Abstract
The management of decentralized energy resources and smart grids needs novel data-driven low-latency applications and services to improve resilience and responsiveness and ensure closer to real-time control. However, the large-scale integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has led to the generation of significant amounts of data at the edge of the grid, posing challenges for the traditional cloud-based smart-grid architectures to meet the stringent latency and response time requirements of emerging applications. In this paper, we delve into the energy grid and computational distribution architectures, including edge–fog–cloud models, computational orchestration, and smart-grid frameworks to support the design and offloading of grid applications across the computational continuum. Key factors influencing the offloading process, such as network performance, data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) processes, computational requirements, application-specific factors, and energy efficiency, are analyzed considering the smart-grid operational requirements. We conduct a comprehensive overview of the current research landscape to support decision-making regarding offloading strategies from cloud to fog or edge. The focus is on metaheuristics for identifying near-optimal solutions and reinforcement learning for adaptively optimizing the process. A macro perspective on determining when and what to offload in the smart grid is provided for the next-generation AI applications, offering an overview of the features and trade-offs for selecting between federated learning and edge AI solutions. Finally, the work contributes to a comprehensive understanding of edge offloading in smart grids, providing a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis to support cost–benefit analysis in decision-making regarding offloading strategies.
1. Introduction
As Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and actuators are deployed in smart grids, operation and control need real-time processing closer to the edge for faster response and to support the development of context-aware, Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven energy services [1]. This trend is accelerated by the integration of renewable energy sources at the edge of the grid, which requires holistic solutions and decentralized energy and computational infrastructures to ensure energy resilience and decrease carbon footprint [2]. However, in smart-grid decentralized scenarios, the offloading of processing workloads towards the edge nodes is challenging due to the heterogeneity, diversity of resources, application characteristics, and edge uncertainty [1]. Challenges like real-time data-processing, reducing latency, and security need to be systematically addressed in the smart grid, and edge and fog computing can play a fundamental role in energy sector decentralization [3].
Different edge-computing and energy-grid-related factors need to be considered to offload and orchestrate in near real-time applications at the edge of the smart grid to address operational problems brought by the integration of renewable energy sources while minimizing data transfers [1,4]. The challenge is to make optimal computational orchestration decisions under uncertain and dynamic conditions [5] given by edge resource capacity demand (e.g., bandwidth and memory), failures (e.g., data network link), the latency of the network, energy consumption of resources, and lifecycle activities of applications. Automation is a key aspect in managing edge-offloading solutions in smart grids and is facilitated by recent advancements in application virtualization, semantic integration, and the data connectivity of edge devices [6].
Moreover, the edge-offloading decisions are also influenced by the contextual aspects of the data, encompassing requirements like low response time and various network performance characteristics [7]. Edge AI is emerging as a new paradigm for the efficient management of smart grids, leveraging the improvement of machine-learning models that can run at the edge of the grid [8]. Edge AI is facilitated by factors such as the development of training pipelines with improved usability and advancements in edge-computing infrastructure, which occur more rapidly than the reduction of wide-area network latency. Additionally, the adoption of IoT devices in the smart grid generates significant big data that requires AI to process, with stringent time processing requirements to prevent energy shortages [5,9]. Edge–fog–cloud federated frameworks offer promising solutions for processing data using AI at the edge nodes and orchestrating a global model in the cloud [10,11]. Nevertheless, their applications in smart-grid scenarios and integration with new real-time context-aware energy asset-management services are rather limited, even though they bring clear benefits in terms of data management in smart grid, privacy, and security, or addressing latency impact on services’ delivery. However, presently, energy services focus on assuring the links and connectors for analyzing data in the cloud, taking advantage of the potential unlimited computational resources [12].
In this context, a comprehensive overview of the current state of research is needed to support sound decisions regarding smart-grid applications offloading from cloud to fog or edge. The edge-offloading implementation is complex, requiring substantial upfront investments and posing integration and security challenges. This report aims to bridge knowledge gaps, serving as a comprehensive guide that explores edge offloading in the energy sector, focusing on architecture, criteria, and decision-making techniques. Existing architecture and offloading decision-making criteria need to be analyzed in the context of the smart grid to support applications orchestration across the computing continuum, supporting the implementation and delivery of AI-driven energy services at the edge of the smart grid. We overview the smart grid and computational distribution architectures, including edge–fog–cloud models, orchestration architecture, and serverless computing, considering decentralization and the case of edge offloading. Despite their potential, these architectures face challenges in coordinating tasks due to the complexity of management across layers. As the optimization problem is computationally complex and involves a high dimensionality of the solution space, it is addressed using heuristics-based computing or reinforcement learning models. We analyze the decision-making variables and optimization algorithms to assess their efficiency and applicability to edge offloading. Finally, we provide a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis to support edge-offloading decision-making in smart grids, improve computational resource allocation, and enhance overall smart-grid decentralized organization.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the basic concepts of edge, fog, and smart grids. Section 3 offers an overview of existing architectures for smart grid and edge offloading. Section 4 analyses the criteria used in offloading decision-making, and Section 5 focuses on heuristics and reinforcement learning solutions. Section 6 concludes the paper and discusses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to edge offloading in smart grid.
2. Basic Concepts
The emergence of new IoT technologies and intelligent infrastructure models has led to a significant increase in the number of network-connected devices and the volume of data that moves across the network. Consequently, traditional data-processing performed entirely in a cloud environment resulted in large communication latencies, making it difficult to deliver real-time results in internet-based applications [13]. These applications run mainly on the end users’ mobile devices, which are limited in terms of computational resources and storage capacity, while data-processing ensures that the functionalities are executed in the cloud. In this context, using the traditional network architecture creates a high network load, and communication becomes completely inefficient [14]. Edge and fog computing paradigms emerged to address the bottlenecks of cloud-based architectures by moving the data-processing at the edge of the network, closer to the place where it is generated and consumed. Edge and fog computing are important in offloading cloud-based applications by providing the required computational and storage resources and services closer to the users (see Figure 1).
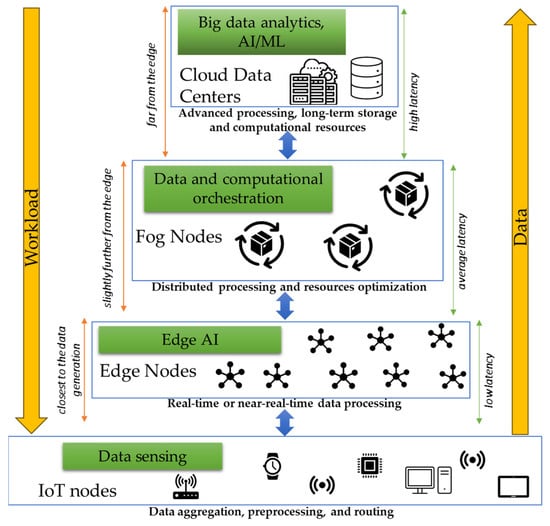
Figure 1.
The edge–fog–cloud architecture.
In the smart-grid context, the integration of IoT monitoring devices has led to the generation of big data that presents challenges to cloud-based applications due to latency and responsiveness problems. In this sense, the edge or fog computing infrastructure could be used between the energy grid monitoring devices and the cloud level, enabling data-processing closer to the edge and reducing the data exchanges with the cloud [15]. Edge servers can be deployed with enough processing capacity to allow the analysis of IoT data and provide faster decision-making for optimizing decentralized energy systems and the data being processed locally. In this context, the problems at the edge devices levels, like data storage and processing capabilities, are usually addressed by forwarding the data to the next computational level, benefiting from better hardware equipment [16]. At the same time, the applications can be offloaded toward the edge levels to increase responsiveness and address latency and bandwidth problems.
2.1. Edge Computing
Edge computing puts computing and data storage near where they are used, usually at the network edge, as opposed to cloud computing, where computing and data storage are done far away in distant data centers. Cao et al. [17] argue that all edge-computing definitions focus on providing services and performing calculations at the network edge closer to the data generation source to meet the critical needs of industry and real-time applications. The edge devices such as IoT devices, smartphones, sensors, and other equipment that generate or consume data often have limited processing and storage capabilities; however, they form an edge infrastructure, which includes the hardware and software resources deployed at the edge.
The architecture of an edge-computing network consists of the terminal layer, boundary layer, and cloud layer [17,18]. End devices, such as sensors and actuators, are positioned at the terminal layer of the computing structure. This front-end environment offers increased interactivity and enhanced responsiveness for end users. Leveraging the available computing capabilities through the numerous nearby end devices, edge computing can deliver real-time services for certain applications. However, given the limited capabilities of these end devices, most demands cannot be met within the terminal layer. Consequently, in such instances, the end devices forward the resource requirements to the edge servers located in the near-end (boundary) layer, where most of the data computation and storage migrates. The edge servers have better computing and storage capabilities, but they are also constrained compared to the cloud servers. This is why the computationally intensive tasks are forwarded to the cloud servers and deployed in the far-end (cloud) layer, but this can result in a significant latency penalty.
Edge devices feature a high degree of heterogeneity, leading to interoperability challenges, a significant obstacle in successful edge offloading. Additionally, network heterogeneity, caused by the diversity of communication technologies, affects edge service delivery. Consequently, ensuring that all edge devices and servers can work together seamlessly is crucial, pushing standardization and interoperability protocols importance for the edge-computing ecosystem. The low latency and high bandwidth are the primary motivations for edge offloading to reduce the delay in sending data to a remote cloud server and receiving a response [18]. This is important for applications that require real-time or near-real-time processing, like some of the time-critical energy management services of the smart grid. Edge offloading aims to achieve bandwidth optimization by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to central data centers or the cloud [19]. Thus, relevant decision-making processes should be implemented on edge servers by considering local and contextual energy data. This becomes particularly important in scenarios with limited data network capacity and stringent response time requirements, making it unfeasible to send the data to the cloud [8].
Finally, additional trade-offs need to be addressed, such as energy efficiency, security, and offloading overhead [20]. Given that many edge devices are battery-powered or have limited power resources, energy consumption is significantly lower in edge-based infrastructures than in cloud data centers. Furthermore, since data are processed closer to the source, there is potential for improved data privacy and reduced exposure to security threats [21].
2.2. Fog Computing
Fog computing distributes services and resources for data-processing, storage, and communication throughout the entire path from the cloud to the connected devices [22]. The main difference compared to edge computing is the hierarchical nature, offering a comprehensive range of computing, networking, storage, control, and services [23]. Consequently, fog jointly works with the cloud and edge nodes, representing the intermediate layer between the near-end and the far-end layers of the general edge architecture. A fog node includes multiple physical devices that offer resources and services and link the edge and cloud environments [24]. Fog nodes are responsible for processing, storing, and transmitting data supporting the offloading towards the network edge [25]. Fog nodes can be placed close to the data source to reduce the latency compared to traditional cloud computing or can be closer to the cloud to provide higher computing power and storage capabilities.
Fog nodes collaborate in a mesh fashion to offer load-balancing, resilience, fault tolerance, data sharing, and reduced reliance on cloud communication [26]. Fog computing systems typically comprise three internal tiers but can include more tiers for specialized applications [22]. At the edge, fog nodes focus on data acquisition, normalization, and sensor and actuator control. In higher tiers, they handle data filtering, compression, and transformation, while nodes near the cloud aggregate data and generate further knowledge. Architecturally, edge–fog nodes require less processing and storage but rely on substantial I/O accelerators for sensor data intake. With more tiers, each level extracts valuable data and executes more computationally intensive tasks.
Fog computing aims to establish a cohesive range of computing services extending seamlessly from the cloud to edge devices, as opposed to the base principle of edge computing, which considers network edges as separate, isolated computing entities. Furthermore, fog provides stronger computing and storage resources than edge does. Thus, a fog node can aggregate data collected and processed by multiple edge nodes.
2.3. Smart Grid
The shift towards a renewable-based energy system impacts the electric power system operation that needs to integrate new Information and Communications Technology (ICT) paradigms, models, architectures, and services to support decentralization [27]. The smart-grid concept is fully connected to the dynamically interactive real-time infrastructure incorporating IoT and ICT-driven solutions everywhere, from electricity generation to delivery and consumption [28] (see Figure 2). Moreover, in decentralized scenarios, digital communication and technology are mandatory to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity production, distribution, and consumption [29].
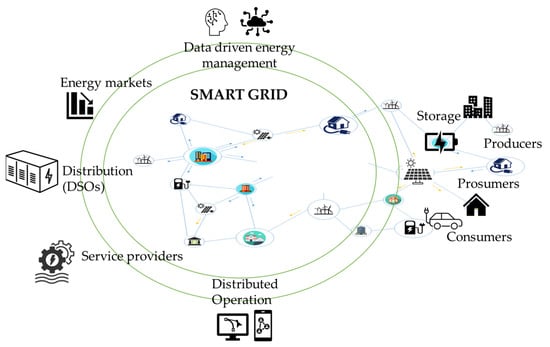
Figure 2.
The smart-grid ecosystem architecture.
Smart grids aim to solve traditional grid problems caused by the energy transition, such as managing the uncertainty of renewable energy sources, managing demand, shifting and shaving, managing congestion, reducing power losses, and offering secure, efficient, and resilient services. Consequently, smart-grid development has added smart data-processing capabilities to the electrical grid [30] to improve the reliability and efficiency of the electric grid, optimize the grid operation and its resources, integrate distributed renewable energy sources (RES), and deploy new technologies for improved metering and automation. On smart grids, data-driven services are implemented to enable real-time management during normal and emergency conditions [31]. They allow for grid-decentralized operation within their safe ranges and reduce the overall costs of energy [32].
The management tools built on top of smart grids require the integration of advanced IoT devices, smart meters, data hubs, and storage systems, as well as AI-driven processes and decentralized components and architectures [28]. The deployment of smart metering devices and the integration of renewable sources may increase the adoption of edge AI [33]. However, new challenges emerge in terms of data-processing scalability and concerns about data privacy and security [24]. By connecting millions of monitoring devices, big data are fed into the distributed grid management systems. Thus, the trade-offs related to latency, bandwidth, and response time need to be carefully considered. Managing and controlling the distributed energy sources at the edge of the grid requires the large-scale adoption and integration of IoT devices. The big data collected on smart-grid operation needs to be managed and processed closer to real-time to ensure reliability in energy distribution. As the complexity of grid operations increases, the volume of data grows, thus making it challenging to ensure a low latency in data analysis and decision-making within acceptable time frames. Processing workloads need to be moved as close as possible to the data generation points to decrease the latency and reduce the amount of data moved to the cloud. Moreover, the prompt processing of data requires high throughput capabilities to handle the data streams generated by the monitoring devices. Additional challenges related to data storage, processing power, and network bandwidth need to be addressed to avoid bottlenecks in data ingestion and efficient AI-based data-processing.
3. Architectures Overview
Offloading in smart grids typically refers to the process of shifting computational tasks or data-processing from local devices to remote servers or cloud platforms and back. In this section, we start by analyzing the most relevant architecture for smart energy grids and then various computational architectures that have been proposed and can eventually facilitate the offloading of applications across the computational continuum.
3.1. Smart-Grid Architectures
There are two widely used smart-grid architectural frameworks providing a structured approach for designing applications architectures, future infrastructures, and reference scenarios: the European smart-grid architecture model (SGAM) proposed by CEN-CENELEC [34] and the American smart-grid conceptual model proposed by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) [35].
SGAM is a layered model defining several interoperability layers [34] (see Figure 3). The asset and component layer models the energy assets and resources installed in the smart grid as well as the communication infrastructure for data exchange. The communication layer facilitates the exchange of data among various components within the smart-grid infrastructure. It integrates the communication protocols and interfaces that enable interoperability among smart-grid components and data exchanges for monitoring and control. The information layer defines the data flows and storage aspects of the energy and computational infrastructure. The function layer addresses the functional capabilities needed to meet business objectives, while the business layer models processes, stakeholders, and objectives. The security layer spans across all layers, offering features for security and privacy.
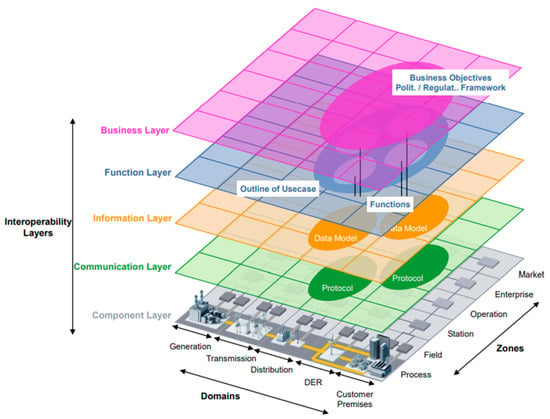
Figure 3.
The SGAM architecture [36].
It considers different electrical grid domains such as generation, transmission, distribution, distributed energy resources (DER), customer premises, etc., and foresees different aggregation zones. The data from the field devices and meters is usually aggregated or concentrated in the station zone to reduce the amount of data to be communicated and processed in the operational zone. At the same time, spatial aggregation can be done from distinct locations to wider areas; for example, multiple decentralized energy resources for a microgrid, smart meters in customer premises are aggregated in the neighborhood or community, etc. As it is a reference architecture, SGAM offers several advantages for designing and implementing decentralized smart-grid scenarios, as it provides a common foundation, facilitates comparative analysis, and includes a specific mapping methodology [37,38,39].
The SGAM framework has been used to model complex energy systems and create high-level designs. The described architecture helps to understand the communication infrastructure and to clarify the data and information exchange problems, etc. SGAM has been adopted in interoperability scenarios where different heterogeneous components interact, and data are integrated for analytics. It has become a best practice, especially for research projects in the energy domain [34], where the model was used to enable ancillary services for distributed energy sources, to test innovative smart-grid technologies, and to evaluate smart-grid-level use cases [38] etc. Over the years, the SGAM framework has also been used in other fields such as industry automation, automotive, legislation, smart cities, maritime, and software development [34].
The smart-grid conceptual model proposed by NIST [35] offers a reference model to guide the development and interoperability of the smart grid, addressing aspects related to ICT models and architecture design and integration, paving the way for decentralized management scenarios (see Figure 4). The conceptual model explains the roles and services of the smart grid in different domains and sub-domains that feature various services, interactions, and stakeholders who interact and communicate to achieve overall system objectives. Examples of such services are demand management, distributed generation aggregation, and outage control.
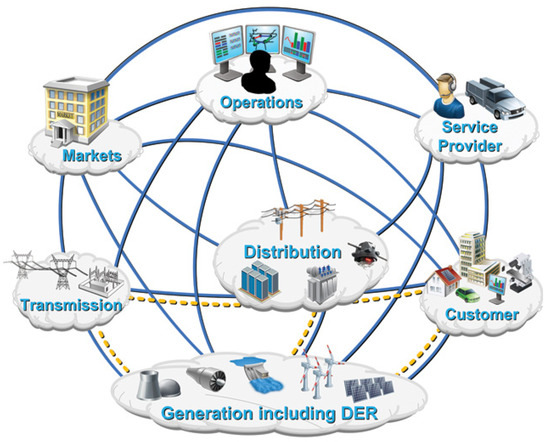
Figure 4.
The NIST smart-grid model [35].
The customer domain represents the end users of electricity, consumers, producers, or prosumers that can consume, generate, and store or manage energy. As a classification, the model considers three classes of customers, each with a different sub-domain: residential, commercial, and industrial. The customers’ boundaries are the smart meters and the energy services interface (ESI). The markets are economic mechanisms and facilitators that offer functionalities for actions to optimize system operation, such as energy selling/buying, storage, etc. The markets domain allows the balancing of supply with demand within the smart grid and can use advanced peer-to-peer (P2P) trading mechanisms based on modern technologies such as blockchain. The entities offering services to the involved actors are marked in the service provider domain. These business activities include usual utility services, like billing and customer accounts, and improved customer services, like controlling energy use, demand response, and energy generation. Operations deal with the administrators of electricity movement, such as smart-grid managers, and involve complex energy management systems to analyze and efficiently operate the grid; transmission refers to the carriers of electricity over long distances, such as Transmission Systems Operators (TSOs), while distribution is the domain for distributors of electricity such as Distribution System Operators (DSOs). Generation (updated with DER inclusion in version 4.0 of the model) refers exclusively to energy producers, including traditional generation sources and DERs. This domain includes all required technologies and infrastructures for generation/storage and participation in demand response programs.
The NIST smart-grid model has been adopted for different scenarios in the energy management domain with specific use cases in residential energy efficiency, industrial energy consumption optimization, electric vehicle (EV) integration in smart grids, energy trading, and DER management. Its defined actors and components allow for customization for any smart energy scenario that can be designed in present smart grids. Apart from testing and validating various smart-grid designs, the NIST model has found applicability in auditing cybersecurity strategies.
The two architectural frameworks discussed above have been influential in developing smart-grid architectures for different cases and scenarios, including decentralization aspects [40]. The choice between the two frameworks depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the project, the level of detail needed, and the area of interest, as well as on their advantages and disadvantages (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of the two smart-grid architectures: (+) advantages and (−) disadvantages.
However, more specific architectures have been designed to address different challenges related to the computational continuum in more depth, such as data management distribution latency and security [2,3,41]. It is worth noting that even though those architectures have benefits related to edge offloading, the implementation can be a complex process and might need significant upfront investment for the initial setup [42,43]. The integration of different smart-grid layers with computational ones, such as edge or fog, and security management for unauthorized access are additional challenges that need to be considered [44]. Table 2 highlights important characteristics of relevant smart-grid architectures.

Table 2.
Characteristics of more specific smart-grid architectures.
Mehmood et al. [41] defined a smart-grid architecture consisting of four layers: the device layer, edge-computing layer, cloud computing layer, and security layer, each layer representing a specific purpose for data collection, preprocessing, storage, analysis, and security management. The device layer consists of sensors, tags, actuators, and smart meters that collect data from the smart grid. The edge-computing layer is located at the network edge with the primary goal of filtering and preprocessing data from the device layer before sending it to the cloud. The cloud computing layer is responsible for storage, computational analysis, and providing different application services while receiving only the summarized data sent from the edge nodes for global analysis. The security layer is responsible for the security of the smart grid, and it should be considered from the early stages of development, including network, computing, and memory management. The framework aims to address challenges such as data management, latency, security, and privacy for the smart grid system based on IoT, improving efficiency, reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources.
Feng et al. have proposed a three-tier architecture for the implementation of electrical engineering scenarios in smart grids [2]. The architecture foresees the thing, edge, and cloud tiers. The thing tier is responsible for the electrical equipment and communication access, executing specific operations in the smart grid, and implementing control orders. The edge tier acts as an intermediary layer between the smart-grid control center and the things, hosting resources for storage, communication, and computing. The energy resources are categorized into sub-layers based on their locations. Although the low-power and fine-performance resources are positioned in the proximity of the things, resources with more robust computing capabilities are located closer to the control center. Additionally, the cloud tier represents the cloud computing resources that empower the computational and offer storage capabilities for the smart grid, offering monitoring solutions.
Molokomme et al. proposed an architecture involving multiple components such as residential, commercial, and industrial devices, edge servers, power systems, IoT devices, and the overall cloud infrastructure [3]. The architecture integrates with edge computing, introducing intelligence for analysis, monitoring, and processing of data at the network’s edge. The edge servers offload the tasks that require significant computation from devices with limited resources, improving the speed and processing capacity of the system. The architecture extends the features with AI algorithms deployed at the edge to improve communication, processing, and caching within the system. The objective is to raise awareness about security threats, efficiently manage power resources, and detect potential issues within smart-grid systems. The architecture may utilize advanced optimization techniques such as federated learning, deep reinforcement learning, and peer-to-peer to enhance the performance and resource usage of the entire system.
3.2. Edge-Offloading Architectures
The architecture addresses the design of systems that involve the distribution of computational tasks between different computing resources, such as edge devices, cloud servers, or other remote processing units.
Several architectures are based on combining different computing models, such as edge and cloud, to enable distributed computing and task-offloading [19,45,46]. They focus on distributing tasks efficiently and optimizing resource usage. However, these benefits come with challenges, such as increased dependency within the network and the management of tasks across multiple layers. Kaur et al. proposed the KEIDS scheduler [45] for managing Kubernetes containers on edge–cloud nodes in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) environment. The edge nodes are responsible for collecting data from IIoT devices and performing initial processing. The cloud nodes empower the processing and storage capability for more complex tasks. The KEIDS controller acts as a central management and scheduling component, with the main objective of improving the allocation of tasks to the available nodes. The controller considers different factors, such as carbon footprint, interference, and energy consumption, in the scheduling decision-making process. By optimizing energy utilization and minimizing interference, the scheduler aims to provide optimal performance to end users in terms of application execution time and utilization. The architecture processes data in real time and offers more flexibility and scalability in the ecosystem of edge–cloud for IIoT. The proposed scheduler faces limitations such as performance degradation and scheduling bottlenecks due to the complexity of the edge environment. The management of containers in dynamic and heterogeneous environments is complex, posing challenges to organizations concerning application configuration. Finally, ensuring data consistency across distributed environments can be challenging, particularly for edge devices that might experience unreliable network conditions. Kovacevic et al. [19] demonstrate the utilization of multi-access edge-computing servers closer to mobile networks, transferring computation and storage from mobile and IoT devices. The edge servers are distributed across the radio access network and contain modest computational capabilities compared with cloud services. The offloading decision aims to minimize the usage of resources while concurrently maximizing the number of accepted requests that are time-critical. The architecture stresses computing power and transmission with latency constraints for computation offloading requests. The objective is to optimize resource allocation to reduce the network traffic and service latency while enhancing the resource utilization and acceptance rate. Limitations still need to be addressed in terms of energy and computational capacity availability towards the edge. The computational offloading solutions can become impractical in the case of applications with strident time execution requirements. The edge servers can reduce the communication delay, but they are limited in size and computational capacity and not only cost-effective solutions. Nguyen et al. present a resource adaptive proxy [46] in an edge-computing environment consisting of multiple components, including the controller manager, scheduler, master server, cloud controller manager, and cloud–edge client. The resource adaptive proxy component is implemented in each worker node of the Kubernetes cluster and is integrated into every worker node within the cluster. The adaptive proxy algorithm consistently gathers resource availability, including central processing unit (CPU) and Random Access Memory (RAM), along with network delays between edge nodes to inform optimal load-balancing decisions. When making load-balancing decisions, the adaptive proxy considers the application resources available on each edge node. Although local nodes are given priority for handling requests, in cases of local node overload, requests are directed to the most suitable edge node to minimize delay. The architecture is designed to reduce request latency and enhance overall throughput within the edge-computing environment. However, if the request is sent to a worker node that is already overloaded, the throughput of the cluster is decreased. Increased request delays are experienced if the worker node has a high network latency, which can lead to increased request delays. Thus, the high latency is a result of network connection delays and bottleneck limitations.
Several architectural designs leverage a hierarchical distribution to achieve optimal task placement and enhanced QoS (Quality of Service) [47,48,49,50]. Pallewatta et al. proposed a distributed architecture for IoT applications, utilizing microservices architecture and fog computing [47]. This framework facilitates the transition from monolithic application to distributed architecture for cloud deployment and task distribution to fog computing. It optimizes high-quality service delivery by strategic placement of microservices. Fog computing, in combination with resource-efficient deployment at the network edge, addresses the latency and bandwidth challenges of IoT applications. Moreover, the architecture allows for the dynamic composition of scalable microservices for achieving optimal performance in fog-based environments. Nevertheless, coordinating tasks across multiple layers can be a challenge due to the complexity of management processes, accurate modeling of microservice architecture, development of microservices placement policy, and microservice composition. Firouzi et al. proposed an edge layer design responsible for communication between sensors and nodes, as well as dedicated interconnections between fog nodes and the cloud [48]. The support for wireless connectivity in nodes relies on several factors, like geographical location, data throughput, mobility, coverage, environmental conditions, spectrum licensing, and energy sources. The architectural viewpoint concerning control and management encompasses life cycle management, registration, provisioning, automated discovery, offloading, load-balancing, task placement, task migration, and resource allocation. This hierarchical structure facilitates the dissemination of intelligence and computation, encompassing AI/machine learning (ML) and big data analytics, to attain optimal solutions within specified constraints. Challenges and limitations arise from the convergence of IoT and cloud computing, such as bandwidth limitations, latency issues, and connectivity concerns. Also, adapting the architecture for multi-layer computing poses challenges. Dupont et al. [49] introduced the concept of IoT offloading, wherein containers are instantiated either at the edge or in the cloud, diverging from deployment on the gateway itself. The realization of this architectural model leverages OpenStack as a virtual machine (VM) manager and Kubernetes as a container manager. Within the OpenStack environment, three controller nodes and two compute nodes are configured, with Kubernetes installed within the latter. The Kubernetes cluster encompasses cloud nodes, edge nodes, and two IoT gateways as distinct nodes. These IoT gateways are constructed using a Raspberry Pi version 3 along with an extension shield capable of supporting diverse wireless communication modules. The gateways deploy Advanced RISC Machine (ARM) versions of Docker and specific editions of IoT function containers tailored for both ARM and i386 architectures. The central orchestrator, utilizing Kubernetes labels, ensures the deployment of the correct container based on the target architecture. The discovery container initiates communication through Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) hardware devices accessible on the gateway. An event notice is communicated to the orchestrator upon device detection, triggering subsequent processes. The solution does not address aspects related to edge-offloading privacy and security in IoT environments, as well as the potential hardware limitations of the gateway devices. Taherizadeh et al. proposed an architecture to optimize smart IoT applications, focusing on achieving elevated QoS, flexibility, and dependability [50]. This framework introduces the concept of microservices, where each business capability is encapsulated as a self-contained service with a clearly defined programmable interface. Employing lightweight container technologies like Docker, the architecture virtualizes and implements the necessary microservices. Components include a container orchestrator, an edge–fog–cloud monitoring system, and infrastructure elements. This edge–fog–cloud architecture ensures that data-processing and computation occur at the most suitable level, enhancing performance, reducing latency, and elevating QoS for IoT applications. The framework facilitates the orchestration of microservices, seamlessly transitioning from edge-computing nodes to fog and cloud servers within the geographical vicinity of mobile IoT devices. In comparison to fixed centralized cloud providers, this distributed computing architecture delivers swifter service response times and enhanced QoS. The limitations of the approach are related to the consideration of the runtime variations in the performance of edge and fog infrastructures, such as processing delays or CPU availability.
Relevant edge orchestration architectures have a primary focus on the organization and scheduling of tasks across both cloud and edge nodes [51,52]. These approaches offer advantages such as resource optimization, but the creation of efficient orchestration strategies can be a complex task. Böhm et al. define an architecture based on a container registry that contains the images of applications and is used to design the nodes within the cloud infrastructure [51]. The autonomic controller distributes responsibilities to various nodes. The distribution is based on a defined strategy, algorithm, or policy. Diverse provisioning models are used to distribute the applications across both cloud and edge layers. Orchestration across both cloud and edge layers ensures a strategic distribution of applications in edge, cloud, and IoT components. The distribution is based on a set of objectives, adopting a multi-objective approach to support optimal efficiency. Complex optimization and scheduling models are required to offer this framework, with the capability of dynamically allocating applications based on resource demand and supply. The main limitation of the proposed solutions is the lack of in-depth consideration of their requirements, like real-time processing or fault tolerance for the offloading of containers. Pérez et al. define intelligent container schedulers for different interfaces within cloud–fog–IoT networks [52]. The schema consists of three primary interfaces: cloud-to-fog, fog-to-IoT, and cloud-to-IoT, each with distinct responsibilities and functionalities. It emphasizes the importance of designing and implementing microservice schedulers for these interfaces, offering several benefits, including the optimization of runtime, adherence to latency restrictions, power consumption reduction, and load-balancing. The schema visually demonstrates the complexity of the network architecture and the need for tailored scheduling strategies for each interface. The authors discuss the existing limitations, such as the need for expert strategies and learning systems for optimizing container scheduling with expert strategies and learning systems to holistically consider QoS requirements like latency, power consumption, and load balance.
Finally, serverless edge-computing architecture [53] emphasizes the integration of serverless functionality to manage event processing to reduce the need for extensive adjustments for IoT devices. However, it is worth mentioning that serverless functions may encounter delays when starting up, which can affect their ability to respond promptly when initially required. Moreover, the restricted duration of execution for serverless functions may function as a limitation for specific applications. From the edge perspective, IoT devices connect to edge nodes with serverless functionality for efficient event processing, while IoT devices require minimal adaptation, following function-based principles. In the cloud, serverless integrates with its edge counterpart.
Table 3 presents an overview of relevant computational offloading architectures and their characteristics.

Table 3.
Characteristics of Offloading Architectures.
4. Offloading Criteria in Smart Grid
In this section, we explore key factors and variables that serve as guiding principles in making informed decisions to determine whether a task or process should be offloaded from a cloud environment to a local edge device or on-premises system (see Figure 5). When discussing offloading in the context of smart grids, the decision-making process is crucial for optimizing resource utilization, improving performance, and minimizing costs across the computing continuum. The process is affected by several variables or factors, such as network performance, data and AI processes, computational requirements, application-specific factors, and energy efficiency.
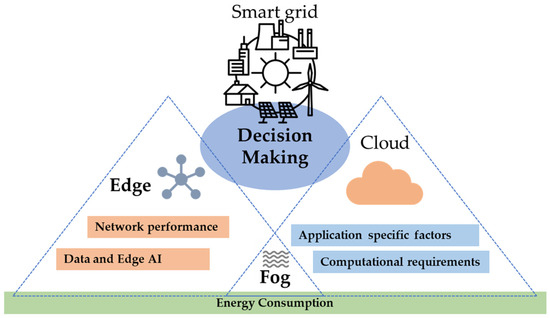
Figure 5.
Offloading decision-making criteria in smart grid.
The key factors and variables involved in the offloading process have been chosen deliberately, with careful consideration given to the operational requirements of smart grids.
Network performance is a key factor for considering edge offloading in smart grids, as they usually feature heterogeneous communication technologies with different bandwidth and latency features. Data network performance affects data transmission among sensors, control systems, and energy grid operators. Low latency and high bandwidth are necessary to ensure that critical data, such as energy demand, grid voltage, and equipment status, is transmitted promptly to enable timely decision-making and control actions. By offloading the processing tasks closer to the edge, the issue of transmitting the big data volumes produced by IoT devices toward the cloud can be mitigated, enabling the process and decision-making closer to the data origin. Reliable data network performance facilitates the data transfer among edge–fog–cloud. However, the data connection among the edge nodes is not always reliable and can expose the offloading process to uncertainty.
AI-powered smart grids require that the data be processed locally and quickly, thus aligning with edge computing and federated learning principles. Modern smart grids can generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to improve grid operations, optimize asset performance, and enable predictive maintenance. At the same time, they pose stringent privacy and security constraints that can be mitigated using federated AI. However, edge devices in the energy grid may have limited computing and storage resources; thus, training AI models locally is challenging. At the same time, sending all data to the cloud server may cause considerable delay and expose the data to potential breaches and risks. Edge AI mitigates some of these challenges, enabling timely data-processing and decision-making closer to the edge by offloading the AI task on the edge.
Computational requirements of offloaded activities play an important role in selecting the edge node in the grid. Offloaded tasks with higher needs should orchestrate edge nodes to secure the computational resources required, and this process is challenging. Algorithms need to predominantly consider the computational requirements and the real-time constraints of smart-grid operation.
Application-specific factors, such as the type (e.g., data-intensive, CPU-intensive, real-time, delay tolerant), Service-Level Agreement (SLA), and containerization requirements, need to be considered. The cost of migration to the edge affects and edge node heterogeneity affects the choice. Thus, the software requirements raise the complexity of the offloading process. The distance and bandwidth need to be considered while maintaining an optimized resource utilization at the edge.
Finally, energy consumption is important for offloading in smart grids. Edge and mobile cloud computing should consider energy efficiency and the integration of renewable sources. The energy consumption at the edge–fog needs to be monitored to avoid raising the grid operation costs.
4.1. Network Performance
Latency, available bandwidth, and response time of a distributed task are important performance metrics in the context of edge offloading for the energy sector [54]. These metrics help to identify the efficiency and effectiveness of making edge-offloading decisions and to assess the performance of applications. In the current literature, several papers proposed solutions applicable to smart-grid scenarios addressing aspects such as the high latency that may limit the ability to react in smart-grid real-time control of assets [55,56,57].
Wang et al. [55] proposed a holistic approach to assess the requirements of different energy services in smart grids. Metrics, such as latency, bandwidth, and response time, are used to create schemes for allocating resources and establishing priorities. They help in making offloading decisions and reducing costs related to task execution delays. The results highlight the efficiency of offloading strategies based on multi-attribute preferences, emphasizing how performance metrics enhance business outcomes in smart power services. Smart-grid components and their performance models influence task execution time, showing the importance of considering energy and latency trade-offs [56]. Network performance metric quantitative measures can be used to optimize the smart-grid performance and energy efficiency. Their assessment can be used to determine optimal offloading strategies based on specific smart-grid requirements, considering factors like energy consumption, response time, and availability [57].
The fog computing infrastructures are used as an intelligent gateway within an IoT framework and offer an effective solution to reduce the latency of applications in edge computing [7]. A multi-period deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm can find an optimal offloading policy to reduce computation, transmission delay, and energy consumption for a collaborative cloud network [58]. Longer communication latency can lead to delays in data transfer, impacting the response of time-critical applications in smart grid. Markos et al. investigate different communication strategies for edge offloading and their impact on energy use and response time [59], concentrating on offloading decisions of the computational tasks for a mobile cloud environment. A multi-objective service provisioning scheme is defined to enhance the overall performance of both network and computation infrastructure while maximizing the usage of the battery lifespan of mobile devices.
Huaming et al. [57] propose the energy-response time-weighted sum and energy-response time product metrics to provide a balanced approach while assessing the trade-off between energy consumption and response time. The metrics combine additive and product factors, prioritizing both aspects without being influenced by different operational scales. Kovacevic et al. [19] emphasize the relevance of performance metrics for assessing applications with critical delays and decision-making related to offloading to improve collaborative resource sharing among cloudlets and mobile cloud providers. Decision-makers can use metrics such as latency, resource utilization, acceptance rate, and resource sharing for efficient cloud offloading in smart grids. Jyothi et al. [60] proposed a dynamic programming solution to offloading using the Hamming Distance Termination. They showcase a strategy for efficiently offloading specific tasks to the cloud, therefore improving execution time and optimizing energy usage. Bandwidth is crucial for proper utilization and efficient data transfer in the cloud. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to performance issues and hinder the overall system’s performance [61].
Huaming et al. [62] use Lyapunov optimization to minimize energy consumption while ensuring that response time meets a given constraint. The prolonged latency of cloud offloading is not suitable for real-time requirements, while direct edge offloading relies on powerful edge servers, which may not be practical for prosumer households in smart-grid scenarios [63]. User-centric perspectives and quality-of-experience-based cost functions have also been considered to optimize the energy-latency trade-off [64]. The shift towards cloud computing has led to the definition of architectures susceptible to latency at different levels [65]. A delayed offloading model has been devised to harness the capabilities of Wi-Fi and mobile networks, considering energy efficiency, performance metrics, and intermittently available access links [57]. Finally, various offloading techniques are defined by Akram et al. [66], including round robin, odds algorithm, and ant colony optimization. These techniques can enhance overall smart-grid system performance, addressing network performance, reliability, stability, and energy efficiency.
4.2. Data and Edge AI
Cloud offloading in the energy sector involves considering the location (physical or logical) and data characteristics such as volume, velocity, and variety. Decisions regarding offloading can be determined by considering the contextual aspects of the data, encompassing requirements like low response time and various other performance characteristics [7]. The adoption of renewable energy sources at the edge of the grid and the integration of IoT sensors and actuators in smart grids require real-time processing [2] and the definition of new AI and data-driven energy services. Edge AI is emerging as a new paradigm for the efficient management of smart grids due to machine and deep learning model improvements [8]. Also, it is facilitated by the recent advancements in computing infrastructure towards edge data-processing and the adoption of IoT devices in the smart grid that generate big data that need to be processed and considered by AI [15].
The distribution of AI models towards the edge aims to reduce latency and integrate with AI-driven management services. In some scenarios, location information can be post-processed in the cloud using raw Global Positioning System (GPS) signal data, resulting in lower energy consumption for location tagging [67]. The objective of computational offloading for traffic in mobile cloud computing is to enhance the performance of both network and computational infrastructure, all while adhering to latency constraints [59]. Offloading strategies within mobile cloud computing strive to optimize effectiveness by transferring workloads either to adjacent cloudlets or to distant cloud computing resources [68]. Energy-aware offloading protocols and architectures are being explored to cope with the increasing number of mobile applications and limitations of battery technologies, with a focus on cloud resource management and green computing [69].
Federated frameworks offer promising models for processing data using ML algorithms at the edge nodes and orchestrating a global model in the cloud [11]. However, their applications in smart-grid scenarios and integration with new real-time context-aware energy asset-management services are limited. Computation offloading frameworks can meet the performance requirements of IoT-enabled services by considering context-based offloading [70]. The offloading decision should consider contextual information to improve accuracy and performance [71]. The dynamic nature of the edge mobile computing environment poses challenges, but a context-sensitive offloading system using machine-learning reasoning techniques can provide accurate offloading decisions [72]. In adaptive offloading systems, energy optimization can be achieved by including context-specific optimization on mobile devices and offloading computational components to a high-performance remote server or the cloud [73]. Current research is focused on improving offloading protocols and architecture to be more energy and contextual-aware. It also enhances scheduling and balancing algorithms to achieve intelligent solutions in the context of edge–cloud offloading in the energy sector [74].
The federated learning distributed the AI process by breaking data silos and limiting the data exchanges between the edge devices and the cloud for model training and updating. Computation offloading of AI processes towards the edge may involve centralized training of the models on the cloud infrastructure and then dynamic relocation of the process towards the edge, considering stringent smart-grid operational or reliability requirements. Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Implementing these solutions in smart grids requires careful consideration of the infrastructure, application nature, and the specific trade-offs summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Feature and trade-offs of federated learning and edge AI solutions in smart grid.
From a training perspective, the edge AI solutions are easier to manage and may exploit the potential unlimited resources of the cloud compared to the federated learning solutions. In federated learning, the models are trained on edge devices, increasing the privacy of the solution as only the model weights are communicated with the centralized cloud. However, it increases the overhead in managing the AI models as multiple versions of the model may exist across different devices, making it more difficult to consider the heterogeneity of edge devices and servers.
Federated learning must consider the heterogeneity of data distributions across different edge devices, making the model convergence more challenging. The data can be non-independently and identically distributed (non-IID), raising statistical challenges for model convergence. Centralized AI model training and its offloading towards the edge may offer advantages in generalization, but it is typically more complex to be containerized, relocated on the edge, and eventually orchestrated. Federated learning may face challenges in scenarios with many smart-grid devices, as coordinating the model updates can be complex and resource-intensive. However, it features better real-time features as the training is decentralized closer to the point of data generation, but the process needs to consider the potential dropout of devices during training rounds.
4.3. Computational Requirements
In IoT-based applications, the node processing capabilities can influence the decision to offload specific tasks from the cloud to the edge and back. These factors are crucial for determining the feasibility and efficiency of the offloaded tasks from edge devices to the cloud infrastructure. The selection of the processing node across the computing continuum depends on several factors: CPU information, memory information, network state information, and average network delays [75]. The challenge is to take optimal edge computational orchestration decisions under uncertain and dynamic conditions [76] impacted by the need for resources in terms of bandwidth and memory, potential failures such as data network issues, network speed, energy consumption, and the lifespan of applications.
The decision to offload specific models is made based on the characteristics and execution patterns of tasks, considering the limitations of the resources for the edge devices and the communication cost between the device and the cloud [77]. The offloading decision algorithm can integrate multiple parameters to reduce application response time, reduce energy consumption, and extend the battery lifetime for the devices [78]. The offloading decisions can be improved by setting threshold values for processing time and employing adaptive algorithms that can dynamically adjust and ascertain the optimal threshold value, ensuring a balanced load on resource-limited devices and edge nodes. Limited resources and energy of edge devices require delegated tasks to the fog and cloud. The presence of augmented computing power and extensive storage capacity can manage the workload more effectively.
Automation is essential in managing cloud–edge platforms in smart grids requiring application virtualization, semantic integration, and data connectivity. Comprehensive orchestration techniques are needed to coordinate, schedule, and run applications across the edge-to-cloud network [4,51]. This will help to deliver real-time energy services at the edge of the smart grid. The dynamic nature of resources in IoT computing farms needs a more robust control mechanism to ensure efficient operation [79]. The offloading architecture aims to minimize the delay while considering energy consumption limitations, and algorithms have been suggested to optimize the delay [80]. Performance improvement can be achieved by offloading computation in cloud robotics due to various factors such as parallel processing capabilities, the availability of resources in the cloud, and communication delays [81]. Based on these factors, decisions regarding offloading are influenced by an assessment of energy consumption, task processing power requirements, and the balance between local execution and offloading tasks.
4.4. Application-Specific Factors
The impact of application type and application migration overhead on the cloud offloading decision is significant. However, the offloading decision process can introduce overhead when implemented on the mobile device. Shifting the offloading decision process to the cloud can reduce this overhead and improve energy savings and execution time [82]. Moreover, a decision-making system that considers the client’s hardware and software resources, location, context, and security capabilities can support dynamic migration and improve the offloading procedure [83]. Different types of applications require cloud resources and services [84]. Selection of the most suitable cloudlet for offloading an application is crucial for reducing energy consumption and latency in application execution [85]. The migration of applications to the cloud introduces overhead and adaptation needs at each layer [86]. The challenges and solutions for migrating different parts of the application to the cloud should be considered, including considerations that apply across various aspects and possible trade-offs before migration to a new environment [87].
In the context of smart grids, cloud offloading decisions are influenced by the application type and associated migration overhead, optimizing resource utilization, reducing costs, and meeting SLA [88]. Atta et al. [84] emphasize the importance of application type in determining the most suitable cloudlet for offloading tasks. Cloudlets demonstrate efficiency in processing diverse application types, impacting load-balancing demands and requiring distinct algorithms [89,90]. To facilitate offloading based on application type, an approach for strategic cloudlet selection is introduced [91], aiming to minimize mobile terminal consumption and latency. This strategy also assists in load-balancing by distributing processing tasks across multiple cloudlets, preventing overload on a single cloudlet.
In smart grids, pivotal roles are played by cloud migration technologies [92]. These technologies strategically place applications across geographically distributed cloud data centers, aiming to reduce costs and adhere to service-level agreements. Considering application migration overhead, including factors such as execution time and energy consumption, is crucial in making informed offloading decisions [93]. Huijun et al. [94] monitor the performance of streaming applications, automatically adjusting the flow of the application graph by offloading computationally intensive operators to virtual machines in the cloud. The primary objectives are to optimize resource utilization and enhance the efficiency of smart-grid applications. The research underscores considerations in cloud offloading decisions for smart grids. Finally, Seyedeh et al. [95] address problems related to application migration and service discontinuity to reduce application delay in hybrid cloud–fog systems. Additionally, factors such as application types, cloudlet selection strategies, migration overhead, and dynamic performance monitoring contribute to the intelligent optimization of smart-grid operations, ensuring efficient resource utilization and overall system efficiency improvements.
4.5. Energy Consumption
Energy consumption plays a pivotal role in making informed decisions to offload specific tasks. Offloading is shifting computation from mobile devices to remote cloud servers, which can help enhance efficiency and minimize battery consumption [96]. The distributed energy-efficient computational offloading reduces data transmission size and energy consumption cost [70]. In fog computing, dual-energy sources, such as solar power and grid power, can support fog nodes and reduce the carbon footprint in IoT systems [97]. Pramod et al. [98] measure the file size and execution time to decide whether to execute the file locally or send it to the core cloud, considering both time and energy savings. Cloud-based software architectures are also being studied to achieve energy-efficient solutions, considering the complexity and investments required for migration and maintenance [99]. Overall, energy efficiency and power consumption play a crucial role in determining the most suitable offloading strategy [100]. Gu et al. [101] propose techniques for energy-efficient computation offloading in the context of 5G networks. Others use energy-efficient frameworks for cloud architectures, which can save up to 25% of the electrical consumption of cloud nodes [102].
Literature reviews on energy-efficient software architectures within cloud environments highlighted the crucial role of energy efficiency in provisioning cloud services [99,103]. Han et al. [104] discuss the definition, principles, and challenges of implementing high energy efficiency in cloud environments. Mobile cloud computing empowers mobile devices to transfer their workloads to distant cloud servers, leveraging the abundant resources of the cloud to optimize efficiency [105]. Fog computing solutions are proposed to alleviate cloud computing’s constraints in terms of latency and high bandwidth requirements by bringing resources closer to users [106]. Power management plays a crucial role in achieving power savings, and changes in architecture, topology, average load/server, and scheduling algorithms can significantly improve energy efficiency [107]. Table 5 shows a comparative analysis of the factors that should be considered when making offloading decisions.

Table 5.
Decision variables in offloading.
5. Decision-Making Techniques
Several decision-making techniques can be employed in the context of cloud offloading to determine when and what to offload. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the application’s characteristics, the dynamic nature of workloads, and the specific goals of offloading. We have classified the techniques based on their type into heuristic optimization-based ones and reinforcement learning-based ones.
Figure 6 summarizes from a macro perspective how to determine when and what to offload in a smart grid. The first step is to analyze the smart-grid energy state to determine if the offloading process could be beneficial. This usually involves using analytics over the data collected on smart-grid operation at low or medium voltage levels as well as specific application factors such as stringent constraints on the response time.
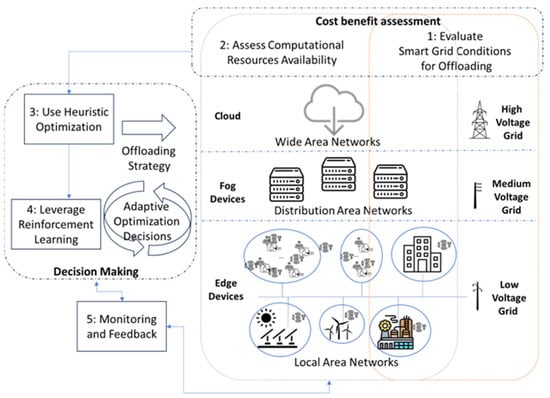
Figure 6.
Macro view on offloading decision-making in smart grid.
The second steps deal with the assessment of the data and computational infrastructure to determine where to offload specific tasks. It involves analyzing the network performance, the computational resources’ availability, data availability, and locality. The first two steps should deal with cost–benefit analysis using the criteria described in Section 4 to assess the potential advantages and drawbacks of offloading. Then, the metaheuristics should be used to address the offloading problem and identify offloading strategies. Even though they offer a near-optimal solution, they are usually fast and relatively easy to adapt to different smart-grid scenarios. As the smart-grid and the cloud–fog–edge infrastructure are dynamic and subject to change over time, the offloading strategies should be flexible and adaptable to accommodate fluctuations in workload, resource availability, and other external factors. Thus, reinforcement learning algorithms should be employed to optimize offloading decisions adaptively over time and continuously improve the strategies. Finally, the performance of offloading decisions should be monitored to address potential problems and inefficient situations.
5.1. Metaheuristic Optimization
Metaheuristic algorithms are iterative, designed to find approximate solutions to optimization problems without relying on mathematical models or properties of the problem at hand. These algorithms are often used when the search space is large, complex, and may contain multiple local optima, which is usually the case in edge offloading. Metaheuristic algorithms are employed to efficiently distribute and manage computational tasks among edge devices based on various criteria such as resource availability, latency, and response time. The integration of heuristic algorithms in the edge-offloading decision process aims not only to address the complexity of the decision space that tends to be large but also to enhance the overall performance and efficiency of edge–cloud systems.
In the context of smart-grid decentralization and local energy systems, they are good choices for optimization problems such as energy and computation resources allocation and scheduling as they may find close to the optimal solutions in large solution spaces where traditional methods may struggle. The metaheuristic is versatile and can be adapted to various scenarios and use cases in smart grids that usually tend to be very heterogeneous where factors like resource availability change and flexibility are required. Finally, they are scalable, considering decision time and computational resource usage, and can handle edge-offloading optimization problems with many variables and constraints. Materwala et al. [108] optimize demand energy by redirecting requests and data from electric vehicles to both edge and cloud servers. It employs an evolutionary genetic algorithm to optimize the energy consumption of edge–cloud integrated computing platforms. An adaptive penalty function is defined to integrate optimization constraints into the genetic algorithm, ensuring that the offloading process meets SLA. The selection of the optimal solution is made using an adaptive fitness function that assesses the proximity to the goal. The algorithm includes stages such as initialization of offloading solutions, evaluation of solutions, selection of fittest solutions, crossover to produce offspring, and mutation of server allocations. The solution archives significant energy savings compared to random and no edge-offloading approaches, with an SLA violation rate of only 0.3%. A solution for collaborative offloading among cloud, edge, and terminal IoT devices, incorporating enhancements to a genetic algorithm, is introduced in [109]. The offloading problem is modeled as a non-linear problem in combinatorial optimization, striving to reduce the overall workload task energy consumption while ensuring compliance with computational delay constraints. The authors consider various types of computational tasks, diverse mobile devices, multiple small-cell base stations, numerous micro base stations, and a cloud server. The solution undergoes theoretical analysis and verification in simulation trials, the results indicating superior performance, particularly when considering diverse quantities and capabilities of mobile devices and servers at the network edge. Shahidinejad et al. [110] proposed an offloading mechanism that adopts a metaheuristic-based approach, utilizing the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) within edge/cloud networks for serving mobile applications. The mechanism is centered on relocating computationally intensive tasks from mobile devices to edge servers by addressing task-offloading as an NP-hard problem. Enhancements to the crossover and mutation operators facilitate faster convergence, setting it apart from other evolutionary algorithms. Employing NSGA-II as a population-based metaheuristic, the mechanism efficiently determines task-offloading decisions within a reasonable timeframe. Numerical evaluation with simulated workloads shows the cost-effectiveness of the proposed mechanism. It can enhance the average utilization of edge servers and reduce energy consumption and execution time compared to alternative task-offloading approaches.
Chen et al. [111] proposed a simulated annealing-binary particle swarm optimization algorithm (SA-BPSO) algorithm which breaks down the edge-offloading optimization problem into three distinct sub-problems: the allocation of computing resources, the allocation of uplink power, and task-offloading. Convex optimization techniques are employed to optimize computing resource allocation, while the bisection method is applied for uplink power allocation. The SA-BPSO algorithm maps the velocity of the particles to the interval [0, 1] using the Sigmoid function and encodes their position in binary. The algorithm effectively reduces the total user overhead compared to other schemes while ensuring the quality of service. Kirana et al. [112] address the optimization of energy consumption of virtual machines in distributed edge–cloud environments using an enhanced particle swarm optimization solution (E-PSO). The primary objective is to minimize energy consumption using the strategic placement of virtual machines in a specific location closer to data sources. It introduces a locally aware fitness function focused on energy considerations and formulates a coding scheme for relocating virtual machines. The E-PSO algorithm identifies an optimal VM replacement strategy, achieving a 22% reduction in overall energy consumption.
A recursive version of the ant colony algorithm is introduced in [113], with the primary objective of addressing potential service-level agreement violations and reducing energy consumption. The workload tasks are modeled as ants. In the monitoring pheromone step, the algorithm keeps track of the pheromone levels and updates the ant’s movement toward the optimal solution. The ants representing tasks select the next city to move based on the pheromone levels and the distance between cities. The outcomes indicate a substantial reduction of approximately 40–42% in energy consumption. Danial et al. [114] proposed an Efficient Ant Colony Cloud Offloading Algorithm (EACO) to reduce energy consumption while considering task completion time constraints. The algorithm divides mobile applications into fine-grained tasks with sequential and parallel topology. It focuses on task scheduling between execution on the mobile device and offloading to the cloud to limit the completion time. It achieves an average energy consumption reduction of 24–59%, with a corresponding increase in completion time of 3.6–28%. Similarly, Tabrizchi et al. [115] use ant colony optimization to minimize energy usage and environmental impact when allocating resources to virtual machines. The use of pheromones by the ants guides their decision-making process as they deposit them along their paths. The algorithm experiences iterative updates of pheromone levels until the quality of solutions discovered by the ants is optimal. The ant colony algorithm achieved an average energy reduction of 24–59% compared with other works.
Samoilenko et al. [116] introduced the whale optimization approach to address challenges in task-offloading within a cloud–fog ecosystem. The runtime dynamic offloading decisions are made using the whale optimization algorithm to enhance the quality of various service metrics, such as execution delay and energy consumption. It employs a population of solutions, represented as whales, to find the optimal solution to the multi-criteria task-offloading problem. Similarly, Anoop et al. [117] combine differential evaluation and whale optimization algorithms to find the optimal solution for edge offloading. By combining the exploration capabilities of whale optimization and the exploitation capabilities of differential equations, the algorithm solves the limitations of conventional heuristic algorithms, such as convergence time, lower exploration and exploitation ability, and implementation difficulties. The spiral bubble-net hunting behavior observed in humpback whales helps to identify the optimization offloading strategies, reducing energy consumption and response time in the process. Finally, Yuan et al. [118] define a hybrid metaheuristic algorithm for the concurrent optimization of computational offloading and resource allocation in mobile edge to reduce total energy consumption. The optimization considers offloading ratio, CPU speeds, allocated bandwidth, and transmission power. It sets a particle swarm optimization framework, defining a fitness function based on penalties using the model constraints. Metropolis acceptance rule inspired by simulated annealing (SA) updates the particle’s velocity and position. It requires reaching the maximum allowable iterations or having a specified percentage of particles attain uniform fitness values. The final solution converts the globally optimal position into task-offloading decision variables.
5.2. Reinforcement Learning
The model-based optimization solutions for edge offloading in smart grids are static in structure, making it complicated to capture dynamic relations and constraints among energy and computational components. The reinforcement learning solutions are model-free alternatives that are a good option for decision-making in a dynamic and changing environment, such as the smart grid. The reinforcement learning algorithms can adapt to these changes and optimize edge-offloading decisions accordingly. They can learn to drive decisions that optimize the utilization of energy and computational resources in the smart grid by learning from previous experiences or existing data, allowing for more adaptive decision-making considering factors such as the energy efficiency of devices, available computational resources, and communication network conditions.
Reinforcement learning solutions can learn optimal edge-offloading policies that yield good results when operating in complex and uncertain environments or with frequent changes. This makes them suitable for decentralized smart-grid scenarios where they can learn to make offloading decisions that minimize energy consumption, reduce latency, and enhance overall grid reliability. Finally, reinforcement learning algorithms do not require prior knowledge and can dynamically adapt to different edge-offloading scenarios without predefined models and structures.
The application of reinforcement learning algorithms to edge-offloading problems faces several challenges that require further research. Learning the optimal strategy for edge offloading requires many data samples, episodes, and action simulations. The design of rewards and penalty functions used in the learning process is complex and affects the overall algorithm convergence and number of episodes. Moreover, in many cases, achieving a good balance between exploration and exploitation is challenging as the decision state and action spaces can be high-dimensional and complex, making it difficult to learn the optimal edge-offloading strategy.
The DDPG (Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient) algorithm, as described in reference [119], represents a model-free, off-policy reinforcement learning approach that emphasizes the advantages of deep neural networks and deterministic policy gradients. The algorithm combines computation offloading, service caching, and resource allocation to reduce energy consumption for a collaborative Mobile Edge-Computing (MEC) system. It includes a Mixed-Integer Non-Linear Programming (MINLP) framework. The DPPG algorithm uses a deep neural network to identify the optimal policy of each decision variable. The critic network assesses the quality of the chosen actions, while the actor network selects the action (i.e., resource allocation, service caching, and offloading decisions) based on the current state. The critic network performs training to approximate the value function, representing the anticipated long-term reward for a specific combination of a state and action. The actor network performs training to maximize the foreseen long-term reward. The training process involves iteratively updating the actor and critic networks using the DDPG algorithm’s update rules, which involve gradient descent and target network updates to stabilize the learning process. During the iterative training process, the DDPG algorithm acquires optimal approaches for offloading computations, caching services, and allocating resources. These findings reduce long-term energy consumption in the collaborative MEC system.
Weichao et al. [120] propose an adaptive strategy for task distribution to address the challenge of environment adaptation. It optimizes objectives related to task latency and device energy consumption. The meta-reinforcement learning algorithm continuously explores and adjusts the edge environment. A task management network, structured on Seq2Seq neural network architecture, is constructed to handle diverse facets of task sequences. Introducing a first-order approximation method accelerates the computation of meta-strategy training for the Seq2Seq network. The algorithm reduces task processing delay and device energy consumption while adapting to needs. Results illustrate the algorithm’s performance over existing methods across various tasks and network landscapes. Antoine et al. [121] define the deep reinforcement learning algorithm for task-offloading to solve the problem of computation offloading with task dependency represented as a directed acyclic graph within the collaborative scenario involving cloud, edge, and end systems, including multi-user environments, multi-core edge servers, and a dedicated cloud server. The Markov decision process supports task-offloading, while deep reinforcement learning incorporates action masking based on task priority. This algorithm uses the computational capabilities of both cloud and edge servers to derive optimal policies for computation offloading. It improves the average energy consumption and time delay experienced by IoT devices. Xin et al. [122] formulate the optimization challenge of collaborative computation offloading between the cloud and edge as a dynamic problem represented using a Markov decision process. It concurrently refines average delay, energy efficiency, and revenue per unit time metrics and combines exploration and exploitation to identify the offloading strategy. The simulation results show the efficiency of the proposed algorithm, especially as the number of tasks offloaded for computation increases. Jie et al. [123] consists of a decomposition of the (offline) value iteration and (online) reinforcement learning, which allows for learning in a batch manner and improves learning convergence speed and runtime performance. The algorithm learns the optimal policy of dynamic workload offloading and edge server provisioning to minimize the long-term system cost, including service delay and operational cost. It uses a post-decision state-based learning approach, exploiting the structure of state transitions in the energy harvesting of the edge–cloud system. Also, the algorithm enables the edge system to determine the optimal offloading and autoscaling policies and solves the “curse of dimensionality” problem associated with large state spaces in Markov Decision Processes. The simulation demonstrates significant improvements in how edge computing performs compared to fixed or short-term optimization methods and traditional reinforcement learning algorithms. Mashael et al. [124] utilize a set of deep neural networks in a distributed manner to find near-optimal computational offloading decisions, aiming to reduce overall energy consumption in cloud offloading scenarios. The algorithm treats the problem as a binary optimization task. Due to the computational complexity of solving this NP-hard problem, an equivalent reinforcement learning form is generated. The distributed deep learning algorithm leverages parallel deep neural networks to find the near-optimal offloading decisions. Results from simulations illustrate that the suggested algorithm rapidly reaches convergence and significantly lowers the system’s total consumption when contrasted with established benchmark solutions. Yongsheng et al. [125] introduce an offloading algorithm based on a deep learning network to calculate the most efficient offloading strategy, considering energy and performance constraints. The algorithm formulates energy and performance considerations into a cost function, and a deep learning network is trained to determine the optimal solution for the offloading scheme. It identifies the best set of components to offload to a nearby server, enhancing the computational capabilities of user equipment for running resource-intensive applications. Important findings illustrate the superior performance of the proposed approach compared to existing methods concerning energy and performance constraints. Sellami et al. [126] introduce a combination of blockchain technology with deep reinforcement learning. The main objective is to raise awareness of energy operations in a classical IoT framework using software-defined networking. Utilizing policies, the approach optimizes various aspects while enhancing reliability, reducing latency, and optimizing energy efficiency. The proposed method prioritizes consumable energy and elevates the QoS in operations. Experimental results show improvements in network latency and energy efficiency compared with traditional algorithms.
The deep reinforcement learning algorithm minimizes power consumption by making informed decisions during each time slot based on content request details and current network conditions [127]. Addressing the issue as a power minimization model allows aggregation of requests and extensive in-network caching deployment. Leveraging past slot data and the present network state, the reinforcement learning algorithm enhances power efficiency in the cloud–edge–terminal collaboration networks. Results highlight the performance of the proposed content task-offloading model in power efficiency compared to current alternatives, demonstrating rapid convergence to a stable state.
Table 6 presents a comparative analysis of the main decision-making techniques used for cloud offloading.

Table 6.
Offloading decision-making alternatives.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we analyzed the architecture, variables, and decision-making algorithms involved in application offloading in IoT-based edge–cloud environments focused on smart-energy-grid decentralization. Our study results show the urgent need to enhance the energy efficiency of cloud offloading and edge computing, especially concerning the specific problems of the smart grid and the transition towards renewable energy. The consideration of application virtualization and microservice organization tailored to the IoT energy metering devices is a practical and forward-looking approach. The computing continuum organization from edge to fog and cloud can improve the service quality and significantly save bandwidth latency in the complex world of IoT-based energy management applications.
Although current decentralized systems and offloading processes show potential, we also highlight their drawbacks, including complexity, high initial costs, and ongoing challenges with integration and security. The integration of smart-grid architectures, known for their layered approach, with an edge–fog–cloud computational resource organization presents promising solutions; however, their use requires careful consideration of smart-grid functional, operational, and organizational requirements to ensure optimal usage.
There is a strong need for an in-depth examination of the cloud–fog–edge architecture in the context of smart-grid decentralization to maximize benefits and effectively address the challenges of renewable energy integration. As the amount of data generated by the smart-grid IoT devices significantly grows, edge offloading and edge AI will be critical for enabling real-time response in emergencies that may affect the grid resilience and, at the same time, will help in addressing challenges related to limited network bandwidth and increased latency which affects decision-making. In this context, we have analyzed and compared decision-making algorithms based on metaheuristics and model-free optimization techniques like reinforcement learning and distributed deep learning for offloading.
These algorithms are fundamental to the improvement of the overall performance of workload offloading in smart-grid scenarios, requiring careful consideration of various decision-making criteria from energy and non-energy fields. In future work, researchers in computer science and the smart grid should focus on validating these algorithms through practical experiments in smart-grid pilots, considering different deployment configurations, various computing resources, and distributed energy assets.
Table 7 presents a SWOT analysis for incorporating cloud offloading into smart grids. Task-offloading enhances overall efficiency by leveraging remote servers for computational tasks, thus allowing for real-time data-processing while reducing latency and improving response time. Edge AI techniques can be used to achieve optimal performance and decentralized energy services delivery in the smart grid. These strengths also lead to the improvement of grid resilience and ensuring energy security. Regarding energy efficiency goals, offloading architectures can meet carbon-saving targets due to better and more reliable management of renewable resources at the far edge of the grid.

Table 7.
SWOT analysis of edge–cloud offloading for smart grids.
The weaknesses of offloading architectures are the complex deployment and integration processes, operation under uncertain network connection or computational resources availability, and interoperability issues over the IoT devices in the smart grid. Some computational architectures lack hierarchical distribution, challenging smart-grid integration. At the same time, some energy applications have requirements or constraints that make them unsuitable for offloading. Distributing tasks across different smart-grid layers will affect coordination and edge-based orchestration, leading to complex management and configuration scenarios. Also, initial costs for designing and deploying edge–cloud offloading solutions in smart grids can be high.
The technological trends in energy, IoT, and AI offer opportunities to improve offloading capabilities in smart grids. Modern AI optimization algorithms can improve edge–cloud offloading strategies, while IoT adoption in smart grids enables the creation of new energy management applications. The smart-grid architecture provides opportunities for customized solutions considering edge–fog–cloud distribution and cost-effective hardware solutions for these solutions, which can increase the adoption of edge–cloud offloading. Solutions such as federated learning or edge AI bring benefits, but careful consideration of implementation trade-offs in smart grids needs to be considered.
Threats for AI task-offloading towards the edge refer to security and privacy, requiring robust measures to prevent unauthorized access. Bandwidth and edge device limitations may affect the effectiveness of offloading, while network stability and non-IID data distribution can impact the performance and reliability of federated learning solutions. Challenges in edge-offloading deployments and data interoperability issues are amplified by the lack of validation in smart-grid pilots to demonstrate their effectiveness. They represent threats that need to be considered when conducting a cost–benefit analysis of offloading decision-making.
In our opinion, future research should focus on more exploration and innovation to tackle the weaknesses and threats, addressing relevant challenges of smart-grid decentralization and IoT adoption while considering emerging resource decentralization trends and AI advancement to continuously improve decision-making strategies. Synergic efforts from energy, IoT, and AI domains are important for the smart grid to increase efficiency through integrating decentralized renewable energy sources and creating sustainable and resilient future energy systems that meet the demands of customers, delivering personalized and context-aware energy services.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.I.A. and T.C.; methodology, T.C. and I.A.; investigation, G.I.A., I.A., A.H. and D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.I.A., T.C., D.L. and I.A.; writing—review and editing, A.H., G.I.A. and D.L.; visualization, I.A., A.H. and T.C.; supervision, T.C.; funding acquisition, T.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program under the Grant Agreement number 101136216. Views and opinions expressed are, however, those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Climate, Infrastructure, and Environment Executive Agency. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aranda, J.A.S.; Costa, R.D.S.; de Vargas, V.W.; da Silva Pereira, P.R.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Vianna, M.P. Context-aware Edge Computing and Internet of Things in Smart Grids: A systematic mapping study. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ding, Y.; Strbac, G.; Kang, C. Smart grid encounters edge computing: Opportunities and applications. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokomme, D.N.; Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Edge Intelligence in Smart Grids: A Survey on Architectures, Offloading Models, Cyber Security Measures, and Challenges. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2022, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, S.B. Prosumer in smart grids based on intelligent edge computing: A review on Artificial Intelligence Scheduling Techniques. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, C.; Xiang, Y.; Li, F. Edge-cloud Computing Systems for Smart Grid: State-of-the-art, Architecture, and Applications. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, R.; Arroba, P.; Risco-Martín, J.L.; Moya, J. Modeling and simulation of smart grid-aware edge computing federations. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 719–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, K.; Jain, S.; Singh, R. Context-Aware Offloading for IoT Application using Fog-Cloud Computing. Int. J. Electr. Electron. Res. 2023, 11, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gill, S.S. Edge AI: A survey. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Antal, M.; Cioara, T.; Anghel, I.; Salomie, I.; Bertoncini, M. A Fog Computing Enabled Virtual Power Plant Model for Delivery of Frequency Restoration Reserve Services. Sensors 2019, 19, 4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, M.; Mihailescu, V.; Cioara, T.; Anghel, I. Blockchain-Based Distributed Federated Learning in Smart Grid. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, R.; Rahmani, R.; Kanter, T. Federated Learning for Distributed Reasoning on Edge Computing. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 184, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terroso-Saenz, F.; González-Vidal, A.; Ramallo-González, A.P.; Skarmeta, A.F. An open IoT platform for the management and analysis of energy data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.Z.; Ahmed, E.; Hakak, S.; Yaqoob, I.; Ahmed, A. Edge computing: A survey. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svorobej, S.; Endo, P.T.; Bendechache, M.; Papadopoulos, C.F.; Giannoutakis, K.M.; Gravvanis, G.A.; Tzovaras, D.; Byrne, J.; Lynn, T. Simulating fog and edge computing scenarios: An overview and research challenges. Future Internet 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Bao, S. Big Data in Smart Grid and Edge Computing of the IoT. In Key Technologies of Internet of Things and Smart Grid. Advanced and Intelligent Manufacturing in China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, A.S.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Kumar, A.; Elmaghraby, A. IoT in Smart Cities: A Survey of Technologies, Practices and Challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Sun, Q. An Overview on Edge Computing Research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85714–85728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A Survey on the Edge Computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, I.; Harjula, E.; Glisic, S.; Lorenzo, B.; Ylianttila, M. Cloud and Edge Computation Offloading for Latency Limited Services. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55764–55776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, K. Edge computing technologies for Internet of Things: A primer. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwarafy, A.; Al-Thelaya, K.A.; Abdallah, M.; Schneider, J.; Hamdi, M. A Survey on Security and Privacy Issues in Edge-Computing-Assisted Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 4004–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, A.; Fung, C.; Nguyen, T.; Kadiyala, K.; Jalali, F.; Niakanlahiji, A.; Kong, J.; Jue, J.P. All one needs to know about fog computing and related edge computing paradigms: A complete survey. J. Syst. Archit. 2019, 98, 289–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, K.; Datta, S.K. Comparison of edge computing implementations: Fog computing, cloudlet and mobile edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS), Geneva, Switzerland, 15 January 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mouradian, C.; Naboulsi, D.; Yangui, S.; Glitho, R.H.; Morrow, M.J.; Polakos, P.A. A Comprehensive Survey on Fog Computing: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 416–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebortta, S.; Tripathy, S.S.; Modibbo, U.M.; Ali, I. An optimal fog-cloud offloading framework for big data optimization in heterogeneous IoT networks. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 8, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, P.; Farhoudi, M.; Kazemian, S.; Khorsandi, S.; Leon-Garcia, A. Fog Computing: A Comprehensive Architectural Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69105–69133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strielkowski, W.; Civín, L.; Tarkhanova, E.; Tvaronavičienė, M.; Petrenko, Y. Renewable Energy in the Sustainable Development of Electrical Power Sector: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavikia, Z.; Shabro, M. A comprehensive layered approach for implementing internet of things-enabled smart grid: A survey. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioara, T.; Pop, C.; Zanc, R.; Anghel, I.; Antal, M.; Salomie, I. Smart Grid Management using Blockchain: Future Scenarios and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2020 19th RoEduNet Conference: Networking in Education and Research (RoEduNet), Bucharest, Romania, 11–12 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Luthra, S.; Kumar, S.; Kharb, R.; Ansari, M.F.; Shimmi, S.L. Adoption of smart grid technologies: An analysis of interactions among barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daki, H.; El Hannani, A.; Aqqal, A. Big Data management in smart grid: Concepts, requirements and implementation. J. Big Data 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Cioara, T.; Antal, M.; Anghel, I.; Salomie, I.; Bertoncini, M. Blockchain Based Decentralized Management of Demand Response Programs in Smart Energy Grids. Sensors 2018, 18, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badidi, E. Edge AI and Blockchain for Smart Sustainable Cities: Promise and Potential. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslar, M.; Rohjans, S.; Neureiter, C.; Pröstl, F.; Velasquez, J.; Steinbrink, C.; Efthymiou, V.; Migliavacca, G.; Horsmanheimo, S.; Brunner, H.; et al. Applying the Smart Grid Architecture Model for Designing and Validating System-of-Systems in the Power and Energy Domain: A European Perspective. Energies 2019, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopstein, A.; Nguyen, C.; O’Fallon, C.; Hastings, N.; Wollman, D. NIST Framework and Roadmap of Smart Grid Interoperability Standards, Release 4.0; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Smart Grid Coordination Group. Smart Grid Reference Architecture; Technical Report; CEN-CENELEC-ETSI: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Menci, S.P.; Valarezo, O. Decoding design characteristics of local flexibility markets for congestion management with a multi-layered taxonomy. Appl. Energy 2024, 357, 122203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; García, A.I.M.; Chassiakos, S.K.; Ageli, O. SGAM-Based Analysis for the Capacity Optimization of Smart Grids Utilizing e-Mobility: The Use Case of Booking a Charge Session. Energies 2023, 16, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.K.; Das, S. Smart grid architecture model for control, optimization and data analytics of future power networks with more renewable energy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 301, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibole, A.; Aljarwan, A.; Rehman, M.H.; Zeineldin, H.H.; Mezher, T.; Salah, K.; Damiani, E.; Svetinovic, D. Blockchain Technology for Smart Grids: Decentralized NIST Conceptual Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 43177–43190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.Y.; Oad, A.; Abrar, M.; Munir, H.M.; Hasan, S.F.; Muqeet HA, U.; Golilarz, N.A. Edge computing for IoT-enabled smart grid. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 5524025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, W.; Man, M. Application and Research of IoT Architecture for End-Net-Cloud Edge Computing. Electronics 2023, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Jin, H.; Li, P. Computation Offloading Toward Edge Computing. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1584–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Wang, F.; Lv, Z.; Nowak, R. A polymorphic heterogeneous security architecture for edge-enabled smart grids. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Ahmed, S.H.; Atiquzzaman, M. KEIDS: Kubernetes-Based Energy and Interference Driven Scheduler for Industrial IoT in Edge-Cloud Ecosystem. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 4228–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-M.; Phan, L.-A.; Kim, T. Load-Balancing of Kubernetes-Based Edge Computing Infrastructure Using Resource Adaptive Proxy. Sensors 2022, 22, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallewatta, S.; Kostakos, V.; Buyya, R. Placement of Microservices-based IoT Applications in Fog Computing: A Taxonomy and Future Directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, F.; Farahani, B.; Marinšek, A. The convergence and interplay of edge, fog, and cloud in the AI-driven Internet of Things (IoT). Inf. Syst. 2022, 107, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Giaffreda, R.; Capra, L. Edge Computing in IoT Context: Horizontal and Vertical Linux Container Migration. In Proceedings of the 2017 Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS), Geneva, Switzerland, 6–9 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherizadeh, S.; Stankovski, V.; Grobelnik, M. A Capillary Computing Architecture for Dynamic Internet of Things: Orchestration of Microservices from Edge Devices to Fog and Cloud Providers. Sensors 2018, 18, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.; Wirtz, G. Towards orchestration of cloud-edge architectures with Kubernetes. EAI EdgeIoT 2021. In Proceedings of the 2nd EAI International Conference on Intelligent Edge Processing in the IoT Era, Online, 24–26 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez de Prado, R.; García-Galán, S.; Muñoz-Expósito, J.E.; Marchewka, A.; Ruiz-Reyes, N. Smart Containers Schedulers for Microservices Provision in Cloud-Fog-IoT Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanpour, M.S.; Toosi, A.N.; Cicconetti, C.; Javadi, B.; Sbarski, P.; Taibi, D.; Assuncao, M.; Gill, S.S.; Gaire, R.; Dustdar, S. Serverless Edge Computing: Vision and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference (ACSW ‘21), Dunedin, New Zealand, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- De Sena, A.S.; Ullah, M.; Nardelli, P.H.J. Edge Computing in Smart Grids. In Handbook of Smart Energy Systems; Fathi, M., Zio, E., Pardalos, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yao, J.; Zheng, W.; Shao, W. Offloading Strategies for Mobile Edge Computing Based on Multi-Attribute Preferences in Smart Grids. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 4–6 March 2022; pp. 1020–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Taami, T.; Krug, S.; O’Nils, M. Experimental Characterization of Latency in Distributed IoT Systems with Cloud Fog Offloading. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems, Sundsvall, Sweden, 27–29 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Knottenbelt, W.; Wolter, K. Analysis of the Energy-Response Time Tradeoff for Mobile Cloud Offloading Using Combined Metrics. In Proceedings of the 2015 27th International Teletraffic Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 8–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, J.; Lee, A.; Nguyen, T.N. Toward an Optimal Latency-Energy Dynamic Offloading Scheme for Collaborative Cloud Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 53091–53102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulos, M.P.; Tzanakaki, A.; Simeonidou, D. Energy-aware offloading in mobile cloud systems with delay considerations. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jyothi, T. Energy Optimization using Cloud Offloading Algorithm. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2017, 6, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wolter, K. Analysis of the Energy-Performance Tradeoff for Delayed Mobile Offloading. Endorsed Trans. Energy Web 2016, 3, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaming, W.; Sun, Y.; Wolter, K. Energy-Efficient Decision Making for Mobile Cloud Offloading. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2020, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Miao, X.; Ma, Q. Trine: Cloud-Edge-Device Cooperated Real-Time Video Analysis for Household Applications. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 22, 4973–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-T.; Kim, H. QoE-Aware Computation Offloading Scheduling to Capture Energy-Latency Tradeoff in Mobile Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking, London, UK, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessert, F.; Wingerath, W.; Ritter, N. Latency in Cloud-Based Applications. In Fast and Scalable Cloud Data Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, J.; Tahir, A.; Munawar, H.S.; Akram, A.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mahmud, M.A.P. Cloud- and Fog-Integrated Smart Grid Model for Efficient Resource Utilisation. Sensors 2021, 21, 7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, L.; Bodhi, P.; Hart, T.; Jin, Y.; Woo, S.L.; Raghunathan, V.; Ramos, H.S.; Wang, Q. CO-GPS: Energy Efficient GPS Sensing with Cloud Offloading. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 15, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Mohammed, A.H.; Karim, S.H.T.; Majeed, M.K.; Masdari, M. Towards Data and Computation Offloading in Mobile Cloud Computing: Taxonomy, Overview, and Future Directions. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 119, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerche, A.; Guan, S.; De Grande, R.E. Sustainable Offloading in Mobile Cloud Computing: Algorithmic Design and Implementation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraz, M.; Gani, A.; Shamim, A.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, R. Energy Efficient Computational Offloading Framework for Mobile Cloud Computing. J. Grid Comput. 2015, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazkar, S.; Sabaei, M. Smart cloud-assisted computation offloading system: A dynamic approach for energy optimization. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering, Shanghai, China, 26 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, W.; Oliveira, E.; Santos, A.; Dias, K.L. A context-sensitive offloading system using machine-learning classification algorithms for mobile cloud environment. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 90, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, K.E. Energy-Aware Adaptive Computational Offloading for Pervasive Community-Based Cloud Computing. Ph.D. Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thanapal, P.; Durai, M.A.S. Energy saving offloading scheme for mobile cloud computing using CloudSim. Int. J. Adv. Intell. Paradig. 2018, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.K.; Liu, J.; Kato, N. Offloading Decision for Mobile Multi-Access Edge Computing in a Multi-Tiered 6G Network. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2022, 10, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, K.; Pranjal Reaj, M.; Sarker, S.; Razzaque, M.A.; Rashid, M.; Roy, P. Task Offloading to Edge Cloud Balancing Utility and Cost for Energy Harvesting Internet of Things. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2023, 221, 103766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Kero, A.; Kumar, D. Mobile cloud computing architecture for computation offloading. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies, Dehradun, India, 14–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, M.; Al-Tuhafi, E.; Al-Hemiary, H. Adaptive Thresholds for Task Offloading in IoT-Edge-Cloud Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference On Cyber Management and Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 26–27 January 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Vidyarthi, D.P. An efficient fuzzy-based task offloading in edge-fog-cloud architecture. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2023, 35, e7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, H.; Rui-Qing, W.; Yiming, K.; Haoran, D.L. Edge node computing offloading decision method in cloud network collaboration environment. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, and Computer Engineering, Xishuangbanna, China, 18–20 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, R.; Cheikhrouhou, O.; Koubâa, A.; Youssef, H.; Hmam, H. Towards a Distributed Computation Offloading Architecture for Cloud Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadad, H.; Touzene, A.; Day, K.; Alzeidir, N. A cloud-side decision offloading scheme for mobile cloud computing. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2018, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, U.; TamilSelvan, L. Computational Analytics of Client Awareness for Mobile Application Offloading with Cloud Migration. Ksii Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2014, 8, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, M.; Madani, S.A.; Khan, S.U. A Survey of Mobile Cloud Computing Application Models. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikopoulos, V.; Binz, T.; Leymann, F.; Strauch, S. How to adapt applications for the Cloud environment Challenges and solutions in migrating applications to the Cloud. Computing 2013, 95, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.G.; De, D.; Mukherjee, A.; Buyya, R. Application-aware cloudlet selection for computation offloading in a multi-cloudlet environment. J. Supercomput. 2017, 73, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Yen, I.L.; Thuraisingham, B. Dynamic Service and Data Migration in the Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2009 33rd Annual IEEE International Computer Software and Applications Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 20–24 July 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. Dynamic Task Offloading in Power Grid Internet of Things: A Fast-Convergent Federated Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Chengdu, China, 23–26 April 2021; pp. 933–937. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, D.; Nandy, S.; Mohan, S.; Al-Otaibi, Y.D.; Alnumay, W.S. Sustainable task scheduling strategy in cloudlets. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2021, 30, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishankumar, R.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Aggarwal, M.; Pamucar, D. An improved entropy function for the intuitionistic fuzzy sets with application to cloud vendor selection. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 7, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Misra, S.; Rodrigues, J.J. Cloud Computing Applications for Smart Grid: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Bala, A.; Singh, A. Virtual Machine Migration for Green Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballari, India, 23–24 April 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Akherfi, K.; Gerndt, M.; Harroud, H. Mobile cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, D.; Bouzefrane, S. Making offloading decisions resistant to network unavailability for mobile cloud collaboration. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing, Austin, TX, USA, 20–23 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, S.N.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Mouradian, C.; Malektaji, S.; Glitho, R.H. Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimization Framework for Application Component Migration in NFV Cloud-Fog Environments. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.; Kavanagh, R.; Djemame, K. Towards an interoperable energy-efficient Cloud computing architecture—Practice & experience. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communication Workshop, London, UK, 8–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Li, W.; Bao, W.; Delicato, F.C.; Pires, P.F.; Dou, Y.; Zomaya, A.Y. Adaptive Energy-Aware Computation Offloading for Cloud of Things Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 23947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldmour, R.; Yousef, S.; Yaghi, M.; Tapasaswi, S.; Pattanaik, K.K.; Cole, M. New cloud offloading algorithm for better energy consumption and process time. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2017, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccianti, G.; Lago, P.; Bevini, S. A systematic literature review on energy efficiency in cloud software architectures. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2014, 7, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michał, P.; Karpowicz, E.; Niewiadomska-Szynkiewicz, P.; Arabas, A.S. Energy and Power Efficiency in Cloud; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, L.; Maharajan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy-Efficient Offloading for Mobile Edge Computing in 5G Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, L.; Orgerie, A.C. Designing and evaluating an energy-efficient Cloud. J. Supercomput. 2010, 51, 352–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, A.; Dahiya, S.; Choudhury, T. Energy efficiency in cloud computing data centers: A survey on software technologies. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 1845–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Cai, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Research on Energy Efficiency Evaluation in the Cloud; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.A.; Elgorashi, T.E.H.; Elmirghani, J.M.H. Energy Efficient Cloud-Fog Architecture. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.06328. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.; Paul, A.; Dholakia, H.; Hossain, G. When not to Offload? Analyzing Offload Feasibility in Mobile Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Mobile and Secure Services, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 2–3 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahem, A.A.R.T.; Ismail, M.; Najm, I.A. Effect of the Architecture and Topology of Cloud Computing on Power Saving. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 785, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materwala, H.; Ismail, L.; Shubair, R.M.; Buyya, R. Energy-SLA-aware genetic algorithm for edge–cloud integrated computation offloading in vehicular networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 135, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahamathunnisa, U.; Sudhakar, K.; Murugan, T.K.; Thivaharan, S.; Rajkumar, M.; Boopathi, S. Cloud Computing Principles for Optimizing Robot Task Offloading Processes. AI-Enabled Soc. Robot. Hum. Care Serv. 2023, 12, 188–211. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidinejad, A.; Ghobaei-Arani, M. A metaheuristic-based computation offloading in edge-cloud environment. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 13, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, S. Resource Allocation and Task Offloading Strategy Base on Hybrid Simulated Annealing-Binary Particle Swarm Optimization in Cloud-Edge Collaborative System. In Proceedings of the 5th Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 16–18 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha Kirana, S.P.; D’Mello, D.A. Energy-efficient enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization for virtual machine consolidation in cloud environment. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirana, U.; Pushpavathi, S.; D’Mello, D. A Recursive Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Energy Consumption in Cloud Computing. Trends Sci. 2022, 19, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, C.W.; Aly, I.; Saroit, I.M.; Shaimaa, M.; Mohamed, M. Energy Efficient Ant Colony Cloud Offloading Algorithm (EACO). In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Software and Information Engineering, Nagoya, Japan, 11–13 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizchi, H.; Kuchaki, R.M. Energy Refining Balance with Ant Colony System for Cloud Placement Machines. J. Grid Comput. 2021, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilenko, S. Whale Optimization-Based Task Offloading Technique in Integrated Cloud-Fog Environment; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, V.R.P.; Bipin, P. Exploitation Whale Optimization-Based Optimal Offloading Approach and Topology Optimization in a Mobile Ad Hoc Cloud Environment. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 13, 1053–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Yuan, H.; Duanmu, S.; Zhou, M.; Abusorrah, A. Energy-Optimized Partial Computation Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing with Genetic Simulated-Annealing-Based Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 3774–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Dong, M.; Leung, V.C.M. Energy Efficient Joint Computation Offloading and Service Caching for Mobile Edge Computing: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2023, 7, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Gu, C. A Meta Reinforcement Learning-Based Task Offloading Strategy for IoT Devices in an Edge Cloud Computing Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, C.; Liu, F. Collaborative Cloud-Edge-End Task Offloading with Task Dependency Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Comput. Commun. 2023, 209, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X. Cloud-Edge Collaborative Computation Offloading: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Networks, Communications and Information Technology, Beijing, China, 17–19 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Ren, S. Online Learning for Offloading and Autoscaling in Energy Harvesting Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2017, 3, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, M.; Elgendy, I.A.; Muthanna, A.; Alshahrani, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Koucheryavy, A. Advanced Deep Learning-Based Computational Offloading for Multilevel Vehicular Edge-Cloud Computing Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 137052–137062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Lv, C.; Cao, S.; Yan, L.; Wang, H. Deep Learning-Based Computation Offloading with Energy and Performance Optimization. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2020, 2020, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, B.; Hakiri, A.; Yahia, S.B. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Energy-Aware Task Offloading in Joint SDN-Blockchain 5G Massive IoT Edge Network. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 137, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Meng, X.; Hu, Z.; Xu, F.; Zeng, D.; Dong, M.; Ni, W. AI-Driven Energy-Efficient Content Task Offloading in Cloud-Edge-End Cooperation Networks. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2022, 3, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).