Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Fed by Voltage Source Inverter: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis on Acoustic Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
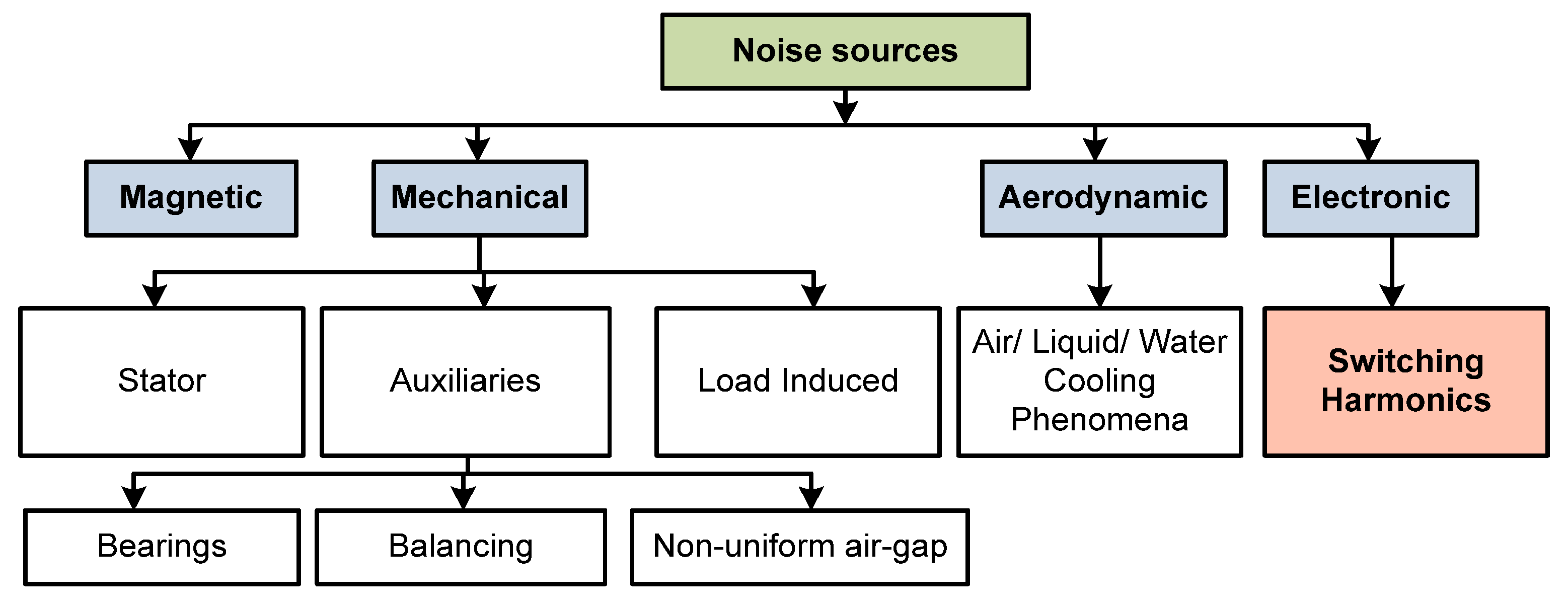
2. Acoustic Noise in Three-Phase Inverter IM Association
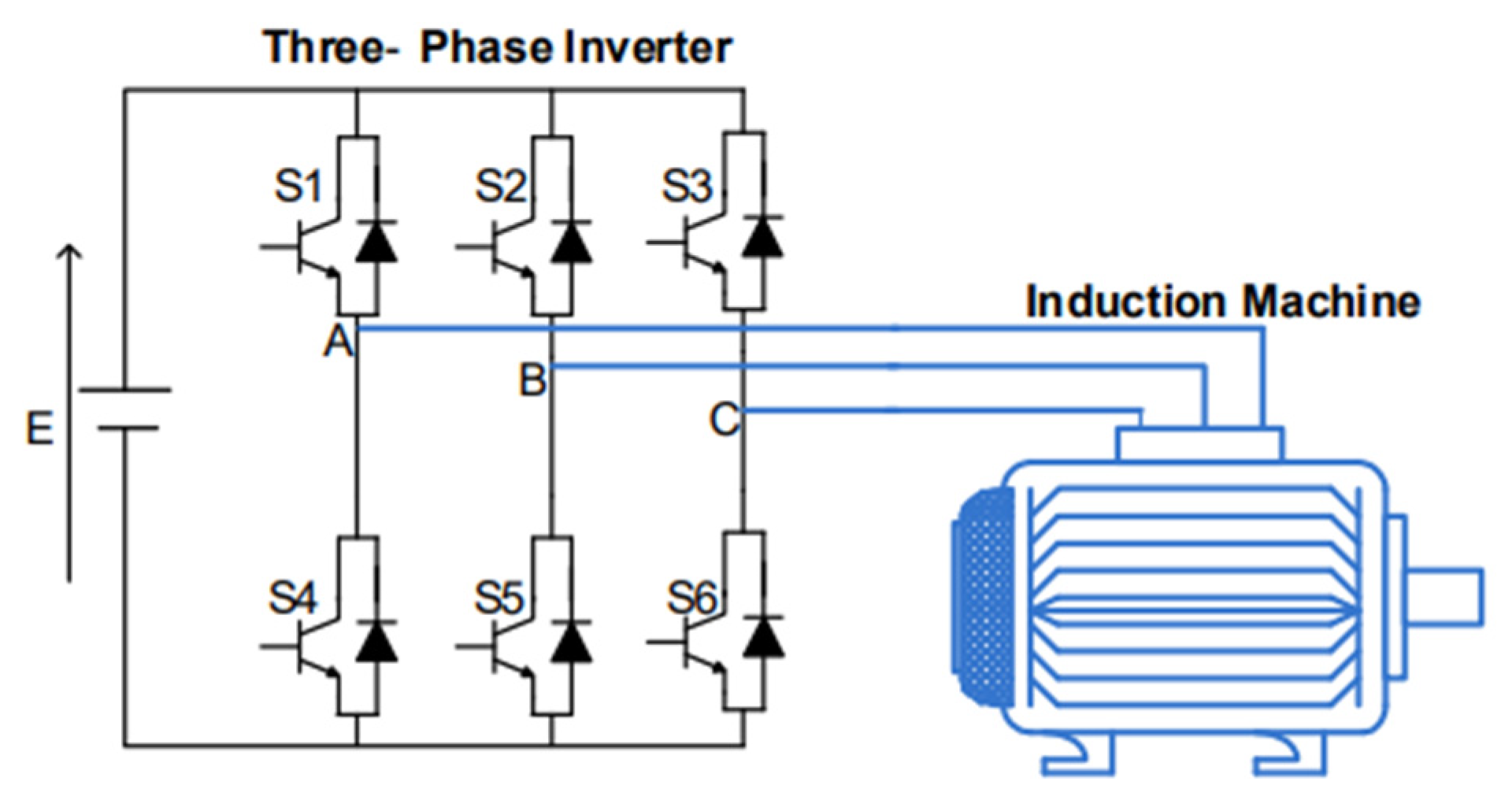
3. Proposed Controls
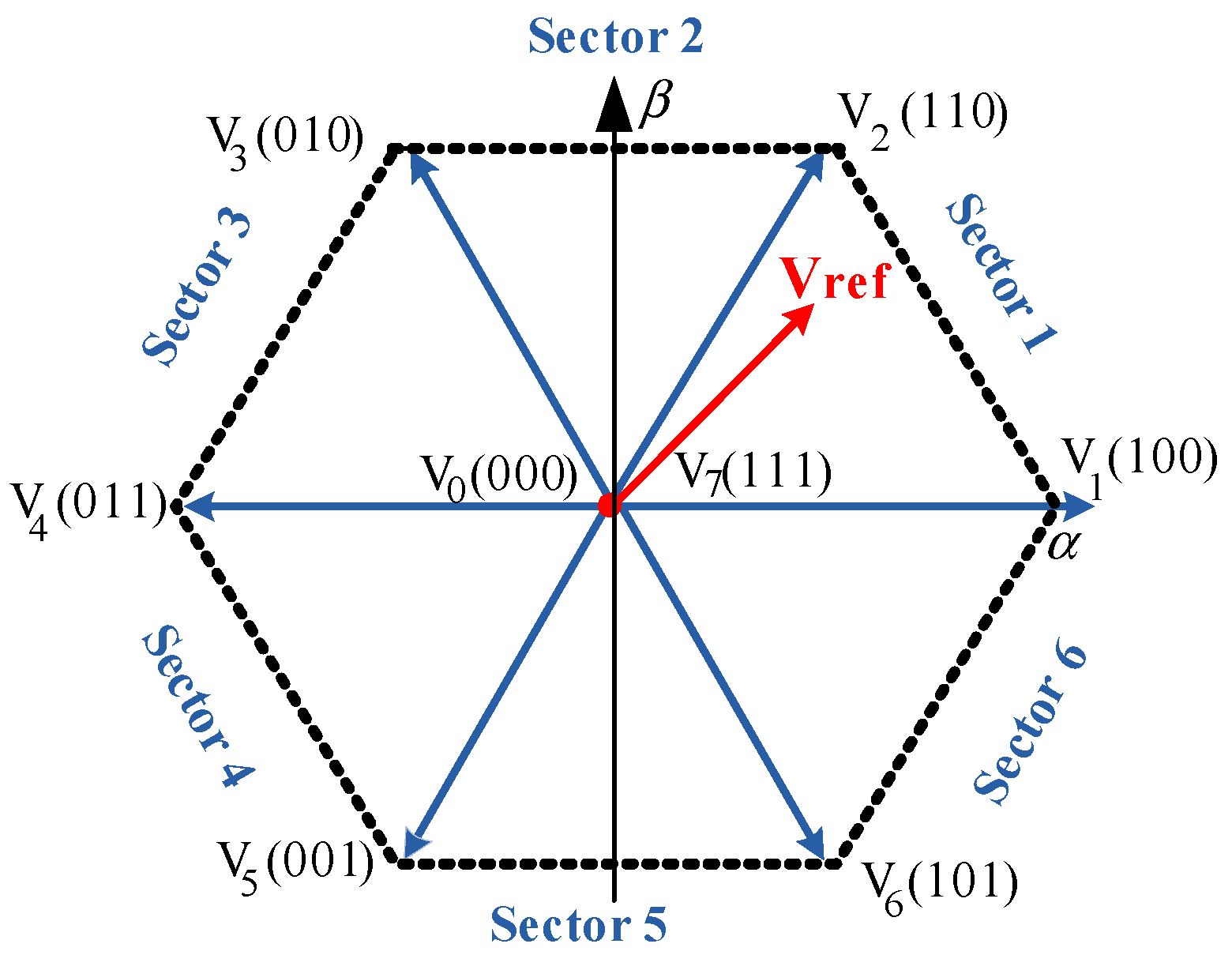
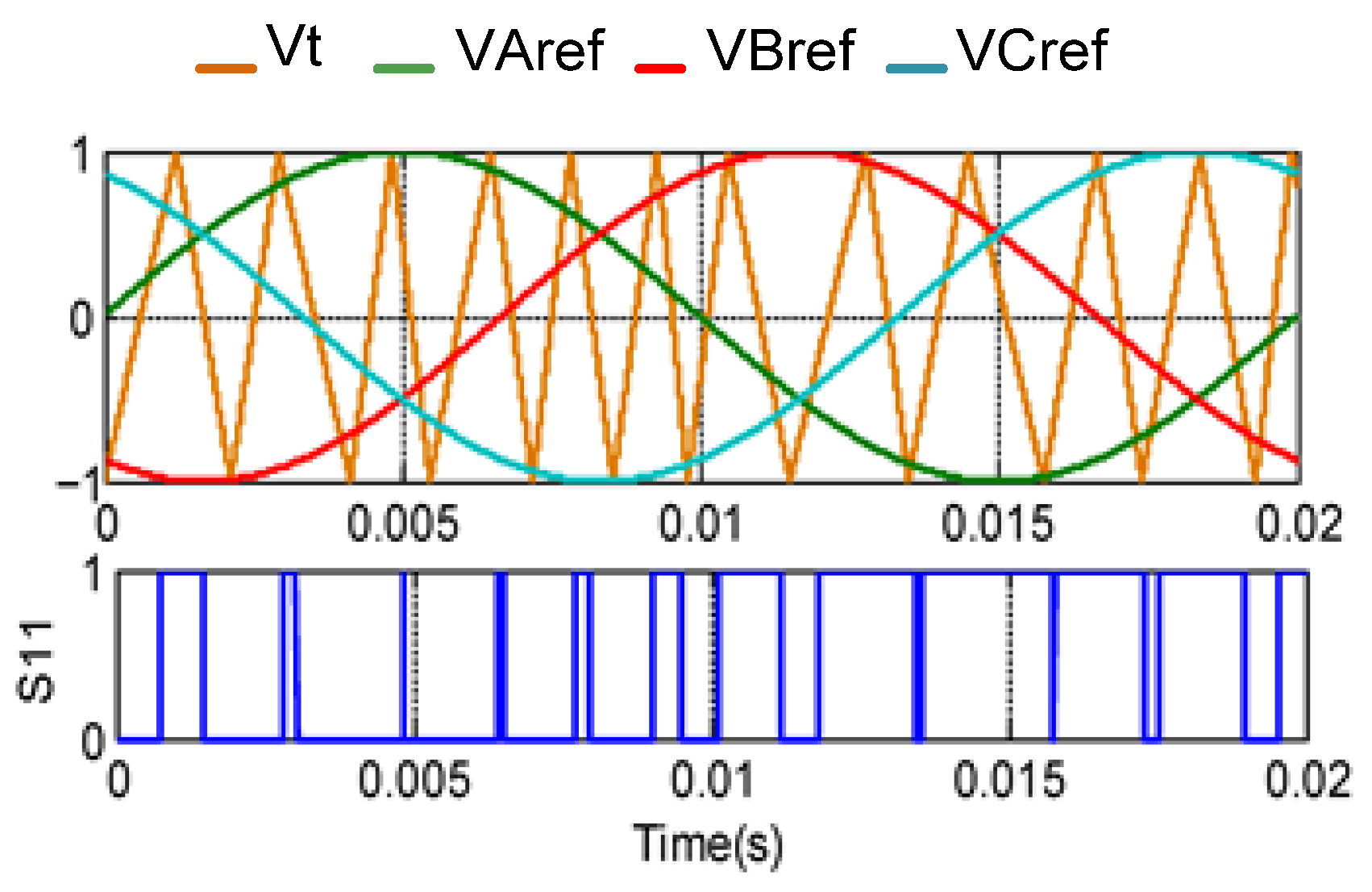
3.1. PWM Techniques
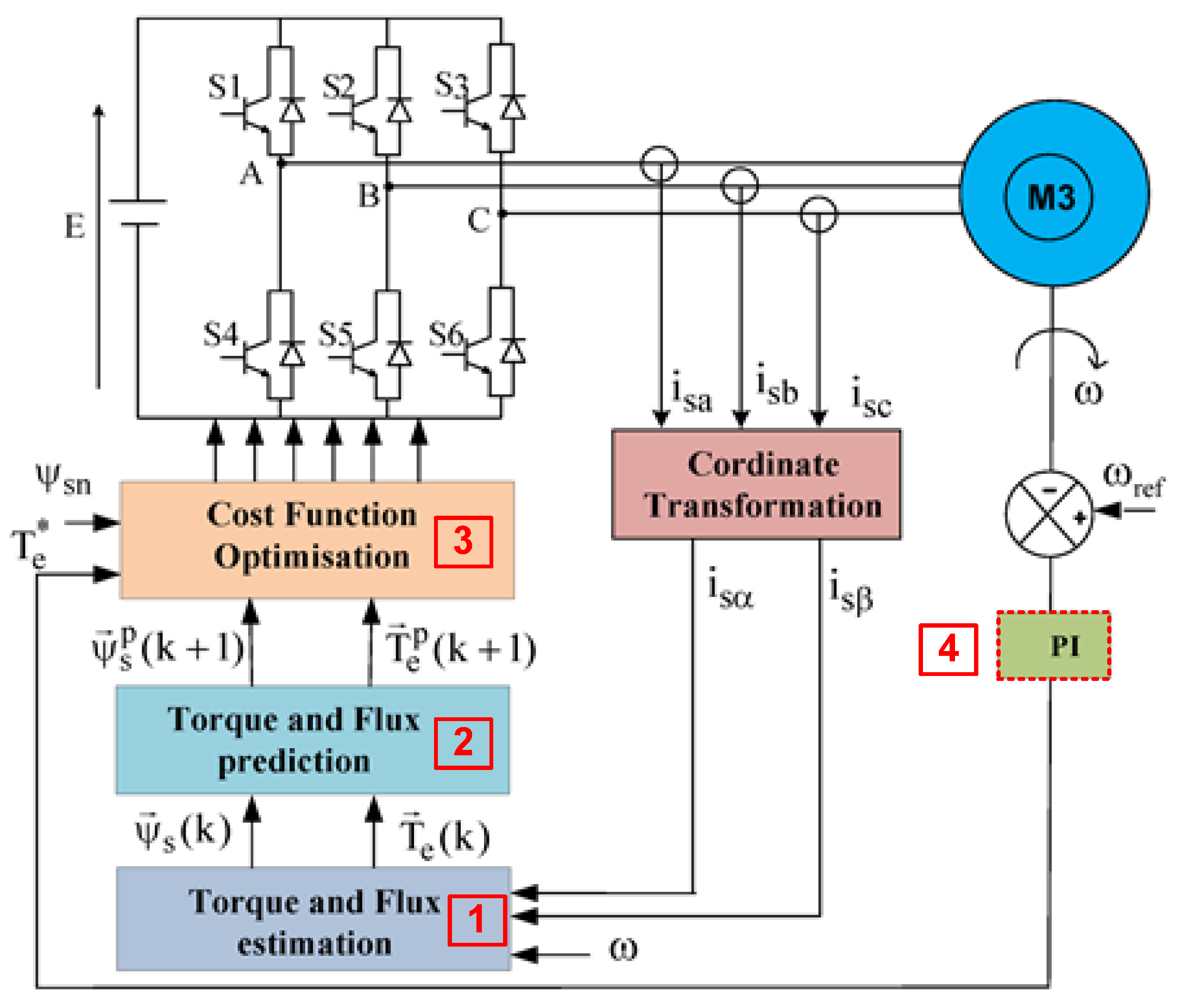
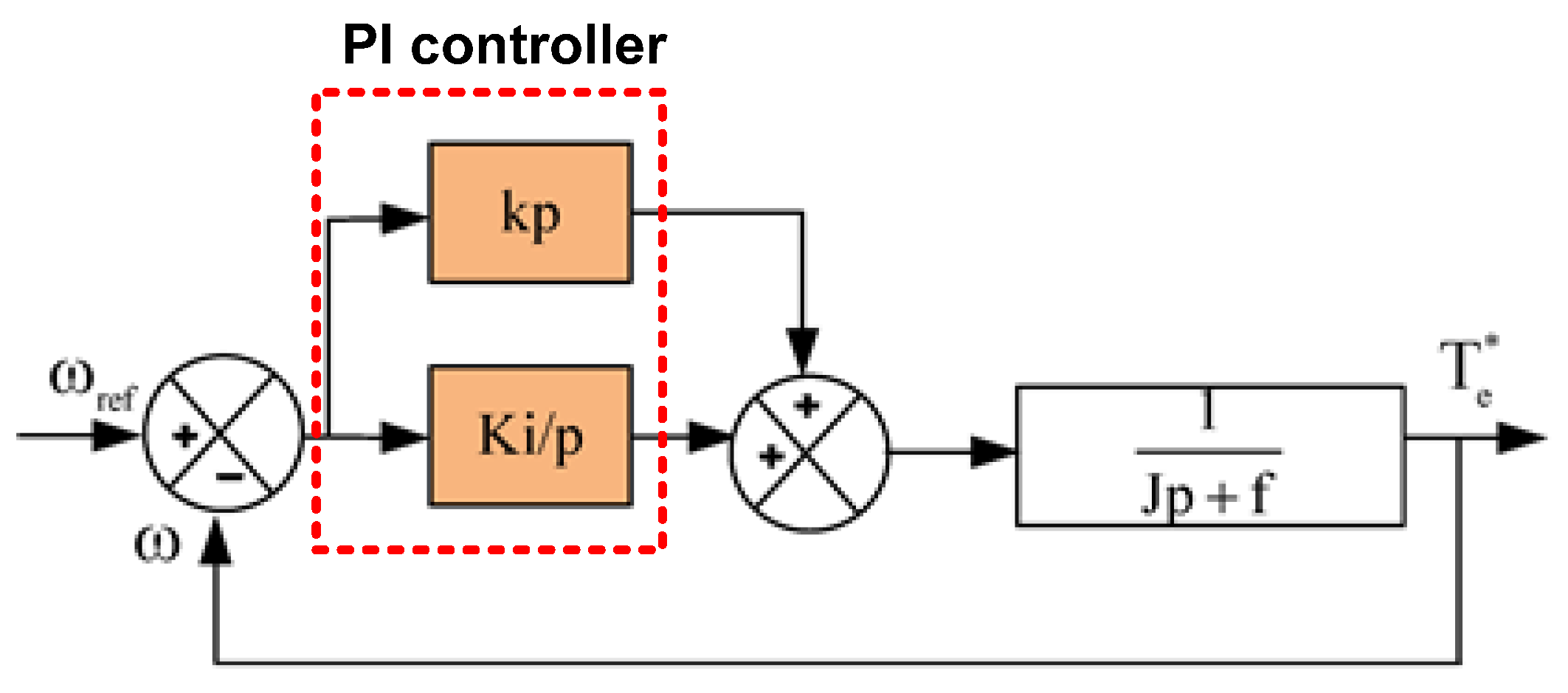
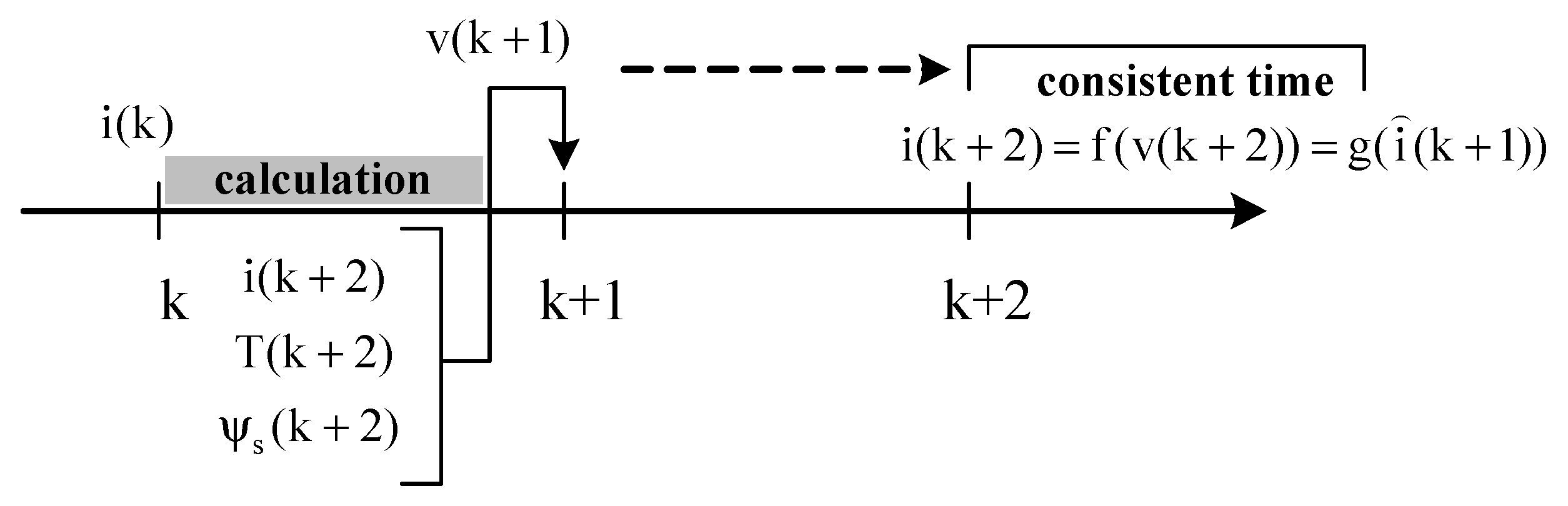
3.2. Predictive Torque Control of Induction Motor Drive
- : rotor inductance;
- : stator inductance;
- : mutual inductance;
- : stator resistance;
- : rotor resistance;
- : rotor flux vector;
- : stator current vector;
- : rotor speed;
- : stator flux vector;
- : total dispersion factor.
- : transient stator time constant ;
- : leakage inductance ;
- : equivalent resistance referred to stator ;
- : real rotor time constant .
- : rated torque;
- : rated stator flux amplitude;
- : reference rated torque;
- : reference rated flux;
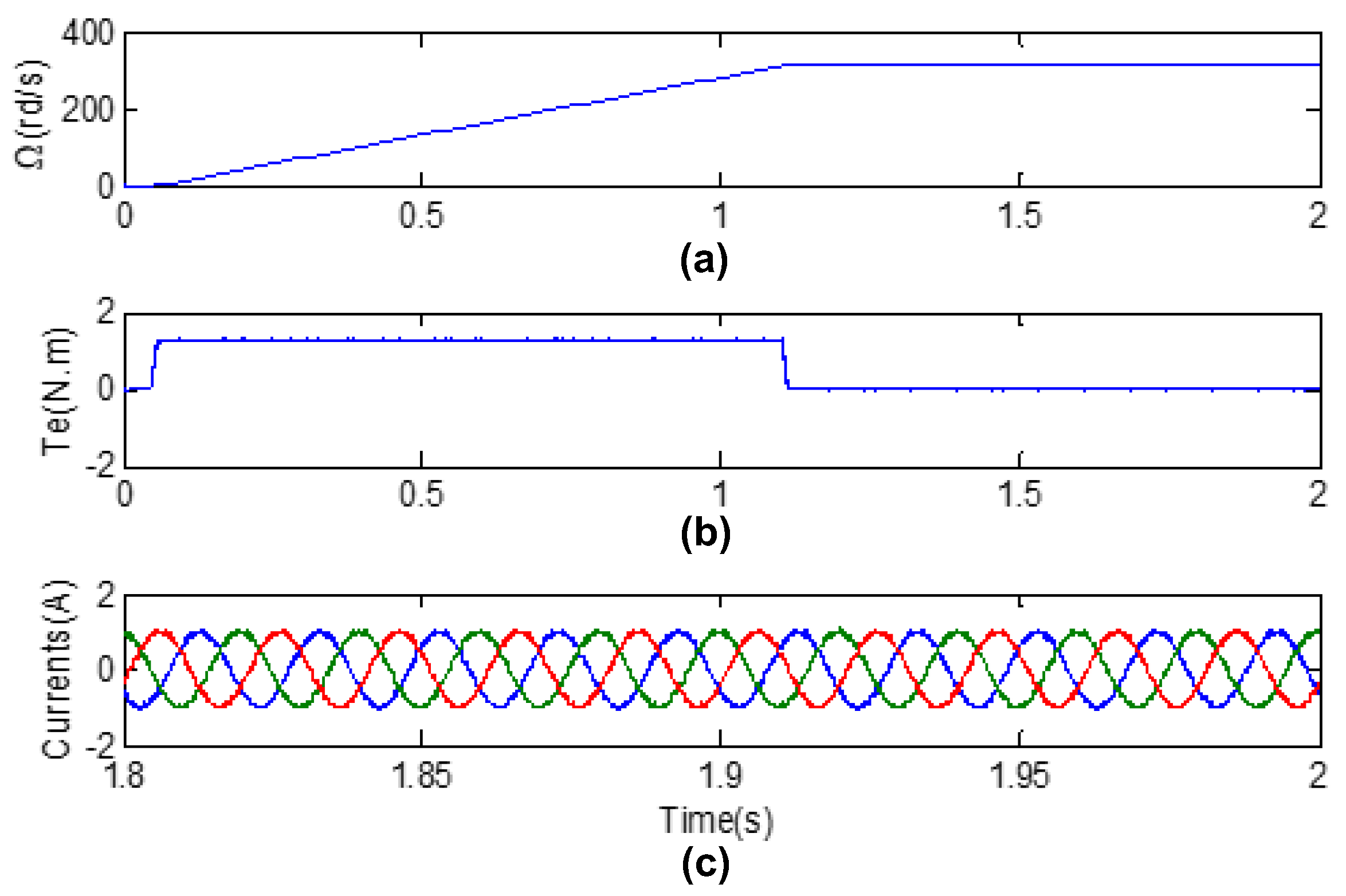
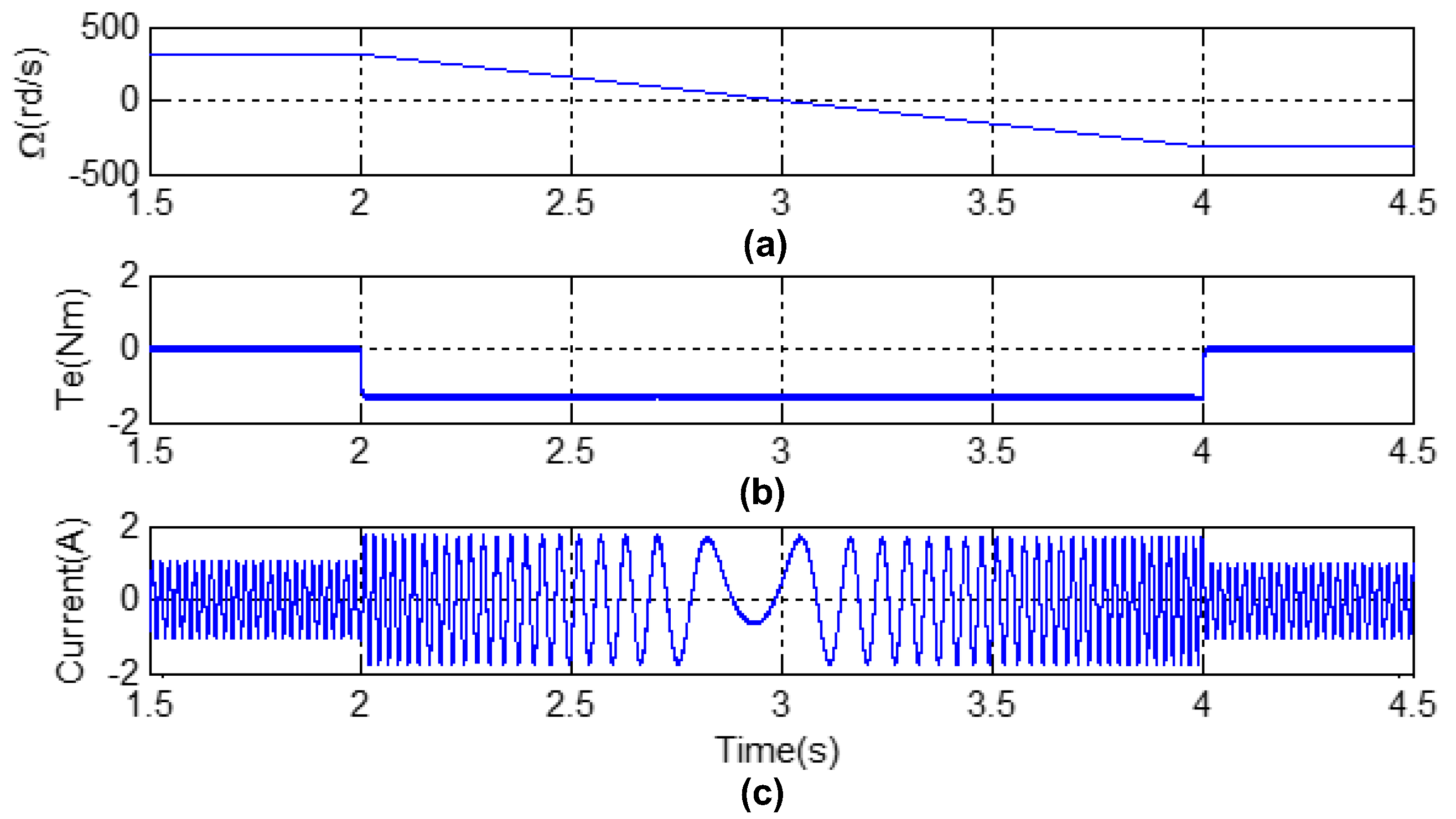
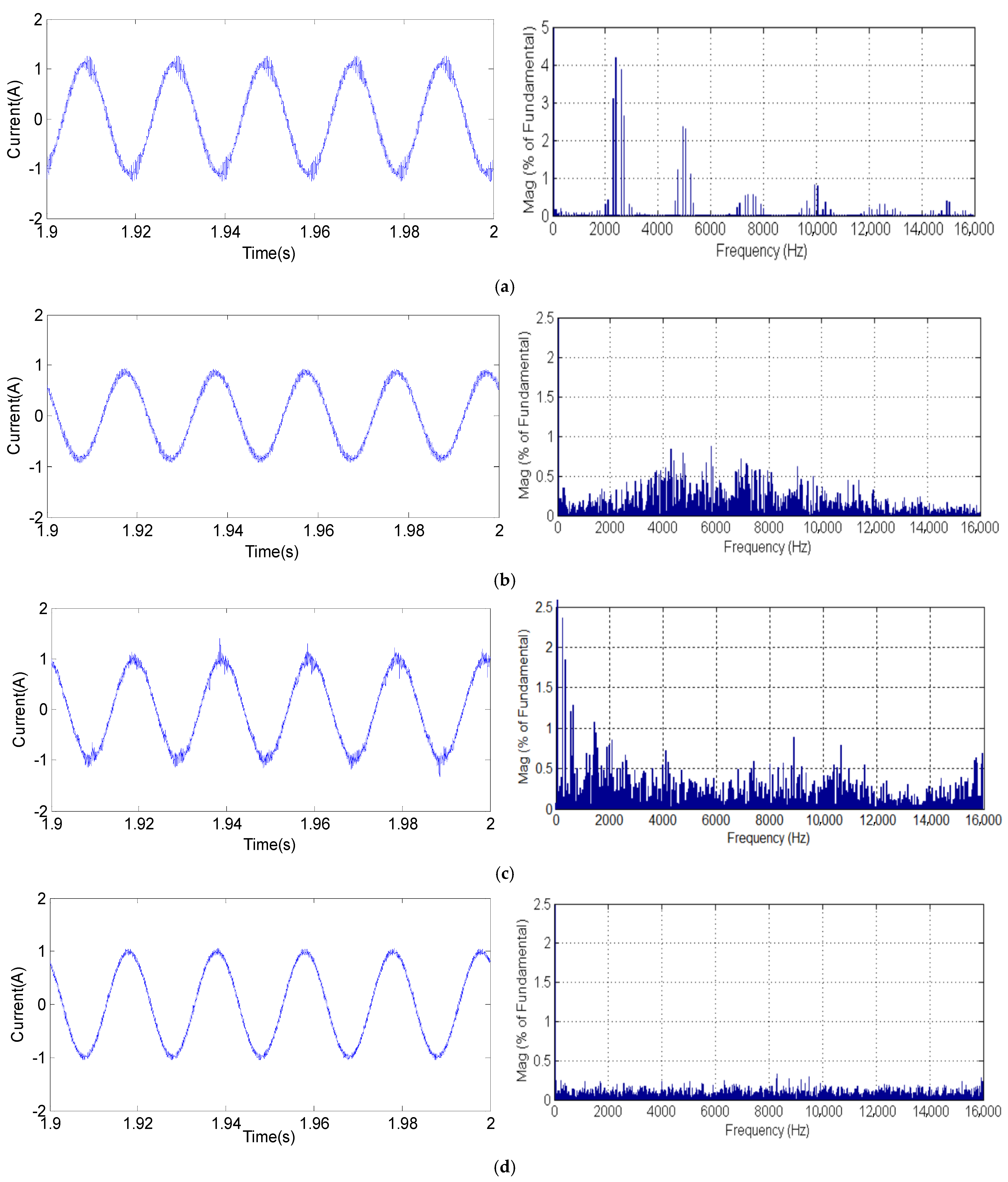
4. Simulation Results
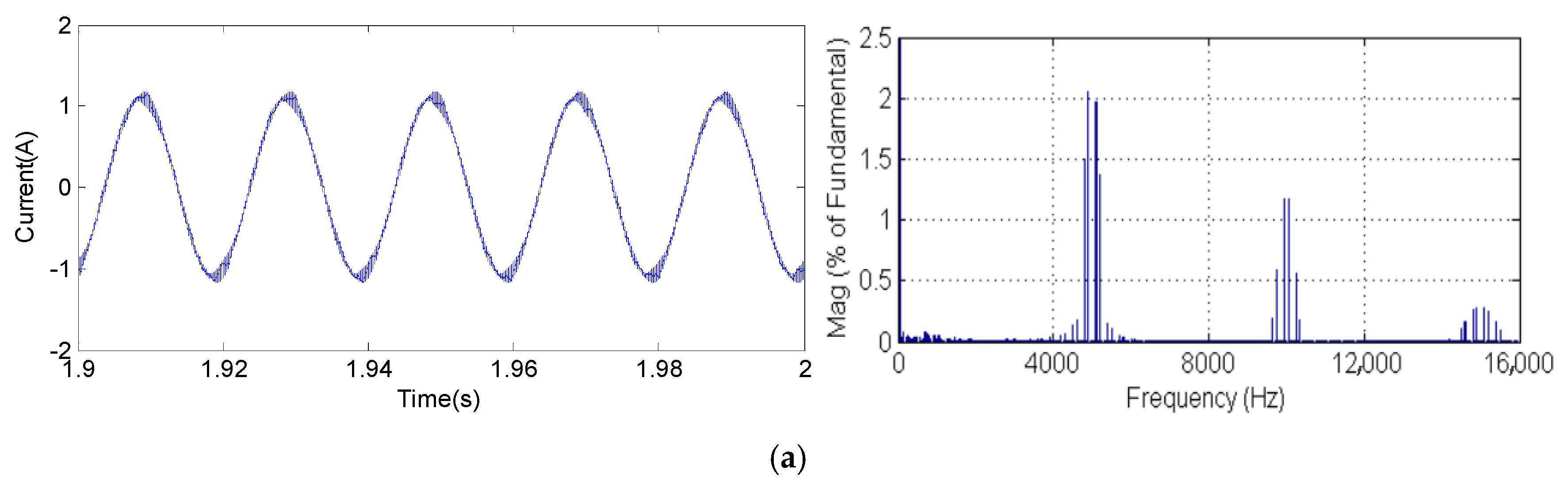
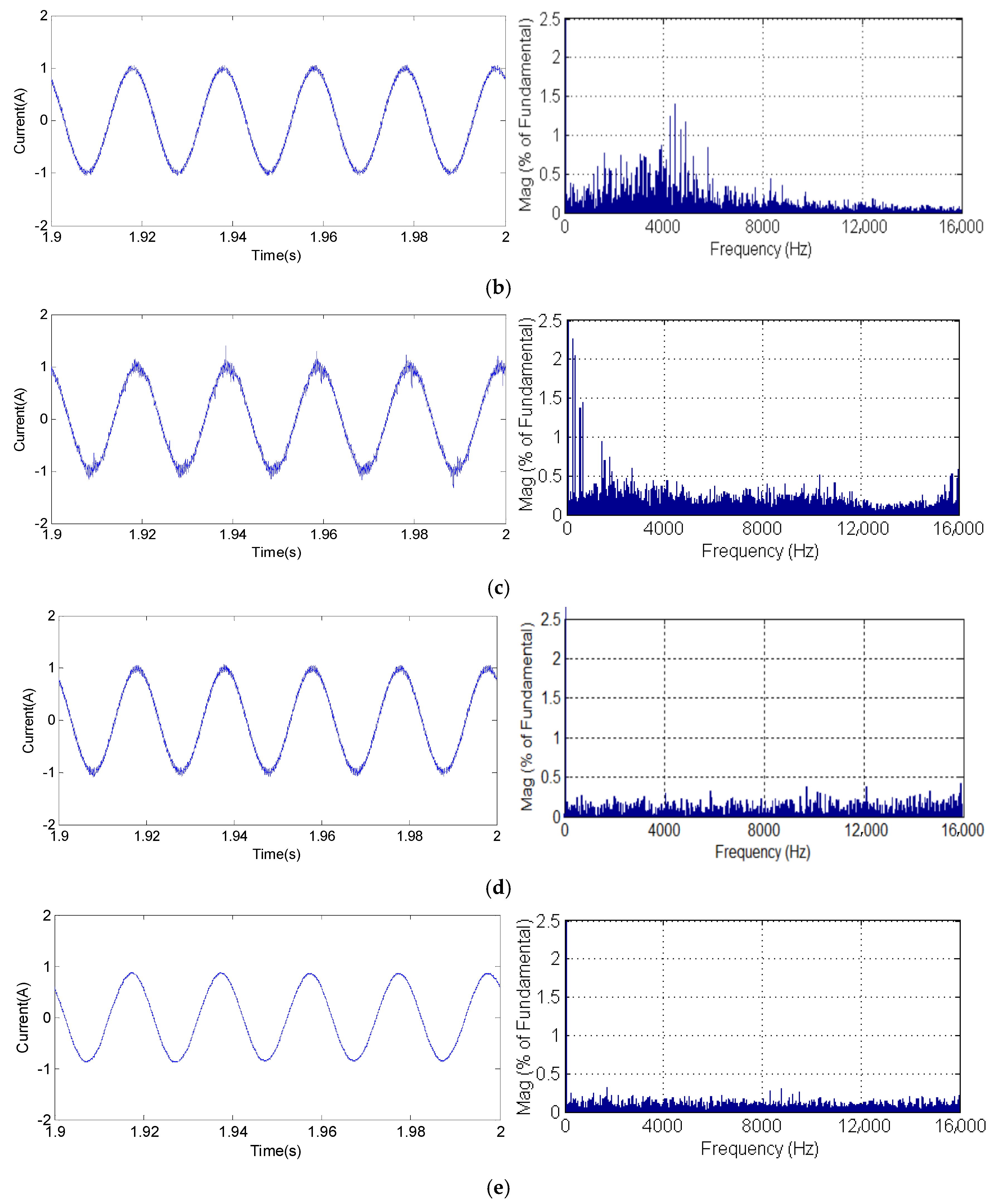
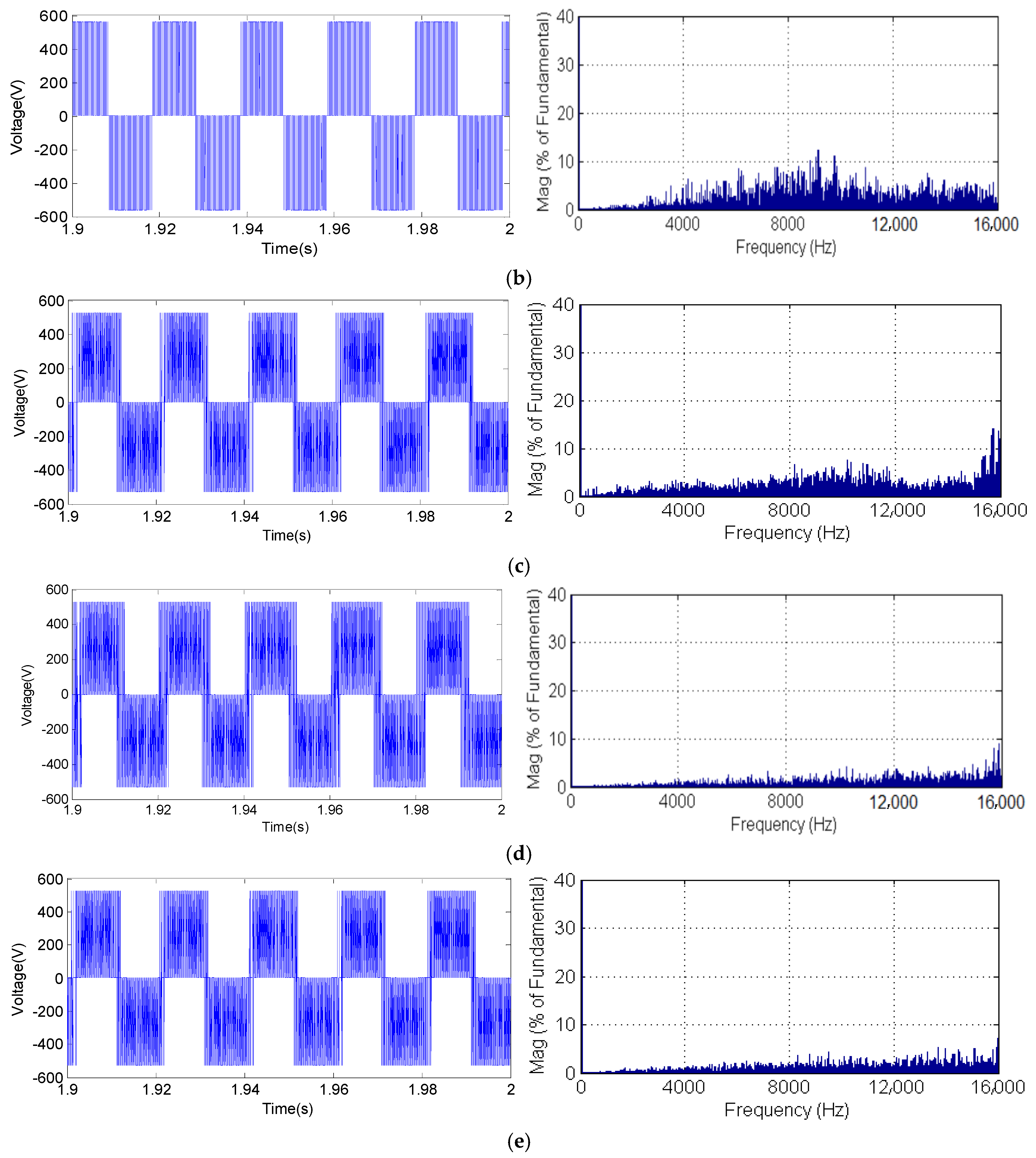
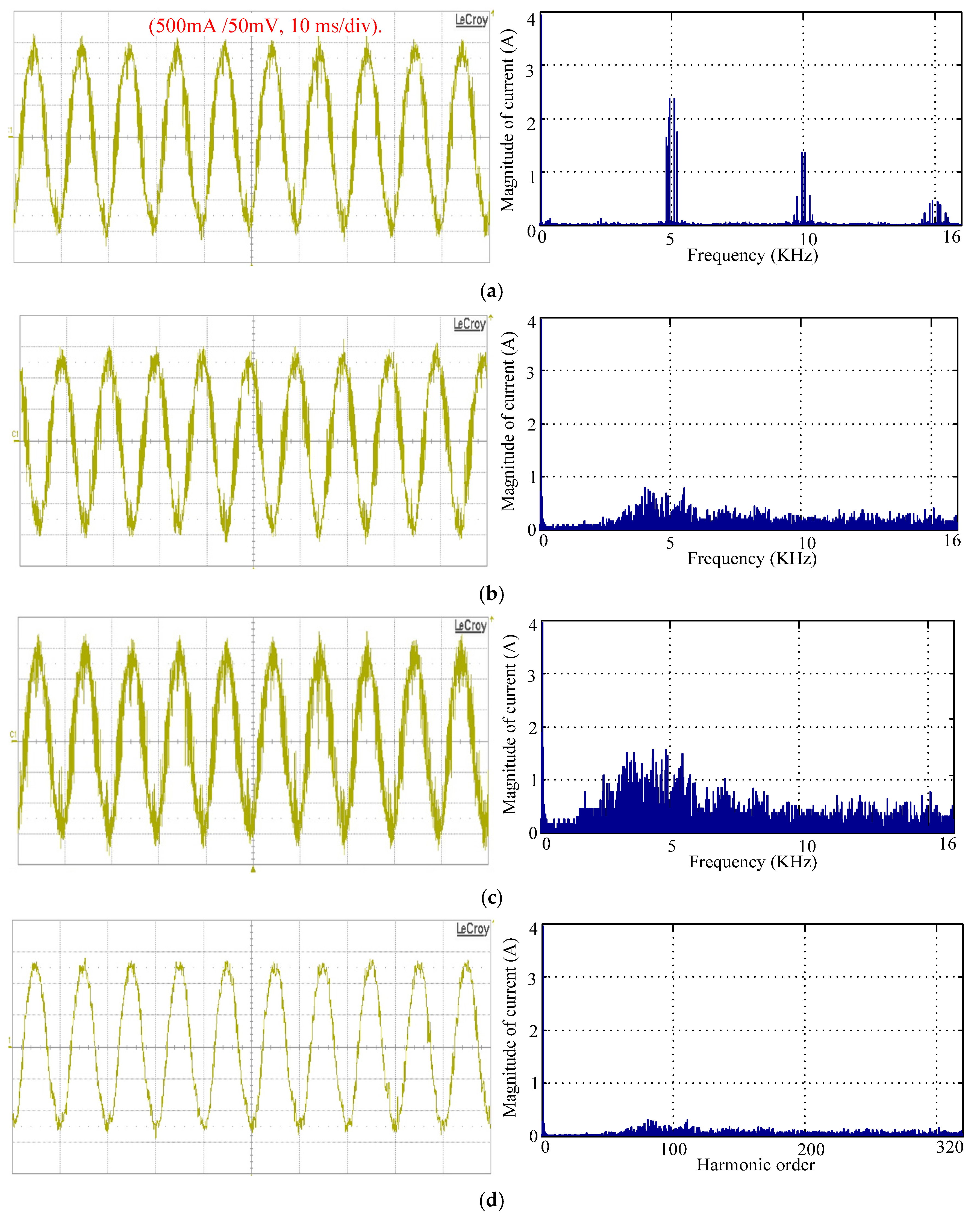
5. Experimental Results
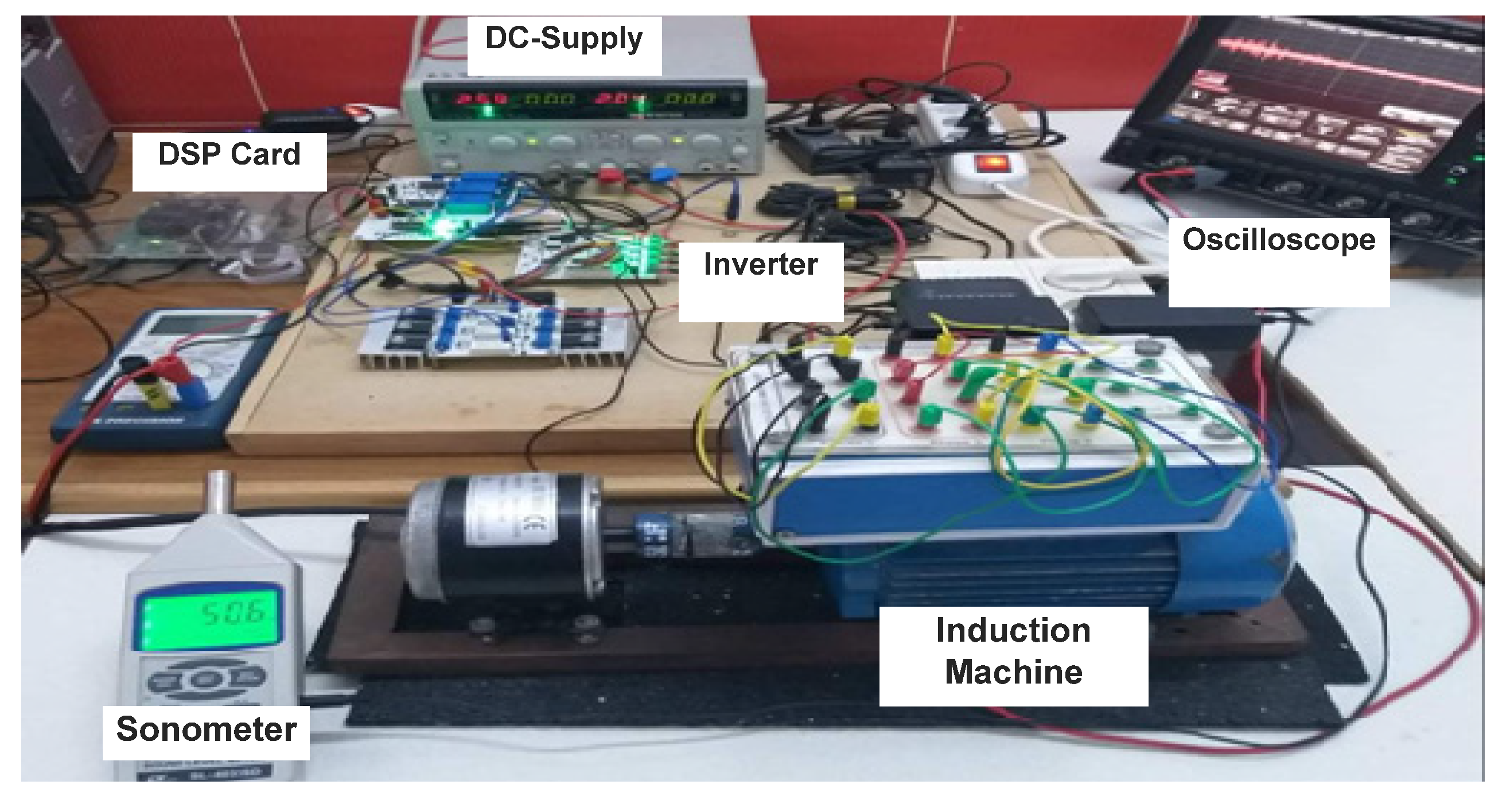
5.1. Setup Description
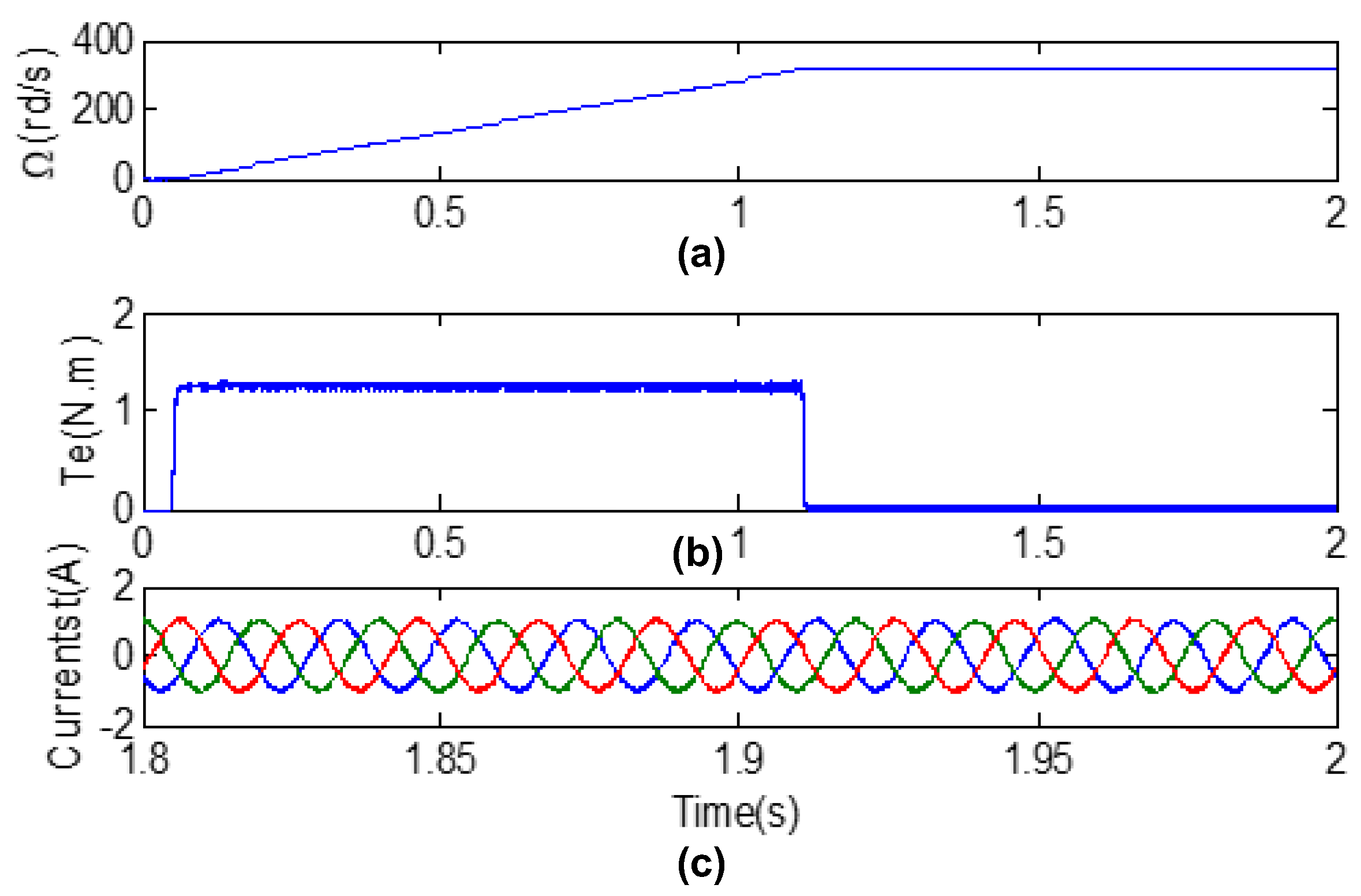
5.2. Obtained Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Lr | Rotor inductance |
| Ls | Stator inductance |
| Lm | Mutual inductance |
| Rs | Stator resistance |
| Rr | Rotor resistance |
| Kr | Real rotor time constant Kr=Lm/Lr |
| Equivalent resistance referred to stator | |
| Total dispersion factor | |
| Transient stator time constant | |
| Tr | Rotor time constant Tr=Lr/Rr |
| Rotor speed | |
| Stator current vector | |
| Rotor current vector | |
| Predicted stator current at time (k + 1) | |
| k | Sampling time |
| Stator voltage vector | |
| Stator flux vector | |
| Rotor flux vector | |
| Rated stator flux amplitude | |
| Predicted stator flux at time (k + 1) | |
| Te | Electromagnetic torque |
| Reference electromagnetic torque | |
| Tn | Rated torque |
| Predicted electromagnetic torque at time (k + 1) | |
| Weighting factor | |
| p(t) | Instantaneous sound pressure |
| Reference sound pressure |
References
- Gieras, J.F.; Wang, C.; Lai, J.C. Noise of Polyphase Electric Motors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan, P.; Krishnan, R. Noise in electric machines: A review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1999, 35, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patxi, G.; Garikoitz, B.; Angel, M. Noise in Electric Motors: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Y.; Zou, J. PWM harmonics reduction for dual-branch three-phase PMSMs using interleaving topology. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.B.; Narayanan, G. Variable-switching frequency PWM technique for induction motor drive to spread acoustic noise spectrum with reduced current ripple. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3927–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Guijie, Y.; Jibin, Z. PWM frequency voltage noise cancelation in three-phase VSI using the novel SVPWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 8596–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luznar, J.; Slavič, J.; Baltežar, M. Experimental research on structure-borne noise at pulse-width-modulation excitation. J. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 137, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, T. Sound quality of the acoustic noise radiated by PWM-fed electric powertrain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 4534–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumandla, S.; Upadhyay, P.; Jayalaxmi, A.; Jaya, P.N. Modulated frequency triangular carrier based space vector PWM technique for spreading induction motor acoustic noise spectrum. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering, Cham, Switzerland, 4–6 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyahi, H.; Smida, K.B.; Khedher, A. Experimental study of PWM strategy effect on acoustic noise generated by inverter-fed induction machine. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. Hybrid periodic carrier frequency modulation technique based on modified SVPWM to reduce the PWM noise. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sio-Iong, A. Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computational Science; Gelmen, L., Ed.; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 39. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.; Shi, K. Applied Intelligent Control of Induction Motor Drives; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoumas, P.; Tischmacher, H. Influence of the inverter’s modulation technique on the audible noise of electric motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, T. Sound quality investigation and improvement of an electric powertrain for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binojkumar, C.; Saritha, B.; Narayanan, G. Acoustic noise characterization of space-vector modulated induction motor drives—An experiment al approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3362–3371. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyahi, H.; Khedher, A. Acoustic Noise of Induction Motor Drive with Voltage-Source Inverter by Random Space Vector PWM: Simulation and Experimentation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wentao, Z.; Zou, J. Hybrid RPWM technique based on modified SVPWM to reduce the PWM acoustic noise. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J. PWM frequency noise cancellation in two-segment three-phase motor using parallel interleaved inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneisl, M.; Šmídl, V.; Peroutka, Z.; Janda, M. Predictive control of IM drive acoustic noise. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5666–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouda, A.; Boudjerda, N.; Aibeche, A. dSPACE-based dual randomized pulse width modulation for acoustic noise mitigation in induction motor. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Pontt, J.; Silva, C.A.; Correa, P.; Lezana, P.; Cortes, P.; Ammann, U. Predictive current control of a voltage source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.; Pacas, M.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive torque control for inverter-fed induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Rivera, M.; Franquelo, L.G. Model predictive control for power converters and drives: Advances and trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Le, S.; Wu, X.; Ruan, Y. An improved model predictive direct torque control for induction machine drives. J. Power Electron. 2017, 17, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comarella, B.V.; Carletti, D.; Yahyaoui, I.; Encarnação, L.F. Theoretical and Experimental Comparative Analysis of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control Strategies. Electronics 2023, 12, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, M.; Lu, D.-C.; Xiao, D.; Rahman, M.F. A simplified finite-state predictive direct torque control for induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3964–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, M. A finite control set model predictive control scheme for single-phase grid-connected inverters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Monrroy, C.A. Multiobjective Finite Control Set Model Predictive Torque and Stator Flux Control of an Induction Machine. Ph.D. Thesis, Federico Santa María Technical University, Valparaíso, Chile, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qiu, L.; Rodriguez, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y. Data-driven finite control-set model predictive control for modular multilevel converter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 11, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Gong, C.; Yan, L.; Wen, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, K. Multiobjective finite control set model predictive control using novel delay compensation technique for PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 35, 11193–11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL-4033SD; Sound Level Meter Model: ISO-9001, CE, and IEC1010. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium; IEC: Worcester, MA, USA, 2013.
- IEEE 85-1973; IEEE Test Procedure for Airborne Sound Measurements on Rotating Electric Machinery. IEEE Power Engineering Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1980.
- Lisner, R.-P.; Timar, P.-L. A new approach to electric motor acoustic noise standards and test procedures. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power | 0.5 Kw |
| Motor speed | 3000 r/min |
| Stator resistance | 24 Ω |
| Stator inductance | 0.66 H |
| Rotor resistance | 10.88 Ω |
| Rotor inductance | 0.66 H |
| Mutual inductance | 0.63 H |
| Friction coefficient | 0.00159 |
| Inertia moment | 0.004 Kg.m2 |
| Pair pole number | 1 |
| SVPWM | RPWM | PTC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| THD current (%) | 4.52 | 3.31 | 1.94 |
| Acoustic noise (dBA) | −29.7 | −57.18 | −80.01 |
| Frequency | Fixed | Random | Fixed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henda, B.; Khedher, A. Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Fed by Voltage Source Inverter: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis on Acoustic Noise. Acoustics 2025, 7, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040063
Henda B, Khedher A. Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Fed by Voltage Source Inverter: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis on Acoustic Noise. Acoustics. 2025; 7(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenda, Bouyahi, and Adel Khedher. 2025. "Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Fed by Voltage Source Inverter: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis on Acoustic Noise" Acoustics 7, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040063
APA StyleHenda, B., & Khedher, A. (2025). Predictive Torque Control for Induction Machine Fed by Voltage Source Inverter: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis on Acoustic Noise. Acoustics, 7(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040063






