Sericulture Mechanization Poses New Challenges for Environmental Disinfection—Evaluating the Effects of Three Newly Introduced Disinfectants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Bacterial Quantification
2.5. Bioluminescence-Based ATP Assay
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
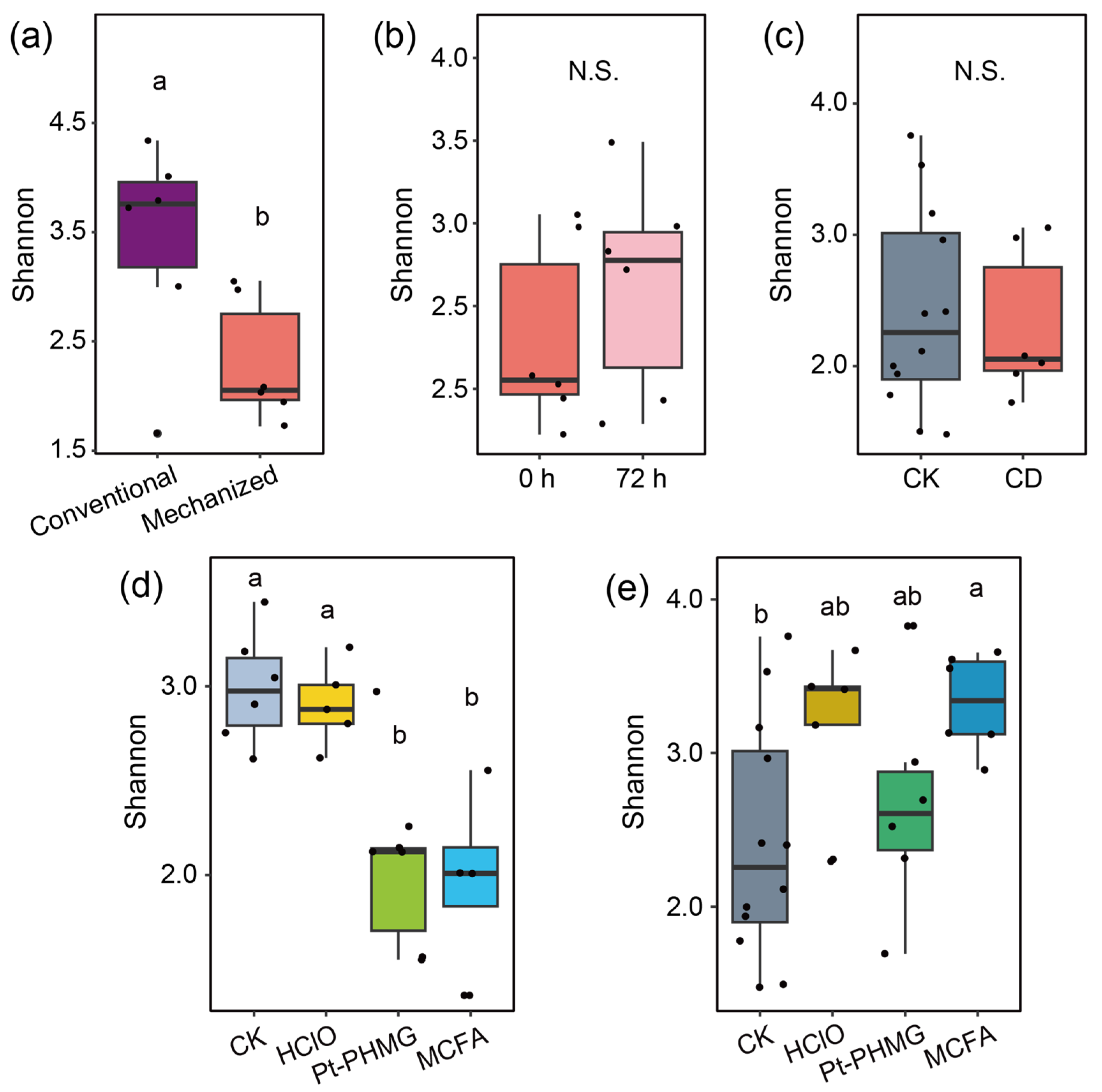
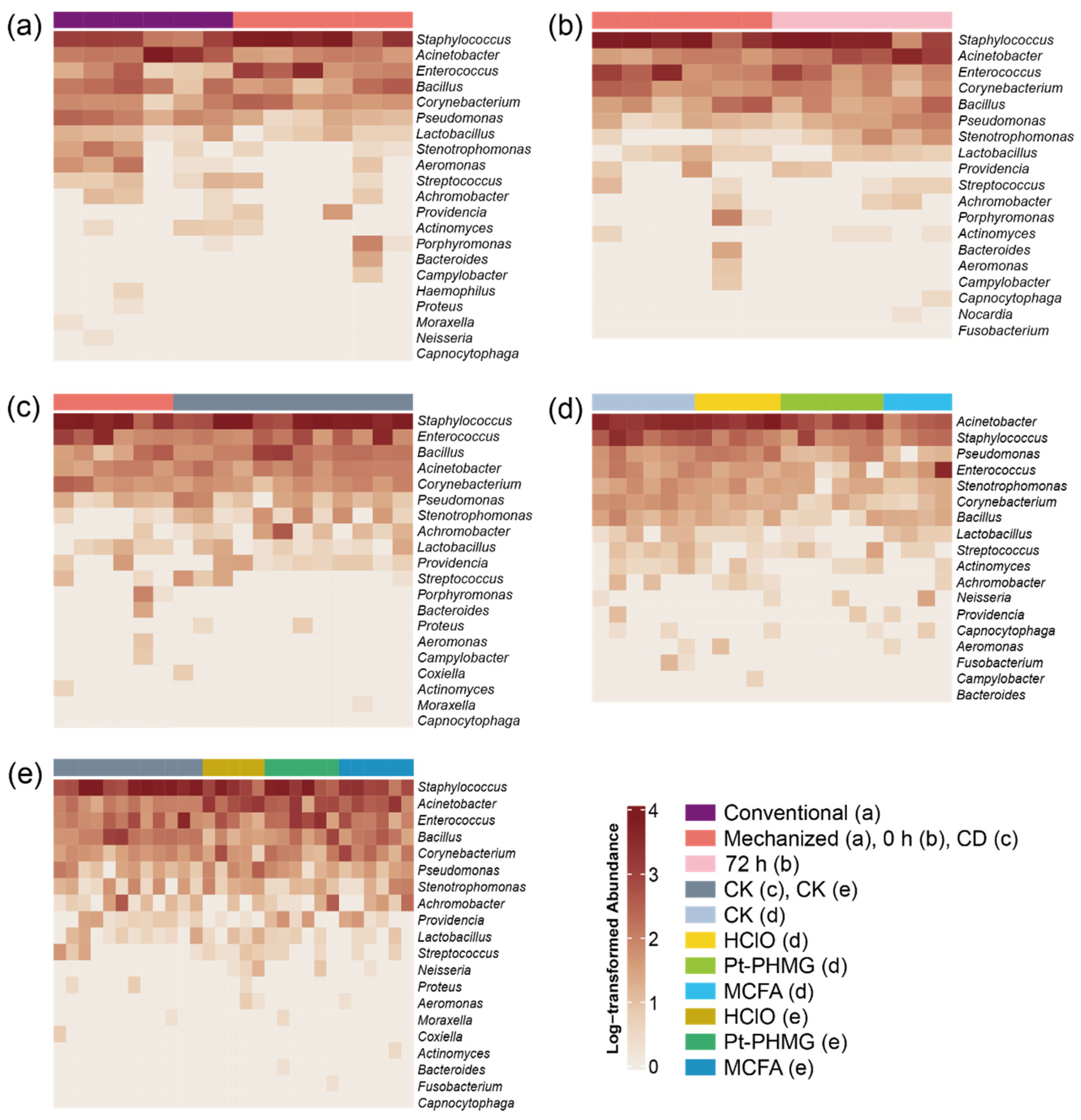
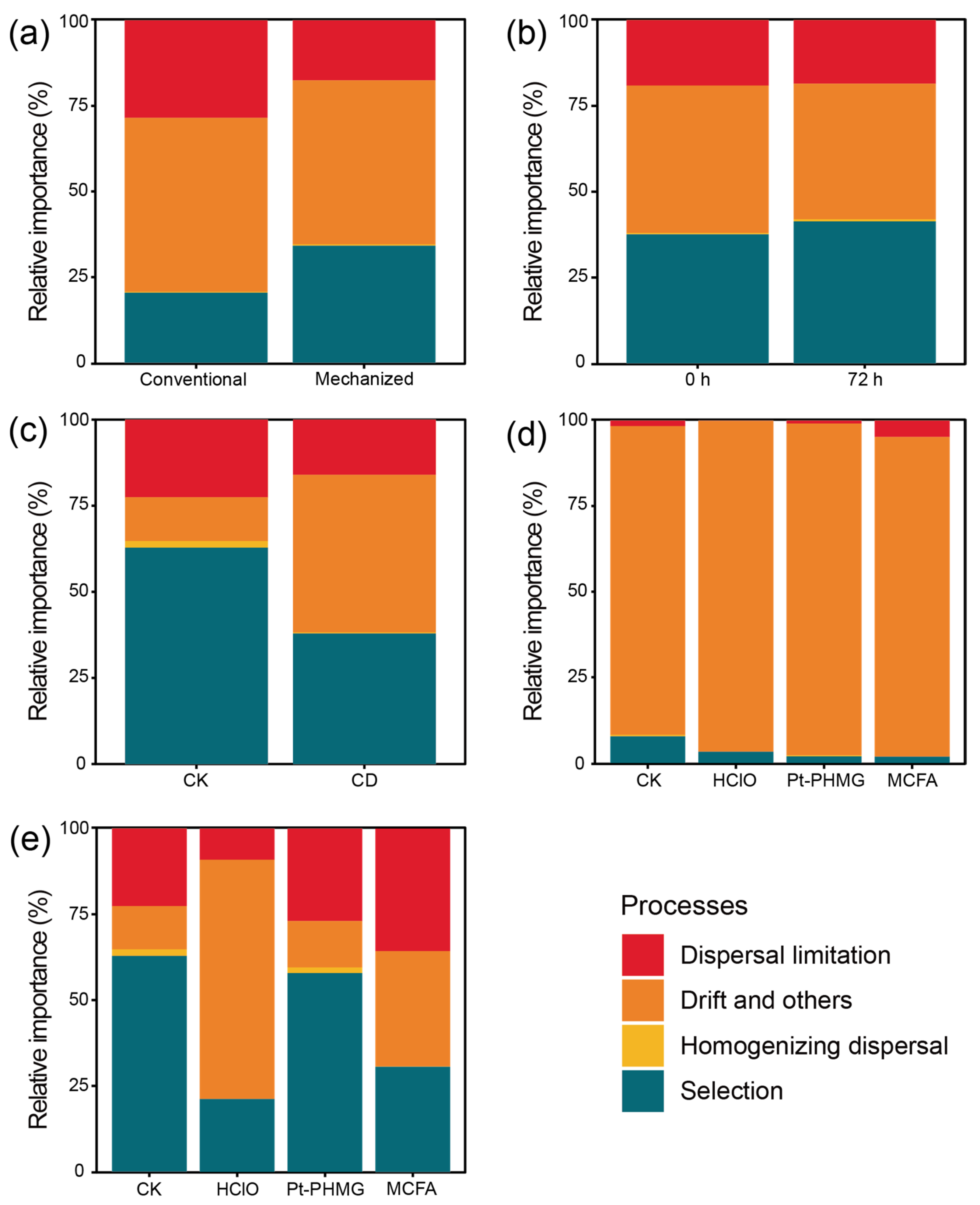
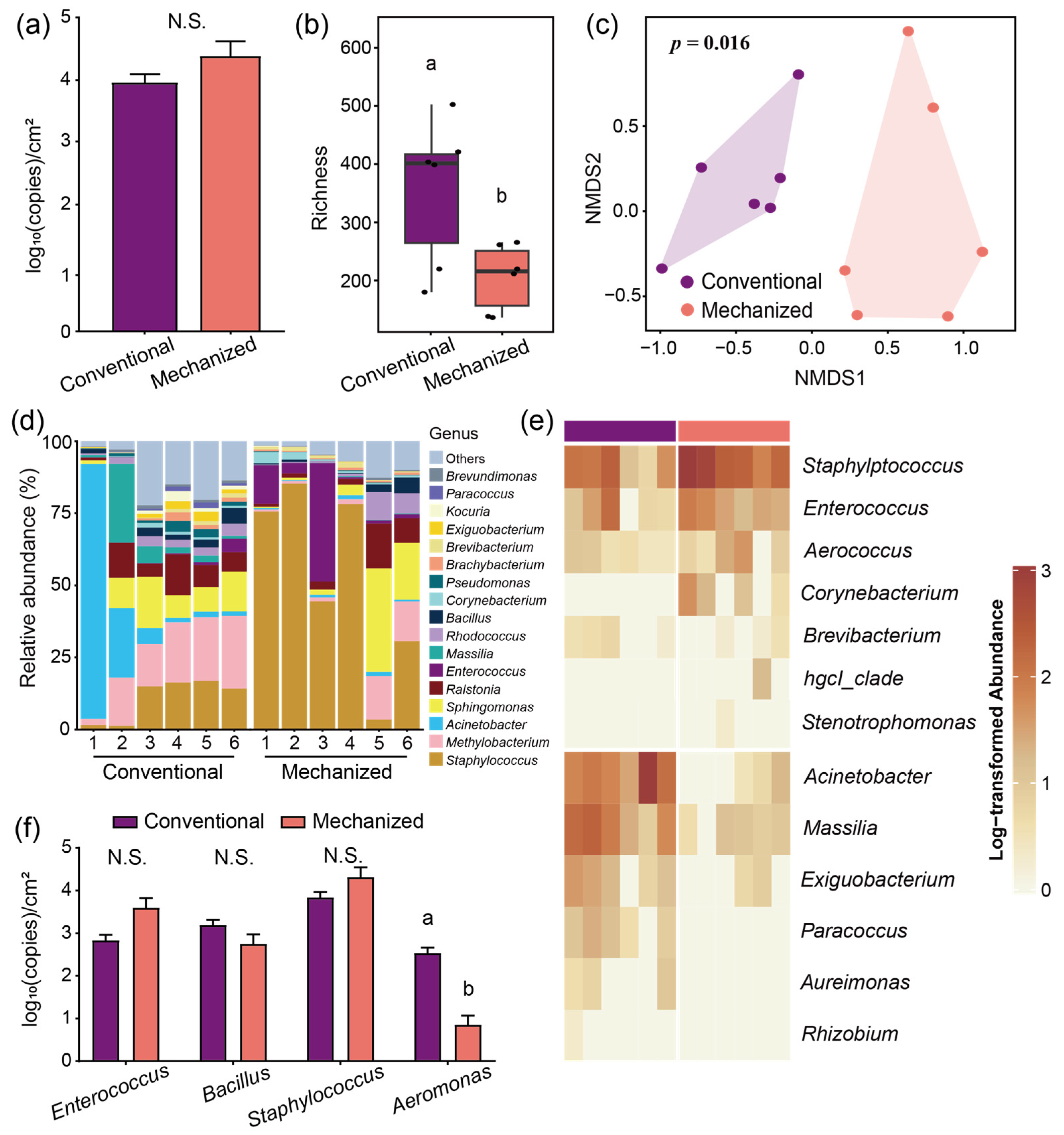
3.1. Environmental Microbiome Differences Between Conventional and Mechanized Silkworm Rearing
3.2. The Bacterial Community Structure Is Stable in the Mechanized Silkworm-Rearing Environment
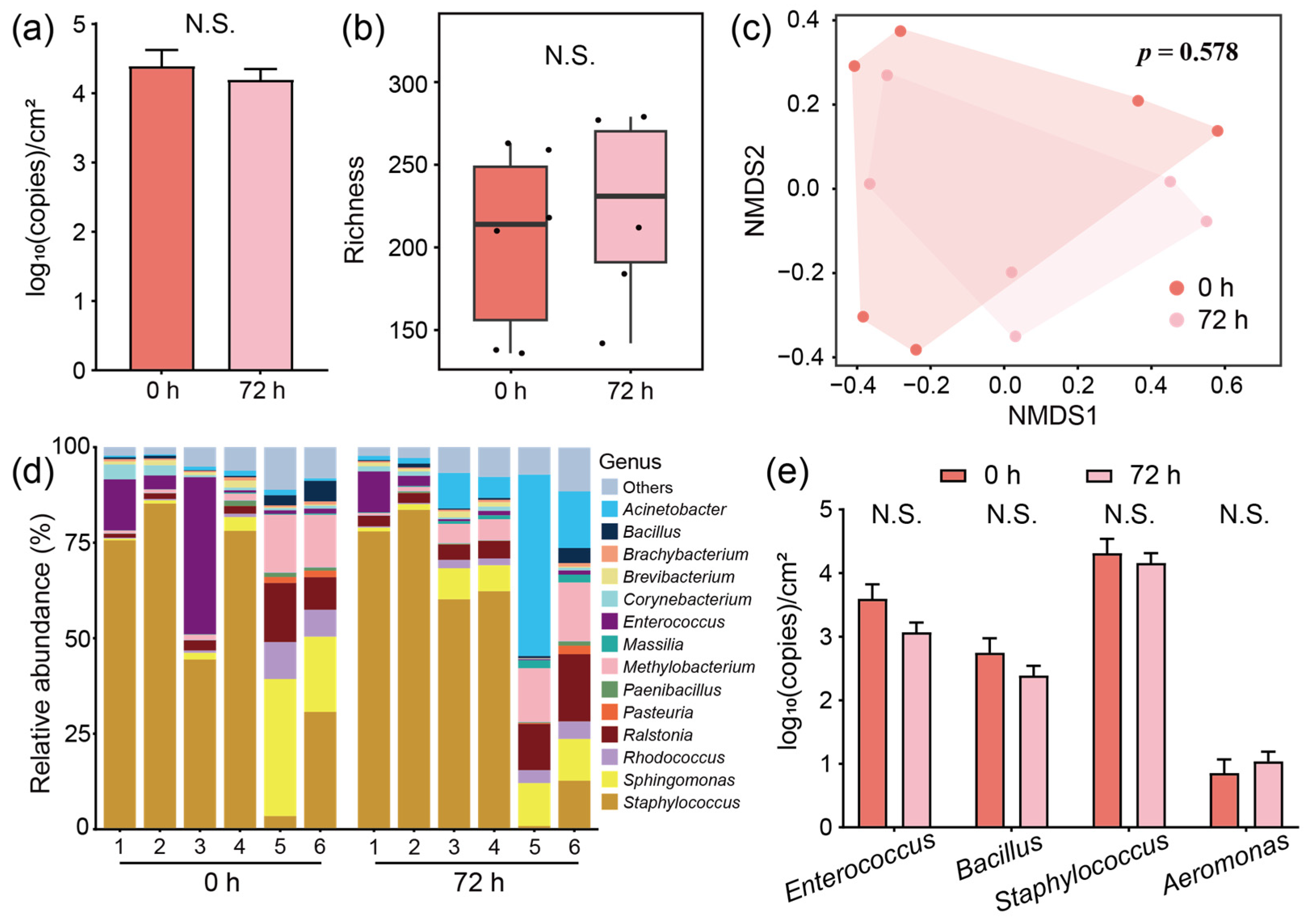
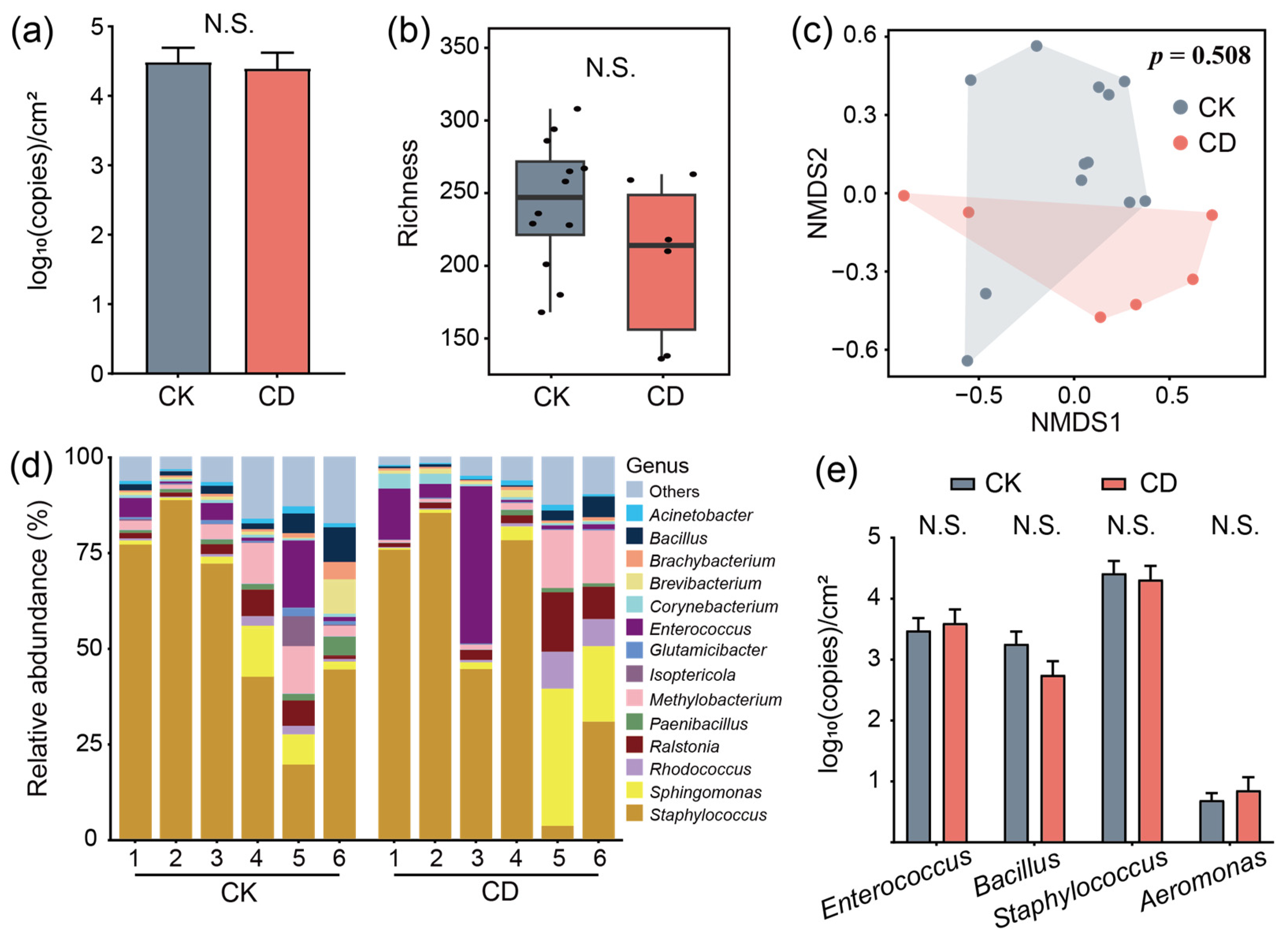
3.3. Only Small Bacterial Changes Occur After Conventional Disinfection Is Applied in the Mechanized Silkworm-Rearing Environment
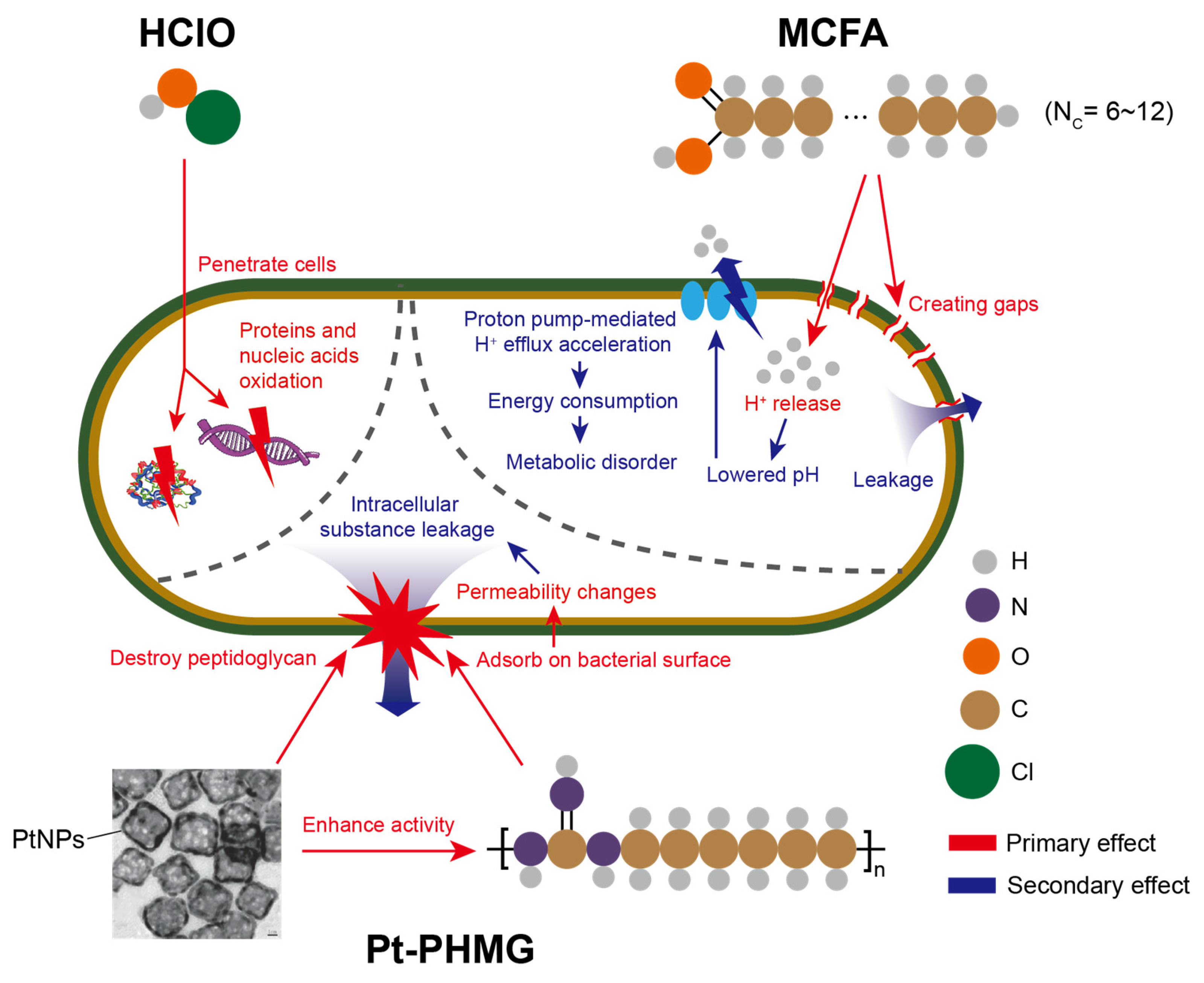
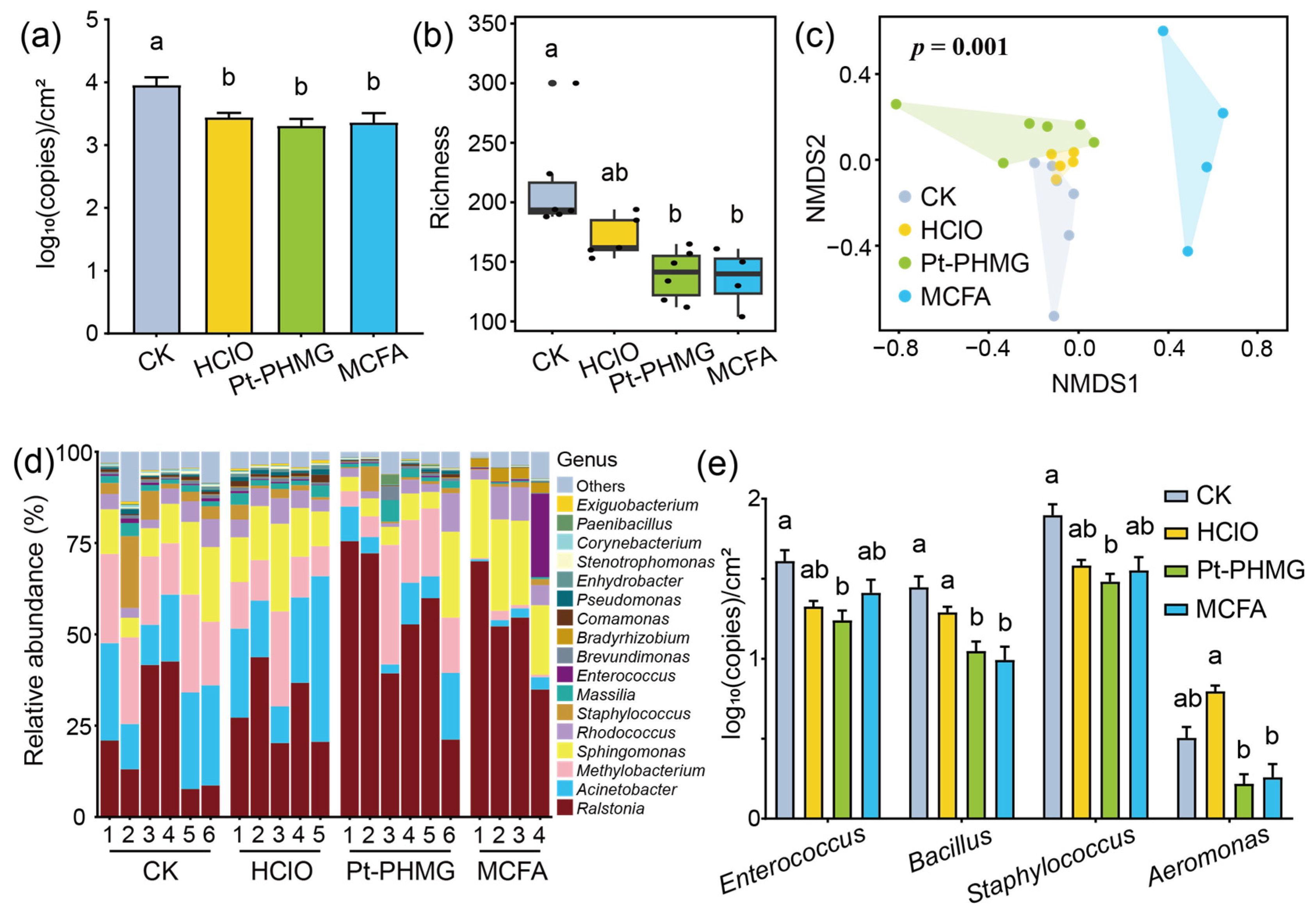
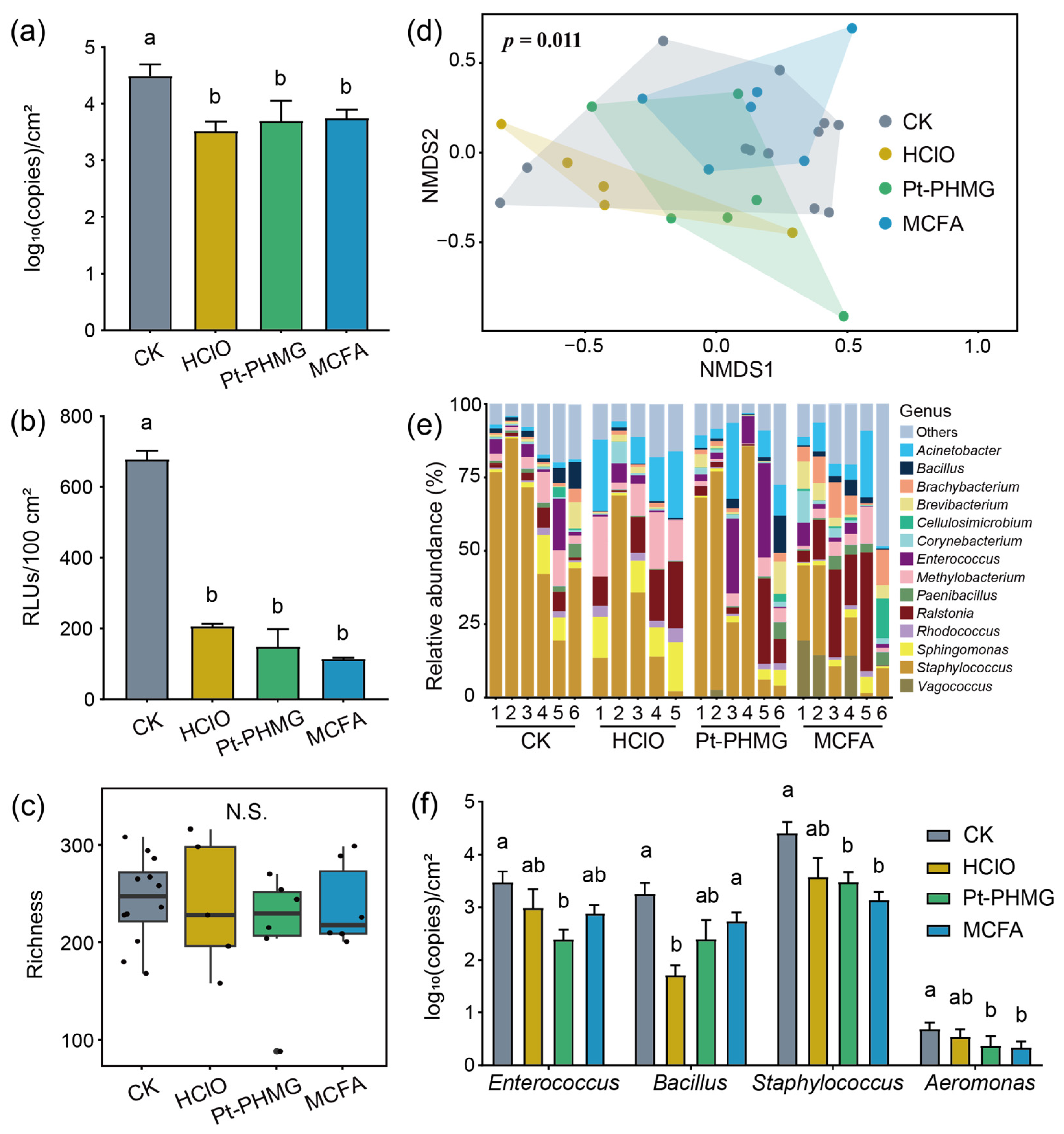
3.4. The Effect of Three Disinfectants Used in Mechanized Silkworm Rearing
3.5. The Performance of Three Disinfectants After Mechanized Mass Silkworm Rearing
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Code Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Meng, X.; Zhu, F.; Chen, K. Silkworm: A Promising Model Organism in Life Science. J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Brogan, E.N.; Park, Y.L.; Matak, K.E.; Jaczynski, J. Characterization of protein in cricket (Acheta domesticus), locust (Locusta migratoria), and silk worm pupae (Bombyx mori) insect powders. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, A.K.; Kalita, U. Human consumption of insects. Science 2023, 379, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malematja, E.; Manyelo, T.G.; Sebola, N.A.; Kolobe, S.D.; Mabelebele, M. The accumulation of heavy metals in feeder insects and their impact on animal production. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat, A.; Biswas, T.; Cardoso, M.H.; Mondal, R.; Ghosh, A.; Dam, P.; Nesa, J.; Chakraborty, J.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Franco, O.L.; et al. Silkworm pupae as a future food with nutritional and medicinal benefits. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 44, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Huang, M.; Xu, Y.; Mu, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, A.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Enzymatic hydrolysis of silkworm pupa and its allergenicity evaluation by animal model with different immunization routes. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, K.; Velickovic, T.C.; Liu, Z. Nutritional, functional, and allergenic properties of silkworm pupae. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4655–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzoli, F.; Antonelli, P.; Saviane, A.; Tassoni, L.; Cappellozza, S.; Belluco, S. Bombyx mori from a food safety perspective: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, L.; Belluco, S.; Marzoli, F.; Contiero, B.; Cremasco, S.; Saviane, A.; Cappellozza, S.; Dalle Zotte, A. Microbiological safety assessment of silkworm farms: A case study. Animal 2024, 18, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, L.; Cappellozza, S.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Belluco, S.; Antonelli, P.; Marzoli, F.; Saviane, A. Nutritional Composition of Bombyx mori Pupae: A Systematic Review. Insects 2022, 13, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, N.; He, J.; Xiao, J.; Shen, X.; Muhammad, A.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y. Fitness effects of synthetic and natural diet preservatives on the edible insect Bombyx mori. npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, K.; Cunfer, G. An Unremembered Diversity: Mixed Husbandry and the American Grasslands. Agric. Hist. 2009, 83, 352–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhemachena, C.; Matchaya, G.; Nhlengethwa, S.; Nhemachena, C.R. Exploring ways to increase public investments in agricultural water management and irrigation for improved agricultural productivity in Southern Africa. Water SA 2018, 44, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, F.; Chen, K. The Mechanisms of Silkworm Resistance to the Baculovirus and Antiviral Breeding. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Xia, H.; Chen, K. Molecular mechanism and potential application of bacterial infection in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 131, 104381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. Actuality and Application of Veterinary Drug for Silkworm Rearing. Bull. Seric. 2009, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Kang, G.; Wu, H.; Sun, B.; Luo, J. Present situation and prospect of veterinary drugs used by silkworm. China Seric. 2014, 35, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, H.A.L.; Fiuza, S.M.; Henriques, C.A.; Antunes, F.E. Antiviral and antibacterial activity of hand sanitizer and surface disinfectant formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, N.J.; Kremer, T.; McDonnell, G. A review of Spaulding’s classification system for effective cleaning, disinfection and sterilization of reusable medical devices: Viewed through a modern-day lens that will inform and enable future sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutala, W.A.; Donskey, C.J.; Weber, D.J. Disinfection and sterilization: New technologies. Am. J. Infect. Control 2023, 51, A13–A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, B.; Xu, M. Dual-Response Ratiometric Electrochemical Microsensor for Effective Simultaneous Monitoring of Hypochlorous Acid and Ascorbic Acid in Human Body Fluids. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15079–15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Moore, D.R.; Jackson, P.L.; Barnes, S.; Lambeth, J.D.; Thannickal, V.J.; Cheng, G. Microbicidal activity of vascular peroxidase 1 in human plasma via generation of hypochlorous acid. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2528–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Experimental study on germicidal properties and metal corrosion of weakly acidic hypochlorite disinfectant. Prev. Med. Trib. 2014, 20, 691–692. [Google Scholar]
- Tenzin, S.; Ogunniyi, A.D.; Khazandi, M.; Ferro, S.; Bartsch, J.; Crabb, S.; Abraham, S.; Deo, P.; Trott, D.J. Decontamination of aerosolised bacteria from a pig farm environment using a pH neutral electrochemically activated solution (Ecas4 anolyte). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, K.; Nazir, S.; Ahmad, A.; Li, B.; Khan, A.U.; Khan, Z.U.; Khan, F.U.; Khan, Q.U.; Khan, A.; Rahman, A.U. Facile and green synthesis of phytochemicals capped platinum nanoparticles and in vitro their superior antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 166, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Hu, R.; Tang, J.; Lv, J.; Xiao, H.; Tan, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Organic Fluorophores with Large Stokes Shift for the Visualization of Rapid Protein and Nucleic Acid Assays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, e202318800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ying, Z.; Luo, Q.; Du, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yan, S.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, W. Poly(hexamethylene guanidine)-based hydrogels with long lasting antimicrobial activity and low toxicity. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Weng, Y. Development of antifouling antibacterial polylactic acid (PLA)-based packaging and application for chicken meat preservation. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, R.; Shen, J.; Hao, Q.; Brash, J.L.; Chen, H. Optimizing the Bacteriostatic and Cytocompatibility Properties of Poly(hexamethylene guanidine) Hydrochloride (PHMG) via the Guanidine/Alkane Ratio. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Qian, W.; Luo, G.; Xia, H. Polyurethane-modified graphene oxide composite bilayer wound dressing with long-lasting antibacterial effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.S.K. Preparation and application of a new type of caged nano-platinum. NTNP China 2021, 1, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Skrivanova, E.; Molatova, Z.; Skrivanova, V.; Marounek, M. Inhibitory activity of rabbit milk and medium-chain fatty acids against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O128. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suiryanrayna, M.V.; Ramana, J.V. A review of the effects of dietary organic acids fed to swine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.; Mohan, S.V.; Chang, Y.C. Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFA) Production Through Anaerobic Fermentation Using Clostridium kluyveri: Effect of Ethanol and Acetate. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Osorio, L.M.; Yepes-Medina, V.; Ballou, A.; Parini, M.; Angel, R. Short and Medium Chain Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives as a Natural Strategy in the Control of Necrotic Enteritis and Microbial Homeostasis in Broiler Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 773372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, R.N.; Hernandez Franco, J.F.; Hogenesch, H.; Dennis, T.S.; Cowles, K.E.; Boerman, J.P. Effect of medium-chain fatty acids on growth, health, and immune response of dairy calves. J. Dairy. Sci. 2022, 105, 7738–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; He, J.; Shen, X.; Sun, C.; Muhammad, A.; Shao, Y. Contribution of sample processing to gut microbiome analysis in the model Lepidoptera, silkworm Bombyx mori. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, T.; Shen, X.; Zhang, N.; Sun, C.; Lu, S.; Shao, Y. Primer selection impacts the evaluation of microecological patterns in environmental microbiomes. iMeta 2023, 2, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, N.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y. Smartphones as an Ecological Niche of Microorganisms: Microbial Activities, Assembly, and Opportunistic Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01508–e01522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Zhang, N.; He, J.; Shen, X.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, J.; Qian, Z.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y. Multiomics analysis reveals the molecular basis for increased body weight in silkworms (Bombyx mori) exposed to environmental concentrations of polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 57, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Du, K.; Sun, C.; Vimalanathan, A.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, X.; Li, L.; Shao, Y. Gut bacterial and fungal communities of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori) and wild mulberry-feeding relatives. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkurt, E.; Fritscher, J.; Soranzo, N.; Ng, D.Y.K.; Davey, R.P.; Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F. LotuS2: An ultrafast and highly accurate tool for amplicon sequencing analysis. Microbiome 2022, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; He, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Lei, X.; Sun, C.; Muhammad, A.; Shao, Y. Assessing the quality and eco-beneficial microbes in the use of silkworm excrement compost. Waste Manag. 2024, 183, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qian, Z.; He, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, X.; Sun, C.; Fan, J.; Felton, G.W.; Shao, Y. Gut bacteria of lepidopteran herbivores facilitate digestion of plant toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2412165121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslova, O.; Mindlin, S.; Beletsky, A.; Mardanov, A.; Petrova, M. Plasmids as Key Players in Acinetobacter Adaptation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, T.L.; Rupp, M.E.; Fey, P.D. Staphylococcus epidermidis. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X. Bacterial disease occurrence and pathogen isolation and identification of BmNPV pressure selected strains in silkworm (Bombyx mori). J. South. Agric. 2023, 54, 3388–3395. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, N.; Sun, S.; Zhu, M.; Pan, J.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Response to Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infection in silkworm: Gut metabolites and microbiota. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 125, 104227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Mason, C.J.; Felton, G.W. Toward an Integrated Understanding of the Lepidoptera Microbiome. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2024, 69, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashora, K.; Roy, S.; Nagpal, A.; Roy, S.M.; Flood, J.; Prasad, A.K.; Khetarpal, R.; Neave, S.; Muraleedharan, N. Pest management through Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) in a tea-silkworm ecosystem: Status and potential prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Tao, Y.; Liu, S.; Long, Z. Identification of a Pathogenic Strain of Bombyx mori and its Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2006, 22, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.L.; Shaw, J.G. Aeromonas spp. clinical microbiology and disease. J. Infect. 2011, 62, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.Z.; Wee, W.; Mohamad, S.S.A.; Che, H.H.; Hanif, R.M.F.; Irwan, K.M.; Van, D.H.; Wen, G.K.; Seong, W.L. Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: A mini-review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1023784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, P.R.B.; Oliveira, W.F.; Marques, D.S.C.; Dos, S.C.M.T.; de Carvalho, E.; Coelho, L. The genus Aeromonas: A general approach. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauzere, C.; Moletta-Denat, M.; Blanquart, H.; Ferreira, S.; Moularat, S.; Godon, J.J.; Robine, E. Stability of airborne microbes in the Louvre Museum over time. Indoor Air 2014, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela, A.; Kokkonen, E.; Kulmala, I.; Veijalainen, A.M.; van Houdt, R.; Leys, N.; Berthier, A.; Viacheslav, I.; Kharin, S.; Morozova, J.; et al. Production and characterization of bioaerosols for model validation in spacecraft environment. J. Environ. Sci 2018, 69, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnert, A.; Haratani, M.; Schmuck, M.; Berg, G. Enriching Beneficial Microbial Diversity of Indoor Plants and Their Surrounding Built Environment with Biostimulants. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arata, C.; Misztal, P.K.; Tian, Y.; Lunderberg, D.M.; Kristensen, K.; Novoselac, A.; Vance, M.E.; Farmer, D.K.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Goldstein, A.H. Volatile organic compound emissions during HOMEChem. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 2099–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, R.J.; Watts, M.; Vale, J.A.; Grieve, J.R.; Schep, L.J. The clinical toxicology of sodium hypochlorite. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovska, N.; Stefanovska, V.V.; Babulovska, A.; Pereska, Z.; Jurukov, I.; Berat-Huseini, A.; Kostadinovski, K.; Naumovski, K. Ingestion of corrosive substances and the endoscopic role in assessing the severity of caustic injury. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2023, 18, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Q.; Suresh, P.; Roy, S.; White, J.F.; Mazzeo, A.D. Paper-based plasma sanitizers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5119–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, M.E. Can Environmental RNA Revolutionize Biodiversity Science? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyntz-Wright, I.P.; Harrison, X.A.; Pedersen, S.; Tyler, C.R. Effectiveness of eDNA for monitoring riverine macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Hartikainen, H.; Jokela, J.; Bertuzzo, E.; Rinaldo, A. Estimating species distribution and abundance in river networks using environmental DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11724–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shogren, A.J.; Tank, J.L.; Andruszkiewicz, E.; Olds, B.; Mahon, A.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Bolster, D. Controls on eDNA movement in streams: Transport, Retention, and Resuspension. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Biessy, L.; Latchford, J.L.; Zaiko, A.; von Ammon, U.; Audrezet, F.; Cristescu, M.E.; Pochon, X. Release and degradation of environmental DNA and RNA in a marine system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkaria, B.D.; Fedorec, A.J.H.; Barnes, C.P. Automated design of synthetic microbial communities. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagg, C.; Hautier, Y.; Pellkofer, S.; Banerjee, S.; Schmid, B.; van der Heijden, M.G. Diversity and asynchrony in soil microbial communities stabilizes ecosystem functioning. eLife 2021, 10, e62813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| 27F | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG |
| 1492R | GGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
| 515modF | GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA |
| 806modR | GGACTACHV GGGTWTCTAAT |
| DB200F | CGGYCCAGACTCCTACGGG |
| DB200R | TTACCGCGGCTGCTGGCAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, Z.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y. Sericulture Mechanization Poses New Challenges for Environmental Disinfection—Evaluating the Effects of Three Newly Introduced Disinfectants. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050143
Zhu X, Xiao J, Li Y, Lei X, Zhang H, Qian Z, Sun C, Shao Y. Sericulture Mechanization Poses New Challenges for Environmental Disinfection—Evaluating the Effects of Three Newly Introduced Disinfectants. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(5):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050143
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xinyue, Jian Xiao, Yu Li, Xiaoyu Lei, Huarui Zhang, Zhaoyi Qian, Chao Sun, and Yongqi Shao. 2025. "Sericulture Mechanization Poses New Challenges for Environmental Disinfection—Evaluating the Effects of Three Newly Introduced Disinfectants" AgriEngineering 7, no. 5: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050143
APA StyleZhu, X., Xiao, J., Li, Y., Lei, X., Zhang, H., Qian, Z., Sun, C., & Shao, Y. (2025). Sericulture Mechanization Poses New Challenges for Environmental Disinfection—Evaluating the Effects of Three Newly Introduced Disinfectants. AgriEngineering, 7(5), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050143







