Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Smart Building
2.1. Concept of Smart Building
2.2. Smart Building Evaluation Frameworks
3. Smart City
3.1. Concept of Smart City
3.2. Role of Digitalization in Smart Cities
3.3. Impact of Digitalization on Smart City Infrastructure
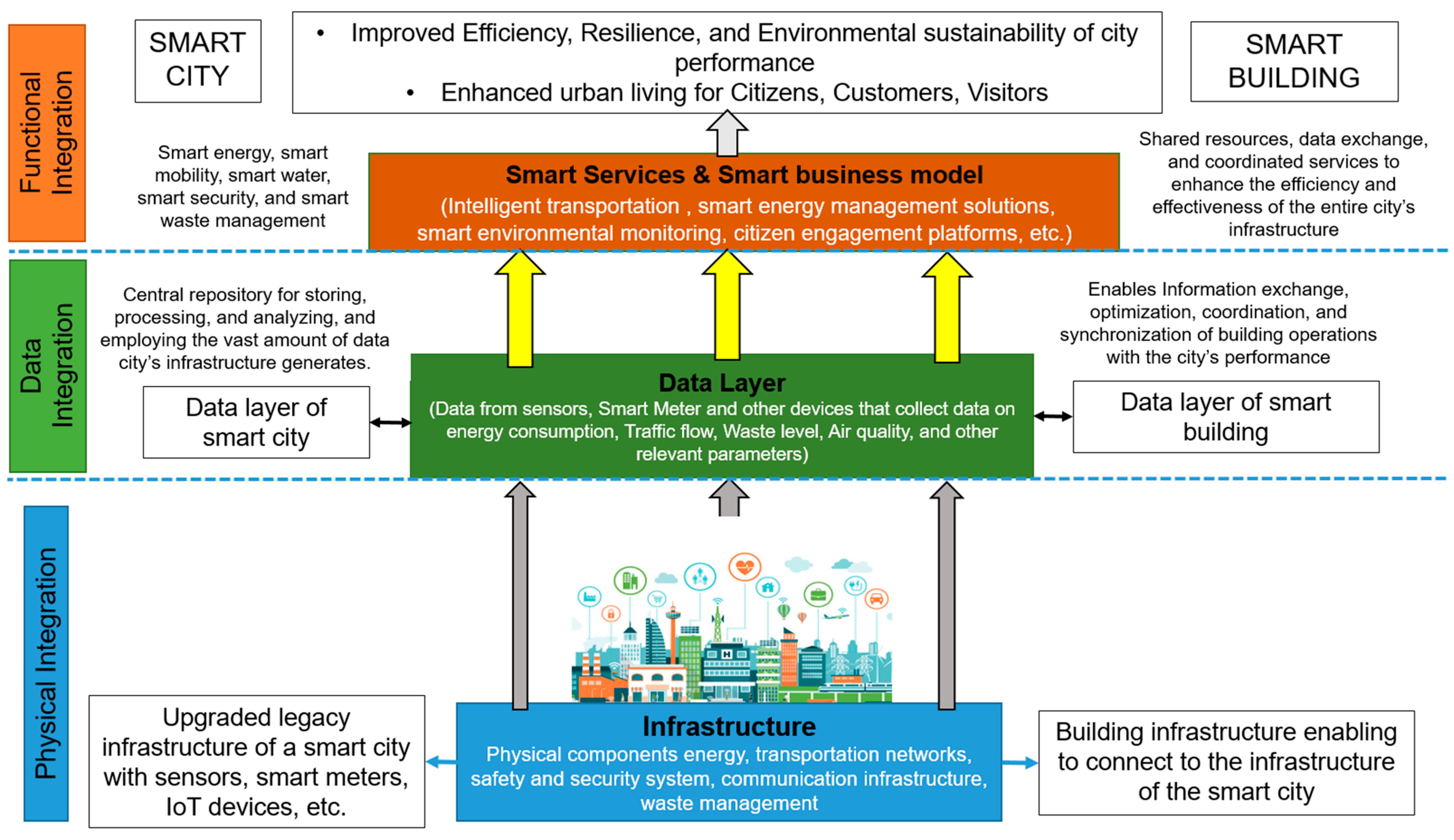
4. Smart Building Integration into Smart City
4.1. Conceptual Framework of Smart Building Integration into a Smart City
4.2. Importance of Integration for Efficiency, Resilience, and Sustainability of City Performance
4.3. Enhanced Urban Living through Smart Services
5. Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City
5.1. Factors Related to Smart Energy
5.2. Factors Related to Smart Mobility
5.3. Factors Related to Smart Water
5.4. Factors Related to Smart Security System
5.5. Factors Related to Smart Waste Management
6. Case Studies of Successful Smart Buildings Integration into Smart Cities
6.1. Introduction to Case Studies
6.2. Case Study Analysis and Results
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Smart Cities Market to Reach US$1.56 Trillion by 2020. 2014. Available online: https://www.frost.com/news/press-releases/frost-sullivan-global-smart-cities-market-reach-us156-trillion-2020/ (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Apanaviciene, R.; Vanagas, A.; Fokaides, P.A. Fokaides, Smart building integration into a smart city (SBISC): Development of a new evaluation framework. Energies 2020, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J. The IoT to Smart Cities-A design science research approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilali, E.; Azougagh, A. Smart City Research between 1997 and 2020: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart City Applications, Castelo Branco, Portugal, 19–21 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver Elbracht, F.F. From City Theory to Smart Tech Reality; Smart Cities World; Siemens: Munich, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Smart Cities and Infrastructure. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ecn162016d2_en.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Apanaviciene, R.; Urbonas, R.; Fokaides, P.A. Smart building integration into a smart city: Comparative study of real estate development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, F.; Delinchant, B. “Smart buildings” integrated in “smart grids”: A key challenge for the energy transition by using physical models and optimization with a “human-in-the-loop” approach. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2017, 18, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapolskytė, S.; Burinskienė, M.; Trépanier, M. Evaluation criteria of smart city mobility system using MCDM method. Balt. J. Road Bridg. Eng. 2020, 15, 196–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turoń, K. Factors Affecting Car-Sharing Services. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bašić, S.; Strmo, N.V.; Sladoljev, M. Smart cities and buildings. J. Croat. Assoc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 71, 949–964. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.-H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.H.; Ye, C.Z.; Hsieh, J.C. Evaluating smart office buildings from a sustainability perspective: A model of hybrid multi-attribute decision-making. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B. Smart Buildings—What’s the Value to Smart Cities? Part Two. 2020. Available online: https://www.iiot-world.com/smart-cities-buildings-infrastructure/smart-buildings/smart-buildings-whats-the-value-to-smart-cities-part-two/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Toli, A.M.; Murtagh, N. The concept of sustainability in smart city definitions. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanavičienė, R.; Maliejus, K.; Fokaides, P. Sustainability assessment of the building construction stage using building sustainability assessment schemes (BSAS). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Changchun, China, 21–23 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Hong, T.; Li, N.; Wang, R.Q.; Chen, J. Linking energy-cyber-physical systems with occupancy prediction and interpretation through WiFi probe-based ensemble classification. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shahidehpour, M.; Liu, X. Cyber-secure decentralized energy management for IoT-enabled active distribution networks. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 6, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lu, Q.; Herrera, M.; Yu, Q.; Parlikad, A.K.; Schooling, J.M. Does historical data still count? Exploring the applicability of smart building applications in the post-pandemic period. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Muhammad, K.; Ullah, A.; Ahmad, J.; Baik, S.W.; Sajjad, M. Enabling automation and edge intelligence over resource constraint IoT devices for smart home. Neurocomputing 2022, 491, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Uddin, M.I.; Amin, M.A. Big data-assisted social media analytics for business model for business decision making system competitive analysis. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.T.; Zhong, R.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, S.; Li, M.; Lin, P.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Shen, L.; Yu, Y.; et al. Cyber physical ecommerce logistics system: An implementation case in Hong Kong. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, W.; Si, P.; Yang, Z.; Yu, F.R. B-ReST: Blockchain-enabled resource sharing and transactions in fog computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, A.H.; Mayfield, M.; Beck, S.B. What is a smart building? Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Gopinathan, D.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. An overview of IoT sensor data processing, fusion, and analysis techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candanedo, L.M.; Feldheim, V.; Deramaix, D. Data driven prediction models of energy use of appliances in a low-energy house. Energy Build. 2017, 140, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietikäinen, S.; Eveillard, P. Level(s): A Guide to Europe’s New Reporting Framework for Sustainable Buildings. Available online: https://apo.org.au/sites/default/files/resource-files/2018-04/apo-nid212906.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Merabet, G.H.; Essaaidi, M.; Haddou, M.B.; Qolomany, B.; Qadir, J.; Anan, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Abid, M.R.; Benhaddou, D. Intelligent building control systems for thermal comfort and energy-efficiency: A systematic review of artificial intelligence-assisted techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Karlsson, M.; Gong, S. Anomaly detection based on machine learning in IoT-based vertical plant wall for indoor climate control. Build. Environ. 2020, 183, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. What Is the SRI? 2018. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/energy-efficiency/energy-efficient-buildings/smart-readiness-indicator/what-sri_en (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- The First Comprehensive Smart Building Assessment and Rating Program.” n.d. UL Solutions. Available online: https://www.ul.com/services/first-comprehensive-smart-building-assessment-and-rating-program (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Nie, J.; Xu, W.-S.; Cheng, D.-Z.; Yu, Y.-L. Digital twin-based smart building management and control framework. DEStech Trans. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botín-Sanabria, D.M.; Mihaita, A.-S.; Peimbert-García, R.E.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A.; Ramírez-Mendoza, R.A.; Lozoya-Santos, J.D.J. Digital twin technology challenges and applications: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAS 181:2014; Smart City Framework. Guide to Establishing Strategies for Smart Cities and Communities. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2014.
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Kalasek, R.; Pichler-Milanovic, N.; Meijers, E. Smart Cities. Ranking of European Medium-sized Cities. Available online: https://www.smart-cities.com/download/city_ranking_final.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Hollands, R.G. Will the real smart city please stand up? City 2008, 12, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.A.A.; Rossi, A. New Trends for Smart Cities. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/docs/projects/cnect/6/270896/080/deliverables/001-D2221NewtrendsforSmartCities.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Grossi, G.; Pianezzi, D. Smart cities: Utopia or neoliberal ideology? Cities 2017, 69, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilova, E.; Hughes, L.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Raman, K.R. Smart cities: Advances in research—An information systems perspective. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 47, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong, S.; Park, J.; Lee, M. Research models and methodologies on the smart city: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Griffor, E.; Wollman, D.; Dunaway, M.; Burns, M.; Rhee, S.; Greer, C. Smart Cities and Communities: A Key Performance Indicators Framework. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=933286 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Commission, E. Smart Cities. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/eu-regional-and-urban-development/topics/cities-and-urban-development/city-initiatives/smart-cities_en#:~:text=Related%20events-,What%20are%20smart%20cities%3F,resource%20use%20and%20less%20emissions (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Alahi, M.E.E.; Sukkuea, A.; Tina, F.W.; Nag, A.; Kurdthongmee, W.; Suwannarat, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Integration of IoT-Enabled Technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart City Scenario: Recent Advancements and Future Trends. Sensors 2023, 23, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrabani, M.M.N.; Apanavičienė, R. Towards integration of smart and resilient city: Literature review. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Taipei, Taiwan, 27–29 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hatuka, T.; Rosen-Zvi, I.; Birnhack, M.; Toch, E.; Zur, H. The political premises of contemporary urban concepts: The global city, the sustainable city, the resilient city, the creative city, and the smart city. Plan. Theory Pract. 2018, 19, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W. Digital systems in smart city and infrastructure: Digital as a service. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.S.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Kumar, A.; Elmaghraby, A. IoT in smart cities: A survey of technologies, practices and challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.; Li, K. ITU-T standardisation activities on smart sustainable cities. IET Smart Cities 2019, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, L.; Cilfone, A.; Davoli, L.; Ferrari, G.; Adorni, P.; Di Nocera, F.; Dall’Olio, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Mordacci, M.; Bertolotti, E. IoT-enabled smart sustainable cities: Challenges and approaches. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1039–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunova, I.; Porras, J. IoT-Enabled Smart Waste Management Systems for Smart Cities: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 73326–73363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, K.; Hassan, M.; Husnain, A.; Mukhtar, S. Information and Communication Technologies for New Generation of Sustainable Smart Cities. In New Generation of Sustainable Smart Cities; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Glasco, J. Smart Mobility: Challenges and Solutions in Smart Cities. Available online: https://www.beesmart.city/en/solutions/smart-mobility/smart-mobility-challenges-and-solutions-in-smart-cities (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Schönig, J. City Digitalization: Welcome to the City 4.0. 2019. Available online: https://www.iiot-world.com/smart-cities-buildings-infrastructure/smart-cities/digitalization-welcome-to-the-city-4-0/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Jonathan Woetzel, J.R.; Boland, B.; Lv, K.; Sinha, S.; Strube, G.; Means, J.; Law, J.; Cadena, A.; von der Tann, V. Smart Cities: Digital Solutions for a More Livable Future. 2018. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/smart-cities-digital-solutions-for-a-more-livable-future (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Mondejar, M.E.; Avtar, R.; Diaz, H.L.B.; Dubey, R.K.; Esteban, J.; Gómez-Morales, A.; Hallam, B.; Mbungu, N.T.; Okolo, C.C.; Prasad, K.A. Digitalization to achieve sustainable development goals: Steps towards a Smart Green Planet. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 794, 148539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchia, A. Smart and digital city: A systematic literature review. In Smart City: How to Create Public and Economic Value with High Technology in Urban Space; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 13–43. [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski, R.; Pałka, P.; Turek, A. Solving “Smart City” Transport Problems by Designing Carpooling Gamification Schemes with Multi-Agent Systems: The Case of the So-Called “Mordor of Warsaw”. Sensors 2018, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, S.; Ramson, S.J.; Senith, S.; Anagnostopoulos, T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Fan, X.; Srinivasan, S.; Kirubaraj, A.A. IoT-Enabled solid waste management in smart cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, I.A.T.; Chang, V.; Anuar, N.B.; Adewole, K.; Yaqoob, I.; Gani, A.; Ahmed, E.; Chiroma, H. The role of big data in smart city. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froufe, M.M.; Chinelli, C.K.; Guedes, A.L.A.; Haddad, A.N.; Hammad, A.W.; Soares, C.A.P. Smart buildings: Systems and drivers. Buildings 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Fashola, O.I.; Olarewaju, T.I.; Onwumere, I. Smart city research: A holistic and state-of-the-art literature review. Cities 2021, 119, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nguyen, X.P. Integrating renewable sources into energy system for smart city as a sagacious strategy towards clean and sustainable process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, S.M.; Hasankhani, A. Intelligent energy management in off-grid smart buildings with energy interaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura, N.; Ojanen, V. Sustainability-oriented innovations in smart cities: A systematic review and emerging themes. Cities 2022, 126, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberascher, M.; Rauch, W.; Sitzenfrei, R. Towards a smart water city: A comprehensive review of applications, data requirements, and communication technologies for integrated management. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalia, A.; Ramage, M. The Edge, Amsterdam Showcasing an Exemplary IoT Building. Available online: https://www.cdbb.cam.ac.uk/system/files/documents/TheEdge_Paper_LOW1.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Shukla, S.; Hait, S. Smart waste management practices in smart cities: Current trends and future perspectives. In Advanced Organic Waste Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 407–424. [Google Scholar]
- Arafah, Y.; Winarso, H.; Suroso, D. Towards smart and resilient city: A conceptual model. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Banda Aceh, Indonesi, 26–27 September 2018; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK; p. 012045. [Google Scholar]
- Tzioutziou, A.; Xenidis, Y. A study on the integration of resilience and smart city concepts in urban systems. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.M.; Babu, T.S.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Kasinathan, P.; Solanki, S.G.; Raveendran, S.K. Empowering smart grid: A comprehensive review of energy storage technology and application with renewable energy integration. J. Energy Storage 2021, 39, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T.M.; Boudreau, M.-C.; Helsen, L.; Henze, G.; Mohammadpour, J.; Noonan, D.; Patteeuw, D.; Pless, S.; Watson, R.T. Ten questions concerning integrating smart buildings into the smart grid. Build. Environ. 2016, 108, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, J.; Mago, P.J.; Lee, K.; Cho, H. Design and implementation of smart buildings: A review of current research trend. Energies 2022, 15, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, T. The Edge. Available online: https://edge.tech/developments/the-edge (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Lyu, C.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Z. Fully decentralized peer-to-peer energy sharing framework for smart buildings with local battery system and aggregated electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2021, 299, 117243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi-Rad, M.H.; Ghasemi-Marzbali, A.; Ahangar, R.A. Modeling and planning of smart buildings energy in power system considering demand response. Energy 2020, 213, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibaseta, D.; García, A.; Álvarez, M.; Garzón, B.; Díez, F.; Coca, P.; Del Pero, C.; Molleda, J. Monitoring and control of energy consumption in buildings using WoT: A novel approach for smart retrofit. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- System, B.E.M. Building Energy Monitoring System. Available online: https://smartertechnologies.com/building-energy-monitoring/ (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Predieri, I. Here’s How We Can Heat, Ventilate and Cool Buildings More Efficiently. 2022. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/10/here-s-how-heat-ventilate-cool-buildings-energy-consumption/ (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Chaudhry, H. Smart HVAC Significant to Sustainability in Smart Cities. 2022. Available online: https://www.hw.ac.uk/news/articles/2022/smart-hvac-significant-to-sustainability-in.htm (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Smart EV Charging in Buildings Is Central to Sustainable, Green Transportation. Available online: https://blog.se.com/energy-management-energy-efficiency/2022/09/29/smart-ev-charging-in-buildings-is-central-to-sustainable-green-transportation/ (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Fahim, A.; Hasan, M.; Chowdhury, M.A. Smart parking systems: Comprehensive review based on various aspects. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JUNG. Jung Smart Showroom in Vilnius. Available online: https://www.jung.de/sg/10846/architects/architects/showrooms-and-brandstores/jung-showroom-vilnius/ (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Anthopoulos, L.G.; Tzimos, D.N. Carpooling platforms as smart city projects: A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.M.; Saleem, Y.; Minerva, R.; Crespi, N. A comparative analysis of machine/deep learning models for parking space availability prediction. Sensors 2020, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemmali, M.; Melhim, L.K.B.; Alharbi, M.T.; Bajahzar, A.; Omri, M.N. Smart-parking management algorithms in smart city. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovation Partner for Impact. Smart Buildings Video Analytics via CCTV. Available online: https://www.ipi-singapore.org/tech-offers/174325/smart-buildings-video-analytics-via-cctv-2.html (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Point, H. Smart Water Management Takes Smart Buildings to the Next Level. 2018. Available online: https://www.hydropoint.com/blog/smart_building_management/ (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Gimpel, H.; Graf-Drasch, V.; Hawlitschek, F.; Neumeier, K. Designing smart and sustainable irrigation: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan Lewit, M.S.; Kaszycki, D.; Morgan, S.; Rankin, J.; Malpani, A.; Kane, M.; Kane, M. What Is the Impact of Smart Buildings on the Security Market? 2017. Available online: https://www.sourcesecurity.com/insights/what-is-the-impact-of-smart-buildings-on-the-security-market.html (accessed on 29 May 2023).
- Sorri, A. How Does Surveillance Help Make a Smarter, Safer City? Available online: https://www.axis.com/blog/secure-insights/surveillance-smarter-safer-city/ (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Reiswig, R. Integrated Life Safety: How Smart Buildings Offer Effective Fire Detection. Available online: https://www.thebigredguide.com/insights/integrated-life-safety-how-smart-buildings-offer-effective-fire-detection.html (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Khairuddin, M.; Shahbudin, S.; Kassim, M. A smart building security system with intelligent face detection and recognition. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Sanya, China, 12–14 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chu, E.T.-H.; Ku, L.-W.; Liu, J.W. Active disaster response system for a smart building. Sensors 2014, 14, 17451–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerche, A.; Coutinho, R.W. Smart disaster detection and response system for smart cities. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Natal, Brazil, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 01102–01107. [Google Scholar]
- Galán-Madruga, D. Environmental Data Control in Smart Buildings: Big Data Analysis and Existing IoT Technological Systems. In IoT Enabled Computer-Aided Systems for Smart Buildings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kalbermatter, R.B.; Brito, T.; Braun, J.; Pereira, A.I.; Ferreira, Â.P.; Valente, A.; Lima, J. Smart Systems for Monitoring Buildings-An IoT Application. In Proceedings of the Optimization, Learning Algorithms and Applications: Second International Conference, OL2A 2022, Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, 24–25 October 2022; pp. 575–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Designing a smart incentive-based recycling system for household recyclable waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 123, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, C.O.S. Automated Waste Collection System Market. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/automated-waste-collection-system-market-A07867#:~:text=An%20automated%20waste%20collection%20system,sealed%20and%20in%20compacted%20containers (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Abou Baker, N.; Szabo-Müller, P.; Handmann, U. Transfer learning-based method for automated e-waste recycling in smart cities. EAI Endorsed Trans. Smart Cities 2021, 5, e1. [Google Scholar]
- Is This the World’s Greenest, Smartest Office Building? Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/03/smart-building-amsterdam-the-edge-sustainability/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Architecture, T.E.P. The Edge/PLP Architecture. Available online: https://www.archdaily.com/785967/the-edge-plp-architecture (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Why Amsterdam’s The Edge Is a Model for Green Offices Worldwide. Available online: https://www.eco-business.com/news/why-amsterdams-the-edge-is-a-model-for-green-offices-worldwide/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- The Edge, Amsterdam. Available online: https://www.breeam.nl/projecten/the-edge-amsterdam-2784 (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Square, A. 1 Angel Square/3D Reid. Available online: https://www.archdaily.com/337430/1-angel-square-3d-reid (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- 1angelsquare. Available online: https://1angelsquare.co.uk/1AngelSquare.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- One Angle Square. Available online: https://sustainability.bam.co.uk/case-studies/2013-08-21-one-angel-square-the-co-operative-group-headquarters (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Fearson, A. National University of Singapore Starts Building Zero-Energy Design School. 2016. Available online: https://www.dezeen.com/2016/11/07/national-university-singapore-building-zero-energy-design-school/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Kai, N.W. NUS Clinches Top BCA Award for Green Buildings after Picking up 50 Green Mark Certifications. 2021. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/environment/nus-clinches-top-bca-award-for-green-buildings-after-picking-up-50-green-mark (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- News, N. New NUS Centre for 5G Digital Building Technology to Augment Digital Capability of Singapore’s Built Environment Industry. 2021. Available online: https://news.nus.edu.sg/new-nus-centre-for-5g-digital-building-technology-to-augment-digital-capability-of-singapores-built-environment-industry/ (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- FInder, H. Ongos Valley—Changing the Face of Windhoek’s Residential Landscape. Available online: https://housefindernam.com/post/ongos-valley-changing-the-face-of-windhoeks-residential-landscape (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Valley, O. All You Need to Know about Ongos Valley. Available online: https://propertynews.com.na/latest-news/all-you-need-to-know-about-ongos-valley (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Valley, O. Ongos Valley—Your Own Home Starts Here. Available online: https://www.ongosvalley.com.na/ (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Limited, M.E.T. Reliance Industrial Plots in Delhi NCR/Reliance MET. Available online: https://theindustrialplots.com/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Plots, R.I. Reliance MET City Highlights. Available online: https://www.industrialplotsncr.com/reliance-met-city/index.html (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Desk, T.C. What Is Haryana’s MET City Project? All You Need to Know. Available online: https://www.timesnownews.com/delhi/what-is-haryana-met-city-project-reliance-met-city-model-economic-township-gurugram-jhajjar-article-100069047 (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Amsterdam. Policy: Sustainability and Energy. Available online: https://www.amsterdam.nl/en/policy/sustainability/ (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Madan, B.; Regmi, J.Z.; Saluja, S. The Asia-Pacific Region’s Transport Sector Needs a Big Push towards Decarbonization. 2022. Available online: https://www.unescap.org/blog/asia-pacific-regions-transport-sector-needs-big-push-towards-decarbonization (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Kersten Heineke, B.K.; von Rüden, A.M.; Möller, T.; Wiemuth, C. Shared Mobility: Sustainable Cities, Shared Destinies. 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/shared-mobility-sustainable-cities-shared-destinies#/ (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Silva, J.A.; Martínez Omaña, M.C. Comparative study of drinking water management in Mexico City and Singapore. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2023, 34, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| References | Smart City Definition | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Giffinger et al. [34] | “The idea of smart cities is rooted in the creation and connection of human capital, social capital, and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) infrastructure to generate a greater and more sustainable economic development and a better quality of life.” | Human capital Social capital ICT |
| Hollands [35] | “Smart City uses the network infrastructure to improve economic and political efficiency, and to allow the social, cultural and urban development.” | Network Infrastructure |
| González et al. [36] | “Smart City, a public administration or authority that delivers (or aims to) a set of new generation services and infrastructure, based on information and communication technologies”. | ICT |
| British Standard Institute [33] | “The effective integration of physical, digital and human systems in the built environment to deliver a sustainable, prosperous and inclusive future for its citizens”. | Physical infrastructure Human capital Digital layer |
| Grossi and Pianezzi [37] | “Smart city or digital city is often referred to as a distributed network that consists of a large number of connected wireless sensor networks (WSNs) and IoT, and WSNs are the basic building blocks of cyber-physical systems (CPS), in particular smart cities.” | Wireless sensor network (WSN) IoT |
| Ismagilova, E. et al. [38] | “Smart cities employ information and communication technologies to improve: the quality of life for their citizens, local economy, transport, traffic management, environment, and interaction with government.” | ICT |
| Angeliki and Niamh [14] | “A smart city is an urban development vision that integrates information and communication technology (ICT), and IoT technology, as well as other physical devices connected to the network, to optimize the efficiency of city operations and services and connect to citizens.” | ICT IoT |
| S Myeong et al. [39] | “A smart city is a sustainable city that solves urban problems and improves citizens’ quality of life through the fourth industrial revolution technology and governance between stakeholders.” | Technology revolution |
| M Serrano et al. [40] | “The efficient use of digital technologies to provide prioritized services and benefits to meet community goals. Without reliable measurement methods for ‘smart’.” | Digital technology |
| European Commission [41] | “A smart city is a place where traditional networks and services are made more efficient with the use of digital solutions for the benefit of its inhabitants and business.” | Digital solution |
| Layer | Description | Example |
| Urban | The stratum at which physical and digital infrastructures converge to generate intelligent edifices, smart transportation systems, smart grids, and smart waste management is referred to as the interface layer. | Smart electricity meter [46] Smart water pipes [47] Smart parking solutions [46,48] Smart waste collection logistics [49] |
| Sensors | This layer is made up of smart devices that measure and monitor numerous parameters of the metropolitan area and its environs. | IoT sensors [46,48] (disaster alert, air pollution, water quality chemical or radiation) |
| Connectivity | This process involves moving data and information from the sensor tier to storage and data aggregators for analysis. | Cloud computing [24] |
| Data Analytics | This pertains to the examination of data obtained from various intelligent infrastructure systems with the aim of forecasting certain occurrences. | Traffic congestion prediction [46] |
| Automation | The interface layer for digital enablement facilitates the automation and scalability of a vast array of devices spanning various domains and verticals. | Smart home solutions [19] |
| Factors | Description | References |
| Electrical energy storage (battery) | Technology helps to stabilize power output and energy demand by storing excess or unused electrical energy and providing it to the grid or customers as needed. | [61,69,70,71,72] |
| Sharing electrical energy storage | A technology concept of utilizing a centralized energy storage system that can be accessed and utilized by multiple buildings within a community or network. | [61,69,70,73] |
| Ability to work off-grid (renewable energy source: solar wind) | Refers to their capability to operate independently from the central power grid, utilizing self-generated or stored energy sources. | [62,71,74] |
| Energy usage monitoring and control, demand-side management | Implementation of systems and technologies to track, analyze, and regulate energy consumption within the building. | [71,75,76] |
| Smart heating, cooling, and hot water preparation | Refers to the smart distribution and utilization of heating and cooling resources among multiple building units or spaces. | [77,78] |
| Thermal energy storage | Implementation of systems and technologies that enable the efficient storage, management, and utilization of thermal energy within building envelopes or components. | [69,72,75] |
| Sharing thermal energy storage | Thermal energy storage systems in a cluster of buildings optimize thermal energy management and efficiency. Thermal energy is stored in pre-heated water tanks. During periods of low demand and low electrical energy cost and then used during periods of high-temperature regulation demand. | [69] |
| Factors | Description | References |
| Smart EV charging | A technology of integration of smart charging solutions for electric vehicles that optimize energy consumption, adapt charging strategies, and provide additional benefits for consumers and the overall energy system. | [9,72,79,81] |
| Carpooling–ride sharing | Refers to the practice of sharing rides among individuals working or residing in the same building or complex. | [9,56,82] |
| Smart parking management system (E-parking) | Sensors, IoT devices, and real-time data to provide management and visibility into parking space. | [9,80,83,84] |
| Sharing parking space | Refers to the practice of allowing multiple individuals or organizations to utilize the same parking area or facility. | [9,80,83,84] |
| Online video surveillance | CCTV cameras with implemented technology use various techniques and algorithms to monitor and analyze video footage in real time, enabling smart systems to detect and respond to mobility-related events. | [9,72,85] |
| Last mile driving | It is a transportation solution to address the final journey from a transportation hub to the final destination point by using self-driving vehicles. | [82] |
| Factors | Description | References |
| Smart water mixtures | Integration of technology and systems to monitor, control, and optimize water usage within building infrastructures, and conservation | [64,81] |
| Smart water monitoring and shutoff (leak detection and prevention) | Smart water management systems detect water leaks and alert building operators | [64,81,86] |
| Smart water irrigation system | An automated irrigation control based on real-time soil moisture, weather, and plant water requirements from soil sensors | [64,81,87] |
| Smart water meter | An advanced metering infrastructure for online water consumption monitoring | [64,81] |
| Greywater recycling | A sustainable solution for repurposing water that is typically discharged from showers, bathtubs, washbasins, laundry, and swimming pools | [64,72] |
| Rainwater collection (harvesting) and reuse | A sustainable method that collects and uses rainwater in the building’s infrastructure to conserve water and prevent flooding | [64,72] |
| Factors | Description | References |
| Smart monitoring and data analytics of the surrounding environment | CCTV cameras and advanced algorithms enable real-time video analytics for face recognition, people counting, attendance management, and emotion analysis. | [72,81,85,89,91] |
| Smart fire management | An application of IoT technologies and advanced systems to enhance fire safety and responses. | [72,81,90] |
| Disaster event communication management | IoT, cloud computing, video surveillance, and communication networks were used to detect and respond to disasters. | [92,93] |
| Smart security lightning | A Lightning system uses advanced technologies like IoT and intelligent control for perimeter security, enhancing smart building security infrastructure and occupant safety. | [72,81] |
| Integrated sensors solutions | IoT sensors integrate various functionalities into a single device, offering a condensed and all-encompassing approach to monitoring environmental factors simultaneously. This integration enables the measurement of temperature, humidity, and air quality in a single unit. | [65,94,95] |
| Factors | Description | References |
|---|---|---|
| Smart waste containers | A waste management solution that leverages technology such as AI, data-driven approach, and IoT sensors to improve waste collection, and optimize waste management processes. | [57,66,96] |
| Automated and robotic waste collection | A gravity and full vacuum system collects garbage and transports it through underground pipes to a nearby station for sorting and compacting, crucial for recycling materials. | [97,98] |
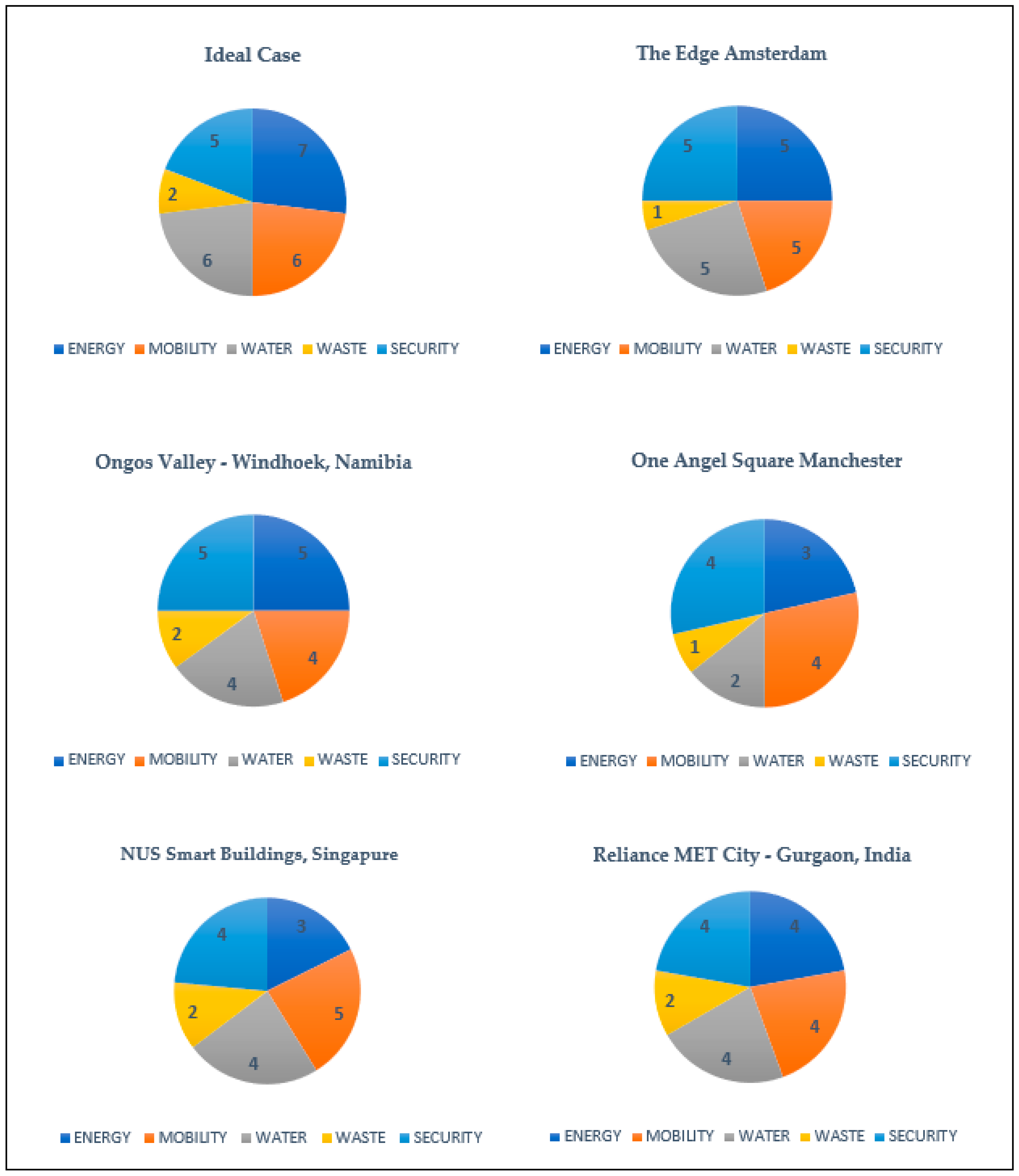
| Domains | Factors Related to the Smart Services | The Edge Amsterdam, the Netherlands | One Angel Square Manchester, UK | (NUS) Smart Buildings, Singapore | Ongos Valley, Windhoek, Namibia | Reliance MET City Gurgaon, India | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENERGY | 1 | Electrical energy storage (batteries) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 2 | Sharing electrical energy storage | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 3 | Ability to work off-grid (renewable energy sources wind–solar) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 4 | Energy usage monitoring and control, demand-side management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 5 | Smart heating, cooling, and hot water preparation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 6 | Thermal energy storage | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 7 | Sharing thermal energy storage | ✓ | |||||
| Total ENERGY | 5 out of 7 | 3 out of 7 | 3 out of 7 | 5 out of 7 | 4 out of 7 | ||
| MOBILITY | 1 | Smart EV charging | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 2 | Carpooling–ride sharing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 3 | Smart parking management system (e-parking) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 4 | Sharing parking space | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 5 | Online video surveillance | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 6 | Last mile driving | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Total MOBILITY | 5 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | 5 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | ||
| WATER | 1 | Smart water mixtures | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 2 | Smart water monitoring and shutoff | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 3 | Smart water irrigation system | ✓ | |||||
| 4 | Smart water meter | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 5 | Greywater recycling | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 6 | Rainwater collection (harvesting) and reuse | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Total WATER | 5 out of 6 | 2 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | 4 out of 6 | ||
| WASTE | 1 | Smart waste containers | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 2 | Automated and robotic waste collection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Total WASTE | 1 out of 2 | 1 out of 2 | 2 out of 2 | 2 out of 2 | 2 out of 2 | ||
| SECURITY | 1 | Monitoring and analysis devices: face detection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 2 | Monitoring and analysis devices: car plate detection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 3 | Smart fire management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 4 | Disaster event communication management | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 5 | Security smart lights | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Total SECURITY | 5 out of 5 | 4 out of 5 | 4 out of 5 | 5 out of 5 | 4 out of 5 | ||
| TOTAL | 21 | 14 | 18 | 20 | 18 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apanavičienė, R.; Shahrabani, M.M.N. Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1832-1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040085
Apanavičienė R, Shahrabani MMN. Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects. Smart Cities. 2023; 6(4):1832-1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleApanavičienė, Rasa, and Mustafa Muthnna Najm Shahrabani. 2023. "Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects" Smart Cities 6, no. 4: 1832-1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040085
APA StyleApanavičienė, R., & Shahrabani, M. M. N. (2023). Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects. Smart Cities, 6(4), 1832-1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6040085






