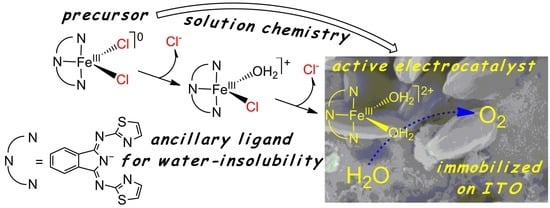
An Iron(III) Complex with Pincer Ligand—Catalytic Water Oxidation through Controllable Ligand Exchange
Abstract
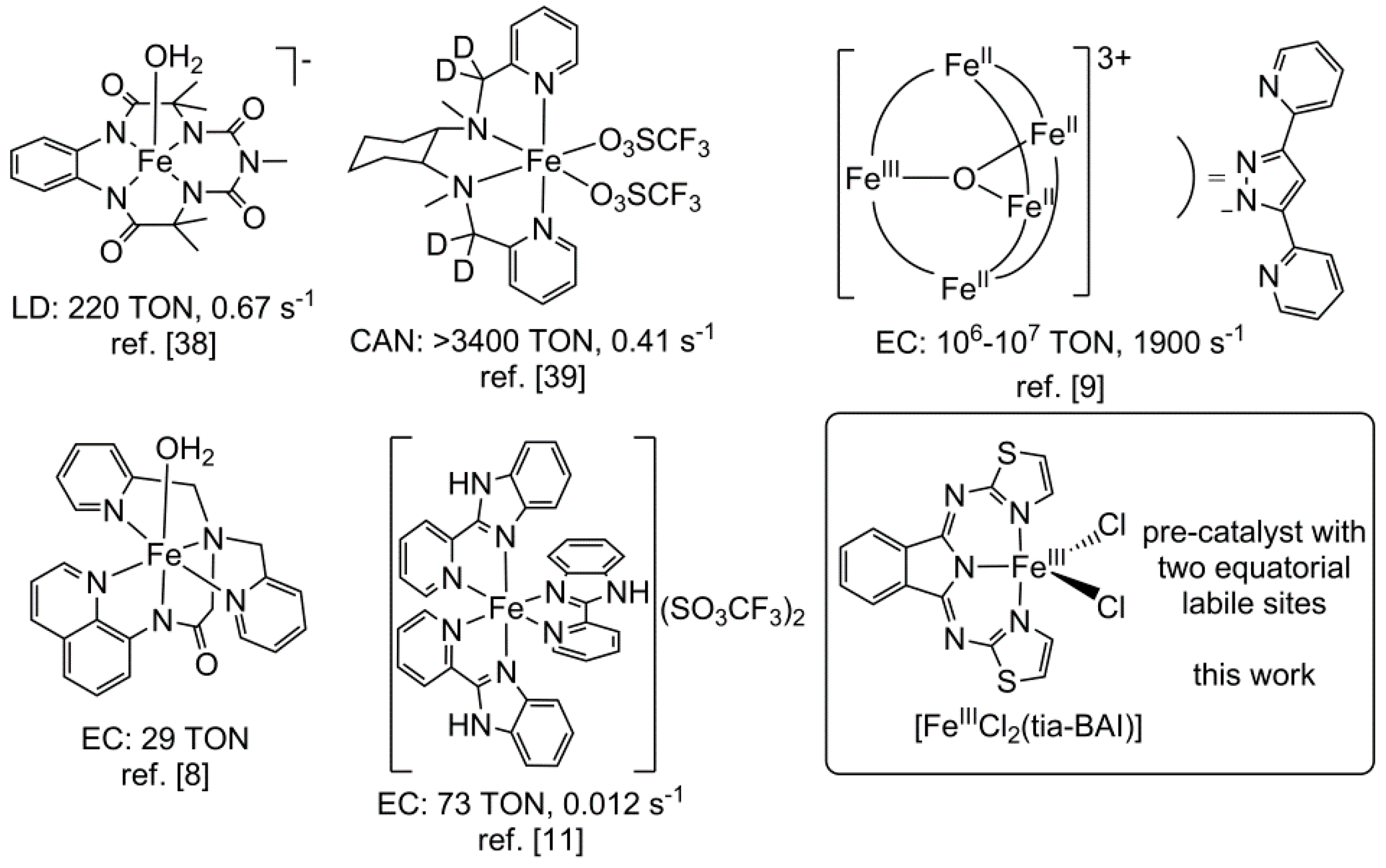
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Physical Characterization
2.2.1. Electrochemistry in Homogeneous Solution
2.2.2. Deposition of the Complexes on Semiconductor (ITO)
2.2.3. Electrochemistry with Drop-Casted Samples
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.2.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.2.6. UV-Visible Spectrophotometry
3. Results and Discussion
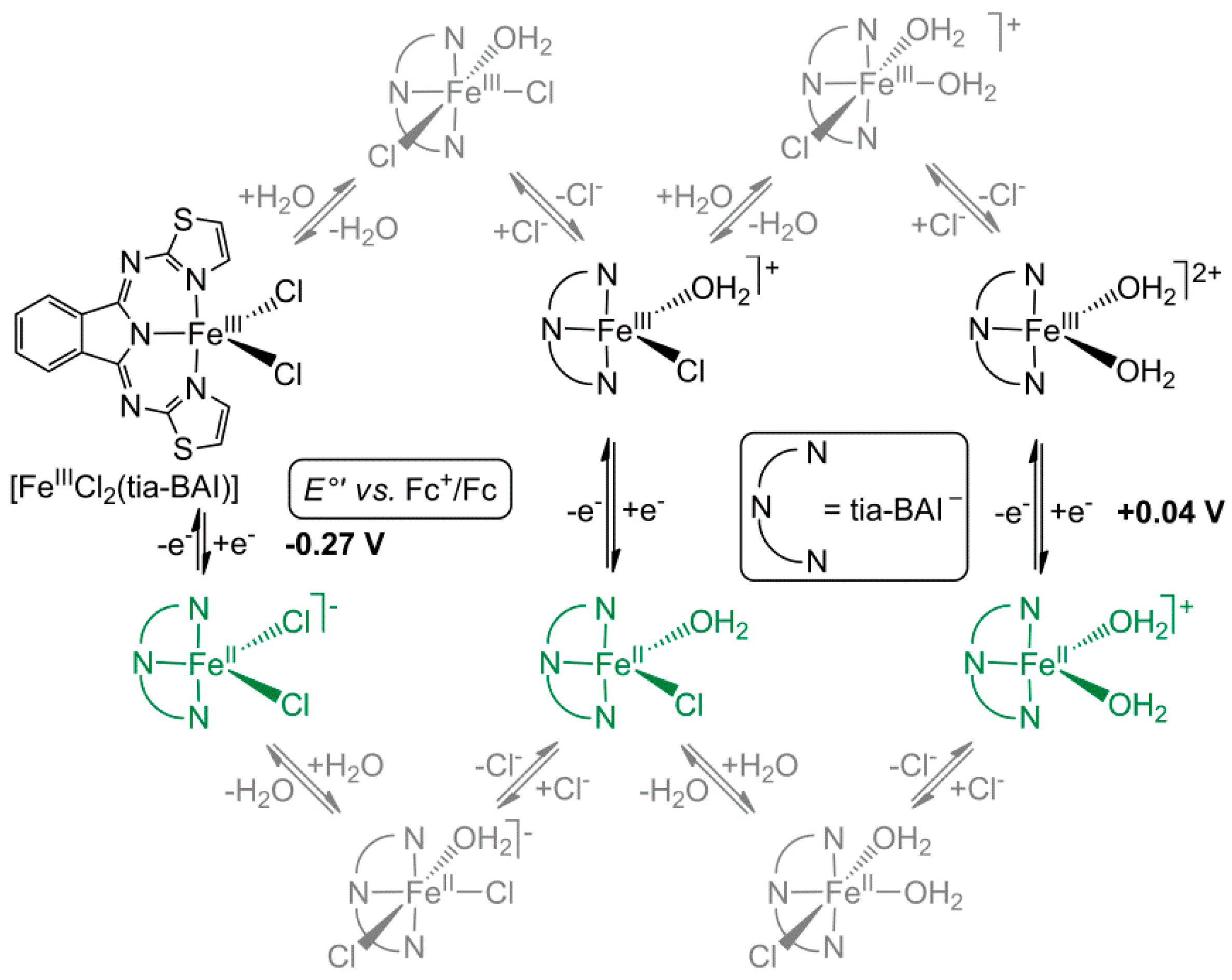
3.1. Structural Properties of [FeIIICl2(tia-BAI)] and Its Behavior in Acetone
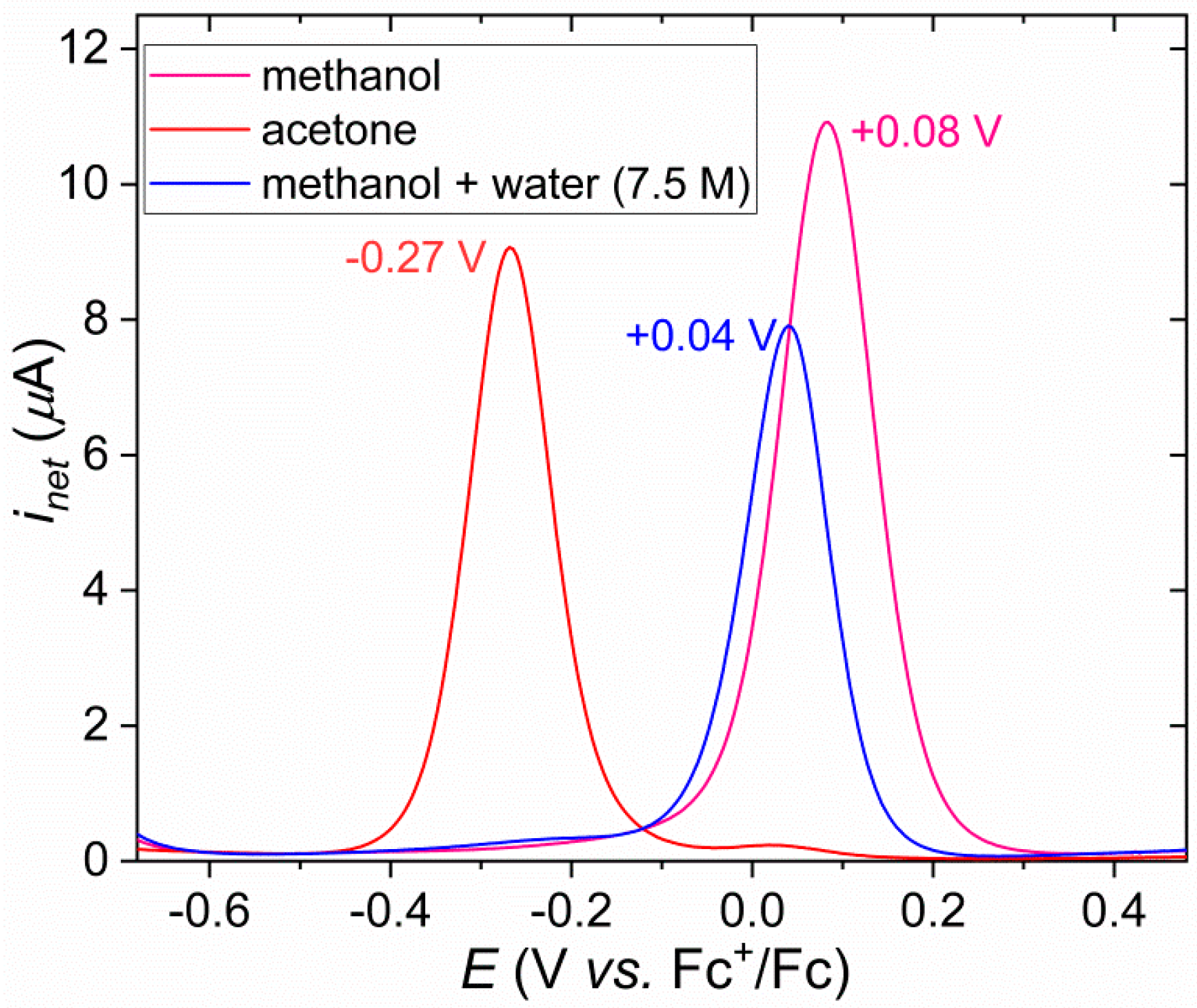
3.2. Addition of Water to the Solution of [FeIIICl2(tia-BAI)] in Acetone
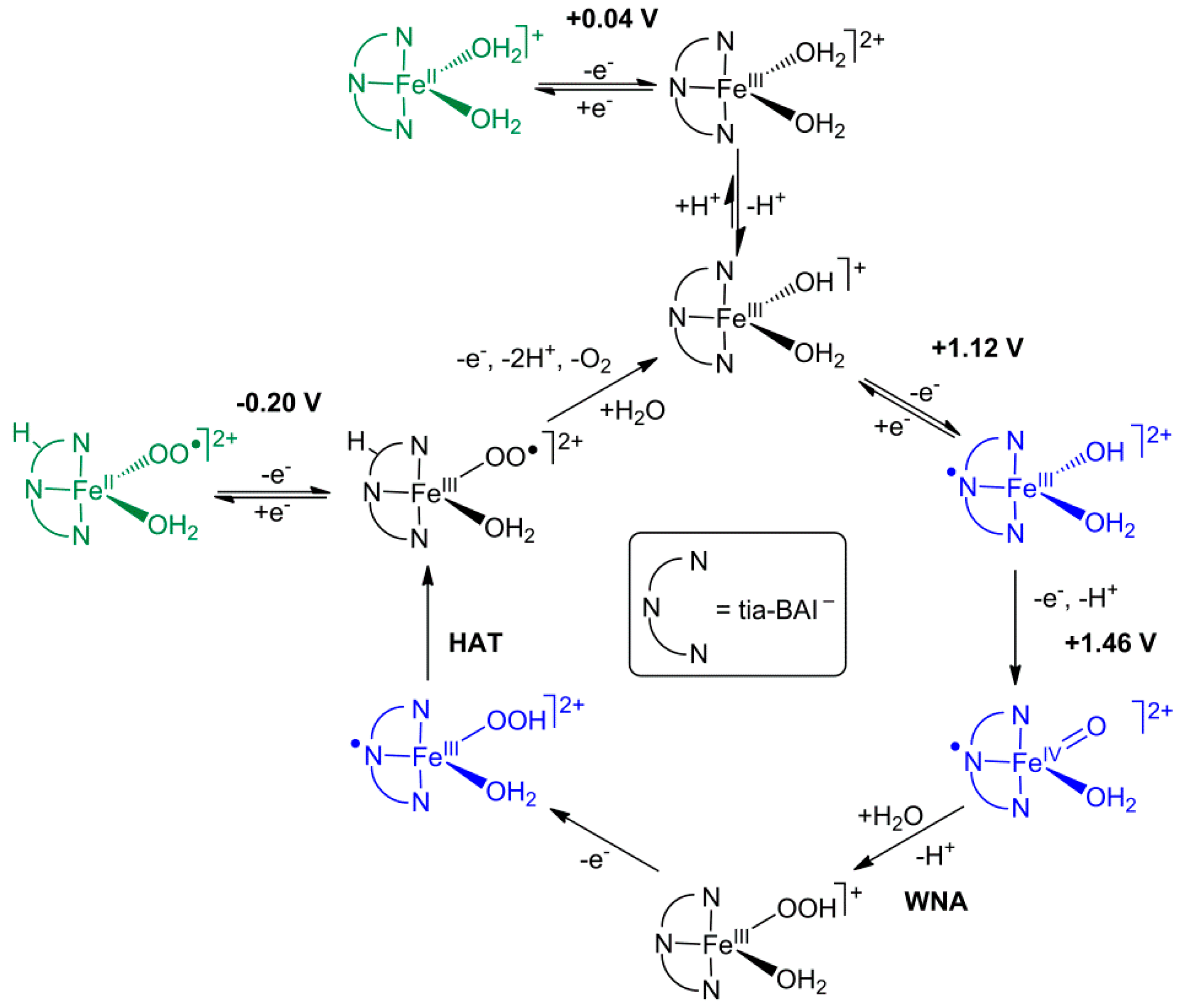
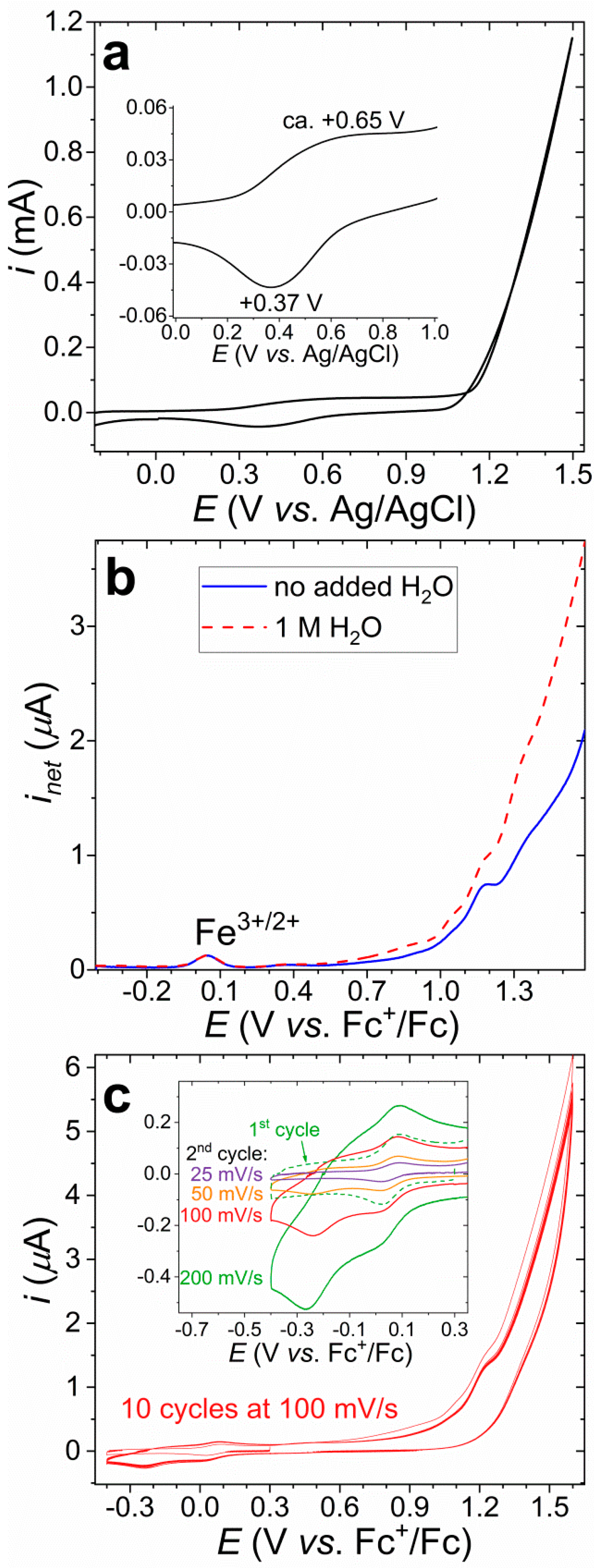
3.3. Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation in Water/Acetone with [FeIIICl2(tia-BAI)]
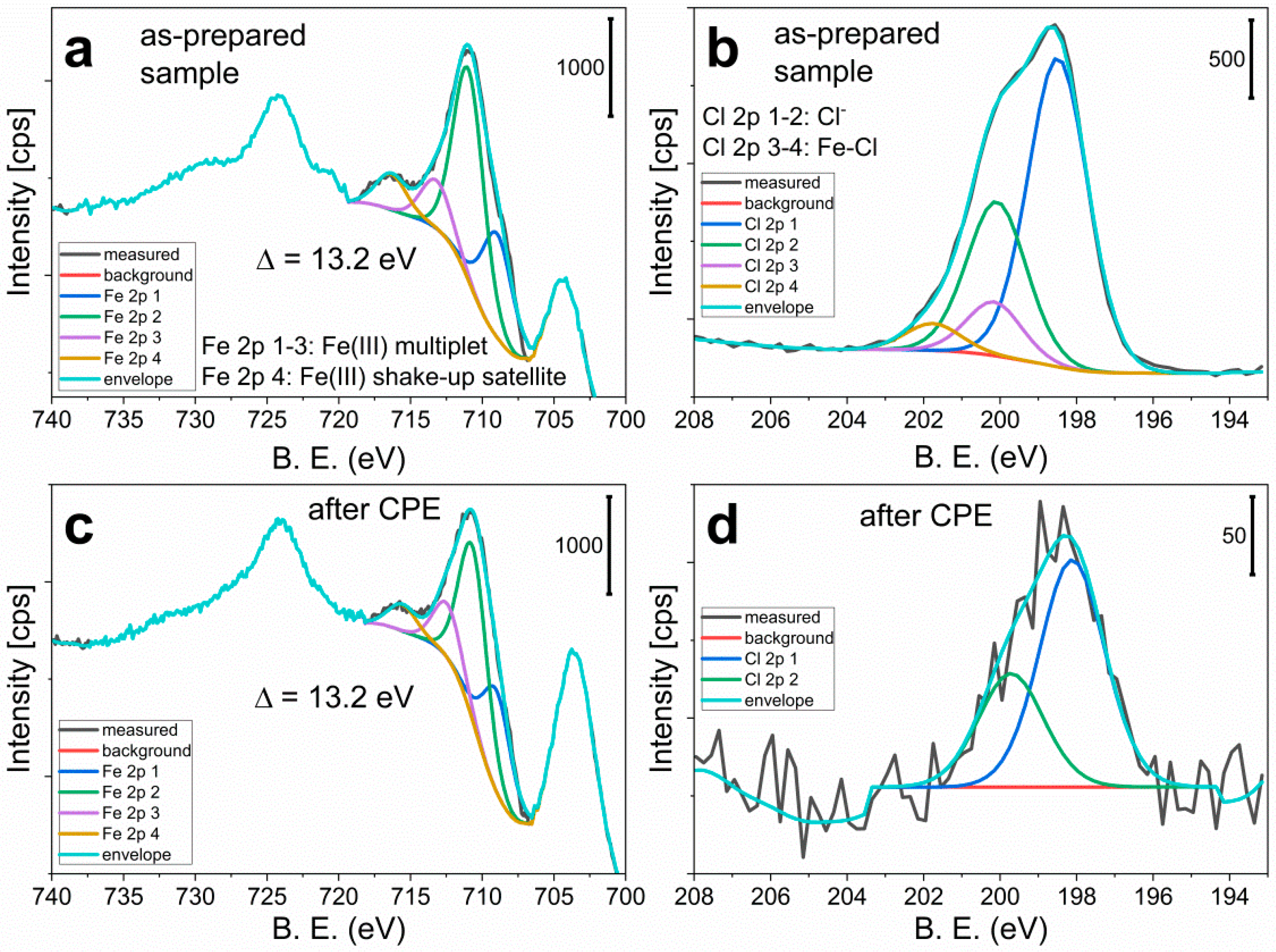
3.4. Characterization of the Complex as a Solid Ad-Layer on Indium Tin Oxide
3.5. Application of the Complex in Water Oxidation as Solid Ad-Layer on Indium Tin Oxide Anode, and Follow-Up Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dau, H.; Limberg, C.; Reier, T.; Risch, M.; Roggan, S.; Strasser, P. The mechanism of water oxidation: From electrolysis via homogeneous to biological catalysis. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 724–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umena, Y.; Kawakami, K.; Shen, J.-R.; Kamiya, N. Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Nature 2011, 473, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Eberhart, M.; Nayak, A.; Brennaman, M.K.; Shan, B.; Meyer, T.J. A molecular silane-derivatized Ru(II) catalyst for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15062–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheu, R.; Ertem, M.Z.; Gimbert-Suriñach, C.; Sala, X.; Llobet, A. Seven coordinated molecular ruthenium–water oxidation catalysts: A coordination chemistry journey. Chem. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, E.A.; Lee, B.-L.; Åkermark, T.; Johnston, E.V.; Kärkäs, M.D.; Sun, J.; Hansson, Ö.; Bäckvall, J.-E.; Åkermark, B. Photosensitized water oxidation by use of a bioinspired manganese catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11715–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kal, S.; Ayensu-Mensah, L.; Dinolfo, P.H. Evidence for catalytic water oxidation by a dimanganese tetrakis-Schiff base macrocycle. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 423, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dismukes, G.C.; Brimblecombe, R.; Felton, G.A.N.; Pryadun, R.S.; Sheats, J.E.; Spiccia, L.; Swiegers, G.F. Development of bioinspired Mn4O4—Cubane water oxidation catalysts: Lessons from photosynthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggins, M.K.; Zhang, M.-T.; Vannucci, A.K.; Dares, C.J.; Meyer, T.J. Electrocatalytic water oxidation by a monomeric amidate-ligated Fe(III)—Aqua complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5531–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Kondo, M.; Kuga, R.; Kurashige, Y.; Yanai, T.; Hayami, S.; Praneeth, V.K.K.; Yoshida, M.; Yoneda, K.; Kawata, S.; et al. A pentanuclear iron catalyst designed for water oxidation. Nature 2016, 530, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.C.; McDaniel, N.D.; Bernhard, S.; Collins, T.J. Fast water oxidation using iron. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10990–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zuraiji, S.M.; Benkó, T.; Illés, L.; Németh, M.; Frey, K.; Sulyok, A.; Pap, J.S. Utilization of hydrophobic ligands for water-insoluble Fe(II) water oxidation catalysts—Immobilization and characterization. J. Catal. 2020, 381, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H.A.; Ahmad, N.; Chughtai, A.H.; Vandichel, M.; Busch, M.; Van Hecke, K.; Yusubov, M.; Song, S.; Verpoort, F. A robust molecular catalyst generated in situ for photo- and electrochemical water oxidation. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Han, A.; Du, P. Cobalt–salen complexes as catalyst precursors for electrocatalytic water oxidation at low overpotential. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8998–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, D.; Anderlund, M.F.; Thapper, A.; Styring, S. Photochemical water oxidation with visible light using a cobalt containing catalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lai, W.; Cao, R. Electrocatalytic water oxidation by a water-soluble nickel porphyrin complex at neutral pH with low overpotential. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 5604–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.-T.; Hou, C.; Ke, Z.-F.; Lu, T.-B. Homogeneous electrocatalytic water oxidation at neutral ph by a robust macrocyclic nickel (II) complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13042–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.J.; Materna, K.L.; Mercado, B.Q.; Crabtree, R.H.; Brudvig, G.W. Electrocatalytic water oxidation by a copper(II) complex of an oxidation-resistant ligand. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3384–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M.; Goldberg, K.I.; Mayer, J.M. A soluble copper–Bipyridine water-oxidation electrocatalyst. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Ng, S.-M.; Man, W.-L.; Lau, T.-C. Chemical and visible-light-driven water oxidation by iron complexes at pH 7-9: Evidence for dual-active intermediates in iron-catalyzed water oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, C.; Bucci, A.; Costas, M.; Lloret-Fillol, J. Water oxidation catalysis with well-defined molecular iron complexes. In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 74, pp. 151–196. ISBN 978-0-12-816082-4. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, A.R.; Que, L. High-valent nonheme iron-oxo complexes: Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberger, J.; Ray, K.; Meyer, K. The biology and chemistry of high-valent iron–oxo and iron–nitrido complexes. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Groves, J.T. Beyond ferryl-mediated hydroxylation: 40 years of the rebound mechanism and C–H activation. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, I.; Knölker, H.-J. Iron catalysis in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3170–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, A. Iron catalysis in organic synthesis: A critical assessment of what it takes to make this base metal a multitasking champion. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asraf, M.d.A.; Younus, H.A.; Yusubov, M.; Verpoort, F. Earth-abundant metal complexes as catalysts for water oxidation; is it homogeneous or heterogeneous? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4901–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolà, Z.; Garcia-Bosch, I.; Acuña-Parés, F.; Prat, I.; Luis, J.M.; Costas, M.; Lloret-Fillol, J. Electronic effects on single-site iron catalysts for water oxidation. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8042–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizarova, G.L.; Matvienko, L.G.; Lozhkina, N.V.; Maizlish, V.E.; Parmon, V.N. Homogeneous catalysts for dioxygen evolution from water. Oxidation of water by trisbipyridylruthenium (III) in the presence of metallophthalocyanines. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1981, 16, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Shiroishi, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Kaneko, M. Photoinduced water oxidation by polymeric iron cyanide complex. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 131, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Orthaber, A.; Ott, S.; Thapper, A. Iron pentapyridyl complexes as molecular water oxidation catalysts: Strong influence of a chloride ligand and pH in altering the mechanism. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylin, S.I.; Pavliuk, M.V.; D’Amario, L.; Mamedov, F.; Sá, J.; Berggren, G.; Fritsky, I.O. Efficient visible light-driven water oxidation catalysed by an iron(IV) clathrochelate complex. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3335–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shylin, S.I.; Pavliuk, M.V.; D’Amario, L.; Fritsky, I.O.; Berggren, G. Photoinduced hole transfer from tris(bipyridine)ruthenium dye to a high-valent iron-based water oxidation catalyst. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 215, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Thapper, A.; Ott, S.; Colbran, S.B. Structural features of molecular electrocatalysts in multi-electron redox processes for renewable energy-recent advances. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2159–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, W.; Mahammed, A.; Fridman, N.; Gross, Z. Water oxidation catalysis by mono- and binuclear iron corroles. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 3764–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; Jung, J.; Nakagawa, T.; Sharma, N.; Lee, Y.-M.; Nam, W.; Fukuzumi, S. Photodriven oxidation of water by plastoquinone analogs with a nonheme iron catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6748–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Samanta, D.; Zangrando, E.; Ghosh, T.; Das, D. A dinuclear iron complex as an efficient electrocatalyst for homogeneous water oxidation reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 2830–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneeth, V.K.K.; Kondo, M.; Okamura, M.; Akai, T.; Izu, H.; Masaoka, S. Pentanuclear iron catalysts for water oxidation: Substituents provide two routes to control onset potentials. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 4628–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, C.; Debgupta, J.; Díaz Díaz, D.; Singh, K.K.; Sen Gupta, S.; Dhar, B.B. Homogeneous photochemical water oxidation by biuret-modified fe-taml: Evidence of FeV(O) intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12273–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolà, Z.; Gamba, I.; Acuña-Parés, F.; Casadevall, C.; Clémancey, M.; Latour, J.-M.; Luis, J.M.; Lloret-Fillol, J.; Costas, M. Design of iron coordination complexes as highly active homogenous water oxidation catalysts by deuteration of oxidation-sensitive sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloret-Fillol, J.; Costas, M. Water oxidation at base metal molecular catalysts. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 71, pp. 1–52. ISBN 978-0-12-817115-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zahran, Z.N.; Tsubonouchi, Y.; Mohamed, E.A.; Yagi, M. Recent advances in the development of molecular catalyst-based anodes for water oxidation toward artificial photosynthesis. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1775–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Nayak, A.; Shao, J.; Meyer, T.J. Crossing the bridge from molecular catalysis to a heterogenous electrode in electrocatalytic water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11153–11158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottrup, K.G.; Hetterscheid, D.G.H. Evaluation of iron-based electrocatalysts for water oxidation-an on-line mass spectrometry approach. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2643–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottrup, K.G.; D’Agostini, S.; van Langevelde, P.H.; Siegler, M.A.; Hetterscheid, D.G.H. Catalytic activity of an iron-based water oxidation catalyst: Substrate effects of graphitic electrodes. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrido-Barros, P.; Gimbert-Suriñach, C.; Moonshiram, D.; Picón, A.; Monge, P.; Batista, V.S.; Llobet, A. Electronic π-Delocalization boosts catalytic water oxidation by Cu(II) molecular catalysts heterogenized on graphene sheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12907–12910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Li, H.; Ding, L.; You, F.; Ge, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K. Facile preparation of unsubstituted iron(II) phthalocyanine/carbon nitride nanocomposites: A multipurpose catalyst with reciprocally enhanced photo/electrocatalytic activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3319–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, E.L.; Hilburg, S.L.; Washburn, N.R.; Collins, T.J.; Kitchin, J.R. Electrocatalytic oxygen evolution with an immobilized TAML activator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5603–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, J.S.; Draksharapu, A.; Giorgi, M.; Browne, W.R.; Kaizer, J.; Speier, G. Stabilisation of μ-peroxido-bridged Fe(III) intermediates with non-symmetric bidentate N-donor ligands. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, M.A.W.; Green, K.-A.; Nelson, P.N.; Lorraine, S.C. Review: Pincer ligands—Tunable, versatile and applicable. Polyhedron 2018, 143, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csonka, R.; Speier, G.; Kaizer, J. Isoindoline-derived ligands and applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18401–18419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Váradi, T.; Pap, J.S.; Giorgi, M.; Párkányi, L.; Csay, T.; Speier, G.; Kaizer, J. Iron(III) complexes with meridional ligands as functional models of intradiol-cleaving catechol dioxygenases. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripli, B.; Baráth, G.; Balogh-Hergovich, É.; Giorgi, M.; Simaan, A.J.; Párkányi, L.; Pap, J.S.; Kaizer, J.; Speier, G. Correlation between the SOD-like activity of hexacoordinate iron(II) complexes and their Fe3+/Fe2+ redox potentials. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, J.S.; Cranswick, M.A.; Balogh-Hergovich, É.; Baráth, G.; Giorgi, M.; Rohde, G.T.; Kaizer, J.; Speier, G.; Que, L. An Iron(II)[1,3-bis(2′-pyridylimino)isoindoline] complex as a catalyst for substrate oxidation with H2O—Evidence for a transient peroxidodiiron(III) species. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 3858–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheja, A.; Baabe, D.; Menzel, D.; Pietzonka, C.; Schweyen, P.; Bröring, M. Spin crossover and valence tautomerism in neutral homoleptic iron complexes of Bis (pyridylimino) isoindolines. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14196–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semino, R.; Longinotti, M.P. Excess protons in water-acetone mixtures. II. A conductivity study. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 164510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruck, M.; Sauer, D.C.; Enders, M.; Wadepohl, H.; Gade, L.H. Bis(2-pyridylimino)isoindolato iron(ii) and cobalt(ii) complexes: Structural chemistry and paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Parés, F.; Codolà, Z.; Costas, M.; Luis, J.M.; Lloret-Fillol, J. Unraveling the mechanism of water oxidation catalyzed by nonheme iron complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 5696–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffert, W.A.; Mock, M.T.; Appel, A.M.; Yang, J.Y. Incorporation of hydrogen-bonding functionalities into the second coordination sphere of iron-based water-oxidation catalysts. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 3846–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codolà, Z.; Gómez, L.; Kleespies, S.T.; Que, L., Jr.; Costas, M.; Lloret-Fillol, J. Evidence for an oxygen evolving iron–oxo–cerium intermediate in iron-catalysed water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsworth, E.C.; Turner, B.; Szulczewski, G. Thermal conversion of [Fe(phen)3](SCN)2 thin films into the spin crossover complex Fe(phen)2(NCS)2. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Craze, A.R.; Akiyoshi, R.; Tsukiashi, A.; Hayami, S.; Mustonen, O.; Bhadbhade, M.M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Marjo, C.E.; Wang, Y.; et al. Direct monitoring of spin transitions in a dinuclear triple-stranded helicate iron(II) complex through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronschinske, A.; Bruce, R.C.; Lewis, G.; Chen, Y.; Calzolari, A.; Buongiorno-Nardelli, M.; Shultz, D.A.; You, W.; Dougherty, D.B. Iron(ii) spin crossover films on Au(111): Scanning probe microscopy and photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floreano, L.; Cossaro, A.; Gotter, R.; Verdini, A.; Bavdek, G.; Evangelista, F.; Ruocco, A.; Morgante, A.; Cvetko, D. Periodic arrays of cu-phthalocyanine chains on Au(110). J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10794–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasola, A.; Abadía, M.; Rogero, C.; Garcia-Lekue, A. Theoretical insights into unexpected molecular core level shifts: Chemical and surface effects. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 5718–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pap, J.S.; Bányai, V.; Szilvási, D.S.; Kaizer, J.; Speier, G.; Giorgi, M. Influence of meridional N3-ligands on supramolecular assembling and redox behavior of carboxylatocopper(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, J.S.; Kripli, B.; Bányai, V.; Giorgi, M.; Korecz, L.; Gajda, T.; Árus, D.; Kaizer, J.; Speier, G. Tetra-, penta- and hexacoordinate copper(II) complexes with N3 donor isoindoline-based ligands: Characterization and SOD-like activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2011, 376, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | Surface Ratio (at.%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh | After CPE | |
| Fe | 2.81 | 2.01 |
| O | 12.34 | 17.15 |
| N | 15.53 | 15.09 |
| C | 54.76 | 53.97 |
| Cl | 3.90 | 0.24 |
| S | 5.05 | 4.86 |
| Sn | 0.64 | 0.68 |
| In | 4.97 | 6.00 |
| N/Fe | 5.5 | 7.5 |
| Cl/Fe | 1.4 | 0.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zuraiji, S.M.; Lukács, D.; Németh, M.; Frey, K.; Benkó, T.; Illés, L.; Pap, J.S. An Iron(III) Complex with Pincer Ligand—Catalytic Water Oxidation through Controllable Ligand Exchange. Reactions 2020, 1, 16-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions1010003
Al-Zuraiji SM, Lukács D, Németh M, Frey K, Benkó T, Illés L, Pap JS. An Iron(III) Complex with Pincer Ligand—Catalytic Water Oxidation through Controllable Ligand Exchange. Reactions. 2020; 1(1):16-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zuraiji, Sahir M., Dávid Lukács, Miklós Németh, Krisztina Frey, Tímea Benkó, Levente Illés, and József S. Pap. 2020. "An Iron(III) Complex with Pincer Ligand—Catalytic Water Oxidation through Controllable Ligand Exchange" Reactions 1, no. 1: 16-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions1010003
APA StyleAl-Zuraiji, S. M., Lukács, D., Németh, M., Frey, K., Benkó, T., Illés, L., & Pap, J. S. (2020). An Iron(III) Complex with Pincer Ligand—Catalytic Water Oxidation through Controllable Ligand Exchange. Reactions, 1(1), 16-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions1010003