Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Gut Microbiome and Hormonal Regulation
Abstract
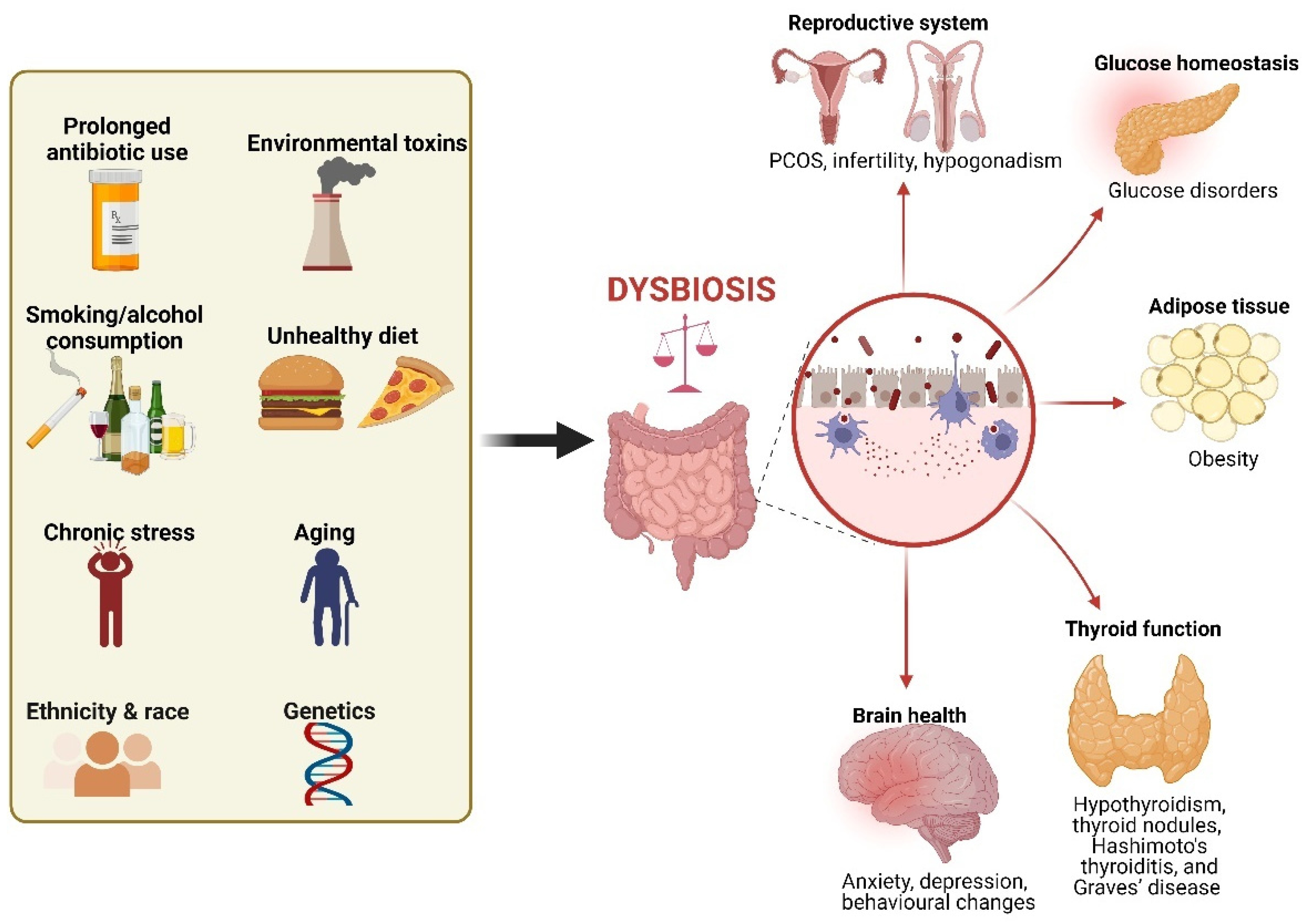
1. Introduction
2. Dysbiosis as a Possible Trigger of Hormonal Disorders
3. Probiotics: Definition, Mechanisms of Action, and Impact
4. Prebiotics: Definition, Mechanisms of Action, and Impact
5. Synergistic Effects of Probiotics and Prebiotics (Synbiotics)
6. Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Management of Endocrine Disorders
| Hormone of Interest | Main Findings | Proposed Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortisol, adrenocorticotropic hormone, (ACTH), aldosterone |
| Tendency to ↑ Cortisol ↑ ACTH ↑ Aldosterone ↑ Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 (Crhr1) mRNA levels ↓ Mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) mRNA levels | [24] |
| ↓ Urinary free cortisol in tested subjects | [47] | |
| ↓ Salivary cortisol | [96] | |
| ↓ Salivary cortisol | [73] | |
| Estrogen | Gut bacterial species containing β-glucuronidases and β-glucuronides enzymes are capable of metabolizing estrogens. | The deconjugation and conjugation of estrogen by the estrobolome modulate the enterohepatic circulation of estrogens, thereby affecting circulating and excreted estrogen levels | [97] |
| In men and postmenopausal women, the level of total urinary estrogens was strongly and directly associated with fecal microbiome richness. | Altering β-glucuronidase activity | [98] | |
| Dysbiosis may influence the progression of endometriosis in females. | ↓ Estrogen level | [27] | |
| ↑ Serum estradiol, upregulate estrogen Receptor α (ERα) in adipose tissue. ↑ SCFA production | [53] | |
| - | [52] | |
| Androgens |
| De-glucuronidation of DHT and testosterone | [52] |
| - | [52] | |
| Insulin |
| Disrupting insulin signaling | [99] |
| Altering host gut microbiota composition | [38] | |
| Increased intestinal permeability, lipopolysaccharide absorption, and inflammatory pathway activation | [100] | |
| ↓ Circulating inflammatory markers and insulin Improves the lipid profile and decreases the atherogenic index | [101] | |
| ↓ Bifidobacterium spp. ↓ Endotoxemia and plasma and adipose tissue proinflammatory cytokines ↑ Colonic mRNA levels of the GLP-1 precursor proglucagon | [102] | |
| Leptin, Ghrelin, GLP-1 |
| SCFAs modulate leptin release via activating GPR41 receptor SCFAs induce GLP-1 release through interacting with enteroendocrine cells SCFAs attenuate ghrelin-mediated signaling via the growth hormone secretagogue receptor-1a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) modulates GLP-1 release via TLR4 | [3,50] |
| ↑ GLP-1 production ↓ Serum ghrelin levels | [71] | |
| Thyroid |
| ↓ SCFA production ↓ Thyroxine levels | [31] |
7. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
8. Limitations, Future Directions, and Research Gaps
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Group, N.H.W.; Peterson, J.; Garges, S.; Giovanni, M.; McInnes, P.; Wang, L.; Schloss, J.A.; Bonazzi, V.; McEwen, J.E.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; et al. The NIH Human Microbiome Project. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijan, S. Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: An overview of recent literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4745–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.M.; Sun, E.W.; Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J. The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Host Metabolism Through the Regulation of Gut Hormone Release. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.J. Microbiome: Insulin signaling shapes gut community composition. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R803–R806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Tian, E.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Peng, Q. Gut microbiota and its roles in the pathogenesis and therapy of endocrine system diseases. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, H.; Debelius, J.W.; Knight, R.; Koren, O. Microbial endocrinology: The interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaie, S.; Nielsen, J. Elucidating the interactions between the human gut microbiota and its host through metabolic modeling. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockray, G.J. Gastrointestinal hormones and the dialogue between gut and brain. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2927–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastelli, M.; Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. The Gut Microbiome Influences Host Endocrine Functions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockray, G.J. Cholecystokinin. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2012, 19, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen-gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Kumari, R.; Dua, A.; Singh, M.; Kumar, R.; Singh, P.; Duyar-Ayerdi, S.; Pradeep, S.; Ojesina, A.I.; Kumar, R. From Gut to Hormones: Unraveling the Role of Gut Microbiota in (Phyto)Estrogen Modulation in Health and Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collden, H.; Landin, A.; Wallenius, V.; Elebring, E.; Fandriks, L.; Nilsson, M.E.; Ryberg, H.; Poutanen, M.; Sjogren, K.; Vandenput, L.; et al. The gut microbiota is a major regulator of androgen metabolism in intestinal contents. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E1182–E1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadchan, S.B.; Singh, V.; Kommagani, R. Female reproductive dysfunctions and the gut microbiota. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, R81–R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yun, C.; Pang, Y.; Qiao, J. The impact of the gut microbiota on the reproductive and metabolic endocrine system. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1894070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Hou, T.; Yang, H.; Wu, B.; Pan, R.; Huang, L. Gut microbiome and reproductive endocrine diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1164186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.E.; Baumler, A.J. Gut dysbiosis: Ecological causes and causative effects on human disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2316579120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkafas, H.; Walls, M.; Al-Hendy, A.; Ismail, N. Gut and genital tract microbiomes: Dysbiosis and link to gynecological disorders. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1059825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Syed, Y.A.; Khan, M.R. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Brain Development and Its Association With Neurodevelopmental Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 880544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.E.; Farzi, A.; Mayerhofer, R.; Reichmann, F.; Jacan, A.; Wagner, B.; Zinser, E.; Bordag, N.; Magnes, C.; Frohlich, E.; et al. Cognitive impairment by antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis: Analysis of gut microbiota-brain communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 56, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, R.; Zeng, B.; Zeng, L.; Cheng, K.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; Fang, L.; Li, W.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Anxiety-Like Behavior and Endocrine Abnormalities in Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609, 609e1–609e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremellen, K.; Pearce, K. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota (DOGMA)--a novel theory for the development of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukrainets, R.V.; Korneva, Y.S.; Dorosevich, A.E. Abnormal gut microbiota-induced hypoestrogenemia as a possible risk factor for malignancy in endometrioid heterotopia. Arkhiv Patol. 2020, 82, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markle, J.G.; Frank, D.N.; Mortin-Toth, S.; Robertson, C.E.; Feazel, L.M.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; von Bergen, M.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J.; Danska, J.S. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science 2013, 339, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Mazzola, M.; Bosco, V.; Tomasello, G.; Damiani, P.; Sinagra, E.; Carini, F. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Hormonal Neuroendocrine Secretion in the Fibromyalgic Patient: Relationship and Correlations. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Palacky Univ. Olomouc 2018, 162, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreznar, J.H.; Keller, M.P.; Traeger, L.L.; Rabaglia, M.E.; Schueler, K.L.; Stapleton, D.S.; Zhao, W.; Vivas, E.I.; Yandell, B.S.; Broman, A.T.; et al. Host Genotype and Gut Microbiome Modulate Insulin Secretion and Diet-Induced Metabolic Phenotypes. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, Z. Gut dysbiosis is associated with primary hypothyroidism with interaction on gut-thyroid axis. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 1521–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Feng, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wei, Y. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Patients. Thyroid 2018, 28, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, H.M.; Mohammad, I.S.; Shahzad, M.; Ma, C.; Raza, M.A.; Wu, X.; Guo, H.; Shi, P.; Xu, J. Molecular Alteration Analysis of Human Gut Microbial Composition in Graves’ disease Patients. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Q.; Liang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mu, X.; et al. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is associated with thyroid cancer and thyroid nodules and correlated with clinical index of thyroid function. Endocrine 2019, 64, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.; Wahl, R. Microbiota and Thyroid Interaction in Health and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanaki, C.; Peppa, M.; Mastorakos, G.; Chrousos, G.P. Examining the gut bacteriome, virome, and mycobiome in glucose metabolism disorders: Are we on the right track? Metabolism 2017, 73, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Backhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Shehzad, A.; Niazi, S.; Zahid, A.; Ashraf, W.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Riaz, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M.; et al. Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingenito, E.; Solway, J.; Lafleur, J.; Lombardo, A.; Drazen, J.M.; Pichurko, B. Dissociation of temperature-gradient and evaporative heat loss during cold gas hyperventilation in cold-induced asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, B.A.; Kebede, B. Probiotics, their prophylactic and therapeutic applications in human health development: A review of the literature. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahire, J.J.; Jakkamsetty, C.; Kashikar, M.S.; Lakshmi, S.G.; Madempudi, R.S. In Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 Isolated from Traditional Indigenous Fermented Food. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Cheng, W.N.; Choi, Y.; Shin, D.M.; Lee, S.; Han, S.G. Quality characteristics of yogurts fermented with short-chain fatty acid-producing probiotics and their effects on mucin production and probiotic adhesion onto human colon epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7415–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accettulli, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Speranza, B.; Campaniello, D.; Racioppo, A.; Altieri, C.; Bevilacqua, A. Psycho-Microbiology, a New Frontier for Probiotics: An Exploratory Overview. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyte, M. Probiotics function mechanistically as delivery vehicles for neuroactive compounds: Microbial endocrinology in the design and use of probiotics. Bioessays 2011, 33, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker-Ladefoged, C.; Langkamp, T.; Mueller-Alcazar, A. The Potential Impact of Selected Bacterial Strains on the Stress Response. Healthcare 2021, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Son, J.; Koekkoek, L.L.; La Fleur, S.E.; Serlie, M.J.; Nieuwdorp, M. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Gut-Brain Axis in Obesity: Mechanisms and Future Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Yang, X.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Gui, J.; Li, J. Association of probiotic ingestion with serum sex steroid hormones among pre- and postmenopausal women from the NHANES, 2013–2016. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota Structure with Probiotics and Isoflavone Alleviates Metabolic Disorder in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.M. The interplay between fiber and the intestinal microbiome in the inflammatory response. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.L.; Erickson, J.M.; Lloyd, B.B.; Slavin, J.L. Health Effects and Sources of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2018, 2, nzy005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Poola, S.; Uraz, S.; Tahan, V. Therapeutic Effects of Prebiotics on Constipation: A Schematic Review. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, D.; Payen, F.; Panserieu, S.; Coulombier, G.; Sobaszek, A.; Lartigau, I.; Brabet, M.; Galmiche, J.P.; Tripodi, D.; Sacher-Huvelin, S.; et al. The effects of regular consumption of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides on digestive comfort of subjects with minor functional bowel disorders. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.O.; Whelan, K.; Stagg, A.J.; Gobin, P.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Rayment, N.; Kamm, M.A.; Knight, S.C.; Forbes, A. Clinical, microbiological, and immunological effects of fructo-oligosaccharide in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gut 2006, 55, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Milner, J.A. Gastrointestinal microflora, food components and colon cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool-Zobel, B.L. Inulin-type fructans and reduction in colon cancer risk: Review of experimental and human data. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93 (Suppl. S1), S73–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollard, R.C.; Senechal, M.; MacIntosh, A.C.; Hay, J.; Wicklow, B.A.; Wittmeier, K.D.; Sellers, E.A.; Dean, H.J.; Ryner, L.; Berard, L.; et al. Dietary determinants of hepatic steatosis and visceral adiposity in overweight and obese youth at risk of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, M.P.; Nicolucci, A.C.; Reimer, R.A. Prebiotic supplementation improves appetite control in children with overweight and obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, T.; Kemps, E.; Bryan, J. Saccharide effects on cognition and well-being in middle-aged adults: A randomized controlled trial. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2010, 35, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurink, P.V.; van Esch, B.C.; Rijnierse, A.; Garssen, J.; Knippels, L.M. Mechanisms underlying immune effects of dietary oligosaccharides. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 572S–577S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Thomson, J.M.; Flint, H.J. The role of pH in determining the species composition of the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, E.C.; Odle, J.; Blikslager, A.T.; Ziegler, A.L. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Epithelial Tight Junctions: A Promising Approach to Modulate Intestinal Barrier Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Faseleh Jahromi, M.; Navidshad, B.; Liang, J.B. Effects of prebiotics on immune system and cytokine expression. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 206, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M. Modulation of glucagon-like peptide 1 and energy metabolism by inulin and oligofructose: Experimental data. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2547S–2551S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarini, J.; Wolever, T.M. The fermentable fibre inulin increases postprandial serum short-chain fatty acids and reduces free-fatty acids and ghrelin in healthy subjects. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 35, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J.; Tzortzis, G.; Errington, S.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Preter, V.; Raemen, H.; Cloetens, L.; Houben, E.; Rutgeerts, P.; Verbeke, K. Effect of dietary intervention with different pre- and probiotics on intestinal bacterial enzyme activities. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.K.; Kumari, I.; Singh, B.; Sharma, K.K.; Tiwari, S.K. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: Safe options for next-generation therapeutics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, S.M.; Gibbons, S.M. Designing synbiotics for improved human health. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.S.; Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Reimer, R.A.; Reid, G.; Verbeke, K.; Scott, K.P.; Holscher, H.D.; Azad, M.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, S.; Banakar, P.S.; Vinay, V.V.; Das, A.; Tyagi, N.; Tyagi, A.K. Synbiotic formulation of Cichorium intybus root powder with Lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC15 and Lactobacillus reuteri BFE7 improves growth performance in Murrah buffalo calves via altering selective gut health indices. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaian, N.; Feizi, A.; Aminorroaya, A.; Amini, M. Probiotic and synbiotic supplementation could improve metabolic syndrome in prediabetic adults: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2991–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafoury, M.E.; Ebrahim, A.T.; Abd-El Hamid Ali, M.S.; Shaker Mehanna, N.; Ibrahim Ramadan, G.E.; Ezzat Morsy, W. Short chain fatty acids and GIT hormones mitigate gut barrier disruption in high fat diet fed rats supplemented by synbiotics. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 16, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemi, Z.; Aarabi, M.H.; Hajijafari, M.; Alizadeh, S.A.; Razzaghi, R.; Mazoochi, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of Synbiotic Food Consumption on Serum Minerals, Liver Enzymes, and Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Double-blind Randomized Cross-over Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Slizewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurry, T. Synbiotic approaches to human health and well-being. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier, D.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Kolida, S. In vitro effects of selected synbiotics on the human faecal microbiota composition. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, B.; Cuk, A.; Hugl, S.; Buttner, R.; Straub, R.H.; Bauer, B.; Daffner, P.; Scholmerich, J.; Palitzsch, K. Association of increased C-peptide serum levels and testosterone in type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 11, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, S.; Kimura, Y.; Sugawara, H.; Kato, Y.; Sekino, H. Effectiveness of pyrodifenium bromide (Padrin) on diseases of the urinary tract. Hinyokika Kiyo 1967, 13, 699–701. [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren, L.; Butler, E.; Axelsson, J.; Astrom, M.; Ohlsson, L. Effects of probiotic supplementation on testosterone levels in healthy ageing men: A 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2024, 39, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Chen, Y.C. Association of the consumption of common drinks with early puberty in both sexes. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 854477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: New signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julich, H.; Klink, K.; Heberling, H.J.; Burkmann, I. Methods of cardiopulmonary functional diagnosis for the expert evaluation of heart patients. Z. Gesamte Inn. Med. 1974, 29, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Skjerve, E.; Wasteson, Y. The situation from Norway’s point of view ecological and health consequences of spreading of pathogenes and genes through an increasing trade in foods. Acta Vet. Scand. Suppl. 1999, 91, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagowska, K.; Malinowska, A.M.; Zawieja, B.; Zawieja, E. Improvement of glucose metabolism in pregnant women through probiotic supplementation depends on gestational diabetes status: Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooy, A.; de Jager, J.; Lehert, P.; Bets, D.; Wulffele, M.G.; Donker, A.J.; Stehouwer, C.D. Long-term effects of metformin on metabolism and microvascular and macrovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.A.; Doughman, T.; Hayes, P.; Nicholson, M.L. The deep circumflex iliac vein for secondary central venous access and haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kenyon, C.J.; Saccoccio, N.A.; Morris, D.J. Aldosterone effects on water and electrolyte metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 1984, 100, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.P.; Hutch, W.; Borre, Y.E.; Kennedy, P.J.; Temko, A.; Boylan, G.; Murphy, E.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Bifidobacterium longum 1714 as a translational psychobiotic: Modulation of stress, electrophysiology and neurocognition in healthy volunteers. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plottel, C.S.; Blaser, M.J. Microbiome and malignancy. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.; Shi, J.; Fuhrman, B.; Xu, X.; Veenstra, T.D.; Gail, M.H.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Goedert, J.J. Fecal microbial determinants of fecal and systemic estrogens and estrogen metabolites: A cross-sectional study. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay-Kumar, M.; Aitken, J.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Cullender, T.C.; Mwangi, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 2010, 328, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricilli, A.M.; Saad, M.J. The role of gut microbiota on insulin resistance. Nutrients 2013, 5, 829–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, H.; Mahmood, N.; Kumar, M.; Varikuti, S.R.; Challa, H.R.; Myakala, S.P. Effect of probiotic (VSL#3) and omega-3 on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, inflammatory markers, and gut colonization in overweight adults: A randomized, controlled trial. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 348959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Knauf, C.; Burcelin, R.G.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Delzenne, N.M. Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Lavergne, V.; Skinner, A.M.; Gonzales-Luna, A.J.; Garey, K.W.; Kelly, C.P.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 Focused Update Guidelines on Management of Clostridioides difficile Infection in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1029–e1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvede, M.; Rask-Madsen, J. Bacteriotherapy for chronic relapsing Clostridium difficile diarrhoea in six patients. Lancet 1989, 1, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamo, Y.; Woodworth, M.H.; Wang, T.; Dhere, T.; Kraft, C.S. Durability and Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Fecal Microbiota Transplant Treatment in Patients With Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Murri, R.; Sciume, G.D.; Impagnatiello, M.; Masucci, L.; Ford, A.C.; Law, G.R.; Tilg, H.; Sanguinetti, M.; Cauda, R.; et al. Incidence of Bloodstream Infections, Length of Hospital Stay, and Survival in Patients With Recurrent Clostridioides difficile Infection Treated With Fecal Microbiota Transplantation or Antibiotics: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boicean, A.; Birlutiu, V.; Ichim, C.; Brusnic, O.; Onisor, D.M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Liver Cirrhosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, R.C.; Jones, S.J.; Rose, A.M. Mutational accessibility of essential genes on chromosome I(left) in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000, 263, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Borgo, F.; Falvo, E.; Caruso, D.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Steroidogenic machinery in the adult rat colon. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 203, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinkler, M.; Bumke-Vogt, C.; Meyer, B.; Bahr, V.; Oelkers, W.; Diederich, S. The human kidney is a progesterone-metabolizing and androgen-producing organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goascogne, C.; Sananes, N.; Eychenne, B.; Gouezou, M.; Baulieu, E.E.; Robel, P. Androgen biosynthesis in the stomach: Expression of cytochrome P450 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase messenger ribonucleic acid and protein, and metabolism of pregnenolone and progesterone by parietal cells of the rat gastric mucosa. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinkler, M.; Sinha, B.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Bujalska, I.J.; Stewart, P.M.; Arlt, W. Androgen generation in adipose tissue in women with simple obesity--a site-specific role for 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, R.M.; Netzer, G.; Hunsicker, L.; Mitchell, B.D.; Rajagopal, K.; Scharf, S.; Eberlein, M. Cardiac size and sex-matching in heart transplantation: Size matters in matters of sex and the heart. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boicean, A.; Ichim, C.; Todor, S.B.; Anderco, P.; Popa, M.L. The Importance of Microbiota and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Pancreatic Disorders. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.T.; Rosas, S.L.B.; Ribeiro, B.E.; Marinho, Y.; de Souza, H.S.P. Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.J.; Barna, V.; Patoni, C.; Demeter, D.; Veres, D.S.; Bunduc, S.; Eross, B.; Hegyi, P.; Foldvari-Nagy, L.; Lenti, K. Probiotic supplementation during antibiotic treatment is unjustified in maintaining the gut microbiome diversity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, E.D.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Starving our microbial self: The deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, D.; Patel, S.; Kim, S.K. Probiotic supplements might not be universally-effective and safe: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basnet, J.; Eissa, M.A.; Yanes Cardozo, L.L.; Romero, D.G.; Rezq, S. Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Gut Microbiome and Hormonal Regulation. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 801-815. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6040056
Basnet J, Eissa MA, Yanes Cardozo LL, Romero DG, Rezq S. Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Gut Microbiome and Hormonal Regulation. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2024; 6(4):801-815. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasnet, Jelina, Manar A. Eissa, Licy L. Yanes Cardozo, Damian G. Romero, and Samar Rezq. 2024. "Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Gut Microbiome and Hormonal Regulation" Gastrointestinal Disorders 6, no. 4: 801-815. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6040056
APA StyleBasnet, J., Eissa, M. A., Yanes Cardozo, L. L., Romero, D. G., & Rezq, S. (2024). Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Gut Microbiome and Hormonal Regulation. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 6(4), 801-815. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6040056






