Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services to Enhance Urban Resilience in the Post-Pandemic Era: The Case of the Pilgrimage City of Makkah
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of the Literature
2.1. Enhancing Resilience to Pandemic Using Smart Technologies
2.2. Role of Digitalization and Smartification in Improving the Resilience of Pilgrim Cities
2.3. Digital and Smart Tools for Enhancing Urban Resilience
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Collection and Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Smart City Development in Makkah during the Pandemic
4.2. Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services in Makkah City
4.3. Improving Makkah’s Resilience through Smartification
4.4. Limitations of the Smartification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2022. Available online: https://covid19.Who.Int/ (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Saher, R.; Anjum, M. Role of technology in COVID-19 pandemic. In Researches and Applications of Artificial Intelligence to Mitigate Pandemics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar]
- Aljizawi, J.; Dalloul, D.; Ghryani, L.; AlDabbagh, S.; Brahimi, T. A Survey of Artificial Intelligence Solutions in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 194, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishya, R.; Javaid, M.; Khan, I.H.; Haleem, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen QV, H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hsu, E.B.; Yang, S.; Eklund, P. Artificial intelligence in the battle against coronavirus (COVID-19): A survey and future research directions. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.07343. [Google Scholar]
- Bereitschaft, B.; Scheller, D. How Might the COVID-19 Pandemic Affect 21st Century Urban Design, Planning, and Development? Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokhdar, H.; Khan, A.; Asiri, S.; Motair, W.; Assiri, A.; Alabdulaali, M. COVID-19 mitigation plans during Hajj 2020: A success story of zero cases. Health Secur. 2021, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Aina, Y.A. Understanding household water-use behavior and consumption patterns during COVID-19 lockdown in Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-Kreiner, N. Dark tourism as/is pilgrimage. Curr. Issues Tour. 2016, 19, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.S.; Azhar, E.I.; Madani, T.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Kock, R.; Dar, O.; Ippolito, G.; McHugh, T.D.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouregh, A.S.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Abubakar, I.R.; Alshihri, F.S.; Alrawaf, T.I.; Ahmed, S.M.; Boureggah, M.S. Investigating the prospect of e-participation in urban planning in Saudi Arabia. Cities 2023, 134, 104186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K.; Yiannakou, A. COVID-19 and urban planning: Built environment, health, and well-being in Greek cities before and during the pandemic. Cities 2021, 121, 103491. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. The COVID-19 pandemic: Impacts on cities and major lessons for urban planning, design, and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apostu, S.A.; Vasile, V.; Vasile, R.; Rosak-Szyrocka, J. Do Smart Cities Represent the Key to Urban Resilience? Rethinking Urban Resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewalska–Opitek, A. Smart city concept–the citizens’ perspective. In International Conference on Transport Systems Telematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Margherita, E.G.; Escobar, S.D.; Esposito, G.; Crutzen, N. Exploring the potential impact of smart urban technologies on urban sustainability using structural topic modelling: Evidence from Belgium. Cities 2023, 141, 104475. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, H.T.; Babar, M.S.; Essar, M.Y.; Ramadhan, M.A.; Ahmad, S. The Hajj and COVID-19: How the pandemic shaped the world’s largest religious gathering. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zumla, A.; Azhar, E.I.; Alqahtani, S.; Shafi, S.; Memish, Z.A. COVID-19 and the scaled-down 2020 Hajj Pilgrimage—Decisive, logical and prudent decision making by Saudi authorities overcomes pre-Hajj public health concerns. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.I.; Aljamaan, I.A.; Al-Fakih, E.A. Forecasting the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia using ARIMA prediction model under current public health interventions. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, M.D.; Hasan, H.; Deris, Z.Z.; Arifin, W.N.; Baaba, A.A. Hajj Pilgrimage amidst COVID-19 pandemic: A review. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2021, 20, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarim, L.; Alrajhi, W.; Aloboud, E. Urban analytics in crowd management in the context of Hajj. In International Conference on Social Computing and Social Media; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.J. Multilingual AI Robots at Makkah’s Grand Mosque Guide Pilgrims. The Siasat Daily, 19 November 2021. Available online: https://www.siasat.com/multilingual-ai-robots-at-makkahs-grand-mosque-guide-pilgrims-2227691/ (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Nihal, M. New Technology to Benefit Pilgrims at Hajj 2022. The National. Available online: https://www.thenationalnews.com/gulf-news/2022/06/21/hajj-2022-new-technology-to-benefit-pilgrims/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Saudi Arabia to Apply Digital Tech, Smart Cards to Facilitate Hajj: Al-Rabiah. Available online: https://www.argaam.com/en/article/articledetail/id/1564867 (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Al-Khudair, D. Smart Tech Paves Way for ‘Holistic Hajj’. Arab News, 19 February 2020. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/1629936/saudi-arabia (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Abalkhail, A.A.A.; Al Amri, S.M.A. Saudi Arabia’s Management of the Hajj Season through Artificial Intelligence and Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14142. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, S.M.; Alsulayyim, A.S.; Alqahtani, J.S.; Aldhahir, A.M. Digital Health platforms in Saudi Arabia: Determinants from the COVID-19 pandemic experience. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1517. [Google Scholar]
- Felemban, E.A.; Rehman, F.U.; Biabani, S.A.A.; Ahmad, A.; Naseer, A.; Majid, A.R.M.A.; Hussain, O.K.; Qamar, A.M.; Falemban, R.; Zanjir, F. Digital revolution for Hajj crowd management: A technology survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 208583–208609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassounah, M.; Raheel, H.; Alhefzi, M. Digital response during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFattani, A.; AlMeharish, A.; Nasim, M.; AlQahtani, K.; AlMudraa, S. Ten public health strategies to control the COVID-19 pandemic: The Saudi Experience. IJID Reg. 2021, 1, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Rapidly escalating COVID-19 cases amid reduced virus surveillance forecasts a challenging autumn and winter in the WHO European Region. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news/item/19-07-2022-rapidly-escalating-covid-19-cases-amid-reduced-virus-surveillance-forecasts-a-challenging-autumn-and-winter-in-the-who-european-region (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Sakurai, M.; Chughtai, H. Resilience against crises: COVID-19 and lessons from natural disasters. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2020, 29, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R.; Kummitha, R.K.R. Kummitha Contributions of Smart City Solutions and Technologies to Resilience against the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, N.A.; Abdel-Kader, R.F. Smart Cities after COVID-19: Building a conceptual framework through a multidisciplinary perspective. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilaki MJ, M.; Abooali, G.; Marzbali, M.H.; Samat, N. Vendors’ attitudes and perceptions towards international tourists in the Malaysia night market: Does the COVID-19 outbreak matter? Sustainability 2021, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar]
- Economou, A. The socioeconomic gradient in coping attitudes towards the COVID-19 measures in social welfare regimes in Europe. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2022, 6, 100334. [Google Scholar]
- Pereirinha JA, C.; Pereira, E. Social resilience and welfare systems under COVID-19: A European comparative perspective. Glob. Soc. Policy 2021, 21, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Using digital technologies to improve resilience and inclusion in Indonesia. 2022. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/governance/using-digital-technologies-improve-resilience-and-inclusion-indonesia (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Tsironis, C.N. Pilgrimage and Religious Tourism in Society, in the Wake of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Paradigmatic Focus on ‘St. Paul’s Route’ in the Central Macedonia Region, Greece. Religions 2022, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.; Raj, R. The importance of religious tourism and pilgrimage: Reflecting on definitions, motives and data. Int. J. Relig. Tour. Pilgr. 2018, 5, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Korstanje, M.E. The impact of coronavirus on religious tourism: Is this the end of pilgrimage? Int. J. Relig. Tour. Pilgr. 2020, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bulchand-Gidumal, J. Post-COVID-19 recovery of island tourism using a smart tourism destination framework. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 23, 100689. [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Lopez, N.; Kuster-Boluda, I. Data mining to reposition a religious tourist destination in COVID-19. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, T.; Budke, C. Tourism in a world with pandemics: Local-global responsibility and action. J. Tour. Futures 2020, 6, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphin, H. COVID-19: An opportunity to review existing grounded theories in event studies. J. Conv. Event Tour. 2021, 22, 3–35. [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin, H.; Jarraud, N. COVID-19: Impacts and perspectives for religious tourism events. The case of Lourdes Pilgrimages. J. Conv. Event Tour. 2022, 23, 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gautret, P.; Angelo, K.M.; Asgeirsson, H.; Duvignaud, A.; van Genderen, P.J.; Bottieau, E.; Chen, L.H.; Parker, S.; Connor, B.A.; Barnett, E.D.; et al. International mass gatherings and travel-associated illness: A GeoSentinel cross-sectional, observational study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 101504. [Google Scholar]
- Hoarau, J.F. Is international tourism responsible for the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic? A cross-country analysis with a special focus on small islands. Rev. World Econ. 2022, 158, 493–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.; Zin, C.S. Religious tourism and mass religious gatherings—The potential link in the spread of COVID-19. Current perspective and future implications. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M.; Yamin, M.; Halikias, G.; Abi Sen, A.A. A Framework for Crowd Management during COVID-19 with Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2021, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traskevich, A.; Fontanari, M. Tourism potentials in post-COVID19: The concept of destination resilience for advanced sustainable management in tourism. Tour. Plan. Dev. 2021, 20, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirutinsky, S.; Cherniak, A.D.; Rosmarin, D.H. COVID-19, mental health, and religious coping among American Orthodox Jews. J. Relig. Health 2020, 59, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsironis, C.N.; Sylaiou, S.; Stergiou, E. Risk, faith and religious tourism in second modernity: Visits to Mount Athos in the COVID-19 era. J. Herit. Tour. 2022, 17, 516–532. [Google Scholar]
- Canete, J.J.O. When expressions of faith in the Philippines becomes a potential COVID-19 ‘superspreader’. J. Public Health 2021, 43, e366–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigala, M. Tourism and COVID-19: Impacts and implications for advancing and resetting industry and research. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 312–321. [Google Scholar]
- Gretzel, U.; Scarpino-Johns, M. Destination resilience and smart tourism destinations. Tour. Rev. Int. 2018, 22, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bifulco, F.; Tregua, M.; Amitrano, C.C.; D’Auria, A. ICT and sustainability in smart cities management. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2016, 29, 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- Del Chiappa, G.; Baggio, R. Knowledge transfer in smart tourism destinations: Analyzing the effects of a network structure. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2015, 4, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Della Corte, V.; Del Gaudio, G.; Sepe, F.; Luongo, S. Destination resilience and innovation for advanced sustainable tourism management: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Won, D.; Park, K. Dynamics from open innovation to evolutionary change. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameri, R.P. Smart City Implementation. Creating Economic and Public Value in Innovative Urban Systems; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bisello, A.; Vettorato, D.; Ludlow, D.; Baranzelli, C. (Eds.) Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin, R. Making sense of smart cities: Addressing present shortcomings. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2015, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, M.; Psaltoglou, A.; Komninos, N.; Kakderi, C.; Tsarchopoulos, P.; Panori, A. Enhancing sustainable urban development through smart city applications. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2018, 9, 146–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbouh, D.; Abbasi, T.; Maasmi, F.; Omar, I.A.; Debe, M.S.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Ellahham, S. Blockchain for COVID-19: Review, Opportunities, and a Trusted Tracking System. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 9895–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamola, V.; Hassija, V.; Gupta, V.; Guizani, M. A Comprehensive Review of the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Role of IoT, Drones, AI, Blockchain, and 5G in Managing its Impact. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90225–90265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.; Akhund, R.; Arshad, H.; Ibrahim, M.T. Exploring the Potential of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to Combat COVID-19 and Existing Opportunities for LMIC: A Scoping Review. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummitha, R.K.R. Smart technologies for fighting pandemics: The techno-and human-driven approaches in controlling the virus transmission. Gov. Inf. Q. 2020, 37, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkov, I.; Trump, B.D.; Hynes, W. Resilience-Based Strategies and Policies to Address Systemic Risks; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development SG/NAEC: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining urban resilience: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirzadeh, M.; Sobhaninia, S.; Buckman, S.T.; Sharifi, A. Towards building resilient cities to pandemics: A review of COVID-19 literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Orford, S.; Hubbard, P. Urban Public Health Emergencies and the COVID-19 Pandemic (2): Infrastructures, urban governance and civil society. Urban Stud. 2023, 60, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champlin, C.; Sirenko, M.; Comes, T. Measuring social resilience in cities: An exploratory spatio-temporal analysis of activity routines in urban spaces during COVID-19. Cities 2023, 135, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Cobbinah, P.B. Can rapid urbanization be sustainable? The case of Saudi Arabian cities. Habitat Int. 2023, 139, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Vazquez, J.A. Identification of COVID-19 can be quicker through artificial intelligence framework using a mobile phone–based survey when cities and towns are under quarantine. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 826–830. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Z. Promoting Public Engagement during the COVID-19 Crisis: How Effective Is the Wuhan Local Government’s Information Release? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, J. From recovery resilience to transformative resilience: How digital platforms reshape public service provision during and post COVID-19. Public Manag. Rev. 2023, 25, 710–733. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.N.I.; Peng, Y.; Yiran, C.; Shouse, R.C. Disaster resilience through big data: Way to environmental sustainability. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101769. [Google Scholar]
- General Authority for Statistics. General Authority for Statistics, Saudi Arabia. 2019. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa/en (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- CIA. Saudi Arabia. The World Factbook. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/saudi-arabia/#economy (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- World Bank. World Development Indicators. 2022. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators/Type/TABLE/preview/on (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Government of Saudi Arabia. The National Transformation Program. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030. 2016. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/v2030/vrps/ntp/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Balogun, A.L.; Adebisi, N.; Abubakar, I.R.; Dano, U.L.; Tella, A. Digitalization for transformative urbanization, climate change adaptation, and sustainable farming in Africa: Trend, opportunities, and challenges. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2022, 19, 17–37. [Google Scholar]
- Aina, Y.A. Achieving smart sustainable cities with GeoICT support: The Saudi evolving smart cities. Cities 2017, 71, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, A.A.; Khan, A.A.; Alamri, F.A.; Almuzaini, Y.S.; Alradini, F.A.; Almohamadi, E.; Alsaeedi, S.; Asiri, S.; Motair, W.; Almadah, A.; et al. Hajj 2021: Role of mitigation measures for health security. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, S.; Itumalla, R. Hajj in the Time of COVID-19. Infect. Dis. Health 2020, 25, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basahel, S.; Alsabban, A.; Yamin, M. Hajj and Umrah management during COVID-19. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binsawad, M.; Albahar, M. A Technology Survey on IoT Applications Serving Umrah and Hajj. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2022, 2022, 1919152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheim, R.M.; Farag, A.A.; Badawi, S. Smart City Vision and Practices across the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—A Review. Smart Cities: Issues and Challenges; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 309–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahim, S.H.; Memish, Z.A. COVID-19: Preparing for superspreader potential among Umrah pilgrims to Saudi Arabia. Lancet 2020, 395, e48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Said, M.; Samuel, M.; Shannan, N.; Bashir, F.M.; Dodo, Y. Novel vision-based thermal people counting tool for tracking infected people with viruses like COVID-19. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2020, 12, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shambour, M.K.; Gutub, A. Progress of IoT research technologies and applications serving Hajj and Umrah. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 1253–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takefuji, Y. Analysis of digital fences against COVID-19. Health Technol. 2021, 11, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takefuji, Y. How to build disaster-resilient cities and societies for making people happy. Build. Environ. 2023, 228, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Alshammari, M.S. Urban planning schemes for developing low-carbon cities in the Gulf Cooperation Council region. Habitat Int. 2023, 138, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.S.; Wiley, K.E.; Tashani, M.; Willaby, H.W.; Heywood, A.E.; BinDhim, N.F.; Booy, R.; Rashid, H. Exploring barriers to and facilitators of preventive measures against infectious diseases among Australian Hajj pilgrims: Cross-sectional studies before and after Hajj. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; McCloskey, B.; Azhar, E.I. COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections at mass gathering religious and sporting events. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, M.D.; Hasan, H.; Wan-Arfah, N.; Naing, N.N.; Deris, Z.Z.; Arifin, W.N.; Baaba, A.A.; Aliyu, A.; Adam, B.M. Health education intervention as an effective means for prevention of respiratory infections among Hajj pilgrims: A review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Alsofayan, Y.; Alahmari, A.; Alowais, J.; Algwizani, A.; Alserehi, H.; Assiri, A.; Jokhdar, H. COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia: The national health response. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2021, 27, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar]
- ICT Infrastructure in Makkah, Madinah Fully Operational for Hajj with 41% Rise in 5G Towers. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2113446/business-economy (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- No COVID-19 Cases Reported among Pilgrims in Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/1803481/saudi-arabia (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Robots to Provide Advice and Answers to Pilgrims in Makkah. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2064071/saudi-arabia (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Hussein, J. Sermon and Adhan Robots to Help Worshippers at Makkah’s Masjid Al-Haram. 2022. Available online: https://www.islamchannel.tv/blog-posts/sermon-adhan-robots-to-help-worshippers-at-makkahs-grand-mosque-masjid-al-haram (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Maximum Technology Utilized by Saudi Authorities to Ensure Safety of Pilgrims. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/1897551/saudi-arabia (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Coronavirus: Saudi Arabia’s Al-Sudais Marks Thermal Cameras Launch in Kaaba. Available online: https://english.alarabiya.net/coronavirus/2020/04/29/Coronavirus-Saudi-Arabia-s-al-Sudais-marks-launch-thermal-cameras-in-Kaaba (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Saudi Press Agency. Health Minister Launches “Holodoctor” Service for Pilgrims. Available online: https://www.spa.gov.sa/viewfullstory.php?lang=en&newsid=2366427 (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Islam Channel. The Tech Companies Providing Virtual Hajj Experience. 2021. Available online: https://www.islamchannel.tv/blog-posts/the-tech-companies-providing-virtual-hajj-experiences (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- OBG. The Saudi Report 2018. Oxford Business Group: London, UK. Available online: https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/reports/saudi-arabia/2018-report (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- The Saudi Ministry of Hajj Unveils 25-Year Strategic Plan. Available online: https://english.alarabiya.net/special-reports/hajj-2014/2014/10/29/Ministry-of-Haj-unveils-25-year-strategic-plan (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- NDU. Smart Hajj—Digital Transformation of Hajj 1440. 2019. Available online: https://ndu.gov.sa/sites/default/files/2021-09/Hajj-report-en.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Ahmed, Q.A.; Memish, Z.A. Hajj 2022 and the post pandemic mass gathering: Epidemiological data and decision making. New Microbes New Infect. 2022, 49, 101033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, S.L.; Ullah, A.; Badshah, S.H.; Ahmad, I. Spread of Novel coronavirus by returning pilgrims from Iran to Pakistan. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Mat, N.F.; Edinur, H.A.; Abdul Razab, M.K.A.; Safuan, S. A single mass gathering resulted in massive transmission of COVID-19 infections in Malaysia with further international spread. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thaqafi, T. Saudi Hajj Minister Launches Online Nusuk Pilgrim Service. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2201711/saudi-arabia (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Shabbir, S. Saudi Minister Signs Road to Makkah Agreement in Pakistan. Arab News. 2023. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2305476/saudi-arabia (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- PEP. The Implementation Plan for Pilgrim Experience Program 2021–2025. 2021. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/media/aypnfomz/pep-delivery-plan-en.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Farag, M. Electric Scooters are Latest Mode of Transport for Hajj Pilgrims. Available online: https://www.thenationalnews.com/gulf-news/2022/07/09/electric-scooter-is-latest-transportation-mode-for-hajj-pilgrims/ (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Yumul, J.S. Arabia’s Eco-Friendly Hajj Seen to Boost Green Tourism. Available online: https://www.chinadailyhk.com/article/283230#S.-Arabia%E2%80%99s-eco-friendly-Hajj-seen-to-boost-green-tourism (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Saudi Gazette. Land Allotted for Al-Faisaliah Airport in Makkah. 2019. Available online: https://saudigazette.com.sa/article/571330 (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Aina, Y.A.; Wafer, A.; Ahmed, F.; Alshuwaikhat, H.M. Top-down sustainable urban development? Urban governance transformation in Saudi Arabia. Cities 2019, 90, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi Gazette. Makkah Transport Approves 6 Bus Routes during Hajj Season. 2022. Available online: https://saudigazette.com.sa/article/622154 (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Al-Thaqafi, T. Trial Runs for Public Transport Buses in Makkah. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2026071/saudi-arabia (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Al-Thaqafi, T. Plans Adopted to Transform Makkah, Madinah into Financial and Business Hub for Islamic World. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/2223911/saudi-arabia (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Saudi Gazette. 96% Jump in Passengers on Haramain Railway this Hajj Compared to Last Year. 2023. Available online: https://saudigazette.com.sa/article/634188/SAUDI-ARABIA/96-jump-in-passengers-on-Haramain-nbspRailway-nbspthis-Hajj-compared-to-last-year (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Alshuwaikhat, H.M.; Aina, Y.A.; Binsaedan, L. Analysis of the implementation of urban computing in smart cities: A framework for the transformation of Saudi cities. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qoradi, M.D.; Al-Harbi, M.S.; Aina, Y.A. Using GIS-based intelligent transportation systems in the enhancement of university campus commuting in a smart city context. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 742. [Google Scholar]
- El Hanandeh, A. Quantifying the carbon footprint of religious tourism: The case of Hajj. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
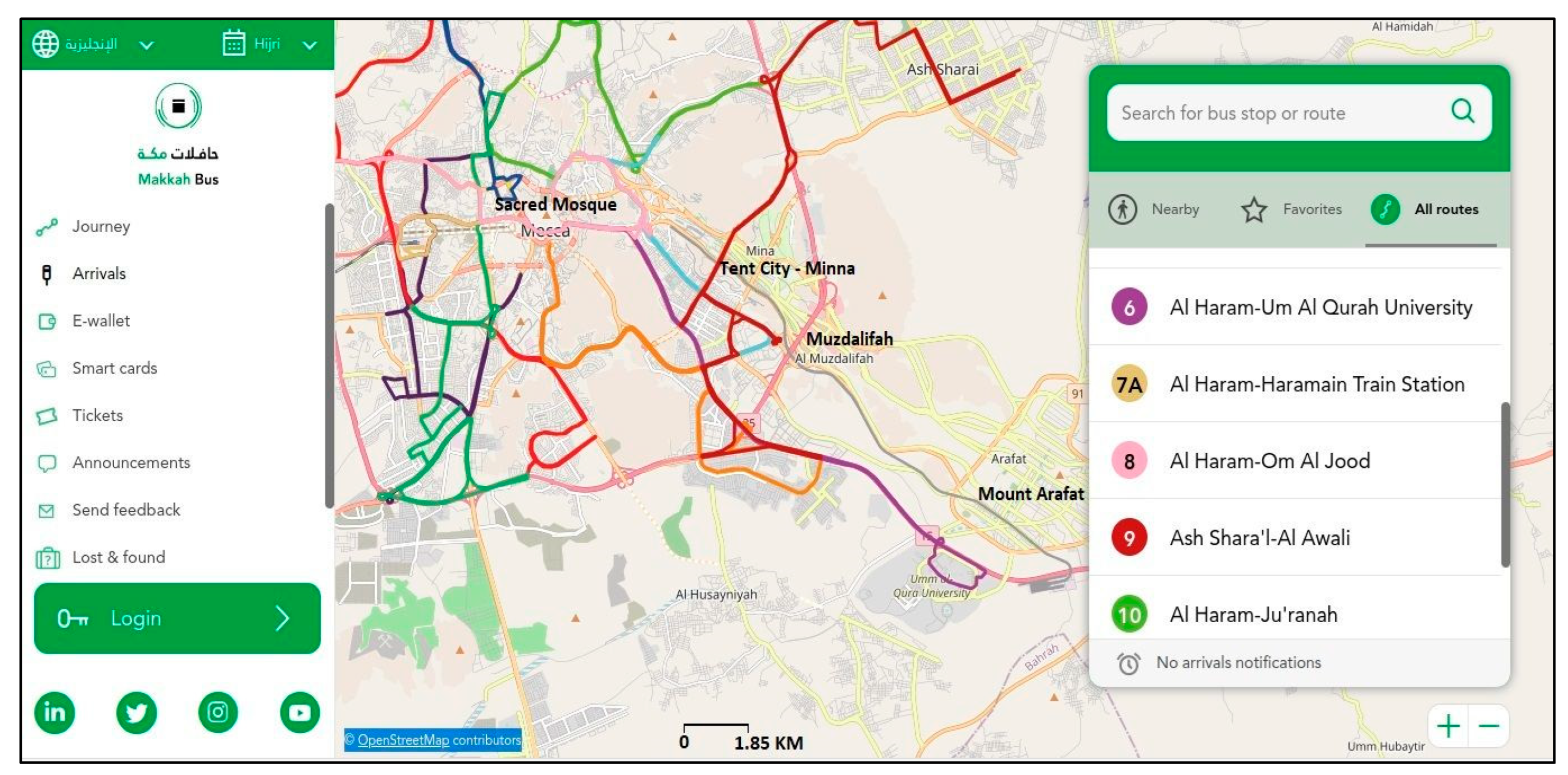
- Makkah Bus. Makka bus web interface. Available online: www.makkahtransit.sa (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Quaium, A.; Al-Nabhan, N.A.; Rahaman, M.; Salim, S.I.; Toha, T.R.; Noor, J.; Hossain, M.; Islam, N.; Mostak, A.; Islam, S.; et al. Towards associating negative experiences and recommendations reported by Hajj pilgrims in a mass-scale survey. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kinani, M.; Al-Thaqafi, T. Occupancy Rate of Makkah Hotels Sees over 30% Rise in Second Half of Ramadan. 2021. Available online: https://www.arabnews.com/node/1854691/business-economy (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Saudi Gazette. Hajj 2023: 1,845,045 Pilgrims Performed Rituals. 2023. Available online: https://saudigazette.com.sa/article/633776 (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Alajmi, A.M.; Ahmed Memon, Z. A review on significant factors causing delays in Saudi Arabia construction projects. Smart Cities 2022, 5, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
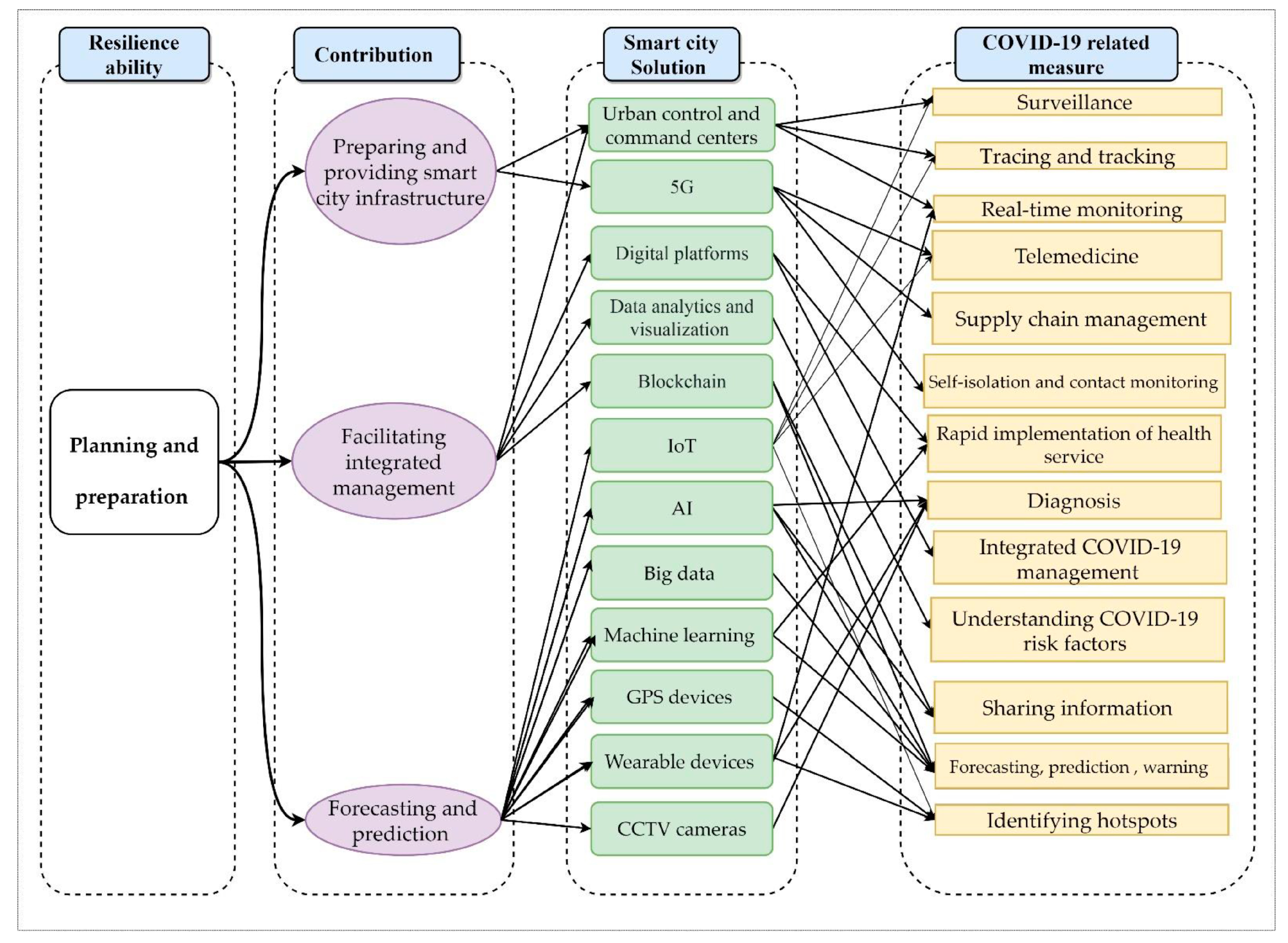




| Resilience Sub-Category | Smart Solution | Applied Measures in Different Contexts |
|---|---|---|
| Planning |
|
|
| Absorption |
|
|
| Recovery |
|
|
| Adaptation |
|
|
| Peer-Reviewed Literature | Grey Literature |
|---|---|
|
|
| Smart Tools | Description | Type of Services | Mode of Delivery | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
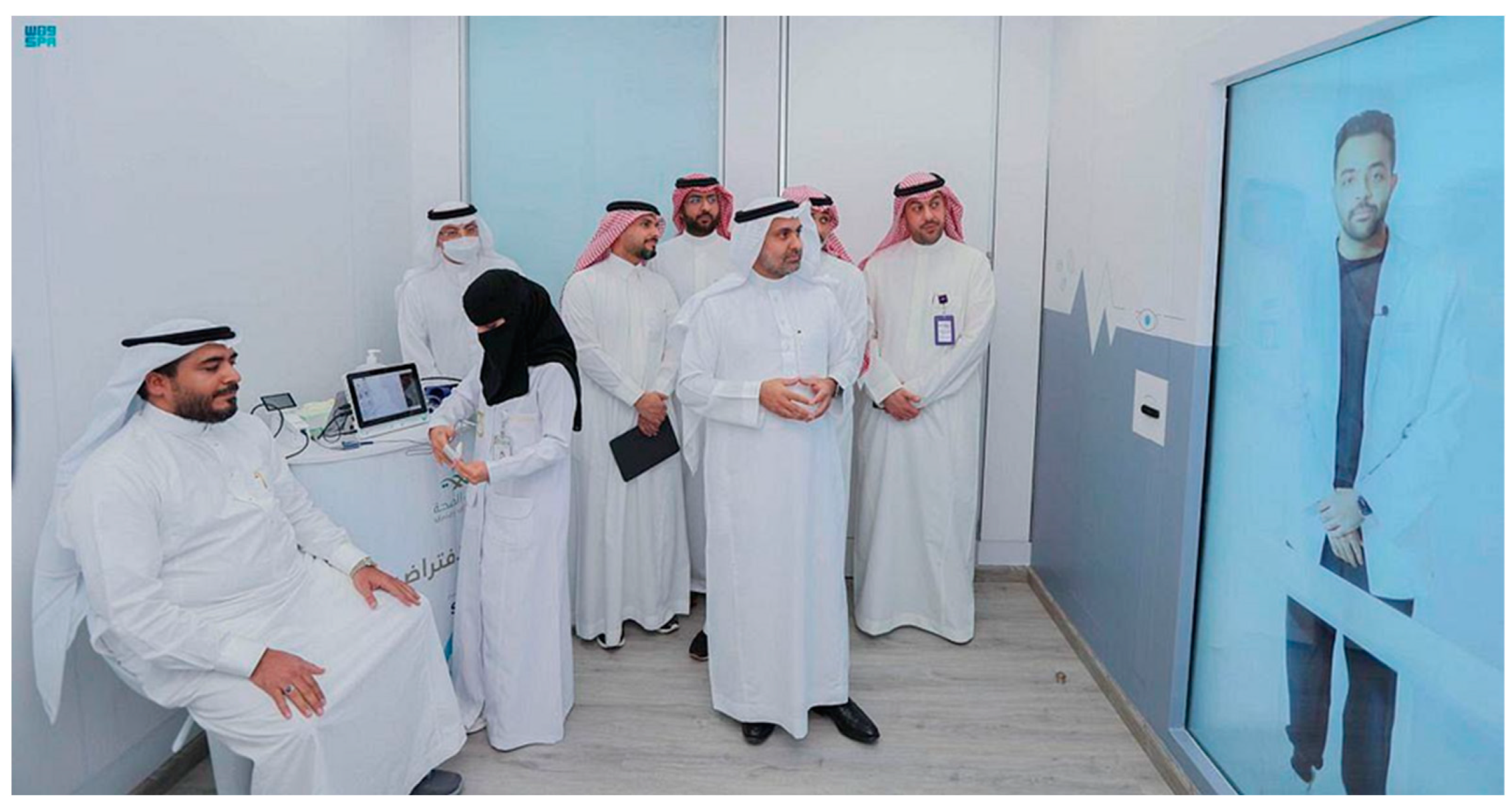
| Holodoctor | Provides medical services to pilgrims | Healthcare | Stationary video conference devices | Shared access |
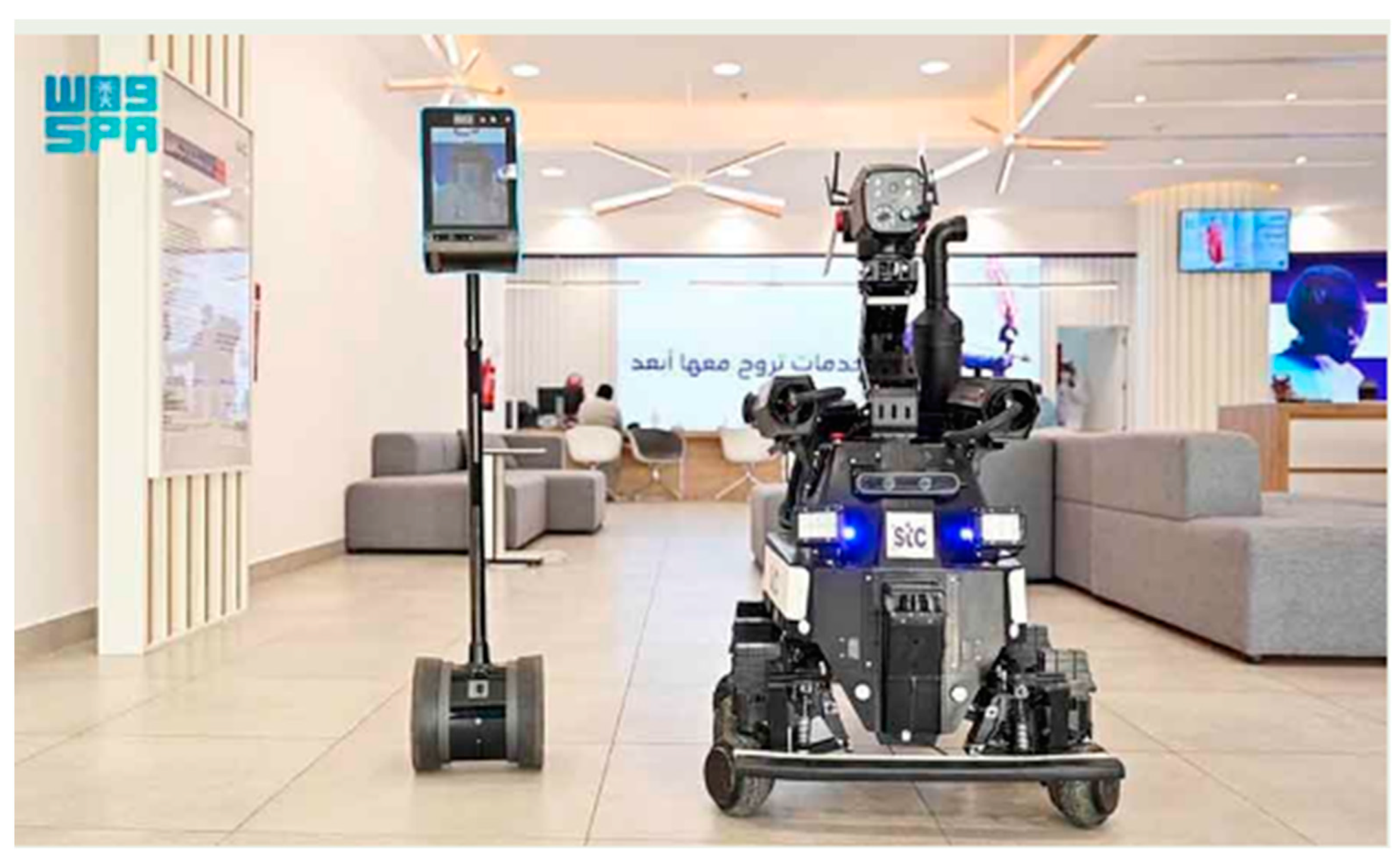
| Smart robots | Offers various services to pilgrims | Dispensing sanitizers, monitoring indoor air quality, distributing Zamzam water, providing guidance and religious information | Stationary via physical contact | Shared access |
| Thermal cameras | Scans body temperature to detect influenza infections and track population data | Disease tracking and diagnostics | Stationary cameras and computers | Shared access |
| Smart bracelets | Provides integrated services for pilgrims including health and personal data | Personal data and health information | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Smart cards | Offers access to various services including health, e-transactions, and navigation | Health and personal information, e-transaction services, navigation and tracking, and detecting illegal pilgrims. | Near-field communication devices | Personalized access |
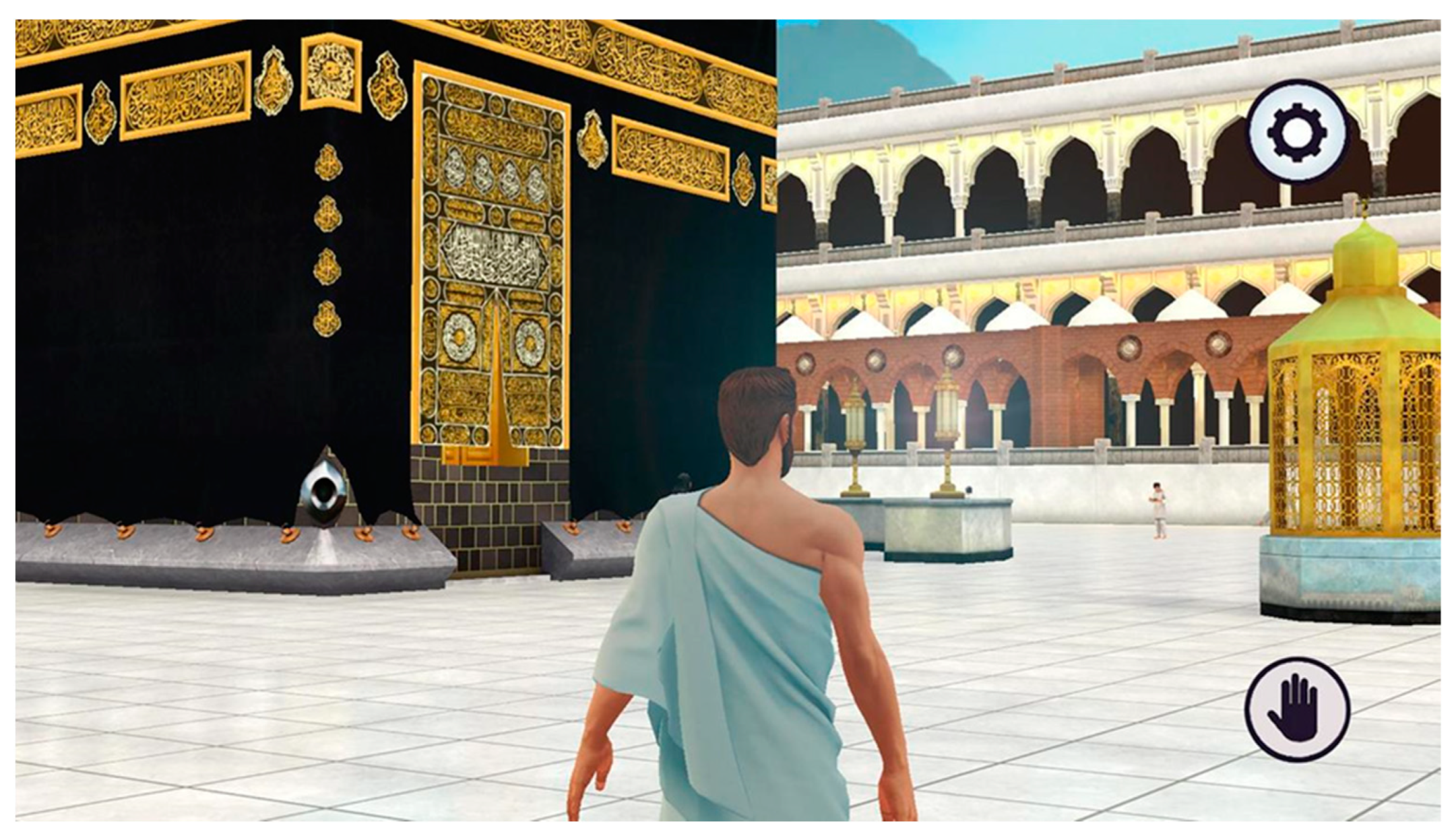
| Virtual reality | Allows pilgrims to experience touching the Black Stone in virtual reality to avoid physical contact | Ritual-related and historical services | Virtual reality devices | Personalized access |
| Tawakkal-na | Provides health-related services, personal information, and booking services | Health-related services, Hajj and Umrah booking, and crowd management | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Tabaud | Offers detection and notification services for COVID-19-infected persons and those in contact with them | Detection, tracking, and alerting services | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Sehhaty | Offers access to virtual clinics for medical consultations, examinations, and prescriptions | Health-related services via audio and video conferences | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Eatamarna | Provides Hajj and Umrah booking servers, entry to the Grand Mosque, and transportation services | Crowd management, Hajj and Umrah booking, and transportation services | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Kollona Amn | Provides e-services for reporting incidents | Pandemic cases, disasters, accidents, crime, and emergency reporting | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Watani | Allows pilgrims to assess, rate, and offer suggestions for improving public services | Public services evaluation | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Mecca Cleanliness | Offers cleaning services of the holy mosque and allows people to report littering or violations | Sanitation services, navigation, and tracking | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Fazaah | Enables the verification of incident reporters’ geographical location | Navigation, tracking, and incident reporting | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Almutawaf | Provides pilgrim services, including the location of sites, rituals, and times | Guidance and religious learning, navigation, and tracking | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Asafny | Enables users to file emergency reports, detect incident locations, support victims, and record medical history | Disaster, accident, and emergency reporting, navigation and tracking, and healthcare | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Turjuman | Translates rituals and health-related instructions or signs into major global languages | Guidance and instruction for pilgrims | Smartphone-based application | Personalized access |
| Category | Actions Taken | Planned Actions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pandemic-related health requirements | Technology for crowd management in Makkah city includes health surveillance, restricting access to holy sites using digital fences, smart mobility through smart bracelets, HEWS for health early warnings, and What3words for accurate location data. | Increase capacity to host 5 million pilgrims in the 2030. Open the new Hajj platform (Nusuk) to pilgrims. Establishing immigration desks at pilgrims’ home airports | [93,111,112,115,116,117] |
| Environmental, psychological principles | The Saudi green initiative includes smart mobility projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Visa for pilgrims to visit other Saudi cities for social networking and tourism. | Eco-friendly projects. Integration of Hajj with green tourism. Al-Faisaliah City Project with solar power plant. | [90,118,119,120] |
| General resilience principles | Adaptable and flexible technologies that maintain connectivity between holy sites via Haramain railway, Makkah Metro, and Makkah bus project. The creation of Makkah Region Development Authority for the planning of Makkah region. | Transformation of Makkah into a financial and business hub. Completion of Makkah Metro’s remaining lines Decentralization of governance. | [121,122,123,124,125] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aina, Y.A.; Abubakar, I.R.; Almulhim, A.I.; Dano, U.L.; Maghsoodi Tilaki, M.J.; Dawood, S.R.S. Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services to Enhance Urban Resilience in the Post-Pandemic Era: The Case of the Pilgrimage City of Makkah. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1973-1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040092
Aina YA, Abubakar IR, Almulhim AI, Dano UL, Maghsoodi Tilaki MJ, Dawood SRS. Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services to Enhance Urban Resilience in the Post-Pandemic Era: The Case of the Pilgrimage City of Makkah. Smart Cities. 2023; 6(4):1973-1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040092
Chicago/Turabian StyleAina, Yusuf A., Ismaila Rimi Abubakar, Abdulaziz I. Almulhim, Umar Lawal Dano, Mohammad Javad Maghsoodi Tilaki, and Sharifah R. S. Dawood. 2023. "Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services to Enhance Urban Resilience in the Post-Pandemic Era: The Case of the Pilgrimage City of Makkah" Smart Cities 6, no. 4: 1973-1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040092
APA StyleAina, Y. A., Abubakar, I. R., Almulhim, A. I., Dano, U. L., Maghsoodi Tilaki, M. J., & Dawood, S. R. S. (2023). Digitalization and Smartification of Urban Services to Enhance Urban Resilience in the Post-Pandemic Era: The Case of the Pilgrimage City of Makkah. Smart Cities, 6(4), 1973-1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040092











