Experimental Study of Airfoil Leading Edge Combs for Turbulence Interaction Noise Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
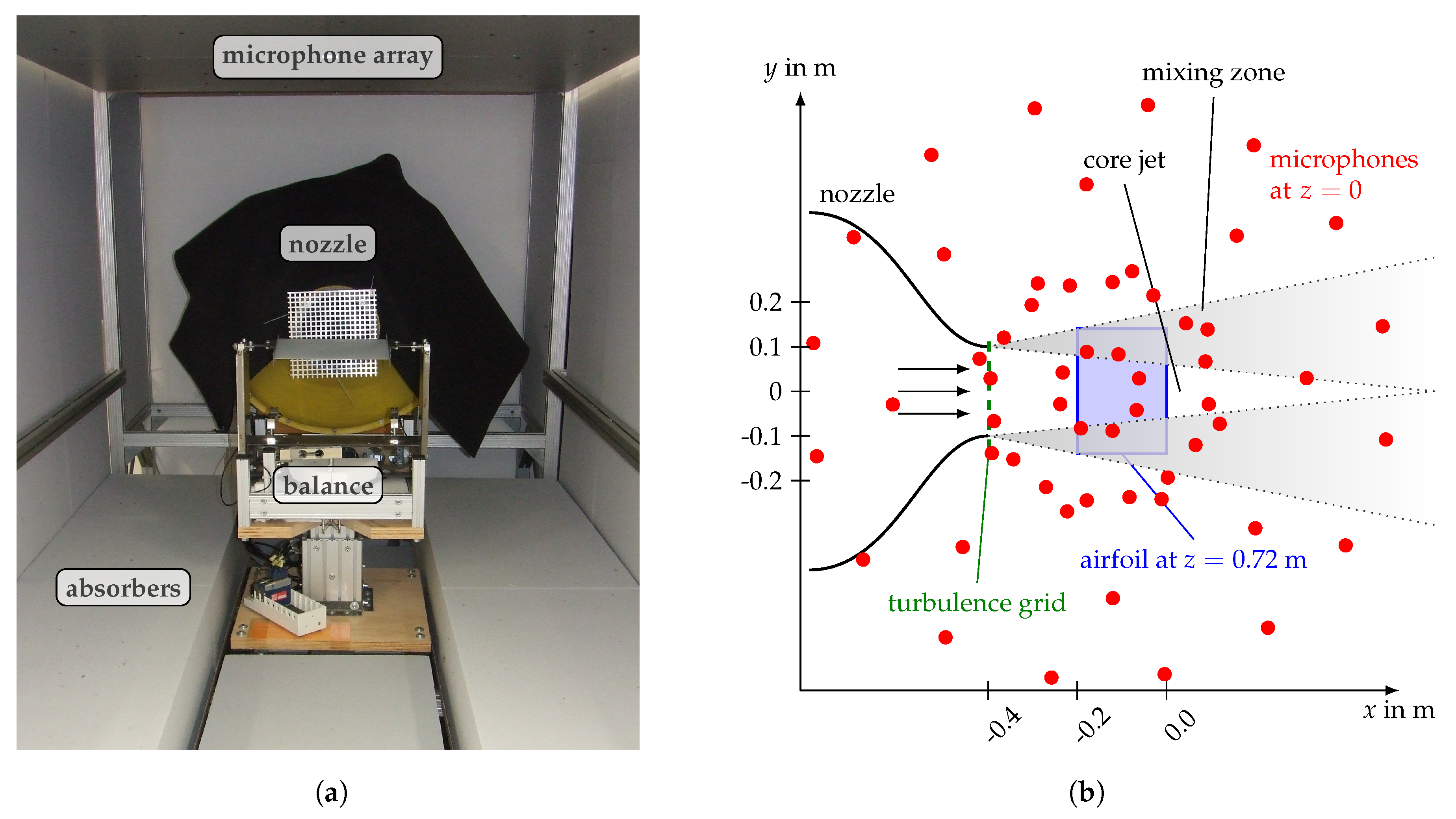
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Wind Tunnel
2.2. Generation of Incident Turbulence
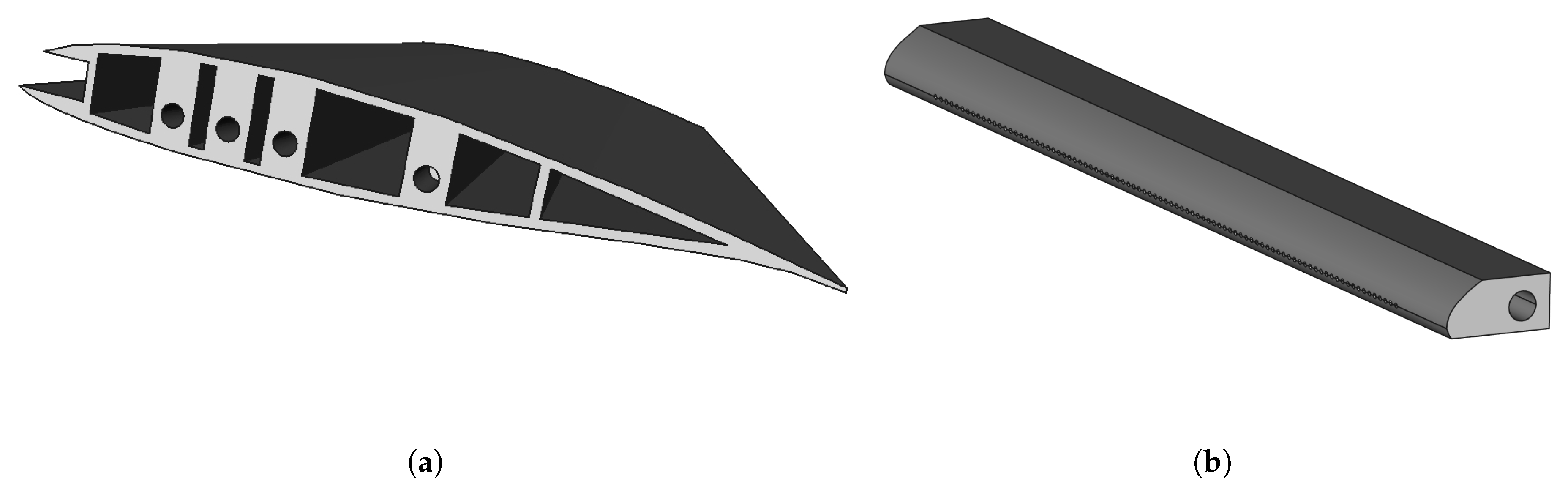
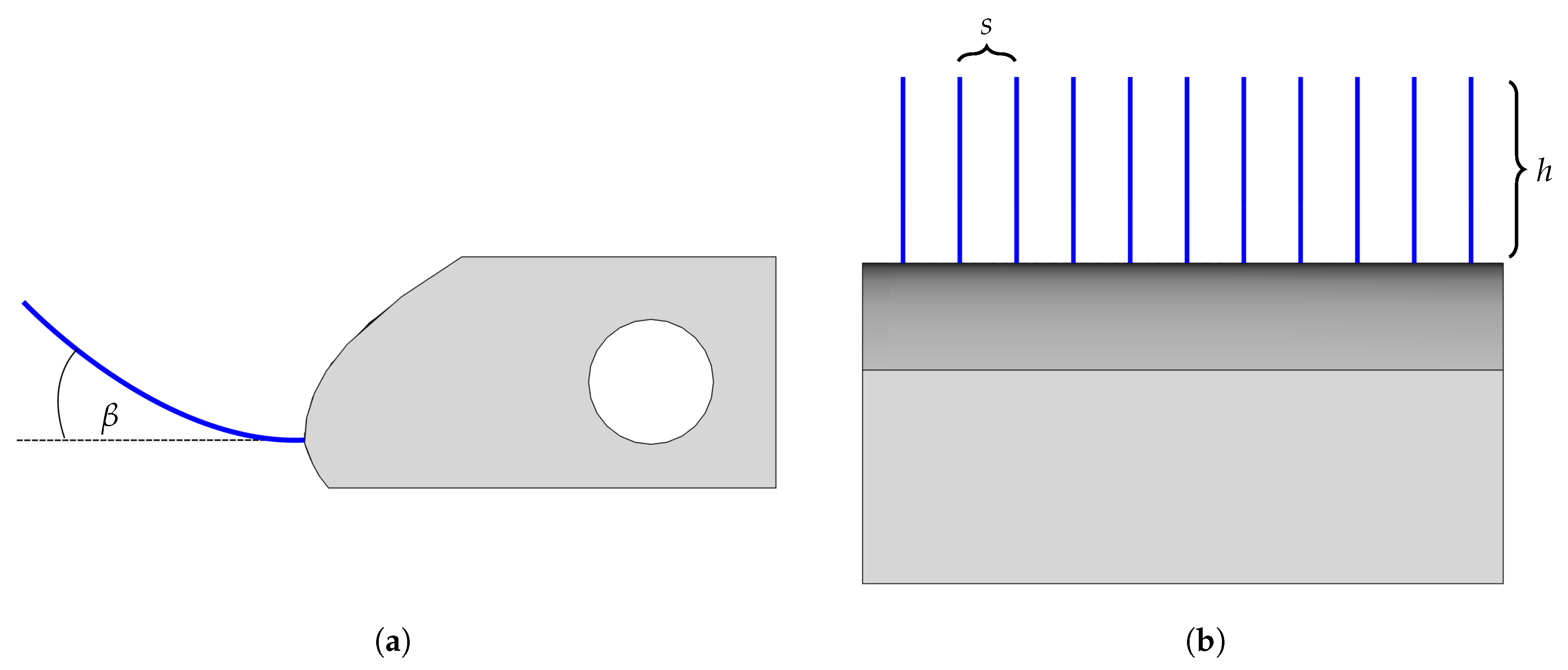
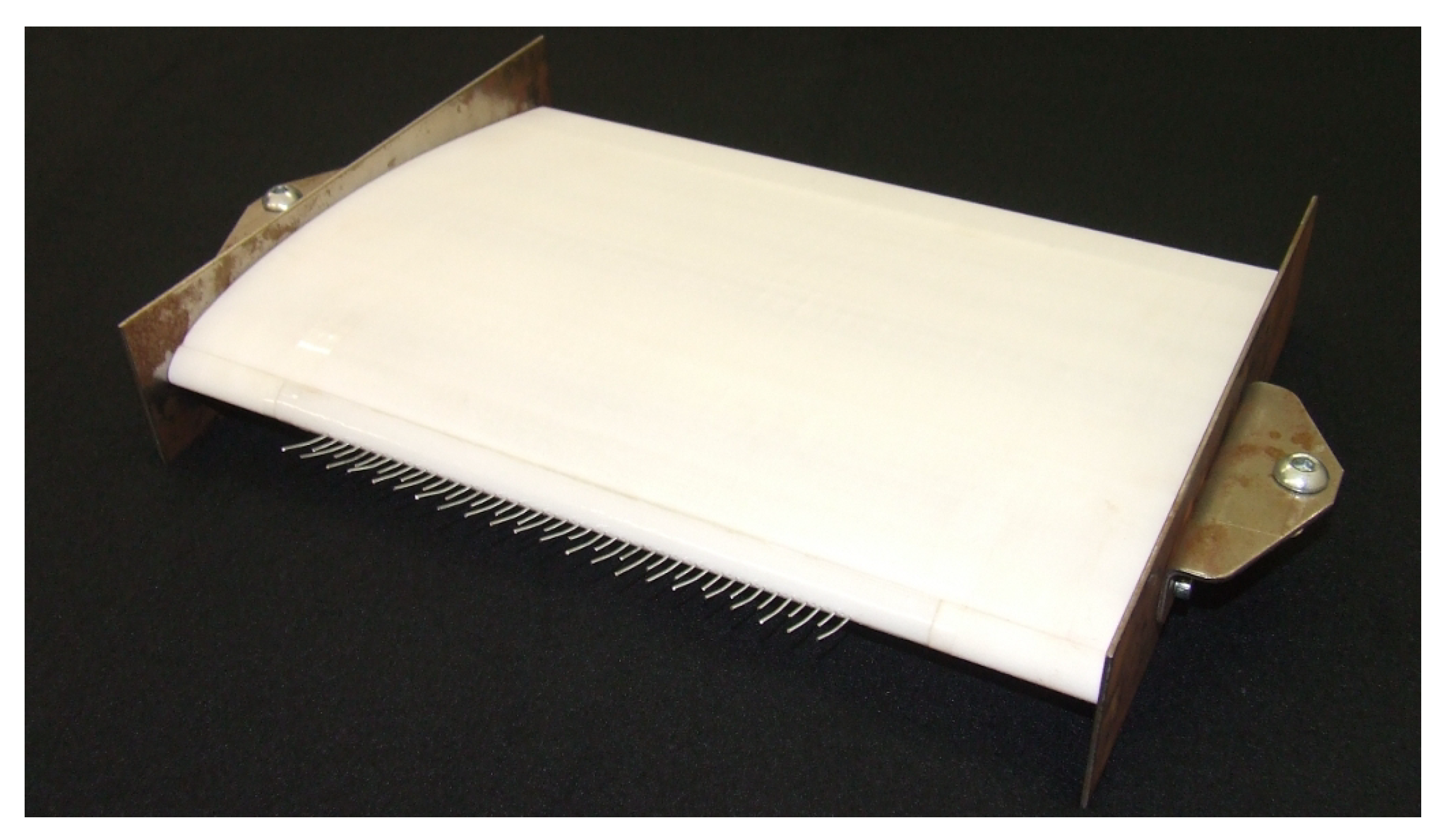
2.3. Leading Edge Comb Structures
2.4. Aerodynamic Measurements
2.5. Microphone Array and Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
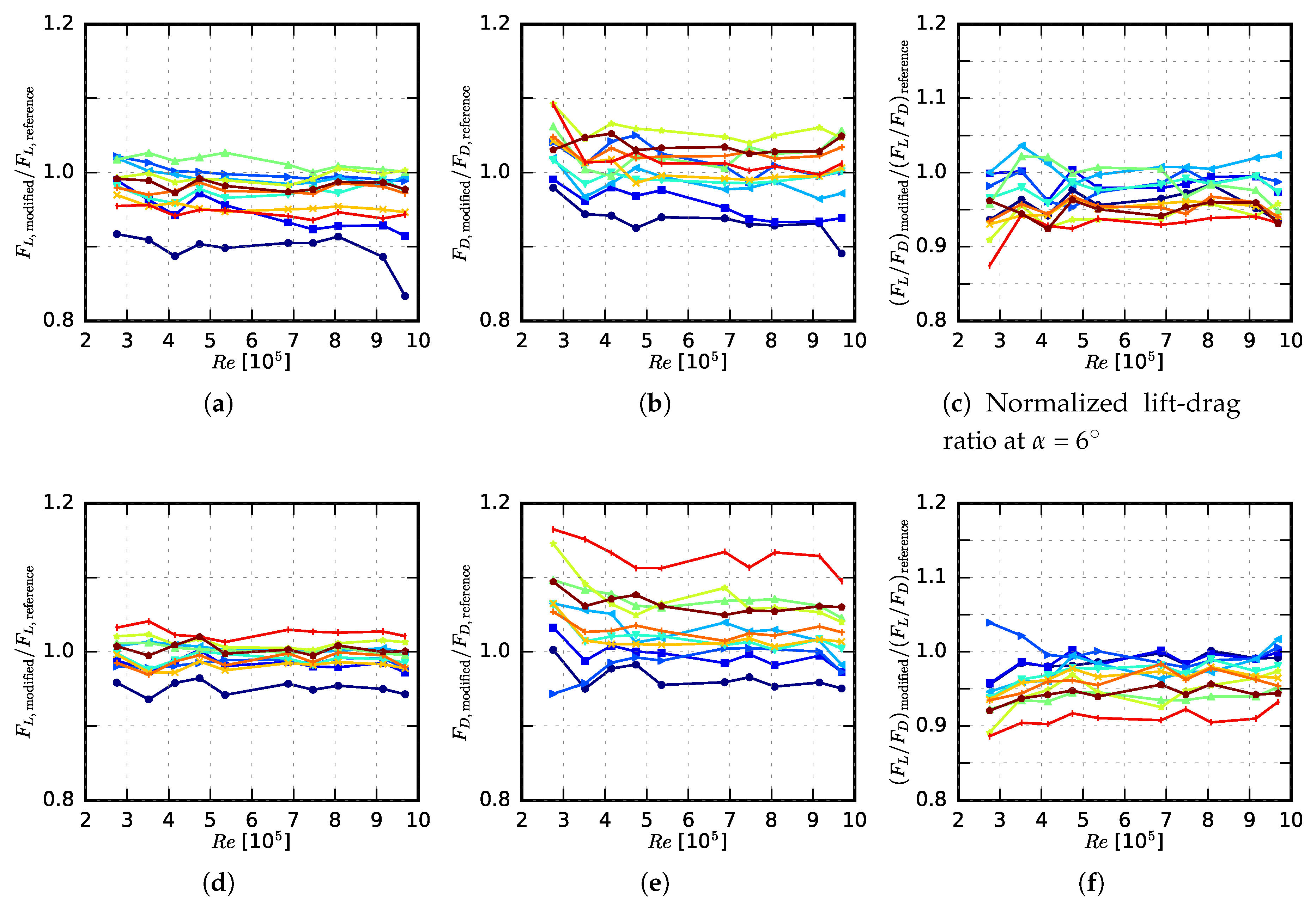
3.1. Aerodynamic Performance
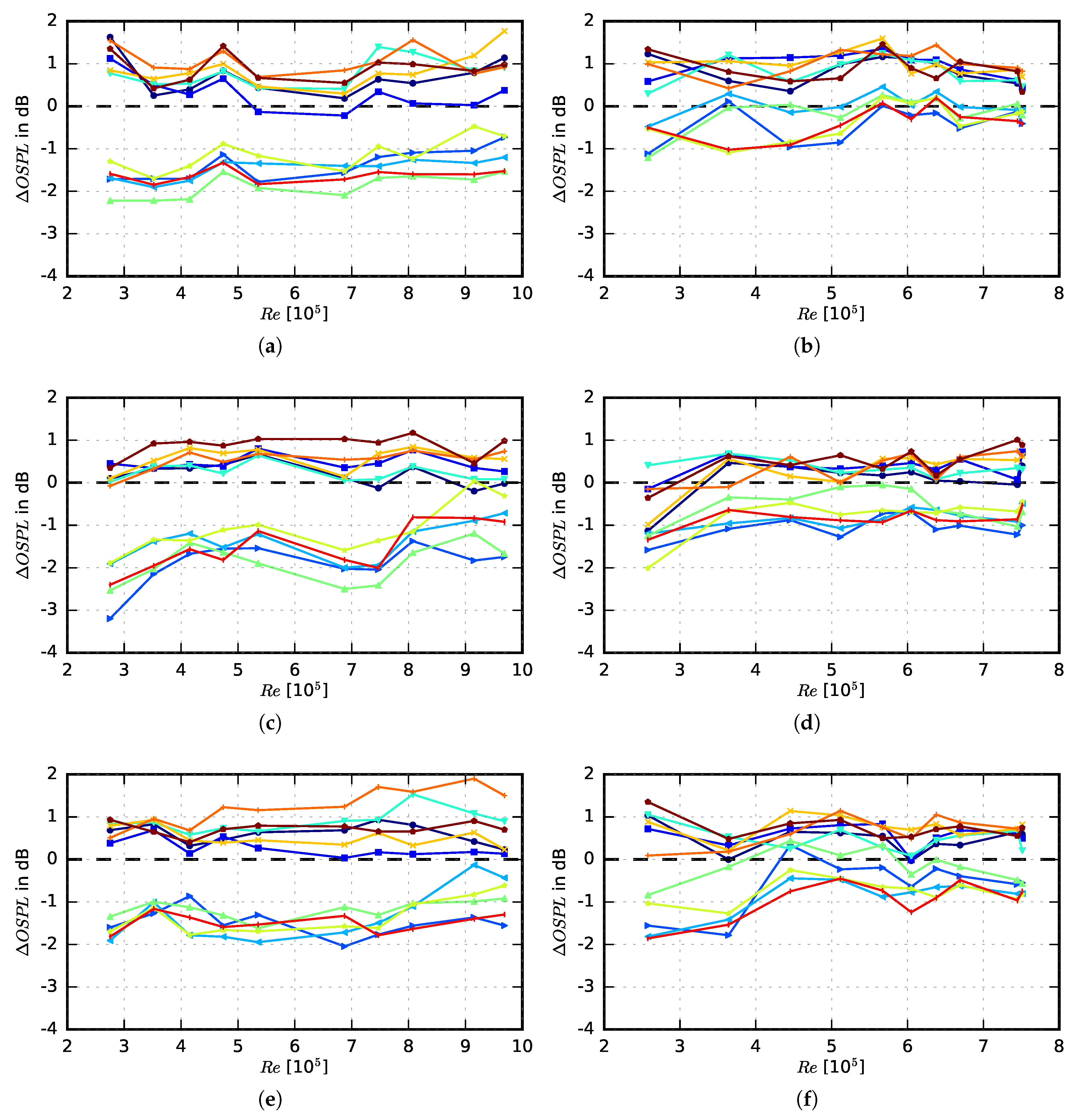
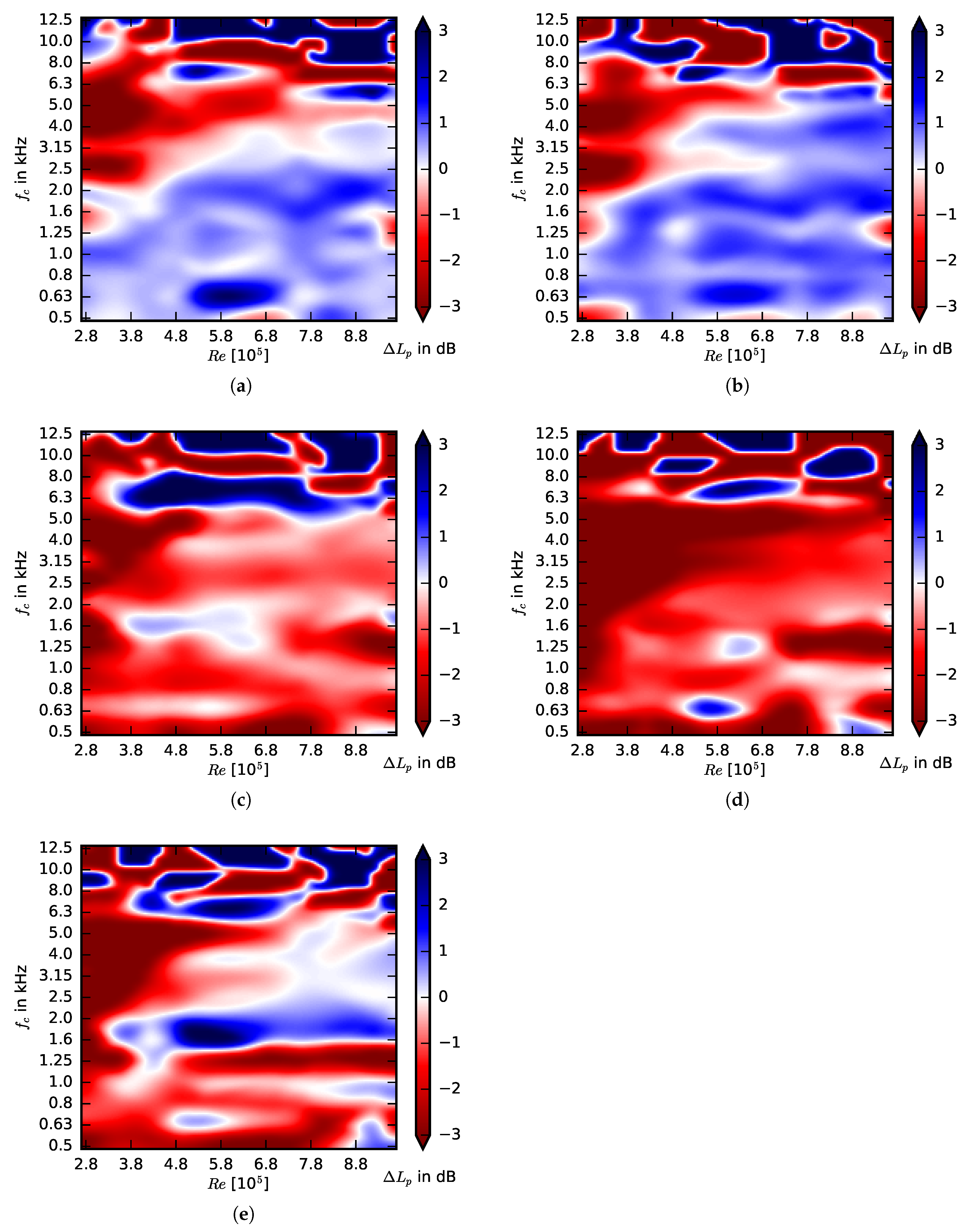
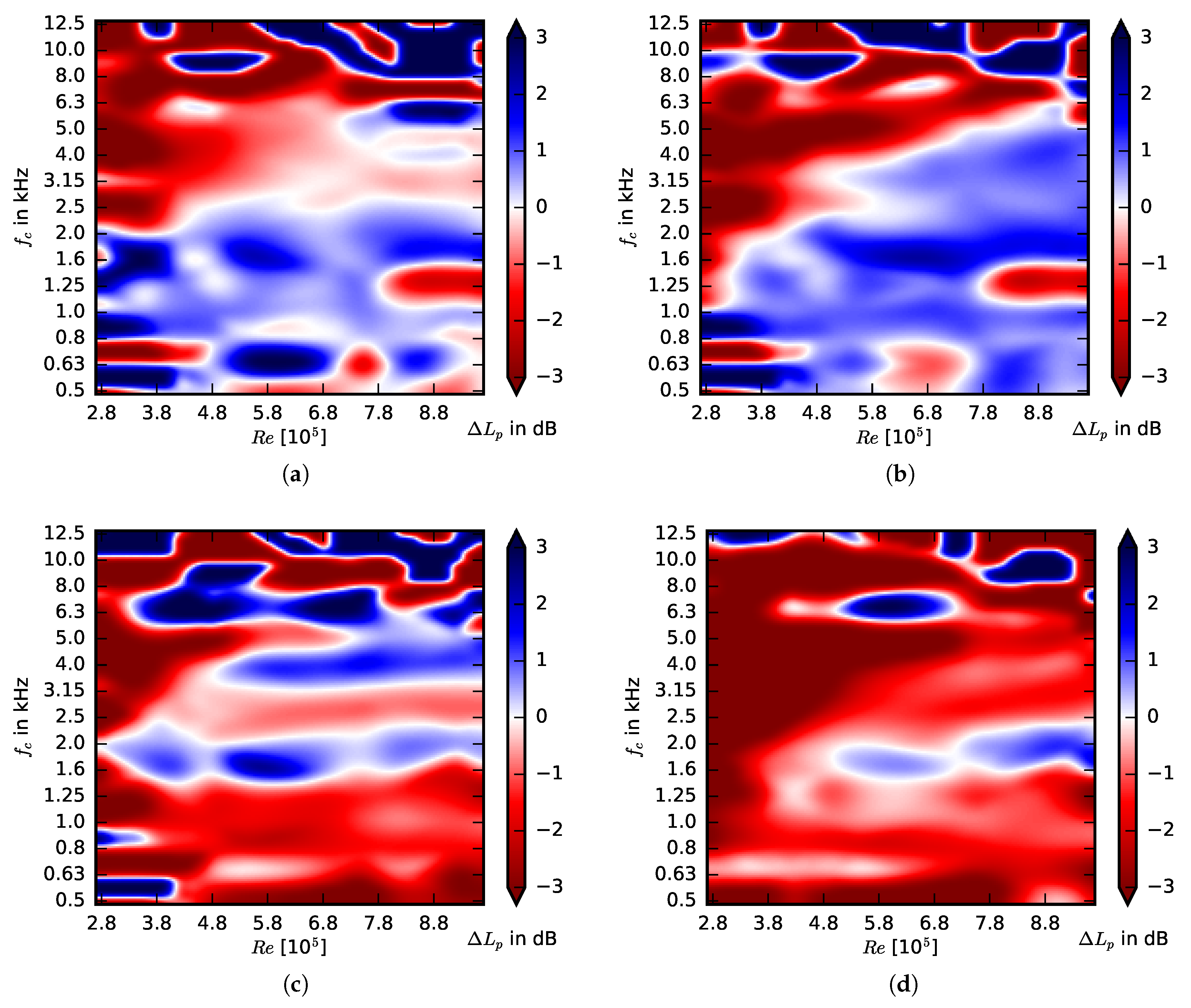
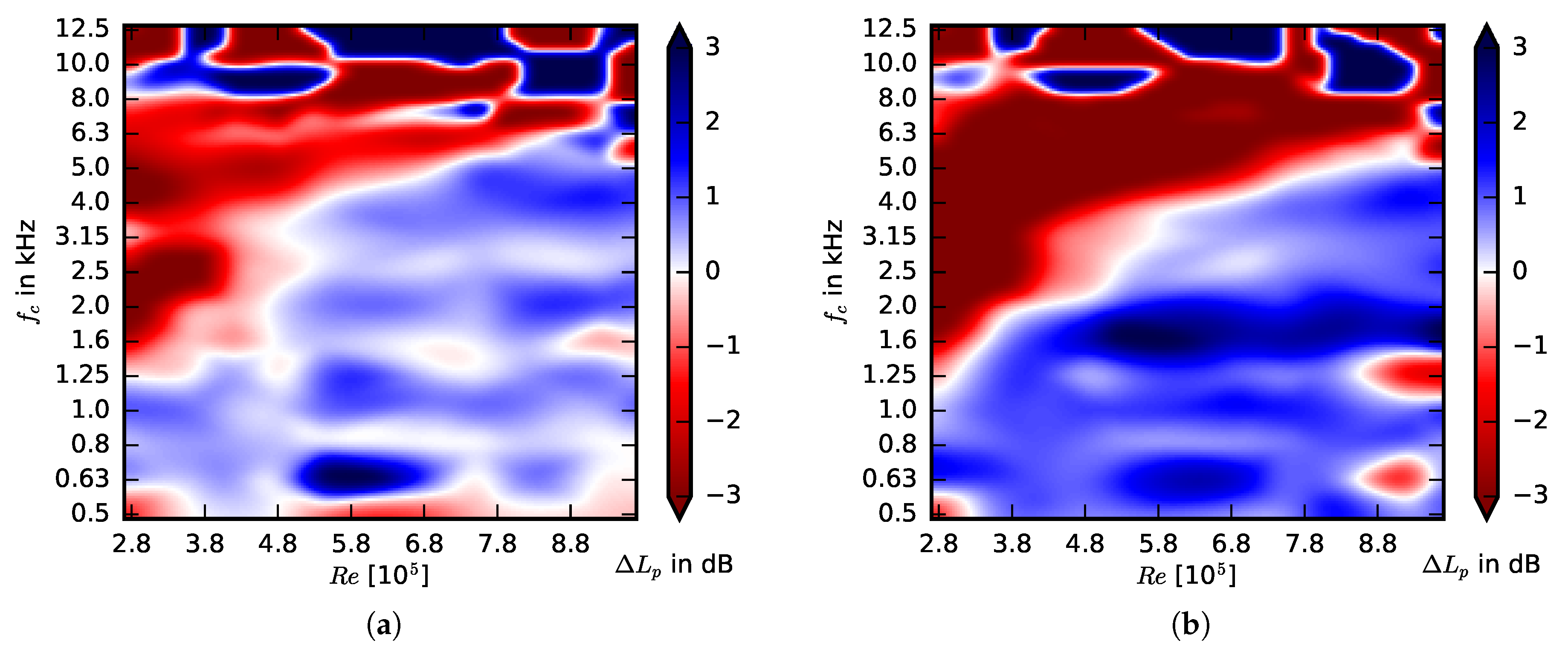
3.2. Acoustic Performance
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPS | Perforated Plate with Square holes |
References
- Soderman, P.T. Leading Edge Serrations Which Reduce the Noise of Low-Speed Rotors; Technical Report, NASA Technical Note D-7371; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1973.
- Hersh, A.S.; Soderman, P.T.; Hayden, R.E. Investigation of acoustic effects of leading-edge serrations on airfoils. J. Aircr. 1974, 11, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M.; Joseph, P.; Polacsek, C.; Chong, T.P. Noise reduction using combined trailing edge and leading edge serrations in a tandem airfoil experiment. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2012-2134, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, M.; Schram, C.; De Santana, L. Reduction of airfoil turbulence-impingement noise by means of leading-edge serrations and/or porous materials. In Proceedings of the 19th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2013-2108, Berlin, Germany, 27–29 May 2013; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Azarpeyvand, M.; Theunissen, R. Aerodynamic and Aeroacoustic Performance of Serrated Airfoils. In Proceedings of the 21st AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2015-2201, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, S.; Chaitanya, P.; Haeri, S.; Joseph, P.; Kim, J.W.; Polacsek, C. Airfoil noise reductions through leading edge serrations. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 025109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juknevicius, A.; Chong, T.P. On the leading edge noise and aerodynamics of thin aerofoil subjected to the straight and curved serrations. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 425, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.L.; Kelso, R.M.; Doolan, C.J. Reduction of flow induced tonal noise through leading edge tubercle modifications. In Proceedings of the 16th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2010-3700, Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 June 2010; Volume 3700. [Google Scholar]
- Polacsek, C.; Reboul, G.; Clair, V.; Le Garrec, T.; Deniau, H. Turbulence-airfoil interaction noise reduction using wavy leading edge: An experimental and numerical study. In Proceedings of the 40th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering (INTER-NOISE), Osaka, Japan, 4–7 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clair, V.; Polacsek, C.; Le Garrec, T.; Reboul, G.; Gruber, M.; Joseph, P. Experimental and numerical investigation of turbulence-airfoil noise reduction using wavy edges. AIAA J. 2013, 51, 2695–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, T.P.; Vathylakis, A.; McEwen, A.; Kemsley, F.; Muhammad, C.; Siddiqi, S. Aeroacoustic and aerodynamic performances of an aerofoil subjected to sinusoidal leading edges. In Proceedings of the 21st AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2015-2200, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P.; Narayanan, S.; Vanderwel, C.; Turner, J.; Kim, J.W.; Ganapathisubramani, B. Performance and mechanism of sinusoidal leading edge serrations for the reduction of turbulence–aerofoil interaction noise. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 818, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P.; Narayanan, S.; Kim, J. Aerofoil broadband noise reductions through double-wavelength leading-edge serrations: A new control concept. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 855, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biedermann, T.M.; Chong, T.P.; Kameier, F.; Paschereit, C.O. Statistical–Empirical Modeling of Airfoil Noise Subjected to Leading-Edge Serrations. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 3128–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, T.M.; Czeckay, P.; Geyer, T.F.; Kameier, F.; Paschereit, C.O. Effect of Inflow Conditions on the Noise Reduction Through Leading Edge Serrations. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 4104–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P. Slitted leading edge profiles for the reduction of turbulence-aerofoil interaction noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 3494–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geyer, T.F.; Sarradj, E.; Giesler, J.; Hobracht, M. Experimental assessment of the noise generated at the leading edge of porous airfoils using microphone array techniques. In Proceedings of the 17th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2011-2713, Portland, OR, USA, 5–8 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, T.F.; Lucius, A.; Schrödter, M.; Schneider, M.; Sarradj, E. Reduction of Turbulence Interaction Noise Through Airfoils With Perforated Leading Edges. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2019, 105, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.S.H.; Haeri, S.; Kim, J.W. The effect of wavy leading edges on aerofoil–gust interaction noise. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 6234–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Qiao, W.; Wang, L.; Tong, F.; Wang, X. Rod-Airfoil Interaction Noise Reduction Using Leading Edge Serrations. In Proceedings of the 21st AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2015-3264, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Haeri, S.; Joseph, P.F. On the reduction of aerofoil–turbulence interaction noise associated with wavy leading edges. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 792, 526–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathews, J.; Peake, N. Noise generation by turbulence interacting with an aerofoil with a serrated leading edge. In Proceedings of the 21st AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 2015-2204, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–26 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Frendi, A. Effect of airfoil leading edge waviness on flow structures and noise. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2016, 26, 1821–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Azarpeyvand, M. On the noise prediction for serrated leading edges. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 826, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayton, L.J. Analytic solution for aerodynamic noise generated by plates with spanwise-varying trailing edges. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 849, 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, F.; Qiao, W.; Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. On the study of wavy leading-edge vanes to achieve low fan interaction noise. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 419, 200–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Ayton, L.J.; Chaitanya, P. On the acoustic optimality of leading-edge serration profiles. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 462, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Reduction of Blade-Vortex Interaction Noise through Porous Leading Edge. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinetti, A.; Kelly, J.; Thomas, R.; Bauer, S. Reduction of Wake-Stator Interaction Noise Using Passive Porosity. In Proceedings of the 40th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, AIAA Paper 2002-1036, Reno, NV, USA, 14–17 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wasala, S.H.; Norris, S.E.; Cater, J.E. Wind turbine noise reduction by blade geometry modification. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Florence, Italy, 12–16 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.R. The silent flight of owls. J. R. Aeronaut. Soc. 1934, 286, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.F.; Claus, V.T.; Hall, P.M.; Sarradj, E. Silent owl flight: The effect of the leading edge comb. Int. J. Aeroacoust. 2017, 16, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, H. Struktur, Form, Bewegung; Otto Krauskopf-Verlag: Mainz, Germany, 1963; [translated version: Milton S. Katz (ed.), Structure, Form, Movement. Reinhold, New York (1966)]. [Google Scholar]
- Lilley, G. A study of the silent flight of the owl. In Proceedings of the 4th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 1998-2340, Toulouse, France, 2–4 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sarradj, E.; Fritzsche, C.; Geyer, T.F.; Giesler, J. Acoustic and Aerodynamic Design and Characterization of a Small-Scale Aeroacoustic Wind Tunnel. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.W. The Generation of Nearly Isotropic Turbulence by Means of Grids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1987, 8, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, T.; Fransson, J.H.M. Grid-generated turbulence revisited. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2009, 41, 021403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.F.; Hobracht, M.; Sarradj, E. Noise generated by a leading edge in anisotropic turbulence. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Hamburg, Germany, 2016; Volume 253, pp. 1176–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Turbulence, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, T.F.; Marcolini, M.A.; Pope, D.S. Airfoil Trailing Edge Flow Measurements and Comparison with Theorie incorporating Open Wind Tunnel Corrections. In Proceedings of the 9th AIAA/NASA Aeroacoustics Conference, AIAA Paper 84-2266, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 15–17 October 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sarradj, E. A fast ray casting method for sound refraction at shear layers. Int. J. Aeroacoust. 2017, 16, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijtsma, P. CLEAN based on Spatial Source Coherence. Int. J. Aeroacoust. 2007, 6, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarradj, E. Three-dimensional acoustic source mapping with different beamforming steering vector formulations. Adv. Acoust. Vib. 2012, 2012, 292695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johari, H.; Henoch, C.; Custodio, D.; Levshin, A. Effects of Leading-Edge Protuberances on Airfoil Performance. AIAA J. 2007, 45, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S. Aerodynamic Influence of Leading-Edge Serrations on an Airfoil in a Low Reynolds Number. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfeld, P. A trivariate Clough–Tocher scheme for tetrahedral data. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 1984, 1, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Bareiss, R.; Guidati, G. Wind Turbine Noise; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.A.; Daly, C.A.; Devenport, W.; Alexander, W.N.; Peake, N.; Jaworski, J.W.; Glegg, S. Bio-inspired canopies for the reduction of roughness noise. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 385, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, I.A.; Alexander, W.N.; Devenport, W.; Glegg, S.; Jaworski, J.W.; Daly, C.; Peake, N. Bioinspired trailing-edge noise control. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McTavish, S.; Feszty, D.; Nitzsche, F. Evaluating Reynolds number effects in small-scale wind turbine experiments. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 120, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Grid No. | Description | Mesh Width W (mm) | Bar Width b (mm) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PPS 12/2 | 12 | 2 | 69 |
| 2 | PPS 14/4 | 14 | 4 | 51 |
| No. | Normalized Teeth Length | Normalized Spacing between Teeth | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 0.038 | straight |
| 2 | 0.06 | 0.038 | straight |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.019 | straight |
| 4 | 0.06 | 0.019 | straight |
| 5 | 0.06/0.1 (alternating) | 0.019 | straight |
| 6 | 0.1 | 0.0095 | straight |
| 7 | 0.06 | 0.0095 | straight |
| 8 | 0.1 | 0.038 | curved |
| 9 | 0.06 | 0.038 | curved |
| 10 | 0.06 | 0.019 | curved |
| 11 | 0.06/0.1 (alternating) | 0.019 | curved |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geyer, T.F.; Wasala, S.H.; Sarradj, E. Experimental Study of Airfoil Leading Edge Combs for Turbulence Interaction Noise Reduction. Acoustics 2020, 2, 207-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020014
Geyer TF, Wasala SH, Sarradj E. Experimental Study of Airfoil Leading Edge Combs for Turbulence Interaction Noise Reduction. Acoustics. 2020; 2(2):207-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeyer, Thomas Fritz, Sahan Hasaranga Wasala, and Ennes Sarradj. 2020. "Experimental Study of Airfoil Leading Edge Combs for Turbulence Interaction Noise Reduction" Acoustics 2, no. 2: 207-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020014
APA StyleGeyer, T. F., Wasala, S. H., & Sarradj, E. (2020). Experimental Study of Airfoil Leading Edge Combs for Turbulence Interaction Noise Reduction. Acoustics, 2(2), 207-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics2020014





