Reporter-Mediated Evaluation of the Circadian Oscillations of SNAIL Across In Vitro Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
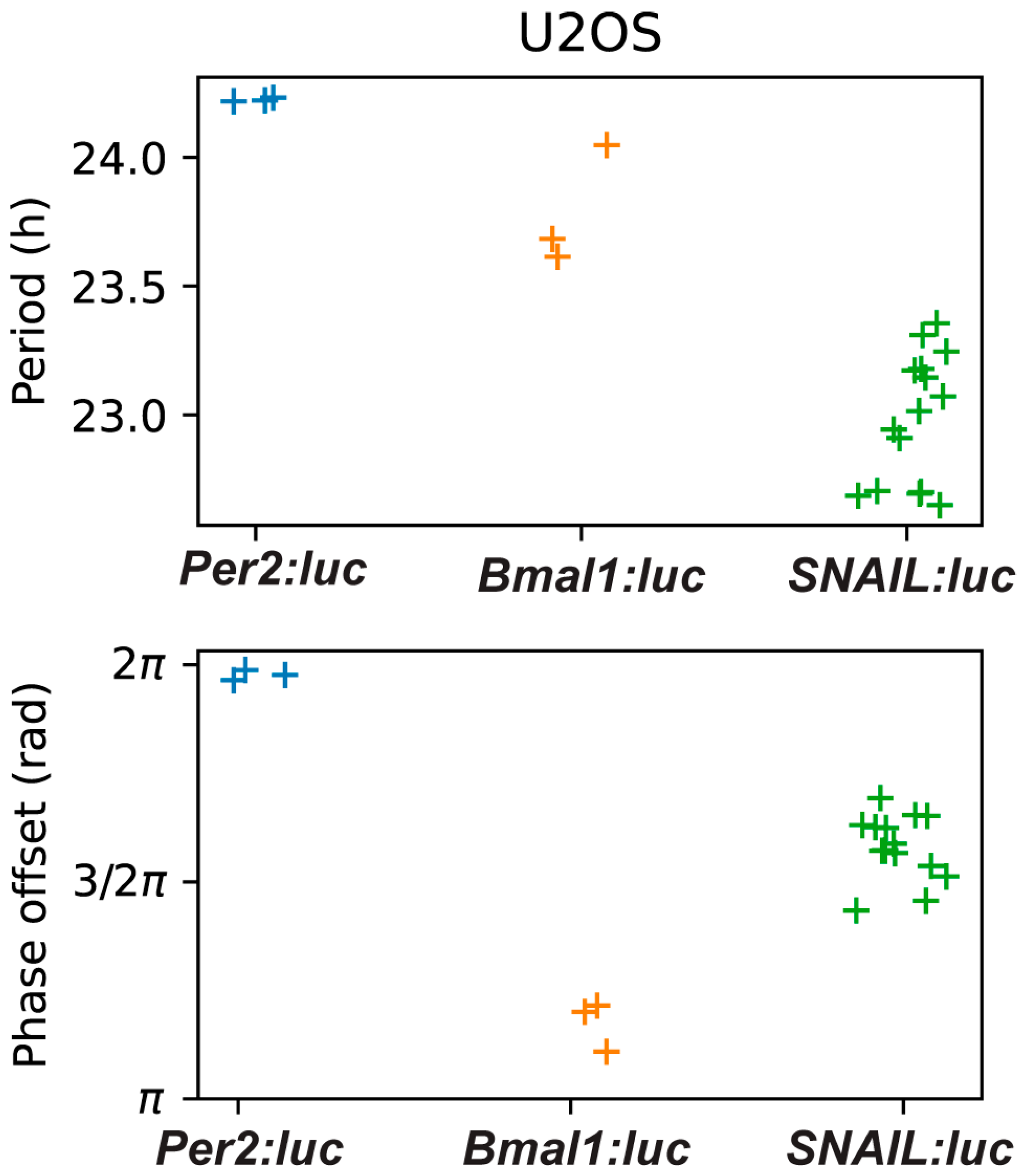
2.1. SNAIL Oscillations Can Be Tracked Using a Luciferase Reporter and Are Circadian in U2OS Cells
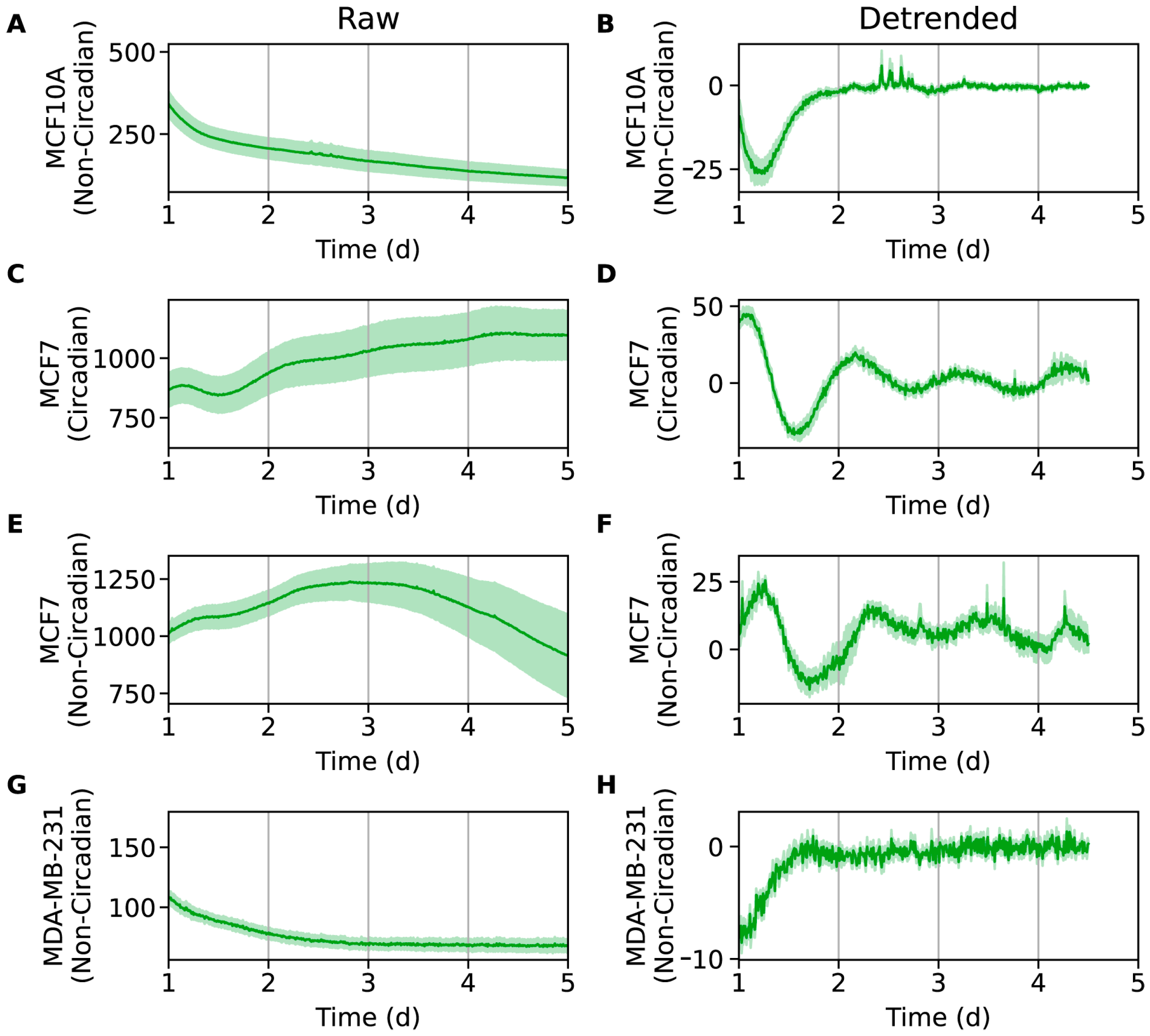
2.2. SNAIL Oscillations in Breast Epithelial and Breast Cancer Cell Lines Vary with Expression Levels and Aggressiveness
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plasmid Construction
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Lentiviral Transduction
3.4. Cell Synchronization and Bioluminescence Recording
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| BMAL1 | Brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 |
| CLOCK | Circadian locomotor output cycles kaput |
| PER | Period |
| CRY | Cryptochrome |
| EMT | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition |
| DEC1 | Differentiated embryo-chondrocyte 1 |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| HGF-1 | Human gingival fibroblasts |
| luc | Luciferase |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
References
- Partch, C.L.; Green, C.B.; Takahashi, J.S. Molecular Architecture of the Mammalian Circadian Clock. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, L.P.; Sriram, S.; Weaver, D.R.; Maywood, E.S.; Chaves, I.; Zheng, B.; Kume, K.; Lee, C.C.; van der, G.T.J.; Horst; et al. Interacting Molecular Loops in the Mammalian Circadian Clock. Science 2000, 288, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, K.; Zylka, M.J.; Sriram, S.; Shearman, L.P.; Weaver, D.R.; Jin, X.; Maywood, E.S.; Hastings, M.H.; Reppert, S.M. mCRY1 and mCRY2 Are Essential Components of the Negative Limb of the Circadian Clock Feedback Loop. Cell 1999, 98, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Kang, T.-H.; Reardon, J.T.; Lee, J.H.; Ozturk, N. Circadian Clock Control of the Cellular Response to DNA Damage. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, H.; Asher, G. Crosstalk between Metabolism and Circadian Clocks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohawk, J.A.; Green, C.B.; Takahashi, J.S. Central and Peripheral Circadian Clocks in Mammals. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelengaris, S.; Khan, M.; Evan, G. c-MYC: More Than Just a Matter of Life and Death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Selb, C.P.; Yang, Y.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Cao, X.; Eynullazada, K.; Sancar, A. Circadian Regulation of c-MYC in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21609–21617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.-L.; Papp, S.J.; Chan, A.B.; Henriksson, E.; Jordan, S.D.; Kriebs, A.; Nguyen, M.; Wallace, M.; Li, Z.; Metallo, C.M.; et al. CRY2 and FBXL3 Cooperatively Degrade C-MYC. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Yamacuchi, S.; Mitsui, S.; Emi, A.; Shimoda, F.; Okamura, H. Control Mechanism of the Circadian Clock for Timing of Cell Division in Vivo. Science 2003, 302, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, S.L.; Vujovic, N.; Williams, J.S.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Impact of Circadian Disruption on Cardiovascular Function and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, E.; Hong, H.K.; Bass, J. Circadian Disruption in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Anjum, B.; Naz, Q.; Raza, S.; Sinha, R.A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Mehdi, A.A.; Verma, N. Night Shift-induced Circadian Disruptions: Links to Initiation of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Risk of Hepatic Cancer. Hepatoma Res. 2024, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.S.; Mrcher, M.; Mohamed, N.E.; Tewari, A.K.; Figueiro, M.G.; Kyprianou, N. Circadian Rhythm Disruption as a Contributor to Racial Disparities in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, G.; Costa, C.; Teodoro, M.; Giambò, F.; Italia, S.; Fenga, C. Women’s Health and Nigh Shift Work: Potential Targets for Future Strategies in Breast Cancer (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2021, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Anand, S.T.; Ebell, M.H.; Vena, J.E.; Robb, S.W. Circadian Disrupting Exposures and Breast Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2015, 88, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, Z.; Lovig, C.; Kommedal, S.; Reszthelyi, R.; Szekeres, G.; Battyani, Z.; Csernus, V.; Nagy, A.D. Altered Expression Patterns of Clock Gene mRNAs and Clock Proteins in Human Skin Tumors. Tumor Biol. 2012, 34, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoun, M.; Eisele, L.; Suzuki, M.; Greally, J.M.; Hüttmann, A.; Aydin, S.; Scholtysik, R.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Dührsen, U.; Dürig, J. Epigenetic Silencing of the Circadian Clock Gene CRY1 Is Associated with an Indolent Clinical Course in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Chang, J.H.; Yeh, K.-T.; Yang, M.-Y.; Liu, T.-C.; Lin, S.-F.; Su, W.-W.; Chang, J.-G. Disturbance of Circadian Gene Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Carinogen. 2008, 47, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L.; Yeh, K.-T.; Lin, P.-M.; Hsu, C.-M.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lin, H.Y.-H.; Lin, S.-F.; Yang, M.-Y. Deregulated Expression of Circadian Clock Genes in Gastric Cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, H.; Takebayashi, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Akahira, J.-I.; Higashimoto, M.; Mashiko, M.; Ito, K.; Niikura, H.; Takenoshita, S.-I.; Yaegashi, N. Clinicopathological Significance of Circadian Rhythm-Related Gene Expression Levels in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2010, 87, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Wei, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Circadian Clock Protein PERIOD2 Suppresses the PI3K/Akt Pathway and Promotes Cisplatin Sensitivity in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11897–11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Bo, C.; Xie, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L. Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Increases Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, A.; Katayose, Y.; Yabuuchi, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Mizuma, M.; Shirasou, S.; Onogawa, T.; Ohtsuka, H.; Yoshida, H.; Hayashi, H.; et al. Clock Gene Mouse Period2 Overexpression Inhibits Growth of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells and Has Synergistic Effect with Cisplatin. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 1201–1209. Available online: https://ar.iiarjournals.org/content/29/4/1201.long (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Jiang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, E.; Hu, G.; Hu, B.; Zheng, P.; Xiao, J.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y.; et al. The Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Acts as a Potential Anti-Oncogene in Pancreatic Cancer by Activating the p53 Tumor Suppressor Pathway. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Gaddameedhi, S.; Ozturk, N.; Ye, R.; Sancar, A. DNA Damage–Specific Control of Cell Death by Cryptochrome in P53-Mutant Ras–Transformed Cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.A.; McNair, C.M.; McCann, J.J.; Alshalalfa, M.; Shostak, A.; Severson, T.M.; Zhu, Y.; Bergman, A.; Gordon, N.; Mandigo, A.C.; et al. The Circadian Cryptochrome, CRY1, Is a pro-Tumorigenic Factor That Rhythmically Modulates DNA Repair. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazley, M.; Sato, M.; Hase, T.; Yamashita, R.; Yoshida, K.; Toyokuni, S.; Ishiguro, F.; Osada, H.; Sekido, Y.; Yokoi, K.; et al. The Circadian Clock Gene BMAL1 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2820–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Xia, K.; Yang, Y.; Aman, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, H. Circadian Protein BMAL1 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Up-Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase9 Expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, R.V.; Kowalczyk, M.S.; de Boer, C.G.; Schneider, R.K.; Miller, P.G.; McConkey, M.; Tothova, Z.; Tejero, H.; Heckl, D.; Järås, M.; et al. Core Circadian Clock Genes Regulate Leukemia Stem Cells in AML. Cell 2016, 165, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Qu, M.; Gimple, R.C.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Prager, B.C.; Wang, X.; Kim, L.J.Y.; Morton, A.R.; et al. Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells through Disruption of the Circadian Clock. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1556–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Su, B.; Mo, L.; Qiu, W.; Ying, J.; Lin, P.; Yang, B.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; et al. Circadian Clock Protein CRY1 Prevents Paclitaxel-induced Senescence of Bladder Cancer Cells by Promoting P53 Degradation. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanos, T.; Theodoropoulos, G.; Gazouli, M.; Vaiopoulou, A.; Karantanou, C.; Lymberi, M.; Pektasides, D. Expression of Clock Genes in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2013, 28, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Zheng, W.; Bai, B.; Hu, J.; Lv, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. BMAL1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through ERK- and JNK-Dependent c-Myc Expression. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 4472–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and Definitions for Research on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; He, Q.; Shang, K.; Xu, X.; Luo, X.; Zhou, D.; Jin, F. The Circadian Clock Gene, BMAL1, Promotes Radiosensitization in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Inhibiting the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the TGF-Β1/Smads/Snail1 Axis. Oral Oncol. 2024, 152, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Herreros, A.G.; Peiró, S.; Nassour, M.; Savagner, P. Snail Family Regulation and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Breast Cancer Progression. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2010, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuault, S.; Tan, E.J.; Peinado, H.; Cano, A.; Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. HMGA2 and Smads Co-Regulate SNAIL1 Expression during Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33437–33446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Jaye, D.L.; Kajita, M.; Geigerman, C.; Moreno, C.S.; Wade, P.A. MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD Complex Subunit, Regulates an Invasive Growth Pathway in Breast Cancer. Cell 2003, 113, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhasarathy, A.; Kajita, M.; Wade, P.A. The Transcription Factor Snail Mediates Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transitions by Repression of Estrogen Receptor-α. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chai, K.; Ying, X.; Zhou, B.P. The Role of Snail in EMT and Tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, S.E.; Perez, D.; Pan, T.; Sarkisian, C.J.; Portocarrero, C.P.; Sterner, C.J.; Notorfrancesco, K.L.; Cardiff, R.D.; Chodosh, L.A. The Transcriptional Repressor Snail Promotes Mammary Tumor Recurrence. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Sato, H.; Jin, D.; Bhawal, U.K.; Wu, Y.; Noshiro, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Seino, H.; Morohashi, S.; et al. Smad3 and Snail Show Circadian Expression in Human Gingival Fibroblasts, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell, and in Mouse Liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Chu, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, P.; Yang, M. Identification and Characterization of the CDK1-BMAL1-UHRF1 Pathway Driving Tumor Progression. iScience 2023, 26, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Devocelle, A.; Desterke, C.; de Souza, L.E.B.; Hadadi, É.; Acloque, H.; Foudi, A.; Xiang, Y.; Ballesta, A.; Chang, Y.; et al. BMAL1 Knockdown Leans Epithelial–Mesenchymal Balance toward Epithelial Properties and Decreases the Chemoresistance of Colon Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró, S.; Escrivà, M.; Puig, I.; Barberà, M.J.; Dave, N.; Herranz, N.; Larriba, M.J.; Takkunen, M.; Francí, C.; Muñoz, A.; et al. Snail1 Transcriptional Repressor Binds to Its Own Promoter and Controls Its Expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Bhawal, U.K.; Yoshimura, T.; Muragaki, Y. DEC1 and DEC2 Crosstalk between Circadian Rhythm and Tumor Progression. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, D.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Zhu, W.; Hu, X.-T.; Liu, C.-W. Effect of DEC1 on the Proliferation, Adhesion, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Osteosarcoma Cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2360–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sato, F.; Yamada, T.; Bhawal, U.K.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Noshiro, M.; Seino, H.; Morohashi, S.; Hakamada, K.; et al. The BHLH Transcription Factor DEC1 Plays an Important Role in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Dauchy, R.T.; Blask, D.E.; Slakey, L.M.; Xiang, S.; Yuan, L.; Dauchy, E.M.; Shan, B.; Brainard, G.C.; Hanifin, J.P.; et al. Circadian Gating of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells via Melatonin-Regulation of GSK3β. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1808–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotegut, S.; von Schweinitz, D.; Christofori, G.; Lehembre, F. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Induces Cell Scattering through MAPK/Egr-1-Mediated Upregulation of Snail. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3534–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, F.; Kawamura, H.; Wu, Y.; Sato, H.; Jin, D.; Bhawal, U.K.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Noshiro, M.; Seino, H.; et al. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor DEC2 Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Tumor Progression in Human Pancreatic Cancer BxPC-3 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.K.; Imaizumi, T.; Kay, S.A. Real-Time Reporting of Circadian-Regulated Gene Expression by Luciferase Imaging in Plants and Mammalian Cells. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 393, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellupitiyage Don, S.S.; Lin, H.-H.; Furtado, J.J.; Qraitem, M.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Circadian Oscillations Persist in Low Malignancy Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Circadian Alterations Increase with Progression in a Patient-Derived Cell Culture Model of Breast Cancer. Clocks Sleep 2021, 3, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.E.; Liu, A.C.; Hirota, T.; Miraglia, L.J.; Welch, G.; Pongsawakul, P.Y.; Liu, X.; Atwood, A.; Huss, J.W.; Janes, J.; et al. A Genome-Wide RNAi Screen for Modifiers of the Circadian Clock in Human Cells. Cell 2009, 139, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, J.E.; Price, T.S.; DiTacchio, L.; Panda, S.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Hogenesch, J.B. Network Features of the Mammalian Circadian Clock. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, T.; Lewis, W.G.; Liu, A.C.; Lee, J.W.; Schultz, P.G.; Kay, S.A. A Chemical Biology Approach Reveals Period Shortening of the Mammalian Circadian Clock by Specific Inhibition of GSK-3β. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20746–20751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, B.; Wendt, S.; Vanselow, J.T.; Wallach, T.; Reischl, S.; Oehmke, S.; Schlosser, A.; Kramer, A. A Large-Scale Functional RNAi Screen Reveals a Role for CK2 in the Mammalian Circadian Clock. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-H.; Robertson, K.L.; Lellupitiyage Don, S.S.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Chemical Modulation of Circadian Rhythms and Assessment of Cellular Behavior via Indirubin and Derivatives. Methods Enzymol. 2020, 639, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeyev, M.F.; Fayzulin, R.; Shokolenko, I.N.; Pastukh, V. A Retro-Lentiviral System for Doxycycline-Inducible Gene Expression and Gene Knockdown in Cells with Limited Proliferative Capacity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 1987–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-H.; Robertson, K.L.; Bisbee, H.A.; Farkas, M.E. Oncogenic and Circadian Effects of Small Molecules Directly and Indirectly Targeting the Core Circadian Clock. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1534735420924094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhe, K.; Hegde, M.S.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Circadian Effects of Melatonin Receptor-Targeting Molecules In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, S.; Sun, C.; Li, B.; Wu, S.A.; Lyu, J.; Shi, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circadian Clocks are Modulated by Compartmentalized Oscillating Translation. Cell 2023, 186, P3245–P3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Fong, S.Y.; Shon, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Brooks, R.; Lahens, N.F.; Chen, D.; Dang, C.V.; Field, J.M.; Sehgal, A. Time-of-Day Specificity of Anticancer Drugs May be Mediated by Circadian Regulation of the Cell Cycle. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Xie, X.; Ye, C.; Dean, K.M.; Laothamatas, I.; Taufique, S.K.T.; Takahashi, J.; Yamazaki, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y. Mammalian Circadian Clock Proteins from Dynamic Interacting Microbodies distinct from Phase Separation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2318274120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Endale, M.; Wang, W.; Morris, A.R.; Francey, L.J.; Harold, R.L.; Hammers, D.W.; Huo, Z.; Partch, C.L.; Hogenesch, J.B.; et al. NF-κB Modifies the Mammalian Circadian Clock through Interaction with the Core Clock Protein BMAL1. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leise, T.L.; Want, C.W.; Gritis, P.J.; Welsh, D.K. Persistent Cell-Autonomous Circadian Oscillations in Fibroblasts Revealed by Six-Week Single-Cell Imaging of PER2::LUC Bioluminescence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padlom, A.; Ono, D.; Hamashima, R.; Furukawa, Y.; Yoshimura, T.; Nishiwaki-Ohkawa, T. Level of Constitutively Expressed BMAL1 Affects the Robustness of Circadian Oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, O.; Luni, C.; Li, Y.; Angiolillo, S.; Qin, W.; Panariello, F.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Takahashi, J.S.; Elvassore, N. Synchronization between Peripheral Circadian Clock and Feeding-Fasting Cycles in Microfluidic Device Sustains Oscillatory Pattern of Transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-H.; Farkas, M.E. Altered Circadian Rhythms and Breast Cancer: From the Human to the Molecular Level. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-H.; Qraitem, M.; Lian, Y.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Analyses of BMAL1 and PER2 Oscillations in a Model of Breast Cancer Progression Reveal Changes With Malignancy. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419836494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre, A.; Damiola, F.; Schibler, U. A Serum Shock Induces Circadian Gene Expression in Mammalian Tissue Culture Cells. Cell 1998, 93, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Mao, L.; Duplessis, T.; Yuan, L.; Dauchy, R.; Dauchy, E.; Blask, D.E.; Frasch, T.; Hill, S.M. Oscillation of Clock and Clock Controlled Genes Induced by Serum Shock in Human Breast Epithelial and Breast Cancer Cells: Regulation by Melatonin. Breast Cancer Basic. Clin. Res. 2012, 6, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagita, K.; Okamura, H. Forskolin Induces Circadian Gene Expression of rPer1, rPer2 and Dbp in Mammalian Rat-1 Fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 2000, 465, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Shi, X.; Bai, J. miR-30a Regulates the Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting Snail. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, S.S.L.; Robertson, K.L.; Lin, H.-H.; Labriola, C.; Harrington, M.E.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Nobiletin Affects Circadian Rhythms and Oncogenic Characteristics in a Cell-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, G.; Ricciardi, M.R.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Zampieri, M.; Ciccarone, F.; Guastafierro, T.; Calabrese, R.; Valentini, E.; Tafuri, A.; Bufalo, D.D.; et al. PARP Inhibitor ABT-888 Affects Response of MDA-MB-231 Cells to Doxorubicin Treatment, Targeting Snail Expression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15008–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, R.; Mallets, E.; Gomez-Cambronero, J. The Transcription Factors Slug (SNAI2) and Snail (SNAI1) Regulate Phospholipase D (PLD) Promoter in Opposite Ways towards Cancer Cell Invasion. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 663–676, Erratum in Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Burton, L.J.; Henderson, V.; Randle, D.D.; Morton, D.J.; Smith, B.A.; Taliaferro-Smith, L.; Nagappan, P.; Yates, C.; Zayzafoon, M.; et al. Snail Promotes Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells in Part via Activation of Nuclear ERK2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chhe, K.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Spielberger, S.A.; Lin, H.-H.; Taylor, S.R.; Farkas, M.E. Reporter-Mediated Evaluation of the Circadian Oscillations of SNAIL Across In Vitro Models. Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040054
Chhe K, Kalyanaraman B, Spielberger SA, Lin H-H, Taylor SR, Farkas ME. Reporter-Mediated Evaluation of the Circadian Oscillations of SNAIL Across In Vitro Models. Clocks & Sleep. 2025; 7(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleChhe, Kaitlyn, Bhavna Kalyanaraman, Sophie A. Spielberger, Hui-Hsien Lin, Stephanie R. Taylor, and Michelle E. Farkas. 2025. "Reporter-Mediated Evaluation of the Circadian Oscillations of SNAIL Across In Vitro Models" Clocks & Sleep 7, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040054
APA StyleChhe, K., Kalyanaraman, B., Spielberger, S. A., Lin, H.-H., Taylor, S. R., & Farkas, M. E. (2025). Reporter-Mediated Evaluation of the Circadian Oscillations of SNAIL Across In Vitro Models. Clocks & Sleep, 7(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040054






