Angle-Dependent Absorption of Sound on Porous Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Material Samples
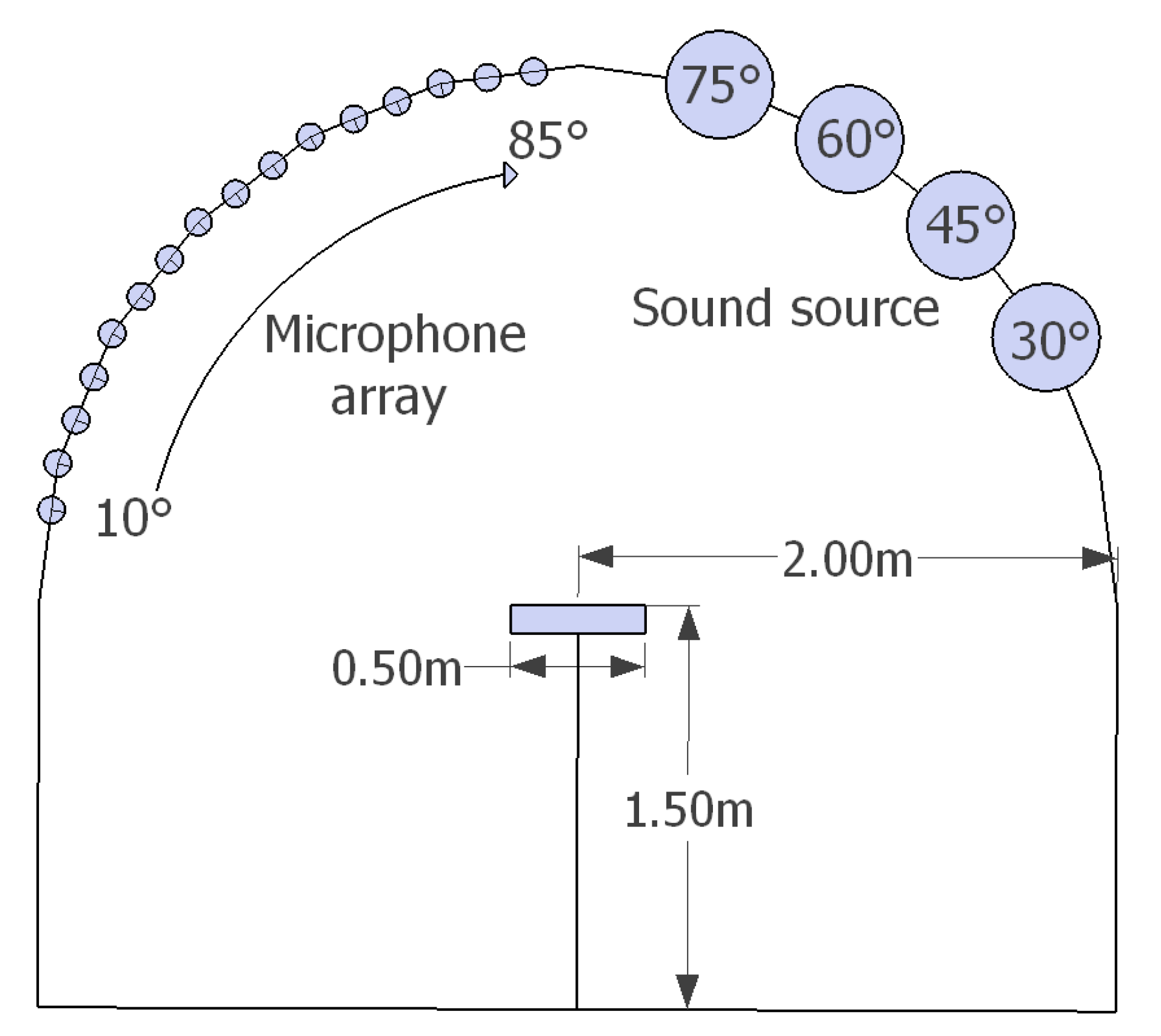
2.2. Experimental Setup
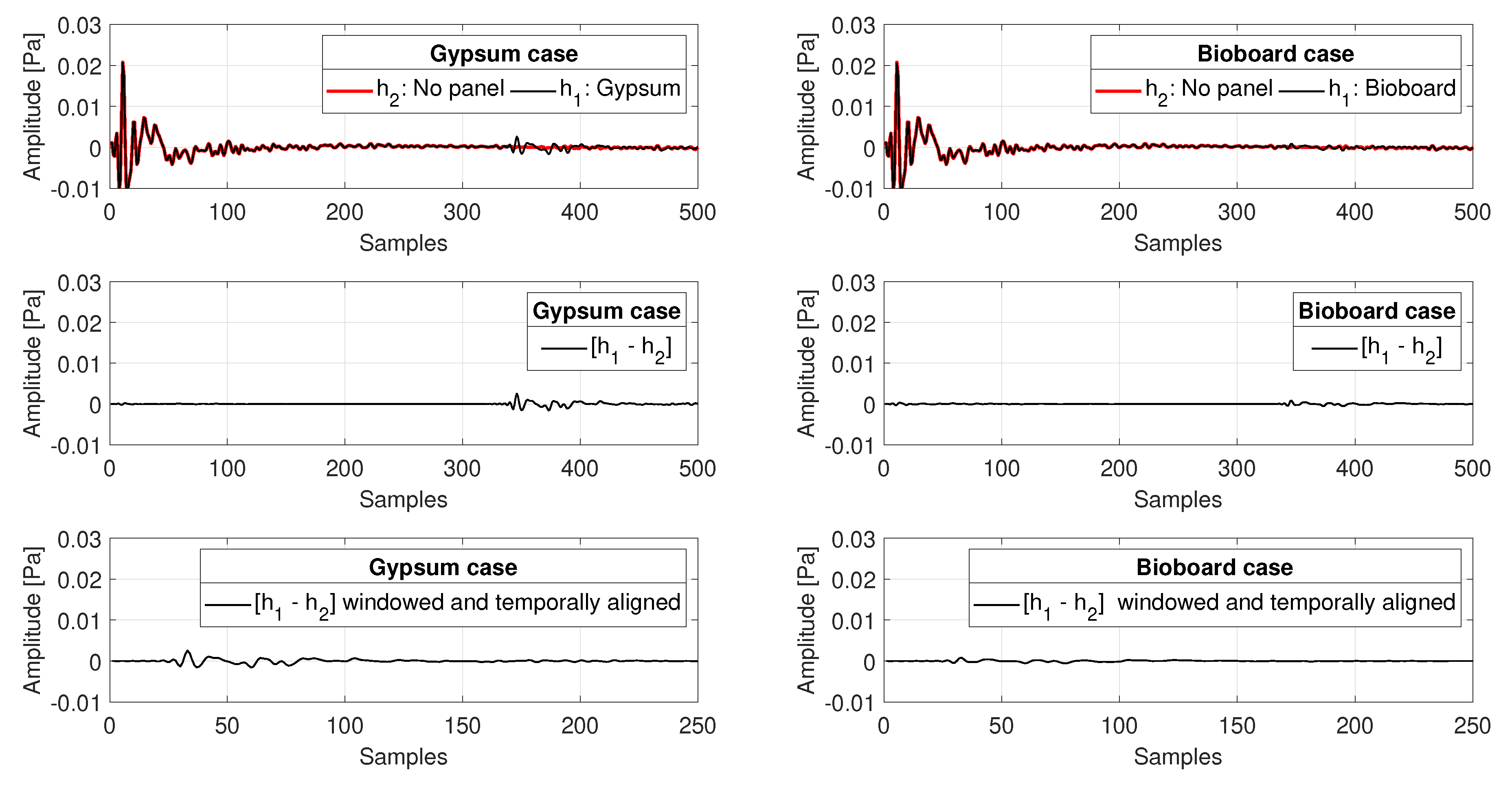
2.3. Compensation of the Measurement Device Responses and Generation of Polar Responses
2.4. Computation of the Angle-Dependent Absorption Coefficients
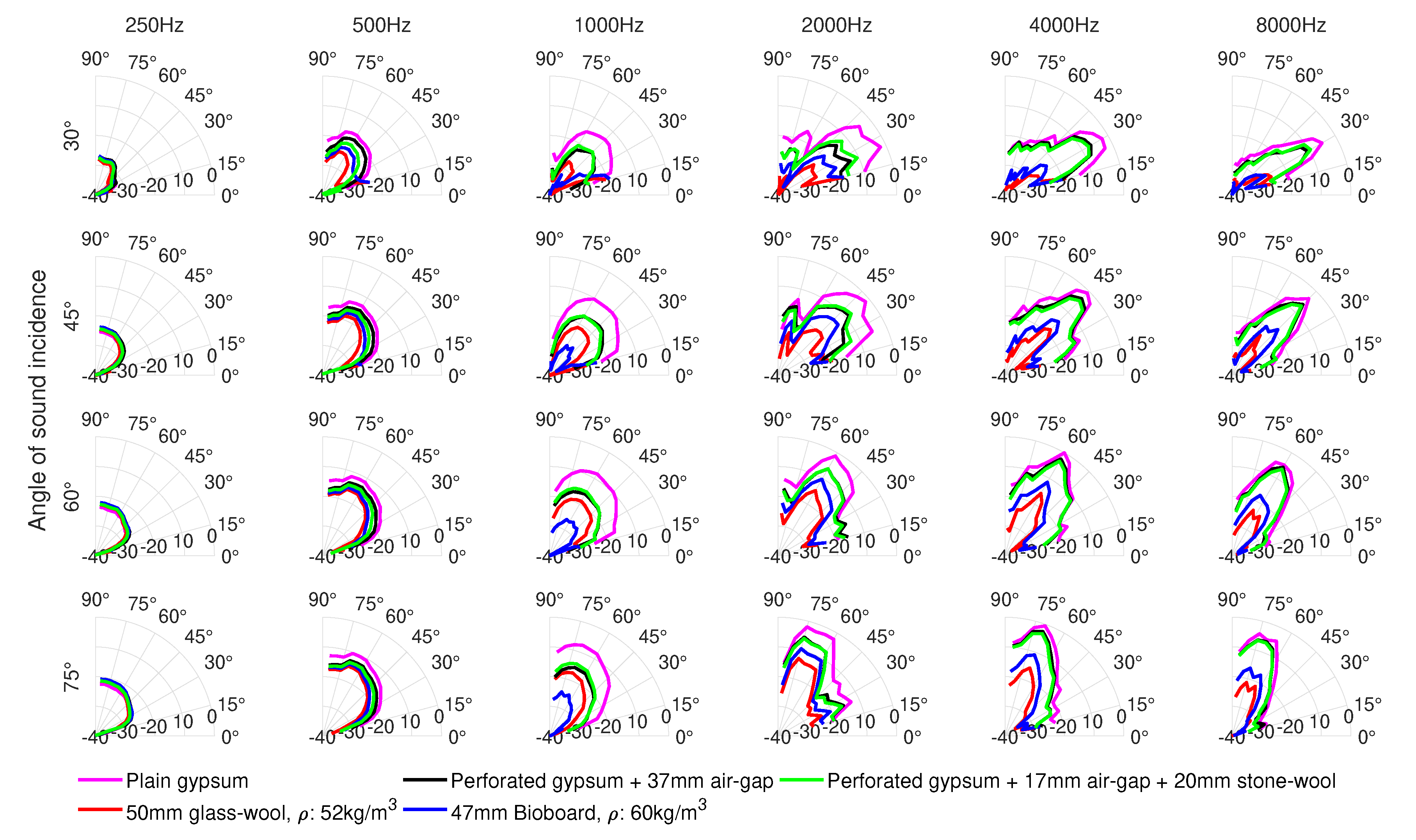
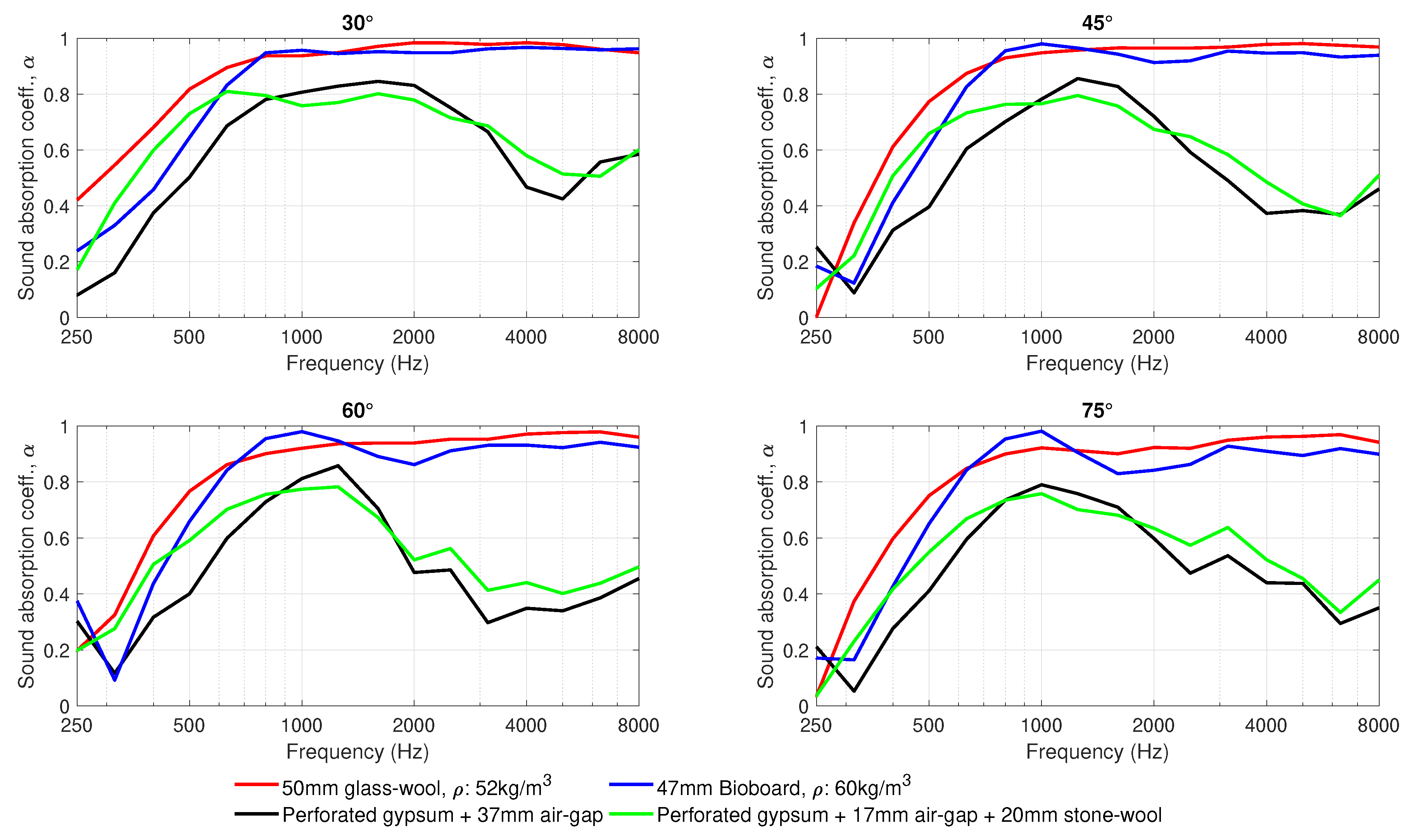
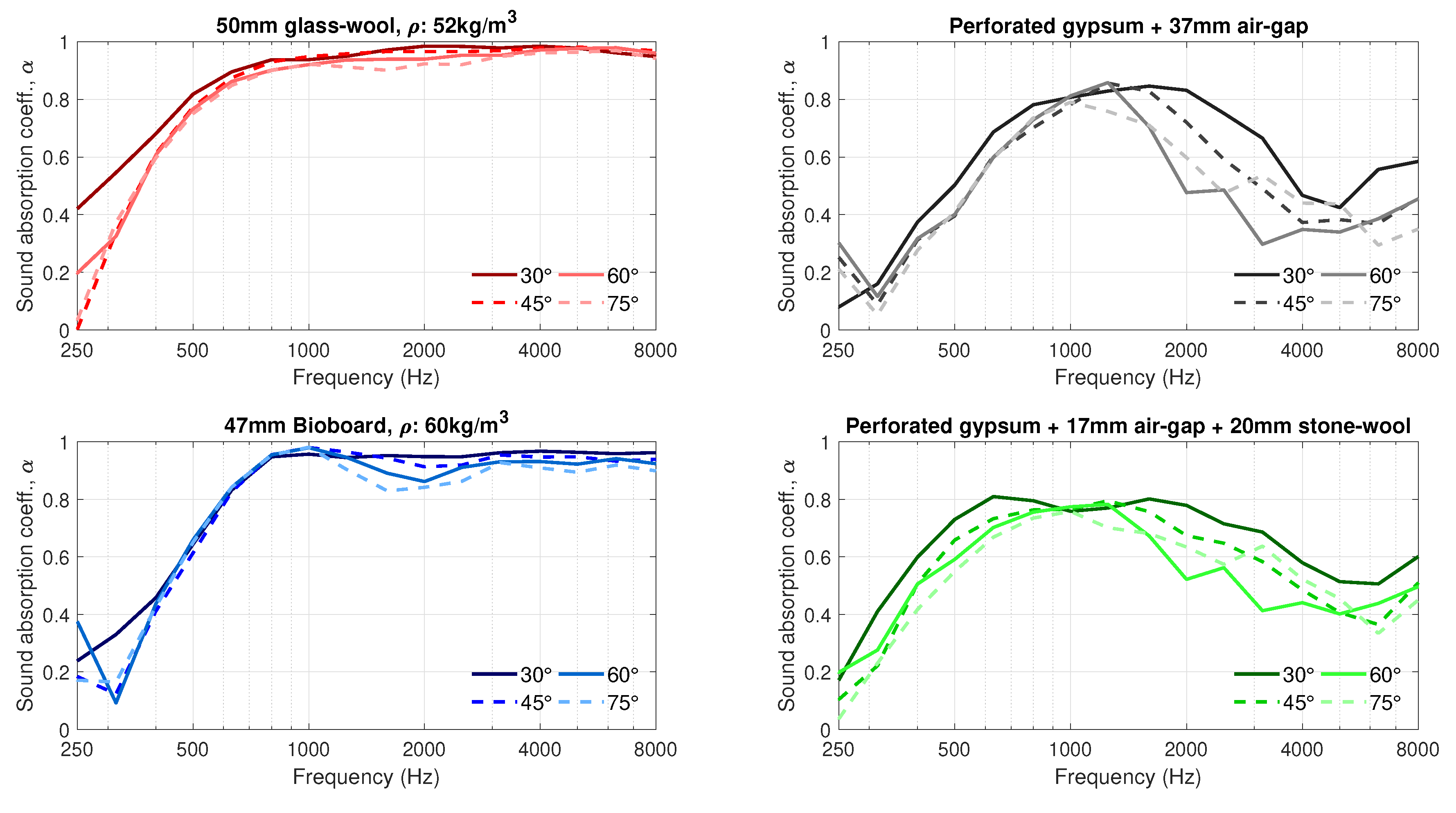
3. Results
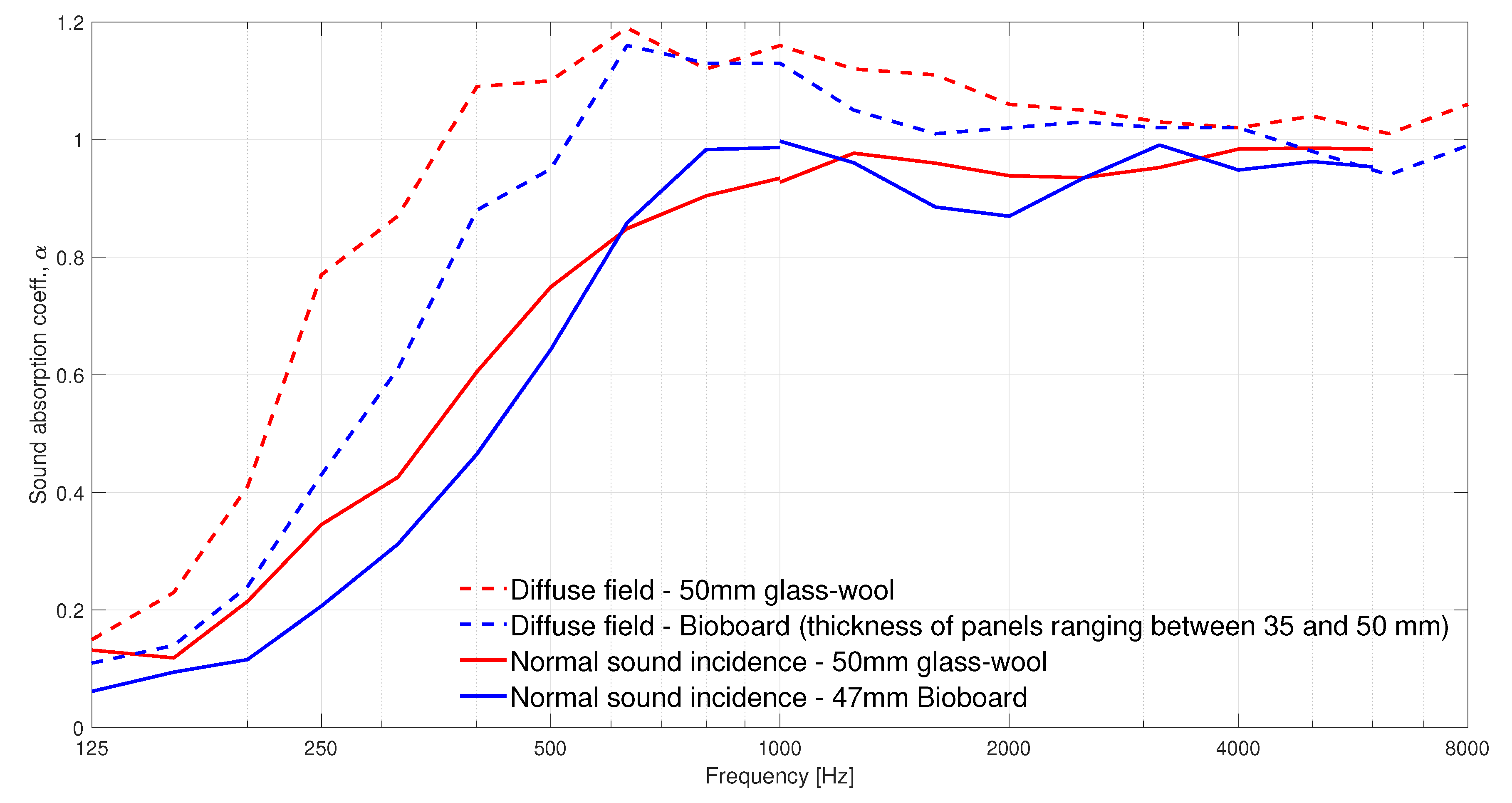
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ISO | International Standard Organization |
| CO | Carbon dioxide |
| AES | Audio Engineering Society |
| ITA | Institute of Technical Acoustics, Aachen, Germany |
| O.d.s. | Overall depth of system |
References
- D’Antonio, P.; Cox, T. Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Venegas, R.; Umnova, O. Influence of sorption on sound propagation in granular activated carbon. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Predicting the sound absorption of natural materials: Best-fit inverse laws for the acoustic impedance and the propagation constant. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 115, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, N.; Romero-García, V.; Pagneux, V.; Groby, J.P. Rainbow-trapping absorbers: Broadband, perfect and asymmetric sound absorption by subwavelength panels for transmission problems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Ren, S.; Meng, H.; Xin, F.; Huang, L.; Chen, T.; Zhang, C.; Lu, T.J. Hybrid acoustic metamaterial as super absorber for broadband low-frequency sound. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, J.P.; Asdrubali, F. Eco-materials with noise reduction properties. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martinez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3031–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Ciers, J.; Mandic, A.; Toth, L.D.; Op’t Veld, G. Carbon Footprint of Academic Air Travel: A Case Study in Switzerland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 354. Acoustics—Measurements of Sound Absorption in a Reverberation Room; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10534-2. Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mommertz, E. Angle-dependent in-situ measurements of reflection coefficients using a subtraction technique. Appl. Acoust. 1995, 46, 251–263, Building Acoustics. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocke, C. In-situ acoustic impedance measurement using a free-field transfer function method. Appl. Acoust. 2000, 59, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, M. Measurement of the sound-absorption coefficient in situ: The reflection method using periodic pseudo-random sequences of maximum length. Appl. Acoust. 1993, 39, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M. Estimation of angle-dependent absorption coefficients from spatially distributed in situ measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, EL119–EL124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, M.; Tikander, M. Reducing Artefacts of In-Situ Surface Impedance Measurements. Available online: http://pcfarina.eng.unipr.it/Public/Standing-Wave/ica01.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Brandão, E.; Lenzi, A.; Paul, S. A Review of the In Situ Impedance and Sound Absorption Measurement Techniques. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2015, 101, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorländer, M.; Mommertz, E. Definition and measurement of random-incidence scattering coefficients. Appl. Acoust. 2000, 60, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17497-1. Acoustics—Sound-Scattering Properties of Surfaces—Part 2: Measurement of the Random-Incidence Scattering Coefficient in a Reverberation Room; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- D’Antonio, P.; Cox, T. AES information document for room acoustics and sound reinforcement systems-characterization and measurement of surface scattering uniformity. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17497-2. Acoustics—Sound-Scattering Properties of Surfaces—Part 2: Measurement of the Directional Diffusion Coefficient in a Free Field; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, P.; Logawa, B.; Korehei, R.; Hodgson, M.; Martinez, D.M.; Olson, J.A. On acoustical properties of novel foam-formed cellulose-based material. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2016, 31, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, R.J.; Schell, C.J. Effects of fiber length and coarseness on pulp flocculation. Tappi J.—(USA) 1995, 78, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Beghello, L.; Eklund, D. Some mechanisms that govern fiber flocculation. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 1997, 12, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, T.; Lehmonen, J. Determinations of bubble size distribution of foam-fibre mixture using circular hough transform. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2012, 27, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimei, Z.; Ma, S.; Wu, Y. Building Materials in Civil Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 80, pp. 81–308. [Google Scholar]
- Berzborn, M.; Bomhardt, R.; Klein, J.; Richter, J.G.; Vorländer, M. The ITA-Toolbox: An open source MATLAB toolbox for acoustic measurements and signal processing. In Proceedings of the 43th Annual German Congress on Acoustics, Kiel, Germany, 6–9 March 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Simultaneous measurement of impulse response and distortion with a swept-sine technique. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 108; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3382-1. Measurement of Room Acoustic Parameters—Part 1: Performance of Spaces; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hald, J.; Song, W.; Haddad, K.; Jeong, C.H.; Richard, A. In-situ impedance and absorption coefficient measurements using a double-layer microphone array. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 143, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datasheet of Perforated Panels Provided by Their Manufacturer Knauf Danoline. Available online: https://knaufdanoline.com/wp-content/uploads/Data_sheet_Solopanel_UK.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Yamaguchi, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Mizuno, T. Sound absorption mechanism of porous asphalt pavement. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E) 1999, 20, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.; Bris, P.; Horoshenkov, K. Acoustic absorption in re-cycled rubber granulate. Appl. Acoust. 1999, 57, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
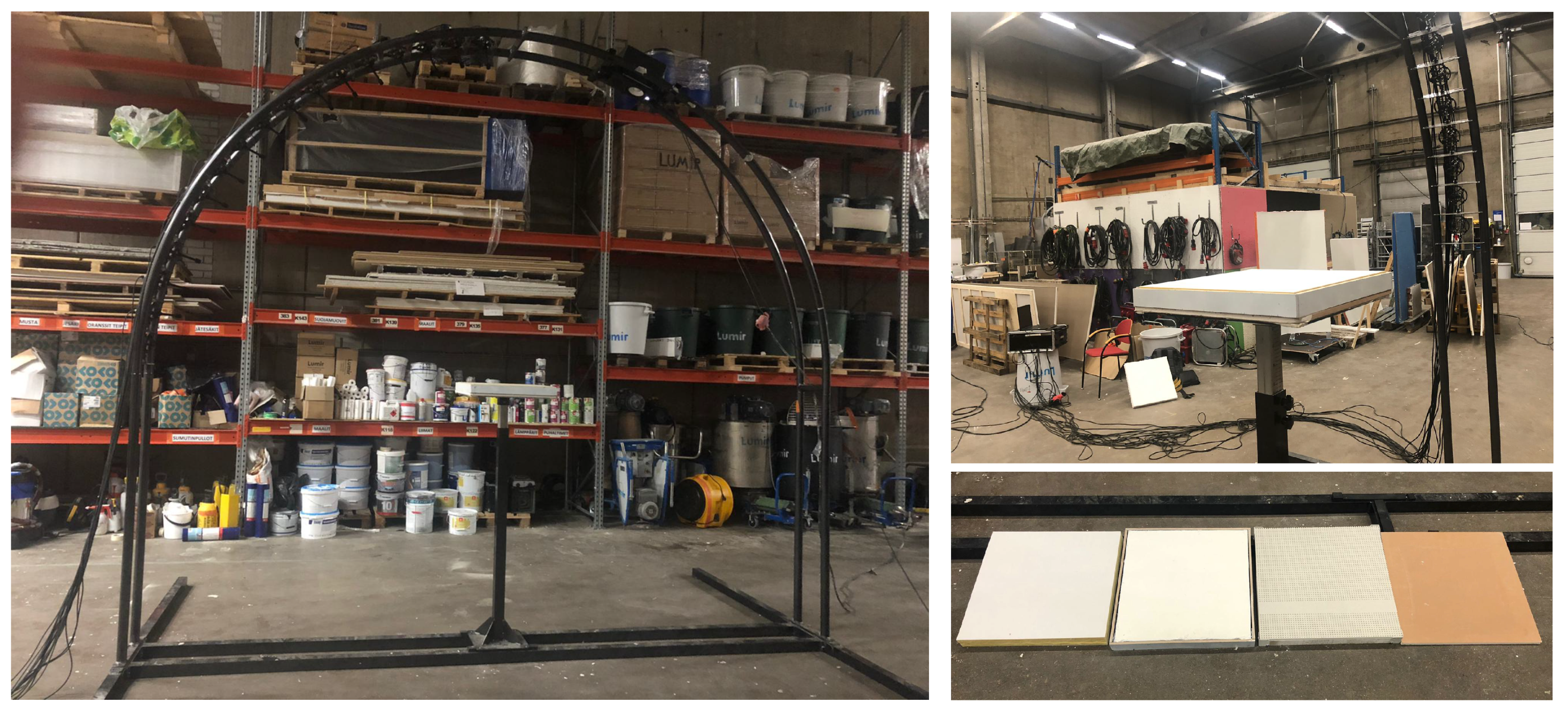
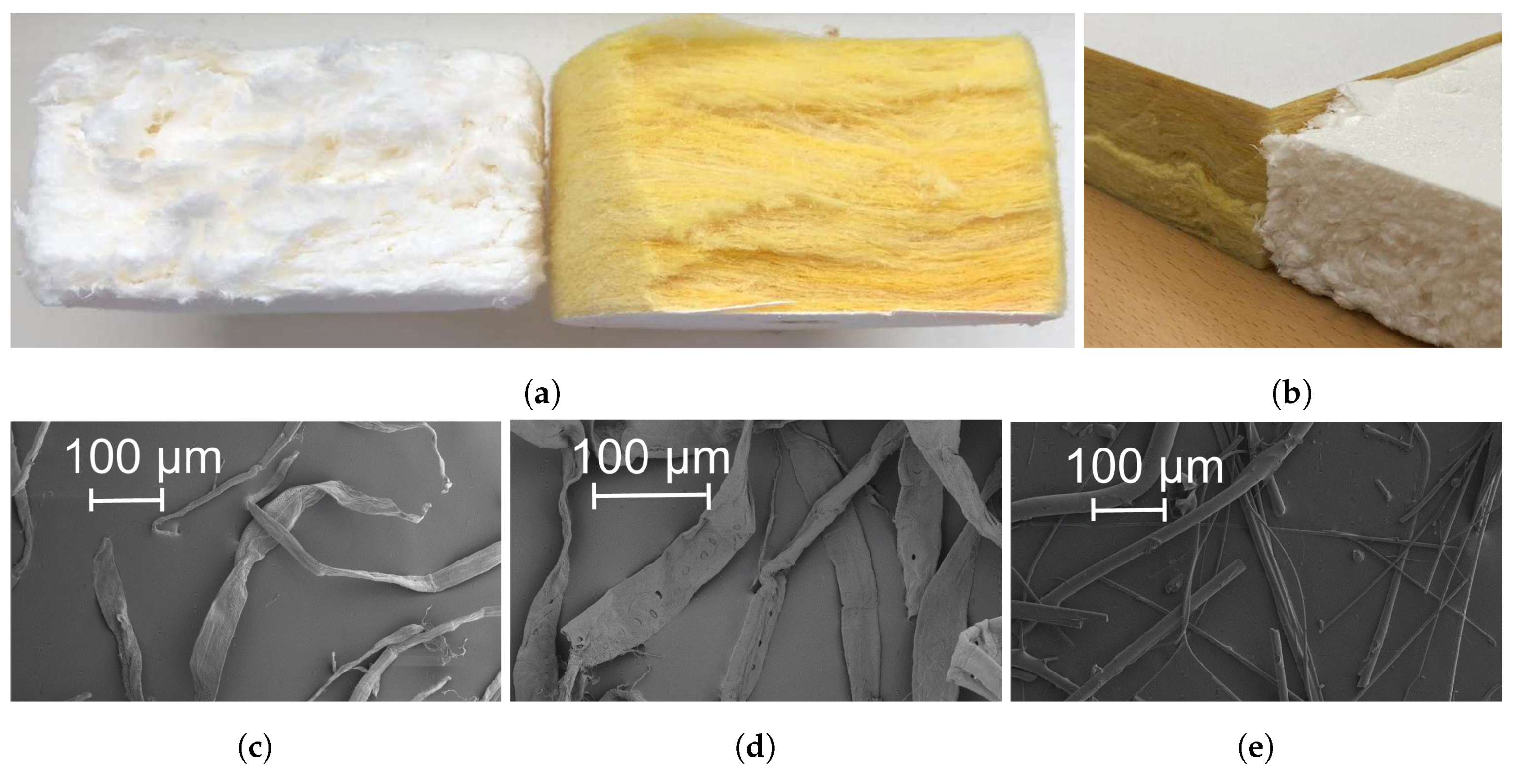

| Material | Manufacturer | o.d.s. | Density | % of Perforation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain gypsum | Knauf | 13 mm | ||
| Knauf | 13 mm + | Square 8 mm, 20% | ||
| 37 mm air-gap | ||||
| Perforated gypsum | Knauf | 13 mm + | Square 8 mm, 20% | |
| 17 mm air-gap + | ||||
| 20 mm stone wool | ||||
| Glass-wool | Ecophon | 50 mm | 52 kg/m | |
| Bioboard | Lumir | 47 mm | 60 kg/m |
| Fiber Type | Length (mm) | Width (m) | Curl (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.73 | 16.32 | 17.7 | |
| 1.97 | 25.36 | 15.4 | |
| 50–150 | 12 |
| Central Frequencies of the Octave Frequency Bands (Hz) | 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | 8000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dB) | 43.2 | 38.6 | 36.3 | 30.8 | 23.4 | 15.6 | 14.4 |
| 10, 15, 20 | 15 |
| 25, 30, 35 | 30 |
| 40, 45, 50 | 45 |
| 55, 60, 65 | 60 |
| 70, 75, 80 | 75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cucharero, J.; Hänninen, T.; Lokki, T. Angle-Dependent Absorption of Sound on Porous Materials. Acoustics 2020, 2, 753-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2040041
Cucharero J, Hänninen T, Lokki T. Angle-Dependent Absorption of Sound on Porous Materials. Acoustics. 2020; 2(4):753-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCucharero, Jose, Tuomas Hänninen, and Tapio Lokki. 2020. "Angle-Dependent Absorption of Sound on Porous Materials" Acoustics 2, no. 4: 753-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2040041
APA StyleCucharero, J., Hänninen, T., & Lokki, T. (2020). Angle-Dependent Absorption of Sound on Porous Materials. Acoustics, 2(4), 753-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2040041





