Unlocking Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Local Governments: Best Practice Lessons from Real-World Implementations
Highlights
- Local governments extensively utilize artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to enhance their diverse array of administrative and operational tasks.
- Despite the availability of numerous AI technologies, only eight of them are actively utilized within local governments, with Natural Language Processing being the most prevalent.
- Developing robust policies is crucial for effectively leveraging responsible adoption and utilization of AI technologies in local government services.
- Local governments engaging with stakeholders and communities ensure that AI technologies are effectively tailored to meet local preferences.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Background
3. Research Design
3.1. Criteria Identification
3.2. Document Search
3.3. Document Filtering
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. General Observations
4.2. AI Technology and Service Distribution
4.2.1. Natural Language Processing in Local Governments
- ▪
- Removing language barriers—Phoenix Council, US, utilises the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lex chatbot to create a conversation interface in both English and Spanish [101];
- ▪
- Freeing up human time from performing repetitive boring tasks—Lewes and Eastbourne Council in the UK employ ELLIS, which covers over 1000 council topics and which was trained on 12,000 resident questions. It has already enabled the relocation of 5 full-time contact agents away from live chat to focus on more complicated tasks [102];
- ▪
- Connecting residents to city council services 24 h a day—the Public Relations Office within the Municipality of Grosseto in Italy implemented digital functions to enhance communication between residents and the administration. A virtual assistant is available 24/7 to guide residents through online procedures and assist with problem solving [103];
- ▪
- Enhancing wide-scale customer experience—the municipalities of Kortrijk, Tournai, and Roubaix collaborated to create the free Tripster chat tourism service, an overarching approach to promoting cross-border tourism and making it more accessible to everyone [104].
4.2.2. Neural Networks in Local Governments
- ▪
- Mapping ideal locations for electric vehicle charging points—implemented by Irving Municipality in the US [107];
- ▪
- Junction improvements—undertaken by Lancashire County Council in the UK [108];
- ▪
- Determining the safest route—implemented by Los Angeles City Council in the US [109];
- ▪
- Assisting citizens in emergency situations such as bridge collapse—utilised by Atlanta City Council, US [110];
- ▪
- Analysing traffic patterns of different mode of transportation—implemented by Kansas City Council in the US [111];
- ▪
- Navigating parking systems—utilised by Hangzhou Municipality [112], among others.
- ▪
- Moreover, NNs have also been utilised for safety and security, including the following:
- ▪
- Predicting crime locations—Chicago Municipality adopted a model to predict when and where violent crimes are likely to occur. The former mayor Rahm Emanuel announced in early 2018 that gun violence was down 25% compared to the previous year [113];
- ▪
- Predicting child abuse—implemented by Hackney Council in the UK [114];
- ▪
- Safeguarding against cybersecurity issues—utilised by Gilbert Town Council in the US [115];
- ▪
- Identifying and addressing anti-social behaviours—undertaken by Sunderland City Council in the UK [116].
4.2.3. Robotic Process Automation in Local Governments
- ▪
- Payslip account management, including a council’s payslip archiving system—implemented by Surrey County Council in the UK [130];
- ▪
- Management of financial assistance processing—undertaken by Strängnäs Municipality in Sweden [131];
- ▪
- Validation of Blue Badge applications and invoice processing—managed by Cumbria County Council, UK [132];
- ▪
- Financial auditing and risk management mitigation—Liverpool City Council, Australia [133];
- ▪
- Mileage calculations and value added tax (VAT) calculations—handled by Gloucestershire County Council [134].
4.2.4. Computer Vision in Local Governments
4.2.5. Other AI Technologies in Local Governments
5. Findings and Discussion
5.1. Why Have NLP and RPA Gained Popularity in Local Governments, and How Can These Technologies Address Specific Challenges?
5.2. Which Service Areas Are Most Affected by AI Technology in Local Governments, and How Does AI Improve the Efficiency in These Service Areas?
5.3. Why Do Public Safety and Law Enforcement Get Less Attention for Local Government AI Applications?
5.4. Why Do Different Local Governments Use Different AI Systems?
5.5. What Are the Key Challenges, Future Impacts, and Trends?
- Policy framework: Establishing a robust policy framework is essential for guiding the ethical deployment and responsible use of AI technologies within local governments [156]. By defining policies that uphold responsible ethical principles of transparency, fairness, equity, and inclusivity, etc, local governments can ensure that AI systems enhance public trust and serve community interests effectively [215].
- Capacity building: The deployment of AI technologies requires a workforce with specialised skills, not only in terms of recruiting new talent but also in training existing employees to operate and manage these advanced systems competently [84,224]. This need for skill development may represent a time-intensive and financially demanding undertaking, adding to the complexity of adopting AI in local government. It underscores the importance of investing in human capital development alongside technological infrastructure to ensure the successful deployment and sustainable functioning of AI solutions within local government contexts.
- Financial support: Securing adequate financial support is pivotal for the successful implementation and sustainability of AI projects within local governments. Financial resources are needed to invest in AI infrastructure, software licenses, data storage solutions, and ongoing maintenance costs [84,90]. Local governments can explore various funding mechanisms, including public–private partnerships, grants, and budget allocations earmarked for digital transformation initiatives. This can achieve long-term cost savings, while meeting community needs effectively [224].
- Stakeholder collaboration: Collaboration with technology vendors, academic institutions, research organisations, and other government agencies is essential for accessing the expertise and resources necessary for successful AI implementation [90]. Partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange, innovation, and the co-creation of AI solutions tailored to local government challenges and objectives. Collaborative initiatives can involve joint research projects, shared data repositories, and collaborative platforms for testing and scaling AI applications [208].
- Monitoring and evaluation: Implementing the monitoring and evaluation mechanisms is critical for assessing the impact and effectiveness of AI initiatives within local governments [29]. Monitoring involves tracking key performance indicators, such as operational efficiencies, cost savings, and citizen satisfaction metrics, to measure the success of AI deployments [33]. Regular evaluation allows local governments to identify areas for improvement, address challenges proactively, and optimize AI systems based on real-world outcomes and feedback.
- Pilot projects: Conducting pilot projects provides local governments with valuable insights into the feasibility, scalability, and potential impact of AI technologies in real-world settings [225]. Pilot initiatives allow for the iterative testing and refinement of AI solutions before full-scale implementation, mitigating risks and optimising resource allocation [226].
- Data governance: Establishing data governance frameworks is essential for ensuring the quality, integrity, and ethical use of data in AI-driven initiatives within local governments [215]. Effective data governance involves defining policies and procedures for data collection, storage, sharing, and access control. It also includes implementing data management practices that uphold privacy regulations, promote data security, and mitigate risks associated with data breaches or misuse [29,156].
- Regulatory compliance: Compliance requirements may include data protection regulations, stakeholder-specific guidelines, and ethical standards for AI development and deployment, etc [158,159]. Local governments must stay abreast of evolving regulatory frameworks and adapt AI strategies and practices accordingly, to mitigate legal risks and ensure adherence to compliance obligations [207,217]. By proactively addressing regulatory considerations, local governments can foster a regulatory environment conducive to responsible AI innovation, while safeguarding public trust and upholding legal standards.
5.6. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Local Government AI Use Cases
| AI Technology | Local Government | Country | General Service | Sub-Service | Year | URL |
| “Inductive logic programming” | California cities | US | Transportation and urban planning | Building regulations | 2019 | “http://logicprogramming.stanford.edu/readings/symbium.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Sea Girt | US | Transportation and urban planning | Building regulations | 2018 | “https://www.govpilot.com/blog/robotic-process-automation-for-local-governments/ (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Norfolk County Council | UK | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2021 | “https://www.blueprism.com/resources/case-studies/norfolk-county-council-enhances-citizens-experience-with-a-digital-workforce/ (accessed on 21 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Brent Council | UK | Transportation and urban planning | Housing services | 2018 | “https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/brent-council-uk-government-rpa (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Surrey County Council | UK | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2018 | “https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/surrey-county-council-improves-employee-experience-with-automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Municipality of Strängnäs | Sweden | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2019 | “https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/strangnas-municipality-government-rpa (accessed on 12 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Municipality of Copenhagen | Denmark | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2015 | “https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/copenhagen-municipality-enterprise-rpa#:~:text=Copenhagen%20has%20deployed%20its%20first,the%20information%20retrieval%20and%20reconciliation (accessed on 12 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Sefton Council | UK | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2015 | “https://www.arvato.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Arvato_UK_rpa_public_sector_whitepaper_updated.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Sefton Council | UK | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2015 | |
| “Robotic process automation” | North Tyneside Council | UK | Transportation and urban planning | Housing services | 2017 | “https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/robots-deliver-award-winning-customer-service-in-north-tyneside/ (accessed on 24 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | North Tyneside Council | UK | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2017 | |
| “Robotic process automation” | Cumbria County Council | UK | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2022 | “https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/automation-as-a-weapon-in-local-government-s-new-battles/ (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Cumbria County Council | UK | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | |
| “Robotic process automation” | Willoughby Council | Australia | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Willoughby Council | Australia | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2020 | “https://www.governmentnews.com.au/type_contributors/dexter-the-robot-improving-customer-experience/ (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | San Francisco Municipality | San Francisco | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2023 | “https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/ (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | City Council of Geneva | Switzerland | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2021 | “https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/#:~:text=Further%2C%20the%20City%20Council%20of,audit%20and%20risk%20management%20processes (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Liverpool City Council | Australia | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2023 | “https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/#:~:text=Further%2C%20the%20City%20Council%20of,audit%20and%20risk%20management%20processes (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Tasman Sea Hawke’s Bay Regional Council | New Zealand | Transportation and urban planning | Resident registry | 2020 | “https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Municipality of Frederiksberg | Denmark | Transportation and urban planning | Resident registry | 2020 | “https://www.fujitsu.com/global/imagesgig5/CS_2020Aug_Frederiksberg-Municipality.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Municipality of Frederiksberg | Denmark | Transportation and urban planning | Resident registry | 2023 | “https://www.fujitsu.com/global/imagesgig5/CS_2020Aug_Frederiksberg-Municipality.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Pecos | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Avondale | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Middlesbrough Council | England | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Burnaby | Canada | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Nottingham City Council | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Leeds City Council | England | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2016 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Glenelg | Australia | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Kingston | Australia | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Grand Forks | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Thurrock Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Gloucestershire County Council | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Porto Alegre | Brazil | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Sundsvall | Sweden | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Alcorcón City Council | Spain | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Norwich City Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Hamilton City Council | Canada | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Ronneby | Sweden | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Culiacán | Mexico | Transportation and urban planning | Planning application processing | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Tuscaloosa Municipality | USA | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Värmdö | Sweden | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Sunshine Coast | Australia | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Devonport | Australia | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Heinola | Finland | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Bellevue | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Tandridge District Council | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Blacktown | Australia | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Auckland | New Zearland | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | South Ayrshire Council | Scotland | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2020 | “https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/oct/28/nearly-half-of-councils-in-great-britain-use-algorithms-to-help-make-claims-decisions (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Erin | Canada | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Stratford | Australia | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/automation (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Brimbank City Council | Australia | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2023 | “https://apo.org.au/sites/default/files/resource-files/2023-08/apo-nid323811_0.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Kitchener | Canada | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2021 | “https://www.kitchener.ca/en/news/locally-made-robots-helping-city-staff-improve-kitchener-sidewalks.aspx (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Municipality of Rotterdam | Netherland | Transportation and urban planning | Building regulations | 2022 | “https://www.spotr.ai/customer-stories/rotterdam (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | City Council of A Western Australian | Australia | Healthcare and wellbeing | Leisure and recreation | 2021 | “https://www.integrasources.com/cases/computer-vision-sports-monitoring/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Helsingborg Municipality | Sweden | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://univrses.com/press-releases/computer-vision-helps-make-helsingborg-a-smarter-city/ (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Helsingborg Municipality | Sweden | Transportation and urban planning | Local road maintenance | 2021 | “https://univrses.com/press-releases/computer-vision-helps-make-helsingborg-a-smarter-city/ (accessed on 30 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Helsingborg Municipality | Sweden | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2021 | “https://univrses.com/press-releases/computer-vision-helps-make-helsingborg-a-smarter-city/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Tuscaloosa Municipality | USA | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://www.planning.org/publications/report/9270237/ (accessed on 12 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Seoul | South Korea | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2019 | “https://www.sparkcognition.com/artificial-intelligence-and-the-new-urban-infrastructure/ (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Tel-Aviv Municipality | Israel | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2019 | “https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/iot/articles/what-is-internet-of-everthing/ (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Las Vegas | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2021 | “https://governmenttechnologyinsider.com/whats-ahead-for-smart-cities/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality | South Africa | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2019 | “https://www.smec.com/au/insights/deploying-artificial-intelligence-for-underground-asset-condition-assessments/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Copenhagen City | Denmark | Environmental management | Local environmental issues | 2019 | “https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/smart-cities-computer-vision-technology-debiprasad-bandopadhyay/ (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Seoul | South Korea | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2019 | “https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/smart-cities-computer-vision-technology-debiprasad-bandopadhyay/ (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Singapore | Singapore | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2018 | “https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/smart-cities-computer-vision-technology-debiprasad-bandopadhyay/ (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Barcelona | Spain | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://www.wowza.com/blog/smart-city-trends (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Blackpool Council | England | Transportation and urban planning | Local road maintenance | 2020 | “https://www.government-transformation.com/data/local-authorities-achieving-results-with-ai-roll-outs (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | BCP Council of Bournemouth, Christchurch, and Poole | England | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “https://www.government-transformation.com/data/local-authorities-achieving-results-with-ai-roll-outs (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Milton Keynes | England | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2018 | “https://www.government-transformation.com/data/local-authorities-achieving-results-with-ai-roll-outs (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Barcelona | Spain | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2004 | “http://www.comune.torino.it/hops/documents/deliverables/brochure_A4_n1.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Turin Municipality | Italy | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2004 | “http://www.comune.torino.it/hops/documents/deliverables/brochure_A4_n1.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | London Borough of Camden | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2004 | “http://www.comune.torino.it/hops/documents/deliverables/brochure_A4_n1.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Beirut Municipality | Lebanon | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2010 | “https://medium.com/beirut-spring/beirut-municipality-website-uses-machine-translation-to-populate-english-and-french-pages-590ff54b502c (accessed on 6 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Wollongong City Council | Australia | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2022 | “https://wollongong.nsw.gov.au/about-google-translate (accessed on 6 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Swindon Council | England | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2019 | “https://cities-today.com/council-slashes-translation-costs-with-machine-learning/ (accessed on 6 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Municipality of Rimini | Italy | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://dt4regions.eu/dt-book/dt-stories/open-digital-assistant (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Phoenix Municipality | USA | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Williamsburg | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Singapore | Singapore | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2014 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kawasaki | Japan | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kawasaki | Japan | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kakegawa City | Japan | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kolkata | India | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kakegawa City | Japan | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Boston | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Derby City Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Cabarrus County | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Los Angeles | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Ronneby | Sweden | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/stories/ten-local-government-chatbots-that-are-making-a-difference (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | San Antonio | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Leisure and recreation | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Fairfield | USA | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Derby City Council | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Stirling | Scotland | Healthcare and wellbeing | Leisure and recreation | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Coral Gables | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Atlanta | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Virginia Beach | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Nottingham City Council | England | Environmental management | Local environmental issues | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kelowna | Canada | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Buenos Aires | Argentina | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Hamilton City Council | Canada | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kawasaki | Japan | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kawasaki | Japan | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Phoenix Municipality | USA | Administrative services | Community services—Interpretation | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Singapore | Singapore | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Telford And Wrekin Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Library maintenance | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/projects/telford-and-wrekin-council-add-three-new-services-thanks-to-tom-their-ai-assistant (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Telford and Wrekin Council | England | Transportation and urban planning | Housing services | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/projects/telford-and-wrekin-council-add-three-new-services-thanks-to-tom-their-ai-assistant (accessed on 30 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Telford and Wrekin Council | England | Transportation and urban planning | Resident registry | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/projects/telford-and-wrekin-council-add-three-new-services-thanks-to-tom-their-ai-assistant (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Lewes and Eastbourne Council | England | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Frankston | Australia | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Leeds City Council | England | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Monmouthshire County Council | England | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Grosseto | Italy | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Treviso | Italy | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Ronneby | Sweden | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Mendoza | Argentina | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kortrijk | Belgium | Healthcare and wellbeing | Leisure and recreation | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Boston | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Devonport | Australia | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Houston | USA | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | London Borough of Redbridge | London | Transportation and urban planning | Planning application processing | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kuusamo | Finland | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Markham | Canada | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Buenos Aires | Argentina | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Markham | Canada | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Buenos Aires | Argentina | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | New Orleans | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2019 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Mogi Das Cruzes | Brazil | Transportation and urban planning | Resident registry | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Sydney | Australia | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Trollhättan | Sweden | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Delta | Canada | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Manningham | Australia | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Sønderborg | Denmark | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Vantaa | Finland | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Duisburg | Germany | Healthcare and wellbeing | Burial grounds and electric crematorium | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Varberg | Sweden | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Hamilton City Council | New Zealand | Administrative services | Community feedback | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Järvenpää | Finland | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Tilburg | Netherlands | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Porvoo | Finland | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Borås | Sweden | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Pori | Finland | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Greater Sudbury | Canada | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Knoxville | USA | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kelowna | Canada | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Maribyrnong | Australia | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Dallas | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Adelaide | Australia | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Adelaide | Australia | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Adelaide | Australia | Healthcare and wellbeing | Library maintenance | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Bellevue | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Goldsboro | USA | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Portland | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Arun District Council | England | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Derby City Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Aberdeen City Council | Scotland | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Williamsburg | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Johns Creek | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Ottawa | Canada | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2019 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Austin | USA | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Johns Creek | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Los Angeles | USA | Administrative services | Back-office work | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | North Charleston | USA | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Kansas City | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Henderson | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2019 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Johns Creek | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Virginia Beach | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Albuquerque | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2017 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Williamsburg | USA | Administrative services | Information management | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | Gilbert | USA | Administrative services | Community feedback | 2018 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/chatbots (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Natural language processing” | San Jose | USA | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2020 | “https://www.govtech.com/opinion/how-ai-helps-state-and-local-governments-work-smarter (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Chicago’s Local Government | USA | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2018 | “https://d3.harvard.edu/platform-rctom/submission/smarter-cities-how-machine-learning-can-improve-municipal-services-in-chicago/ (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Cartagena, Medellin, and Monteria | Colombia | Administrative services | Community feedback | 2020 | “https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/08955f48-en/index.html?itemId=/content/component/08955f48-en (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Los Angeles | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Housing services | 2018 | “https://www.govtech.com/opinion/how-ai-helps-state-and-local-governments-work-smarter (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | North Tyneside Council | England | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2021 | “https://www.theguardian.com/society/2019/oct/15/councils-using-algorithms-make-welfare-decisions-benefits (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Hackney Council | England | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2021 | “https://www.theguardian.com/society/2019/oct/15/councils-using-algorithms-make-welfare-decisions-benefits (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Municipality of Amsterdam | Netherlands | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2022 | “https://www.xomnia.com/xomnia-supports-the-municipality-of-amsterdam-with-machine-learning-expertise/ (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | City of Ryde | Australia | Environmental management | Urban forestry | 2020 | “https://www.govtechreview.com.au/content/gov-tech-review-topics/white-paper/local-government-stays-green-with-machine-learning-783314431/preparing_download (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Swindon Borough Council | England | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Buffalo | USA | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Irving | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2023 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | East Lansing | USA | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Lancashire County Council | England | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | North Tyneside Council | England | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Aberdeen City Council | Scotland | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Gilbert | USA | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2019 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Sunderland City Council | England | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Sunderland City Council | England | Administrative services | Local tax collection | 2022 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Philadelphia | USA | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2021 | “https://govlaunch.com/collections/machine-learning (accessed on 21 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Los Angeles | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2022 | “https://ascend.thentia.com/process/applications-of-machine-learning-in-digital-government/ (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | City of Atlanta | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2017 | “https://ascend.thentia.com/process/applications-of-machine-learning-in-digital-government/ (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Kansas City | USA | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2017 | “https://ascend.thentia.com/process/applications-of-machine-learning-in-digital-government/ (accessed on 29 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Ogaki City | Japan | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/01/15/national/city-hall-gifu-prefecture-first-japan-deploy-autonomous-robots-aid-residents/ (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Pittsburgh | USA | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2016 | “https://www.automate.org/blogs/autonomous-robots-are-moving-from-below-the-streets-and-on-to-highways (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Upplands-Bro Municipality | Sweden | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2020 | “https://www.smartcitiesworld.net/news/swedish-municipality-deploys-robots-for-safer-recruitment-5251 (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Municipalities in Finland | Finland | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2016 | “https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1386505619300498?ref=pdf_downloadandfr=RR-2andrr=8381b903ac20a7ff (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Pune Municipality | India | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2022 | “https://ilougemedia.com/pune-municipal-corporation-introduces-advanced-robots-to-clean-manholes/ (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Bucher Municipality | Singapore | Transportation and urban planning | Local road maintenance | 2020 | “https://www.buchermunicipal.com/int/news/bucher-municipal-acquires-enway (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | London Borough | England | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2016 | “https://www.theguardian.com/public-leaders-network/2016/jul/04/robot-amelia-future-local-government-enfield-council (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Ku-ring-gai Council | Australia | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2019 | “https://www.climatechange.environment.nsw.gov.au/sites/default/files/2022-09/Simtable_modelling_toolKu-ring-gai_Council.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Hangzhou | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2019 | “https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/12/24/art_812262_59046787.html?eqid=f360863400062d0b000000026486e33e (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Hangzhou | China | Transportation and urban planning | Town planning | 2019 | “https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/12/24/art_812262_59046787.html?eqid=f360863400062d0b000000026486e33e (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Hangzhou | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2019 | “https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/12/24/art_812262_59046787.html?eqid=f360863400062d0b000000026486e33e (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Hangzhou | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Leisure and recreation | 2019 | “https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/12/24/art_812262_59046787.html?eqid=f360863400062d0b000000026486e33e (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Hangzhou | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2019 | “https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/12/24/art_812262_59046787.html?eqid=f360863400062d0b000000026486e33e (accessed on 27 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Hangzhou | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2016 | “http://www.cac.gov.cn/2018-11/27/c_1123771419.htm?isappinstalled=0 (accessed on 3 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Guiyang | China | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2018 | “http://www.cac.gov.cn/2018-11/27/c_1123771419.htm?isappinstalled=0 (accessed on 3 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Shenzhen | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2018 | “http://www.cac.gov.cn/2018-11/27/c_1123771419.htm?isappinstalled=0 (accessed on 3 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Shanghai | China | Administrative services | Community services—interpretation | 2018 | “https://www.sast.gov.cn/content.html?id=kjb228884 (accessed on 6 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Chengdu | China | Environmental management | River management | 2018 | “https://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10778/10876/2024/1/10/f30e99b8b89947b895a7399b114c3152.shtml (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Yanan | China | Transportation and urban planning | Planning application processing | 2018 | “http://www.cac.gov.cn/2018-06/03/c_1122925064.htm (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Guangzhou | China | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2019 | “http://www.cac.gov.cn/2019-10/25/c_1573534978283427.htm (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Wuhan | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2019 | “http://www.mod.gov.cn/gfbw/gfjy_index/zyhd/4852807.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Changsha | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Changsha | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Changsha | China | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2021 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Financial assistance and economic development | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 9 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Changsha | China | Public safety and law enforcement | meteorological services | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Changsha | China | Transportation and urban planning | Town planning | 2020 | “http://www.tianxin.gov.cn/zjtx23/ytx67/mtjj4/202006/t20200601_8156353.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Chongqing | China | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2020 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Chongqing | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2020 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Chongqing | China | Transportation and urban planning | Town planning | 2020 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Chongqing | China | Environmental management | Local environmental issues | 2020 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Chongqing | China | Transportation and urban planning | Town planning | 2020 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Huhehaote | China | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2020 | “https://zwfw.nmg.gov.cn/pub/fwzx/202012/t20201224_19302.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Chongqing | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “http://www.wz.gov.cn/zwxx_266/jdtp/202009/t20200917_7890266_wap.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Hangzhou | China | Environmental management | Water and sewerage services | 2021 | “http://www.linan.gov.cn/art/2021/10/19/art_1229601278_59061028.html (accessed on 26 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Hangzhou | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Pest control services | 2021 | “https://www.linan.gov.cn/art/2021/10/19/art_1229601278_59061028.html (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| Autonomous System | Anyang | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2021 | “https://dsj.henan.gov.cn/2021/09-26/2318831.html (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Guangzhou | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2022 | “https://www.hp.gov.cn/xwzx/mtxx/content/post_8663139.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Weihai | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “http://www.wendeng.gov.cn/art/2022/9/8/art_99344_2970189.html (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Beijing | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://www.bjtzh.gov.cn/bjtz/xxfb/202208/1610401.shtml (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Beijing | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2022 | “https://www.beijing.gov.cn/ywdt/gqrd/202203/t20220304_2622495.html (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Hanzhong | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2023 | “http://www.hanzhong.gov.cn/hzszf/xwzx/bmdt/202307/aa783e1c4a8f4f2d9f9a6b3abb5f735f.shtml (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Yinchuan | China | Administrative services | Community services—complaints | 2024 | “https://www.gov.cn/govweb/lianbo/difang/202401/content_6925551.htm (accessed on 22 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Jinan | China | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2022 | “http://www.jinan.gov.cn/art/2022/8/22/art_80993_4926510.html (accessed on 19 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Harbin | China | Transportation and urban planning | Permits granting and licensing | 2021 | “https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fgfg/dfxx/202109/t20210917_1296931.html (accessed on 17 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Jiaxin | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2020 | “https://www.jiaxing.gov.cn/art/2020/9/29/art_1685305_58831028.html (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shenzhen | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2017 | “http://ka.sz.gov.cn/ztzl/zt001/content/post_2291748.html (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Beijing | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2017 | “https://jtgl.beijing.gov.cn/jgj/jgxx/94246/95332/537586/index.html (accessed on 13 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shanghai | China | Environmental management | Maintaining public amenities | 2018 | “https://www.shwm.gov.cn/TrueCMS/shwmw/xyesdxzzsh/content/2d025728-f2d0-4980-87c7-a04db74ce82b.html (accessed on 13 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shanghai | China | Environmental management | River management | 2018 | “https://www.shwm.gov.cn/TrueCMS/shwmw/xyesdxzzsh/content/2d025728-f2d0-4980-87c7-a04db74ce82b.html (accessed on 12 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shenzhen | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2019 | “http://wjw.sz.gov.cn/ztzl/ygsn/cxal/content/post_3119990.html (accessed on 23 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Shenzhen | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2019 | “http://jtys.sz.gov.cn/zwgk/ztzl/msss/2019wcr/mrhd/content/post_4205133.html (accessed on 29 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shenzhen | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2020 | “http://www.szss.gov.cn/sstbhzq/qtdy/zlqmdqyqfkhfgfcssl/content/post_7387911.html (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Autonomous System” | Shanghai | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2021 | “http://jtyst.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2021/2/5/art_41775_9666644.html (accessed on 16 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Shenzhen | China | Environmental management | Urban forestry | 2022 | “http://meeb.sz.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/10/10159/post_10159242.html#3765 (accessed on 18 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Shanghai | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://www.shanghai.gov.cn/gwk/search/content/7aa19db8864a41a39d111039617a49a7?eqid=862b4aad0002618c00000003647d95a7 (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Beijing | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://www.beijing.gov.cn/gate/big5/www.beijing.gov.cn/ywdt/zwzt/dah/bxyw/202201/t20220120_2596203.html (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Natural Language Processing” | Chengdu | China | Administrative services | Community feedback | 2022 | “https://cdswszw.gov.cn/tzgg/Detail.aspx?id=27136 (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Hangzhou | China | Environmental management | Waste collection and management | 2022 | “http://epb.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2022/12/7/art_1692261_59025412.html (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| “Robotic process automation” | Shenzhen | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://www.sz.gov.cn/cn/xxgk/zfxxgj/gqdt/content/post_10001478.html (accessed on 8 January 2024) |
| “Neural Network” | Guangzhou | China | Healthcare and wellbeing | Public health | 2022 | “https://www.gz.gov.cn/zfjg/gzsylbzj/bmdt/content/post_8701201.html (accessed on 8 January 2024)” |
| Computer vision | Chengdu | China | Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management | 2023 | “https://www.mot.gov.cn/jiaotongyaowen/202303/t20230302_3767032.html (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Neural Network” | Shanghai | China | Administrative services | Information management | 2023 | “https://app.sheitc.sh.gov.cn/gydt/691296.htm (accessed on 10 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Beijing | China | Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security | 2023 | “https://www.beijing.gov.cn/fuwu/bmfw/sy/jrts/202304/t20230414_3032789.html (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
| “Computer vision” | Guangzhou | China | Environmental management | Local environmental issues | 2023 | “http://gxj.gz.gov.cn/zt/dlys/aljd/content/post_9384756.html (accessed on 15 January 2024)” |
References
- Vincent, C. Local Government Capacity building and Development: Lessons, Challenges and Opportunities. J. Political Sci. Public Aff. 2015, 3, 1000149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Corchado, J.; Mehmood, R.; Li, R.; Mossberger, K.; Desouza, K. Responsible Urban Innovation with Local Government Artificial Intelligence (AI): A Conceptual Framework and Research Agenda. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, S.; Esteve, M.; Campion, A. Artificial intelligence for the public sector: Opportunities and challenges of cross-sector collaboration. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2018, 376, 20170357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, I.; Hannibal, C.; Keating, B.; Chester Buxton, R.; Bateman, N. Toward a public service management: Past, present, and future directions. J. Serv. Manag. 2017, 28, 998–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Li, R.; Corchado, J.; Cheong, P.; Mossberger, K.; Mehmood, R. Understanding Local Government Digital Technology Adoption Strategies: A PRISMA Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Du, J.; Han, Y.; Newman, G.; Retchless, D.; Zou, L.; Ham, Y.; Cai, Z. Developing human-centered urban digital twins for community infrastructure resilience: A research agenda. J. Plan. Lit. 2023, 38, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, Z.; Treleaven, P. Algorithmic Government: Automating Public Services and Supporting Civil Servants in using Data Science Technologies. Comput. J. 2019, 62, 448–460. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Degirmenci, K.; Butler, L.; Desouza, K. What are the key factors affecting smart city transformation readiness? Evidence from Australian cities. Cities 2022, 120, 103434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchelt, A.; Adrowitzer, A.; Kieseberg, P.; Gollob, C.; Nothdurft, A.; Eresheim, S.; Tschiatschek, S.; Stampfer, K.; Holzinger, A. Exploring artificial intelligence for applications of drones in forest ecology and management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 551, 121530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado-Grande, J.I.; Gil-García, J.R. Creating Public Value through Smart Technologies and Strategies. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2019, 32, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regona, M.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Hon, C.; Teo, M. Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Development Goals: Systematic Literature Review of the Construction Industry. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbya, H.; Davenport, T.H.; Pachidi, S. Artificial Intelligence in Organizations: Current State and Future Opportunities. MIS Q. Exec. 2020, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, Z.; Ahamed, F.; Mayer, W.; Patel, N.; Grossmann, G.; Stumptner, M.; Kuusk, A. Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0: Systematic review of applications, challenges, and opportunities. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 216, 119456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, V. Exploring the Transformational Potential of Emerging Technologies in Human Resource Analytics: A Comparative Study of the Applications of IoT, AI, and Cloud Computing. J. Humanit. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 2, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, S.; Pandl, K.; Teigeler, H.; Thiebes, S.; Bayer, C.; Sunyaev, A. Artificial Intelligence as a Service. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2021, 63, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, R.; Ashok, M. AI adoption and diffusion in public administration: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. Gov. Inf. Q. 2022, 40, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbal, A.; Ali, M.; Abuzaraida, M. Artificial Intelligence Trust, Risk and Security Management (AI TRiSM): Frameworks, applications, challenges and future research directions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 240, 122442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Huang, J.; Krogstie, J. Artificial Intelligence of Things for Synergizing Smarter Eco-City Brain, Metabolism, and Platform: Pioneering Data-driven Environmental Governance. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Huang, J.; Jagatheesaperumal, S.K.; Krogstie, J. The synergistic interplay of artificial intelligence and digital twin in environmentally planning sustainable smart cities: A comprehensive systematic review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 20, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micozzi, N.; Yigitcanlar, T. Understanding Smart City Policy: Insights from the Strategy Documents of 52 Local Governments. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, H. Exploring Driving Factors of Digital Transformation among Local Governments: Foundations for Smart City Construction in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mańka-Szulik, M.; Krawczyk, D.; Wodarski, K. Residents’ Perceptions of Challenges Related to Implementation of Smart City Solutions by Local Government. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Senadheera, S.; Marasinghe, R.; Bibri, S.; Sanchez, T.; Cugurullo, F.; Sieber, R. Artificial intelligence and the local government: A five-decade scientometric analysis on the evolution, state-of-the-art, and emerging trends. Cities 2024, 152, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, A. Comparing and Contrasting Quantitative and Qualitative Research Approaches in Education: The Peculiar Situation of Medical Education. Educ. Med. J. 2018, 10, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohajan, H. Qualitative Research Methodology in Social Sciences and Related Subjects. 2018. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/85654/1/MPRA_paper_85654.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Polanin, J.; Tanner-Smith, E.; Hennessy, E. Estimating the Difference Between Published and Unpublished Effect Sizes. Rev. Educ. Res. 2016, 86, 207–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, A. Grey Literature: An Important Resource in Systematic Reviews. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2017, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y. Artificial intelligence: A survey on evolution, models, applications and future trends. J. Manag. Anal. 2019, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Emerging challenges, opportunities, and Agenda for research, Practice and Policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Xu, M.; Ottaviani, C.; Patros, P.; Bahsoon, R.; Shaghaghi, A.; Golec, M.; Stankovski, V.; Wu, H.; Abraham, A.; et al. AI for next generation computing: Emerging trends and future directions. Internet Things 2022, 19, 100514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Empowering Things with Intelligence: A Survey of the Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 10, 7789–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ye, X.; Jankowski, P.; Sanchez, T.W.; Mai, G. Artificial intelligence enabled participatory planning: A review. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2023, 28, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, V.; Jaiswal, M.; Wang, H.; Jayakody, D.; Basnayaka, C.; Muthanna, A. Recent Trends in AI-Based Intelligent Sensing. Electronics 2022, 11, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wu, L.; Lemke, M.; Valera, P.; Sackey, J. Defining computational urban science. In New Thinking in GIScience; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Bibri, S.; Keel, P. Generative Spatial Artificial Intelligence: Towards a pioneering foundation model for urban flows tailored for sustainable smart city digital twin. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2024, in press.
- Clarke, R. Why the world wants controls over Artificial Intelligence. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2019, 35, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.; Krogstie, J.; Kaboli, A.; Alahi, A. Smarter eco-cities and their leading-edge artificial intelligence of things solutions for environmental sustainability: A comprehensive systematic review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 19, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Mehmood, R.; Corchado, J. Green artificial intelligence: Towards an efficient, sustainable, and equitable technology for smart cities and futures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo Arrieta, A.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; Garcia, S.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts taxonomies opportunities challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I. AI-Based Modeling: Techniques, Applications and Research Issues Towards Automation, Intelligent and Smart Systems. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyoha, R. The History of Artificial Intelligence. 2017. Available online: https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2017/history-artificial-intelligence/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Roser, M. The Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: The World Has Changed Fast—What Might Be Next? 2022. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/brief-history-of-ai (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Sevilla, J.; Heim, L.; Ho, A.; Besiroglu, T.; Hobbhahn, M.; Villalobos, P. Compute trends across three eras of machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Corea, F.; AI Knowledge Map: How to Classify AI Technologies. Forbes. 2018. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2018/08/22/ai-knowledge-map-how-to-classify-ai-technologies/ (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Nesta. The Future of Minds and Machines: How Artificial Intelligence Can Enhance Collective Intelligence. 2020. Available online: https://media.nesta.org.uk/documents/FINAL_The_future_of_minds_and_machines.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Muggleton, S. Inductive logic programming. New Gener. Comput. 1991, 8, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggleton, S.; de Raedt, L. Inductive Logic Programming: Theory and methods. J. Log. Program. 1994, 19–20, 629–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Aalst, W.; Bichler, M.; Heinzl, A. Robotic Process Automation. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2018, 60, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Suriadi, S.; Adams, M.; Bandara, W.; Leemans, S.; Ouyang, C.; ter Hofstede, A.; van de Weerd, I.; Wynn, M.; Reijers, H. Robotic Process Automation: Contemporary themes and challenges. Comput. Ind. 2020, 115, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, P. Fault diagnosis in dynamic systems using analytical and knowledge-based redundancy. Autom. 1990, 26, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Deshmukh, A. Application of Bayesian decision networks to life cycle engineering in green design and manufacturing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2003, 16, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraffi, C.; Cattani, S.; Grisleri, P. Off-Road Path and Obstacle Detection Using Decision Networks and Stereo Vision. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2007, 8, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasinghe, R.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Mayere, S.; Washington, T.; Limb, M. Computer vision applications for urban planning: A systematic review of opportunities and constraints. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 100, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navigli, R.; Ponzetto, S. BabelNet: The automatic construction, evaluation and application of a wide-coverage multilingual semantic network. Artif. Intell. 2012, 193, 217–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano-Garcia, H.; Wozny, G. Chance constrained optimization of process systems under uncertainty: I. Strict monotonicity. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 1568–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.H.; Broecheler, M.; Huang, B.; Getoor, L. Hinge-Loss Markov Random Fields and Probabilistic Soft Logic. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, N.; Pal, S. A review on image segmentation techniques. Pattern Recognit. 1993, 26, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savidis, A.; Stephanidis, C. Distributed interface bits: Dynamic dialogue composition from ambient computing resources. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2004, 9, 142–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, F. Ambient intelligence. ACM Comput. Surv. 2011, 43, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, K.; Abbas, R.; Roussos, G.; Scornavacca, E.; Fosso-Wamba, S. Ethics in AI and autonomous system applications design. IEEE Trans. Technol. Soc. 2020, 1, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz, A.; Harned, Z.; Banerjee, O.; Abràmoff, M.; Rajpurkar, P. Autonomous AI systems in the face of liability, regulations and costs. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, P.; Veloso, M. Multiagent systems: A survey from a machine learning perspective. Auton. Robot. 2000, 8, 345–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, N.; Heydt, G.; Mili, L. Power system stability agents using robust wide area control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 17, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 687–697. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-Based Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar]
- Gracias, J.; Parnell, G.; Specking, E.; Pohl, E.; Buchanan, R. Smart Cities—A Structured Literature Review. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1719–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, X. Data-driven service planning in the Petabyte Age: The case of Arlington, Texas. Urban Inform. 2023, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Verma, S.; Das, R.; Dwivedi, Y. Social companionship with artificial intelligence: Recent trends and future avenues. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 193, 122634. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalov, F.; Santandreu Calonge, D.; Gurrib, I. New Era of Artificial Intelligence in Education: Towards a Sustainable Multifaceted Revolution. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruetzemacher, R.; Dorner, F.; Bernaola-Alvarez, N.; Giattino, C.; Manheim, D. Forecasting AI progress: A research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 170, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehr, H. Artificial Intelligence for Citizen Services and Government. 2017. Available online: https://creatingfutureus.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Mehr-2017-AIforGovCitizenServices.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Lovell, R.; Klingenstein, J.; Du, J.; Overman, L.; Sabo, D.; Ye, X.; Flannery, D. Using machine learning to assess rape reports: Sentiment analysis detection of officers “signaling” about victims’ credibility. J. Crim. Justice 2023, 88, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, S.; Das, S.; Du, J. Enhancing routes selection with real-time weather data integration in spatial decision support systems. In Spatial Information Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Desouza, K. Delivering Artificial Intelligence in Government: Challenges and Opportunities. 2019. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/10774705/delivering-artificial-intelligence-in-government/11652635/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Sousa, W.; Melo, E.; Bermejo, P.; Farias, R.; Gomes, A. How and where is artificial intelligence in the public sector going? A literature review and research agenda. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragno, G.; Tangi, L.; Gastaldi, L.; Benedetti, M. The spread of Artificial Intelligence in the public sector: A worldwide overview. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance, Athens, Greece, 6–8 October 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Teo, T.; Janssen, M. Public and private value creation using artificial intelligence: An empirical study of AI voice robot users in Chinese public sector. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 61, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, B.; Weyerer, J.; Geyer, C. Artificial Intelligence and the Public Sector—Applications and Challenges. Int. J. Public Adm. 2018, 42, 596–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwisongo, A.; Nabyonga-Orem, J. Global health initiatives in Africa—Governance, priorities, harmonisation and alignment. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, N.; Rode, P.; McQuarrie, M. New urban governance: A review of current themes and future priorities. J. Urban Aff. 2018, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, L. Public Administration and Governance for the SDGs: Navigating between Change and Stability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Agdas, D.; Degirmenci, K. Artificial intelligence in local governments: Perceptions of city managers on prospects, constraints and choices. AI Soc. 2023, 38, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Li, R.; Beeramoole, P.; Paz, A. Artificial intelligence in local government services: Public perceptions from Australia and Hong Kong. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distor, C.; Khaltar, O.; Moon, J. Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Local Governments: An Exploratory Study on the Attitudes and Perceptions of Officials in a Municipal Government in the Philippines. J. Public Aff. Dev. 2021, 8, 33–65. [Google Scholar]
- Vogl, T.M. Artificial intelligence in local government: Enabling artificial intelligence for good governance in UK local authorities. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3840222 (accessed on 8 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Smart, P.; Huff, A. Shades of Grey: Guidelines for Working with the Grey Literature in Systematic Reviews for Management and Organizational Studies. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2017, 19, 432–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, L. New measurements for search engine evaluation proposed and tested. Inf. Process. Manag. 2004, 40, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M. Analysing Google rankings through search engine optimization data. Internet Res. 2007, 17, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egri, G.; Bayrak, C. The Role of Search Engine Optimization on Keeping the User on the Site. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 36, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShebli, B.; Memon, S.; Evans, J.; Rahwan, T. China and the U.S. Produce More Impactful AI Research When Collaborating. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/370160336_China_and_the_US_produce_more_impactful_AI_research_when_collaborating_together (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Hine, E.; Floridi, L. Artificial intelligence with American values and Chinese characteristics: A comparative analysis of American and Chinese governmental AI policies. AI Soc. 2022, 39, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, L.; Chen, Y. Data mining from web search queries: A comparison of google trends and baidu index. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 66, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C.; Kalinowski, M.; Romero Felizardo, K.; Mendes, E. Successful combination of database search and snowballing for identification of primary studies in systematic literature studies. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2022, 147, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AZ Business Magazine. Phoenix Named a 2021 Digital Cities Survey Winner. 2021. Available online: https://azbigmedia.com/business/phoenix-named-a-2021-digital-cities-survey-winner/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Lewes and Eastbourne Council. ELLIS—Your Intelligent Chatbot. 2022. Available online: https://www.lewes-eastbourne.gov.uk/ellis (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Municipality of Grosseto. The Distances between Users and the Administration Are Shortened. 2021. Available online: https://new.comune.grosseto.it/web/comunicati/urp-si-accorciano-le-distanze-tra-utenza-e-amministrazione (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Tripster. Discover Courtrai—Creative City on the Leie. 2021. Available online: https://tripster-local.eu/nl/kortrijk-nl/# (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Bhatia, A. Kolkata’s WhatsApp Chatbot Helped 75,000 People Avail COVID Vaccines. 2021. Available online: https://special.ndtv.com/indias-helping-hands-93/news-detail/kolkatas-whatsapp-chatbot-helped-75-000-people-avail-covid-vaccines-2462893/7 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Hamilton City Council. New Online Tools Help Hamilton Voters Prepare for Municipal Election. 2022. Available online: https://www.hamilton.ca/city-council/news-notices/news-releases/new-online-tools-help-hamilton-voters-prepare-municipal (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Volta News. Volta Powers the City of Irving’s Community EV Charging Infrastructure Plan Using PredictEV Services. 2023. Available online: https://voltacharging.com/press/irving-community-ev-charging-infrastructure-plan-predictev (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Say, M. Lancashire County Council Deploys Analysis Tool at Bus Junctions. 2022. Available online: https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/lancashire-county-council-deploys-analysis-tool-at-bus-junctions/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Fast Company. This Map Shows Commuters How Many Pedestrians and Cyclists Died on Their Route. 2017. Available online: https://www.fastcompany.com/40416527/this-map-shows-commuters-how-many-pedestrians-and-cyclists-died-on-their-route (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Statescoop. Atlanta Responds to Bridge Collapse with Real-Time Traffic Map. 2017. Available online: https://statescoop.com/atlanta-responds-to-bridge-collapse-with-real-time-traffic-map (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Route-Fifty. KC Shares Its Smart City Data, Best Practices. 2017. Available online: https://www.route-fifty.com/digital-government/2017/02/kc-shares-its-smart-city-data-best-practices/304668 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Ascend Editorial Team. Real-World Examples of Machine Learning in Digital Government. 2022. Available online: https://ascend.thentia.com/process/applications-of-machine-learning-in-digital-government (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Emanuel, N. Smarter Cities: How Machine Learning Can Improve Municipal Services in Chicago. 2018. Available online: https://d3.harvard.edu/platform-rctom/submission/smarter-cities-how-machine-learning-can-improve-municipal-services-in-chicago/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Marsh, S. One in Three Councils Using Algorithms to Make Welfare Decisions. 2019. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/society/2019/oct/15/councils-using-algorithms-make-welfare-decisions-benefits (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Diaz, K. Gilbert, Ariz., Gets Strategic About Cyber Resilience, Defense. 2022. Available online: https://www.govtech.com/security/gilbert-ariz-gets-strategic-about-cyber-resilience-defense?utm_campaign=Newsletter%20-%20GT%20-%20GovTech%20Cybersecurity (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Wray, S. Sunderland Connects the Data Dots with Smart City Platform. 2022. Available online: https://cities-today.com/sunderland-targets-anti-social-behaviour-with-data-platform/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Anagnoste, S. Robotic Automation Process—The next major revolution in terms of back-office operations improvement. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excell. 2017, 11, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, V.; Suresh, M.; Aramvalarthan, S. Lean in service industries: A literature review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 149, 012008. [Google Scholar]
- Makridakis, S. The forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolution: Its impact on society and firms. Futures 2017, 90, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkers, V. The governance of back-office integration. Public Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paagman, A.; Tate, M.; Furtmueller, E.; de Bloom, J. An integrative literature review and empirical validation of motives for introducing shared services in government organizations. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 35, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, S.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Desouza, K.C.; Mossberger, K.; Corchado, J.; Mehmood, R.; Li, R.Y.M.; Cheong, P.H. Understanding Chatbot Adoption in Local Governments: A Review and Framework. J. Urban Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowu, D. Local institutional and political structures and processes: Recent experience in Africa. Public Adm. Dev. 2003, 23, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, S. The Local Government System in Bangladesh: An Anatomy of Perspectives & Practices. South Asian J. Policy Gov. 2020, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gharib, N.M.; Amyot, D. Robotic process automation using process mining—A systematic literature review. Data Knowl. Eng. 2023, 148, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, W.A.; Diya, P.; Patil, S.; Patil, S. A review on robotic process automation-the future of business organizations. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Science & Technology (ICAST), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2–4 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plattfaut, R.; Borghoff, V. Robotic process automation: A literature-based research agenda. J. Inf. Syst. 2022, 36, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewerka, J.; Reichert, M. Robotic process automation-a systematic mapping study and classification framework. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2023, 17, 1986862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.K.; Sultana, R.; Bera, R.; Sil, S.; Alfred, Q.M. A Comprehensive Review on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for the Development of Smart Cities. In Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Robotic Process Automation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 289–311. [Google Scholar]
- Surrey County Council. Improving Citizen and Employee Experience with Automation. 2018. Available online: https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/surrey-county-council-improves-employee-experience-with-automation (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Strängnäs Municipality. The Municipality of Strängnäs Saves Four Million SEK a Year via Automation. 2019. Available online: https://www.uipath.com/resources/automation-case-studies/strangnas-municipality-government-rpa (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- UK Authority. Automation as a Weapon in Local Government’s New Battles. 2022. Available online: https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/automation-as-a-weapon-in-local-government-s-new-battles (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Zinnov. Intelligent Automation in the Public Sector. 2023. Available online: https://zinnov.com/automation/intelligent-automation-driving-government-digital-transformation-blog/#:~:text=Further%2C%20the%20City%20Council%20of (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Gloucestershire County Council. Working More Effectively. 2018. Available online: https://cdn.filestackcontent.com/yBWvbe7QCSBbRUOgAo1Q (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Norfolk County Council. Norfolk County Council Digital Workforce Enhances Citizens’ Experience. 2021. Available online: https://www.blueprism.com/resources/case-studies/norfolk-county-council-enhances-citizens-experience-with-a-digital-workforce/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Blacktown City Council. Water Sensitive Urban Design Compliance Program. 2020. Available online: https://cdn.filestackcontent.com/FBG1aZJuRKuc4Tz8wb4e (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Alcorcón City Council. Alcorcón, MD Is Implementing a Bilateral Automatic Loading System for Its Waste Collection Fleet. 2022. Available online: https://govlaunch.com/governments/alcorcon-md/projects/alcorcon-md-is-implementing-a-bilateral-automatic-loading-system-for-its-waste-collection-fleet (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Shanghai City Council. The Smartest: The Future Science and Technology Test Island. 2018. Available online: https://www.shwm.gov.cn/TrueCMS/shwmw/xyesdxzzsh/content/2d025728-f2d0-4980-87c7-a04db74ce82b.html (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Australian Research Council. AI Governance in the Smart City: A Case Study of Garbage Truck Mounted Machine Vision for Roadside Maintenance. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.25916/a2fn-yb49 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Hornblad, J. Computer Vision Helps Make Helsingborg a Smarter City. 2022. Available online: https://univrses.com/press-releases/computer-vision-helps-make-helsingborg-a-smarter-city/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Sanchez, T. Planning with Artificial Intelligence. 2021. Available online: https://www.planning.org/publications/report/9270237 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Japan Times. City Hall in Gifu Prefecture Is First in Japan to Deploy Autonomous Robots to Aid Residents. 2019. Available online: https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/01/15/national/city-hall-gifu-prefecture-first-japan-deploy-autonomous-robots-aid-residents (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Bibri, S. Affective behavioral features of AmI: Affective context-aware, emotion-aware, context-aware affective, and emotionally intelligent systems. In The Human Face of Ambient Intelligence: Cognitive, Emotional, Affective, Behavioural and Conversational Aspects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 403–459. [Google Scholar]
- Bibri, S. Ambient intelligence: A new computing paradigm a vision of a next wave in ICT. In The Human Face of Ambient Intelligence: Cognitive, Emotional, Affective, Behavioral and Conversational Aspects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 23–66. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, W. Robot Amelia—A Glimpse of the Future for Local Government. 2016. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/public-leaders-network/2016/jul/04/robot-amelia-future-local-government-enfield-council (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Krueger, T.; Mohapatra, A.; Genesereth, M. Symbium: Using Logic Programming to Streamline Citizen-to-Government Interactions. 2019. Available online: http://logicprogramming.stanford.edu/readings/symbium.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Ku-ring-gai Council. Using Ambient Computing Technology to Simulate Extreme Climate Events. 2019. Available online: https://www.climatechange.environment.nsw.gov.au/sites/default/files/2022-09/Simtable_modelling_toolKu-ring-gai_Council.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, X. Understanding the determinants in the different government AI adoption stages: Evidence of local government chatbots in China. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2022, 40, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pang, P.; Wong, D.; Kan, H. Natural Language Processing Adoption in Governments and Future Research Directions: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulou, A.; Karacapilidis, N.; Loukis, E.; Charalabidis, Y. Transforming the communication between citizens and government through AI-guided chatbots. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Cediel, M.; Segura-Tinoco, A.; Cantador, I.; Rodríguez Bolívar, M. Trends and challenges of e-government chatbots: Advances in exploring open government data and citizen participation content. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Janssen, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. It Is Me, Chatbot: Working to Address the COVID-19 Outbreak-Related Mental Health Issues in China. User Experience, Satisfaction, and Influencing Factors. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2022, 22, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Meng, Q.; Sun, F.; Liu, L.; Singh, S. Citizen preferences and government chatbot social characteristics: Evidence from a discrete choice experiment. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz-Małyjurek, K. Whether AI adoption challenges matter for public managers? The case of Polish cities. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, C.; Kim, J.; Chi, S. Natural language processing-based characterization of top-down communication in smart cities for enhancing citizen alignment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wei, G. Public sentiment analysis on urban regeneration: A massive data study based on sentiment knowledge enhanced pre-training and latent Dirichlet allocation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Xu, J.; Wei, J. Understanding the effects of the textual complexity on government communication: Insights from China’s online public service platform. Telemat. Inform. 2023, 83, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, A.; Ziora, L. The Use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as an Element of Smart City Implementation: A Case Study of Electricity Billing Document Management at Bydgoszcz City Hall. Energies 2021, 14, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.; Lee, D.; Chae, U.; Ko, J.; Lee, J. Improvement of Business Productivity by Applying Robotic Process Automation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.; Thomsen, M.; Åkesson, M. Public value creation and robotic process automation: Normative, descriptive and prescriptive issues in municipal administration. Transform. Gov. People Process Policy 2022, 17, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranerup, A.; Henriksen, H. Value positions viewed through the lens of automated decision-making: The case of social services. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, W.; Monasterio, L.; Fochezatto, A. Automation in the future of public sector employment: The case of Brazilian Federal Government. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, B.; Müller, W. An integrated artificial intelligence framework for public management. Public Manag. Rev. 2018, 21, 1076–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujran, O.; Alarabiat, A.; Al-Adwan, A.S.; Al-Debei, M. Digitally transforming electronic governments into smart governments: SMARTGOV, an extended maturity model. Inf. Dev. 2023, 39, 811–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencheva, I.; Esteve, M.; Mikhaylov, S. Big Data and AI—A transformational shift for government: So, what next for research? Public Policy Adm. 2018, 35, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susar, D.; Aquaro, V. Artificial intelligence: Opportunities and challenges for the public sector. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance, Melbourne, Australia, 3–5 April 2019; pp. 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, L. AI Fairness in Data Management and Analytics: A Review on Challenges, Methodologies and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Wu, H.; Patros, P.; Ottaviani, C.; Arora, P.; Pujol, V.C.; Haunschild, D.; Parlikad, A.K.; Cetinkaya, O.; Lutfiyya, H.; et al. Modern computing: Vision and challenges. Telemat. Inform. Rep. 2024, 13, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licardo, J.; Domjan, M.; Orehovački, T. Intelligent Robotics—A Systematic Review of Emerging Technologies and Trends. Electronics 2024, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.K. Artificial Intelligence and the New Urban Infrastructure. SparkCognition. Available online: https://www.sparkcognition.com/artificial-intelligence-and-the-new-urban-infrastructure/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Tuinhof, T. Enriching 3D Models with Artificial Intelligence: The Municipality of Rotterdam Proves It’s Possible. SPOTR. 2023. Available online: https://www.spotr.ai/customer-stories/rotterdam (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Kamrowska-Załuska, D. Impact of AI-Based Tools and Urban Big Data Analytics on the Design and Planning of Cities. Land 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.; Weedon, Z.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Sanchez, T.; Corchado, J.; Mehmood, R. Algorithmic Urban Planning for Smart and Sustainable Development: Systematic Review of the Literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 94, 104562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, S.; van Leeuwen, C. The challenges of water, waste and climate change in cities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 19, 385–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Poku-Boansi, M.; Peprah, C. Urban environmental problems in Ghana. Environ. Dev. 2017, 23, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangzhou Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment. The Construction of a “Zero-Waste city” in Hangzhou|Lin’an District’s Waste “Wisdom” Explores a New Model of “Closed-Loop” Waste Reduction and Efficient Utilization. 2022. Available online: http://epb.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2022/12/7/art_1692261_59025412.html (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- National Development and Reform Commission. Chongqing Releases Ten Application Scenarios: Artificial Intelligence Is Changing Life in the Mountain City. 2020. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/szhzxhbxd/gfdt/202007/t20200713_1233659.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Buyya, R.; Netto, M.; Toosi, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Llorente, I.; Vimercati, S.; Samarati, P.; Milojicic, D.; Varela, C.; Bahsoon, R.; et al. A Manifesto for Future Generation Cloud Computing. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Swami, S.; Malhotra, S.K. Artificial Intelligence Adoption in the Post COVID-19 New-Normal and Role of Smart Technologies in Transforming Business: A Review. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2022, 15, 506–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.G.; Peixoto, J.P.J. COVID-19 pandemic: A review of smart cities initiatives to face new outbreaks. IET Smart Cities 2020, 2, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City of Boston. Food Resources Chatbot and Food Donations Platform Launched. Food Resources Chatbot and Food Donations Platform Launched|Boston.gov. 2021. Available online: https://www.boston.gov/news/food-resources-chatbot-and-food-donations-platform-launched (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Norwich City Council. Norwich City Council Awarded for Innovative Approach to Tackling Rising Debt Concerns. LocalGov. 2022. Available online: https://www.localgov.co.uk/Norwich-City-Council-Awarded-for-Innovative-Approach-to-Tackling-Rising-Debt-Concerns/53541. (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- City of Stirling. Stirling Trials Artificial Intelligence Platform in WA-First. 2023. Available online: https://www.stirling.wa.gov.au/your-city/news/2023/july/stirling-trials-artificial-intelligence-platform-i (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Madurai Elavarasan, R.; Pugazhendhi, R. Restructured society and environment: A review on potential technological strategies to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 180, 138858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M.; Sukkuea, A.; Tina, F.; Nag, A.; Kurdthongmee, W.; Suwannarat, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Integration of IoT-Enabled Technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart City Scenario: Recent Advancements and Future Trends. Sensors 2023, 23, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, R.; Lotfi, M.; Baghaian, A.; Ruiz, R.; Rezapour, S. Mass casualty management in disaster scene: A systematic review of OR&MS research in humanitarian operations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 787–819. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.; Peixoto, J.; Jesus, T.; Portugal, P.; Vasques, F.; Rangel, E.; Peixoto, M. A Survey of Emergencies Management Systems in Smart Cities. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 61843–61872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, D. Smart Cities with Computer Vision Technology. 2019. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/smart-cities-computer-vision-technology-debiprasad-bandopadhyay (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Van Dijk, A.J.; Herrington, V.; Crofts, N.; Breunig, R.; Burris, S.; Sullivan, H.; Middleton, J.; Sherman, S.; Thomson, N. Law enforcement and public health: Recognition and enhancement of joined-up solutions. Lancet 2019, 393, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, A.; Kamal, M. Ethical Dilemmas in AI-Powered Decision-Making: A Deep Dive into Big Data-Driven Ethical Considerations. Int. J. Responsible Artif. Intell. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gentzel, M. Biased Face Recognition Technology Used by Government: A Problem for Liberal Democracy. Philos. Technol. 2021, 34, 1639–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelzer, R. AI Is Here to Stay in Your City and Local Government. 2020. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2020/11/08/ai-is-here-to-stay-in-your-city-and-local-government/?sh=78f1926d77a3 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Fukuda-Parr, S.; Gibbons, E. Emerging Consensus on “Ethical AI”: Human Rights Critique of Stakeholder Guidelines. Global Policy 2021, 12, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, R.; Hoehner, C.; Day, K.; Forsyth, A.; Sallis, J. Measuring the Built Environment for Physical Activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 36, S99–S123.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Taeihagh, A. Smart City Governance in Developing Countries: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y. Artificial Intelligence for Decision Making in the Era of Big Data—Evolution, Challenges and Research Agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, N.; Antunes, P.; Johnstone, D. Factors influencing the decision to crowdsource: A systematic literature review. Inf. Syst. Front. 2015, 18, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, A.; Valecha, R.; Najafirad, P.; Rao, H. Artificial Intelligence in Tactical Human Resource Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Kaye, S.; Oviedo-Trespalacios, O. What Factors Contribute to Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence? A Systematic Review. Telemat. Inform. 2022, 77, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păvăloaia, V.; Necula, S. Artificial Intelligence as a Disruptive Technology—A Systematic Literature Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madumo, O. Developmental Local Government Challenges and Progress in South Africa. 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2263/50230 (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Mikalef, P.; Lemmer, K.; Schaefer, C.; Ylinen, M.; Fjørtoft, S.O.; Torvatn, H.Y.; Gupta, M.; Niehaves, B. Enabling AI capabilities in government agencies: A study of determinants for European municipalities. Gov. Inf. Q. 2022, 39, 101596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, R.; Jia, X.; Lee, J.; Sun, K.; Colombo, A.; Barata, J. Industrial Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0—Systematic Review, Challenges and Outlook. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 220121–220139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynon-Davies, P.; Martin, S. Electronic Local Government and the Modernisation Agenda: Progress and Prospects for Public Service Improvement. Local Gov. Stud. 2004, 30, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G. Stakeholder roles in artificial intelligence projects. Proj. Leadersh. Soc. 2022, 3, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafoe, A. AI Governance: A Research Agenda. 2017. Available online: https://www.fhi.ox.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/GovAI-Agenda.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Sun, T.; Medaglia, R. Mapping the challenges of Artificial Intelligence in the public sector: Evidence from public healthcare. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gangadhari, R.; Li, Z. Analyzing the Adoption Challenges of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart Cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, A.; Dennehy, D.; Mäntymäki, M. An attention-based view of AI assimilation in public sector organizations: The case of Saudi Arabia. Gov. Inf. Q. 2021, 39, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N. An experimental study of public trust in AI chatbots in the public sector. Gov. Inf. Q. 2020, 37, 101490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guo, W.; Gao, X.; Liang, Z. AI-based self-service technology in public service delivery: User experience and influencing factors. Gov. Inf. Q. 2020, 38, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrams, A.; Kaufmann, W.; Jacobs, D. In AI we trust? Citizen perceptions of AI in government decision making. Policy Internet 2022, 14, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarti, S.; Fadzlul Rahman, F.; Naufal, M.; Risky, M.; Febriyanto, K.; Masnina, R. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Opportunities and risk for future. Gac. Sanit. 2021, 35, S67–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaamala, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nili, A.; Nyandega, D. Algorithmic Green Infrastructure Optimisation: Review of Artificial Intelligence Driven Approaches for Tackling Climate Change. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Browne, W.; Nili, A. The Making of Responsible Innovation and Technology: An Overview and Framework. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1996–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, W.; Omlin, C. Explainable AI (XAI): A systematic meta-survey of current challenges and future opportunities. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2023, 263, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, A.; Gasco-Hernandez, M.; Jankin Mikhaylov, S.; Esteve, M. Overcoming the Challenges of Collaboratively Adopting Artificial Intelligence in the Public Sector. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2020, 40, 089443932097995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nili, A.; Browne, W. Tech Giants’ Responsible Innovation and Technology Strategy: An International Policy Review. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 3454–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzobonimpa, S.; Savard, J. Ready but irresponsible? Analysis of the Government Artificial Intelligence Readiness Index. Policy Internet 2023, 15, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.; Philip, L.; Farrington, J.; Fairhurst, G. “Digital by Default” and the “hard to reach”: Exploring solutions to digital exclusion in remote rural areas. Local Econ. J. Local Econ. Policy Unit 2016, 31, 757–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C. Coping with vulnerability: The effect of trust in AI and privacy-protective behaviour on the use of AI-based services. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, D. Digital divide, e-government, and trust in public service: The key role of education. Front. Sociol. 2023, 8, 1140416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.T.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nguyen, K.; Xu, Y. Understanding Local Government Cybersecurity Policy: A Concept Map and Framework. Information 2024, 15, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Fjørtoft, S.; Torvatn, H. Artificial Intelligence in the Public Sector: A Study of Challenges and Opportunities for Norwegian Municipalities. In Digital Transformation for a Sustainable Society in the 21st Century: 18th IFIP WG 6.11 Conference on e-Business, e-Services, and e-Society, I3E 2019, Trondheim, Norway, 18–20 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 267–277. [Google Scholar]
- Van Winden, W.; van den Buuse, D. Smart City Pilot Projects: Exploring the Dimensions and Conditions of Scaling Up. J. Urban Technol. 2017, 24, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar-Landgren, D. Local Autonomy in Temporary Organizations: The Case of Smart City Pilots. Adm. Soc. 2021, 53, 009539972110098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
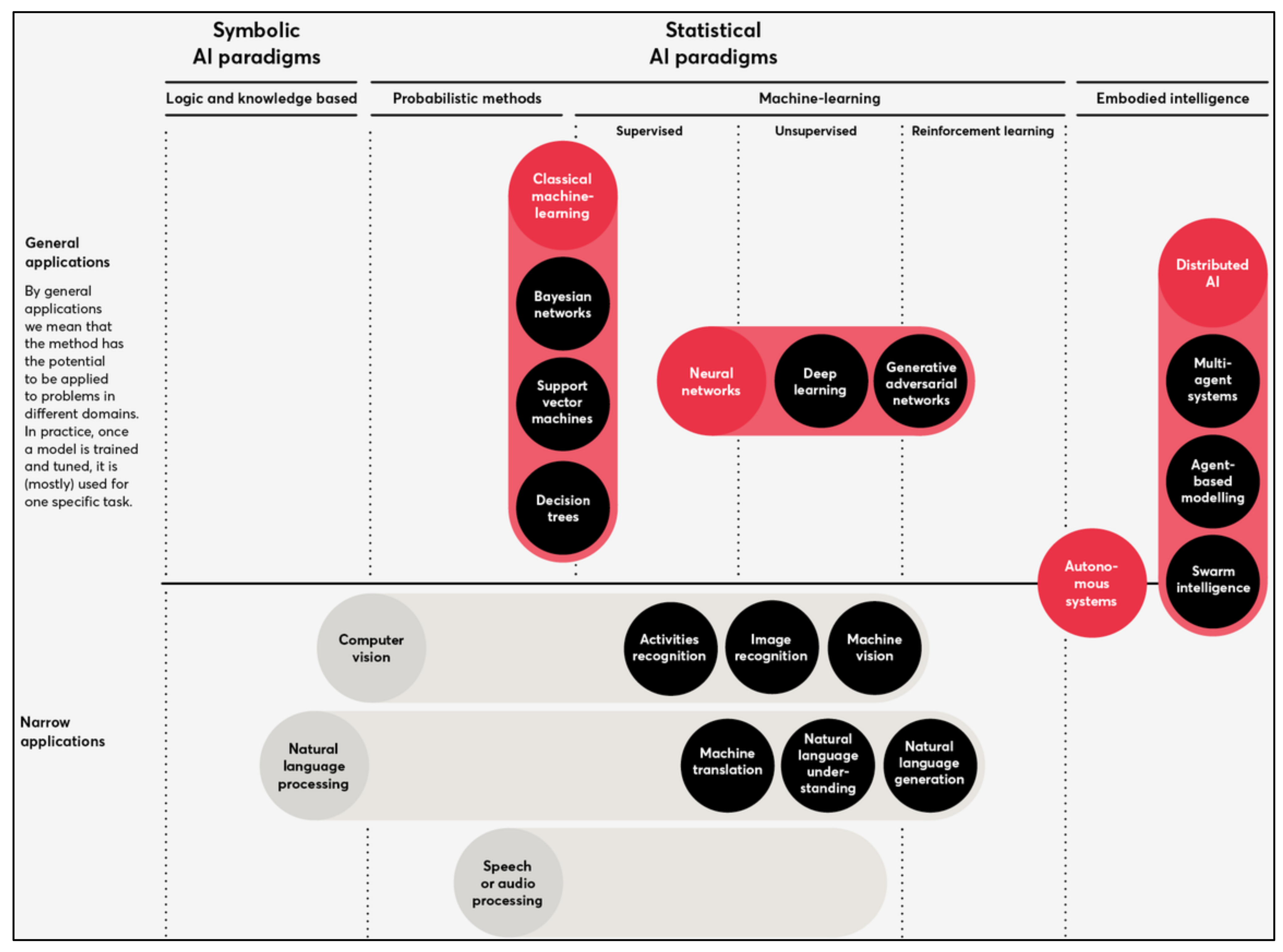
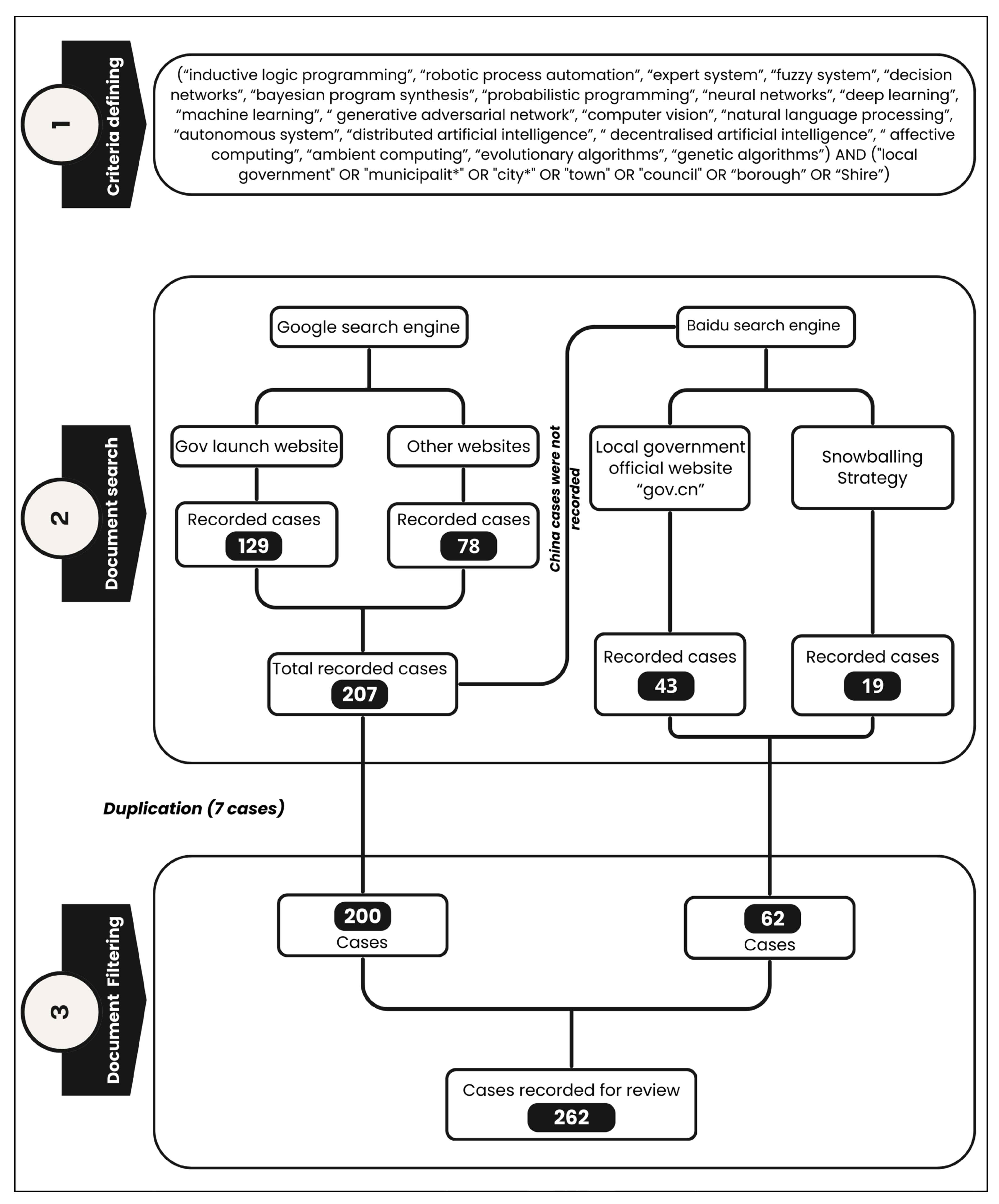
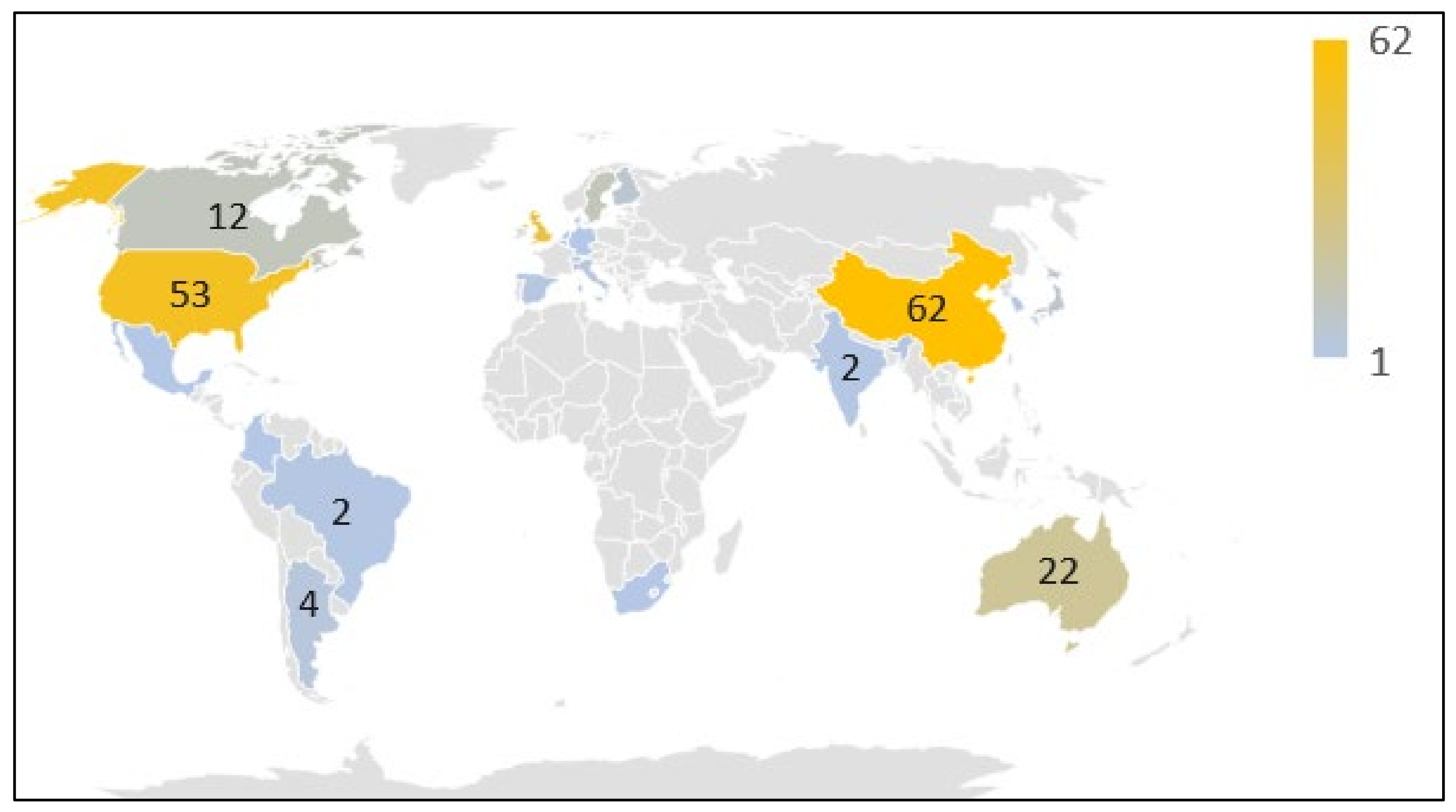
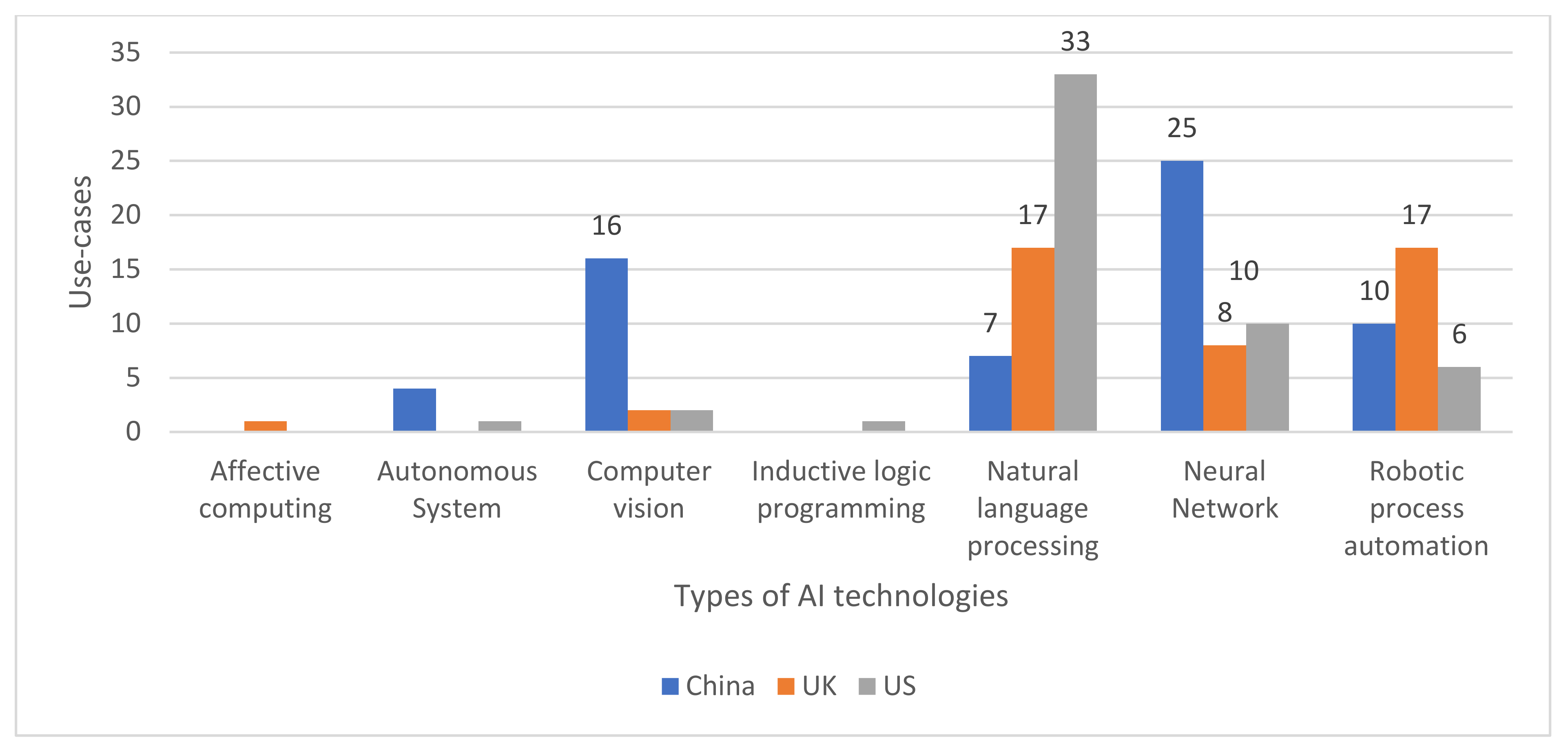
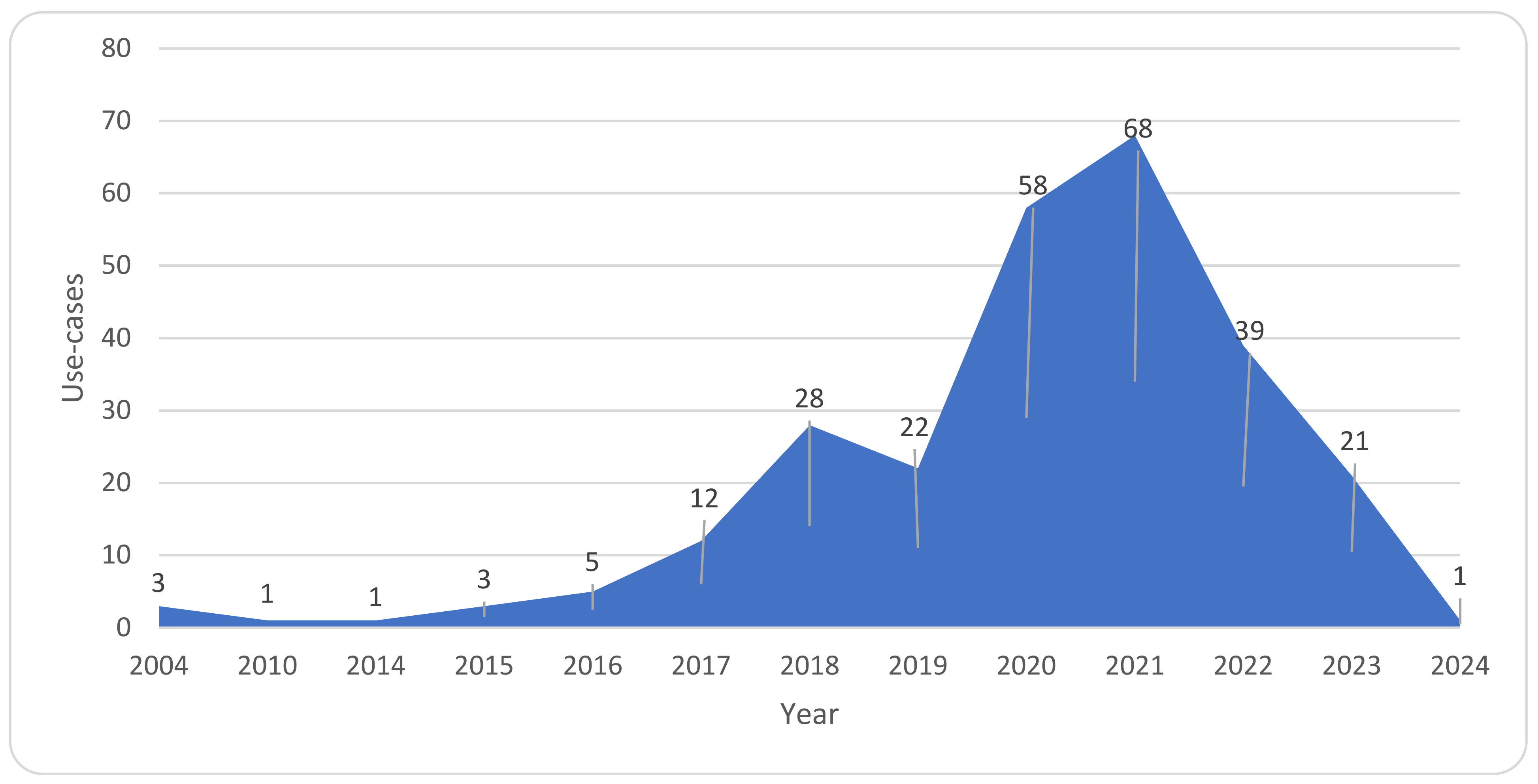
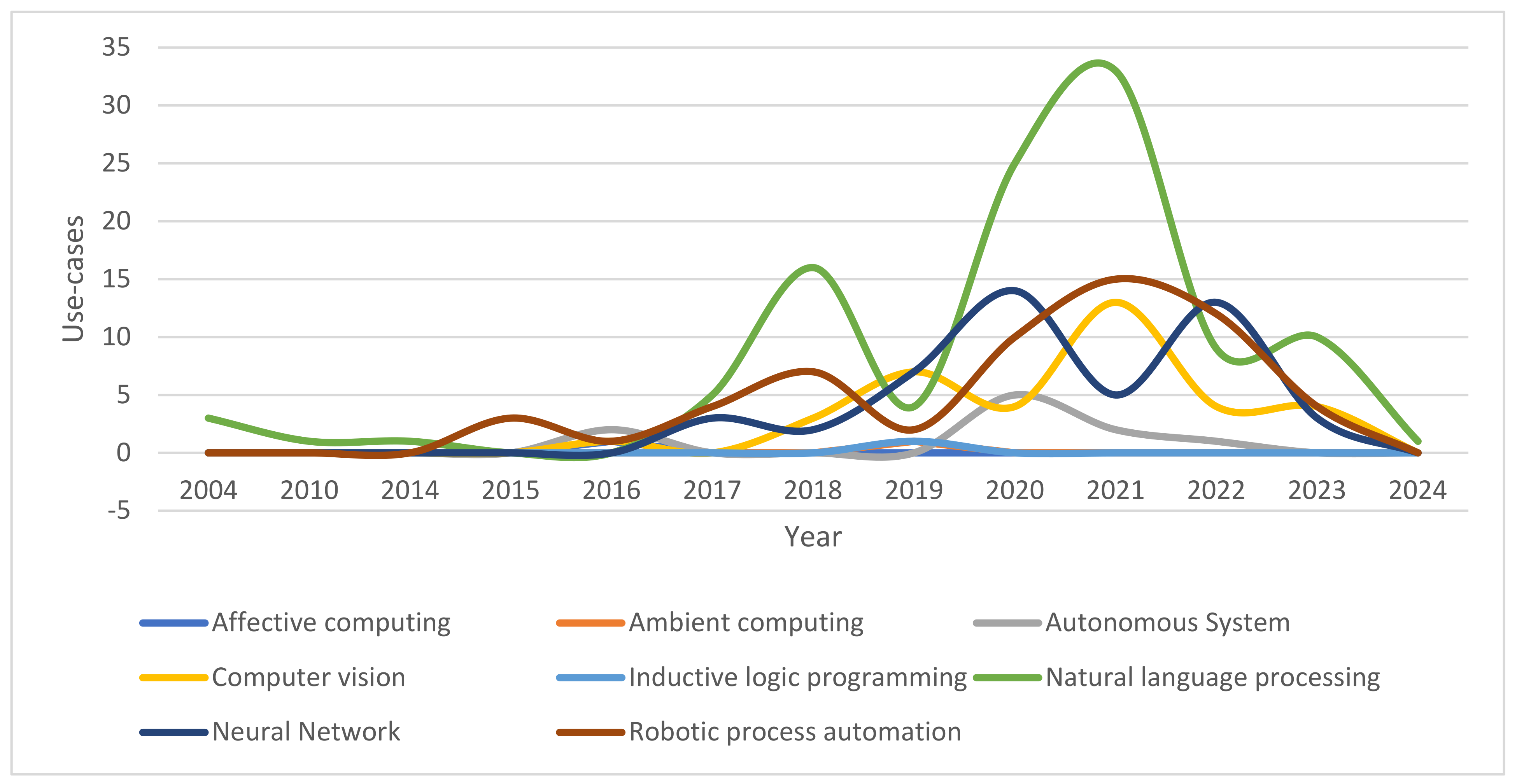

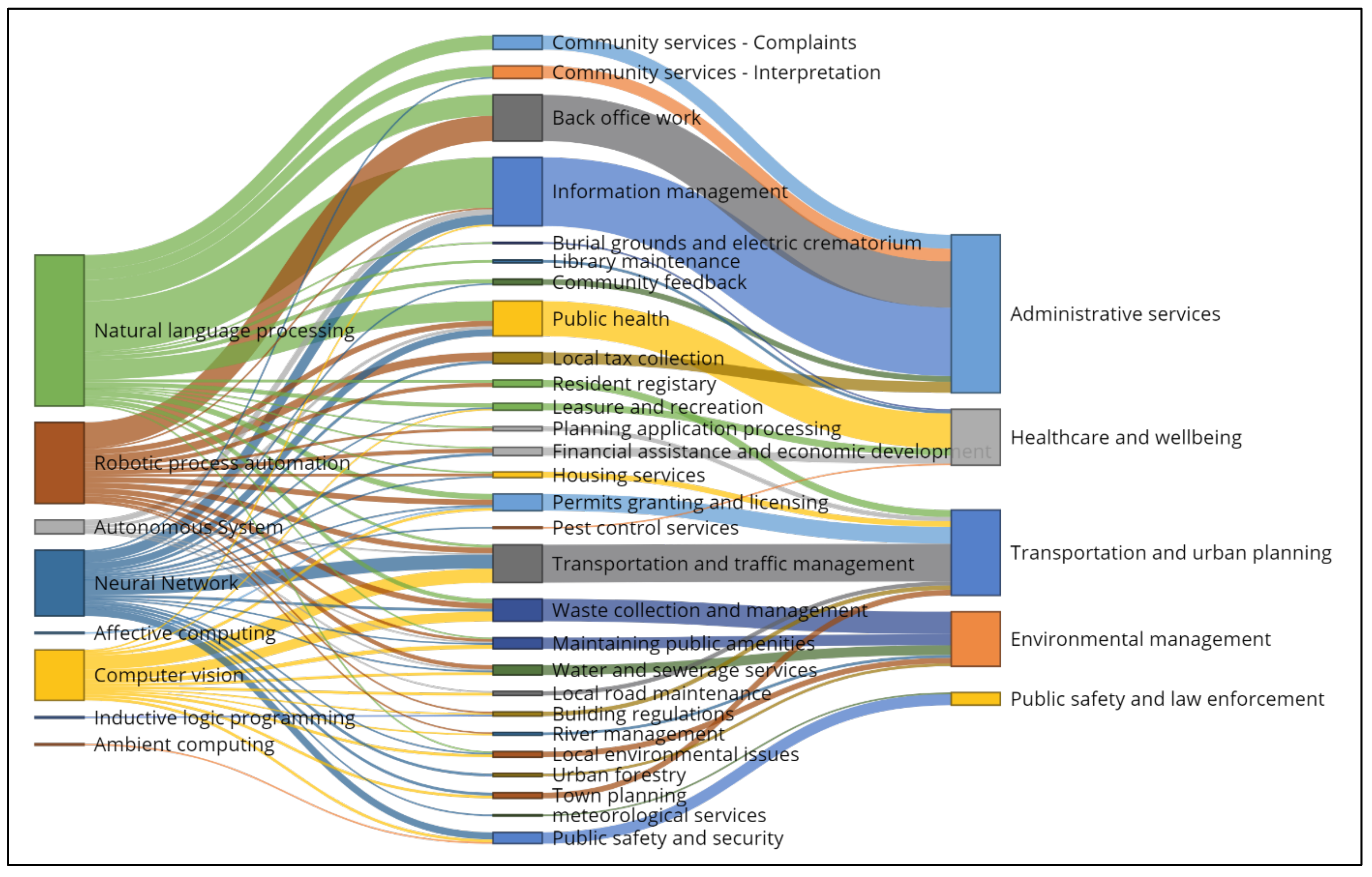
| AI Technology | Definition | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| “Inductive Logic Programming (ILP)” | “ILP uses first-order logic to represent data and hypotheses, allowing it to create logical models from real-world data to learn complex relationships” | [48,49] |
| “Robotic Process Automation (RPA)” | “RPA refers to a technology that enables the automation of business processes using software robots, typically handling repetitive tasks carried out by human workers” | [50,51] |
| “Expert System (ES)” | “ES simulates the decision-making abilities of a human expert by employing a knowledge-based approach with rules of inference to address problems within a specific domain” | [40,52] |
| “Decision Network (DN)” | “DN is a type of probabilistic graphical model that can extend such as Bayesian Networks, for example, by incorporating chance nodes, decision nodes, and utility nodes, facilitating effective decision-making in uncertain scenarios” | [53,54] |
| “Computer Vision (CV)” | “CV enables computers to interpret visual data from the world by using algorithms that recognise patterns, objects, and environments in images and videos, mirroring human visual perception” | [55,56,57] |
| “Natural Language Processing (NLP)” | “NLP seeks to empower computers to comprehend, interpret, and respond to human language by analysing the intricacies of language and translating them into computational models” | [58,59] |
| “Probabilistic Programming (PP)” | “PP is a programming approach designed for dealing with uncertainty in data, where probabilistic models are defined using programming constructs” | [60,61] |
| “Neural Network (NN)” | “NN, inspired by the human brain for processing data and making decisions, consists of layers of nodes to handle information, including an input layer that receives data, hidden layers for data processing, and an output layer for generating results” | [62,63,64] |
| “Affective Computing (AC)” | “AC refers to a digital setting where computational processes are seamlessly integrated into everyday objects and surroundings, becoming an integral aspect of people’s daily lives” | [65,66] |
| “Autonomous system (AS)” | “AS is an AI system that can operate independently without human intervention” | [67,68] |
| “Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI)” | “DAI represents a category of technologies that fosters collaborative interactions among multiple autonomous intelligent agents, each with distinct capabilities, to solve complex problems” | [69,70] |
| “Ambient Computing (AmC)” | “AmC refers to a digital setting where computational processes are seamlessly integrated into everyday objects and surroundings, becoming an integral aspect of people’s daily lives” | [65,66] |
| “Evolutionary Algorithms (EA)” | “EA, inspired by biological evolution, is an optimisation algorithm that employs biomimetic mechanisms to solve tasks beyond the reach of traditional analytical methods within a practical timeframe” | [71,72] |
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Published websites, government reports, newsletters, news releases, blogs, technical repots, interviews, etc. | Academic journal articles, nooks, chapters, conference proceedings |
| Available online | Unavailable online |
| Relevant to study aim/question | Not relevant to study aim |
| In English language | Unavailable in English |
| Case study: Local government | Case study: National, regional, and other departments or private organisations at local government level |
| Timeline: open ended |
| Main Services | Sub-Services |
|---|---|
| Administrative services | Information management |
| Back-office work | |
| Community services—complaints | |
| Community services—interpretation | |
| Local tax collection | |
| Community feedback | |
| Environmental management | Waste collection and management |
| Maintaining public amenities | |
| Water and sewerage services | |
| Local environmental issues | |
| River management | |
| Urban forestry | |
| Healthcare and wellbeing services | Public health |
| Financial assistance and economic development | |
| Leisure and recreation | |
| Library maintenance | |
| Burial grounds and electric crematorium | |
| Pest control services | |
| Public safety and law enforcement | Public safety and security |
| Meteorological services | |
| Transportation and urban planning | Transportation and traffic management |
| Permits granting and licensing | |
| Resident registry | |
| Housing services | |
| Town planning | |
| Building regulations | |
| Local road maintenance | |
| Planning application processing |
| AI Technology | Use Case Number |
|---|---|
| Natural language processing (NLP) | 108 |
| Robotic process automation (RAP) | 58 |
| Neural network (NN) | 47 |
| Computer vision (CV) | 36 |
| Autonomous system (AS) | 10 |
| Affective computing (AC) | 1 |
| Ambient computing (AmC) | 1 |
| Inductive logic programming (ILP) | 1 |
| Total | 262 |
| Local Government | Country | Use Case Number |
|---|---|---|
| Changsha | China | 11 |
| Hangzhou | China | 9 |
| Shenzhen | China | 7 |
| Chongqing | China | 6 |
| Shanghai | China | 6 |
| Beijing | China | 5 |
| Guangzhou | China | 4 |
| Kawasaki | Japan | 4 |
| Los Angeles | US | 4 |
| North Tyneside Council | UK | 4 |
| Adelaide | Australia | 3 |
| Buenos Aires | Argentina | 3 |
| Chengdu | China | 3 |
| Derby City Council | UK | 3 |
| Helsingborg Municipality | Sweden | 3 |
| Johns Creek | US | 3 |
| Ronneby | Sweden | 3 |
| Singapore | Singapore | 3 |
| Telford and Wrekin Council | UK | 3 |
| Williamsburg | US | 3 |
| Service | Use Case Number |
|---|---|
| Information management | 49 |
| Back-office work | 33 |
| Transportation and traffic management | 27 |
| Public health | 25 |
| Waste collection and management | 16 |
| Permits granting and licensing | 12 |
| Community services—complaints | 10 |
| Community services—interpretation | 9 |
| Local tax collection | 8 |
| Maintaining public amenities | 8 |
| Public safety and security | 8 |
| Water and sewerage services | 7 |
| Financial assistance and economic development | 6 |
| Leisure and recreation | 5 |
| Resident registry | 5 |
| Community feedback | 4 |
| Housing services | 4 |
| Local environmental issues | 4 |
| Town planning | 4 |
| Building regulations | 3 |
| Local road maintenance | 3 |
| Planning application processing | 3 |
| Library maintenance | 2 |
| River management | 2 |
| Urban forestry | 2 |
| Burial grounds and electric crematorium | 1 |
| Meteorological services | 1 |
| Pest control services | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yigitcanlar, T.; David, A.; Li, W.; Fookes, C.; Bibri, S.E.; Ye, X. Unlocking Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Local Governments: Best Practice Lessons from Real-World Implementations. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 1576-1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040064
Yigitcanlar T, David A, Li W, Fookes C, Bibri SE, Ye X. Unlocking Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Local Governments: Best Practice Lessons from Real-World Implementations. Smart Cities. 2024; 7(4):1576-1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleYigitcanlar, Tan, Anne David, Wenda Li, Clinton Fookes, Simon Elias Bibri, and Xinyue Ye. 2024. "Unlocking Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Local Governments: Best Practice Lessons from Real-World Implementations" Smart Cities 7, no. 4: 1576-1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040064
APA StyleYigitcanlar, T., David, A., Li, W., Fookes, C., Bibri, S. E., & Ye, X. (2024). Unlocking Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Local Governments: Best Practice Lessons from Real-World Implementations. Smart Cities, 7(4), 1576-1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7040064







