Social Deprivation and Ethnicity Are Associated with More Problematic Sleep in Middle-Aged and Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inadequacy of Sleep Duration
2.2. Individual Sleep Problems
2.3. Problematic Sleep Index
3. Method
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Data Sources and Management
3.3. Statistical Analyses
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohayon, M.M.; Carskadon, M.A.; Guilleminault, C.; Vitiello, M.V. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: Developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep 2004, 27, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Monica, C.; Johnsen, S.; Atzori, G.; Groeger, J.A.; Dijk, D.J. Rapid eye movement sleep, sleep continuity and slow wave sleep as predictors of cognition, mood, and subjective sleep quality in healthy men and women, aged 20–84 years. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klerman, E.B.; Dijk, D.-J. Age-related reduction in the maximal capacity for sleep--implications for insomnia. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliwise, D.L.; King, A.C.; Harris, R.B.; Haskell, W.L. Prevalence of self-reported poor sleep in a healthy population aged 50–65. Soc. Sci. Med. 1992, 34, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, M.V.; Larsen, L.H.; Moe, K.E. Age-related sleep change: Gender and estrogen effects on the subjective-objective sleep quality relationships of healthy, noncomplaining older men and women. J. Psychosom. Res. 2004, 56, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmot, M. Social determinants of health inequalities. Lancet 2005, 365, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, O.; Jike, M.; Watanabe, N.; Kaneita, Y. Short sleep duration and health outcomes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Sleep Med. 2017, 32, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jike, M.; Itani, O.; Watanabe, N.; Buysse, D.J.; Kaneita, Y. Long sleep duration and health outcomes: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 39, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Taggart, F.M.; Kandala, N.-B.; Currie, A.; Peile, E.; Stranges, S.; Miller, M.A. Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 2008, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallicchio, L.; Kalesan, B. Sleep duration and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sleep Res. 2009, 18, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurina, L.M.; McClintock, M.K.; Chen, J.H.; Waite, L.J.; Thisted, R.A.; Lauderdale, D.S. Sleep duration and all-cause mortality: A critical review of measurement and associations. Ann. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, J.A.; Zijlstra, F.R.H.; Dijk, D.-J. Sleep quantity, sleep difficulties and their perceived consequences in a representative sample of some 2000 British adults. J. Sleep Res. 2004, 13, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Katz, E.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; et al. National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: Methodology and results summary. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Hillard, P.J.; Katz, E.S.; et al. National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: Final report. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerstedt, T.; Ghilotti, F.; Grotta, A.; Zhao, H.; Adami, H.O.; Trolle-Lagerros, Y.; Bellocco, R. Sleep duration and mortality—Does weekend sleep matter? J. Sleep Res. 2019, 28, e12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allshouse, A.; Pavlovic, J.; Santoro, N. Menstrual cycle hormone changes associated with reproductive aging and how they may relate to symptoms. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 45, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.; Wickwire, E.M.; Hirshkowitz, M. National Sleep Foundation’s sleep quality recommendations: First report. Sleep Health 2017, 3, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandner, M.A. Sleep, health, and society. Sleep Med. Clin. 2017, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, M.E.; DeCoster, J.; Lichstein, K.L.; Jacobs, L. Sleep disorders in African-American and Caucasian-Americans: A meta-analysis. Behav. Sleep Med. 2010, 8, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, M.E.; DeCoster, J.; Lichstein, K.L.; Jacobs, L. Normal sleep in African-Americans and Caucasian-Americans: A meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Chavez, P.J.; Zee, P.C.; Kim, K.; Liu, K.; Goldberger, J.J.; Ng, J.; Knutson, K.L. Disparities in sleep characteristics by race/ethnicity in a population-based sample: Chicago area sleep study. Sleep Med. 2016, 18, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller-Rowell, T.E.; Curtis, D.S.; El-Sheikh, M.; Chae, D.H.; Boylan, J.M.; Ryff, C.D. Racial disparities in sleep: The role of neighborhood disadvantage. Sleep Med. 2016, 27–28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.L.; Hu, F.B.; Redline, S.; Williams, D.R.; Mattei, J.; Kawachi, I. Racial/ethnic disparities in short sleep duration by occupation: The contribution of immigrant status. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 118, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, L.; Do, D.P. Racial differences in self-reports of sleep duration in a population-based study. Sleep 2007, 30, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Hall, K.A.; Reynolds, A.; Palmer, L.J.; Mukherjee, S. The relationship of sleep duration with ethnicity and chronic disease in a Canadian general population cohort. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.; Phillimore, P.; Beattie, A. Health and Deprivation: Inequality and the North; Routledge: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, S.; Bonsall, A. UK Townsend Deprivation Scores from 2011 Census Data; The UK Data Service: London, UK; The Department for Education: London, UK, 2017.
- Good, I.J. C140 Standardized tail-area probabilities. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1982, 16, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, C.R. Effect Size Guidelines, Sample Size Calculations, and Statistical Power in Gerontology. Innov. Aging 2019, 3, igz036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, D.A.; Millert, D.T. When small effects are impressive. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besedovsky, L.; Lange, T.; Haack, M. The sleep-immune crosstalk in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1325–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, K. Differences in sleep duration among four different population groups of older adults in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadie, A.; Shafto, M.; Leng, Y.; Kievit, R.A. How are age-related differences in sleep quality associated with health outcomes? an epidemiological investigation in a UK cohort of 2406 adults. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Billings, M.E.; Lauren Hale, L. Environmental determinants of insufficient sleep and sleep disorders: Implications for population health. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, M.E.; Hale, L.; Johnson, D.A. Physical and social environment relationship with sleep health and disorders. Chest 2020, 157, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepsomali, P.; Groeger, J.A. Examining the role of systemic chronic inflammation in diet and sleep relationship. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.C.; Colman, A.M. Optimal number of response categories in rating scales: Reliability, validity, discriminating power, and respondent preferences. Acta Psychol. 2000, 104, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Paek, I. In Search of the Optimal Number of Response Categories in a Rating Scale. J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 2014, 32, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, K.A.; Bauldry, S. Three Cs in measurement models: Causal indicators, composite indicators, and covariates. Psychol. Methods 2011, 16, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, A.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Sudlow, C.; Doherty, N.; Adamska, L.; Sprosen, T.; Collins, R.; Allen, N.E. Comparison of Sociodemographic and Health-Related characteristics of UK Biobank participants with those of the general population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

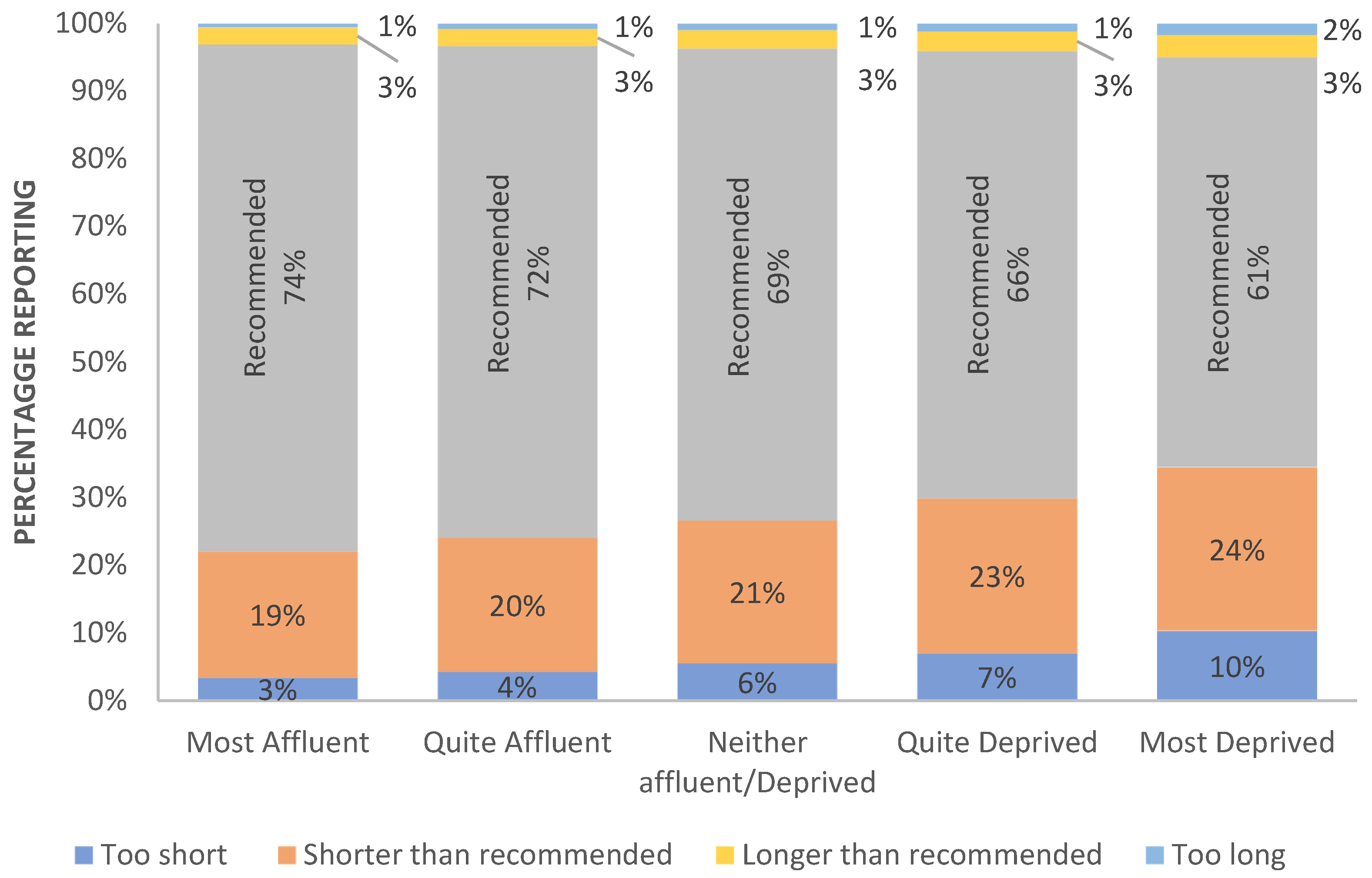
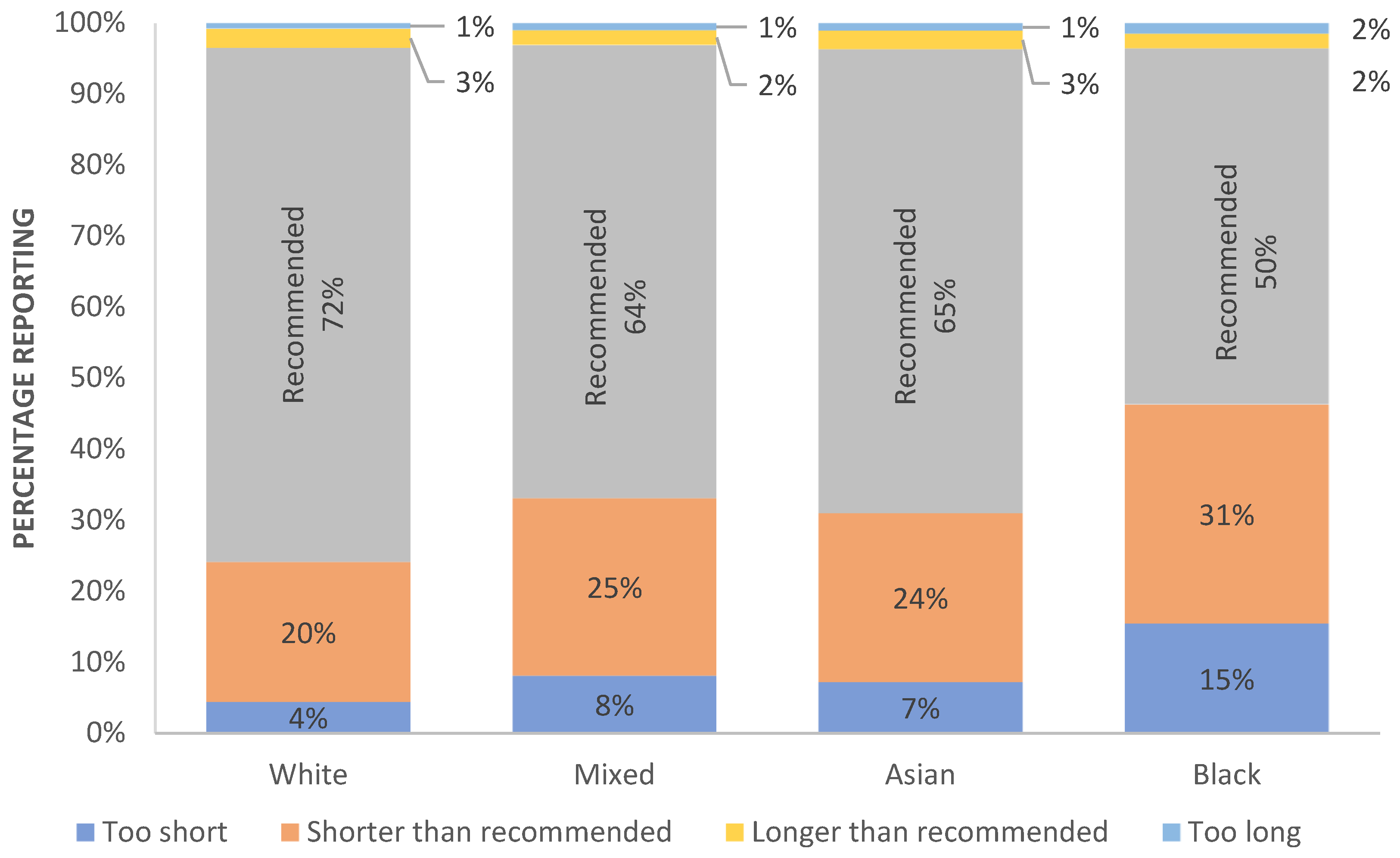
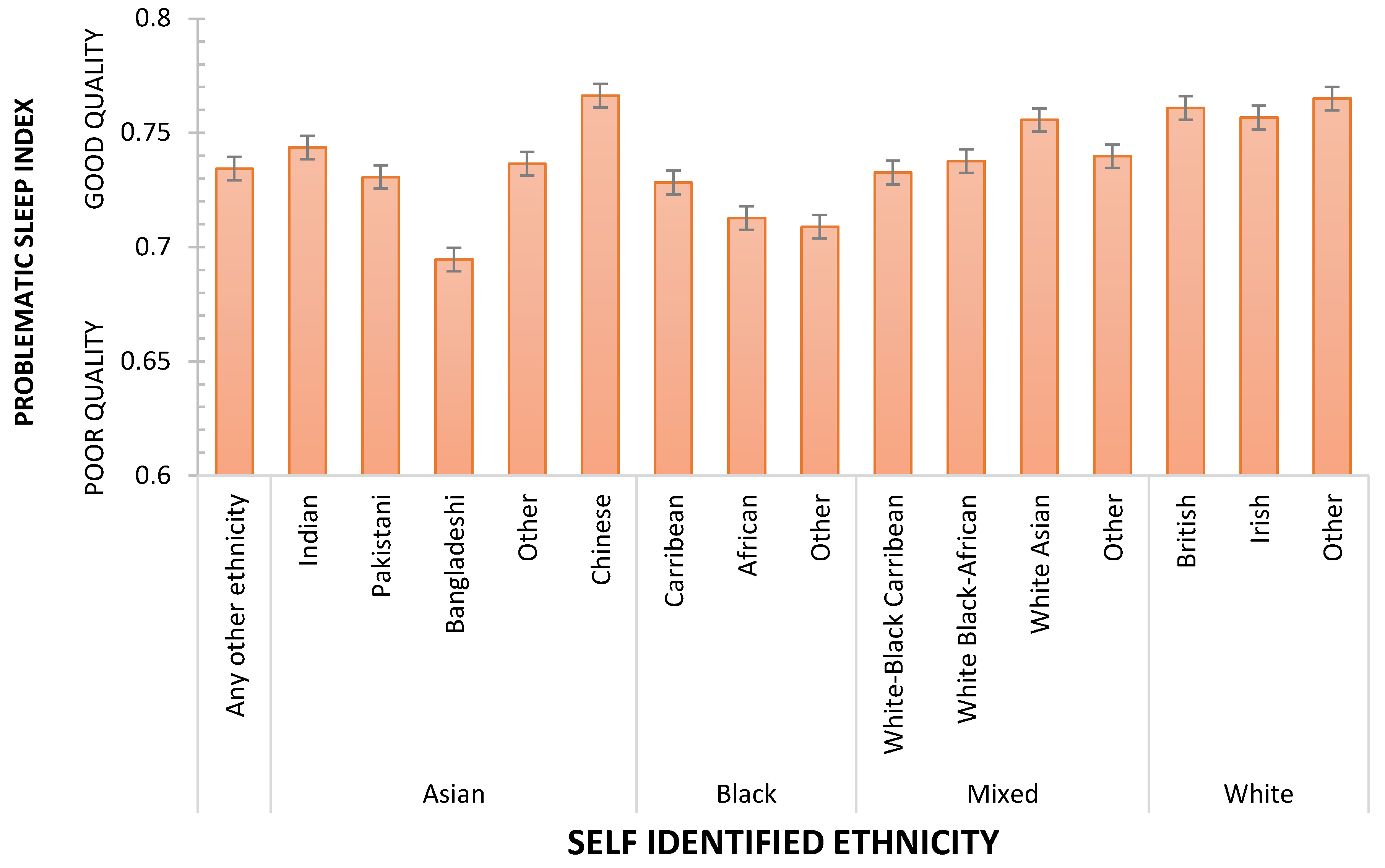

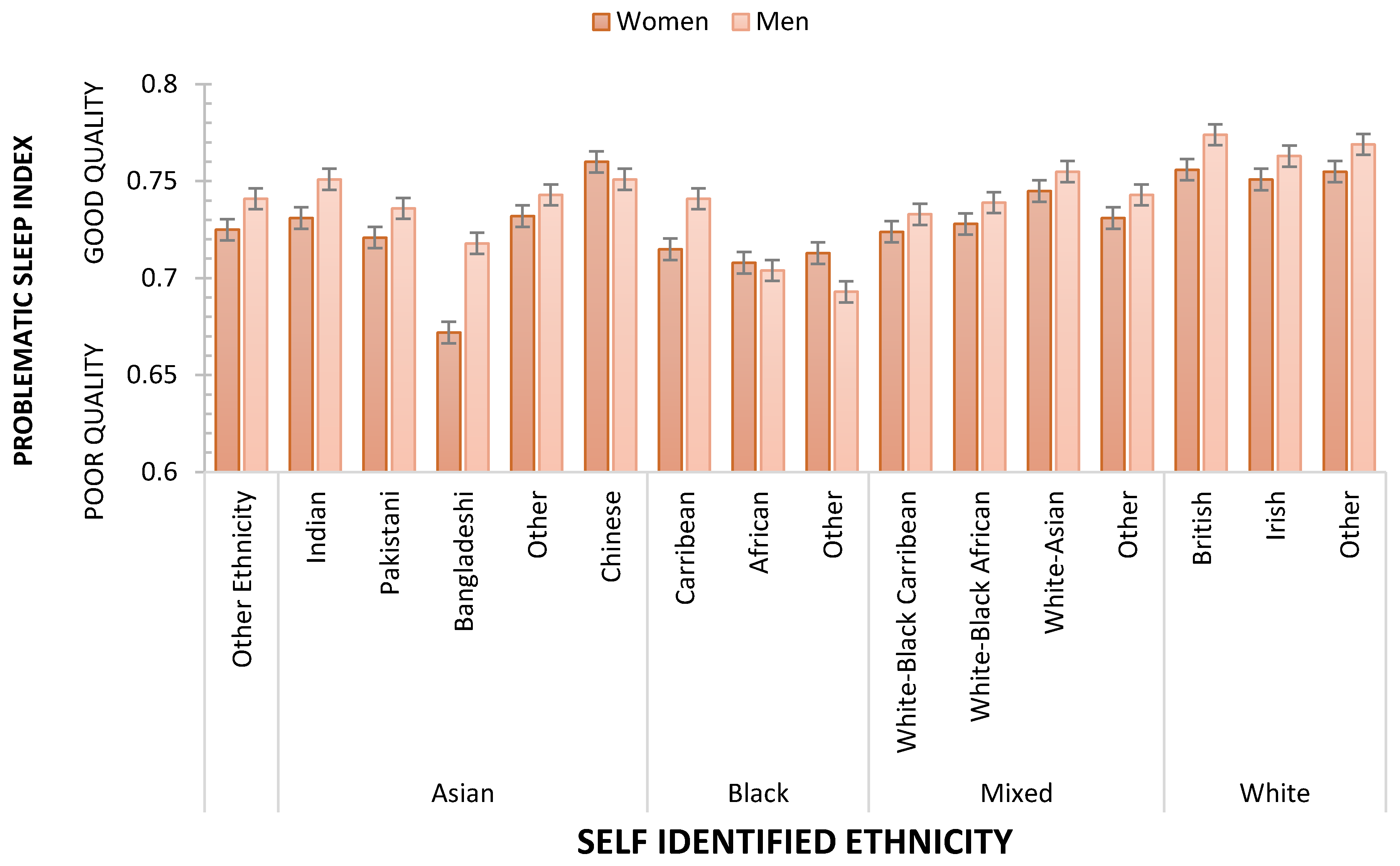
| ETHNICITY/RACE | N | Most Affluent | Quite Affluent | Neither Affluent/Deprived | Quite Deprived | Most Deprived |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTHER ETHNICITY/RACE | 4542 | 19 (58) | 15 (61) | 19 (57) | 24 (59) | 23 (50) |
| ASIAN | ||||||
| Indian | 5944 | 25 (49) | 23 (49) | 26 (51) | 20 (48) | 6 (46) |
| Pakistani | 1835 | 17 (41) | 16 (44) | 19 (39) | 32 (38) | 15 (35) |
| Bangladeshi | 236 | 9 (38) | 14 (38) | 16 (45) | 22 (25) | 39 (25) |
| Other | 1851 | 21 (53) | 17 (48) | 25 (43) | 22 (44) | 15 (42) |
| Chinese | 1569 | 36 (62) | 20 (67) | 21 (62) | 15 (63) | 9 (59) |
| BLACK | ||||||
| Caribbean | 4511 | 11 (60) | 15 (61) | 21 (64) | 29 (66) | 24 (63) |
| African | 3380 | 7 (58) | 9 (48) | 15 (51) | 26 (51) | 44 (48) |
| Other | 150 | 8 (58) | 15 (59) | 20 (77) | 25 (76) | 33 (57) |
| MIXED | ||||||
| White-Black Caribbean | 620 | 22 (56) | 18 (72) | 19 (66) | 25 (62) | 17 (60) |
| White-Black African | 425 | 19 (62) | 14 (57) | 21 (73) | 25 (72) | 21 (80) |
| White Asian | 831 | 34 (61) | 20 (56) | 19 (60) | 19 (55) | 9 (55) |
| Other | 1081 | 27 (66) | 19 (65) | 18 (65) | 21 (61) | 15 (57) |
| WHITE | ||||||
| British | 44,2059 | 48 (54) | 22 (55) | 14 (55) | 11 (54) | 4 (49) |
| Irish | 13,195 | 36 (54) | 22 (54) | 17 (53) | 15 (49) | 9 (45) |
| Other | 16,879 | 32 (61) | 21 (62) | 19 (61) | 18 (61) | 10 (57) |
| B | SE | β | 95% CI | t | p | Cohen’s f 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Constant) | 0.8072 | 0.0020 | 409.3759 | 0.0000 | |||
| Sex (0, F; 1, M) | 0.0164 | 0.0004 | 0.0756 | 0.8034, 0.8111 | 44.9533 | 0.0000 | 0.00566 |
| Age (40,45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70+, 1–7) | −0.0023 | 0.0001 | −0.0347 | 0.0157, 0.0171 | −17.0040 | <0.001 | 0.00078 |
| Qualifications (Degree to none) | −0.0020 | 0.0001 | −0.0346 | −0.0026, −0.0020 | −19.4605 | <0.001 | 0.00103 |
| Deprivation (Most to Least Affluent, 1–5) | −0.0046 | 0.0002 | −0.0537 | −0.0022, −0.0018 | −27.2523 | <0.001 | 0.00212 |
| Ethnicity/Race (White, 1; Mixed, 2; Asian, 3; Black, 4) | −0.0087 | 0.0006 | −0.0266 | −0.0050, −0.0043 | −13.7062 | <0.001 | 0.00053 |
| Nativity (1-UK born, 0: Migrant) | −0.0015 | 0.0007 | −0.0039 | −0.0099, −0.0074 | −1.9689 | 0.0490 | 0.00001 |
| Accommodation (House,1; Flat, 2; Mobile,3) | −0.0008 | 0.0006 | −0.0025 | −0.0029, 0.0000 | −1.2828 | 0.1996 | 0.00000 |
| Owning, renting, living rent free (1,2,3) | −0.0148 | 0.0006 | −0.0461 | −0.0020, 0.0004 | −23.6342 | <0.001 | 0.00152 |
| Number in household | −0.0002 | 0.0002 | −0.0021 | −0.0160, −0.0135 | −1.0372 | 0.2997 | 0.00003 |
| Number in household years at address | −0.0004 | 0.0001 | −0.0058 | −0.0006, 0.0002 | −3.1297 | 0.0017 | 0.00000 |
| Total household income | 0.0069 | 0.0002 | 0.0765 | −0.0007, −0.0002 | 34.9370 | <0.001 | 0.00338 |
| Number of vehicles | 0.0005 | 0.0003 | 0.0042 | 0.0065, 0.0073 | 1.9813 | 0.0476 | 0.00001 |
| Paid job, 1; Retired, 2; Home/Carer, 3; Voluntary, 4; Unable, 5; Unemployed, 6 | −0.0123 | 0.0002 | −0.1169 | 0.0000, 0.0010 | −64.7604 | 0.0000 | 0.01180 |
| ASIAN | BLACK | MIXED | WHITE | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Ethnicity | Indian | Pakistani | Bangladeshi | Other | Chinese | Caribbean | African | Other | White-Caribbean | White-Black African | White Asian | Other | British | Irish | Other | |
| OTHER ETHNICITY/RACE | p * | N * | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||||
| ASIAN | ||||||||||||||||
| Indian | N * | N * | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||||
| Pakistani | p * | N * | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||||
| Bangladeshi | p * | p * | ||||||||||||||
| Other | N * | p * | p * | |||||||||||||
| Chinese | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | |||||||||||
| BLACK | ||||||||||||||||
| Caribbean | p * | p * | N * | p * | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||
| African | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | ||||
| Other | p * | p * | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||||
| MIXED | ||||||||||||||||
| White-Caribbean | p * | p * | p * | |||||||||||||
| White-Black African | N * | p * | p * | |||||||||||||
| White Asian | N * | N * | N * | |||||||||||||
| Other | N * | p * | p * | p * | ||||||||||||
| WHITE | ||||||||||||||||
| British | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | ||||
| Irish | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | p * | p * | ||||||
| Other | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | N * | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Groeger, J.A.; Hepsomali, P. Social Deprivation and Ethnicity Are Associated with More Problematic Sleep in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Clocks & Sleep 2023, 5, 399-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030030
Groeger JA, Hepsomali P. Social Deprivation and Ethnicity Are Associated with More Problematic Sleep in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Clocks & Sleep. 2023; 5(3):399-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleGroeger, John A., and Piril Hepsomali. 2023. "Social Deprivation and Ethnicity Are Associated with More Problematic Sleep in Middle-Aged and Older Adults" Clocks & Sleep 5, no. 3: 399-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030030
APA StyleGroeger, J. A., & Hepsomali, P. (2023). Social Deprivation and Ethnicity Are Associated with More Problematic Sleep in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Clocks & Sleep, 5(3), 399-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030030







