Evolving Optimised Convolutional Neural Networks for Lung Cancer Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
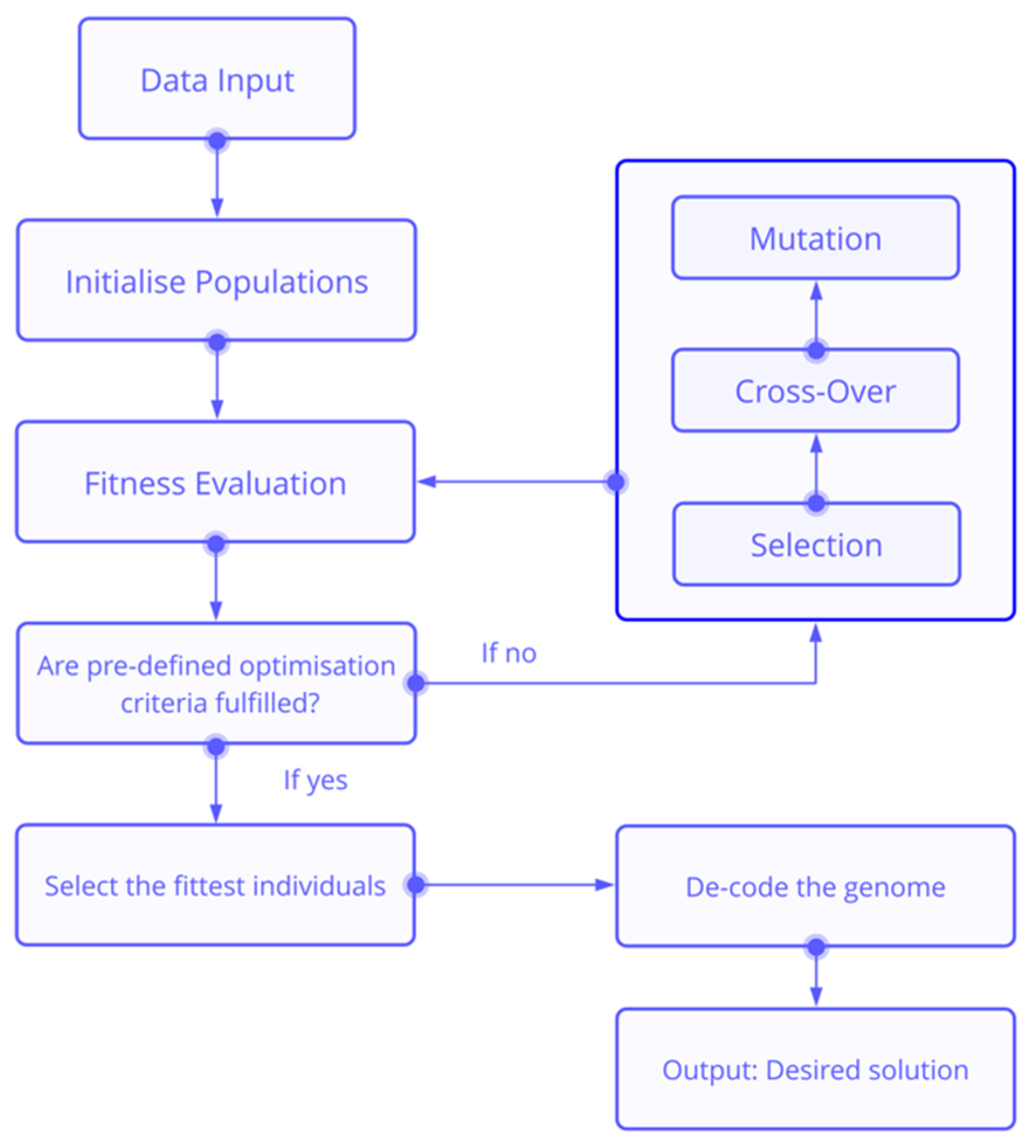
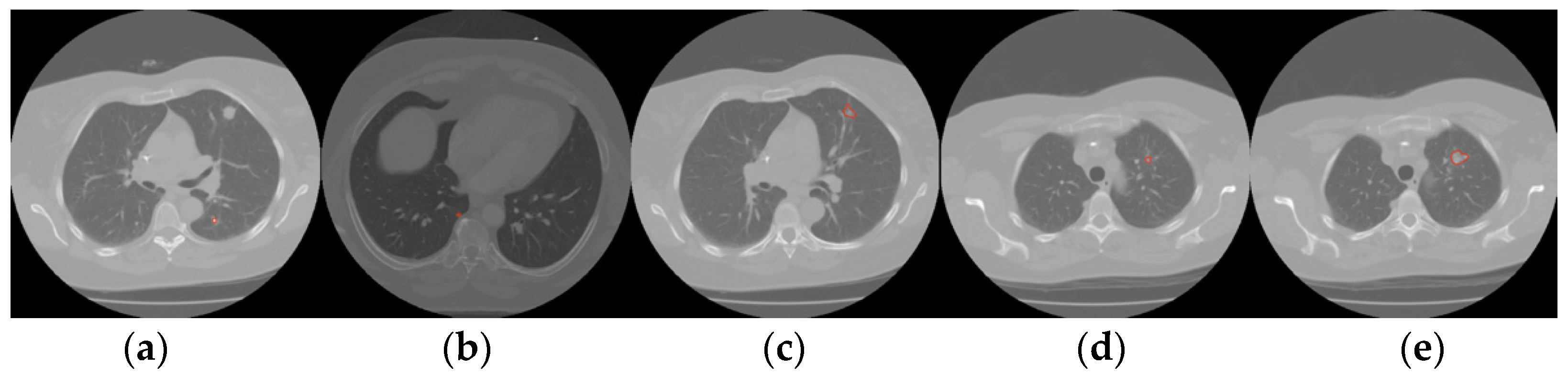
2. Materials and Methods
3. Experimental Setup
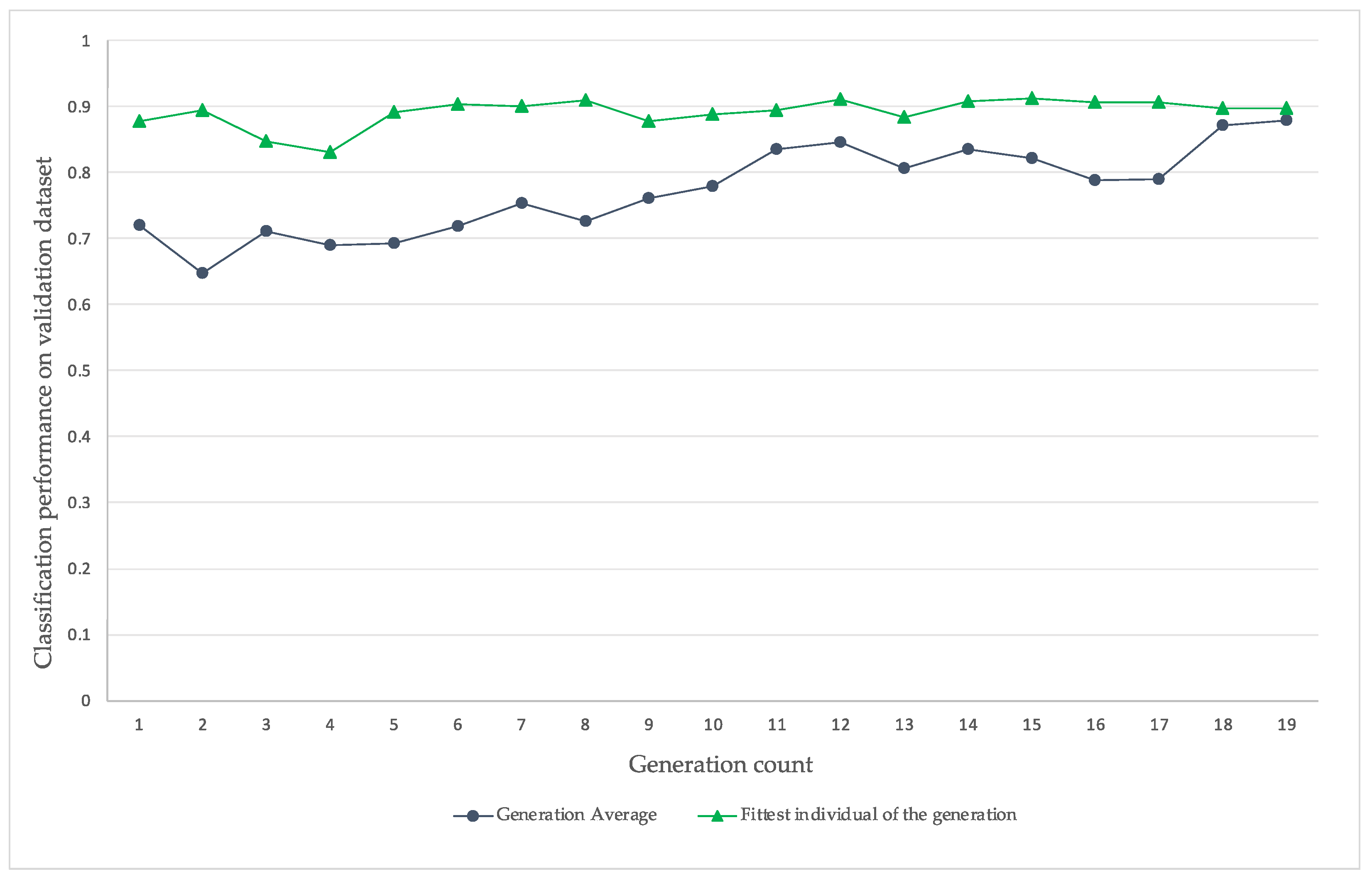
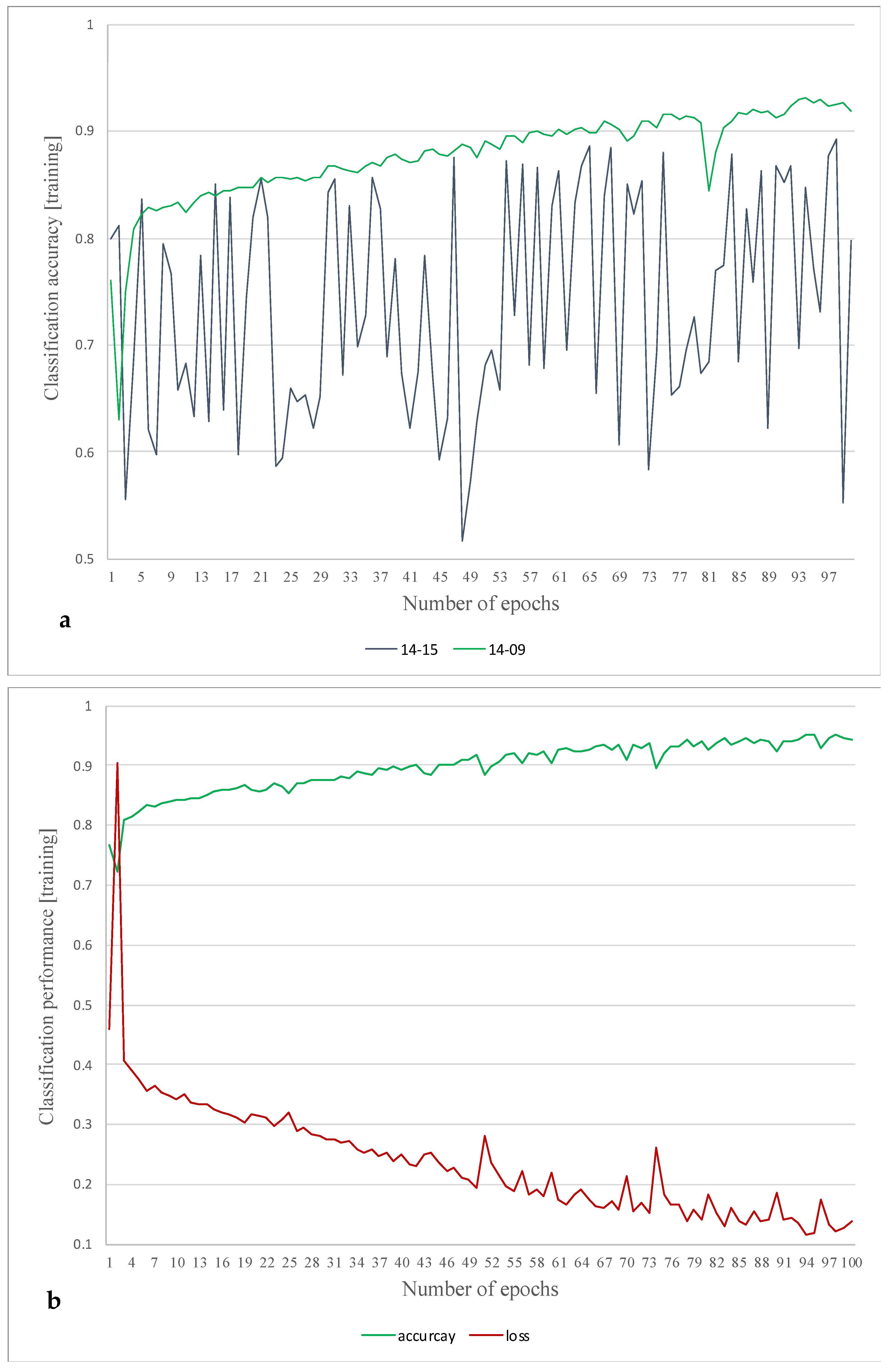
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment (PDQ)—Patient Version. 2016. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20160229172247/http://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/patient/non-small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Pasławski, M.; Krzyzanowski, K.; Złomaniec, J.; Gwizdak, J. Morphological characteristics of malignant solitary pulmonary nodules. Ann. Univ. Mariae Curie-Skłodowska Sect. D Med. 2004, 59, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.W.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3303.0—Causes of Death, Australia, 2015. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/Lookup/bySubject/3303.0~2015~MainFeatures~Lungcancer~10004 (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.B.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD. Health at a Glance: Europe 2020, 19 November 2020. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/health-at-a-glance-europe-2020_82129230-en (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Lu, T.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Yin, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q. Trends in the incidence, treatment, and survival of patients with lung cancer in the last four decades. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merck, Lung Carcinoma: Tumors of the Lungs/Merck Manual Professional. 2007. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20070816142739/http://www.merck.com/mmpe/sec05/ch062/ch062b.html#sec05-ch062-ch062b-1405 (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Collins, L.G.; Haines, C.; Perkel, R.; Enck, R.E. Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician. 2007, 75, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Einav, L.; Finkelstein, A.; Mahoney, N. Provider Incentives and Healthcare Costs: Evidence From Long-Term Care Hospitals. Econometrica 2018, 86, 2161–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messay, T.; Hardie, R.C.; Rogers, S.K. A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med. Image Anal. 2010, 14, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singadkar, G.; Mahajan, A.; Thakur, M.; Talbar, S. Deep Deconvolutional Residual Network Based Automatic Lung Nodule Segmentation. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Yen, G.G. Automatically Designing CNN Architectures Using Genetic Algorithm for Image Classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.03818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassanelli, S.; Mahmud, M. Trends and challenges in neuroengineering: Toward ‘intelligent’ neuroprostheses through brain-“brain inspired systems” communication. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesapane, F.; Codari, M.; Sardanelli, F. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: Threat or opportunity? Radiologists again at the forefront of innovation in medicine. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahiner, B.; Pezeshk, A.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Wang, X.; Drukker, K.; Cha, K.H.; Summers, R.M.; Giger, M.L. Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e1–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) on Machine Learning and Computational Neuroscience, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Pan, S.; Schuller, B. Classification of Lung Nodules Based on Deep Residual Networks and Migration Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 8975078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, A.; Edla, D.R.; Kuppili, V. Lung Nodule Classification on Computed Tomography Images Using Fractalnet. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 119, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Application of Modified Inception-ResNet and CondenseNet in Lung Nodule Classification. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Engineering, Information Science & Application Technology, Chongqing, China, 30–31 May 2019; pp. 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Lan, B.L.; Chan, W.Y.; Ng, K.H.; Tan, M. Lung nodule classification using deep local-global networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, G.; Maire, M.; Shakhnarovich, G. FractalNet: Ultra-deep neural networks without residuals. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Goodfellow, I.; Metaxas, D.; Odena, A. Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks. PMLR 2019, 97, 7354–7363. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.R.; Rose, D.C.; Karnowski, T.P.; Lim, S.H.; Patton, R.M. Optimizing deep learning hyper-parameters through an evolutionary algorithm. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Machine Learning in High-Performance Computing Environments, Austin, TX, USA, 15 November 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuel, T.M. The Effects of Hyperparameters on SGD Training of Neural Networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.02788. [Google Scholar]
- Turing, A.M.I. Computing Machinery and Intelligence; Oxford University Press on behalf of Mind: London, UK, 1950; Volume LIX, pp. 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, M.; Patnaik, L.M. Adaptive Probabilities of Crossover Genetic in Mu tation and Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syste. Man Cybern. 1994, 24, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Yen, G.G.; Yi, Z. IGD Indicator-Based Evolutionary Algorithm for Many-Objective Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, W. Number—The Language of Science. By Tobias Dantzig. London: George Allen & Unwin, Ltd., 1930. Large crown 8vo. Pp. 260. Price 10 s. J. Ment. Sci. 1931, 77, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuri, S.; Bäck, T.; Heitkotter, J. The zero/one multiple knapsack problem and genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–8 March 1994; Volume F129433, pp. 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristakeva, M.; Shrestha, D. Solving the 0-1 Knapsack Problem with Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advanced Communication, Control and Computing Technologies (ICACCCT), Ramanathapuram, India, 8–10 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sivanandam, S.N.; Deepa, S.N. Genetic Algorithms. In Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Eiben, A.E.; Raué, P.E.; Ruttkay, Z. Genetic algorithms with multi-parent recombination. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 866, pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S. Genetic algorithms: Principles of natural selection applied to computation. Science 1993, 261, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and operating a public information repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, B.L.; Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms, Tournament Selection, and the Effects of Noise. Complex Syst. 1995, 9, 193–212. Available online: https://content.wolfram.com/uploads/sites/13/2018/02/09-3-2.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, W.; Guo, J. Elitism and distance strategy for selection of evolutionary algorithms. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 44531–44541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Fernando, C.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Hierarchical representations for efficient architecture search. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00436. [Google Scholar]
- Real, E.; Moore, S.; Selle, A.; Saxena, S.; Suematsu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Le, Q.V.; Kurakin, A. Large-Scale Evolution of Image Classifiers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Imaging Archive. LIDC-IDRI—The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) Public Access—Cancer Imaging Archive Wiki. 2021. Available online: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/LIDC-IDRI (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Diethelm, K. The limits of reproducibility in numerical simulation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2012, 14, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Nature Publishing Group. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vis, C.; Bührmann, L.; Riper, H.; Ossebaard, H.C. Health technology assessment frameworks for eHealth: A systematic review. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2020, 36, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salathé, M.; Wiegand, T.; Wenzel, M. Focus Group on Artificial Intelligence for Health; Fraunhofer-Institut für Nachrichtentechnik, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327643779_Focus_Group_on_Artificial_Intelligence_for_Health/fulltext/5b9b2d4d92851ca9ed064891/Focus-Group-on-Artificial-Intelligence-for-Health.pdf?origin=publication_detail (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Prosperi, M.; Min, J.S.; Bian, J.; Modave, F. Big data hurdles in precision medicine and precision public health. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Allan, S.; Coghlan, S.; Cooper, P. A governance model for the application of AI in health care. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2000, 27, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.J.E.; Eldabi, T.; Monks, T.; Rabe, M.; Uhrmacher, A.M. Crisis, what crisis—Does reproducibility in modeling & simulation really matter? In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, National Harbor, MD, USA, 8–11 December 2019; pp. 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Method | Training Time [h] | Classification Accuracy [%] |
|---|---|---|
| FractalNet | 1 | 82.0 |
| Local-Global-Master | 1 | 89.0 |
| CNN-GA | 79 | 91.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfeffer, M.A.; Ling, S.H. Evolving Optimised Convolutional Neural Networks for Lung Cancer Classification. Signals 2022, 3, 284-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3020018
Pfeffer MA, Ling SH. Evolving Optimised Convolutional Neural Networks for Lung Cancer Classification. Signals. 2022; 3(2):284-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3020018
Chicago/Turabian StylePfeffer, Maximilian Achim, and Sai Ho Ling. 2022. "Evolving Optimised Convolutional Neural Networks for Lung Cancer Classification" Signals 3, no. 2: 284-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3020018
APA StylePfeffer, M. A., & Ling, S. H. (2022). Evolving Optimised Convolutional Neural Networks for Lung Cancer Classification. Signals, 3(2), 284-295. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3020018







