Clinical Evaluation and Management of Overlap Syndrome (OS) and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sleep Protocol
4.2. Pulmonary Function Test
4.3. Blood Gas Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.L.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, P.; Fanfulla, F.; Sabato, R.; Scioscia, G.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea-Hypopnoea Syndrome (OSAHS): State of the art. Minerva Med. 2022; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Manyari, P.A.; Arriola-Guillén, L.E.; Jimenez-Valdivia, L.M.; Dias-Da Silveira, H.L.; Boessio-Vizzotto, M. Effect of the application of software on the volumetric and cross-sectional assessment of the oropharyngeal airway of patients with and without an open bite: A CBCT study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2022, 59, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastan, F.; Ghaffari, H.; Shishvan, H.H.; Zareiyan, M.; Akhlaghian, M.; Shahab, S. Correlation between the upper airway volume and the hyoid bone position, palatal depth, nasal septum deviation, and concha bullosa in different types of malocclusion: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriondo, G.; Scioscia, G.; Soccio, P.; Tondo, P.; De Pace, C.C.; Sabato, R.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. Effect of Hypoxia-Induced Micro-RNAs Expression on Oncogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanik, D.; Gać, P.; Martynowicz, H.; Poręba, M.; Podgórski, M.; Negrusz-Kawecka, M.; Mazur, G.; Sobieszczańska, M.; Poręba, R. Obstructive sleep apnea as a predictor of reduced heart rate variability. Sleep Med. 2019, 54, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gać, P.; Urbanik, D.; Macek, P.; Martynowicz, H.; Mazur, G.; Poręba, R. Coexistence of cardiovascular risk factors and obstructive sleep apnoea in polysomnography. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2022, 295, 103782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanik, D.; Gać, P.; Martynowicz, H.; Podgórski, M.; Poręba, M.; Mazur, G.; Poręba, R. Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a Predictor of Arrhythmias in 24-h ECG Holter Monitoring. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, P.; Fanfulla, F.; Scioscia, G.; Sabato, R.; Salvemini, M.; De Pace, C.C.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. The Burden of Respiratory Alterations during Sleep on Comorbidities in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA). Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutrakul, S.; Mokhlesi, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Diabetes: A State of the Art Review. Chest 2017, 152, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia, D.; Landriscina, M.; Scioscia, G.; Tondo, P.; Caccavo, I.; Bruno, G.; Giordano, G.; Piscazzi, A.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Worsens Progression-Free and Overall Survival in Human Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5528303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaggi, H.K.; Concato, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Lichtman, J.H.; Brass, L.M.; Mohsenin, V. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, S.; Williams, L.J.; Roguski, A.; Vennelle, M.; Douglas, N.J.; Kotoulas, S.C.; Riha, R.L. Mortality and morbidity in obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome: Results from a 30-year prospective cohort study. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00057–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholas, W.T. COPD-OSA Overlap Syndrome: Evolving Evidence Regarding Epidemiology, Clinical Consequences, and Management. Chest 2017, 152, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendzerska, T.; Leung, R.S.; Aaron, S.D.; Ayas, N.; Sandoz, J.S.; Gershon, A.S. Cardiovascular Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Overlap Syndrome). Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhlesi, B.; Masa, J.F.; Brozek, J.L.; Gurubhagavatula, I.; Murphy, P.B.; Piper, A.J.; Tulaimat, A.; Afshar, M.; Balachandran, J.S.; Dweik, R.A.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e6–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masa, J.F.; Pépin, J.L.; Borel, J.C.; Mokhlesi, B.; Murphy, P.B.; Sánchez-Quiroga, M.Á. Obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2019, 28, 180097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.; Whitman, K. Lack of benefit of continuous positive airway pressure on lung function in patients with overlap syndrome. Lung 2005, 183, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biselli, P.; Grossman, P.R.; Kirkness, J.P.; Patil, S.P.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R.; Schneider, H. The effect of increased lung volume in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on upper airway obstruction during sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachman, S.L.; Tiwari, R.; Vega, M.E.; Yu, D.; Soler, X.; Jaffe, F.; Kim, V.; Swift, I.; D’Alonzo, G.E.; Criner, G.J.; et al. Effect of Emphysema Severity on the Apnea-Hypopnea Index in Smokers with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Peppard, P.E.; Gottlieb, D.J. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: A population health perspective. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholas, W.T.; Hansson, D.; Schiza, S.; Grote, L. Sleep in chronic respiratory disease: COPD and hypoventilation disorders. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2019, 28, 190064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BaHammam, A. Excessive daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, A.L.; Zwillich, C. The obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kaur, H.; Singh, S.; Khawaja, I. The Overlap Syndrome. Cureus 2018, 10, e3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia, D.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Aliani, M.; Sabato, R.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Spanevello, A.; Carone, M.; Fanfulla, F. Daytime PaO2 in OSAS, COPD and the combination of the two (overlap syndrome). Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioachimescu, O.C.; Janocko, N.J.; Ciavatta, M.M.; Howard, M.; Warnock, M.V. Obstructive Lung Disease and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OLDOSA) cohort study: 10-year assessment. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia, D.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Patricelli, G.; Carone, M.; Gallo, C.; Caccavo, I.; Sabato, R.; Depalo, A.; Aliani, M.; Capozzolo, A.; et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, overlap syndrome and obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, R.L.; Malhotra, A. Sleep-disordered breathing and COPD: The over-lap syndrome. Respir. Care 2010, 55, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Kreivi, H.R.; Itäluoma, T.; Bachour, A. Effect of ventilation therapy on mortality rate among obesity hypoventilation syndrome and obstructive sleep apnoea patients. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00101–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budweiser, S.; Riedl, S.G.; Jörres, R.A.; Heinemann, F.; Pfeifer, M. Mortality and prognostic factors in patients with obesity-hypoventilation syndrome undergoing noninvasive ventilation. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soghier, I.; Brożek, J.L.; Afshar, M.; Tamae Kakazu, M.; Wilson, K.C.; Masa, J.F.; Mokhlesi, B. Noninvasive Ventilation versus CPAP as Initial Treatment of Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Sheng, W.; Huai, D.; Cao, J.; Su, M.; Ning, D.; Xue, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X. Comparison between auto-trilevel and bilevel positive airway pressure ventilation for treatment of patients with concurrent obesity hypoventilation syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. Schlaf Atm. 2019, 23, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Maric, M.P.; Hamm, C.; Duiverman, M.L.; Schwarz, S.; Callegari, J.; Storre, J.H.; Schmoor, C.; Spielmanns, M.; Galetke, W.; Windisch, W. Obesity hypoventilation syndrome treated with non-invasive ventilation: Is a switch to CPAP therapy feasible? Respirology 2020, 25, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, P.; Pronzato, C.; Risi, I.; D’Artavilla Lupo, N.; Trentin, R.; Arcovio, S.; Fanfulla, F. Switch of Nocturnal Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NPPV) in Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiamonte, P.; Mazzuca, E.; Gruttad’Auria, C.I.; Castrogiovanni, A.; Marino, C.; Lo Nardo, D.; Basile, M.; Algeri, M.; Battaglia, S.; Marrone, O.; et al. Use of autobilevel ventilation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: An observational study. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Agusti, A.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Criner, G.J.; Frith, P.; Halpin, D.; Han, M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: The GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1900164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Quan, S.F.; Troester, M.T.; Vaughn, B.V. AASM Scoring Manual Updates for 2017 (Version 2.4). J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, C.A.; Chediak, A.; Berry, R.B.; Brown, L.K.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; Rowley, J.A.; Positive Airway Pressure Titration Task Force; et al. Clinical guidelines for the manual titration of positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 157–171. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Total |
|---|---|
| n = 132 | |
| Sex, male, % | 77% |
| Age, years | 64.4 ± 11.63 |
| BMI, kg·m−2 | 33.65 ± 7.67 |
| Neck, cm | 45.76 ± 4.13 |
| Smoking habits, % | 27% |
| Comorbidities | |
| CVD, % | 39% |
| Hypertension, % | 70% |
| Cerebrovascular, % | 9% |
| Endocrinological disorders-non-diabetes, % | 12% |
| Diabetes, % | 27% |
| Daytime sleepiness | |
| ESS score, points | 11.51 ± 6.08 |
| ESS ≥ 9 points, % | 67% |
| ESS ≥ 11 points, % | 51% |
| Sleep data | |
| AHI, events·h−1 | 46.21 ± 24.29 |
| Severe OSA, % | 74% |
| ODI, events·h−1 | 45.96 ± 27.06 |
| Minimum SaO2, % | 71.26 ± 15.91 |
| T90, % | 34.39 ± 31.61 |
| NH (T90 > 30%), % | 47% |
| Respiratory and performance status | |
| FVC, % predicted | 84.76 ± 17.26 |
| FEV1, % predicted | 70.33 ± 19.33 |
| FEV1·FVC−1 | 63.73 ± 12.68 |
| pH | 7.42 ± 0.03 |
| PaO2, mmHg | 70.66 ± 10.47 |
| PaCO2, mmHg | 41.73 ± 5.93 |
| SaO2, % | 94.12 ± 2.74 |
| HCO3−, mmol·l−1 | 25.84 ± 3.23 |
| 6MWT, mt | 295.29 ± 112.35 |
| Night-time therapy | |
| Reject PAP, % | 1% |
| CPAP, % | 88% |
| CPAP Pressure, cmH2O | 11.01 ± 1.92 |
| CPAP ≥ 8 cmH2O, % | 97% |
| CPAP ≥ 10 cmH2O, % | 83% |
| CPAP ≥ 12 cmH2O, % | 31% |
| BPAP, % | 7% |
| APAP, % | 4% |
| PAP compliance, % | 90% |
| O2 supplement, % | 29% |
| Variables | OS | OHS | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 105 | n = 27 | ||
| Sex, male, % | 80% | 63% | 0.063 |
| Age, years | 66.16 ± 10.87 | 57.32 ± 12.11 | 0.001 |
| BMI, kg·m−2 | 32.17 ± 6.74 | 39.06 ± 8.54 | <0.001 |
| Neck, cm | 45.78 ± 3.85 | 45.72 ± 4.6 | 0.965 |
| Smoking habits, % | 23% | 41% | 0.098 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| CVD, % | 37% | 48% | 0.3 |
| Hypertension, % | 69% | 74% | 0.582 |
| Cerebrovascular, % | 10% | 4% | 0.278 |
| Endocrinological disorders-non-diabetes, % | 12% | 11% | 0.858 |
| Diabetes, % | 24% | 41% | 0.079 |
| Daytime sleepiness | |||
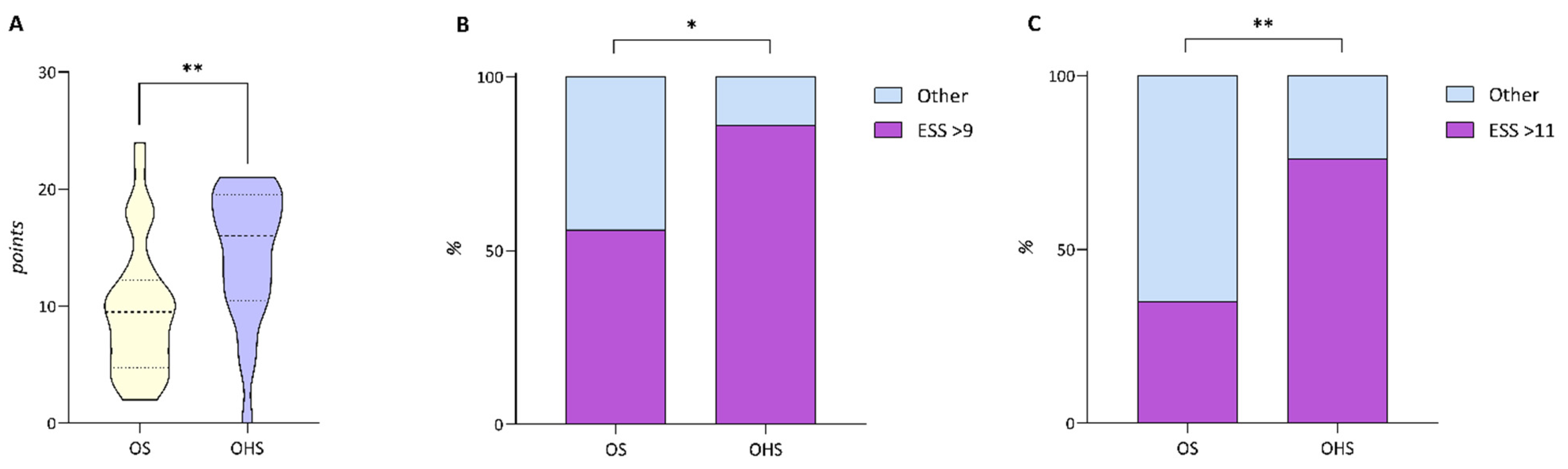
| ESS score, points | 9.74 ± 5.7 | 14.38 ± 5.69 | 0.005 |
| ESS ≥ 9 points, % | 56% | 86% | 0.022 |
| ESS ≥ 11 points, % | 35% | 76% | 0.003 |
| Sleep data | |||
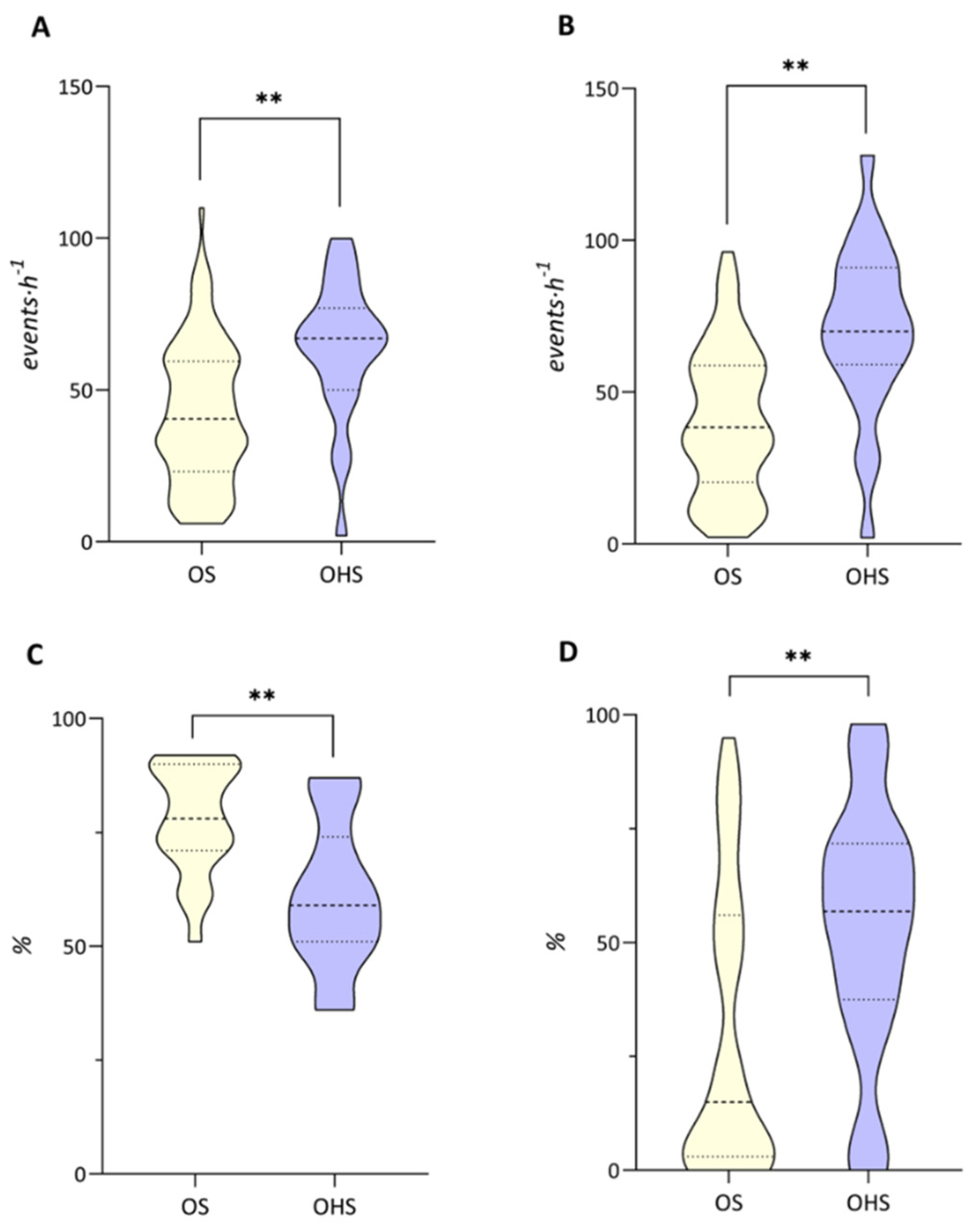
| AHI, events·h−1 | 42.21 ± 22.91 | 63.61 ± 22.79 | <0.001 |
| Severe OSA, % | 70% | 91% | 0.036 |
| ODI, events·h−1 | 40.37 ± 23.69 | 70.26 ± 27.87 | <0.001 |
| Minimum SaO2, % | 77.95 ± 11.76 | 61 ± 16.28 | 0.001 |
| T90, % | 30.23 ± 31.05 | 53.09 ± 27.6 | 0.002 |
| NH (T90 > 30%), % | 39% | 82% | <0.0001 |
| Respiratory and performance status | |||
| FVC, % predicted | 85.4 ± 17.74 | 82.2 ± 15.28 | 0.409 |
| FEV1, % predicted | 67.39 ± 18.45 | 82.32 ± 18.5 | <0.001 |
| FEV1·FVC−1 | 59.49 ± 10.03 | 80.88 ± 5.98 | <0.001 |
| pH | 7.42 ± 0.03 | 7.4 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| PaO2, mmHg | 71.07 ± 10.97 | 69.1 ± 8.27 | 0.385 |
| PaCO2, mmHg | 39.99 ± 4.87 | 48.48 ± 4.76 | <0.001 |
| SaO2, % | 94.16 ± 2.92 | 93.94 ± 1.9 | 0.709 |
| HCO3−, mmol·l−1 | 25.05 ± 2.89 | 28.89 ± 2.65 | <0.001 |
| 6MWT. mt | 294.75 ± 110.97 | 299.86 ± 133.04 | 0.91 |
| Night-time therapy | |||
| Reject PAP, % | 0% | 5% | 0.058 |
| CPAP, % | 92% | 71% | 0.011 |
| CPAP Pressure, cmH2O | 10.95 ± 2.05 | 11.29 ± 1.13 | 0.579 |
| CPAP ≥ 8 cmH2O, % | 97% | 100% | 0.524 |
| CPAP ≥ 10 cmH2O, % | 80% | 100% | 0.089 |
| CPAP ≥ 12 cmH2O, % | 32% | 25% | 0.629 |
| BPAP, % | 7% | 10% | 0.66 |
| APAP, % | 1% | 14% | 0.008 |
| PAP compliance, % | 90% | 89% | 0.977 |
| O2 supplement, % | 26% | 50% | 0.091 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tondo, P.; Scioscia, G.; Hoxhallari, A.; Sabato, R.; Sorangelo, S.; Mansueto, G.; Giuliani, A.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. Clinical Evaluation and Management of Overlap Syndrome (OS) and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS). Clocks & Sleep 2022, 4, 735-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4040055
Tondo P, Scioscia G, Hoxhallari A, Sabato R, Sorangelo S, Mansueto G, Giuliani A, Foschino Barbaro MP, Lacedonia D. Clinical Evaluation and Management of Overlap Syndrome (OS) and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS). Clocks & Sleep. 2022; 4(4):735-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4040055
Chicago/Turabian StyleTondo, Pasquale, Giulia Scioscia, Anela Hoxhallari, Roberto Sabato, Simone Sorangelo, Giuseppe Mansueto, Antonella Giuliani, Maria Pia Foschino Barbaro, and Donato Lacedonia. 2022. "Clinical Evaluation and Management of Overlap Syndrome (OS) and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)" Clocks & Sleep 4, no. 4: 735-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4040055
APA StyleTondo, P., Scioscia, G., Hoxhallari, A., Sabato, R., Sorangelo, S., Mansueto, G., Giuliani, A., Foschino Barbaro, M. P., & Lacedonia, D. (2022). Clinical Evaluation and Management of Overlap Syndrome (OS) and Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS). Clocks & Sleep, 4(4), 735-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4040055






