 1989, 52, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
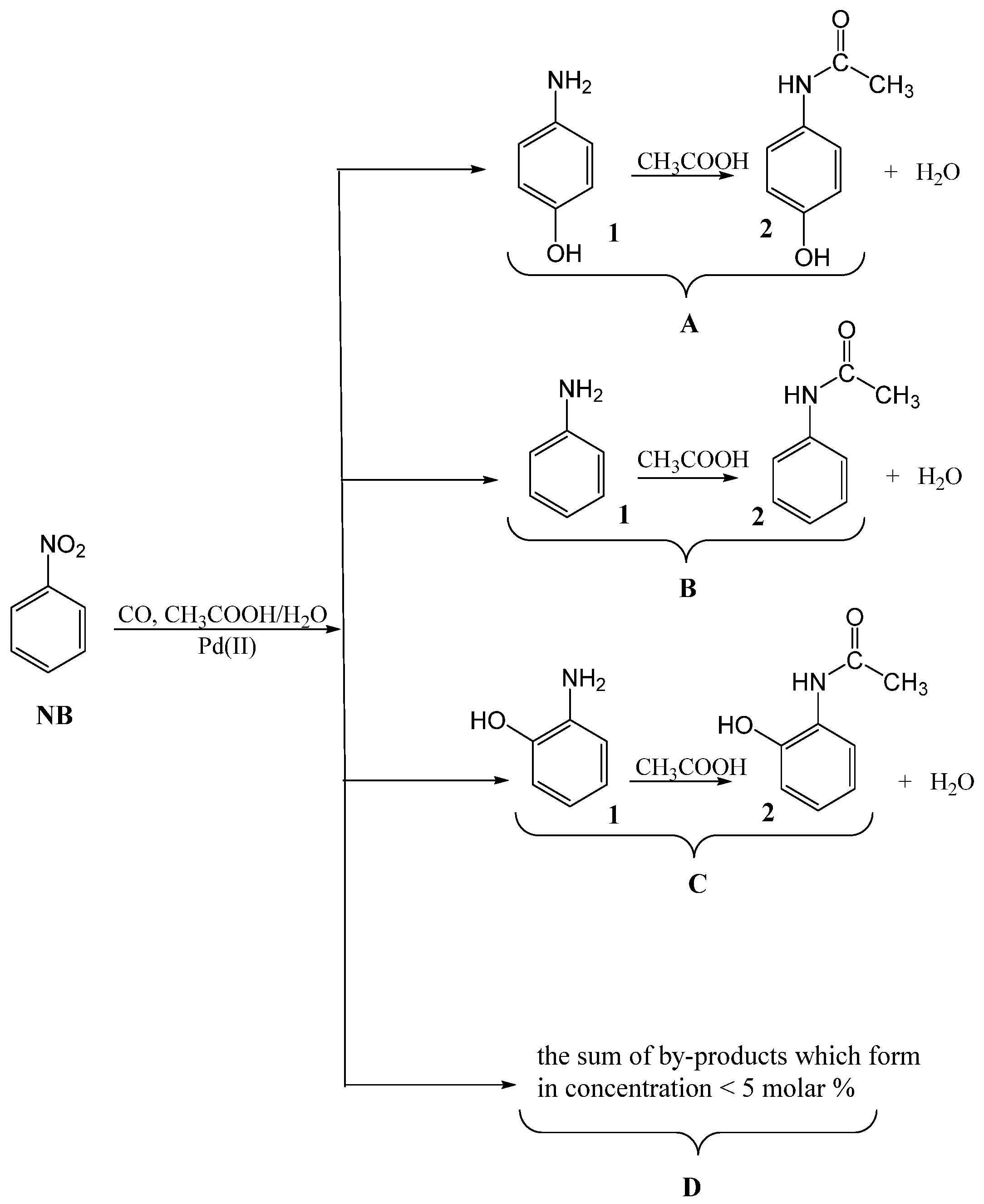

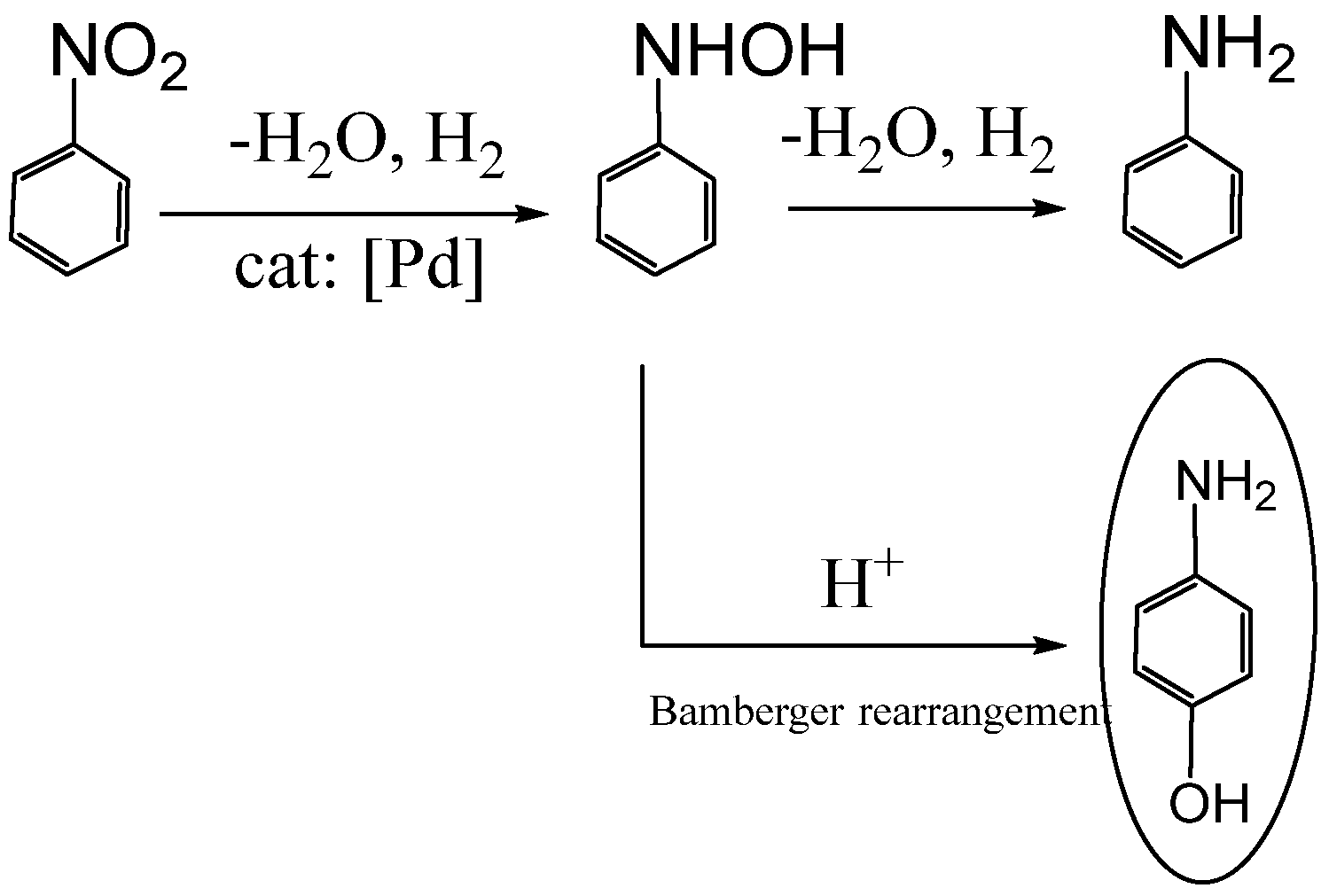
| Entry | Catalyst | Conversion | TON | Selectivity (mol %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n° | mol * % | mol */mol Pd | 4-Aminophenol | Acetaminophen | Aniline | Acetanilide | Other | |
| 1 | [PdCl2(dppe)] | 4 | 78 | 15 | 6 | 40 | 30 | 9 |
| 2 | [PdCl2(dppp)] | 22 | 432 | 15 | 7 | 36 | 30 | 12 |
| 3 | [PdCl2(dppb)] | 60 | 1178 | 19 | 8 | 33 | 25 | 15 |
| 4 | [PdCl2(dppf)] | 55 | 1080 | 16 | 7 | 32 | 28 | 17 |
| 5 | [PdCl2(Xantphos)] | 14 | 276 | 15 | 7 | 38 | 25 | 15 |
| 6 | [Pd(AcO)2(dppe)] | 2 | 39 | 13 | 5 | 43 | 30 | 9 |
| 7 | [Pd(AcO)2(dppp)] | 20 | 393 | 14 | 6 | 38 | 30 | 12 |
| 8 | [Pd(AcO)2(dppb)] | 58 | 1139 | 15 | 6 | 39 | 25 | 15 |
| 9 | [Pd(AcO)2(dppf)] | 57 | 1119 | 14 | 5 | 36 | 28 | 17 |
| 10 | [Pd(AcO)2(Xantphos)] | 15 | 296 | 14 | 6 | 40 | 27 | 13 |
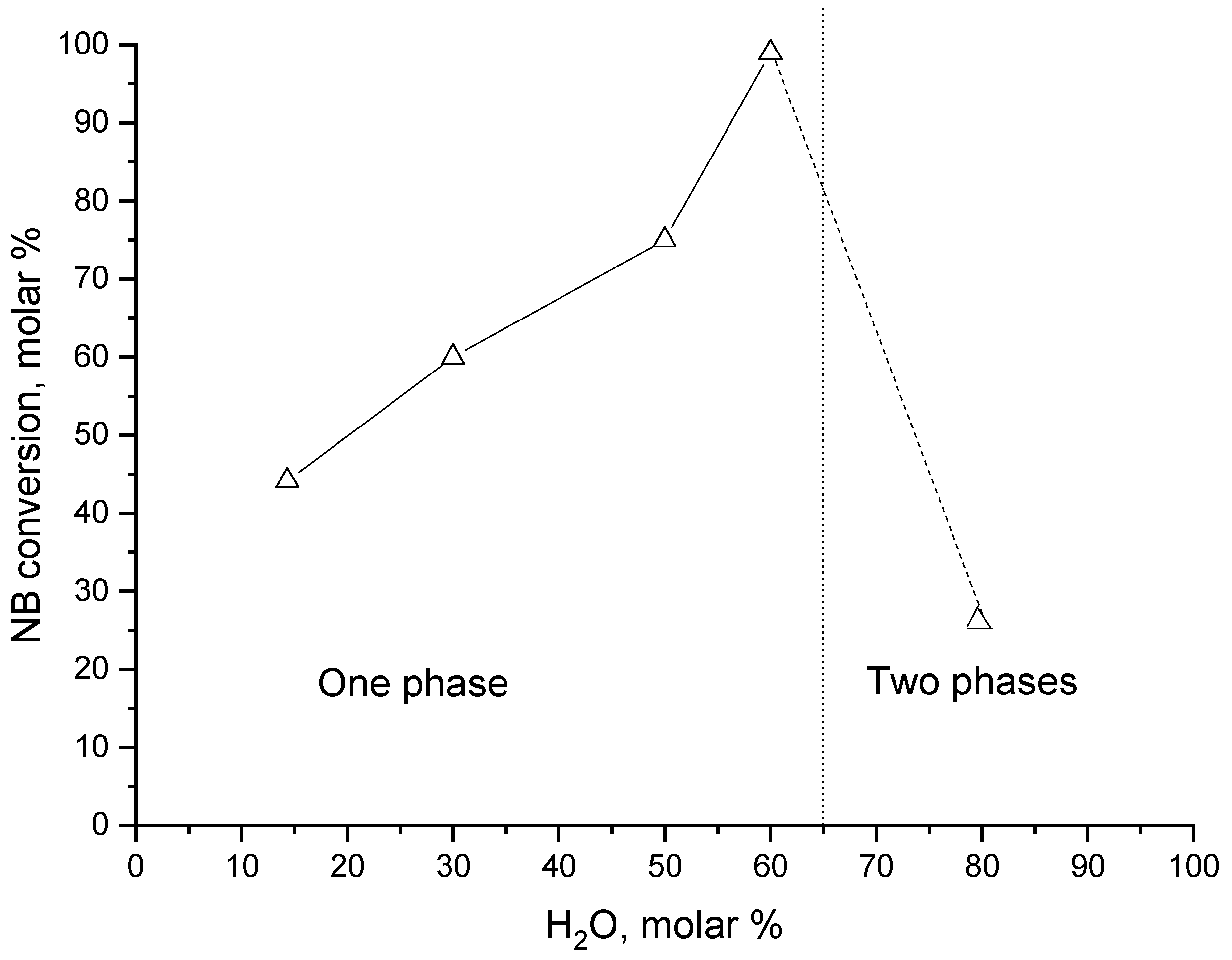
| Entry | H2O (AcOH) mol % | NB Conversion mol % | TON mol/mol | Selectivity (mol %) A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 (93) | 39 | 765 | 8 | 92 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 2 | 14 (86) | 44 | 863 | 18 | 80 | 2 | n.d. |
| 3 | 30 (70) | 60 | 1177 | 27 | 58 | 12 | 3 |
| 4 | 50 (50) | 75 | 1472 | 34 | 42 | 12 | 12 |
| 5 | 60 (40) | 99 | 1942 | 40 | 30 | 18 | 12 |
| Entry | H2O (AcOH) | Sel. to A * | Composition of A (mol %) | Sel. to B * (mol %) | Composition of B (mol %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n° | mol % | mol % | 4-Aminophenol | Acetaminophen | Aniline | Acetaniline | |
| 1 | 7 (93) | 8 | 99 | 1 | 92 | 82 | 18 |
| 2 | 14 (86) | 18 | 70 | 30 | 80 | 57 | 43 |
| 3 | 30 (70) | 27 | 60 | 40 | 58 | 47 | 53 |
| 4 | 50 (50) | 34 | 42 | 58 | 42 | 33 | 67 |
| 5 | 60 (40) | 40 | 28 | 72 | 30 | 9 | 91 |
| P | NB Conversion | Selectivity (mol %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | mol % | A | B | C | D |
| 2.5 | 53 | 65 | 20 | 7 | 8 |
| 4.0 | 75 | 64 | 25 | 6 | 5 |
| 5.0 | 99 | 65 | 19 | 11 | 5 |
| 6.0 | 100 | 67 | 20 | 11 | 2 |
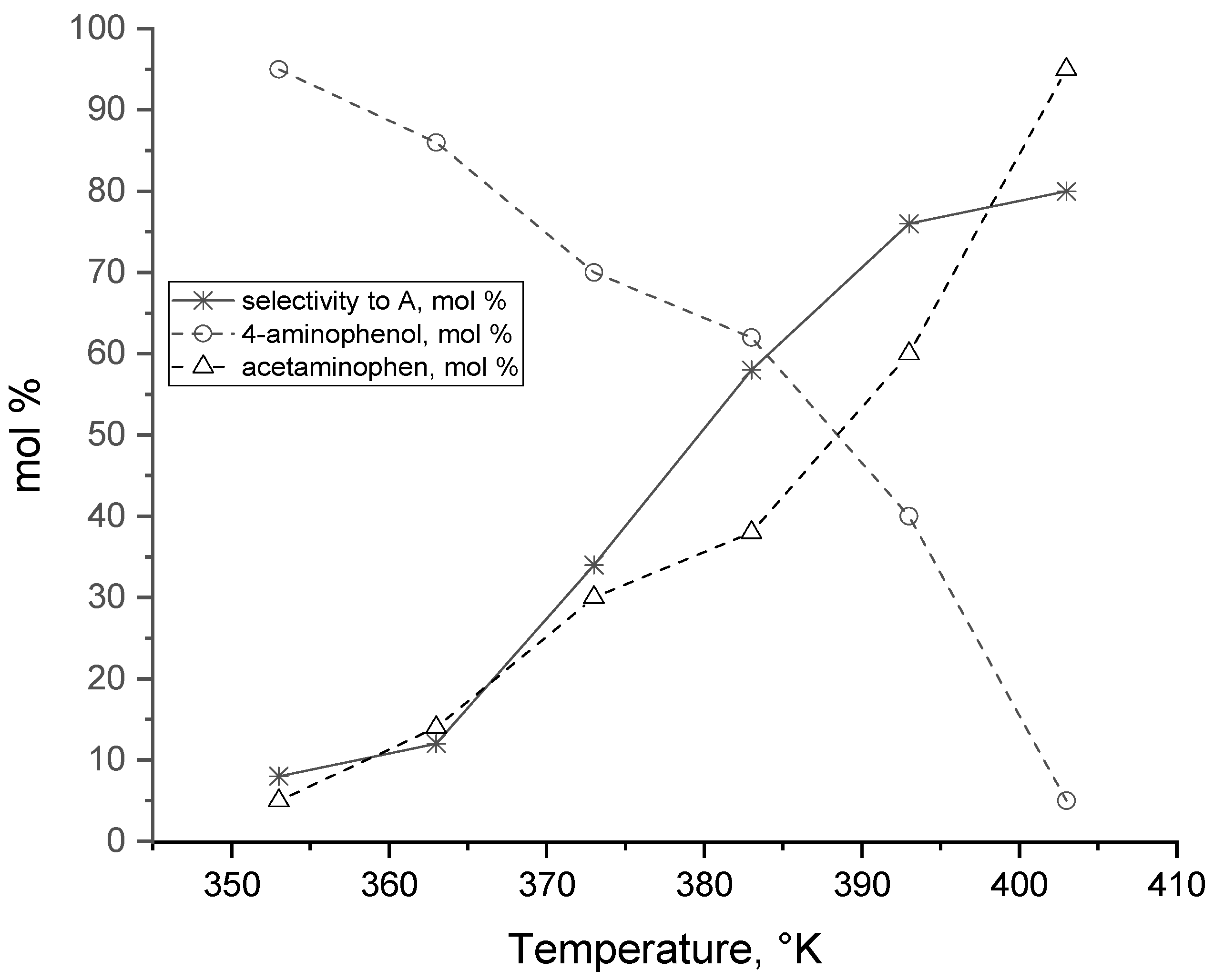
| T | NB Conversion | Selectivity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
K | mol % | A (mol %) | B (mol %) | C (mol %) | D (mol %) |
| 333 | 18 | 17 | 64 | 7 | 12 |
| 343 | 24 | 19 | 60 | 9 | 12 |
| 373 | 75 | 34 | 45 | 10 | 11 |
| 393 | 99 | 65 | 19 | 11 | 5 |
| 403 | 100 | 85 | 8 | 5 | 2 |
| 413 | 90 | 81 | 7 | 10 | 2 |
| 433 | 70 | 80 | 7 | 11 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vavasori, A.; Capponi, M.; Ronchin, L. A New Pd-Based Catalytic System for the Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene to Form N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide Selectively in One Pot. Reactions 2023, 4, 725-736. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040042
Vavasori A, Capponi M, Ronchin L. A New Pd-Based Catalytic System for the Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene to Form N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide Selectively in One Pot. Reactions. 2023; 4(4):725-736. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleVavasori, Andrea, Marco Capponi, and Lucio Ronchin. 2023. "A New Pd-Based Catalytic System for the Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene to Form N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide Selectively in One Pot" Reactions 4, no. 4: 725-736. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040042
APA StyleVavasori, A., Capponi, M., & Ronchin, L. (2023). A New Pd-Based Catalytic System for the Reductive Carbonylation of Nitrobenzene to Form N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide Selectively in One Pot. Reactions, 4(4), 725-736. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4040042







