Effect of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Released from Its Aluminum Tri-Polyphosphate Intercalate (ATP-6-AHA) on the Corrosion Protection Mechanism of Steel in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. ATP-6-AHA Synthesis Procedure
2.2. Characterizations Methods
2.3. Materials and Low Carbon Steel Surface Preparation
2.4. Corrosion Tests
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition
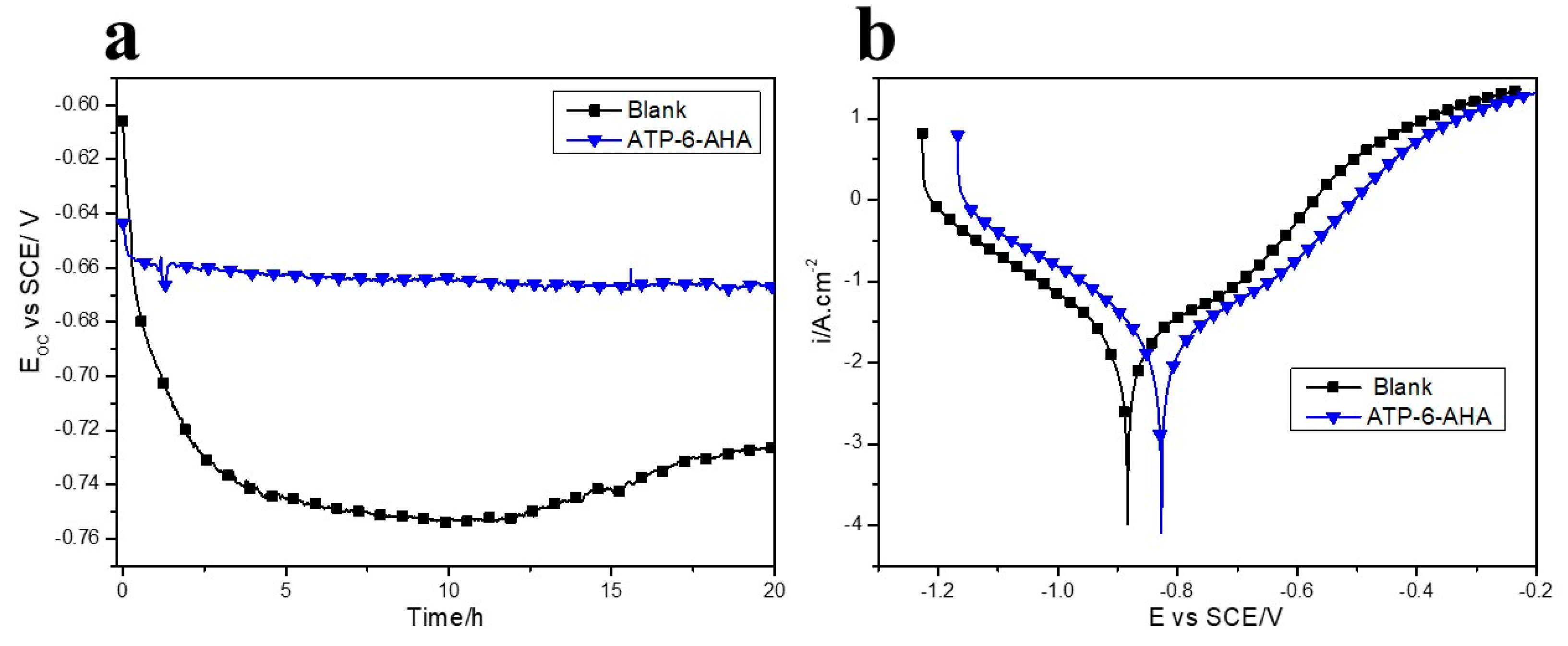
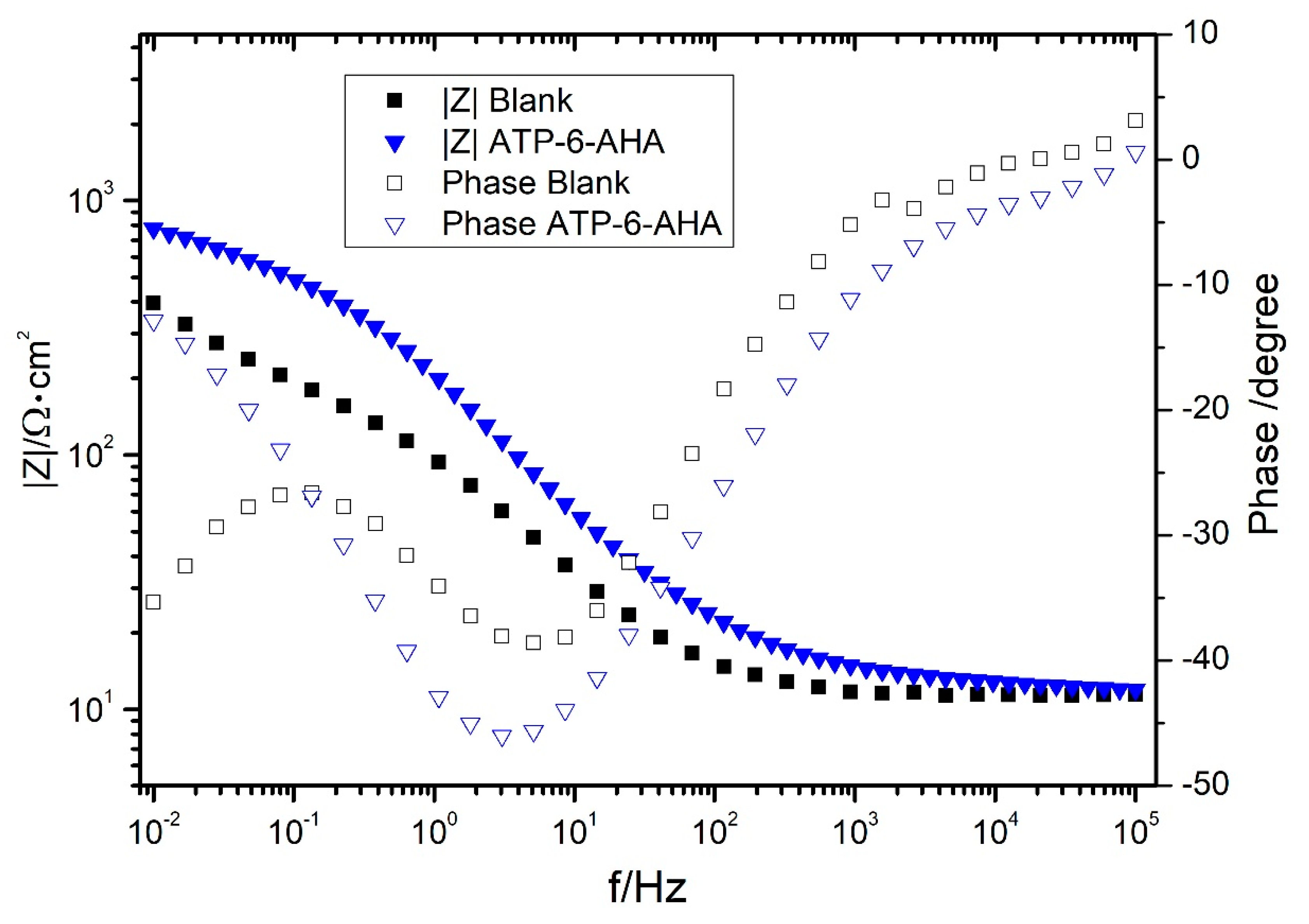
3.2. Gravimetric and Electrochemical Measurements
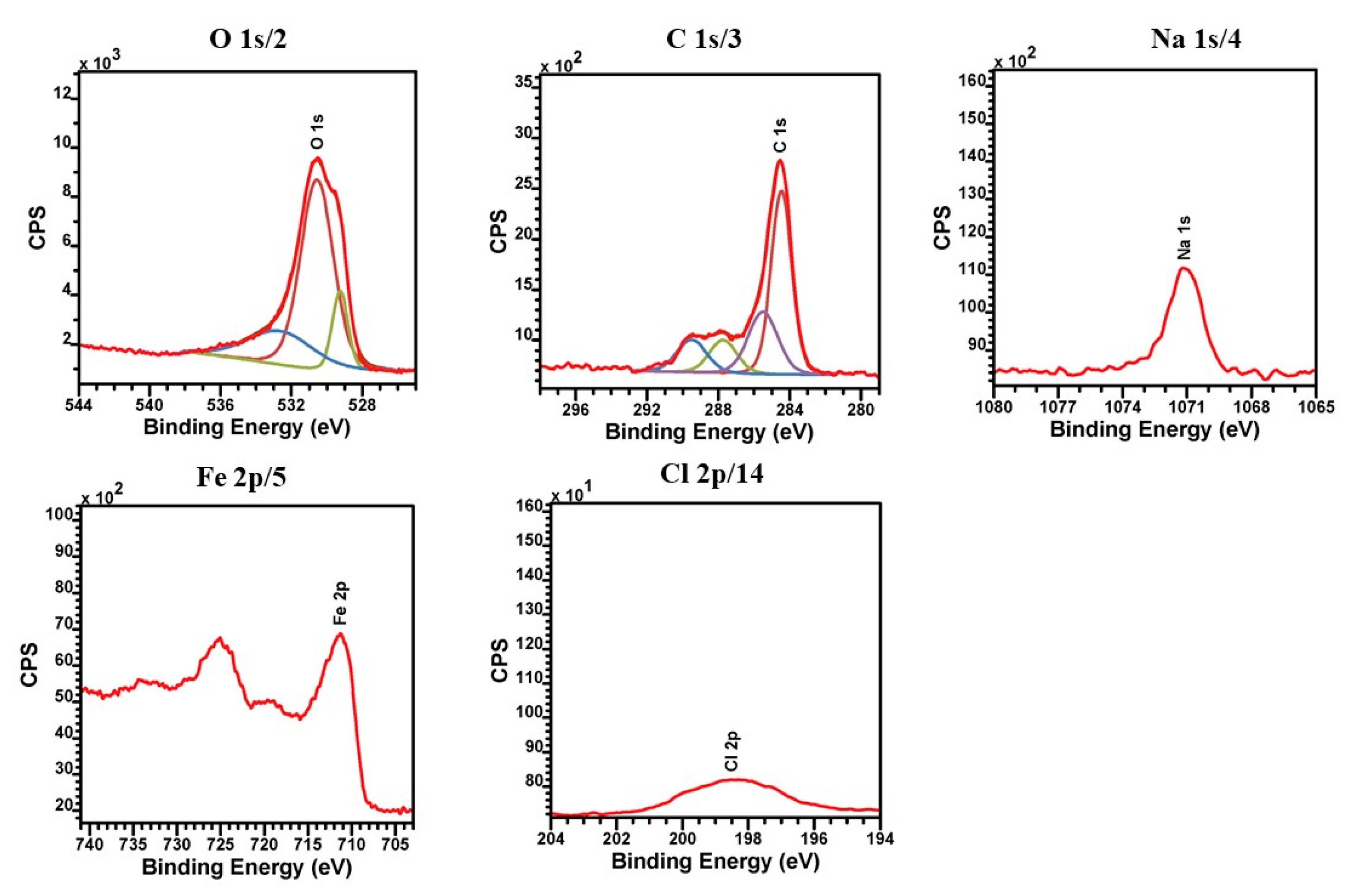
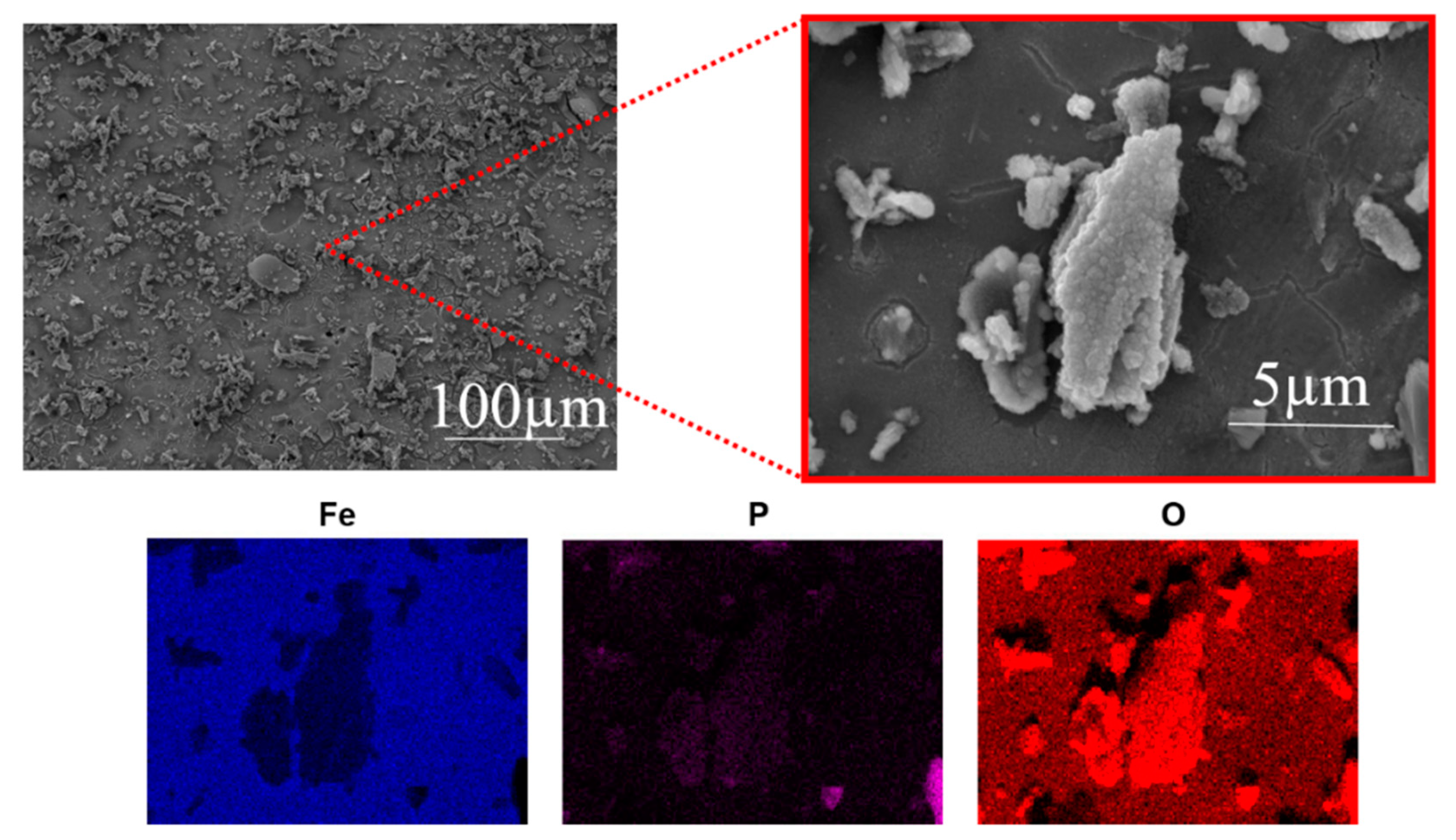
3.3. XPS Analysis of Corrosion Products
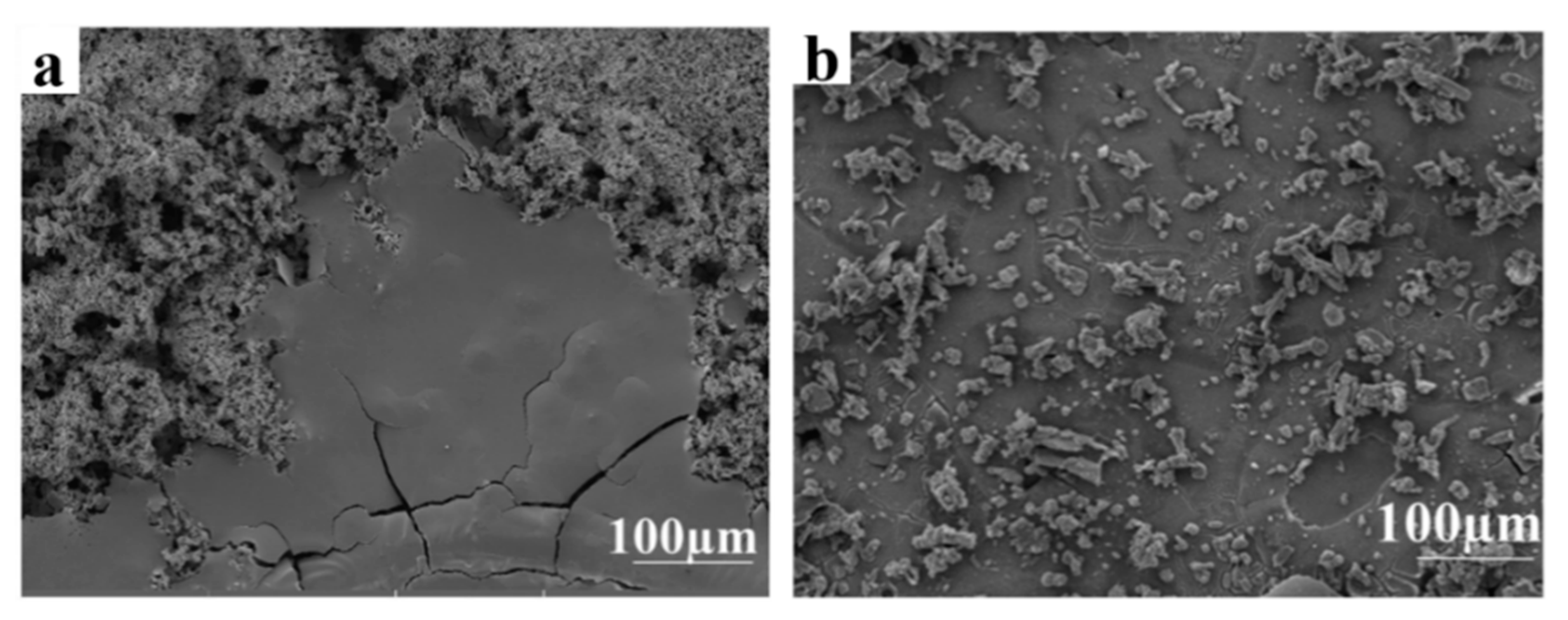
3.4. Morphology of Corrosion Products
- ▪
- A non-uniform film covering the S235 steel surface.
- ▪
- Consists of particles in the form of flowery and sandy platelets, which are the typical shapes of crystallized iron oxides/hydroxides and oxyhydroxide FeO(OH) [27].
- ▪
- Slightly denser and more compact.
- ▪
- It consists rather of broad plates such as crystals with different sizes that are evenly dispersed and a layered region.
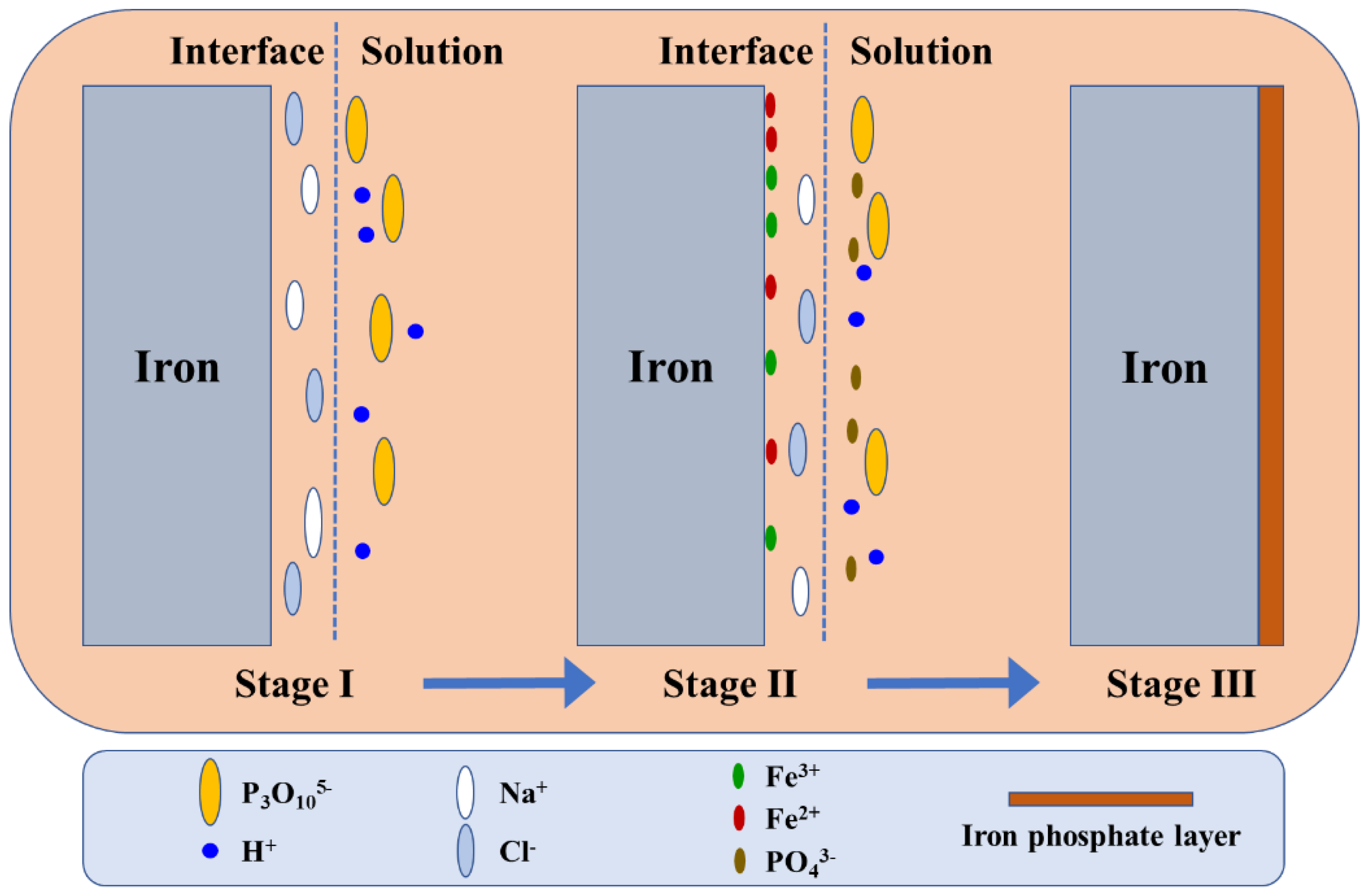
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The decomposition of ATP-6-AHA can lead to the formation of and H+.
- The dissolution of steel takes place, and iron cations appear.
- The formation of the iron phosphate layer on the steel surface was confirmed by the current SEM and XPS analysis.
- The XPS and SEM analysis for ATP–6–AHA show that all of the P, C, O, and N atoms of the inhibitor are involved in the formation of the protective film, increasing its stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haque, J.; Srivastava, V.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, A.M. Experimental and quantum chemical analysis of 2-amino-3-((4-((S)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)thio) propionic acid as new and green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; Rémazeilles, C.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Marine Environments: Role of the Corrosion Product Layer. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadian, S.; Yousefi, A.; Neshati, J. Synergistic effect of mixed cationic and anionic surfactants on the corrosion inhibitor behavior of mild steel in 3.5% NaCl. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheib, A.; Attar, M.M.; Zarebidaki, A. Evaluation of Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl Solution by Cerium Nitrate. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishami, S.; Naderi, R.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Fabrication and characterization of zinc acetylacetonate/Urtica Dioica leaves extract complex as an effective organic/inorganic hybrid corrosion inhibitive pigment for mild steel protection in chloride solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Naderi, R.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Synthesis and characterization of an effective organic/inorganic hybrid green corrosion inhibitive complex based on zinc acetate/Urtica Dioica. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Liang, G. Effects of CaO and MgO on Anticorrosive Performance of Aluminum Dihydrogen Tripolyphosphate on Mild Steel. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13578–13585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyá, M.; di Sarli, A.R.; del Amo, B.; Romagnoli, R. Performance of anticorrosive coatings containing tripolyphosphates in aggressive environments. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 7038–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeli, M.; Ahmadi, N.P.; Khosroshahi, R.A. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid by 6-aminohexanoic acid. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejjaj, C.; Aghzzaf, A.A.; Bouali, I.; Hakkou, R.; Dahbi, M.; Fischer, C.B. Layered aluminum tri-polyphosphate as intercalation host for 6-aminohexanoic acid—Synthesis, characterization and application as corrosion protection inhibitor for low carbon steel. Corros. Sci. 2021, 181, 109239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, M.R.; Hong, X.; Hong, S.X.; Dong, B. Electrochemical properties of aluminum tripolyphosphate modified chemically bonded phosphate ceramic anticorrosion coating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y. The influence of aluminum tri-polyphosphate on the protective behavior of Mg-rich epoxy coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 93, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Gao, J.; Shen, L.; Wan, H.; Li, X. The Influence of Aluminum Tripolyphosphate on the Protective Behavior of an Acrylic Water-Based Paint Applied to Rusty Steels. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 618971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradityana, A.; Shahab, A.; Noerochim, L.; Susanti, D. Inhibition of Corrosion of Carbon Steel in 3.5% NaCl Solution by Myrmecodia Pendans Extract. Int. J. Corros. 2016, 2016, 6058286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Haddad, M.N. Hydroxyethylcellulose used as an eco-friendly inhibitor for 1018 c-steel corrosion in 3.5% NaCl solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norouzi, B.; Yousefi, J.; Nami, N. Preparation of poly(naphthylamine-formaldehyde); Application as a new and an effective inhibitor of steel in hydrochloride acid solution. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2016, 89, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishi, S.K.; Kariuki, B.M.; Checker, N.J.; Godber, J.; Wright, A.J. Synthesis and crystal structure of AlH2P3O102HO; a new structure-type for layered acid phosphates. Chem. Commun. 2006, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifuddin, M.; Kim, S.; Aziz, A.; Kim, K.S. Mechanistic study of phosphorus adsorption onto Iron Z-A: Spectroscopic and experimental approach. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Su, H.; Dong, C.; Li, X. Passivation and electrochemical behavior of 316L stainless steel in chlorinated simulated concrete pore solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglin, M.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of tribostressed samples in the presence of ZnDTP: A combinatorial approach. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 15, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Gao, Z.; Pan, H.; Cheng, X. The initiation and formation of a double-layer phosphate conversion coating on steel. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 114, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, K.; Chahine, A.; Touhami, M.E.; Alauzun, J.G.; Manseri, A. Preparation and characterization of phosphate-nickel-titanium composite coatings obtained by sol–gel process for corrosion protection. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feliu, S.; Samaniego, A.; Bermudez, E.A.; El-Hadad, A.A.; Llorente, I.; Galván, J.C. Effect of native oxide film on commercial magnesium alloys substrates and carbonate conversion coating growth and corrosion resistance. Materials 2014, 7, 2534–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Njoku, D.I.; Li, Y.; Lgaz, H.; Oguzie, E.E. Dispersive adsorption of Xylopia aethiopica constituents on carbon steel in acid-chloride medium: A combined experimental and theoretical approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanova, I.N.; Chausov, F.F.; Naimushina, E.A.; Somov, N.V. XPS characterization of new corrosion inhibitor: Zinc aminophosphonate coordination comple. Surf. Interface Anal. 2014, 46, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, D.; Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; Jiménez, J.A.; Morcillo, M. Characterisation of rust surfaces formed on mild steel exposed to marine atmospheres using XRD and SEM/Micro-Raman techniques. Corros. Sci. 2016, 110, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yuan, P. Corrosion protection mechanism of aluminum triphosphate modified by organic acids as a rust converter. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejjaj, C.; Aghzzaf, A.A.; Scharnagl, N.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Hakkou, R.; Fischer, C.B. Introduction of an innovative corrosion-protective alkyd steel coating based on a novel layered aluminum tripolyphosphate loaded with 6-amino hexanoic acid (ATP-6-AHA). Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
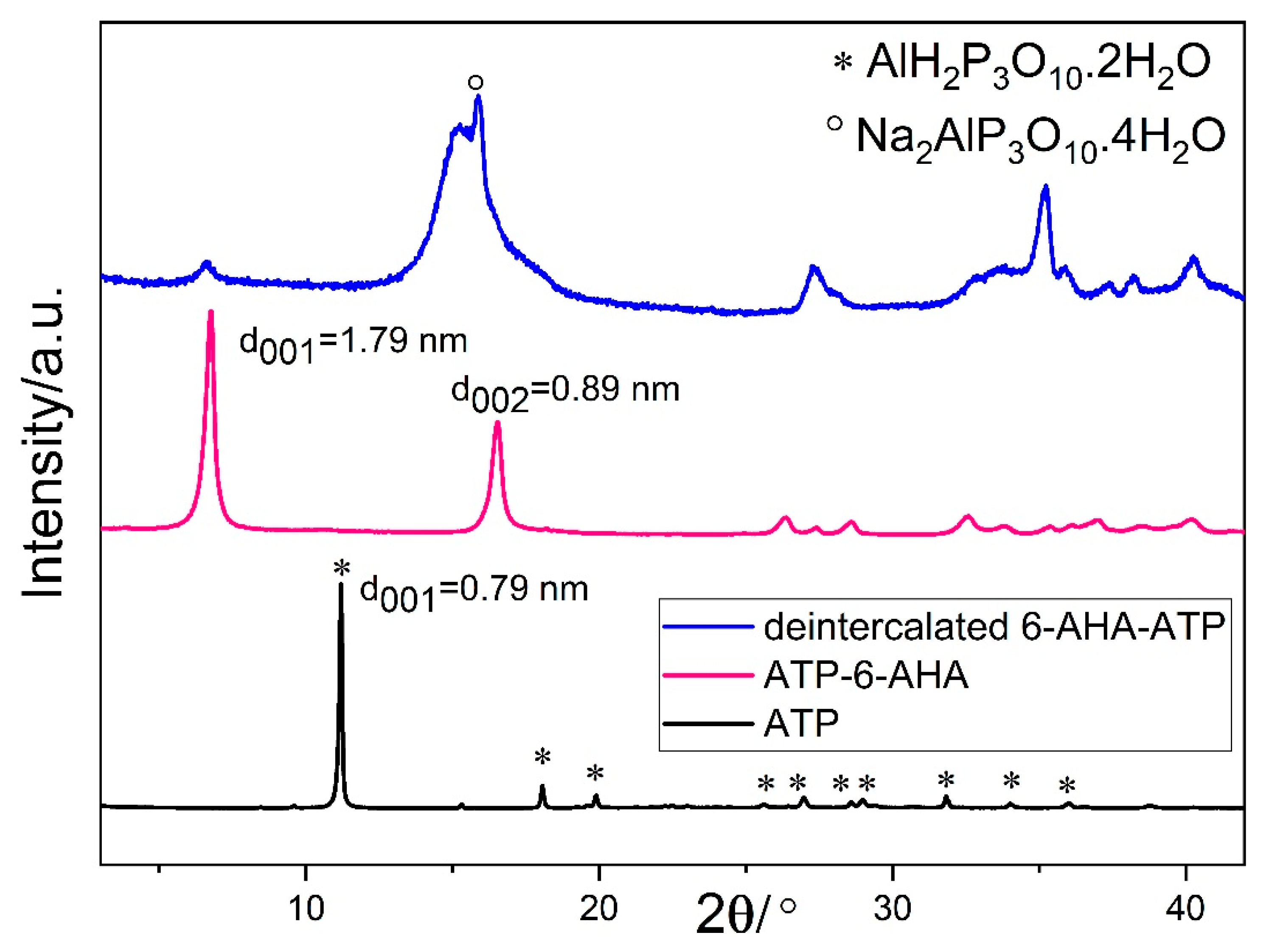


| ATP | ATP-6AHA | Deintercalated Form (6-AHA-ATP) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate | 50.05 | 44.84 | 29.05 |
| Alumina | 11.17 | 11.05 | 8.65 |
| Ecorr/V vs. SCE | icorr/µA cm−2 | CR (mm/y) | η/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | −883 ± 11 | 18.5 ± 1.3 | 0.213 | - |
| ATP-6-AHA | −817 ± 15 | 6.2 ± 2.1 | 0.072 | 66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hejjaj, C.; Aghzzaf, A.A.; Scharnagl, N.; Makha, M.; Dahbi, M.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Hakkou, R.; Fischer, C.B. Effect of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Released from Its Aluminum Tri-Polyphosphate Intercalate (ATP-6-AHA) on the Corrosion Protection Mechanism of Steel in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 666-677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2040036
Hejjaj C, Aghzzaf AA, Scharnagl N, Makha M, Dahbi M, Zheludkevich ML, Hakkou R, Fischer CB. Effect of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Released from Its Aluminum Tri-Polyphosphate Intercalate (ATP-6-AHA) on the Corrosion Protection Mechanism of Steel in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2021; 2(4):666-677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleHejjaj, Chaymae, Ahmed Ait Aghzzaf, Nico Scharnagl, Mohammed Makha, Mouad Dahbi, Mikhail L. Zheludkevich, Rachid Hakkou, and Christian B. Fischer. 2021. "Effect of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Released from Its Aluminum Tri-Polyphosphate Intercalate (ATP-6-AHA) on the Corrosion Protection Mechanism of Steel in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 2, no. 4: 666-677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2040036
APA StyleHejjaj, C., Aghzzaf, A. A., Scharnagl, N., Makha, M., Dahbi, M., Zheludkevich, M. L., Hakkou, R., & Fischer, C. B. (2021). Effect of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid Released from Its Aluminum Tri-Polyphosphate Intercalate (ATP-6-AHA) on the Corrosion Protection Mechanism of Steel in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 2(4), 666-677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd2040036










