Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Smart Seaports: The Role of Cyber Technologies
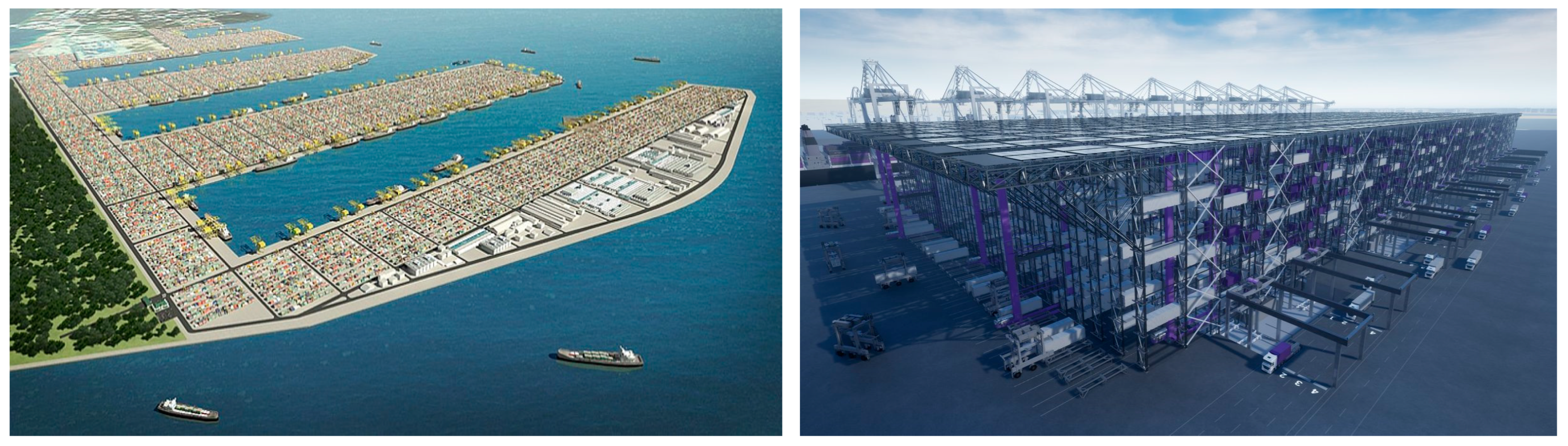
2.1. Seaport Automation: The Ports of Singapore and Jebel Ali
2.2. Incorporation of 5G at Seaports: The Ports of Shangai and Santos
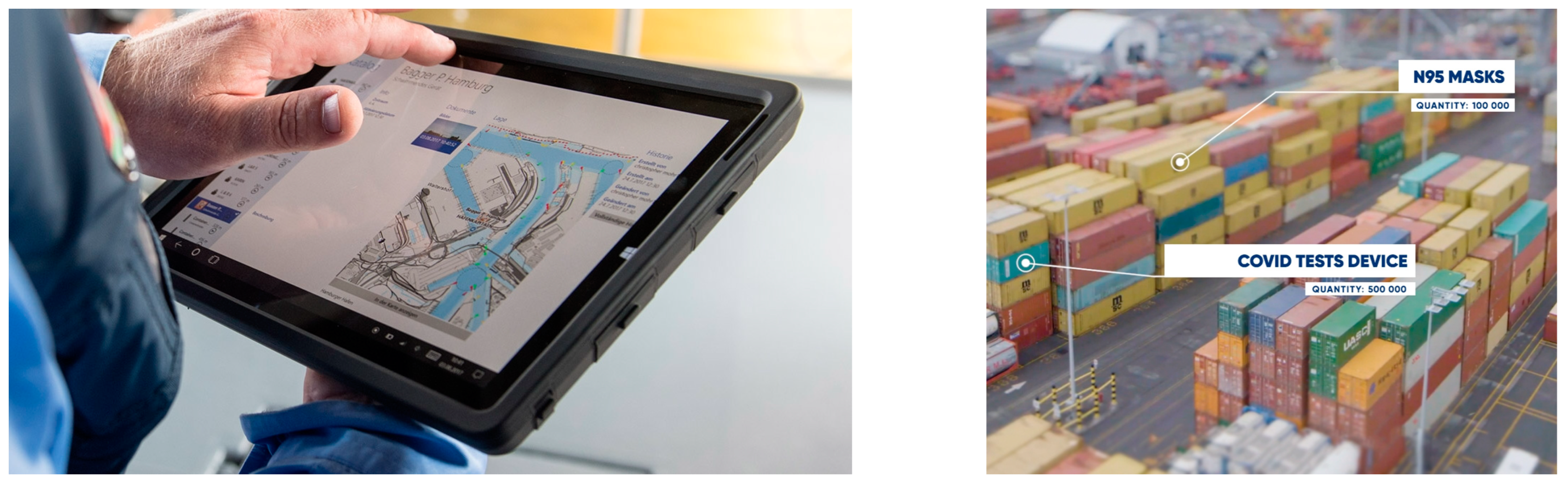
2.3. From AI to Blockchain at Seaports: The Ports of Montreal and Hamburg
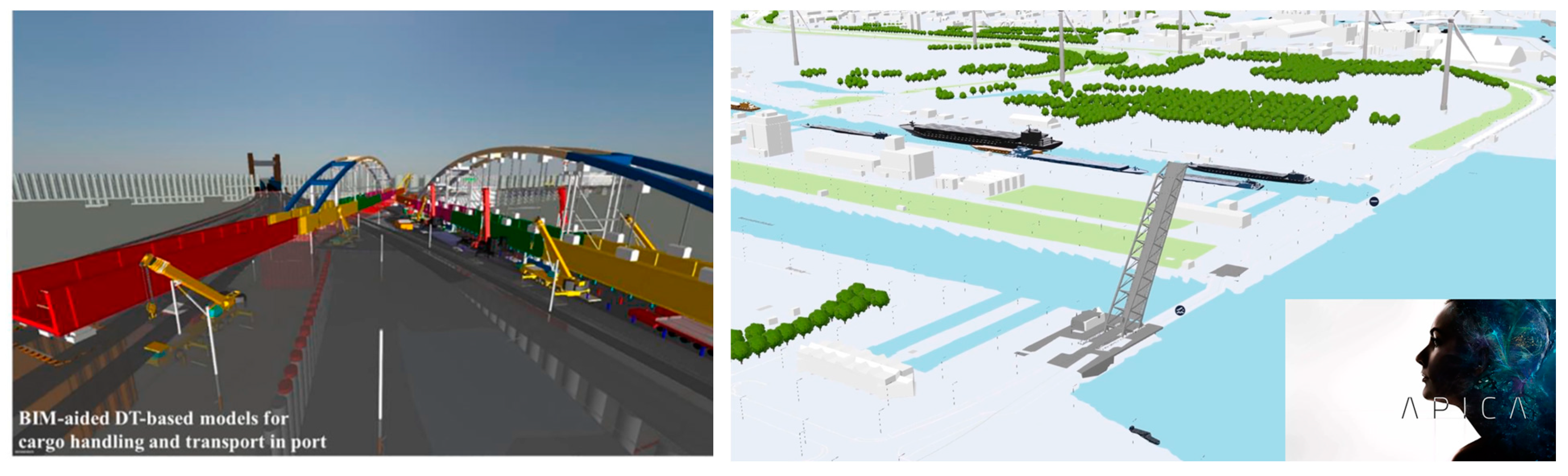
2.4. Digital Twins of Seaports: The Ports of Rotterdam and Antwerp-Bruges
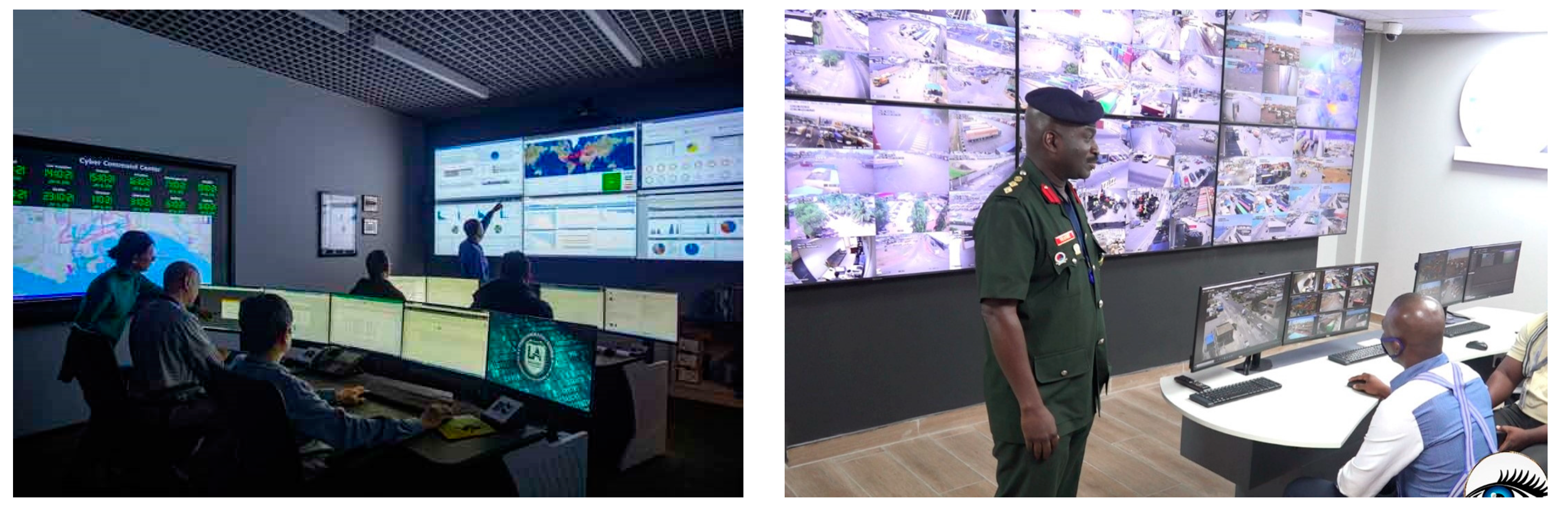
2.5. Cybersecurity in Seaports: The Ports of Los Angeles and Tema
3. Sustainable Seaports: The Role of Marine Renewable Energy
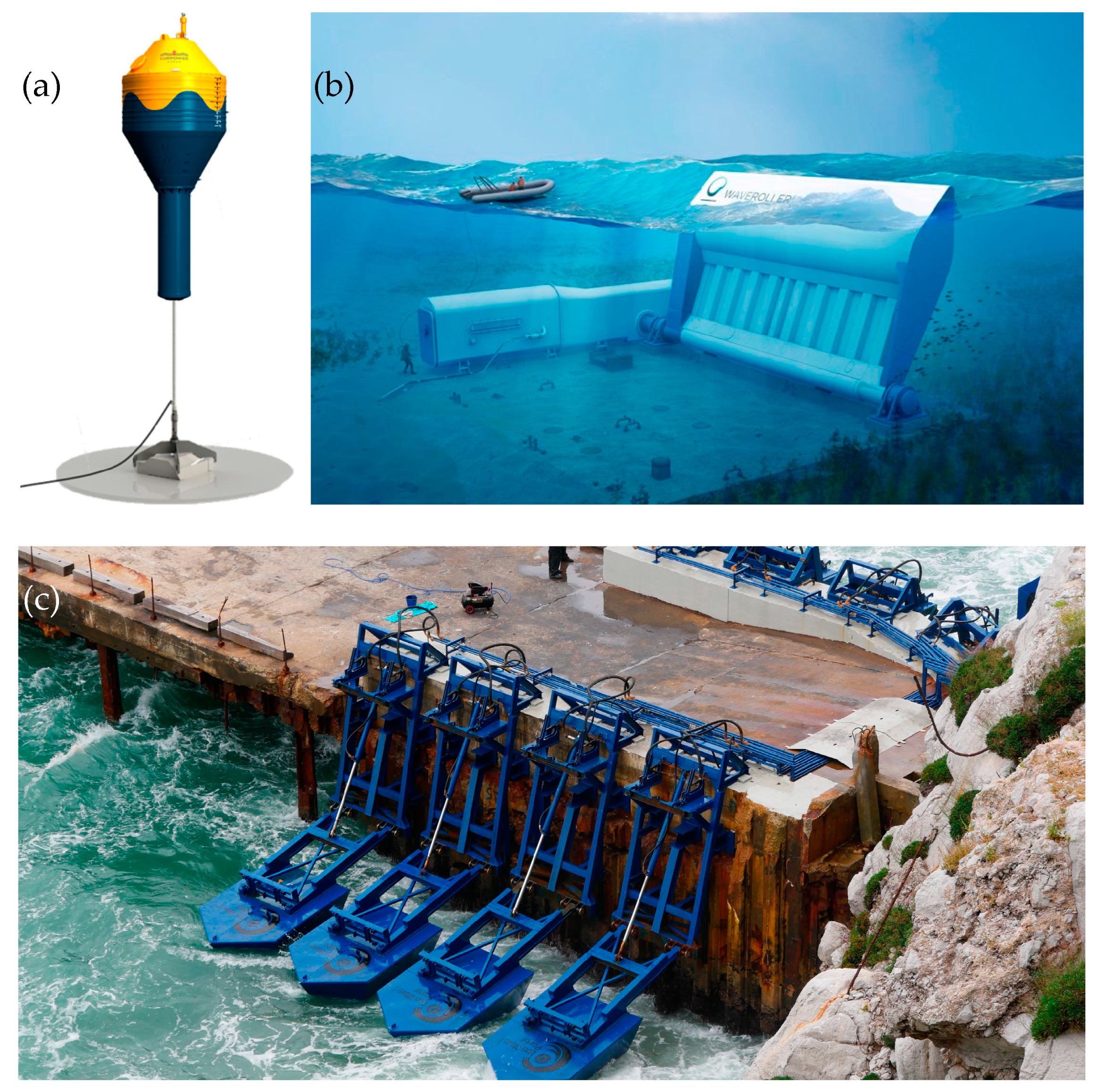
3.1. Wave Energy: Resource, Converters and Port Integration
3.2. Ports Using Locally Generated Electricity from Renewable Sources
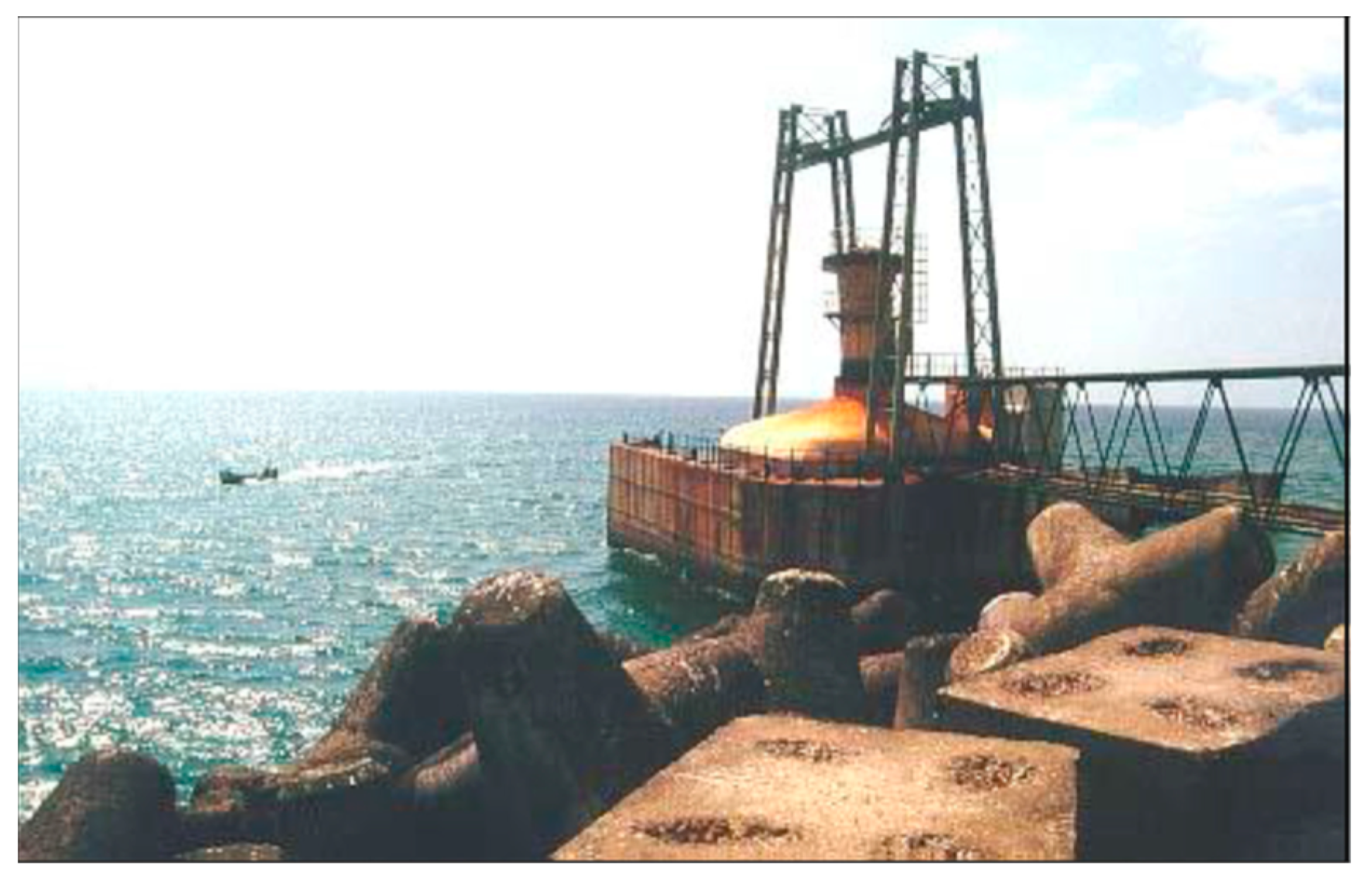
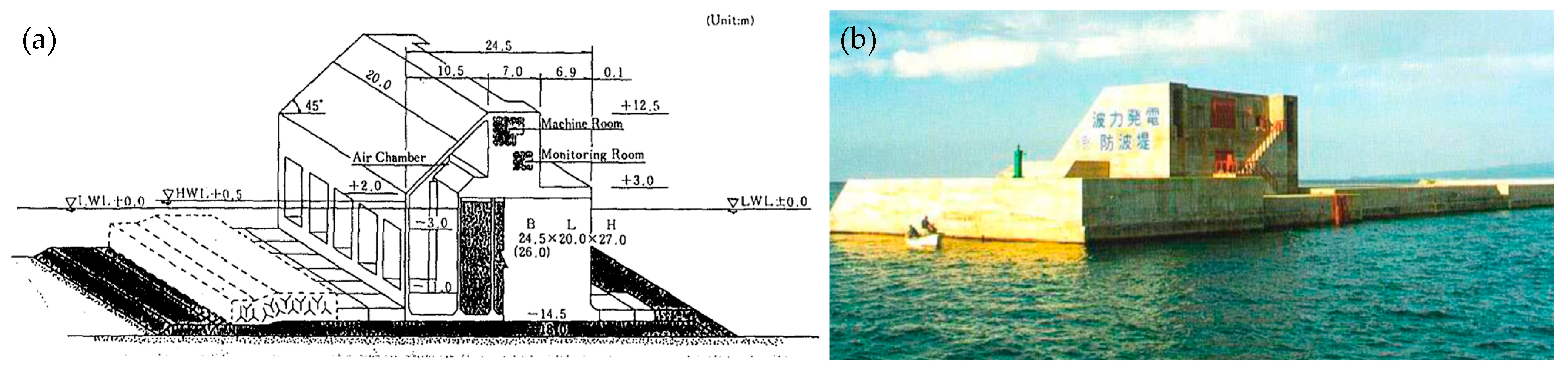
- OWC integrated into the breakwater of the Port of Sakata, Japan
- 2.
- OWC caisson in India
- 3.
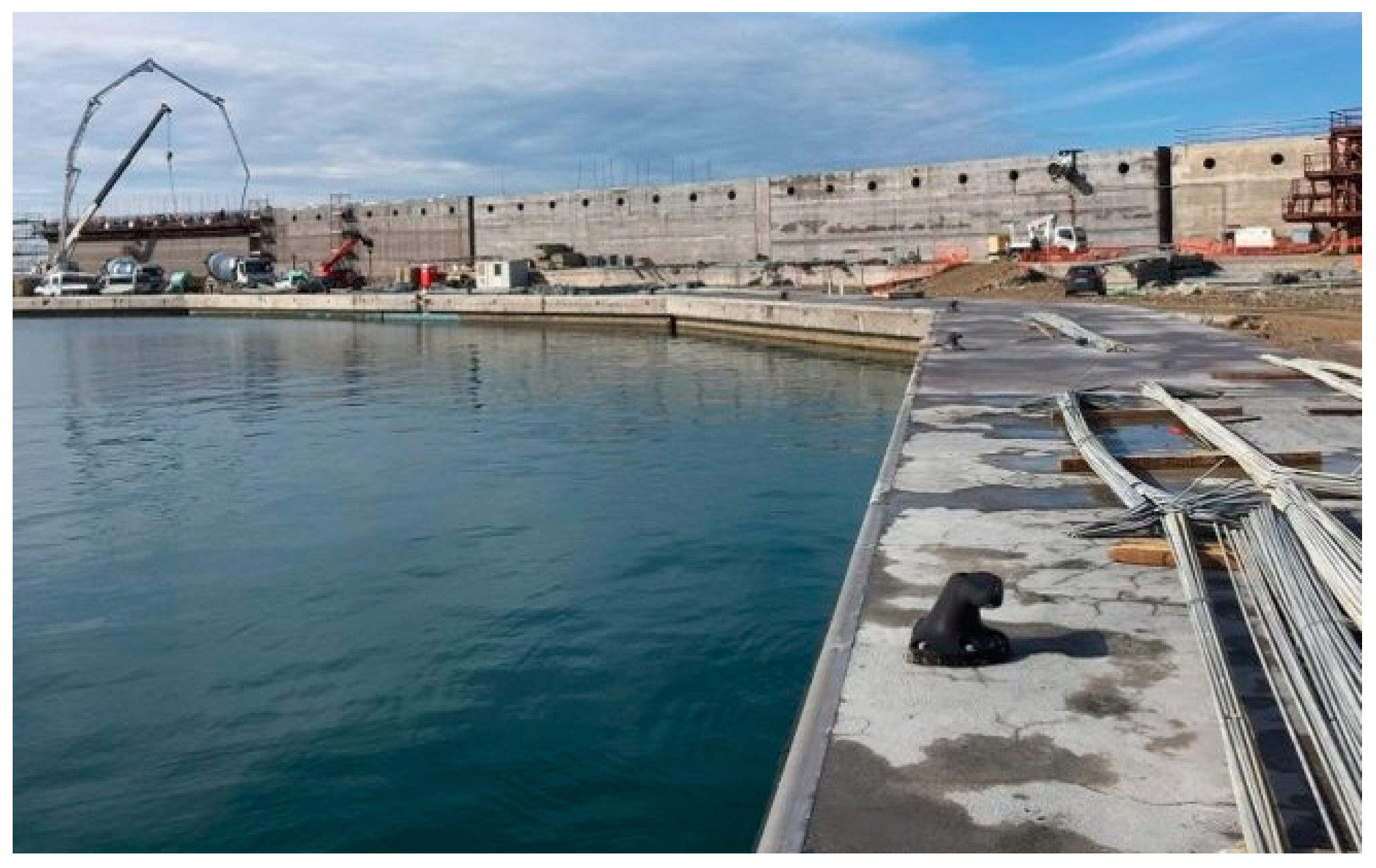
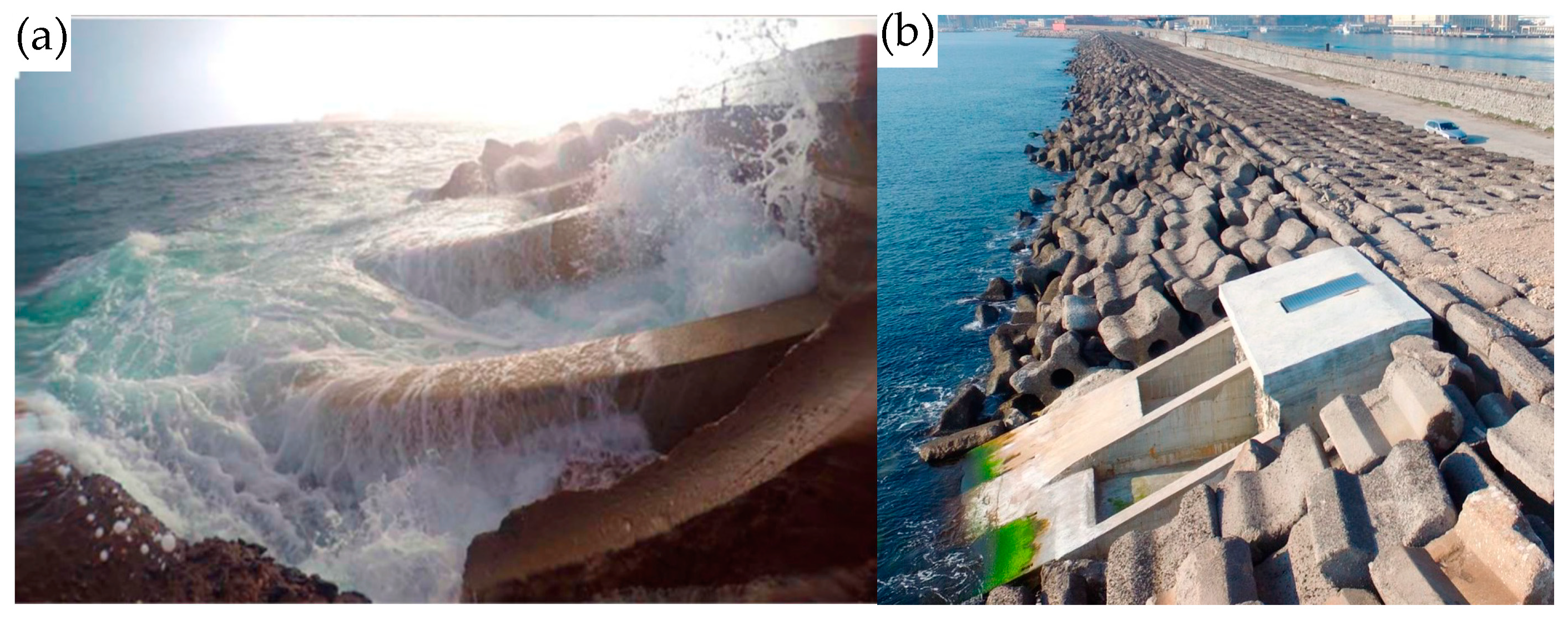
- OWC integrated into the breakwater of the Port of Mutriku, Spain
- 4.
- OWC integrated into the breakwater of the Civitavecchia Harbor, Italy
- 5.
- OBREC
- 6.
- Seahorse
- 7.
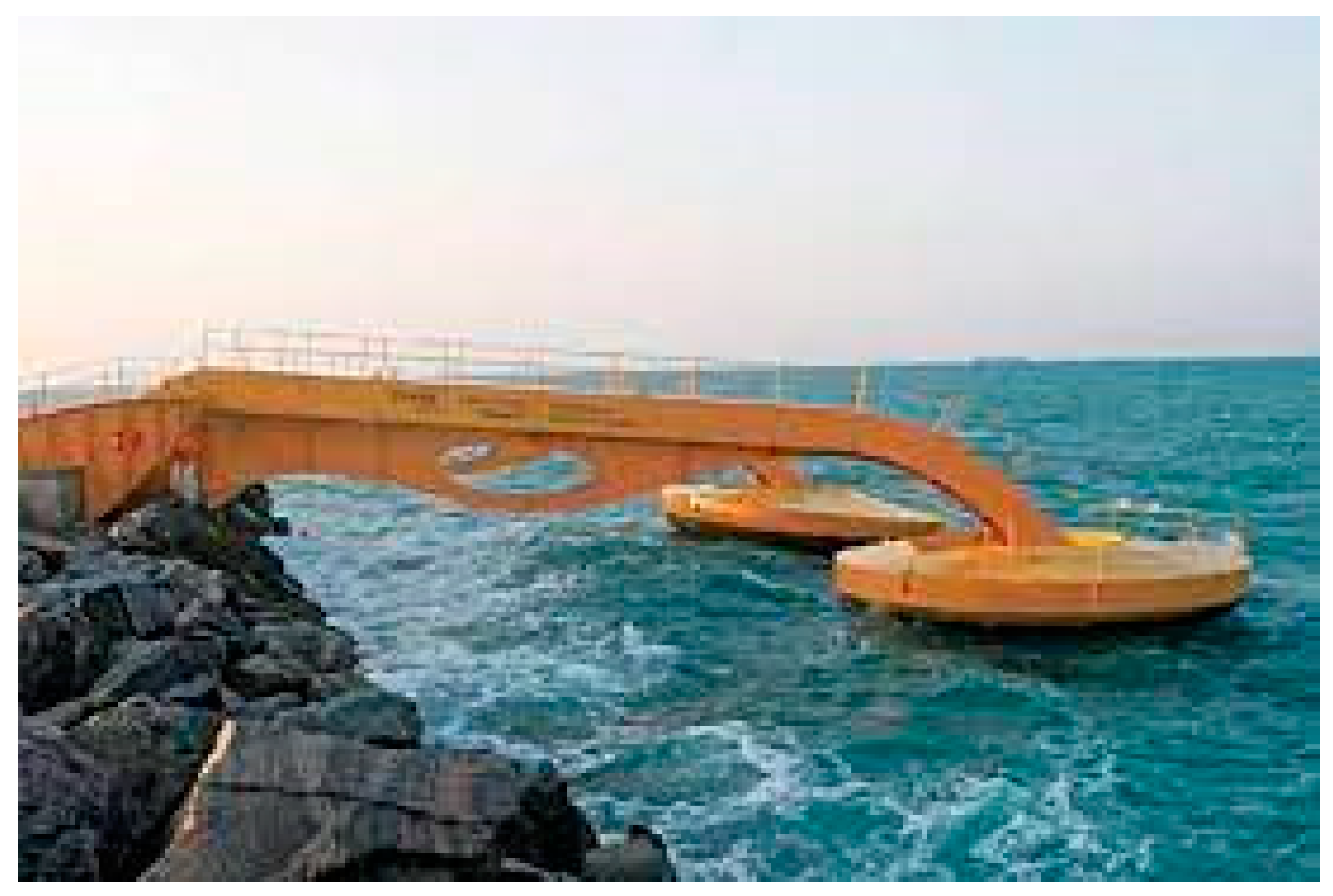
- Eco Wave Power
3.3. Alternative MRE Approaches in Ports
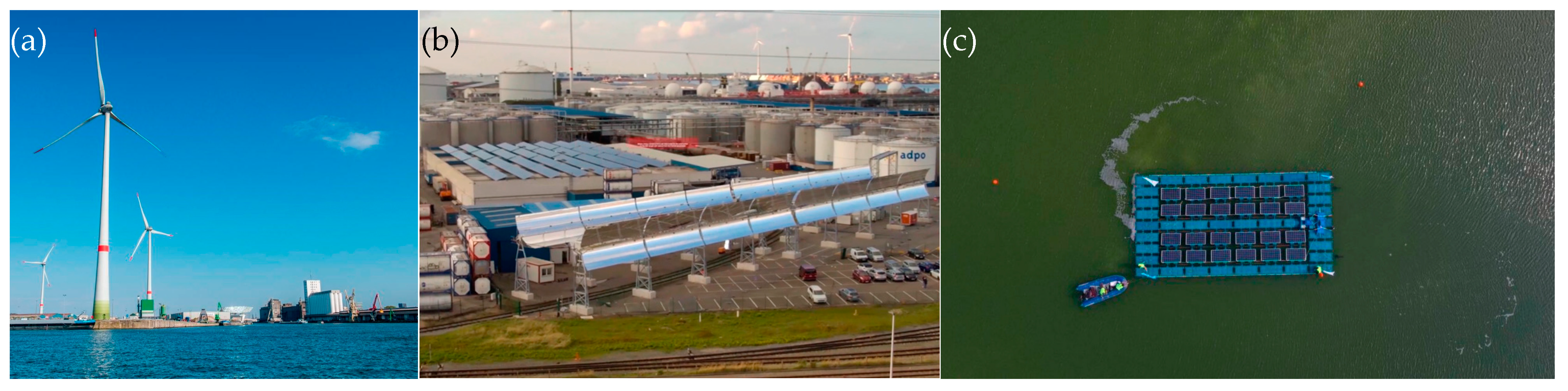
3.3.1. Wind and Solar Energy
3.3.2. Hybrid Devices
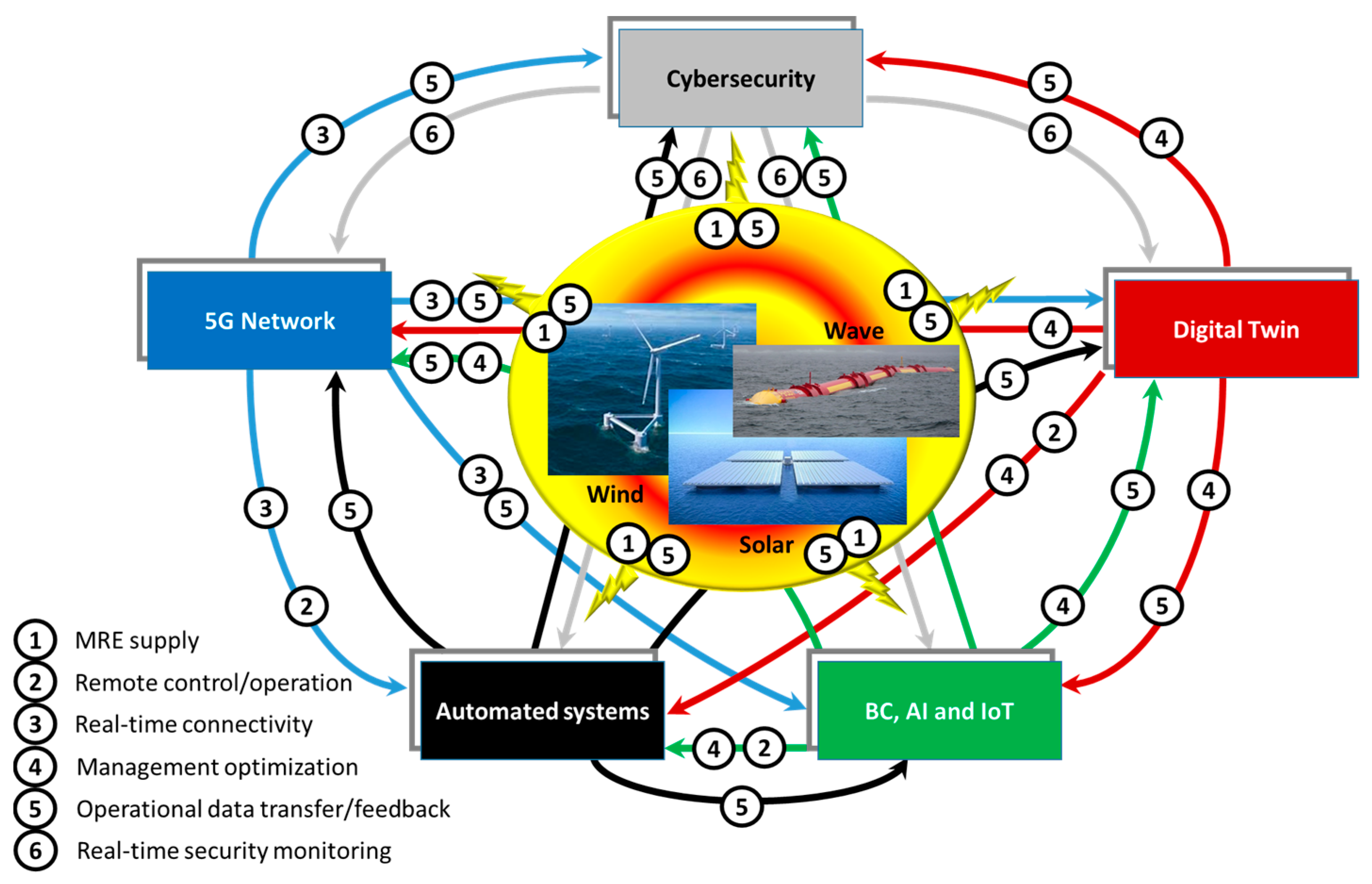
4. Discussion and Model Seaport Proposal
4.1. Conceptual Framework Overview
4.2. Smart- and Energy-Sustainable-Seaport Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Abbreviation | Expansion |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AGV | Autonomous Guided Vehicle |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| APICA | Advanced Port Information & Control Assistant |
| BC | Blockchain |
| CC | Cloud Computing |
| CCTV | Closed-Circuit Television |
| CRC | Cyber Resilience Center |
| CSOC | Cyber Security Operations Center |
| DT | Digital Twin |
| ESPO | European Sea Ports Organization |
| GPHA | Ghana Ports & Harbors Authorities |
| MRE | Marine Renewable Energy |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IT | Information Technology |
| LCoE | Levelized Cost of Energy |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| OD | Overtopping Device |
| OTD | Overtopping Device |
| OWC | Oscillating Water Column |
| PTO | Power Take-Off |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| RFID | Radio-Frequency Identification |
| RO-RO | Roll-On Roll-Off |
| SSP | Shore-to-Ship Power |
| Tapchan | Tapered Channel Wave Power Device |
| TEU | Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| WAB | Wave-Activated Body |
| WEC | Wave Energy Converter |
References
- UN. Review of Maritime Transport 2018. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2021; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Becker, A.H.; Acciaro, M.; Asariotis, R.; Cabrera, E.; Cretegny, L.; Crist, P.; Esteban, M.; Mather, A.; Messner, S.; Naruse, S.; et al. A note on climate change adaptation for seaports: A challenge for global ports, a challenge for global society. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Inoue, S.; Fischer, M.; Schwegler, B. Climate change impacts on international seaports: Knowledge, perceptions, and planning efforts among port administrators. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranandani, V. Sustainable development in seaports: A multi-case study. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2014, 13, 127–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilin, I.; Jahn, C.; Weigell, J.; Kalyazina, S. Digital Technology Implementation for Smart City and Smart Port Cooperation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Technologies in Logistics and Infrastructure (ICDTLI 2019), St. Petersburg, Russia, 4–5 April 2019; Atlantis Press: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019; p. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H. Developing a smart port architecture and essential elements in the era of Industry 4.0. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2022, 24, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, C.A.; Fernández-Campusano, C.; Carrasco, R.; Vargas, M.; Navarrete, A. Boosting the Decision-Making in Smart Ports by Using Blockchain. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 128055–128068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeerth, P.S.; Lakshmy, K.V. Blockchain based Smart Contracts in Automation of Shipping Ports. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 20–22 January 2021; pp. 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhmas, K.; Sedqui, P.A. Toward a smart port congestion optimizing model. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 13th International Colloquium of Logistics and Supply Chain Management (LOGISTIQUA), Fez, Morocco, 2–4 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xue, T.; Wang, D.; Qi, Y.; Su, M. Development Direction of Automated Terminal and Systematic Planning of Smart Port. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE), Nanchang, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zun, Z.; Qian, X. Multi-aspect applications and development challenges of digital twin-driven management in global smart ports. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2021, 9, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, B.; Kayisoglu, G.; Bolat, P. Cyber security risk assessment for seaports: A case study of a container port. Comput. Secur. 2021, 103, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizelis, C.-A.; Mavroeidakos, T.; Marinakis, A.; Litke, A.; Moulos, V. Towards a Smart Port: The Role of the Telecom Industry. In Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations.AIAI 2020 IFIP WG 12.5 International Workshops; Maglogiannis, I., Iliadis, L., Pimenidis, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, R.; Fiore, U.; Musella, G.; Perla, F.; Punzo, G.; Risitano, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Zanetti, P. Do Digital and Communication Technologies Improve Smart Ports? A Fuzzy DEA Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5674–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Ali, S.W.; Terriche, Y.; Mutarraf, M.U.; Hassan, M.A.; Hamid, K.; Ali, Z.; Sze, J.Y.; Su, C.-L.; Guerrero, J.M. Future Greener Seaports: A Review of New Infrastructure, Challenges, and Energy Efficiency Measures. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 75568–75587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, D.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. On the potential synergies and applications of wave energy converters: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Majidi, A.G.; Ramos, V.; Giannini, G.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Development and Assessment of a Hybrid Breakwater-Integrated Wave Energy Converter. Int. Mar. Energy J. 2022, 5, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachvarova, E.; Spasova, T.; Marinski, J. Air Pollution and Specific Meteorological Conditions at the Adjacent Areas of Sea Ports. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnes, H.; Styhre, L.; Fridell, E. Reducing GHG emissions from ships in port areas. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2015, 17, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdoukopoulos, E.; Boile, M.; Tromaras, A.; Anastasiadis, N. Energy Efficiency in European Ports: State-Of-Practice and Insights on the Way Forward. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascajo, R.; García, E.; Quiles, E.; Correcher, A.; Morant, F. Integration of Marine Wave Energy Converters into Seaports: A Case Study in the Port of Valencia. Energies 2019, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPO. ESPO Environmental Report 2022. Available online: https://www.espo.be/media/ESP-2959%20(Sustainability%20Report%202022)_V8 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Falcão, A.F.d.O. Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, A.; Kofoed, J.P. (Eds.) Handbook of Ocean Wave Energy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, D.; Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Hydraulic and Structural Assessment of a Rubble-Mound Breakwater with a Hybrid Wave Energy Converter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astariz, S.; Vazquez, A.; Iglesias, G. Evaluation and comparison of the levelized cost of tidal, wave, and offshore wind energy. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 053112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Jones, C.A.; Roberts, J.D.; Neary, V.S. A comprehensive evaluation of factors affecting the levelized cost of wave energy conversion projects. Renew. Energy 2018, 127, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taveira-Pinto, F.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Fazeres-Ferradosa, T. Marine renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uihlein, A.; Monfardini, R.; Magagna, D. JRC Ocean Energy Status Report: 2016 Edition; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2021; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; ISBN 978-92-9260-452-3. [Google Scholar]
- The Set Plan Temporary Working Group. SET-Plan Ocean Energy Implementation Plan. Available online: https://oceanenergy-sweden.se/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/set_plan_ocean_implementation_plan.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Têtu, A.; Fernandez Chozas, J. A Proposed Guidance for the Economic Assessment of Wave Energy Converters at Early Development Stages. Energies 2021, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, V.; Giannini, G.; Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. An Integrated Approach to Assessing the Wave Potential for the Energy Supply of Ports: A Case Study. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannasiraj, S.A.; Sundar, V. Assessment of wave energy potential and its harvesting approach along the Indian coast. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, K.; Sundar, V. Reassessment of tidal energy potential in India and a decision-making tool for tidal energy technology selection. Int. J. Ocean Clim. Syst. 2017, 8, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, H.; Fonseca, R.; Guedes Soares, C. Site selection process for floating offshore wind farms in Madeira Islands. In Advances in Renewable Energies Offshore; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2018; pp. 729–737. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, R.; Prause, G.; Olaniyi, E.O.; Lemke, F. Towards Green and Smart Seaports: Renewable Energy and Automation Technologies for Bulk Cargo Loading Operations. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2021, 25, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlić Skender, H.; Ribarić, E.; Jović, M. An Overview of Modern Technologies in Leading Global Seaports. Pomor. Zb. 2020, 59, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Jović, M.; Kavran, N.; Aksentijević, S.; Tijan, E. The Transition of Croatian Seaports into Smart Ports. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1386–1390. [Google Scholar]
- APDL. A Janela Única Logística—Alargamento da Cobertura Digital às Cadeias Logísticas. 2021. Available online: https://www.apdl.pt/en_US/-/a-janela-unica-logistica-alargamento-da-cobertura-digital-as-cadeias-logisticas?inheritRedirect=true (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Effah, J.; Amankwah-Sarfo, F.; Boateng, R. Affordances and constraints processes of smart service systems: Insights from the case of seaport security in Ghana. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Piris, A.; Díaz-Ruiz-Navamuel, E.; Pérez-Labajos, C.A.; Oria Chaveli, J. Reduction of CO2 emissions with automatic mooring systems. The case of the port of Santander. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Ghoroghi, A. Decarbonisation of seaports: A review and directions for future research. Energy Strategy Rev. 2021, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandra, J.O. Tuas Port Opens with 3 Berths as It Progresses to Become World’s Largest Fully Automated Port. Offshore Energy. 2022. Available online: https://www.offshore-energy.biz/tuas-port-opens-with-3-berths-as-it-progresses-to-become-worlds-largest-fully-automated-port/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore. Port of the Future. Maritime & Port Authority of Singapore (MPA). 2022. Available online: http://www.mpa.gov.sg/maritime-singapore/port-of-the-future (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Ng, D.; Pei, W.C. Future-Ready Learners: Learning, Lifework, Living, and Habits of Practices, 1st ed.; National Institute of Education (NIE), Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tardo, A.; Pagano, P.; Antonelli, S.; Rao, S. Addressing digitalization though out a prototyping framework for agile smart services development: The case of Livorno Port. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2311, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bawaba. ENOC Enhances Technology at Jebel Ali Port to Boost Fuelling Efficiency. Al Bawaba 2017. Available online: https://www.albawaba.com/business/pr/enoc-enhances-technology-jebel-ali-port-boost-fuelling-efficiency-945592 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Port Technology Team. DGWorld to Boost Jebel Ali Port with Autonomous Vehicles. Port Technology International. 2020. Available online: https://www.porttechnology.org/news/dgworld-to-boost-jebel-ali-port-with-autonomous-vehicles/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Arabian Business. How Dubai Is at the Centre of a Global Port Revolution. 2021. Available online: https://www.arabianbusiness.com/industries/technology/467239-how-dubai-is-at-the-centre-of-global-port-revolution (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- DP World. UAE Region Implements Locally Developed ZODIAC System in Jebel Ali Port’s Terminal 3 to Enable 100% Automation of Facilities. 2021. Available online: https://www.dpworld.com/en/uae/news/latest-news/dp-world-uae-region-implements-locally-developed-zodiac-system (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Moore, R. DP World Launches TOS for 100% Automation in Jebel Ali Terminal. Riviera. 2021. Available online: https://www.rivieramm.com/news-content-hub/news-content-hub/dp-world-launches-tos-for-100-automation-in-jebel-ali-terminal-63880 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Elnajjar, H.M.; Shehata, A.S.; Elbatran, A.H.A.; Shehadeh, M.F. Experimental and techno-economic feasibility analysis of renewable energy technologies for Jabel Ali Port in UAE. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányai, T.; Bányai, Á.; Kaczmar, I. (Eds.) Supply Chain—Recent Advances and New Perspectives in the Industry 4.0 Era; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Li, Q.; Kim, K.J.; López-Pérez, D.; Dobre, O.A.; Poor, H.V.; Popovski, P.; Tsiftsis, T.A. Private 5G Networks: Concepts, Architectures, and Research Landscape. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaib, R.M.; Onireti, O.; Sambo, Y.; Imran, M.A. Network Slicing for Beyond 5G Systems: An Overview of the Smart Port Use Case. Electronics 2021, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, N.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, R.; Yan, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y. A 5G-Based VR Application for Efficient Port Management. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzhiy, A.; Kalyazina, S.; Maydanova, S.; Marchenko, R. Port and City Integration: Transportation Aspect. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, M.; Saarni, J.; Saurama, A. Innovation in Smart Ports: Future Directions of Digitalization in Container Ports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BNamericas. How South America’s Main Port Operator Advances through Technology. BNamericasCom. 2021. Available online: https://www.bnamericas.com/en/features/how-south-americas-main-port-operator-advances-through-technology (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- SPA. Santos Port Authority. Santos Port Authority. 2023. Available online: https://www.portodesantos.com.br/en/ (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- BNamericas. Brazil’s Santos Port to Deploy a Private 5G Network. BNamericasCom n.d. Available online: https://www.bnamericas.com/en/news/brazils-santos-port-to-deploy-a-private-5g-network (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- PTM. BTP, TIM and Nokia Partner for First Ever 5G Latin America Port Network. Port Technology International. 2022. Available online: https://www.porttechnology.org/news/btp-tim-and-nokia-partner-for-first-ever-5g-latin-america-port-network/ (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Yau, K.-L.A.; Peng, S.; Qadir, J.; Low, Y.-C.; Ling, M.H. Towards Smart Port Infrastructures: Enhancing Port Activities Using Information and Communications Technology. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83387–83404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.-Y.; Huang, X.-R.; Chen, L.-B. Smart ports: Sustainable smart business port operation schemes based on the Artificial Intelligence of Things and blockchain technologies. IEEE Potentials 2022, 41, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovač, M. Autonomous AI, Smart Seaports, and Supply Chain Management: Challenges and Risks. In Regulating Artificial Intelligence in Industry, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Sun, Y.; Rameezdeen, R.; Chow, C. Understanding data governance requirements in IoT adoption for smart ports—A gap analysis. Marit. Policy Manag. 2022, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapkaeva, N.; Gurzhiy, A.; Maydanova, S.; Levina, A. Digital Platform for Maritime Port Ecosystem: Port of Hamburg Case. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M.; Renken, K.; Dirzka, C. Integrated Port Cities: The Case of Hamburg. In European Port Cities in Transition: Moving Towards More Sustainable Sea Transport Hubs; Carpenter, A., Lozano, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterland, 2020; pp. 287–301. ISBN 978-3-030-36464-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hamburg News. Blockchain Technology to Boost Release Processes in Ports. Hamburg News. 2021. Available online: https://www.hamburg-news.hamburg/en/location/blockchain-technology-boost-release-processes-ports (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Hackius, N.; Reimers, S.; Kersten, W. The Privacy Barrier for Blockchain in Logistics: First Lessons from the Port of Hamburg. In Logistics Management; Bierwirth, C., Kirschstein, T., Sackmann, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterland, 2019; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HPA. SMARTPORT—The Intelligent Port. 2023. Available online: https://www.hamburg-port-authority.de/en/hpa-360/smartport (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Abu Aisha, T.; Ouhimmou, M.; Paquet, M. Optimization of Container Terminal Layouts in the Seaport—Case of Port of Montreal. Sustainability 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Szopik-Depczyńska, K.; Dembińska, I.; Ioppolo, G. Smart and sustainable logistics of Port cities: A framework for comprehending enabling factors, domains and goals. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPA. Canscan: The Technology That Checks All the Boxes for Shippers’ Benefit. 2023. Available online: https://www.port-montreal.com/en/the-port-of-montreal/news/news/logbook/canscan-en (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- MPA. Artificial Intelligence at the Service of Port Operations in This Time of Health Crisis. 2020. Available online: https://www.port-montreal.com/en/the-port-of-montreal/news/news/artificial-intelligence (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- PTM. Port of Montréal Optimises Workforce Planning with AI-Powered Tool. Port Technology International. 2022. Available online: https://www.porttechnology.org/news/port-of-montreal-optimises-workforce-planning-with-ai-powered-tool/ (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- MPA. The Port of Montreal Joins Maersk IBM Platform. 2018. Available online: https://www.port-montreal.com/en/the-port-of-montreal/news/news/press-release/tradelens (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- HPA. Digital Testing Ground. 2023. Available online: https://www.hamburg-port-authority.de/en/themenseiten/digital-testing-ground (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- MPA. PreVu3D: Rethinking Port Space. 2023. Available online: https://www.port-montreal.com/en/the-port-of-montreal/news/news/logbook/prevu3d-rethinking-port-space (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- MPA. Agility and Resilience through Tech: A Lifeline for Distribution Logistics. 2023. Available online: https://www.port-montreal.com/en/the-port-of-montreal/news/news/resilience-en (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Yao, H.; Wang, D.; Su, M.; Qi, Y. Application of Digital Twins in Port System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1846, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Mahmood, A.; Auer, G. Realizing 5G smart-port use cases with a digital twin. Ericsson Technol. Rev. 2022, 2022, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, J.; Miller-Hooks, E.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, L.H.; Chew, E.P.; Li, H. Analytics with digital-twinning: A decision support system for maintaining a resilient port. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 143, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port of Antwerp Bulkchain. 2023. Available online: https://www.nxtport.com/market/live/bulkchain (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Jović, M.; Tijan, E.; Aksentijević, S.; Čišić, D. An Overview of Security Challenges of Seaport IoT Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port of Antwerp Smart Port|Port of Antwerp-Bruges. 2023. Available online: https://www.portofantwerpbruges.com/en/our-port/port-future/smart-port (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Port of Los Angeles about Cybersecurity at the Port of Los Angeles. 2023. Available online: https://www.portoflosangeles.org/business/cybersecurity (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- GPHA. Ghana Ports & Harbours Authority: Welcome to Port of Tema. Company Website. 2023. Available online: https://ghanaports.gov.gh/page/index/4/ZE4GGQFA/Welcome-to-Port-Of-Tema (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- GPHA GPHA Takes Key Step to Upgrade Security Surveillance at Port of Tema. 2021. Available online: https://www.ghanaports.gov.gh/media/news-details/323/HZR851WMJDE/GPHA-TAKES-KEY-STEP-TO-UPGRADE-SECURITY-SURVEILLANCE-AT-PORT-OF-TEMA (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Yun, P.E.N.G.; Xiangda, L.I.; Wenyuan, W.A.N.G.; Ke, L.I.U.; Chuan, L.I. A simulation-based research on carbon emission mitigation strategies for green container terminals. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, S.; Sekban, D.M. Emphasizing the importance of using cold-ironing technology by determining the share of hotelling emission value within the total emission. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIRECTIVE 2014/94/EU OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32014L0094 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Gunn, K.; Stock-Williams, C. Quantifying the global wave power resource. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerdata Electricity Domestic Consumption. 2021. Available online: https://yearbook.enerdata.net/electricity/electricity-domestic-consumption-data.html (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Reguero, B.G.; Losada, I.J.; Méndez, F.J. A global wave power resource and its seasonal, interannual and long-term variability. Appl. Energy 2015, 148, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REN21. Renewables 2022 Global status report; REN21 Secretariat: Paris, France, 2022; pp. 1–309. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. An EU Strategy to harness the potential of offshore renewable energy for a climate neutral future. Available online: https://climate-laws.org/documents/an-eu-strategy-to-harness-the-potential-of-offshore-renewable-energy-for-a-climate-neutral-future_0290 (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Whittaker, T.; McIlwaine, S.; Raghunathan, S. A review of the Islay shoreline wave power station. In Proceedings of the First European Wave Energy Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 30 October–1 November 1993; pp. 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ohneda, H.; Igarashi, S.; Shinbo, O.; Sekihara, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kubota, H.; Morita, H. Construction procedure of a wave power extracting caisson breakwater. In Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on Ocean Energy Utilization, Tokyo, Japan, 22–23 January 1991; pp. 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, M.; Koola, P.M. Energy from sea waves—The Indian wave energy programme. Curr. Sci. 1991, 60, 676–680. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlum, E. TAPCHAN; Evans, D.V., de Falcão, A.F.O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.C.C.; Portillo, J.C.C.; Gato, L.M.C.; Gomes, R.P.F.; Ferreira, D.N.; Falcão, A.F.O. Design of oscillating-water-column wave energy converters with an application to self-powered sensor buoys. Energy 2016, 112, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Capital Media. Energy Capital—The Magazine. Energy Capital Media. 2023. Available online: https://energycapitalmedia.com/ (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- AW-Energy Oy. WaveRoller—AW-Energy Oy. 2022. Available online: https://aw-energy.com/waveroller/ (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- EWP. The Future Is Here: Europe’s First Grid Connected Wave Energy Array. 2016. Available online: https://www.multivu.com/players/uk/7851451-eco-wave-europe-first-grid-connected-energy/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Vicinanza, D.; Lauro, E.D.; Contestabile, P.; Gisonni, C.; Lara, J.L.; Losada, I.J. Review of Innovative Harbor Breakwaters for Wave-Energy Conversion. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2019, 145, 03119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Nakada, H.; Ohneda, H.; Shikamori, M. Wave Power Conversion by a Prototype Wave Power Extracting Caisson in Sakata Port. Coast. Eng. 1992, 1993, 3440–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.O.; Henriques, J.C.C. Oscillating-water-column wave energy converters and air turbines: A review. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1391–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V.; Jayakumar, J.; Neelamani, S. Concrete Caisson For Also Kw Wave Energy Pilot Plant: Design, Construction and Installation Aspects. In Proceedings of the Second International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–19 June 1992; OnePetro, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Torre-Enciso, Y.; Ortubia, I.; de Aguileta, L.I.L.; Marqués, J. Mutriku Wave Power Plant: From the Thinking out to the Reality. In Proceedings of the 8th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Uppsala, Sweden, 7–11 September 2009; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Boccotti, P. Comparison between a U-OWC and a conventional OWC. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, F.; Romolo, A.; Malara, G.; Fiamma, V.; Laface, V. The First Full Operative U-OWC Plants in the Port of Civitavecchia. Volume 10: Ocean Renewable Energy; ASME: Trondheim, Norway, 2017; p. V010T09A022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WAVENERGY.it. ReWEC3 in the Port of Civitavecchia. WavenergyIt. 2023. Available online: https://www.wavenergy.it/projects/rewec3-in-the-port-of-civitavecchia/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Contestabile, P.; Iuppa, C.; Di Lauro, E.; Cavallaro, L.; Andersen, T.L.; Vicinanza, D. Wave loadings acting on innovative rubble mound breakwater for overtopping wave energy conversion. Coast. Eng. 2017, 122, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, P.; Vincenzo, F.; Di Lauro, E.; Vicinanza, D. Full-scale prototype of an overtopping breakwater for wave energy conversion. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, D.; Franzitta, V.; Guercio, A. Sea Wave Energy. A Review of the Current Technologies and Perspectives. Energies 2021, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florêncio, M.; Trigoso, F. Pesquisas e Projetos Desenvolvidos No Brasil Para o Aproveitamento do Potencial de Geração de Energia Elétrica com Ondas e Marés; Lepidus Tecnologia: Fortaleza, Brasil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, A.; Rodrigues, D.; Kalid, R.; Torres, E. Potencial energético das ondas na costa brasileira. Rev. Bras. Energ. 2017, 23, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- SEAHORSE. Seahorse Wave Energy. Seahorse Wave Energy. 2023. Available online: http://www.seahorseenergy.com.br/en/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Enerdata. Share of Wind and Solar in Electricity Production. 2021. Available online: https://yearbook.enerdata.net/renewables/wind-solar-share-electricity-production.html (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Acciaro, M.; Ghiara, H.; Cusano, M.I. Energy management in seaports: A new role for port authorities. Energy Policy 2014, 71, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port of Antwerp-Bruges Climate and Energy Transition. 2023. Available online: https://www.portofantwerpbruges.com/en/our-port/climate-and-energy-transition#hernieuwbaar (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, B. An Exploratory Study on Low-Carbon Ports Development Strategy in China. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2011, 27, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port of Antwerp-Bruges. Our Port in a Single Click|Port of Antwerp-Bruges. Company Website. 2023. Available online: https://www.portofantwerpbruges.com/en (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Greenpipe. Greenpipe—Experts on Divisible Cable Protection. Greenpipe. 2023. Available online: https://greenpipegroup.com/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Ramos, V.; Giannini, G.; Calheiros-Cabral, T.; López, M.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Assessing the Effectiveness of a Novel WEC Concept as a Co-Located Solution for Offshore Wind Farms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Collazo, C.; Greaves, D.; Iglesias, G. Hydrodynamic response of the WEC sub-system of a novel hybrid wind-wave energy converter. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Collazo, C.; Pemberton, R.; Greaves, D.; Iglesias, G. Monopile-mounted wave energy converter for a hybrid wind-wave system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Law, A.W.-K. Co-locating offshore wind and floating solar farms—Effect of high wind and wave conditions on solar power performance. Energy 2023, 266, 126437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunla, A.; Rominiyi, O.; Adaramola, B.; Adeoye, A. Development of a wind turbine for a hybrid solar-wind power system. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, M.; Elgarhy, A.; Elkholy, M.H.; Farahat, M.A. Integration of fuel cells into an off-grid hybrid system using wave and solar energy. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 130, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, D.; Rodrigues, C.; Esteves, R.; Correia, J.; Pereira, A.M.; Ventura, J.O.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Martins, P. Experimental Performance Analysis of a Hybrid Wave Energy Harvesting System Combining E-Motions with Triboelectric Nanogenerators. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Theoretical modelling of a new hybrid wave energy converter in regular waves. Renew. Energy 2018, 128, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, T.; Clemente, D.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Morais, T.; Belga, F.; Cestaro, H. Performance Assessment of a Hybrid Wave Energy Converter Integrated into a Harbor Breakwater. Energies 2020, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Clemente, D.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Ramos, V.; Morais, T.; Cestaro, H. Evaluation of the annual electricity production of a hybrid breakwater-integrated wave energy converter. Energy 2020, 213, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Clemente, D.; Cabral, T.; Fiorentin, F.; Belga, F.; Morais, T. Experimental Study of a Hybrid Wave Energy Converter Integrated in a Harbor Breakwater. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutrouveli, T.I.; Di Lauro, E.; das Neves, L.; Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Proof of Concept of a Breakwater-Integrated Hybrid Wave Energy Converter Using a Composite Modelling Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukos, G.; Giannopoulos, A.; Bizakis, A. Efficient Management of Operations in Ro-Ro/Ro-Pax Terminals Using a Cloud-Based Yard Management Platform. In Smart Energy for Smart Transport; Nathanail, E.G., Gavanas, N., Adamos, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourraja, M.N.; Kringos, N.; Meijer, S. Exploiting simulation model potential in investigating handling capacity of Ro-Ro terminals: The case study of Norvik seaport. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 117, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourraja, M.N.; Rouky, N.; Kornevs, M.; Meijer, S.; Kringos, N. A simulation-based decision support framework devoted to Ro–Ro terminals: Design, implementation and evaluation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 180, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, V.; Sebrechts, M.; Moons, B.; Hoebeke, J.; De Turck, F.; Volckaert, B. Design and evaluation of a scalable Internet of Things backend for smart ports. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2021, 51, 1557–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscoso-Lopez, J.A.; Ruiz-Aguilar, J.J.; Gonzalez-Enrique, J.; Urda, D.; Mesa, H.; Turias, I.J. Ro-Ro Freight Prediction Using a Hybrid Approach Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition, Permutation Entropy and Artificial Neural Networks. In Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems; Pérez García, H., Sánchez González, L., Castejón Limas, M., Quintián Pardo, H., Corchado Rodríguez, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clemente, D.; Calheiros-Cabral, T.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1560-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030074
Clemente D, Calheiros-Cabral T, Rosa-Santos P, Taveira-Pinto F. Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future. Smart Cities. 2023; 6(3):1560-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030074
Chicago/Turabian StyleClemente, Daniel, Tomás Calheiros-Cabral, Paulo Rosa-Santos, and Francisco Taveira-Pinto. 2023. "Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future" Smart Cities 6, no. 3: 1560-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030074
APA StyleClemente, D., Calheiros-Cabral, T., Rosa-Santos, P., & Taveira-Pinto, F. (2023). Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future. Smart Cities, 6(3), 1560-1588. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030074











