Abstract
A modified strain-hardening cementitious composite (SHCC) material, fabricated using corundum aggregates (SHCC-Cor), has been proposed for roadway applications as it offers high structural performance and high skid resistance. However, the acoustic performance of SHCC is unclear and has not been well studied in the past. Theoretically, SHCC may not provide the optimum solution in acoustic performance as it provides a low texture profile, high density, and low porosity. In this study, the acoustic performance of pavement slabs made of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor are investigated using a nondestructive method to determine the surface roughness (macro texture) of slab surfaces. The pavement–tire noise level was then simulated using SPERoN software. As result, the noise level coming from the pavement made of SHCC could be up to 65 dB(A), while the noise level for SHCC-Cor increased up to 69.2 dB(A) because of the lower shape factor (G) due to a rougher surface as a result of the existence of corundum aggregate on the SHCC surface. The aeroacoustics were also increased compared to the SHCC slab. The modification of SHCC-Cor by introducing grooves (SHCC-Cor-Gro) successfully reduced the sound level coming from the vibration.
Keywords:
pavement–tire noise; acoustic performance; SHCC; pavement; road; texture; shape factor; SPERON 1. Introduction
Strain-hardening cementitious composites (SHCCs) represent a unique class of higher-performance fiber-reinforced cementitious composite (HPFRCC) materials. SHCC can be characterized as a material with the ability to resist increased tensile force, showing extreme tensile ductility of several percent, while exhibiting multiple cracks and strain hardening beyond the point of first cracking [1,2,3]. These advantages of SHCC material offer high suitability for designing a resilient infrastructure. Due to its advantages, SHCC has been introduced in various infrastructure applications, including earth retaining walls [4], surface repairment of irrigation channels [5], expansion joints for bridges [6], coupling beams in high-rise buildings [7], and roadway applications [2,8]. A pavement made of SHCC can benefit from higher efficiency due to the lower pavement thickness, jointless nature, larger joint spacing, and less maintenance required [9]. Long-term monitoring has shown that SHCC material can handle high traffic loads [10].
Although SHCC has high potential for being used to design a resilient roadway infrastructure, potential shortcomings have been observed due to lacking texture. The conventional SHCC mixture design omits coarse aggregates and includes only micro-silica sand to reduce matrix toughness and increase ductility [11]. Therefore, using SHCC material for roadway applications can be a concern as low texture may lead to a hydroplaning effect and the risk of skidding accidents. Pavement design requires having good structural and functional performance [12].
On the other hand, noise pollution on roadways is a growing concern globally. High levels of exposure to road traffic noise are associated with adverse health effects, as concluded in a study by the World Health Organization [13]. A major contribution to roadway noise results from the pavement–tire interface. Authorities in the USA, including the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) and the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), have conducted research on quiet pavements to reduce traffic noise [14,15]. In Singapore, many residential areas have been developed close to expressways and major arterial roads with high traffic densities, producing high noise pollution. It was reported that local communities have made public complaints about noise pollution [16]. The local authority of Singapore implemented residential noise limits for different periods of the day, ranging from 65 dB during the day to 55 dB during the night [17]. According to the technical guidelines for land traffic noise impact assessment, the noise limit levels at any façade of a building should not exceed 67 dBA in the construction of new roads and expressways. Quieter pavements are considered one of the solutions by the Land Transport Authority (LTA) of Singapore [18]. Noise-reducing asphalt pavements based on stone mastic asphalt (SMA) have been used in Germany [19]. In Arizona, asphalt rubber friction course (ARFC) is used in many locations aimed at obtaining quieter pavements [20].
There are three main parameters to be considered for obtaining quieter pavements: texture, porosity, and stiffness. Firstly, the texture must remain small (less than 5 mm) and negative. Secondly, higher porosity (>20%) is preferred as it helps to absorb noise and reduce contact area; however, air voids might affect durability. Thus, the porosity must be carefully designed. Lastly, stiffer pavements tend to be quieter [21]. Nevertheless, the acoustic performance of SHCC is unclear and has not been well studied in the past, particularly for roadway applications. Hypothetically, SHCC may not provide the optimum solution in terms of acoustic performance as it provides a low texture profile, high density, and low porosity.
The objective of this study was to investigate the acoustic performance of SHCC material for resilient roadway infrastructure as a function of its pavement–tire mechanism. SHCC and modified Strain-hardening cementitious composites mixed with corundum aggregate (SHCC-Cor) incorporating hard aggregates (i.e., corundum) were developed, and their mechanical properties, including the microtexture, macrotexture, shape factor, and sound level from vibration and air, were studied. A noise reduction method is also proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mixture Design
A control SHCC mixture (SHCC) was prepared. The mixture design of SHCC consisted of type I Portland cement, class F fly ash (FA), micro-silica sand (mean and maximum grain size of 110 μm and 200 μm, respectively), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers (length of 12 mm, diameter of 39 μm, and nominal tensile strength of 1600 MPa), and a high-range water-reducing (HRWR) admixture.
A modified SHCC mixture design was developed using similar materials to the SHCC mixture design, except with micro-silica sand replaced with corundum at 80% dosage. All SHCC-Cor mixtures had a low water-to-cementitious material ratio (w/cm) of 0.27. The mixture design of SHCC-Cor consisted of type I Portland cement, class F fly ash (FA), micro-silica sand, PVA fibers, and a high-range water-reducing admixture. In the modified SHCC-Cor, corundum aggregates (SHCC-Cor) were introduced to fulfill the requirements of high structural performance and high skid resistance for roadway applications.
The objective of incorporating corundum as fine aggregates into the SHCC mixture is to improve the surface microtexture. To enhance the skid resistance, corundum with a maximum particle size of 2.38 mm was used as fine aggregates for improving the surface texture of SHCC. The mixture designs of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor are outlined in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mixture design of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor.
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Corundum is extremely hard (rated 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness). In comparison, diamond is rated 10, while a common mineral quartz is only rated 7 [22]. The application of surface treatment in pavement applications using corundum has been reported in Switzerland, Germany, and Austria [23], where corundum material with particle sizes of 1 to 3 mm has been applied to provide a high grip on the road surface.
2.2. Specimen Preparation
The SHCC mixture was prepared in a planetary mixer. Cement, fly ash, and micro-silica sand were dried and mixed. Water was then added, followed by the addition of a superplasticizer, and the mixture was combined for 3–5 min until it achieved the required consistency. Lastly, PVA fiber was added before mixing for another 3–5 min. The fresh mixture was cast into steel formwork with dimensions of 2000 mm by 500 mm by 80 mm. Specimens were removed from the mold after 1 day and were cured in normal laboratory air (25 ± 3 °C, 70% RH) for another 27 days before further testing.
Similarly, a modified SHCC-Cor mixture was mixed in a planetary mixer. Cement, fly ash, and micro-silica sand were dried and mixed. Water was then added, followed by the addition of a superplasticizer, and the mixture was combined for 3–5 min until it achieved the required consistency. Lastly, the PVA fiber and corundum were added before mixing for another 3–5 min. The fresh mixture was cast into steel formwork with dimensions of 2000 mm by 500 mm by 80 mm. Specimens were removed from the mold after 1 day and were cured in normal laboratory air (25 ± 3 °C, 70% RH) for another 27 days before further testing. At the predetermined age of 1 day, the top surface of plate specimens was treated using a steel brush to expose the corundum on the surface.
To study the effects of surface macrotexture on the skid resistance and acoustic performance of SHCC-Cor, parallel grooves were created on the surface of SHCC-Cor specimens using silicone rubber. The groove design dimensions using SHCC-Cor-Gro (Strain-hardening cementitious composites mixed with corundum aggregate with grooves), along with an illustration, are shown in Table 2. The groove design consisted of a land area of 25 mm, groove width of 3.2 mm, and groove height of 3.2 mm.

Table 2.
Groove dimensions for SHCC-Cor-Gro.
2.3. Test
The test program in this study included two stages: (1) investigating the mechanical properties of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor, and (2) investigating the acoustic performance of the tire–pavement mechanism on SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor.
To investigate the mechanical properties of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor, four-point bending tests in accordance with ASTM [24] were carried out on a prism specimen with dimensions of 280 mm by 70 mm by 50 mm to evaluate the flexural strength. The loading span (80 mm) was one-third of the support span (240 mm), and the rate of deflection at the loading points was controlled at 0.3 mm/min. At least four specimens were tested for each mix of SHCC and SHCC-Cor. The modulus of rupture (MOR) was calculated, and the ductility was estimated by means of a reverse calculation method [25]. Microscopic skid resistance was evaluated following the ASTM Standard Test Method for Measuring Surface Frictional Properties Using the British Pendulum Tester [26]. The test results are reported as the British pendulum number (BPN). The tests were conducted in wet test conditions by spraying water on the specimens. At least three random locations on the surface of specimens were evaluated for each mix, and a minimum of five tests were performed for each specimen.
To investigate the acoustic performance of the tire–pavement mechanism of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor, laboratory measurements and noise prediction analyses were performed. The laboratory measurements were conducted with a contact-free measuring method, which allows for a nondestructive determination of the surface roughness (macrotexture) of slab surfaces. The measurement and description of the surface texture were carried out using a profilometer, which was set according to ISO 13473 “Characterization of pavement texture by use of surface profiles”, Parts 1–4.
The slab surface was scanned using a laser triangulation measuring system over the whole length according to the method of continuous measurements. The profilometer was connected to the power source and a computer which had the controls and software to record and save the measurements attained by the laser. The mean profile depth of the slab was measured by the equipment based on a triangulation laser measurement system. The percentage of the laser beams failing to reflect is called the dropout rate. This determines the accuracy of the measurement. According to ISO 18743, a dropout percentage of 5% is allowed for one trial. The texture of three slabs (SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro) was measured using a surface profilometer, which can be seen in Figure 1, to evaluate the tire–pavement-noise. The results, in terms of texture depth, are required as input for the software. The measured data had to contain at least six parallel measurement lines with a length of at least 2 m each. Therefore, the tested SHCC-Cor slabs were created with a minimum length of 2 m. Detailed surface images of the three slabs are shown in Figure 2.
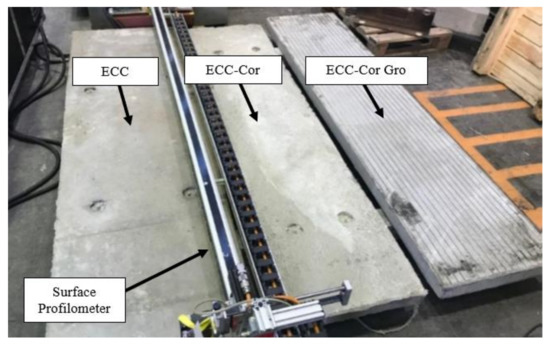
Figure 1.
Specimen preparation for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro (SHCC: strain-hardening cementitious composite, SHCC-Cor: Strain-hardening cementitious composites mixed with corundum aggregate, SHCC-Cor-Gro: Strain-hardening cementitious composites mixed with corundum aggregate with grooves).

Figure 2.
Detailed surface images of SHCC (left), modified SHCC-Cor (center), and SHCC-Cor-Gro (right).
As can be seen in Figure 3, the laser scanning equipment was aligned parallelly over the slab. Slopes or slants in both vertical and horizontal directions were avoided to allow the movement of the laser scanner in a straight line. Once the setup was complete, a trial run was conducted over the full length of the slab to ensure that the laser ran in a straight line. A total of 96 line areas were scanned along the length of the slab with an offset of 2 mm. The total run time for the 96 line areas on one slab was approximately 20 min. The process was repeated for all three slabs. The resolution of the applied measuring system was 200 μm horizontally and 8 μm vertically. Data were then processed to predict the noise level by evaluating the MPD value (according to ISO 13473-1) and the shape factor of the profile; these two values gave a good indication of whether the road surface was suitable to reduce the tire–road noises.

Figure 3.
Laser profilometer for surface texture measurement.
The tire–pavement noise was predicted using SPERoN (Statistical Physical Explanation of Rolling Noise) software version 3.0, as a function of the preprocessed input data of texture. SPERoN was developed by Müller-BBM. The SPERoN model has been validated and used for noise investigation (e.g., in Sperenberg, Berlin [27]). The validated model combines both physical and statistical sub-models. The physical sub-model considers texture properties and air pumping effects, replicates the same condition, and simulates the rolling behavior of the tire in detail. The details describe the contact area of the tire–pavement interaction and the contact forces at a particular speed [28].
The statistical sub-model is outfitted with the average third octave band spectrum noise levels of the relevant contact area and forces. The vibrations produced by the contact forces are fitted into a time domain. The time loop starts with the loading of the tire on the pavement, followed by rolling of the tire for a few revolutions on the surface until a steady state is achieved, and then ends as the tire comes to a static position. This time loop makes sure that noise from all spectra is calculated. The statistical model functions with some formulas of a multiple regression model. The SPERoN model calculates the coast-by noise of a vehicle by considering four parameters (tire vibrations, the aerodynamic sound sources, the tire cavity modes, and the residual sound sources [29]), which is then followed by the statistical model [30]. The equations can be seen below.
where 𝑎, b, c, and d are the regression coefficients per third octave band, α1, α2, α3, b1,γ1, and 𝛿1 are the exponents, Fc is the contact force in N, Γ is the tire/pavement contact air flow resistance in Pa·s/m, B is the tire width in m, and S is the tire tread stiffness in N/m, Gpattern is the spectral power of the tread pattern variation, and V is spectral power of the tread pattern variation driving speed in m/s.
The SPERoN model requires inputs, including the texture of the pavement. The texture profile length should be at minimum equal to the circumference of the tire used, and the width should overlap with at least the tire pavement contact patch. The peaks and troughs in the texture are determined in such a way that the overall roughness can refer to the zero values of the surface. The SPERoN model also requires tire specification, including material, tread profile, and hardness. Additional inputs are required, including airflow resistance and vehicle driving speed.
The input characteristics of the road surface are necessary to obtain results on the coast-by noise including road texture (roughness of the road surface), acoustical impedance (a measure for the sound reflection and absorption properties of a road surface with 0% as totally reflecting and 100% as totally absorbing), airflow resistance, and mechanical impedance (as the ratio of the input force and vibration velocity measured at a certain point of the structure). The SPERoN calculations were performed with a tire called “Michelin Energy Saver”, which was used as a standard tire, with a speed of 50 km/h. The SPERoN model and results were validated by investigating and comparing eight coast-by measurement results from the model and field tests. The validation was carried out through a database of several thousands of physical coast-by noise levels measured with a wide variety of tires, road surfaces, and driving velocities. The data used for validation for this study were obtained from the Deufrako study, where the validation was performed using coast-by noise levels from eight different surfaces at a speed of 90 km/h. The results showed that the total sound levels for all investigated road surfaces had a mean precision of 1.5 dB [31,32].
3. Results
3.1. Mechanical Properties
Table 3 summarizes the mechanical properties of SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor mixtures. The first cracking strength results were obtained directly from the four-point bending test results, while the tensile strain capacity was inversely calculated from the load–deflection curve in accordance with ASTM C78/C78M. As can be seen from the table, the first cracking strength of SHCC increased, while the tensile strain capacity decreased when corundum was incorporated into the mix. This was attributed to the introduction of corundum with a high hardness, which increased the matrix toughness and, thus, reduced the strain hardening and multiple cracking potentials [33]. Nevertheless, all SHCC-Cor mixtures still possessed an adequate tensile strain capacity of around 1%, which is sufficient for pavement application. Both SHCC and SHCC-Cor mixtures showed high flexural strength. The addition of corundum aggregate did not significantly affect the flexural strength as both mixtures maintained a high flexural strength of around 11 MPa.

Table 3.
Mechanical properties for SHCC and modified SHCC-Cor.
3.2. Microtexture and Macrotexture
Table 4 summarizes the microtexture and macrotexture of SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and modified SHCC-Cor-Gro specimens. The microtexture was measured as the British pendulum number (BPN), and macrotexture was measured as the mean profile depth (MPD) in mm. As can be seen, the BPN for the SHCC-Cor specimens was further improved from 54 BPN to 72 BPN. The macrotexture of SHCC-Cor was improved twofold compared to SHCC, resulting in 0.21 mm for SHCC-Cor and 0.1 mm for SHCC.

Table 4.
Microtexture and macrotexture for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
Furthermore, the macrotexture for SHCC-Cor-Gro was significantly increased due to grooving design enhancement. Both modified SHCC-Cor and SHCC-Cor-Gro (in longitudinal direction) resulted in satisfactory performance in terms of high skid resistance of more than 70 BPN, without negatively affecting the mechanical properties, which remained high.
It was observed that the macrotexture of SHCC-Cor-Gro was three times higher than that of SHCC-Cor, yet SHCC-Cor-Gro resulted in the same BPN. This is because the British pendulum test was conducted in a longitudinal direction. A similar observation was found by Hall et al. and Henry, indicating that longitudinal grooves would not significantly affect skid resistance. Although transversal grooves could increase skid resistance, they produced more noise [34,35].
3.3. Texture Depth Based on Profilometer Measurement and Shape Factor
The surface texture depth from three slabs (SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor Gro) was measured. The texture depth of SHCC was flatter in comparison to the other surfaces, with less than 100 μm deviation. Meanwhile, SHCC-Cor had a rougher texture depth with about 350 μm deviation due to the corundum. Lastly, SHCC-Cor-Gro had a similar rough texture to SHCC-Cor, with additional spikes due to the grooves.
The texture measurement of the three slabs was performed using a contactless sensor. This is a nondestructive testing method of the surface texture which complies with ISO 13473. The texture measurement was performed with a contactless sensor mounted on a solid frame. The sensors were fitted and positioned in such a way that they could move both horizontally and vertically. The translation of the sensor was 1.2 m in the horizontal direction and 30 cm in the vertical direction. This allowed the sensors to plot data points in both X- and Y-directions, creating a 3D texture profile. The oriented plane of the sensors was not perfectly horizontal, thus resulting in a slope of 0.5% in the recorded profile output.
Throughout the measurement with the laser profilometer, the shape factor parameter was measured for each slab. In addition to the macrotexture, these two parameters were necessary, as they were later used for the calculation of the total sound level. Previous studies mentioned that two road surfaces with identical texture amplitude spectra do not necessarily show identical acoustical behavior. Therefore, the shape factor needs to be considered as it corresponds to the percentage contact length within the characteristic profile length [36]. The shape factor for SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Shape factor of SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
3.4. Sound Level
The calculation with SPERoN was performed for three slabs with texture depth as one of the main inputs. As result, four different noise levels were produced with different parameters including vibration, air, cavity, and residual noise. Those four noise parameters were expressed in Equations (1)–(5). The results of sound pressure level, which are summarized in Table 6, Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9, are presented as a function of the octave band center frequency, reported in Hertz (Hz), indicating how fast the small air pressure changes occurred. Similar to the sound level, the perception of frequency was also nonlinear.

Table 6.
Sound level (vibration) for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.

Table 7.
Sound level (air) for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.

Table 8.
Sound level (cavity) for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.

Table 9.
Sound level (residual) for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
The results of each standalone parameter, including vibration, air, cavity, and residual noise, and the aggregated total noise are shown in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. The results were derived from the validated SPERoN model [31,32].
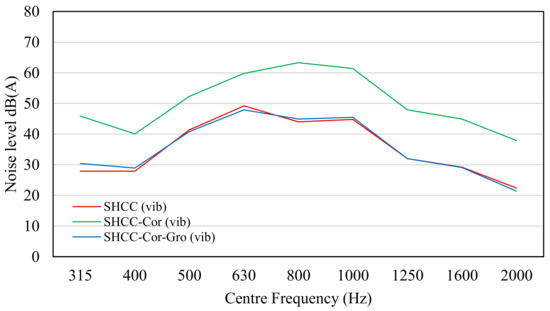
Figure 4.
Noise level of SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro based on vibration parameter.
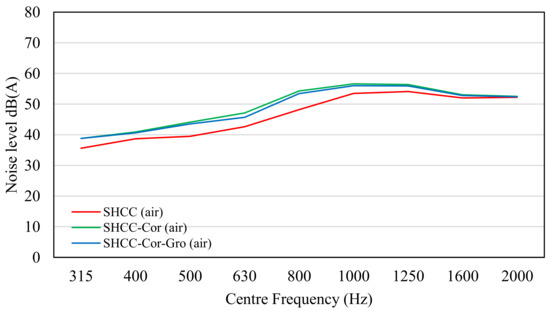
Figure 5.
Noise level of SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro based on air parameter.
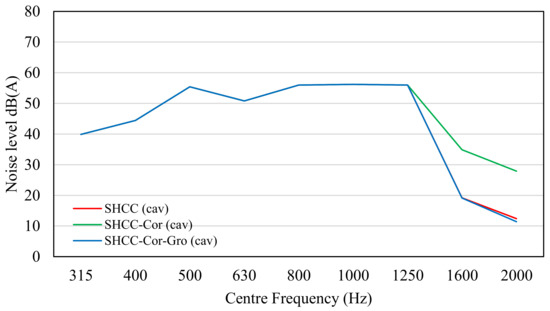
Figure 6.
Noise level of SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro based on cavity parameter.
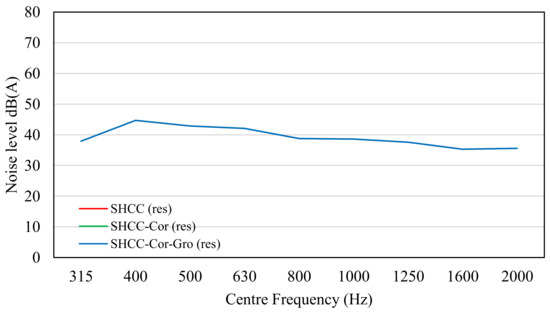
Figure 7.
Noise level of SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro based on residual parameter.
The two main sources of sound level are vibration and air [36]. As can be seen, the sound level for SHCC-Cor was higher than that for SHCC. The higher sound level of SHCC-Cor occurred because of the lower shape factor (G) due to a rougher surface as a result of the existence of corundum aggregate on the SHCC surface.
Throughout the measurement with the laser profilometer, parameters were measured, including the macrotexture, mean profile depth (MPD), and shape factor for each slab. These parameters were necessary as they were later used for the calculation of the total sound level.
Tire cavity is mainly determined by the tire pattern and is less affected by the road surface. Due to the use of the same standard tire, there were no notable differences. The residual component was the cumulation of all airflow noises caused by the frame of the vehicles, which was statistical and only dependent on the velocity. Therefore, all results of the noise level for the slabs are similar, except that the noise level in the cavity parameter was different for a center frequency higher than 1250 Hz as it was more sensitive.
4. Discussion
The main objective of incorporating fine aggregates into SHCC mixtures is to introduce texture for resilient roadway applications, which require both structural and functional performance. It needs to be investigated whether the incorporation of aggregates negatively impacts the mechanical properties of SHCC, as it is required to handle traffic and temperature loading.
According to the tests conducted, the tensile strain capacity of SHCC-Cor generally decreased with the incorporation of aggregates [37,38,39,40]. However, the tensile strain capacity of SHCC-Cor was still higher than 1%, which is 100 times higher than the concrete conventionally used in pavement. Meanwhile, the first crack strength was higher than 5 MPa. These mechanical properties of modified SHCC-Cor are satisfactory for resilient road pavement infrastructure.
Conventional SHCC produced no texture on its surface, as it consisted of neither coarse nor fine aggregates. As result, SHCC provided low skid resistance with only 54 BPN, which is below the required minimum limit for new roadways. For example, the Land Transport Authority of Singapore requires 55 BPN for new roadway infrastructure. According to the Transport Road and Research Laboratory (TRRL), motorways in the UK also require a minimum of 55 BPN [41,42]. The test methods for skid resistance include the British pendulum tester and sideway-force coefficient routine investigation machine (SCRIM) [43,44]. The addition of corundum aggregates to the SHCC mixtures improved the microtexture of SHCC, resulting in a high skid resistance of more than 70 BPN.
The noise level coming from the pavement made of SHCC could be up to 65 dB(A), which is quite safe as it is below the standard values regulated by the authorities. However, from the perspective of skid resistance, the SHCC slab is not safe to be used for roadways. The addition of aggregates could increase the skid resistance, but also increase the noise level. The evaluation of the MPD value (according to ISO 13473-1) and the shape factor of the profile can give a good indication of whether the road surface is suitable to reduce the tire–pavement noises.
The noise level resulting from SHCC-Cor was higher than that resulting from SHCC. The noise level for SHCC-Cor increased to 69.2 dB(A) because of the lower shape factor (G) due to a rougher surface as a result of the existence of corundum aggregate on the SHCC surface. The shape factor of SHCC-Cor was 55%, which was lower than that of SHCC. As can be seen from the results in Table 6, Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9, the biggest difference was found in the vibrational noises as SHCC-Cor had a rougher surface than SHCC, which stimulated the tire to vibrate more. The aeroacoustics of SHCC-Cor were also slightly increased compared to the SHCC slab.
The noise level resulting from SHCC-Cor-Gro was reduced to 64.6 dB(A) due to the additional treatment of grooving in a longitudinal direction. The reasons behind the improvement include several factors. The shape factor of SHCC-Cor-Gro increased from 55.4% to 59.1%. Furthermore, the vibration noise level for SHCC-Cor-Gro decreased from 66.8 dB(A) to 51.6 dB(A), becoming similar to SHCC with a noise level of 51.9 dB(A). The remaining three parameters of aeroacoustics noise, cavity noise, and residual noise of SHCC-Cor-Gro were also improved and reached the same level as SHCC, with 59.6 dB(A), 62.3 dB(A), and 50 dB(A), respectively. The total sound level for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro can be seen in Table 10.

Table 10.
Sound level (total) for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
The spectra for the total noise level resulting from SHCC, modified SHCC, and modified SHCC-Cor-Gro are shown in Figure 8. As can be seen from the figure, SHCC and SHCC-Cor-Gro showed almost similar characteristics. The comparison of total noise for SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro are shown in Figure 9.
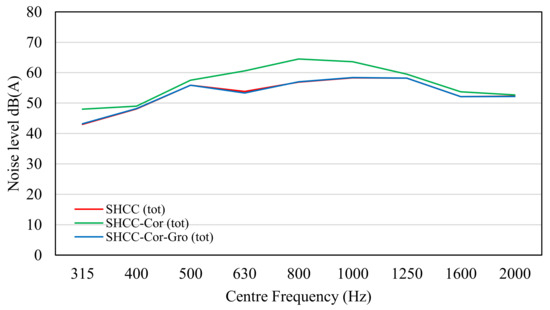
Figure 8.
Total noise level of SHCC, modified SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
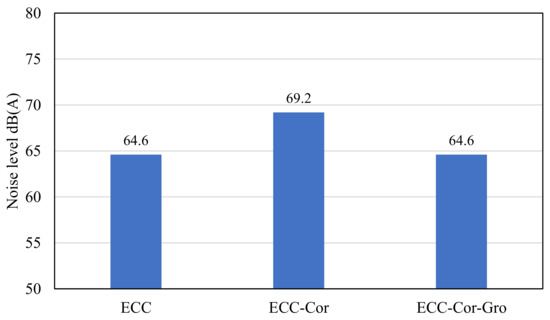
Figure 9.
Noise level dB(A) comparison of SHCC, SHCC-Cor, and SHCC-Cor-Gro.
SHCC-Cor-Gro represents a potential solution for resilient roadways with pavement made of SHCC. The modification of SHCC-Cor by introducing grooves (SHCC-Cor-Gro) successfully reduced the sound level coming from the vibration. The sound level from the air parameter was slightly reduced, mainly in the frequency from 315 to 1250 Hz. The shape factor was then increased for SHCC-Cor-Gro. As result, the total sound level for SHCC-Cor-Gro was reduced significantly from 69.2 (SHCC-Cor without grooves) to 64.6 dB.
SHCC-Cor-Gro produced low noise levels and resulted in a high skid resistance of 72 BPN, indicating that it can produce high functional performance for road applications. Furthermore, SHCC-Cor-Gro produced high structural performance with a first crack strength of 5.9 MPa and tensile strain capacity of 1.0%. In summary, SHCC-Cor-Gro can be considered a good option for resilient road pavement applications, as it provides good structural and functional performance.
Further research investigating the acoustic performance on SHCC material is suggested by conducting noise absorption measurements on the SHCC and modified SHCC material. Noise absorption measurements can be considered to study the effect of texture and porosity, as this technology is reliable, handy, and able to be used in the laboratory and in situ [36,45]. In addition, dynamic wayside traffic noise measurements can be performed, e.g., statistical pass-by (SPB) test, controlled pass-by (CPB) test, or continuous-flow traffic time-integrated model (CTIM). It is also important to balance the structural and functional performance of pavement made of SHCC by modifying the SHCC mixture design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.B., B.L., N.N. and E.-H.Y.; methodology, A.A.B., B.L. and E.-H.Y.; software, M.E.-B. and A.A.B.; validation, M.E.-B. and A.A.B.; formal analysis, M.E.-B., A.A.B. and J.T.; resources, E.-H.Y., C.S., B.L. and S.F.; data curation, J.T., M.E.-B. and A.A.B., writing—original draft preparation, M.E.-B., A.A.B. and J.T.; writing—review and editing, B.L., C.S., E.-H.Y. and S.F.; visualization, M.E.-B., A.A.B., and J.T.; supervision, A.A.B. and B.L.; project administration, A.A.B., N.N. and B.L.; funding acquisition, A.A.B. and N.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Singapore National Research Foundation under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) program.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their useful remarks, which helped us to improve the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Fischer, G.; Li, V.C. Deformation Behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Reinforced Engineered Cementitious Composite (ECC) Flexural Members under Reversed Cyclic Loading Conditions. ACI Struct. J. 2003, 100, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Li, V. Durable pavement with ECC. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Microstructure Related Durability of Cementitious Composites, Nanjing, China, 13–15 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Junxia, L.; Jishen, Q.; Shan He Yang, E.-H. Micromechanics-Based Design of Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites (SHCC). In RILEM Book Series, Proceedings of the Strain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites, Dresden, Germany, 18–20 September 2017; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokugo, K.; Kunieda, M.; Lim, S.C. Patching Repair with ECC on Cracked Concrete Surface; University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rokugo, K. Applications of SHCC in Japan—Tools and tips for promoting its use. In Proceedings of the Strain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites, Dresden, Germany, 18–20 September 2017; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lepech, M.D.; Li, V.C. Application of ECC for bridge deck link slabs. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C.; Kanda, T. Engineered Cementitious Composites for Structural Applications. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1998, 10, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawono, A.A.; NguyenDinh, N.; Lechner, B. Evaluation of highway pavement skid resistance performance made of engineered cementitious composite (ECC). In Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields; CRC Press: Athens, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Keoleian, G.; Lepech, M. An integrated life cycle assessment and life cycle analysis model for pavement overlay systems. In Life-Cycle Civil Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, S.; Mechtcherine, V. Use of Strain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites (SHCC) in Real Scale Applications. In RILEM Book Series, Proceedings of theStrain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites, Dresden, Germany, 18–20 September 2017; Mechtcherine, V., Slowik, V., Kabele, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawono, A.A.; Lechner, B.; Yang, E.-H. Bright and slip-proof engineered cementitious composites with visible light activated photo-catalysis property for pavement in tunnels. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 104, 103387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawono, A.A. State of the Art: Functional Performance of Pavement. In Engineered Cementitious Composites for Electrified Roadway in Megacities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Gelb, J. Cyclists’ Exposure to Road Traffic Noise: A Comparison of Three North American and European Cities. Acoustics 2020, 2, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.O.; Bernhard, R.; Sandberg, U.; Mun, E.P. The Little Book of Quieter Pavements; Federal Highway Administration FHWA: Austin, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Scheffler, B.; Piotrowski, S. Multi-Functional Noise Reducing Pavements Made of UHPC—Materials. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Concrete Block Pavement, Dresden, Germany, 8–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanap, I. An analysis of roadway noise at residential estates in close proximity to expressways in Singapore. Noise Health 2013, 15, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, G.C. Noise Pollution in Singapore: When Buzz Becomes Noise. 2010. Available online: http://wildsingaporenews.blogspot.sg/2010/11/noise-pollution-in-singaporewhen-buzz.html#.WBMRYC196Uk (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- National Environment Agency of Singapore. In Technical Guideline for Land Traffic Noise Impact Assessment; National Environment Agency of Singapore: Singapore, 2016.
- Gibbs David, C.; Randell, I.; Robert, B.; James, B.; Douglas, C.; Christopher, C.; Kenneth, F.; Thomas, H., Jr.; Kevin, M.; David, N. Quiet Pavement Systems in Europe; Federal Highway Administration: Richmond, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, H.; Lu, Q.; Kohler, E. Temperature Influence on Road Traffic Noise Californian OBSI Measurement Study; University of California Pavement Research Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodico, D.; Donavan, P. Quieter Pavement: Acoustic Measurement and Performance. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 97th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 7–11 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tubey, L.; Hosking, J. Synthetic Aggregates of High Resistance to Polishing—Corundum Rich Aggregates; Road Research Laboratory: Crowthorne, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, R.; Peck, M. Kreisverkehrsflächen in Beton: Erfahrungen in der Schweiz, Deutschland und Österreich. In Aktuelles zum Thema Betonstrassen Update 3/10: Swiss. 2010. Available online: https://www.zement.at/downloads/update3_10.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- ASTM C78/78M; Committee. Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Li, V.C. Simplified Inverse Method for Determining the Tensile Strain Capacity of Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2007, 5, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E303-93; ASTM Standard Test Method for Measuring Surface Frictional Properties Using the British Pendulum Tester. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993.
- Auerbach, M.; Berengier, M. Prediction and propagation of rolling noise. In Proceedings of the Transport Research Arena 2008, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 21–25 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Beckenbauer, T. Effect of Pavement on Tyre/Pavement Noise; 11/12 June 2008; Bundesministerium fuür Verkehr, Bau- und Wohnungswesen. Informationstage, Geräuschmindernde Fahrbahnbeläge in der Praxis—Lärmaktionsplanung: Munich, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-BBM. SPERoN—Rolling Noise Prediction Model. Available online: https://www.muellerbbm.com/environment/traffic-environment/speron/ (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Beckenbauer, T.; Kuijpers, A. Prediction of pass-by levels depending on road surface parameters by means of a hybrid model. In Proceedings of the 2001 International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering, Hague, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Beckenbauer, T.; Klein, P.; Hamet, J.; Kropp, W. Tyre/road noise prediction: A comparison between the SPERoN and HyRoNE models—Part 1. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.; Maennel, M. Application of Speron to the development of low noise road surfaces. In Proceedings of the EuroRegio2016, Porto, Portugal, 13–15 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bawono, A.A. State of the Art: Engineered Cementitious Composites Precast Ultra-Thin Whitetopping (ECC-PUTW). In Engineered Cementitious Composites for Electrified Roadway in Megacities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.; Smith, K.; Titus-Glover, L.; Wambold, J.; Yager, T.; Rado, Z. Guide for Pavement Friction; NCHRP 108; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J.J. Evaluation of Pavement Friction Characteristics. In A Synthesis of Highway Practice; NCHRP Synthesis 291; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, M.; Wehr, R.; Conter, M.; Kriegisch, M.; Gasparoni, S. Texture and noise characteristics of exposed aggregate concrete road surfaces. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Concrete Roads, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bawono, A.A.; Lechner, B.; Yang, E.-H. Skid resistance and surface water drainage performance of engineered cementitious composites for pavement applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, E.-H. Macroscopic and microstructural properties of engineered cementitious composites incorporating recycled concrete fines. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 78, 33–42. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10220/42497 (accessed on 7 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Kawamoto, A. Influence of Coarse Aggregate on the Mechanical Behavior of Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites.). In RILEM Book Series, Proceedings of theStrain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites, Dresden, Germany, 18–20 September 2017; Mechtcherine, V., Slowik, V., Kabele, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawono, A.A. The Functional Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites Material for Electrified Roadway Application in Singapore. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- TRRL. Instructions for Using the Portable Skid Resistance Tester; Road Research Laboratory: Crowthorne, UK, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- UK Highway Agency. Design Manual for Roads and Bridges: Skid Resistance; UK Highway Agency: Guildford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Land Transport Authority. Code of Practice for Works on Public Streets, 6th ed.; Land Transport Authority: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Land Transport Authority. Materials and Workmanship Specification for Civil and Structural Works; Land Transport Authority: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keulen, V.; Li, W.; Ceylan, M.; Molenaar, H.; Van, A.; Ven, M. SIROTOL: Statistical model of tyre-road noise for thin layer surfacing. Noise Control Eng. J. 2017, 65, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).