Spectral-Spatial Fusion for Soybean Quality Evaluation Using Hyperspectral Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A reflectance-mode HSI system with a single light source is introduced, eliminating the need for complex dual-light configurations typically used in earlier soybean classification systems.
- A spectral–spatial data fusion framework is proposed that improves classification robustness and accuracy compared to models using only spectral or spatial features.
- A broad evaluation of eight machine learning classifiers shows that the proposed approach achieves near state-of-the-art classification performance across four soybean categories using a simplified and potentially scalable setup suitable for integration into automated industrial environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Preparation of Soybean
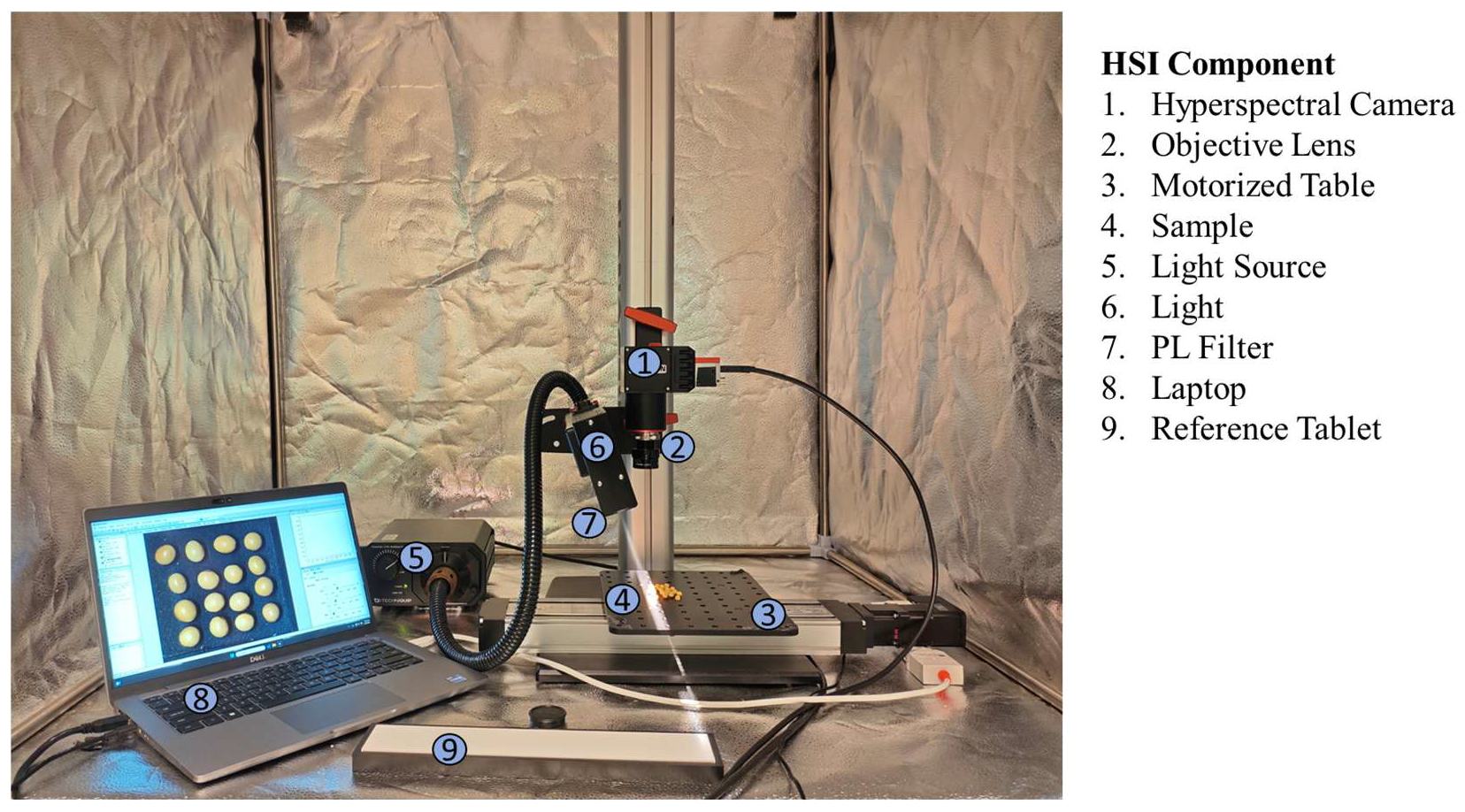
2.2. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition
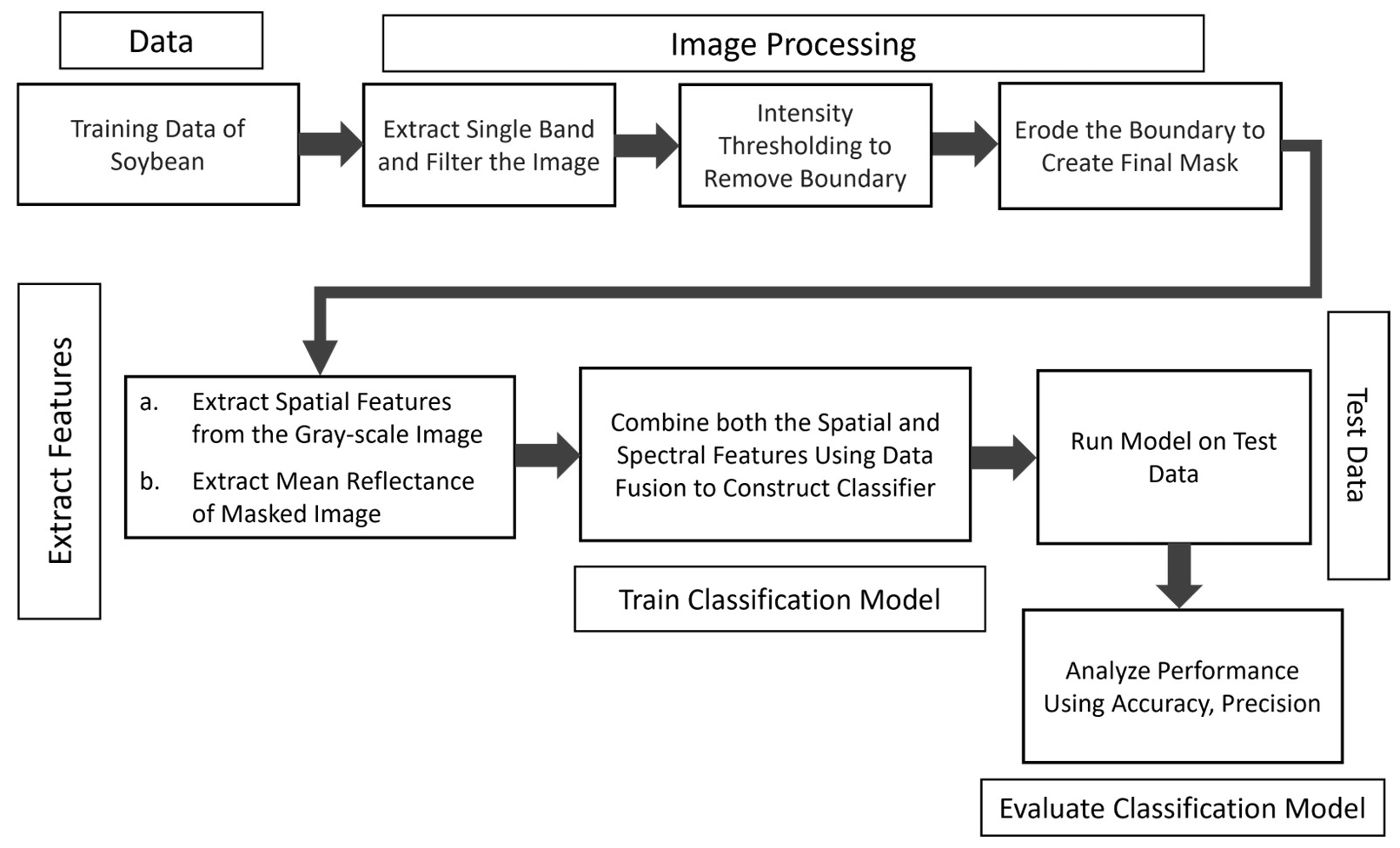
2.3. Proposed Method
2.4. Data Processing
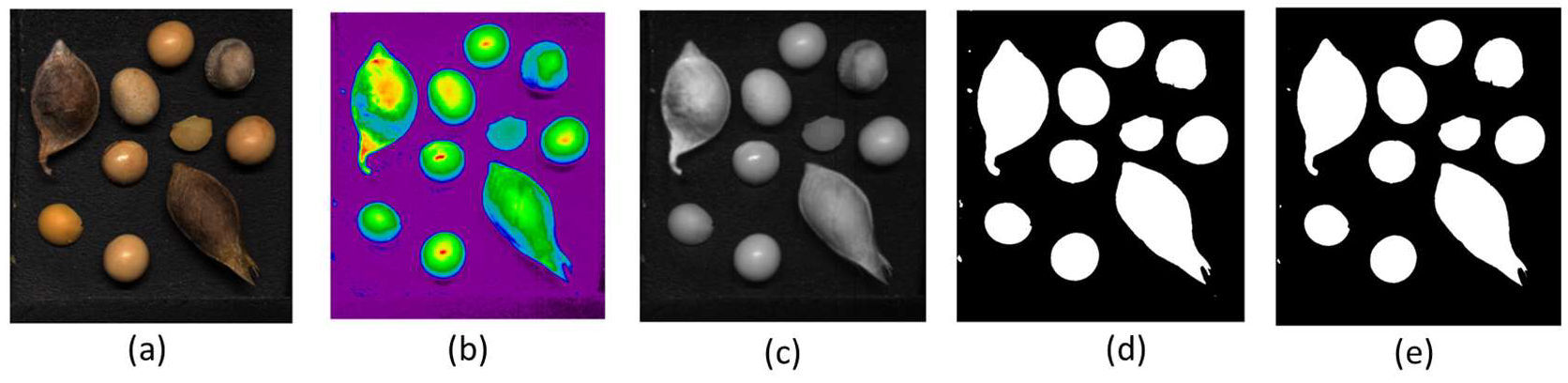
2.4.1. Spatial Data Processing
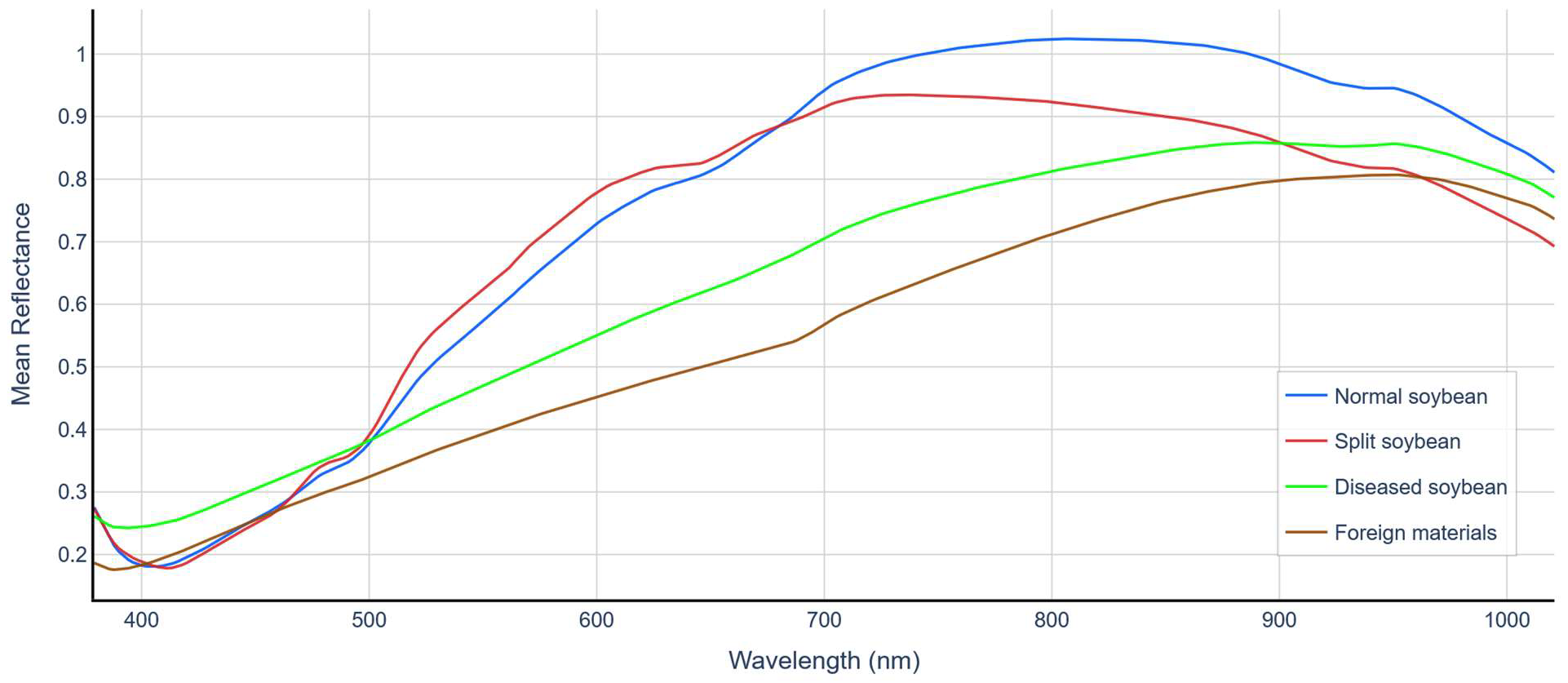
2.4.2. Spectral Data Processing
2.5. Feature Extraction
2.5.1. Spatial Feature Extraction
2.5.2. Spectral Feature Extraction
2.6. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.7. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Performance
3.1.1. Using Spatial Features
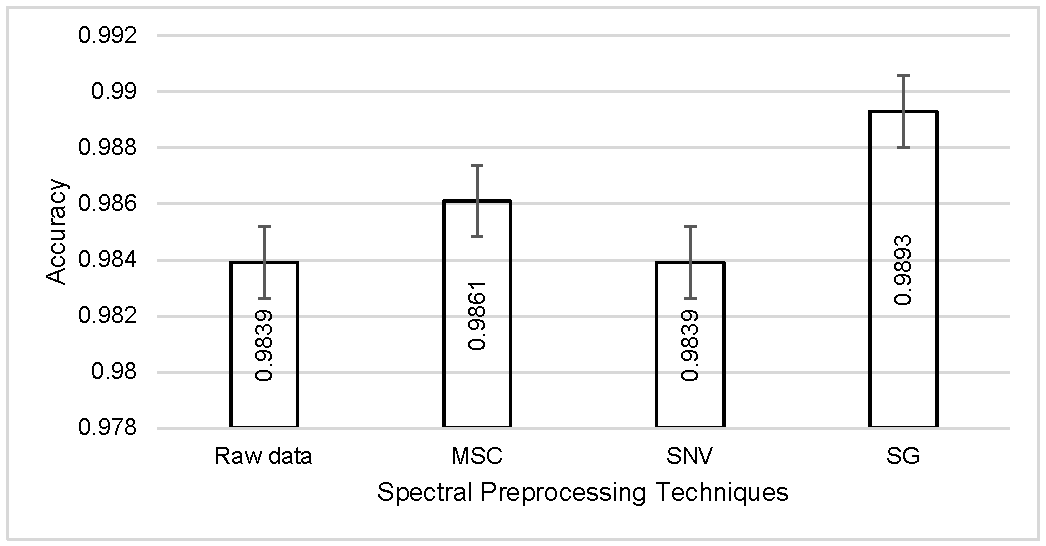
3.1.2. Using Spectral Features
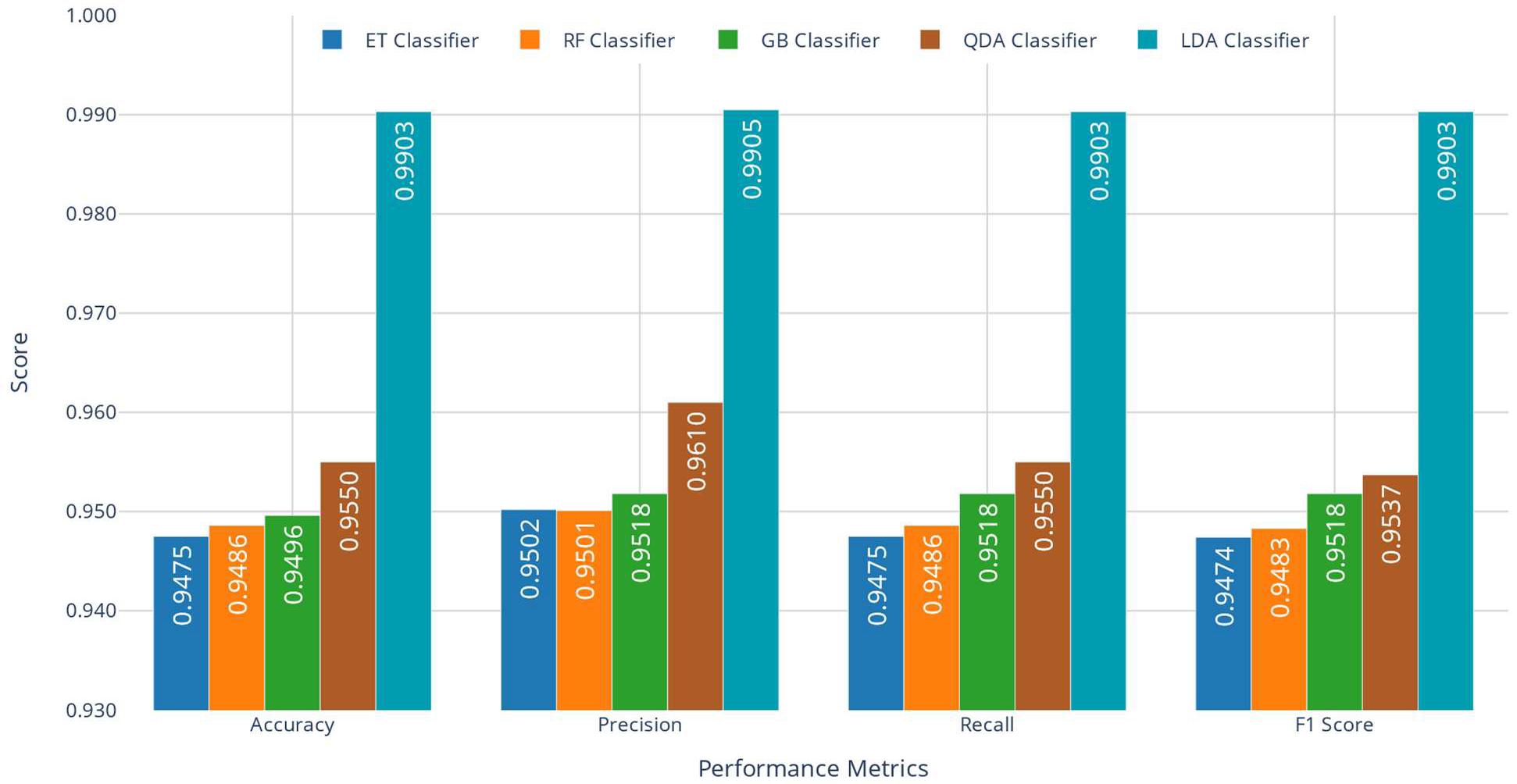
3.1.3. Data Fusion
3.1.4. Model Performance Comparison
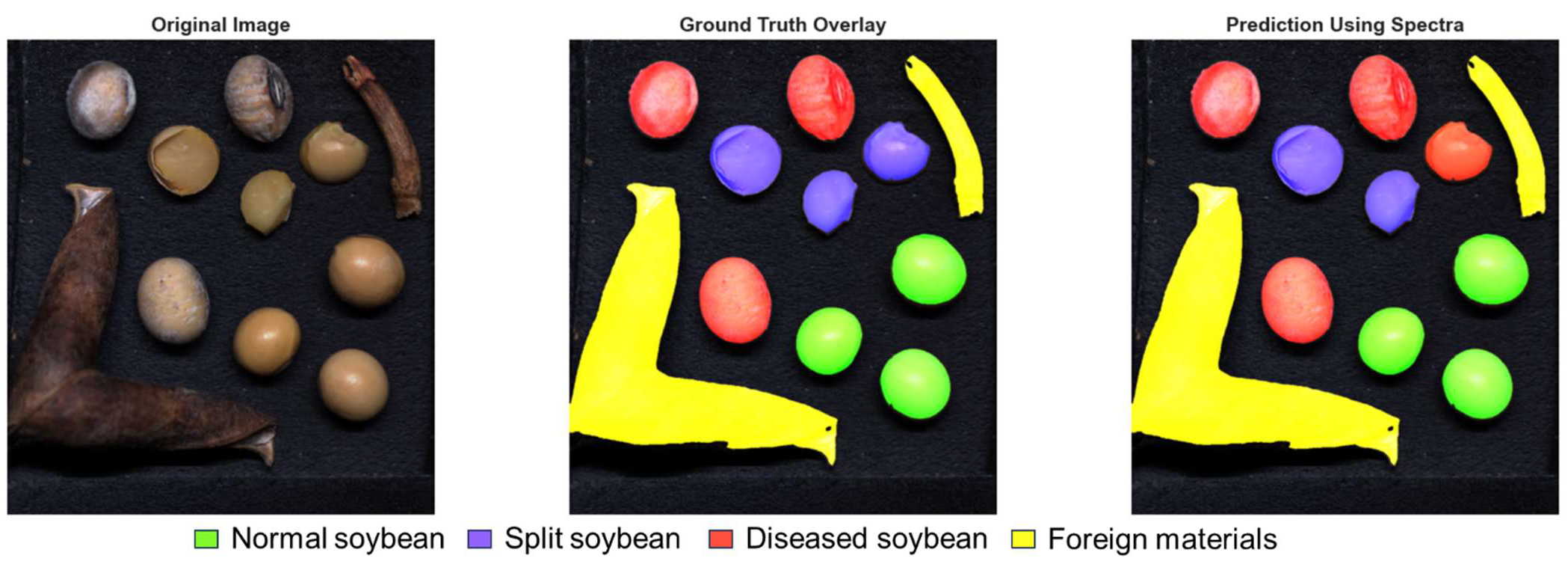
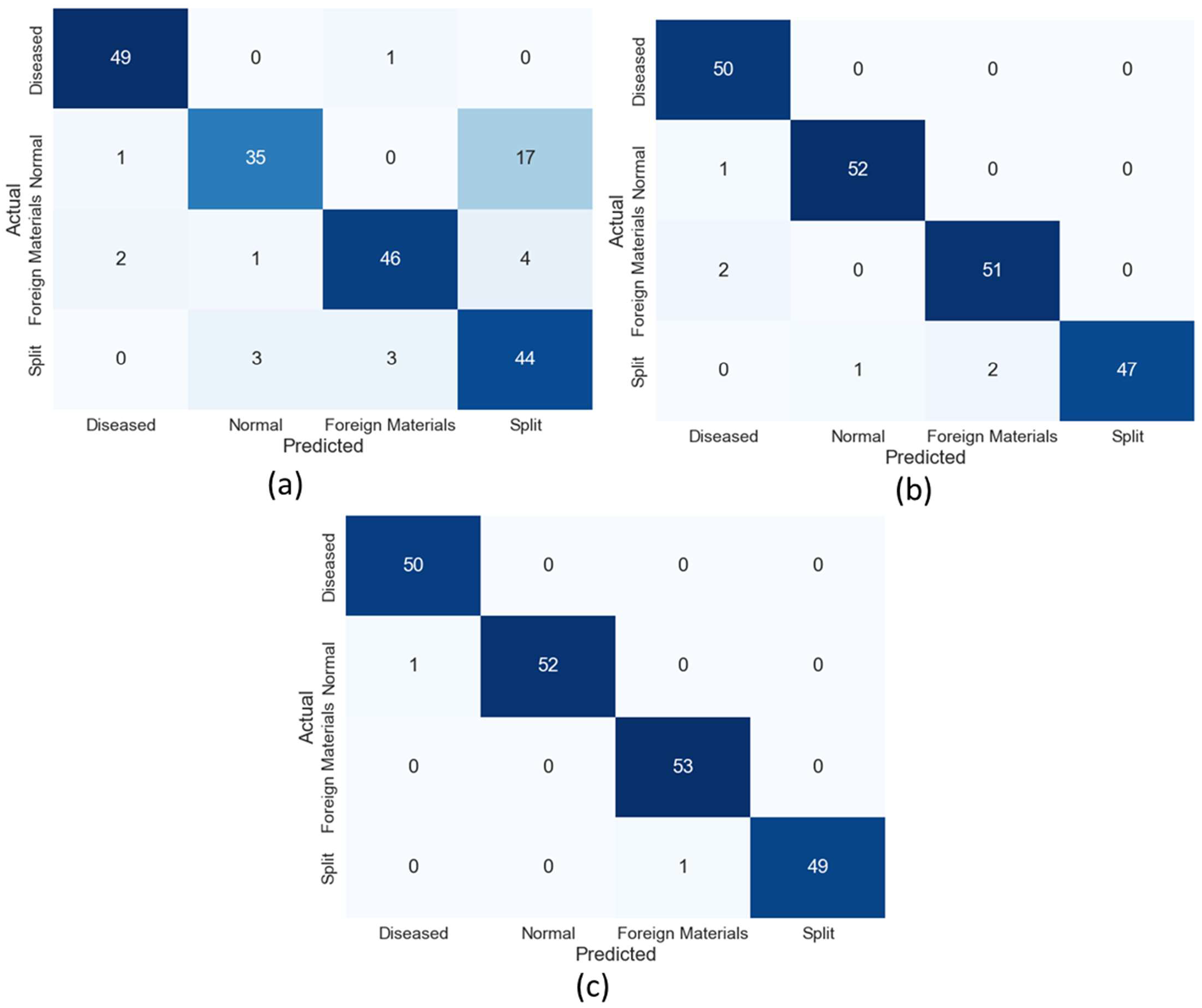
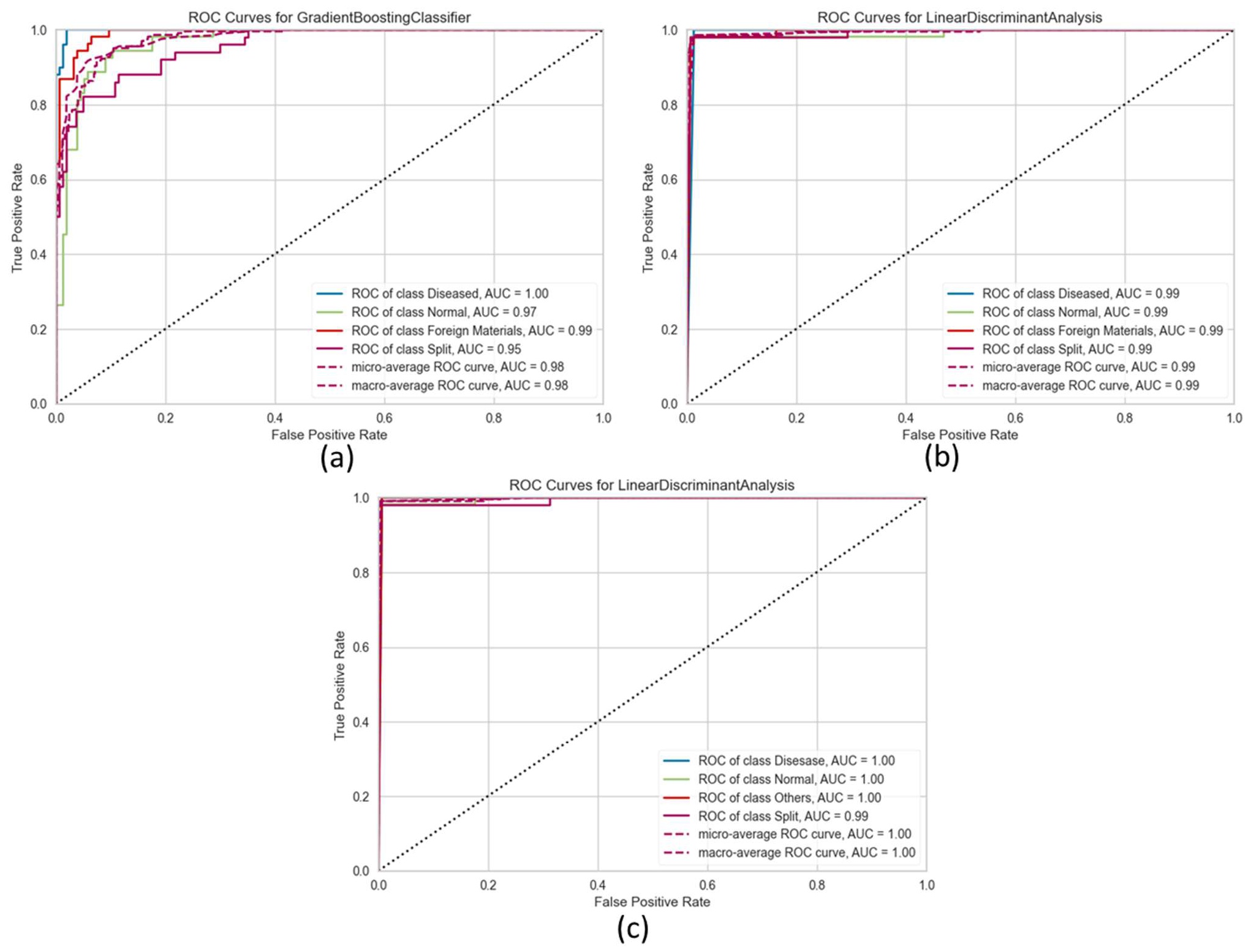
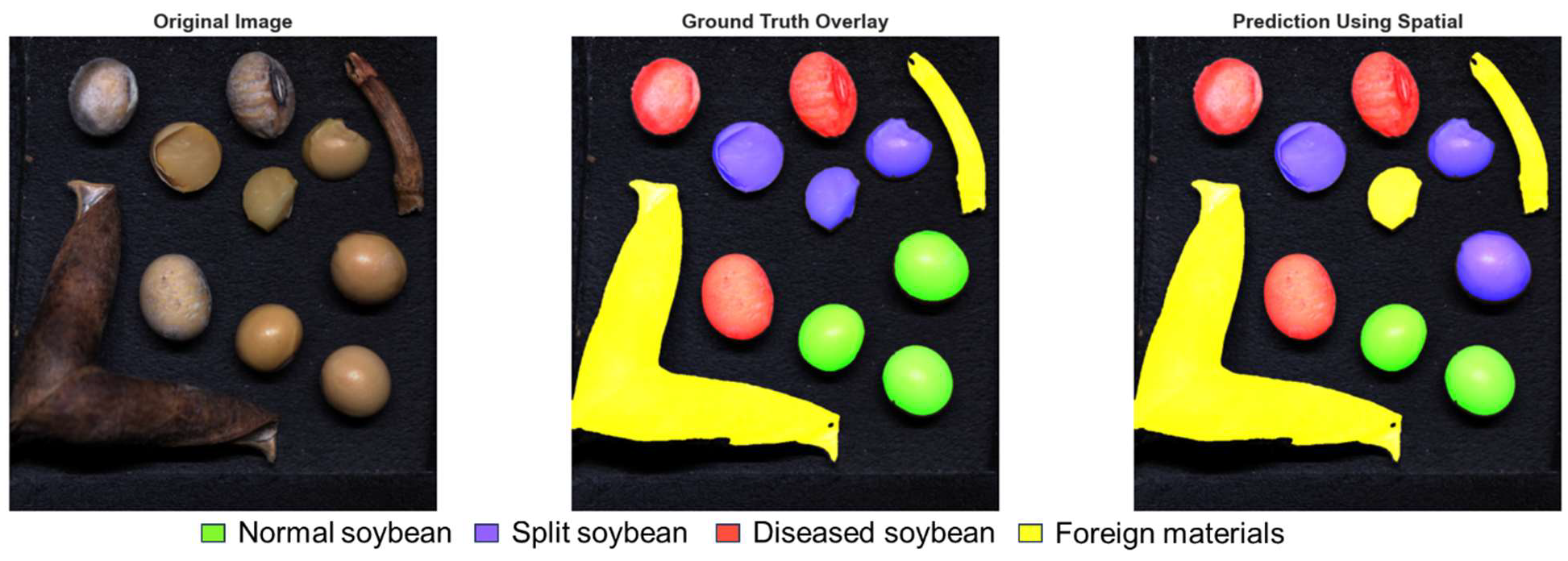
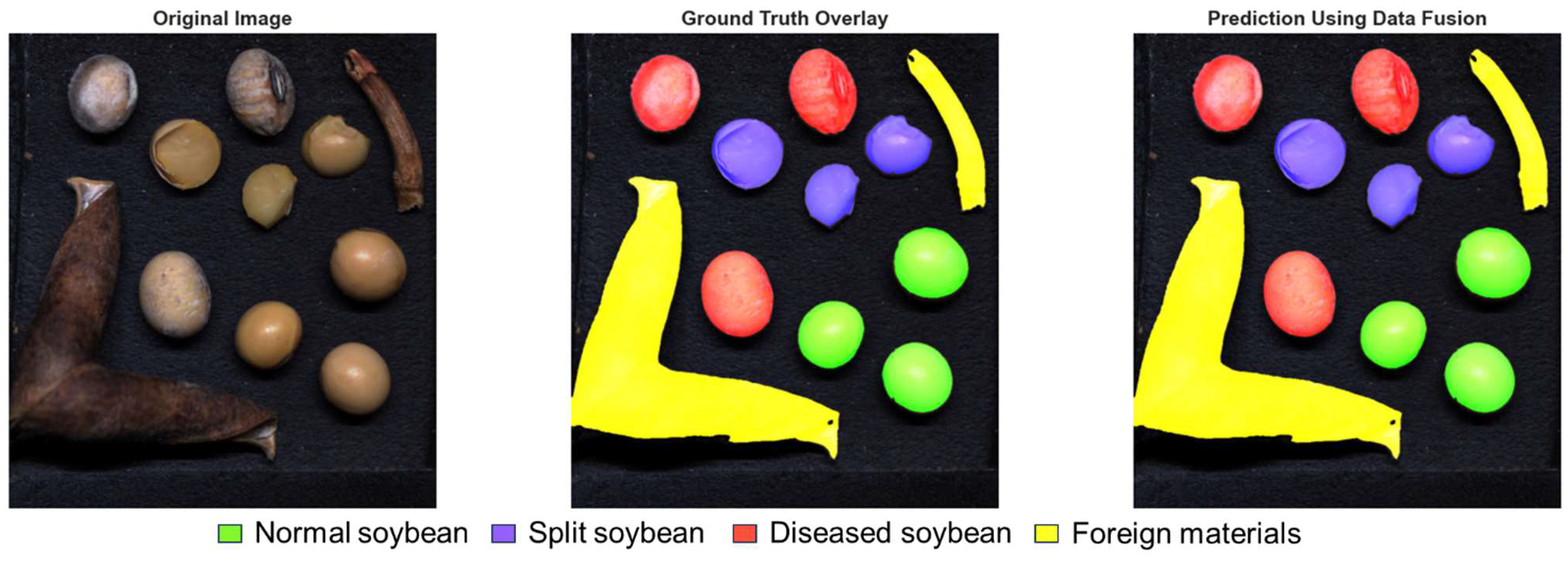
3.2. Visualization of Model Prediction
3.2.1. Inference Using Spatial Features
3.2.2. Inference Using Spectral Features
3.2.3. Inference Using Data Fusion
3.3. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, P.; Xiaoli, L.; Li, D.; Jiang, S.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y. Rapidly and Exactly Determining Postharvest Dry Soybean Seed Quality Based on Machine Vision Technology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. USDA: 2024 Soybean Production up 5%. Biomass Magazine. 14 January 2025. Available online: https://biomassmagazine.com/articles/usda-2024-soybean-production-up-5 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Tan, K.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xia, H.; Yao, S. Estimation of Soybean Internal Quality Based on Improved Support Vector Regression Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm Applying Hyperspectral Reflectance and Chemometric Calibrations. Agriculture 2024, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chang, Z.; Jin, C.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S.; Ni, Y. Classification and Recognition of Soybean Quality Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and Random Forest Methods. Sensors 2025, 25, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, S. Development of a General Prediction Model of Moisture Content in Maize Seeds Based on LW-NIR Hyperspectral Imaging. Agriculture 2023, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Yim, D.G.; Kim, G.; Jo, C. Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with Multivariate Analyses for Efficient Prediction of Chemical, Biological and Physical Properties of Seafood Products. Food Eng. Rev. 2023, 15, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsi, A.; Momin, A.; Ayres, V. Moisture Prediction in Chicken Litter Using Hyperspectral Data and Machine Learning. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 11, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviara, N.A.; Liberty, J.T.; Olatunbosun, O.S.; Shoyombo, H.A.; Oyeniyi, S.K. Potential Application of Hyperspectral Imaging in Food Grain Quality Inspection, Evaluation and Control during Bulk Storage. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.M.L.; Foleis, J.H.; De Souza Brito, A.; Bertolini, D. A Database for Soybean Seed Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 37th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Manaus, Brazil, 30 September–3 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Teng, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Du, J. Deep Learning Based Soybean Seed Classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, M. Semantic Segmentation-Based Mechanized Harvesting Soybean Quality Detection. Sci. Prog. 2022, 105, 00368504221108518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, A.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, A.; Jang, N.; Ahn, S.; Islam, M.S.; Mansoor, S.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, Y. Automatic Evaluation of Soybean Seed Traits Using RGB Image Data and a Python Algorithm. Plants 2023, 12, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M.; Earl, H.J.; Tulpan, D.; Sulik, J.; Eskandari, M. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in Plant Breeding: Predicting Yield From Hyperspectral Reflectance in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 624273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Quan, L.; Li, H.; Feng, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, R. Real-Time Recognition System of Soybean Seed Full-Surface Defects Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, A.; Singh, P.; Kaur, A.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W. Quantifying Soybean Defects: A Computational Approach to Seed Classification Using Deep Learning Techniques. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fei, L.; Deng, L.; Yang, H.; Han, M.; Han, Z.; Zhao, L. Identification of Soybean Mutant Lines Based on Dual-Branch CNN Model Fusion Framework Utilizing Images from Different Organs. Plants 2023, 12, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulzar, Y.; Hamid, Y.; Soomro, A.B.; Alwan, A.A.; Journaux, L. A Convolution Neural Network-Based Seed Classification System. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, Y. Enhancing Soybean Classification with Modified Inception Model: A Transfer Learning Approach. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2024, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Li, L. Nondestructive Classification of Soybean Seed Varieties by Hyperspectral Imaging and Ensemble Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2020, 20, 6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Gong, Z. Discriminating Soybean Seed Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekramirad, N.; Doyle, L.; Loeb, J.; Santra, D.; Adedeji, A.A. Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning as a Nondestructive Method for Proso Millet Seed Detection and Classification. Foods 2024, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, M.A.; Yamamoto, K.; Miyamoto, M.; Kondo, N.; Grift, T. Machine Vision Based Soybean Quality Evaluation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, M.H.; Korganbayev, S.; Aboughaleb, I.H.; Hussein, A.A.; Abbass, M.A.; Abdlaty, R.; Sabry, Y.M.; Saccomandi, P.; Youssef, A.B.M. Custom Hyperspectral Imaging System Reveals Unique Spectral Signatures of Heart, Kidney, and Liver Tissues. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 305, 123363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Li, S. Hyperspectral Imaging Analysis for Early Detection of Tomato Bacterial Leaf Spot Disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaeifar, A.; Yang, C.; Min, A.; Jones, C.R.; Michaels, T.E.; Krueger, Q.J.; Barnes, R.; Velte, T.J. Noninvasive Early Detection of Nutrient Deficiencies in Greenhouse-Grown Industrial Hemp Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Niu, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Classification of Toona Sinensis Young Leaves Using Machine Learning and UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Imagery. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 940327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lao, C.; Wang, H. Quantitative Estimation of Wastewater Quality Parameters by Hyperspectral Band Screening Using GC, VIP and SPA. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; MacDougall, D.; Martens, H. Linearization and Scatter-Correction for Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectra of Meat. Appl. Spectrosc. 1985, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard Normal Variate Transformation and De-Trending of near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, S.; Xie, L. Improving the Identification Accuracy of Sugar Orange Suffering from Granulation through Diameter Correction and Stepwise Variable Selection. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 200, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Fei, S. Preprocessing Methods for Near-Infrared Spectrum Calibration. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Dinstein, I.; Shanmugam, K. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazala, I.F.S.; Sahoo, R.N.; Pandey, R.; Mandal, B.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, R.; Sinha, P. Spectral Reflectance Pattern in Soybean for Assessing Yellow Mosaic Disease. Indian. J. Virol. 2013, 24, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelladurai, V.; Karuppiah, K.; Jayas, D.S.; Fields, P.G.; White, N.D.G. Detection of Callosobruchus Maculatus (F.) Infestation in Soybean Using Soft X-Ray and NIR Hyperspectral Imaging Techniques. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 57, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, D.C.; de Oliveira, I.C.; de Oliveira, J.L.G.; Baio, F.H.R.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; da Silva Junior, C.A.; Seron, A.C.C.; Ítavo, L.C.V.; Coradi, P.C.; Teodoro, P.E. High-Throughput Phenotyping Using VIS/NIR Spectroscopy in the Classification of Soybean Genotypes for Grain Yield and Industrial Traits. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 310, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, E.; Hossain, M.F.; Rahaman, M.A. A Color and Texture Based Approach for the Detection and Classification of Plant Leaf Disease Using KNN Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’sBazar, Bangladesh, 7–9 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, S.B.; Mahanta, S.; Moore, J.M.C.; Kalafatis, S. Machine Learning-Based Analysis of Nutrient and Water Uptake in Hydroponically Grown Soybeans. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, E.; Kouchaki, S.; Ramazi, S.; Ghanati, F. Machine Learning Techniques for Soybean Charcoal Rot Disease Prediction. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 590529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; He, S.; Xu, X.; He, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Tang, F.; Gong, T.; Wang, W.; et al. Estimation of Soybean Yield Based on High-Throughput Phenotyping and Machine Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1395760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, N.; Bhatia, V.; Mishra, A.K. Deep Learning-Based Robust Analysis of Laser Bio-Speckle Data for Detection of Fungal-Infected Soybean Seeds. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 89331–89348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, D. Fusion of Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) and RGB for Identification of Soybean Kernel Damages Using ShuffleNet with Convolutional Optimization and Cross Stage Partial Architecture. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1098864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, E.; Li, F.; Ghidoni, S.; Zanuttigh, P.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, E.; Li, F. A Soybean Classification Method Based on Data Balance and Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Object Type | Training Dataset | Test Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| Normal soybean | 230 | 53 |
| Split soybean | 250 | 50 |
| Diseased soybean | 240 | 50 |
| Forgien materials | 214 | 53 |
| Total | 934 | 206 |
| GLCM Features | Normal Soybean | Split Soybean | Diseased Soybean | Foreign Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular second moment | 0.001166411 | 0.001468802 | 0.00060536 | 0.000800113 |
| Contrast | 9.9873399 | 6.42387764 | 41.7277266 | 54.2942626 |
| Correlation | 0.995690085 | 0.996226727 | 0.984167122 | 0.977210946 |
| Difference entropy | 2.690342632 | 2.467046877 | 3.592117992 | 3.704523883 |
| Difference variance | 0.00083119 | 0.001122403 | 0.000494607 | 0.000451044 |
| Entropy | 10.36128538 | 9.940645824 | 11.28466308 | 11.20165864 |
| Information measure of correlation 1 | −0.541876642 | −0.55026881 | −0.40437518 | −0.37690467 |
| Information measure of correlation 2 | 0.99975887 | 0.999714277 | 0.998191315 | 0.996879067 |
| Inverse difference moment | 0.400746661 | 0.41733519 | 0.246150516 | 0.262414697 |
| Maximal correlation coefficient | 3.253406957 | 3.026776646 | 3.946432939 | 4.852678038 |
| Sum average | 235.7983282 | 229.8465888 | 240.6570153 | 119.0831582 |
| Sum entropy | 8.094178612 | 7.847192389 | 8.051474218 | 7.892176898 |
| Sum of squares: variance | 1159.904379 | 852.2120745 | 1319.660286 | 1191.164885 |
| Sum variance | 4629.630174 | 3402.42442 | 5236.913416 | 4710.365278 |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB | 0.8811 | 0.8847 | 0.8811 | 0.8802 |
| LightGBM | 0.8747 | 0.8786 | 0.8747 | 0.8739 |
| ET | 0.8715 | 0.8738 | 0.8715 | 0.8708 |
| RF | 0.8544 | 0.8593 | 0.8544 | 0.8533 |
| LDA | 0.8339 | 0.8414 | 0.8339 | 0.8309 |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.9893 | 0.9900 | 0.9893 | 0.9893 |
| LR | 0.9314 | 0.9378 | 0.9314 | 0.9311 |
| QDA | 0.9314 | 0.9415 | 0.9314 | 0.9285 |
| ET | 0.9229 | 0.9263 | 0.9229 | 0.9227 |
| KNN | 0.9165 | 0.9221 | 0.9165 | 0.9162 |
| Work | Model Architecture | Classes of Objects | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Method | Data-fusion (Spectral + Spatial) | 4 | 99.03% |
| Kaler et al. [41] | CNN | 2 | 97.72% |
| Zheng et al. [42] | ShuffleNet | 4 | 98.36% |
| N. Zhang et al. [43] | DenseNet | 4 | 98.48% |
| Gulzar et al. [18] | InceptionV3 | 4 | 98.73% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.B.; Tulsi, A.; Momin, A. Spectral-Spatial Fusion for Soybean Quality Evaluation Using Hyperspectral Imaging. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090274
Rahman MB, Tulsi A, Momin A. Spectral-Spatial Fusion for Soybean Quality Evaluation Using Hyperspectral Imaging. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(9):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090274
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Bayazid, Ahmad Tulsi, and Abdul Momin. 2025. "Spectral-Spatial Fusion for Soybean Quality Evaluation Using Hyperspectral Imaging" AgriEngineering 7, no. 9: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090274
APA StyleRahman, M. B., Tulsi, A., & Momin, A. (2025). Spectral-Spatial Fusion for Soybean Quality Evaluation Using Hyperspectral Imaging. AgriEngineering, 7(9), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090274







