Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Related Sepsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Predisposing Factors for NEC
3. Biomolecular Mechanisms of NEC
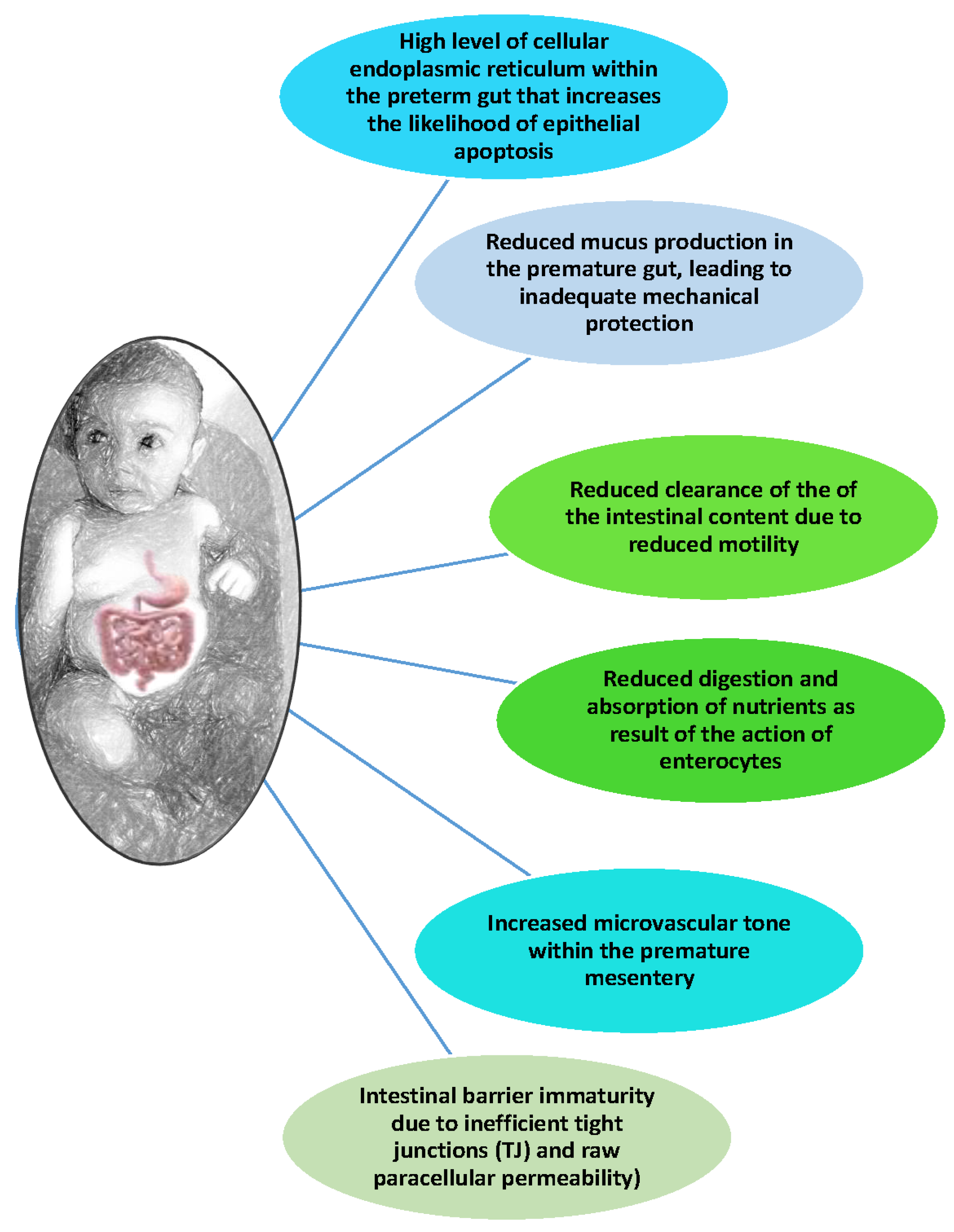
3.1. Hyperactive Premature Intestine and Inflammatory Response
3.2. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sylvester, K.G.; Liu, G.Y.; Albanese, C.T. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. In Pediatric Surgery (Ch. 94), 7th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1187–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbi-Goutel, A.; Brévaut-Malaty, V.; Panuel, M.; Michel, F.; Merrot, T.; Gire, C. Prognostic value of abdominal sonography in necrotizing enterocolitis of premature infants born before 33 weeks gestational age. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 49, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenton, A.B.; O’Donovan, D.; Cass, D.L.; Helmrath, M.A.; Smith, E.O.; Fernandes, C.J.; Washburn, K.; Weihe, E.K.; Brandt, M.L. Severe thrombocytopenia predicts outcome in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzarro, M.J.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Gallagher, P.G. Concurrent bloodstream infections in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, G.; Carta, M.; Cimador, M.; Corsello, A.; Giuffrè, M.; Schierz, I.A.M.; Serra, G.; Corsello, G. Necrotizing enterocolitis in the preterm: Newborns medical and nutritional Management in a Single-Center Study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J. Emerging trends in neonatal intestinal disease. J. Perinatol. 2008, 28, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gephart, S.M.; McGrath, J.M.; Effken, J.A.; Halpern, M.D. Necrotizing enterocolitis risk: State of the science. Adv. Neonatal Care 2012, 12, 77–87; quiz 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, W.T. Necrotizing enterocolitis: Etiology, presentation, management, and outcomes. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 2009, 23, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, J.; Sriram, S.; Patton, T.; Jericho, H.; Gokhale, R.; Weinstein, D.; Sentongo, T. Manifestations of Cow’s-Milk Protein Intolerance in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.R.; Rellinger, E.J.; Hatch, L.D.; Weitkamp, J.-H.; Speck, K.E.; Danko, M.; Blakely, M.L. Surgical necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Polin, R.A. Treatment and prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Neonatol. 2003, 8, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaied, A.; Islam, N.; Thalib, L. Global incidence of Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, A.; Pierro, A. Necrotizing enterocolitis: Controversies and challenges. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, W. The predictors of necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns with low birth weight: A retrospective analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e28789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, G.; Yu, M.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Duan, L.; Huang, L. Analysis of Factors Influencing Outcomes in Preterm Infants With Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 768107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergenekon, E.; Tayman, C.; Özkan, H. Turkish Neonatal Society Necrotizing Enterocolitis Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention Guidelines. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2021, 56, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, W.H.; Soraisham, A.S.; Shah, V.S.; Aziz, K.; Yoon, W.; Lee, S.K.; Canadian Neonatal Network. Incidence and timing of presentation of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e298–e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Castellaneta, F.; D’agostino, D. Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Subbarao, G.C.; Maheshwari, A. Haematological abnormalities in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25 (Suppl. S4), 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Serio, F.; Lovero, R.; D’Agostino, D.; Nisi, L.; Miragliotta, G.; Contino, R.; Man, A.; Ciccone, M.M.; Santacroce, L. Evaluation of procalcitonin, Vitamin D and C-reactive protein levels in septic patients with positive emocoltures. Our preliminary experience. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Colella, M.; Charitos, I.A.; Di Domenico, M.; Palmirotta, R.; Jirillo, E. Microbial and Host Metabolites at the Backstage of Fever: Current Knowledge about the Co-Ordinate Action of Receptors and Molecules Underlying Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Metabolites 2023, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.C.; Sadeghirad, B.; Florez, I.D.; Chang, Y.; Forutan, F.; Zeraatkar, D.; Morgan, R.L.; Shahid, S.; Bala, M.M.; Beyene, J.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Prophylactic Therapies for Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: Protocol for a Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottalico, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The war against bacteria, from the past to present and beyond. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 681–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Di Domenico, M.; Montagnani, M.; Jirillo, E. Antibiotic Resistance and Microbiota Response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginglen, J.G.; Butki, N. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513357/ (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Chauhan, K.; Kashif, S.; Awadalla, S. Role of the Penrose drain in the management of VLBW infants with perforated necrotising enterocolitis. Ir. Med. J. 2007, 100, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, C. Early postoperative outcomes of surgery for intestinal perforation in NEC based on intestinal location of disease. Medicine 2018, 97, e12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplina, A.; Kononova, S.; Zaikova, E.; Pervunina, T.; Petrova, N.; Sitkin, S. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of Hypoxia, Gut Microbiome, and Microbial Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-L.; An, Y.; He, Y.; Hu, X.-Y.; Guo, L.; Li, Q.-Y.; Liu, L.; Li, L.-Q. Risk factors of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates with sepsis: A retrospective case-control study. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420963818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, S.e.M.e.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Derikx, J.P.M.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; Ballón, A.E.; de Graaf, M.; de Boode, W.P.; Cossey, V.; Hulzebos, C.V.; van Kaam, A.H.; et al. Predictive factors for surgical treatment in preterm neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis: A multicenter case-control study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Graham, E. Preterm birth: An overview of risk factors and obstetrical management. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2010, 16, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cionci, N.B.; Lucaccioni, L.; Pietrella, E.; Ficara, M.; Spada, C.; Torelli, P.; Bedetti, L.; Lugli, L.; Di Gioia, D.; Berardi, A. Antibiotic Exposure, Common Morbidities and Main Intestinal Microbial Groups in Very Preterm Neonates: A Pilot Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R.J.; Chambers, C.D.; Ryckman, K.K.; Oltman, S.P.; Rand, L.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L. Risk of preterm and early term birth by maternal drug use. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. National Institute on Drug Abuse. Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/substance-use-in-women/substance-use-while-pregnant-breastfeeding (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Stafford, I.A.; Rodrigue, E.; Berra, A.; Adams, W.; Heard, A.J.; Hagan, J.L.; Stafford, S.J. The strong correlation between neonatal early-onset Group B Streptococcal disease and necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 223, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Obstetric Care consensus No. 6: Periviable Birth. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 130, e187–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilanova, C.S.; Hirakata, V.N.; Buriol, V.C.d.S.; Nunes, M.; Goldani, M.Z.; da Silva, C.H. The relationship between the different low birth weight strata of newborns with infant mortality and the influence of the main health determinants in the extreme south of Brazil. Popul. Health Metr. 2019, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzi, G.; Santoro, G. Patent ductus arteriosus: Patho-physiology, hemodynamic effects and clinical complications. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2011, 24 (Suppl. S1), 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, J.L.; Reagan, P.B.; Bapat, R.V.; Newman, T.B.; Klebanoff, M.A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory administration and patent ductus arteriosus ligation, a survey of practice preferences at US children’s hospitals. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammers, A.L.; Sanchez-Ramos, L.; Kaunitz, A.M. Antenatal exposure to indomethacin increases the risk of severe intraventricular hemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, and periventricular leukomalacia: A systematic review with metaanalysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 505.e1–505.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, D.; Dargaville, P.A.; Davis, P.G.; Hutchison, A.A.; Owen, L.S. Acute Neonatal Respiratory Failure. Pediatric and Neonatal Mechanical Ventilation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1185–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.M.; Agrawal, R.P.; Sharan, H.; Kumar, B.; Sharma, D.; Bhatia, S.S. “Neonatal Sepsis”: Bacteria & their Susceptibility Pattern towards Antibiotics in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 2511–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trentadue, R.; Fiore, F.; Massaro, F.; Papa, F.; Iuso, A.; Scacco, S.; Santacroce, L.; Brienza, N. Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in human fibroblast cultures exposed to serum from septic patients. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejiofor, O.S.; Ajunwa, O.M.; Ezeudu, C.E.; Emechebe, G.O.; Okeke, K.N.; Ifezulike, C.C.; Ekejindu, I.M.; Okoyeh, J.N.; Osuala, E.O.; Oli, A.N. The Bacteriology and Its Virulence Factors in Neonatal Infections: Threats to Child Survival Strategies. J. Pathog. 2018, 2018, 4801247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.; Rees, C.M.; Hall, N.J. Current Research on the Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Management of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Neonatology 2017, 111, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verduci, E.; Banderali, G.; Barberi, S.; Radaelli, G.; Lops, A.; Betti, F.; Riva, E.; Giovannini, M. Epigenetic effects of human breast milk. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altobelli, E.; Angeletti, P.M.; Verrotti, A.; Petrocelli, R. The Impact of Human Milk on Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresesti, I.; Salvatore, S.; Valetti, G.; Baj, A.; Giaroni, C.; Agosti, M. The Microbiota-Gut Axis in Premature Infants: Physio-Pathological Implications. Cells 2022, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.D.; Simmer, K. Practice of parenteral nutrition in VLBW and ELBW infants. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 110, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, R.E.; Coe, K.L. Clinical Presentation and Multifactorial Pathogenesis of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in the Preterm Infant. Adv. Neonatal Care 2021, 21, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameer, A.S.; Nissar, S. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs): Structure, Functions, Signaling, and Role of Their Polymorphisms in Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1157023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Paglino, J.; Eslami-Varzaneh, F.; Edberg, S.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 2004, 118, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Sodhi, C.P.; Hackam, D.J. Toll-like receptor regulation of intestinal development and inflammation in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pathophysiology 2014, 21, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomart, A.; Vallée, A.; Lecarpentier, Y. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: LPS/TLR4-Induced Crosstalk Between Canonical TGF-β/Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways and PPARγ. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 713344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazji, I.; Sodhi, C.P.; Lee, E.K.; Good, M.; Egan, C.E.; Afrazi, A.; Neal, M.D.; Jia, H.; Lin, J.; Ma, C.; et al. Endothelial TLR4 activation impairs intestinal microcirculatory perfusion in necrotizing enterocolitis via eNOS–NO–nitrite signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9451–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siggers, R.H.; Siggers, J.; Thymann, T.; Boye, M.; Sangild, P.T. Nutritional modulation of the gut microbiota and immune system in preterm neonates susceptible to necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdams, R.M.; Juul, S.E. The role of cytokines and inflammatory cells in perinatal brain injury. Neurol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 561494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.R.; Soave, D.F.; da Silva, M.V.; de Menezes, L.B.; Etchebehere, R.M.; Monteiro, M.L.G.d.R.; dos Reis, M.A.; Corrêa, R.R.M.; Celes, M.R.N. Neonatal sepsis and inflammatory mediators. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 269681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, C.; Pellegrini, G.; Panero, A.; De Luca, T.; Assumma, M.; Signore, F.; Pacifico, L. Umbilical cord interleukin-6 levels are elevated in term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, J.M.; Moss, T.J.M. The immune consequences of preterm birth. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, M.S.; Sun, X.; Hsueh, W. Hypoxia, PAF, and necrotizing enterocolitis. Lipids 1991, 26, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.B.J.; Keely, S.J.; Keely, S.J. Oxygen in the regulation of intestinal epithelial transport. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulhan, J.; Dicken, B.; Hartling, L.; Larsen, B.M. Current Knowledge of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants and the Impact of Different Types of Enteral Nutrition Products. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2017, 8, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappenden, K.A. Provision of phosphorylatable substrate during hypoxia decreases jejunal barrier function. Nutrition 2002, 18, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieryńska, M.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Struzik, J.; Mielcarska, M.B.; Gregorczyk-Zboroch, K.P. Integrity of the Intestinal Barrier: The Involvement of Epithelial Cells and Microbiota—A Mutual Relationship. Animals 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabina, S.-A.; Ninio, E. Plasma PAF-acetylhydrolase: An unfulfilled promise? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, M.S.; Simon, D.; Jilling, T. The role of PAF, TLR, and the inflammatory response in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 14, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackam, D.; Caplan, M. Necrotizing enterocolitis: Pathophysiology from a historical context. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 27, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.; Charitos, I.A.; Ballini, A.; Cafiero, C.; Topi, S.; Palmirotta, R.; Santacroce, L. Microbiota revolution: How gut microbes regulate our lives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 4368–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The Connection between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Haberer, P.; Snel, J.; Schillinger, U.; Veld, J.H.H.I. Overview of gut flora and probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aureli, P.; Capurso, L.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Clerici, M.; Giovannini, M.; Morelli, L.; Poli, A.; Pregliasco, F.; Salvini, F.; Zuccotti, G.V. Probiotics and health: An evidence-based review. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.I. Honor thy gut symbionts redux. Science 2012, 336, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballini, A.; Charitos, I.A.; Cantore, S.; Topi, S.; Bottalico, L.; Santacroce, L. About Functional Foods: The Probiotics and Prebiotics State of Art. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeno, L.; Barone, M.; Mosca, A.; Viggiani, M.T.; Joukar, F.; Mansour-Ghanaei, F.; Mavaddati, S.; Daniele, A.; Debellis, L.; Bilancia, M.; et al. Soy Metabolism by Gut Microbiota from Patients with Precancerous Intestinal Lesions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polimeno, L.; Barone, M.; Mosca, A.; Viggiani, M.T.; Di Leo, A.; Debellis, L.; Troisi, M.; Daniele, A.; Santacroce, L. Gut Microbiota Imbalance is Related to Sporadic Colorectal Neoplasms. A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; St Amand, A.L.; Feldman, R.A.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; Pace, N.R. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Mazmanian Has the microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system? Science 2010, 330, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; Deboy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.; Ciurea, C.N.; Pasaroiu, D.; Savin, A.-I.; Toma, F.; Sular, F.; Santacroce, L.; Mare, A. New perspectives on the nutritional factors influencing growth rate of Candida albicans in diabetics. An in vitro study. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, C.J.; Mahnert, A.; Kumpitsch, C.; Kiu, R.; Dalby, M.J.; Kujawska, M.; Madl, T.; Kurath-Koller, S.; Urlesberger, B.; Resch, B.; et al. Clinical NEC prevention practices drive different microbiome profiles and functional responses in the preterm intestine. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Cagiano, R.; Del Prete, R.; Bottalico, L.; Sabatini, R.; Carlaio, R.G.; Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric MALTomas: An up-to-date and therapy highlight. Clin. Ter 2008, 159, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsukumo, D.M.; Carvalho, B.M.; Carvalho-Filho, M.A.; Saad, M.J. Translational research into gut microbiota: New horizons in obesity treatment. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2009, 53, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckburg, E.M.; Bik, C.N.; Bernstein, E.; Purdom, L.; Dethlefsen, M.; Sargent, S.R.; Gill, K.E.; Nelson, D.A. Relman Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammi, M.; De Plaen, I.G.; Maheshwari, A. Recent Advances in Necrotizing Enterocolitis Research: Strategies for Implementation in Clinical Practice. Clin. Perinatol. 2020, 47, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeramilli, V.; Cheddadi, R.; Benjamin, H.; Martin, C. The Impact of Stress, Microbial Dysbiosis, and Inflammation on Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brower-Sinning, R.; Zhong, D.; Good, M.; Firek, B.; Baker, R.; Sodhi, C.P.; Hackam, D.J.; Morowitz, M.J. Mucosa-associated bacterial diversity in necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, M.S.; Jilling, T. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: Possible role of probiotic supplementation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 30 (Suppl. S2), S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, D.A.; Leclair, J.; Macone, A. Bacterial colonization of neonates admitted to an intensive care environment. J. Pediatr. 1978, 93, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragan, M.V.; Wala, S.J.; Goodman, S.D.; Bailey, M.T.; Besner, G.E. Next-Generation Probiotic Therapy to Protect the Intestines From Injury. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 863949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.A.; Baumgartel, K.; Morowitz, M.J.; Giangrasso, V.; Demirci, J.R. The Role of Human Milk in Decreasing Necrotizing Enterocolitis through Modulation of the Infant Gut Microbiome: A Scoping Review. J. Hum. Lact. 2020, 36, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, J. Preterm infant nutrition, gut bacteria, and necrotizing enterocolitis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedberg, D.E.; Lebwohl, B.; Abrams, J.A. The impact of proton pump inhibitors on the human gastrointestinal microbiome. Clin. Lab. Med. 2014, 34, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakshasbhuvankar, A.; Rao, S.; Minutillo, C.; Gollow, I.; Kolar, S. Peritoneal drainage versus laparotomy for perforated necrotising enterocolitis or spontaneous intestinal perforation: A retrospective cohort study. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 48, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Geng, M.; Zhu, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.; Du, X.; Wang, N. Protective Effects and Mechanism of a Novel Probiotic Strain Ligilactobacillus salivarius YL20 against Cronobacter sakazakii-Induced Necrotizing Enterocolitis In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.L.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Barnhart, D.C.; Sylvester, K.G.; Brown, R.L.; Powell, D.M.; Islam, S.; Langer, J.C.; Sato, T.T.; Brandt, M.L.; et al. Laparotomy versus peritoneal drainage for necrotizing enterocolitis and perforation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.E.; Huisman, E.; Miller, M.R.; Ulrich, C.; Reid, G.; da Silva, O. Enteral supplementation with probiotics in preterm infants: A retrospective cohort study and 6-year follow-up. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1063121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nita, R.; Aryati; Matulatan, F. Necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm newborn with a history of maternal COVID-19: A case report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 2630–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, M.K.; Blood, D.; Gomez-Duarte, O.G.; Davidson, L. Necrotizing Enterocolitis in a 34-Week Premature Infant with COVID-19. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2021, 2021, 1442447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Del Prete, R. COVID-19 in Italy: An Overview from the First Case to Date. Electron. J. Gen. Med. 2020, 17, em235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovero, R.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Castellaneta, F.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Colella, M. Current Views about the Link between SARS-CoV-2 and the Liver: Friends or Foe? Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets 2024, 24, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidatt, M.; Sghair, Y.; Ghaddour, T.; Ahmed, M.; Kaderd, F.; Habib, L.; Abass, A.; Bounaty, A. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis due to COVID-19. A case report. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 2022, 16, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term gastrointestinal outcomes of COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Carretta, D.M.; De Nitto, E.; Lovero, R. The human coronaviruses (HCoVs) and the molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, Z.; Sinaei, R.; Estabragh, E.R.; Ahangaran, A. Sigmoid colon perforation in a SARS-CoV-2 positive neonate: A uniqueness report and a brief review. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.; Imagawa, K.; Tagawa, M.; Sakamoto, N.; Takada, H. Case report: Immunological characteristics of de novo ulcerative colitis in a child post COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1107808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerbaux, L.-A.; Filipovska, J.; Muñoz, A.; Petrillo, M.; Coecke, S.; Amorim, M.-J.; Grenga, L. Mechanisms Leading to Gut Dysbiosis in COVID-19: Current Evidence and Uncertainties Based on Adverse Outcome Pathways. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreefa, Z.; Barbier, M.T.; Koksal, A.R.; Love, G.; Del Valle, L. Pathogenesis and Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Intestine, Liver, and Pancreas. Cells 2023, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, F.; Obrova, K.; Haas, M.; Tucek, E.; Kosulin, K.; Fortschegger, M.; Fürhacker, P.; Walter, C.; Größlinger, L.; Peter, S.; et al. Intestinal Shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in Children: No Evidence for Infectious Potential. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, A.; Tedbury, P.R.; Mwangi, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Merlin, D.; Gracz, A.D.; He, P.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Srinivasan, S. SARS-CoV-2 Induces Epithelial-Enteric Neuronal Crosstalk Stimulating VIP Release. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck-Friis, T.; Kärmander, A.; Nyström, K.; Wang, H.; Gisslén, M.; Andersson, L.-M.; Norder, H. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 spike RNA sequences in feces and nasopharynx indicates intestinal replication. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.-J.; Zhou, M.-Y.; He, X.-Q.; Wu, Y.; Xie, X.-L. The Role of Human Coronavirus Infection in Pediatric Acute Gastroenteritis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Tsuda, M.; Li, Y. SARS-CoV-2 infection of intestinal epithelia cells sensed by RIG-I and DHX-15 evokes innate immune response and immune cross-talk. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1035711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, N.A.; Vento, M.; Claud, E.C.; Wang, C.E.; Caplan, M.S. Oropharyngeal administration of mother’s colostrum, health outcomes of premature infants: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2015, 16, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, B.; Dutta, S.; Singh, R.; Prasad, R.; Kumar, P. Bovine Colostrum in Prevention of Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Pilot Trial. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2017, 63, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greecher, C.P.; Doheny, K.K.; Glass, K.M. Oropharyngeal Administration of Colostrum Increases Salivary Secretory IgA Levels in Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudeep, K.C.; Kumar, J.; Ray, S.; Dutta, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Kumar, P. Oral Application of Colostrum and Mother’s Own Milk in Preterm Infants—A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 89, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahnfeldt, A.M.; Aunsholt, L.; Hansen, B.M.; Hoest, B.; Jóhannsdóttir, V.; Kappel, S.S.; Klamer, A.; Möller, S.; Moeller, B.K.; Sangild, P.T.; et al. Bovine colostrum as a fortifier to human milk in very preterm infants—A randomized controlled trial (FortiColos). Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, F.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Latour, J.M. Oropharyngeal Colostrum Administration in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial*. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 18, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.; Eldegla, H.; Khashaba, M.; Nasef, N. Oropharyngeal Administration of Mother’s Milk Prior to Gavage Feeding in Preterm Infants: A Pilot Randomized Control Trial. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OuYang, X.; Yang, C.-Y.; Xiu, W.-L.; Hu, Y.-H.; Mei, S.-S.; Lin, Q. Oropharyngeal administration of colostrum for preventing necrotizing enterocolitis and late-onset sepsis in preterm infants with gestational age ≤ 32 weeks: A pilot single-center randomized controlled trial. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2021, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Plakkal, N.; Bhat, V. Does oropharyngeal administration of colostrum reduce morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants? A randomised parallel-group controlled trial. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 57, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, R.I.H.; Awad, H.A.; Imam, S.S.; Gad, G.I.; Aboushady, N.M.; Abdou, R.M.; Eissa, D.S.; Azzam, N.T.; Barakat, M.M.; Yassin, M.M.; et al. Gut priming with bovine colostrum and T regulatory cells in preterm neonates: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Predisposing Factors for NEC | ||
|---|---|---|
| Maternal/Obstetric | Neonate | Nutritional |
| Mother’s age, multiple pregnancy, premature birth related to pregnancy complications (such as pre-eclampsia, premature rupture of membranes (PROM), and others), caesarean delivery, anemia, use of drugs (such as antibiotics, steroids, and others), substance abuse (such as cocaine and others), and chorioamnionitis. | Low birth weight, prematurity, gender of infant (occurs more in males), Apgar score <7, anemia, transfusions, postnatal systemic infection/sepsis, use of drugs after delivery (such as steroids, indomethacin, ibuprofen, and antibiotics), intubation and long-term mechanical ventilation, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), hyaline membrane disease (HMD), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and intra-abdominal bleeding. | The early initiation of enteral feeding (first 48 h), either with mother’s or modified cow’s milk, and large amount of milk, are aggravating factors. Breast milk plays a protective role, strengthening the immune system of premature infants. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jirillo, E.; Topi, S.; Charitos, I.A.; Santacroce, L.; Gaxhja, E.; Colella, M. Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Related Sepsis. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 431-445. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020029
Jirillo E, Topi S, Charitos IA, Santacroce L, Gaxhja E, Colella M. Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Related Sepsis. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2024; 6(2):431-445. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleJirillo, Emilio, Skender Topi, Ioannis Alexandros Charitos, Luigi Santacroce, Elona Gaxhja, and Marica Colella. 2024. "Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Related Sepsis" Gastrointestinal Disorders 6, no. 2: 431-445. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020029
APA StyleJirillo, E., Topi, S., Charitos, I. A., Santacroce, L., Gaxhja, E., & Colella, M. (2024). Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Related Sepsis. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 6(2), 431-445. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6020029


.png)







