MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
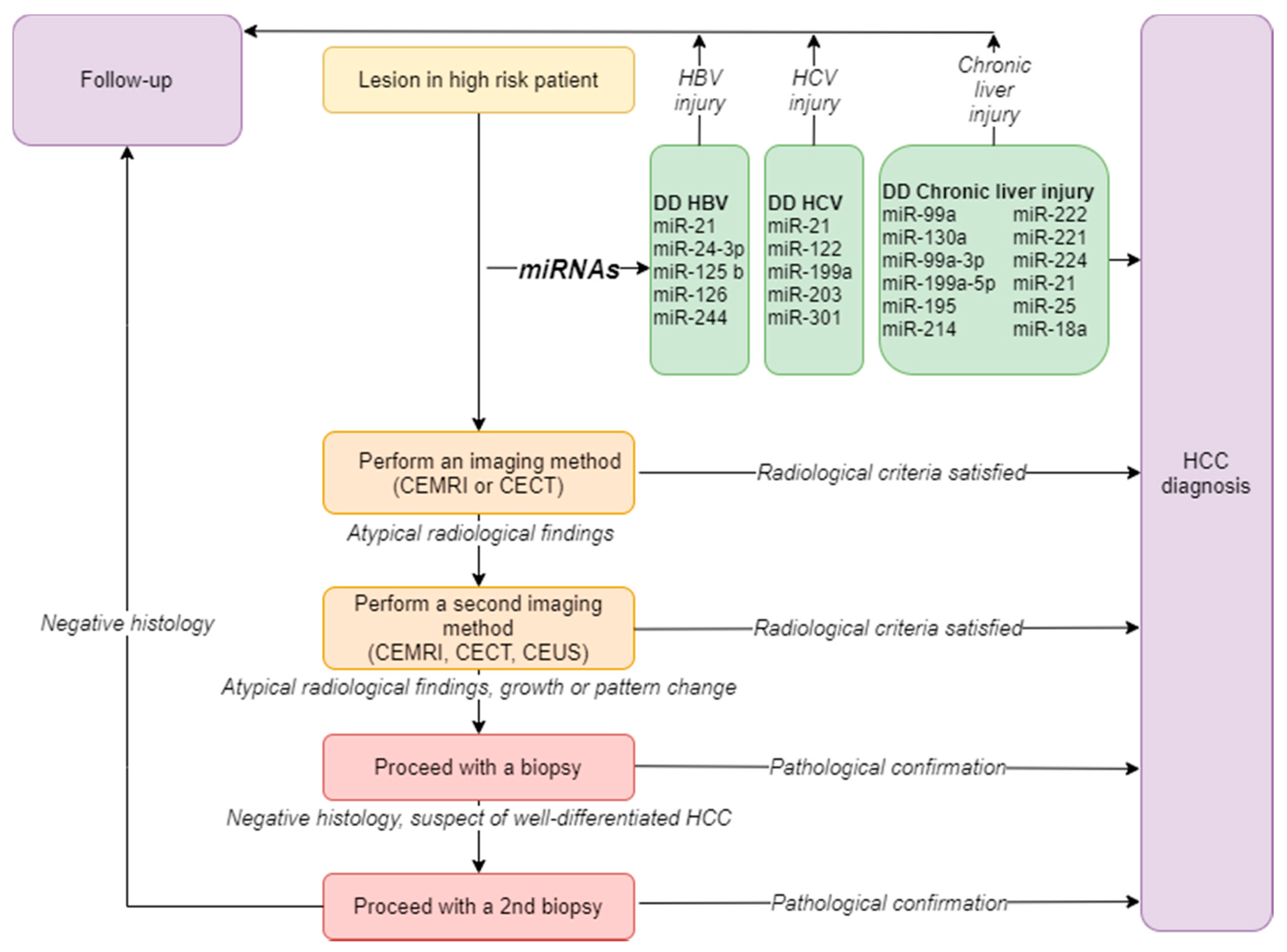
1.2. Diagnosis
1.3. MicroRNAs
1.4. MicroRNAs and HCC
2. The Diagnostic Role of microRNAs in HCC
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.; Ronnebaum, S.; Patel, D.; Doleh, Y.; Benavente, F. Epidemiologic, humanistic and economic burden of hepatocellular carcinoma in the USA: A systematic literature review. Hepat. Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, J.L.; Florio, A.A.; Loomba, R.; McGlynn, K.A. Have incidence rates of liver cancer peaked in the United States? Cancer 2020, 126, 3151–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- But, D.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Natural history of hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.; Asch, S.M.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Cao, Y.; El-Serag, H.B. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in HCV Patients Treated With Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, L. Conditional survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse, S.F.; Henley, S.J.; Cucinelli, J.E.; McGlynn, K.A. Changing hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and liver cancer mortality rates in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.; Volk, M.L.; Waljee, A.; Salgia, R.; Higgins, P.; Rogers, M.A.; Marrero, J.A. Meta-analysis: Surveillance with ultrasound for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Li, J.W.; Lu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lin, L.; Shi, Y.J.; Li, T.; Liu, J.B.; Lyshchik, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of CEUS LI-RADS for the Characterization of Liver Nodules 20 mm or Smaller in Patients at Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2020, 294, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzi, E.; Iavarone, M.; Pompili, M.; Veronese, L.; Cabibbo, G.; Fraquelli, M.; Riccardi, L.; de Bonis, L.; Sangiovanni, A.; Leoni, S.; et al. Contrast ultrasound LI-RADS LR-5 identifies hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis in a multicenter restropective study of 1,006 nodules. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2015, 275, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolondi, L.; Gaiani, S.; Celli, N.; Golfieri, R.; Grigioni, W.F.; Leoni, S.; Venturi, A.M.; Piscaglia, F. Characterization of small nodules in cirrhosis by assessment of vascularity: The problem of hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005, 42, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigliano, R.; Marelli, L.; Yu, D.; Davies, N.; Patch, D.; Burroughs, A.K. Seeding following percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. What is the risk and the outcome? Seeding risk for percutaneous approach of HCC. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, V.; Crouan, A.; Esvan, M.; Oberti, F.; Michalak, S.; Gallix, B.; Seror, O.; Paisant, A.; Vilgrain, V.; Aube, C.; et al. Suspicious liver nodule in chronic liver disease: Usefulness of a second biopsy. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.H.; Shrestha, S.; Yang, C.D.; Chang, N.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Liao, K.W.; Huang, W.C.; Sun, T.H.; Tu, S.J.; Lee, W.H.; et al. miRTarBase update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D296–D302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Regulation, function, and clinical implications. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 924206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krek, A.; Grun, D.; Poy, M.N.; Wolf, R.; Rosenberg, L.; Epstein, E.J.; MacMenamin, P.; da Piedade, I.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Stoffel, M.; et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Shen, J.; Zheng, H.; Fan, W. The role and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Tanahashi, T.; Okada, R.; Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Enomoto, M.; Tamori, A.; Kawada, N.; Taguchi, Y.H.; Azuma, T. Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma miRNA expression profiling as evaluated by next generation sequencing and microarray. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcicka, A.; Swierniak, M.; Kornasiewicz, O.; Gierlikowski, W.; Maciag, M.; Kolanowska, M.; Kotlarek, M.; Gornicka, B.; Koperski, L.; Niewinski, G.; et al. Next generation sequencing reveals microRNA isoforms in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 53, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghidini, M.; Braconi, C. Non-Coding RNAs in Primary Liver Cancer. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2015, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.W.; Croce, C.M.; Dejean, A. miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffanin, S.; Alsinet, C.; Cornella, H.; Sia, D.; Llovet, J.M. microRNAs and the MYC network: A major piece in the puzzle of liver cancer. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Q.K.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ge, Y.Y.; Yang, J.R.; Su, H.; Zhuang, S.M. A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene is associated with the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Chung, R.T.; Everhart, J.E.; Dienstag, J.L.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Wright, E.C.; Everson, G.T.; Lindsay, K.L.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with advanced hepatitis C: Results from the HALT-C Trial. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Sterling, R.K.; Everhart, J.E.; Wright, E.E.C.; Hoefs, J.C.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Morgan, T.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein as biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.N.; Chayama, K. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Csak, T. Role of MicroRNAs in NAFLD/NASH. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.L.; Wang, W.; Jia, W.D. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of serum miR-24-3p in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. miR-122--a key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. Chromosomal rearrangements and microRNAs: A new cancer link with clinical implications. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Wei, Y.; Liang, H.; Yuan, M.; Jin, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, L.; et al. Nuclear miR-122 directly regulates the biogenesis of cell survival oncomiR miR-21 at the posttranscriptional level. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2012–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yu, X.F.; OUYang, N.; Luo, Q.; Tong, J.; Chen, T.; Li, J. Role of DNA methylation regulation of miR-130b expression in human lung cancer using bioinformatics analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2019, 82, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casero, D.; Sandoval, S.; Seet, C.S.; Scholes, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ha, V.L.; Luong, A.; Parekh, C.; Crooks, G.M. Long non-coding RNA profiling of human lymphoid progenitor cells reveals transcriptional divergence of B cell and T cell lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemeery, M.N.; Badr, A.N.; Mohamed, M.A.; Ghareeb, D.A. Validation of a serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma post-hepatitis C infection in Egyptian patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3864–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Dong, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, N.; Yu, F. High expression of serum miR-17-5p associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2013, 60, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorop, A.; Iacob, R.; Iacob, S.; Constantinescu, D.; Chitoiu, L.; Fertig, T.E.; Dinischiotu, A.; Chivu-Economescu, M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Savu, L.; et al. Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived miR-21-5p and miR-92a-3p as Potential Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Hou, J.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, W.; et al. MicroRNA-99a inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and correlates with prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36677–36685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, A.; Perra, A.; Schernhuber, K.; Cargnelutti, M.; Salvi, A.; Migliore, C.; Ghiso, E.; Benetti, A.; Barlati, S.; Ledda-Columbano, G.M.; et al. Sequential analysis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis reveals that miR-100 and PLK1 dysregulation is an early event maintained along tumor progression. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4517–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Peng, J.; Huang, D.; Sun, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, W.; et al. miRNA-99b-5p suppresses liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating mTOR. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24448–24462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Liu, H.; Lv, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Ding, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; et al. MiRNA-99a directly regulates AGO2 through translational repression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Huang, P.; Qiu, J.; Liao, Y.; Hong, J.; Yuan, Y. MicroRNA-130a is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and associates with poor prognosis. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Rao, J.; Wang, X. miR-1301 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis by decreasing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through targeting BCL9. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Pollutri, D.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L. MiR-199a-3p regulates mTOR and c-Met to influence the doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5184–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatseva, T.; Lee, D.Y.; Deng, Z.; Yang, B.B. MicroRNA miR-199a-3p regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting caveolin-2. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Luo, Y.; Xia, L.; Xue, F.; Xia, Q. Cisplatin-induced downregulation of miR-199a-5p increases drug resistance by activating autophagy in HCC cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Wang, Z.H.; Mi, X.G.; Liu, L.; Tan, Y. MiR-199a/b-3p suppresses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by downregulating PAK4/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jing, L.; Yin, X.R.; Wang, M.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Guo, Y.; Nan, K.J.; Han, L.L. MiR-195 suppresses the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting YAP. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99757–99771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shih, T.C.; Tien, Y.J.; Wen, C.J.; Yeh, T.S.; Yu, M.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yen, T.C.; Hsieh, S.Y. MicroRNA-214 downregulation contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, J. MiR-214 inhibits cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of beta-catenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, L. microRNA-18a Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion Through Inhibiting Dicer l Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2017, 32, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.T.; Liu, S.M.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Circulating miRNAs for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Loya, K.; Rani, B.; Mobus, S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Lamle, J.; Cathomen, T.; Vogel, A.; Manns, M.P.; Ott, M.; et al. MicroRNA-221 overexpression accelerates hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 2013, 57, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, F.; Qian, L.; Zhang, P.; Lv, F.; Cheng, W.; Hou, R. MiR-221 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Migration via Targeting PHF2. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4371405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galardi, S.; Mercatelli, N.; Giorda, E.; Massalini, S.; Frajese, G.V.; Ciafre, S.A.; Farace, M.G. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23716–23724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.H.; Wu, S.Y.; Zuchini, R.; Lin, X.Z.; Su, I.J.; Tsai, T.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, C.T.; Liu, H.S. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology 2014, 59, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visone, R.; Russo, L.; Pallante, P.; de Martino, I.; Ferraro, A.; Leone, V.; Borbone, E.; Petrocca, F.; Alder, H.; Croce, C.M.; et al. MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels and cell cycle. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Dong, R.; Shi, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-regulation of miR-23b may contribute to activation of the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signalling pathway during the termination stage of liver regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Cheng, S.Q.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.F.; Gao, C.F. Serum microRNAs as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, C.; Che, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, T.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Tan, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Circulating microRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampoka, K.; Muangpaisarn, P.; Khongnomnan, K.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Payungporn, S. Serum miR-29a and miR-122 as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Microrna 2018, 7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, O.; Puri, P.; Eicken, C.; Contos, M.J.; Mirshahi, F.; Maher, J.W.; Kellum, J.M.; Min, H.; Luketic, V.A.; Sanyal, A.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic MicroRNA expression. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y. Downregulation of miRNA-638 promotes angiogenesis and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGF. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30702–30711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, S.D.; Hsu, C.S.; Lai, T.C.; Chen, S.J.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tsai, T.F.; et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Yoshida, E.M.; Rathi, S.; Marquez, V.; Kim, P.; Erb, S.R.; Salh, B.S. Biomarkers for hepatocellular cancer. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.G.; Xu, H.; Gu, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Zu, M.H. Comparison osteopontin vs AFP for the diagnosis of HCC: A meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2014, 38, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tao, Y.; Shan, L.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Qian, Z.; Cai, F.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y. The Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhao, M.; Zou, X.; Zhou, J.; Bai, Z. MicroRNA polymorphism: A target for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma? Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tao, H. The Diagnostic Value of MicroRNAs as a Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5179048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MiRNAs | Targets | Mechanisms | Expression | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-99a | PLK1, IGF-1R | Down | [45,46,47,48] | |
| miR-130a | ROCK2 | metastasis | Down | [49,50] |
| miR199a-3p | mTOR, PAK4, caveolin-2 | drug resistance, cell growth | Down | [50,51,52,53,54] |
| miR199a-5p | DDR1, ATG7 | invasion, autophagy | Down | [52,53] |
| miR-195 | cyclin D1, CDK6, E2F3, LATS2 | cell cycle, tumorigenesis, apoptosis | Down | [55] |
| miR-214 | HDGF, β-catenin | cell growth, angiogenesis, metastasis | Down | [56,57] |
| miR-18a | ER1a | proliferation | Up | [58] |
| miR-21 | PTEN, RHOB, PDCD4 | metastasis, drug resistance | Up | [59] |
| miR-25 | TRAIL | apoptosis | Up | [6] |
| miR-221 | p27, p57, ARNT, CDK inhibitors | apoptosis, proliferation, angiogenesis | Up | [61,62,63,64] |
| miR-222 | p27, DDIT4 | tumorigenesis | Up | [28,65,66] |
| miR-224 | ATG5, SMAD4, autophagy, API5 | tumorigenesis, autophagy | Up | [64] |
| miR-24-3p | Metallothionein 1M | proliferation, apoptosis | Up | [35] |
| miR122 | BCL-w, ADAM17, WNT1 | apoptosis, proliferation, angiogenesis | Up/Down | [67,68,69,70,71,72,74] |
| miR-17-5p | PTEN, GALNT7, vimentin | proliferation, invasion | Up/Down | [43] |
| miR-92a-3p | PTEN, AKT/Snail | proliferation | Down | [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evangelista, J.; Zaninotto, E.; Gaglio, A.; Ghidini, M.; Raimondi, L. MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastrointest. Disord. 2021, 3, 237-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040022
Evangelista J, Zaninotto E, Gaglio A, Ghidini M, Raimondi L. MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2021; 3(4):237-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvangelista, Jessica, Elisa Zaninotto, Annalisa Gaglio, Michele Ghidini, and Lucrezia Raimondi. 2021. "MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Gastrointestinal Disorders 3, no. 4: 237-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040022
APA StyleEvangelista, J., Zaninotto, E., Gaglio, A., Ghidini, M., & Raimondi, L. (2021). MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Tools in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 3(4), 237-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord3040022







