Evaluation of the Incidence of Mineral Fertilizer Entrapment in Organic Matrix of Residual Biosolids, Cellulose and Sawdust in Maize (Zea mays) Crop
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions and Design
2.2. Preparation of Organic Matrix Entrapped NPK Fertilizer
2.3. Measurement of Biomass Growth and Nutrient Assimilation of Maize (Zea mays) Cultivated in Pots
2.4. Statistical Treatment of Nutrient Release Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Supporting Material
3.2. Characterization of the Occluded Fertilizers
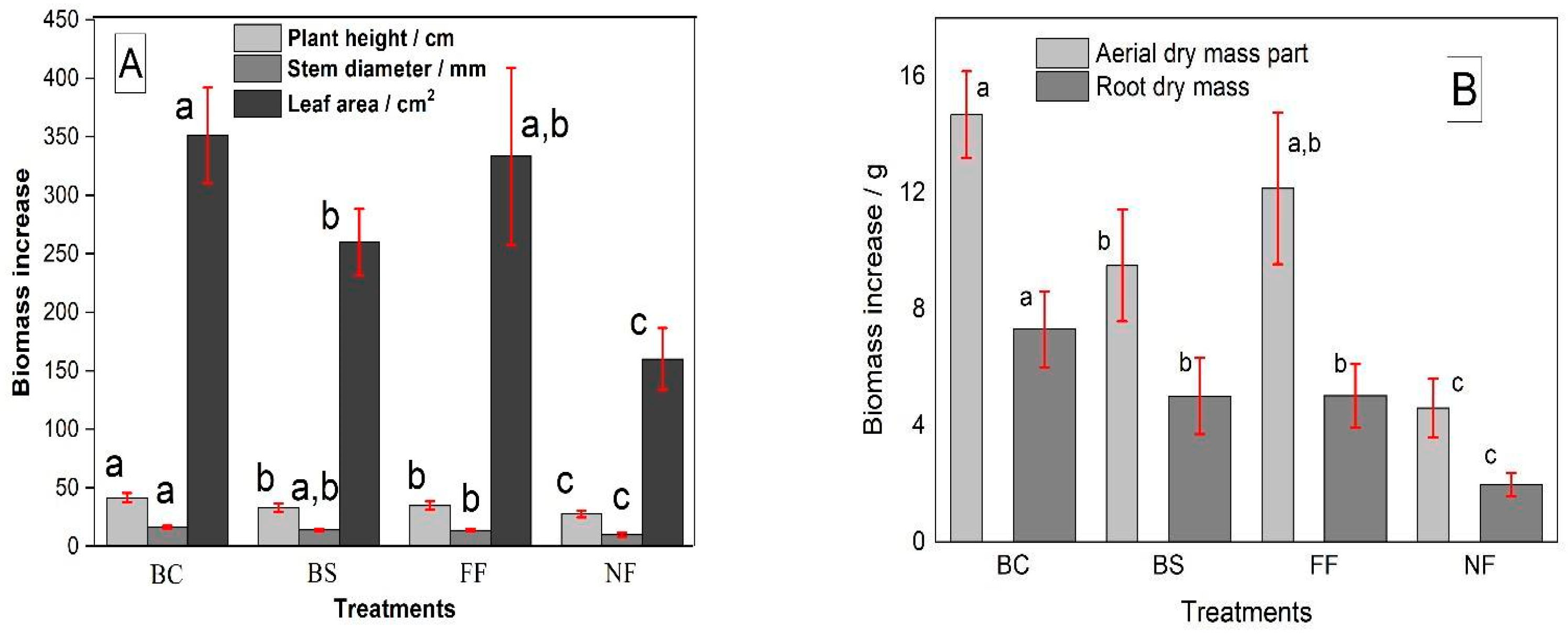
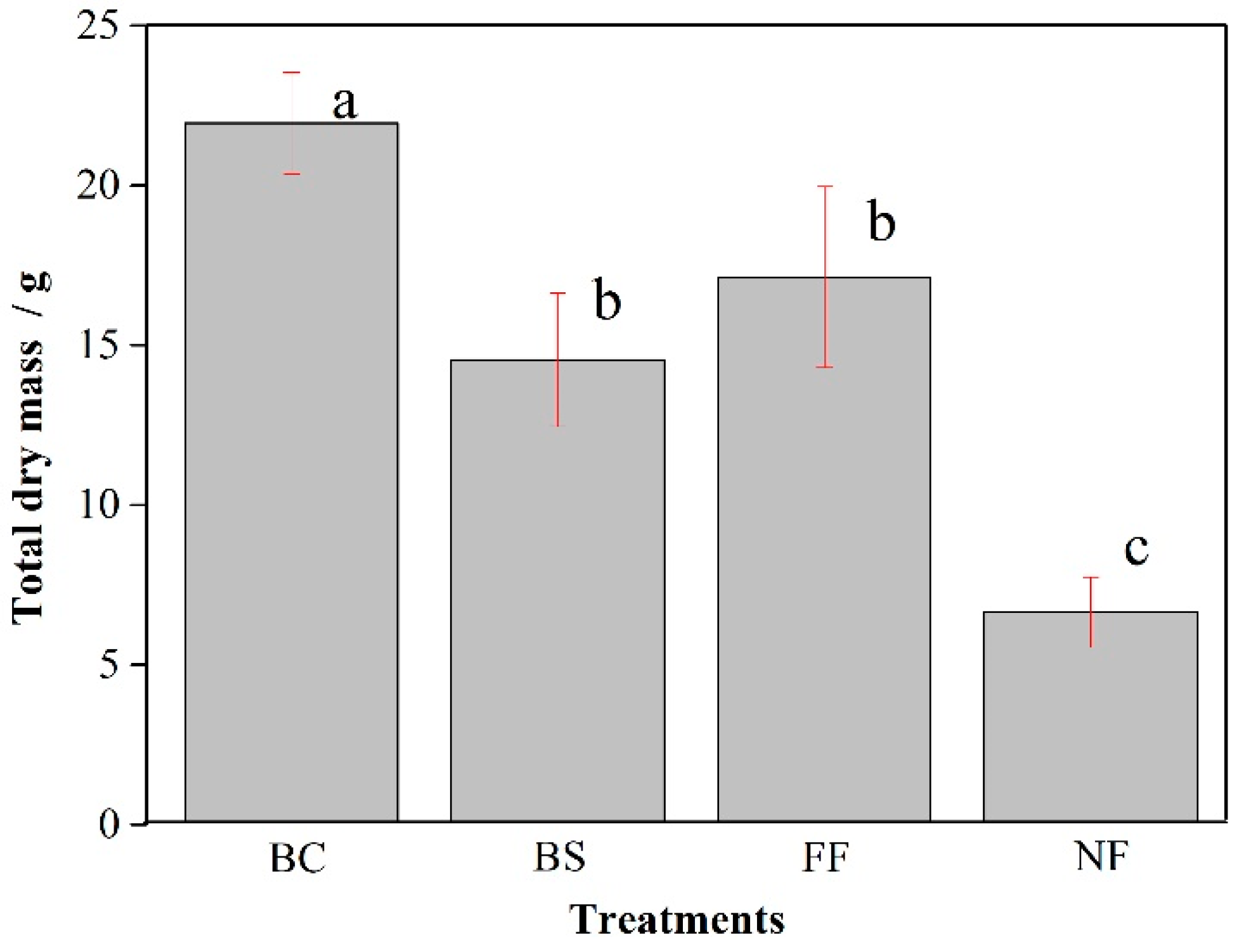
3.3. Biomass Growth of Maize (Zea mays), Under Uncoated NPK and Ma-Trix-Based OMF Treatments
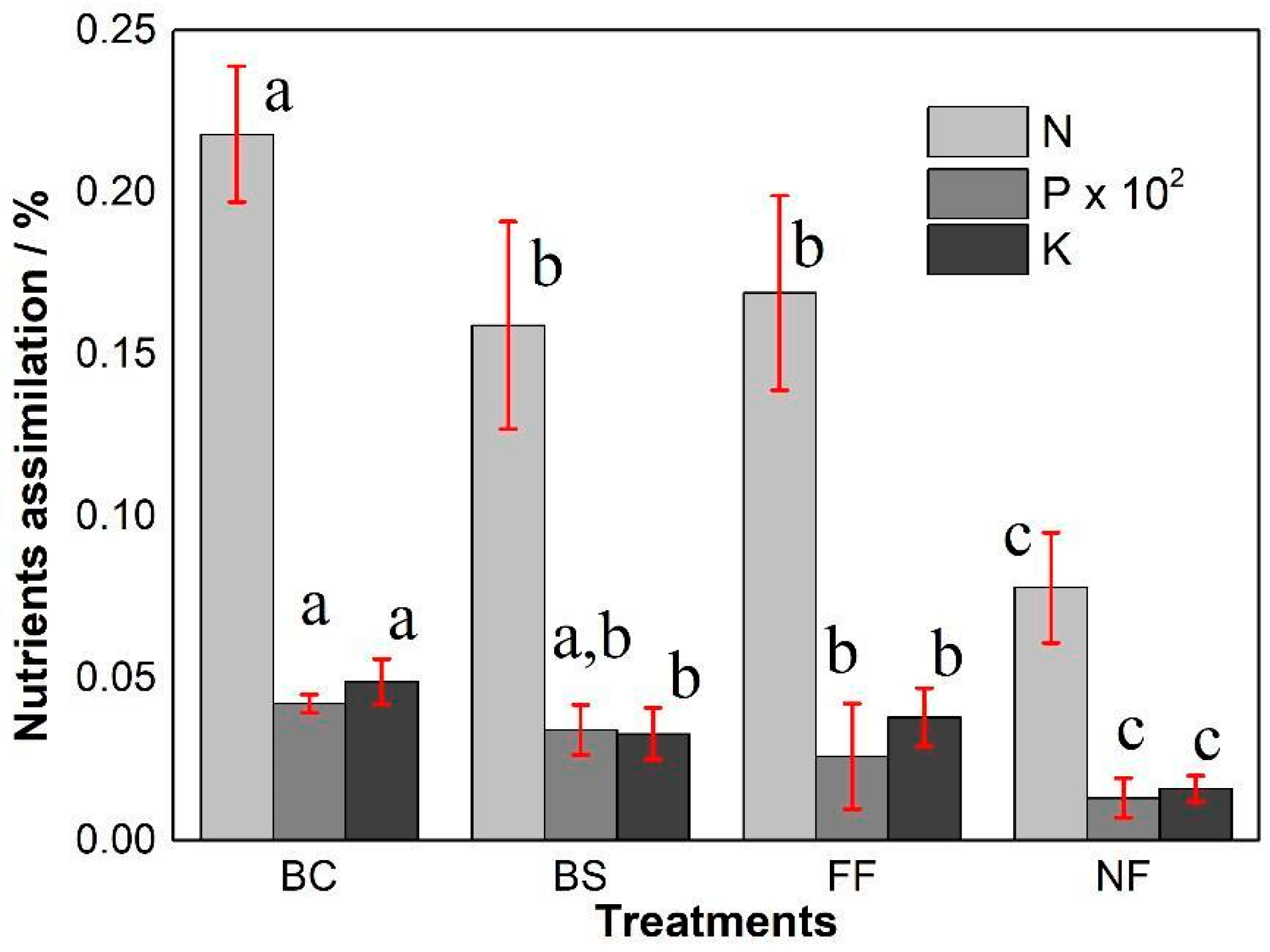
3.4. Nutrient Assimilation in Maize (Zea mays), Under Uncoated NPK and Ma-Trix-Based OMF Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbrev. | Meaning |
| dw | dry-weight basis |
| OM | organic matter |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| TKN | total Kjeldahl nitrogen |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| AAS/FAAS | (Flame) atomic absorption spectrometry |
| CEC | cation-exchange capacity |
| WRC | water-retention capacity (used consistently; replaces legacy CRA) |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SRF | slow-release fertilizer |
| F | uncoated (mineral) fertilizer |
| FOMI/FOMII | functionalized organic matrices I/II |
| LOD/LOQ | limit of detection/quantification |
| CI | confidence interval |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Margulis, M.E.; Hopewell, K.; Qereshniku, E. Food, famine and the free trade fallacy: The dangers of market fundamentalism in an era of climate emergency. J. Peasant. Stud. 2023, 50, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Coello, F.; Sardans, J. A better use of fertilisers is needed for global food security and environmental sustainability. Agric. Food Secur. 2023, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sagasti, M.T.; Alkorta, I.; Becerril, J.M.; Epelde, L.; Anza, M.; Garbisu, C. Microbial monitoring of the recovery of soil quality during heavy metal phytoremediation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, K.; Xuan, T.D.; Noori, Z.; Aryan, S.; Gulab, G. Effects of organic and inorganic fertiliser application on growth, yield, and grain quality of rice. Agriculture 2020, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.N.; Luo, J.H.; Su, C.L.; Wu, X.F.; Zhao, M. Reduced inorganic fertiliser in combination with an alkaline humic acid fertiliser amendment on acid growth media properties and cherry tomato growth. N. Z. J. Crop. Hortic. Sci. 2021, 49, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Giri, A. Swelling dynamics of a macromolecular hydrophilic network and evaluation of its potential for controlled release of agrochemicals. React. Funct. Polym. 2002, 53, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegat, S.; Ledo, A.; Tirado, R. Greenhouse gas emissions from global production and use of nitrogen synthetic fertilisers in agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusin, F.M.; Akhir, N.I.M.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Awang, M. The impact of nitrogen fertiliser use on greenhouse gas emissions in an oil palm plantation associated with land use change. Atmosfera 2015, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Qu, N.; Jiang, Q.; Han, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, T.; Liang, D.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, Z. Preparation and properties of multifunctional eco- friendly slow-release urea fertiliser encapsulated by diatomite filter aid waste-based superabsorbent. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 183, 107747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, C. Encapsulation and characterization of slow-release microbial fertiliser from the composites of bentonite and alginate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 109–110, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Jiang, S.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Song, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, L. Fabrication, evaluation methodologies and models of slow-release fertilisers: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Liu, M. Preparation and properties of coated nitrogen fertiliser with slow release and water retention. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8610–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Channab, B.E.; Zahouily, M. A comprehensive review on starch: Structure, modification, and applications in slow/controlled-release fertilisers in agriculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M.; Jarosiewicz, A.; Karakulski, K. Physical and chemical characteristics of polymer coatings in CRF formulation. Desalination 2002, 146, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Lewis, T.D. Development of fertilisers for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency—Trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, K.; Selby-Pham, J.; Simovich, T.; Gill, H. Enhancement of capsicum (Capsicum annuum L.) functional food value through nutrient supplementation with a biostimulant complex comprising triacontanol, phosphate, and potassium. N. Z. J. Crop. Hortic. Sci. 2023, 53, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantigny, M.H. Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: A review on the influence of land use and management practices. Geoderma 2003, 113, 357–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabi-Floody, M.; Medina, J.; Rumpel, C.; Condron, L.M.; Hernandez, M.; Dumont, M.; de la Luz Mora, M. Smart fertilisers as a strategy for sustainable agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2018, 147, 119–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.; Sridharan, A.; Philip, J. Influence of dielectric constant of pore fluids on double-layer swelling: A validation study. Indian Geotech. J. 2022, 52, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, B.S.; Sari, G.L.; Rosmalina, R.T.; Effendi, A.J.; Hadrah. An overview of electrokinetic soil flushing and its effect on bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Gunn, S.K.; Rotz, C.A.; Karsten, H.; Roth, G.; Buda, A.; Stoner, A.M.K.; Rutherford, S. Projected climate and agronomic implications for maize production in the Northeastern United States. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTC 5167; Productos Orgánicos Utilizados Como Abonos o Fertilizantes y Enmiendas de Suelos. Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación (ICONTEC): Bogotá, Colombia, 2011.
- EN 13037:2011; Soil Improvers and Growing Media—Determination of pH. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. Available online: https://www.cen.eu/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO 14235:1998; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic Carbon by Sulfochromic Oxidation (Walkley–Black). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO 11261:1995; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Modified Kjeldahl Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO 6878:2004; Water Quality—Determination of Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Method 3111: Metals by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.standardmethods.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ISO/TS 22171:2023; Soil Quality—Determination of Potential Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) and Exchangeable Cations Buffered at pH 7, Using a Molar Ammonium Acetate Solution. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Gungula, D.T.; Andrew, F.P.; Joseph, J.; Kareem, S.A.; Barminas, J.T.; Adebayo, E.F.; Saddiq, A.M.; Tame, V.T.; Dere, I.; Ahinda, W.J.; et al. Formulation and characterization of water retention and slow-release urea fertiliser based on Borassus aethiopum starch and Maesopsis eminii hydrogels. Results Mater. 2021, 12, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 18644:2016; Fertilizers and Soil Conditioners—Controlled-Release Fertilizer—General Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 4831:2006; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Coliforms—Most Probable Number Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Jechalke, S.; Schierstaedt, J.; Becker, M.; Flemer, B.; Grosch, R.; Smalla, K.; Schikora, A. Salmonella establishment in agricultural soil and colonization of crop plants depend on soil type and plant species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturin, L.; Peeler, J.T. Aerobic Plate Count. In Bacteriological Analytical Manual; US Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, L.K.; Chaney, K.; Murray, C.; Sakrabani, R.; Gedara, S.; Le, M.S.; Tyrrel, S.; Pawlett, M.; Read, R.; Smith, G.H. A new sludge-derived organo-mineral fertiliser gives similar crop yields as conventional fertilisers. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.A. Simple microdetermination of Kjeldahl nitrogen in biological materials. Anal. Chem. 1958, 30, 1692–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA 530-R-99-009; Biosolids Generation, Use and Disposal in the United States. United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Yaganza, E.S.; Tweddell, R.J.; Arul, J. Osmotic stress, crenation and death of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica caused by inorganic salts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4659–4665. [Google Scholar]
- Shatruk, M.; Avendano, C.; Dunbar, K.R. Cyanide-Bridged Complexes of Transition Metals: A Molecular Magnetism Perspective. Prog. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 56, 171–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebube, N.K.; Jones, A.B. Sustained release of acetaminophen from a heterogeneous mixture of two hydrophilic non-ionic cellulose ether polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 272, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, D.M.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Kazmi, A.A. Assessment of compost maturity-stability indices and recent development of composting bin. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, V.; Muñiz, G.; Celzard, A.; Furdin, G. Activation of delignified cellulosic material by heat treatment and its application for the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Filiatrault, M.; D’Acremont, L.; Gendron, R.; Laroche, G. Delignified lignocellulosic fibres as promising carriers for controlled release of biomolecules. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Charge distribution and diffuse double layer in a membrane filtration system: A theoretical and experimental study. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 574, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, C.; Opp, C. Ecologically relevant phosphorus pools in soils and their dynamics: The story so far. Geoderma 2018, 325, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhami, D.; McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M. Role of organic anions and phosphatase enzymes in phosphorus acquisition in the rhizospheres of legumes and grasses grown in a low phosphorus pasture soil. Plants 2020, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Giles, C.; Darch, T.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.; Stutter, M.; Shand, C.; Lumsdon, D.; Cooper, P.; Wendler, R.; et al. Opportunities for mobilizing recalcitrant phosphorus from agricultural soils: A review. Plant and Soil. 2018, 427, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiliyagodage, C.; Jayanetti, M.; Mendis, A.; Ekanayake, G.; Liyanaarachchi, H.; Vigneswaran, S. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Applications—A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.; Man, Z.B.; Basit, A.; Thanh, T.H. Review on materials and techniques for controlled release fertiliser. J. Control. Release 2014, 181, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Khadiran, T.; Abdullah, R.; Ahmad, N. Controlled release fertiliser: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, W. Ammonia volatilization losses from a rice paddy with different irrigation and nitrogen managements. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled release fertilisers: A review on coating materials and mechanism of release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Gao, L.; Kong, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J. Ammonia volatilization losses from urea application influenced by rice straw biochar. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 525–533. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aziz, H.M.M.; Hasaneen, M.N.A.; Omer, A.M. Nano chitosan-NPK fertilizer enhances the growth and productivity of wheat plants grown in sandy soil. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 14, e0902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, C.; Li, F. Long-term effects of organic manure and inorganic fertilisation on sustainability and chemical soil quality indicators of soybean–wheat cropping system in the Indian mid- Himalayas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest, M.H.; Beauchamp, C.J. Composting of de-inking paper sludge with poultry manure at three nitrogen levels using mechanical turning: Behavior of physico-chemical parameters. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 81, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gea, T.; Barrena, R.; Artola, A.; Sánchez, A. Monitoring the biological activity of the composting process: Oxygen uptake rate (OUR), respirometric index (RI), and respiratory quotient (RQ). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzmann, T.J.; Sica, P.; Zavattaro, L.; Moretti, B.; Grignani, C.; Oberson, A. An isotope study on nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiency and movement in agricultural systems. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2024, 7, e20473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disciglio, G.; Tarantino, A.; Frabboni, L. Yield and fruit characteristics of tomato crops grown with mineral macronutrients: Impact of organo-mineral ferti-lizers through foliar or soil applications. Plants 2024, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao Ch Naik, M.R.; Naorem, A.; Chandana, M.; Baral, K. Organo-mineral fertilizers for sustainable agriculture. Indian J. Fert. 2024, 20, 366–383. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, C.; Giannetta, B.; Fernández, J.M.; López-de-Sa, E.G.; Polo, A.; Gascó, G.; Méndez, A.; Zaccone, C.; Shotbolt, L.; Fernández-Getino, A.M.; et al. Soil organic matter: A key player in soil quality and a major constraint for global food security. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Long-term application of an organo-mineral fertiliser improves soil microbial community structure and enzyme activities in a maize cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108398. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 5.2 |
| Phosphorus, mg dm−3 | 12 |
| Sulfur (S), mg dm−3 | 3 |
| Calcium (Ca), mmol dm−3 | 16 |
| Magnesium (Mg), mmol dm−3 | 5 |
| Sodium (Na), mmol dm−3 | N.D. |
| Potassium (K), mmol dm−3 | 1.4 |
| Aluminum (Al)mmol dm−3 | N.D. |
| Organic matter (OM) g dm−3 | 14 |
| Cation exchange (CEC) meq 100 g−1 | 40.3 |
| Base saturation, % | 45 |
| Iron (Fe2O3), hematite g kg−1 | 192 |
| Density, g dm−3 | 1.2 |
| Treatment | Composition | Dose per 5.5-dm3 pot (g) | Application Schedule (Day After Sowing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC Cellulose/biosolids/fertilizer | (1:1) 2.0 g 4-14-8 NPK + 2.0 g cellulose/biosolids matrix | 4.0 g formulation | 4 × 1.0 g tablets, Day 0 |
| BS Sawdust/biosolids/fertilizer | (1:1) 2.0 g 4-14-8 NPK + 2.0 g sawdust/biosolids matrix | 4.0 g formulation | 4 × 1.0 g tablets, Day 0 |
| FF (Free Fertilizer) | NPK 4-14-8 (no matrix) | 4.0 g NPK fertilizer (no matrix) | 2 × 1.0 g tablets, Day 0 + 2 × 1.0 g tablets, Day 30 |
| NF (No Fertilizer) | Oxisol only | N.D. | N.D. |
| Parameter | Biosolids | Cellulose | Sawdust |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total nitrogen (N)% | 2.46 ± 0.88 | 0.38 ± 0.50 | 0.14 ± 0.25 |
| Total phosphorus (P2O5), % | 2.10 ± 1.29 | 0.46 ± 0.98 | 0.20 ± 0.1 |
| Total potassium (K2O), % | 0.64 ± 0.65 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Water retention capacity (WRC), % | 112.50 ± 0.03 | 264 ± 0.08 | 1.91 ± 0.09 |
| Cation exchange (CEC), meq 100 g−1 | 35.27 ± 2.03 | 9.31 ± 0.04 | 69.7 ± 0.07 |
| Humidity (H), % | 59.66 ± 0.58 | 55.60 ± 0.05 | 59.4 ± 0.03 |
| pH | 7.01 ± 0.48 | 7.73 ± 0.03 | 5.91 ± 0.07 |
| Electric conductivity (EC), dS m−1 | 4.76 ± 0.17 | 0.02 ± 0.12 | 7.10 ± 0.017 |
| Organic matter (OM), % | 14.64 ± 2.22 | 22.90 ± 1.20 | 46.9 ± 1.02 |
| Ashes, % | 64.01 ± 2.88 | 42 ± 0.03 | 15.5 ± 0.09 |
| Carbon nitrogen ratio C/N,% | 6.68 ± 3.20 | 67 ± 0.06 | 72.80 ± 0.08 |
| Density, g cm−3 | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ± 0.008 | 0.19 ± 0.02 |
| Microbiological parameter | |||
| Mesophiles CFU g−1 | 9.48 × 1010 | 1.3 × 109 | 3.3 × 1010 |
| Thermophiles CFU g−1 | 4.52 × 108 | 8.8 × 108 | 8.0 × 107 |
| Enterobacteria CFU g−1 | 1.0 × 105 | 2.0 × 101 | 2.5 × 101 |
| Salmonella sp. (absent in 25 g) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Metals | |||
| Na% | 0.17± 0.10 | N.D. | N.D. |
| CaO% | 3.78 ± 0.317 | 9.12 ± 0.02 | N.D. |
| MgO% | 0.56 ± 0.31 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | N.D. |
| Zn, ppm | 0.39 ± 0.27 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cr, ppm | 381.57 ± 3.0 | 55.18 ± 0.35 | N.D. |
| Cd, ppm | 2.72 ± 2.51 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Pb, ppm | 36.98 ± 2.22 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Ni, ppm | 149.38 ± 2.88 | 11.71 ± 0.77 | N.D. |
| As, ppm | 0.18 ± 3.20 | 16.51 ± 0.67 | N.D. |
| Parameter | BC/NPK | BS/NPK |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.7 | 6.6 |
| Organic matter (OM), % | 17.4 | 10 |
| Cation exchange (CEC) meq 100 g−1 | 82.6 | 76.8 |
| Water retention capacity (WRC) | 205 | 138.5 |
| Carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N) | 13.80 | 7.54 |
| Total nitrogen (N), (%) | 4 | 4 |
| Phosphorus (P), (%) | 14 | 14 |
| Potassium (K), % | 8 | 8 |
| Enterobacteria CFU g−1 | 9.5 × 102 | 2.2 × 102 |
| Mesophiles CFU g−1 | 2.5 × 106 | 6.4 × 108 |
| Thermophiles CFU g−1 | 2.4 × 1010 | 7.5 × 108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palacios, R.R.; Melo, W.J.; Rocha, A.M.S.; Araújo, A.S.F.; Restrepo-Sánchez, N.; Jaramillo, C.A.P. Evaluation of the Incidence of Mineral Fertilizer Entrapment in Organic Matrix of Residual Biosolids, Cellulose and Sawdust in Maize (Zea mays) Crop. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7100343
Palacios RR, Melo WJ, Rocha AMS, Araújo ASF, Restrepo-Sánchez N, Jaramillo CAP. Evaluation of the Incidence of Mineral Fertilizer Entrapment in Organic Matrix of Residual Biosolids, Cellulose and Sawdust in Maize (Zea mays) Crop. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(10):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7100343
Chicago/Turabian StylePalacios, Rodrigo Ramírez, Wanderley José Melo, Antonio Mauricio Souza Rocha, Ademir Sérgio Ferreira Araújo, Nora Restrepo-Sánchez, and Carlos Alberto Peláez Jaramillo. 2025. "Evaluation of the Incidence of Mineral Fertilizer Entrapment in Organic Matrix of Residual Biosolids, Cellulose and Sawdust in Maize (Zea mays) Crop" AgriEngineering 7, no. 10: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7100343
APA StylePalacios, R. R., Melo, W. J., Rocha, A. M. S., Araújo, A. S. F., Restrepo-Sánchez, N., & Jaramillo, C. A. P. (2025). Evaluation of the Incidence of Mineral Fertilizer Entrapment in Organic Matrix of Residual Biosolids, Cellulose and Sawdust in Maize (Zea mays) Crop. AgriEngineering, 7(10), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7100343






