Abstract
Advances in nanotechnology have contributed to many innovative approaches in the forensic sciences, including the development of new techniques and protocols for latent fingermark detection. Among other nanomaterials, metal-based nanoparticles have been explored as suitable developers for fingermarks present on surfaces that challenge traditionally established methods. The present study explored, for the first time in the forensic science literature, the application of greenly synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for latent fingermark surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI MS) analysis. A leaf extract of a native plant from the Cerrado biome was used for green synthesis of the AgNPs, and their hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity index (PdI), and Zeta potential values were evaluated. Latent fingermarks were produced by three distinct donors and treated with α-CHCA matrix or AgNP suspension and were further investigated using commercial matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)-TOF MS equipment in the m/z range of 100–1000. Characterization results of the AgNPs indicated an average hydrodynamic diameter of 25.94 ± 0.30 nm, a PdI of 0.659 ± 0.085, and a Zeta potential of −33.4 ± 2.6 mV. The silver ions detected showed a relative intensity at least 20× higher for greenly synthesized AgNPs than for AgNO3 suspension, which may be advantageous for the detection of molecular species, especially olefins, present in forensic traces. The AgNP-based SALDI MS approach for the analysis of latent fingermarks showed intense ions at m/z 106.9, 215.8, and 322.7, referring to silver cation species that have been reported as important internal calibrants. The detection of components from endogenous and exogenous sources in latent fingermarks was achieved using the present approach. Greenly synthesized AgNPs may offer a new cost-effective, eco-friendly, and easily scaled up method for application in the chemical analysis of fingermarks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, nanotechnology has been considered to provide new possibilities in forensic science, including the detection and treatment of latent fingermarks [1]. Its advantages include the higher-surface-area-to-volume ratio of nanomaterials when compared to bulk materials, which is desirable for selectivity and sensibility in surface-based science [2]. Additionally, other physical attributes such as surface functionalization [3], optical [4], and electron transport properties [5] may be useful for the detection of the marks. Thus, applications of nanotechnology for the development of latent fingermarks have gained growing popularity among researchers [6,7].
Latent fingermarks consist of a complex mixture of skin secretions and contaminants that are transferred to manipulated objects and may provide relevant information on the identification and activity of suspects at crime scenes. Usually, such traces are composed of endogenous and exogenous materials and require one or more developing agents to provide visible ridges, which are necessary to achieve a positive identification. Natural compounds of eccrine origin include proteins, amino acids, urea, ammonia, uric acid, creatinine, and salts; and others of sebum origin include fatty acids, wax esters, di and triglycerides, cholesterol, and squalene [8]. Also, contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, explosives [9], or drugs [10] may be detected. Many factors may influence the composition of the fingermarks and potentially affect the efficiency of the developing agent [8].
As reported in a critical review on emerging fields in latent fingermark detection [11], a considerable increase in the number of publications focusing on the applications of nanomaterials in latent fingermarks has been noted over the past decade. In addition to the use as novel agents for developing latent fingermarks, different types of nanomaterials have been used for treatment as ionizing agents for molecular analysis. For example, silicon-based nanoparticles, besides showing promising results as developing agents [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], including fluorescent porous-graphite-carbon-nitride-based silica gel powder [15], have been applied to the surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI MS) detection of endogenous compounds [16], drugs [10], and other contaminants [17,18] in fingermarks.
Considering metal-based nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been extensively used in multi-metal deposition (MMD) and also in single metal deposition (SMD) fingermark developing techniques [1,2,19], probably due to gold’s stability regarding oxidation [2]. Also, silver physical developer (Ag-PD), which is based on the interaction between colloidal silver particles and the mixture of compounds or emulsions in fingermark secretions [20], is not frequently applied in forensic laboratories, particularly due to its complex procedure and inconsistent results [20]. The Ag-PD composition is a mixture of an aqueous solution of silver nitrate and an iron (II) and iron (III) redox couple; an acid buffer (usually citric acid); and Synperonic N or Tween 20 detergent [21,22]. Although accepted as a development technique, it has not been coupled with analytical approaches for fingermark composition investigation.
As chemical synthesis methods to produce nanomaterials lead to the presence of some toxic chemicals adsorbed onto the surface that may have adverse effects to users and the environment, routes of green synthesis offer significant advantages in terms of environmentally friendly and cheaper routes using antioxidants or reducing properties of biological resources like aqueous extracts from several organisms, including plants [23]. This is particularly relevant for a technology that uses chemicals for fingermark detection and analytical approaches in forensic laboratories.
The use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in SALDI MS has been studied for the analyses of various low-molecular-weight (LMW) organic compounds [23,24,25,26,27], including in forensic analysis of fingermarks with AgNP-supported laser desorption ionization (LDI) imaging [28]. It is accepted that the laser energy dissociates the binding interaction between the analyte and AgNP surface and transmits the analyte into the gas phase. Advantages such as the high tolerance to salts, elimination of interference of matrix-related ions, reproducible signals, and presence of internal silver-related calibrants have also been reported [23].
Several studies have reported the possibility of applying AgNPs produced through green synthesis routes to different fields, such as catalysis [29], sensors [30], biomedicine, and medicine [31,32,33]. The benefits of green AgNPs may encompass overcoming the challenges often observed in traditional physicochemical synthesis methods, such as cluster formation, aggregation, larger particle sizes, and instability [34]. Also, the substitution of toxic chemicals for compounds from plant extracts, which act as reducing and capping agents, provides enhanced safety in laboratory procedures and the environment. However, the use of such greenly produced metallic nanosystems in forensic sciences still deserves research and development to evaluate the feasibility and potential for practical uses in the field. Therefore, the present study explored, for the first time in the scientific and technical literature, the applicability of a stable AgNP suspension, synthesized using a green approach from a Cerrado biome plant extract, for the chemical investigation of latent fingermarks through SALDI-TOF MS analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (α-CHCA), acetonitrile (ACN), and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) were purchased from Bruker Daltonics (Billerica, MA, USA), JT Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA), and Mallinckrodt (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA), respectively. AgNO3 salt was purchased from Plat-Lab (Guarulhos, Brazil). Also, a commercial clothing softener was purchased in a local market.
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
The leaf extract of a native plant from the Cerrado biome (authorization for access to the genetic patrimony—CGEN n. 02001.007580/2014-95) was used for green synthesis of AgNPs (patent pending). The AgNPs were produced according to the protocol previously described by Bonatto and Silva [35] with some adaptations: 500 µL of the leaf extract was added to 49.5 mL of 1 mM aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3) solution. The procedures were carried out in dark conditions for 150 min at 75 °C. AgNP synthesis was monitored through visible spectrophotometry using an UV-Vis spectrophotometer Q898U (Quimis, Diadema, Brazil) at 450 nm for 2.5 h using 1 cm path-length plastic cuvettes. At the end of the reaction synthesis, the sample was characterized using the absorption curve at 350–550 nm to evaluate the maximum absorption peak.
2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential
The hydrodynamic diameter and polydispersity index (PdI) of the AgNPs were analyzed through photon correlation spectroscopy, and the Zeta potential was analyzed through electrophoretic mobility. The measurements were acquired using a ZetaSizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, United Kingdom) with a He-Ne laser (4 mW) operating at 633 nm with the detection of light in 173°. Three measurements were performed in automatic mode, at room temperature, and the acquired data were processed using ZetaSizer version 7.11 software.
2.4. Instrument and Sample Preparation for LDI-TOF MS
Chemical analyses were performed using commercial MALDI-TOF MS equipment (Autoflex Speed, Bruker Daltonics) equipped with a nitrogen laser (337 nm) with external calibration (α-CHCA matrix ions at m/z 190.04 and 379.09) in reflector-positive mode ranging from m/z 100 to 1000, with 100 laser shots per point (2000 summed shots per spectrum). Droplets of 1 µL of α-CHCA matrix (10 mg/mL of α-CHCA in 70:30 ACN–0.5% TFA aq.) or AgNP suspension (1 mM) were dropped onto clean individual target spots or where the samples were present on a ground steel target plate (MTP 384, Bruker Daltonics). The spotted reagents were left to air-dry at ambient conditions prior to MALDI- or SALDI-TOF MS analyses. Natural latent fingermarks, without previous rubbing, were deposited directly onto a MALDI target plate by the contact with moderate intensity (without noticeable struggle) between the index fingers and the surface of the plate. Furthermore, it is important to note that the hands were not washed, and there was no contact with clothing softener prior to the deposition of the fingermarks, to simulate a real-world scenario where fingermarks are deposited in a more natural and unaltered state. Samples were produced by three non-smoking donors: a pregnant 26-year-old female, with omnivorous diet, using progesterone; a 33-year-old female, with no red meat in diet; and a 49-year-old male, with omnivorous diet, using rosuvastatin. All analyses were performed in three distinct regions (spots) of the same fingermark, allowing an evaluation of reproducibility. Also, to investigate a potential source of contamination in fingermarks, droplets of 1 µL of the clothing softener were air-dried onto the target plate and analyzed without any treatment.
3. Results
3.1. Silver Nanoparticle Characterization
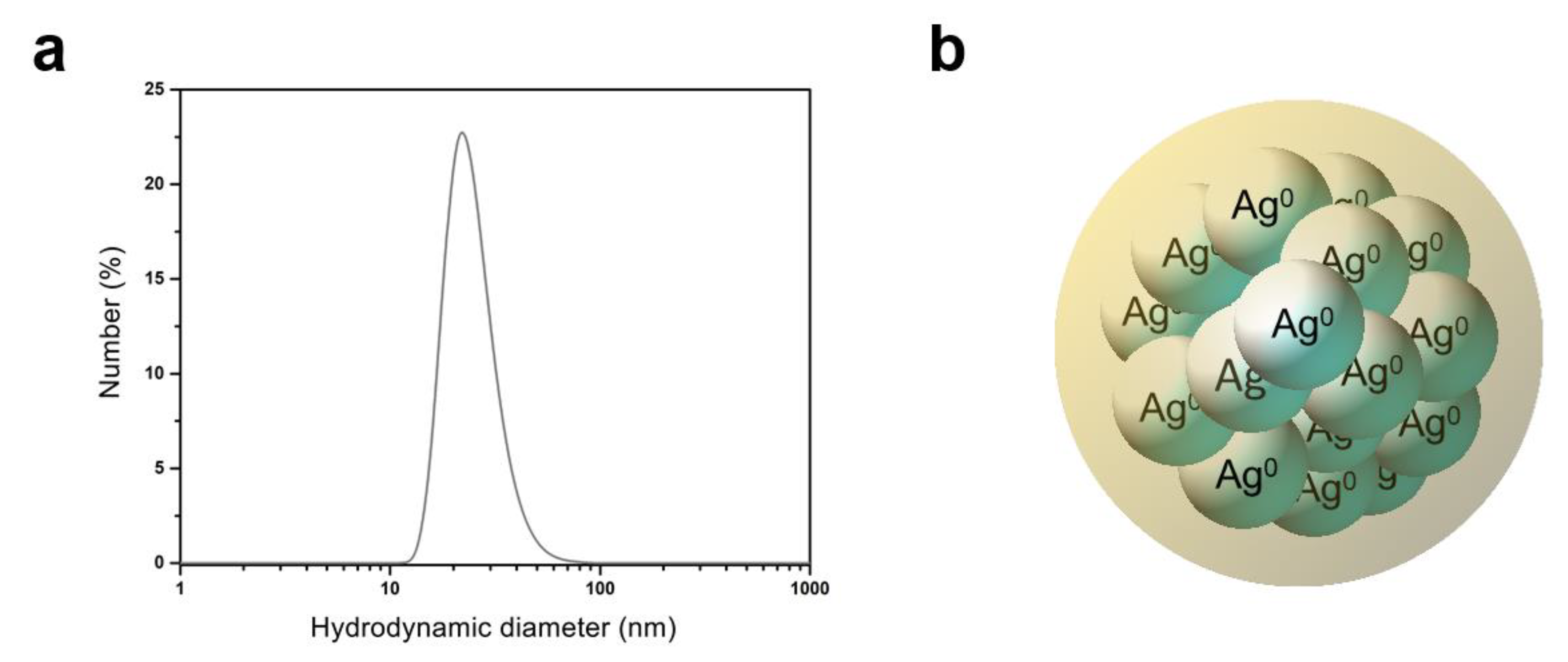
The maximum band of absorbance observed at 420 nm indicates the formation and corresponds to the SPR of the greenly synthesized AgNPs selected to be used in this study. The nanometer size and moderate polydispersity of the AgNPs were verified using DLS analysis. An average hydrodynamic diameter of 25.94 ± 0.30 nm and a PdI of 0.659 ± 0.085 were obtained. Additionally, the AgNPs presented a Zeta potential of −33.4 ± 2.6 mV, indicating a moderate colloidal stability. Figure 1 illustrates the obtained distribution curve of hydrodynamic diameters and a schematic representation of an AgNP.
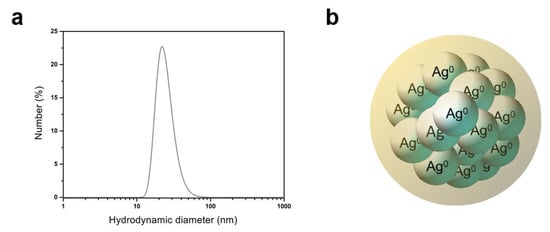
Figure 1.
AgNP suspension greenly synthesized with aqueous leaf extract acting to reduce ionic silver and promote particle coating, attaining colloidal stability. Distribution curve of hydrodynamic diameters (data in number %) obtained through dynamic light scattering (a) and schematic representation of a nanoparticle (b).
3.2. Greenly Synthesized AgNPs for SALDI-TOF MS
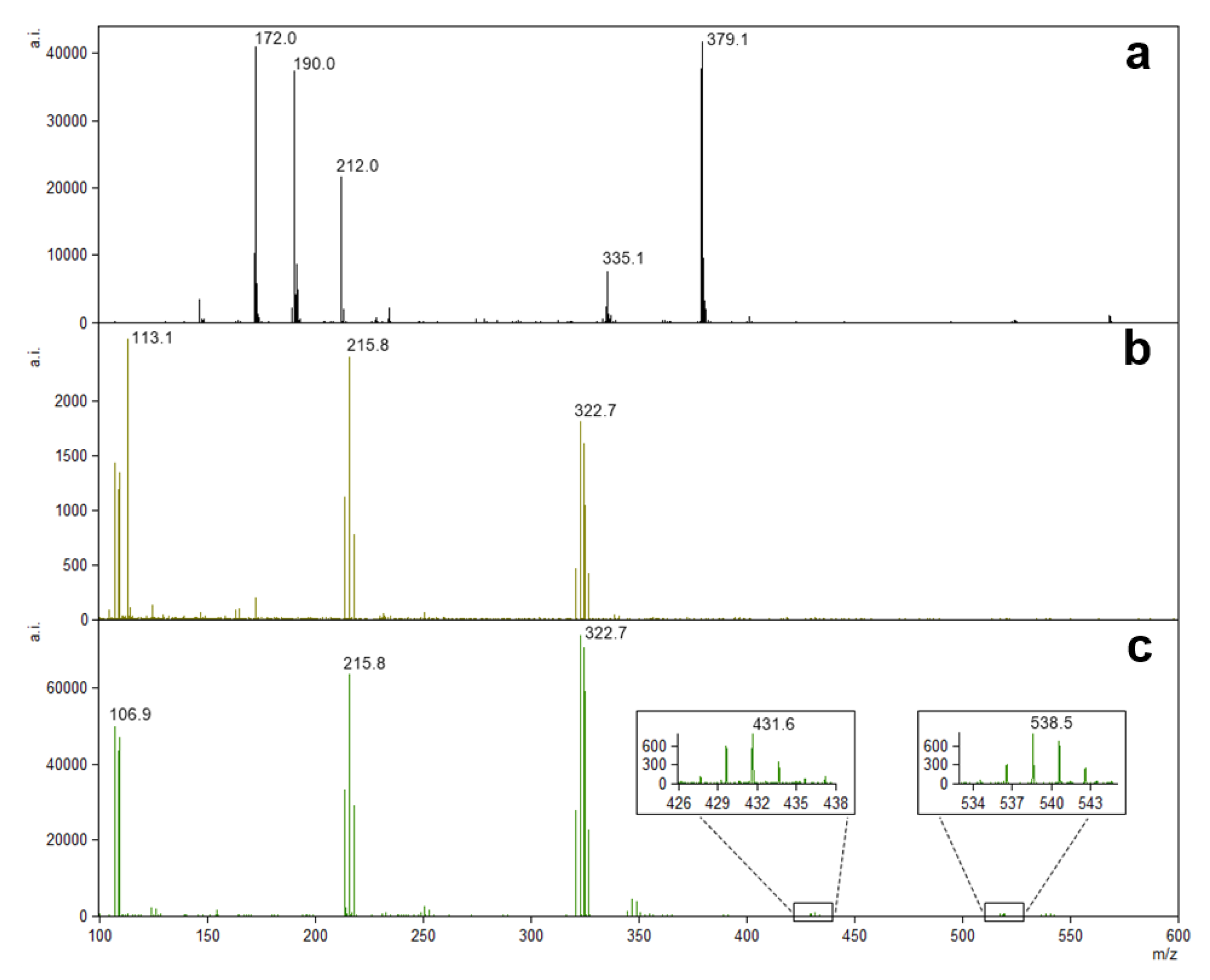
Figure 2 shows spectra for the AgNO3 solution or AgNP suspension obtained in the low-molecular-mass range, with a decreased background when compared to the spectrum of α-CHCA matrix. Silver ions detected in the spectrum of AgNO3 solution (Ag+, Ag2+, and Ag3+, respectively, at m/z 106.9, 215.8, and 322.7) were also present and showed a relative intensity at least 20× higher for greenly synthesized AgNPs (Figure 2b,c). Ions corresponding to Ag4+ at m/z 431.6 and Ag5+ at m/z 538.5 were also detected but showed a lower intensity than the previously mentioned molecular components (Figure 2c, insets).

Figure 2.
Representative low-mass-molecular-component spectra of α-CHCA matrix (a), AgNO3 solution (b), and greenly synthesized AgNP suspension (c). Insets show less intense Ag4+ and Ag5+ ions.
3.3. SALDI-TOF MS Analysis of Latent Fingermarks
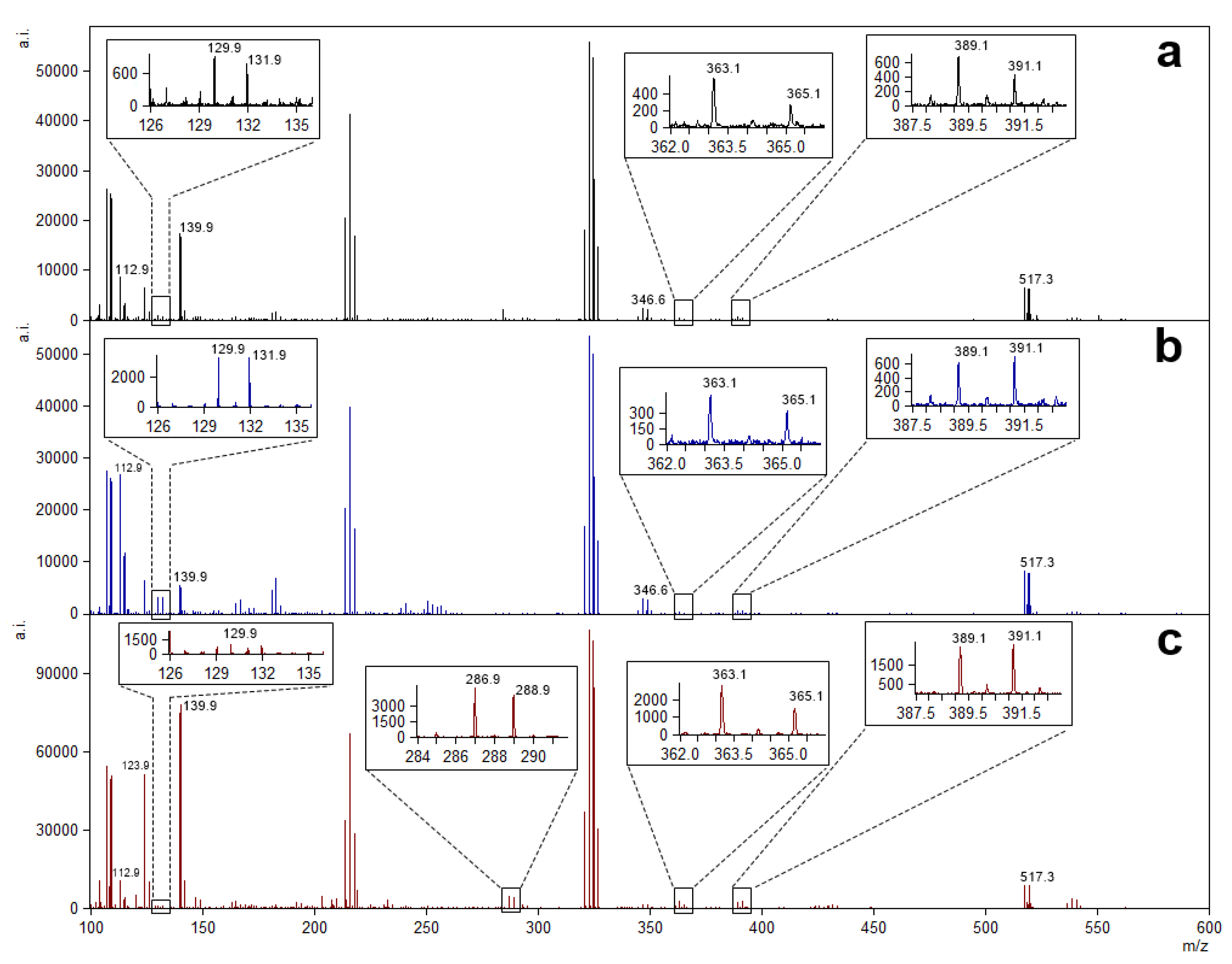
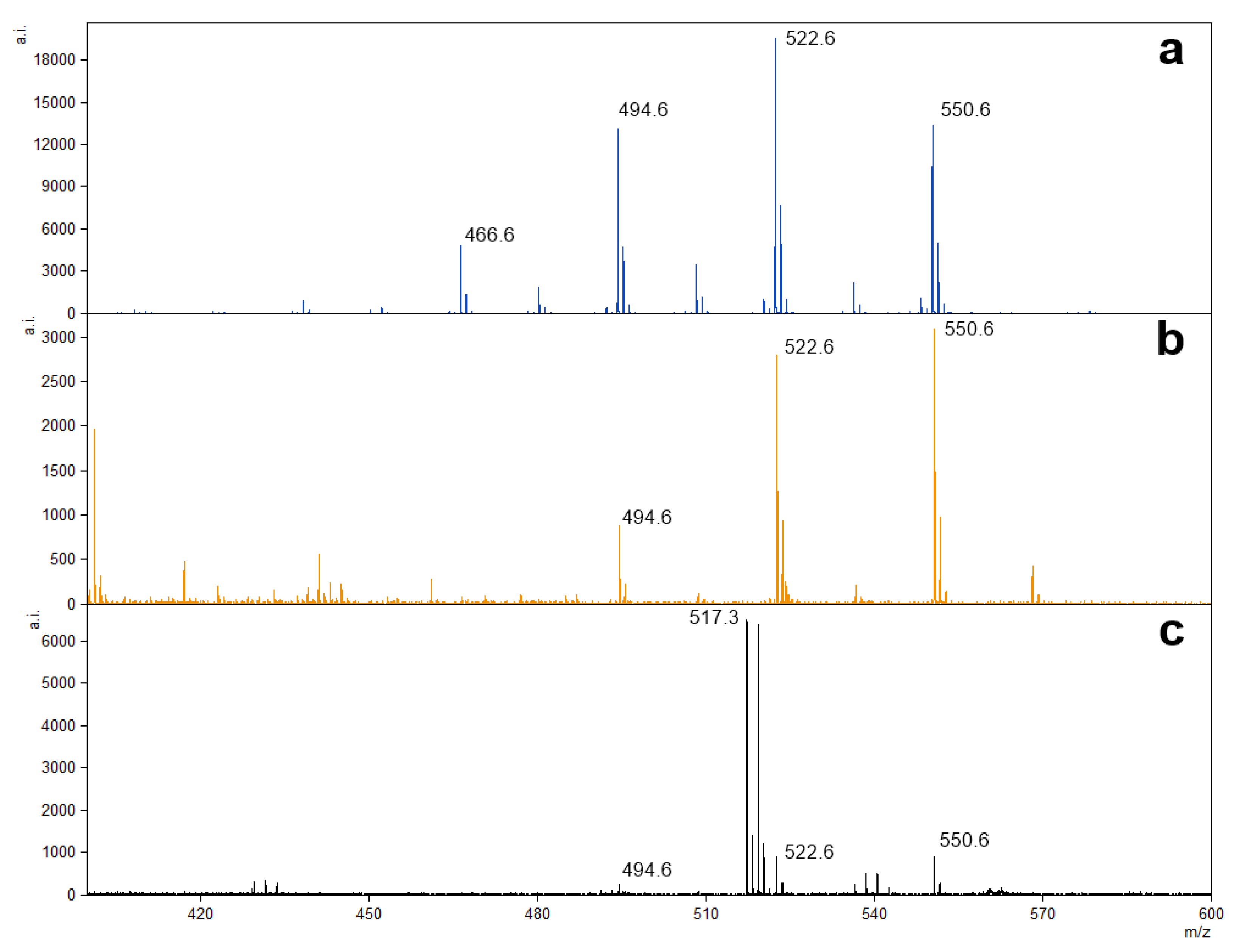
Ions detected at m/z 112.9 and 123.9 were observed with higher intensity in the evaluated fingermarks treated with the AgNP suspension (Figure 3) but were also detected in the greenly synthesized AgNP control sample. In the fingermark from the 33-year-old female donor, a relatively intense ion was detected at m/z 286.9 (Figure 3c, insert), but its identity should be confirmed by further studies. Also, the clearly discernible species observed at m/z 517.3 was detected in samples from all donors and possibly corresponds to the squalene silver ion [M + 107Ag]+. Ions at m/z 550.6, 522.6, and 494.6 may correspond to the exogenous compound dimethyldioctadecylammonium and its fragments, respectively. Higher-relative-intensity ions were detected using matrix-free LDI MS analysis of a commercial clothing softener sample from Brazil (Figure 4).

Figure 3.
Representative spectra of low-mass molecular components detected on fingermarks from a 26-year-old female (a), a 49-year-old male (b), and a 33-year-old female (c) treated with the greenly synthesized AgNP suspension. Insets show less intense peaks with the isotopic pattern observed for silver adducts.

Figure 4.
Representative spectra of low-mass molecular components detected on a commercial clothing softener (without treatment) (a); a fingermark from a 26-year-old female treated with α-CHCA matrix (b); and a fingermark from a 26-year-old female treated with the greenly synthesized AgNP suspension (c) (species at m/z 517.3 possibly corresponds to the squalene silver ion [M + 107Ag]+).
3.4. Additional Findings and Challenges
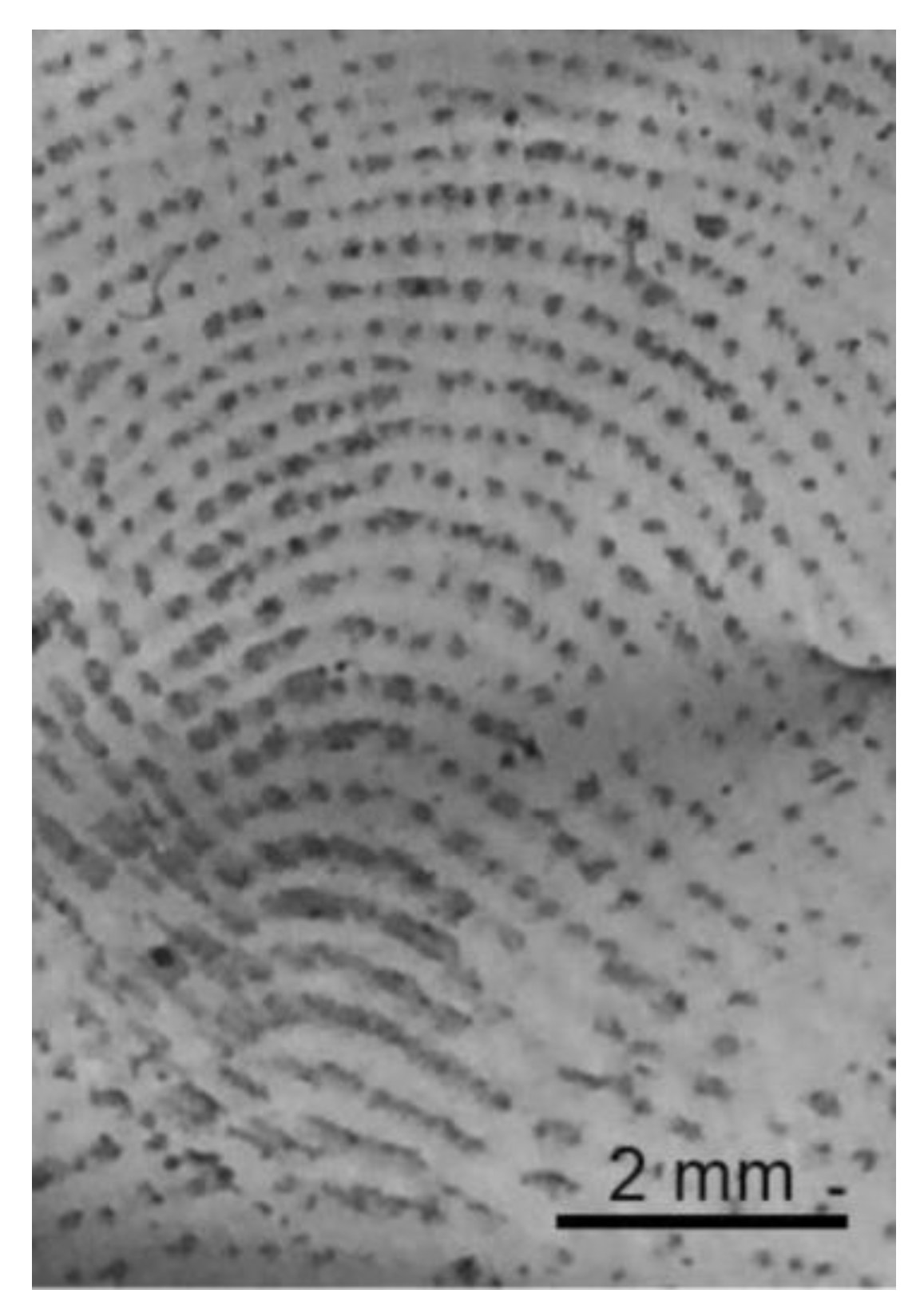
Although it was not the focus of the present study, the greenly synthesized AgNP suspension was also preliminary used to develop latent fingermarks on the aluminum foil surface, as shown in Figure 5. No pretreatment of the surface or UV light exposure was performed.

Figure 5.
Photography under white light of a latent fingermark from a 29-year-old female donor deposited on aluminum foil and treated with the greenly synthesized AgNP suspension for 24 h.
4. Discussion
The synthesis of AgNPs through a chemical route involves the utilization of reducing and stabilizing agents that are typically toxic and may lead to adverse and harmful effects on both human health and the environment. In contrast, green synthesis routes employ relatively non-toxic, biodegradable, and cost-effective components to synthesize nanomaterials, sourced from biological organisms or their constituents, such as biomolecules, commonly found in plants. In this context, biological components derived from plants can exert a direct influence on specific interactions between biomolecules and metal ions, thereby controlling the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of micro- and nanoparticles that are synthesized. The Cerrado plants consist of numerous primary metabolites (proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates) and secondary metabolites (phenolic compounds, flavonoids, phenols, terpenoids, among others), which are attributed to their role in reducing metal ions.
Color changes of a suspension and spectrophotometric parameters are commonly used to monitor AgNP formation. In this study, the confirmation of successful AgNP formation and their surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect were achieved through the absorbance band at 420 nm, indicative of AgNP presence in the suspension. These facts align with the principle that AgNPs absorb radiation in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the optical properties have been directly related to the SPR effect [4,36].
When comparing the results obtained in this study for DLS and Zeta potential analysis with those reported in a recent study by Yaday and Preet [37], it becomes evident that the greenly synthesized AgNPs presented here exhibit a significantly smaller hydrodynamic diameter (26 nm) compared to clove-synthesized AgNPs (100 nm), chemically synthesized borohydride AgNPs (136 nm), and GSH-capped AgNPs (173 nm). Although all cases showed polydisperse characteristics based on their PdI values, our green AgNPs demonstrated a Zeta potential of −33.4 mV, whereas clove-synthesized, borohydride, and GSH-capped AgNPs exhibited values of −28.5 mV, −18.6 mV, and −23.5 mV, respectively. It is well established that AgNPs achieve stability at Zeta potential values around ±30 mV, so the green synthesis of AgNPs could favor stability gain. The remarkable parameters exhibited by the green AgNPs presented in this study suggest exploring distinct possibilities of applications.
Considering the inconveniences of matrices commonly used for MALDI-TOF MS analysis, alternative approaches have been investigated to achieve clearer and accurate detection of small molecules [38]. In this context, the use of AgNPs, as showcased in this study, offers a straightforward and effective means to enhance the identification and analysis of specific molecular components in various surface applications. In addition, silver ions have been pointed out as good candidates for internal calibration, possibly offering an advantage of improving accuracy in detection [25,26,28]. It is important to emphasize that while the use of internal calibrants is not particularly common in SALDI MS techniques, it is not exclusive to AgNPs. Furthermore, matrix adducts of compounds such as α-CHCA are indeed commonly employed for this purpose in MALDI MS.
As previously described [39], silver adducts can be easily determined by the presence of 107Ag and 109Ag isotopic patterns, with relative abundances of 52% and 48%, respectively. Other possible advantages of AgNP use in LDI MS include a reliable and narrow peak window, high resolution, lack of sweet spots, and a large variety of applications [24]. The observation of ions at m/z 129.9 and 131.9 was previously suggested for fingermark ridge localization using imaging techniques [24], possibly corresponding to [107AgNa]+ and [109AgNa]+, respectively. One of the possible sources for sodium is the secretion from sweat glands present in friction ridge skin in relatively large quantities. Due to the notable propensity of silver for conjugating with double bonds, it is considered a viable option for mass spectrometry analysis of a wide range of molecules, suggesting the potential use of AgNO3 as a primary method for analyzing olefins [40]. Squalene, a precursor to cholesterol, contains multiple double bonds in its isoprenoid side chains, potentially facilitating the formation of silver ions, as indicated by species at 517.3 m/z, as previously detected in fingermarks using silver-assisted mass spectrometry [39]. Considering the higher signal obtained with the AgNP suspension compared to the AgNO3 solution in our study, employing AgNPs for chemical investigations of traces with minimal molecular content may be preferable for detection optimization of certain molecules.
Distinctly, ions detected at m/z 550.6, 522.6, and 494.6 may correspond to the exogenous compound dimethyldioctadecylammonium, along with its fragments. These molecular components are commonly identified in fingermarks through different approaches [18,41,42,43] and the probable source is clothing softeners, as higher-relative-intensity ions were detected through matrix-free LDI MS analysis of a commercial clothing softener sample from Brazil.
While the primary focus of this study was distinct, a preliminary test was performed to evaluate if the greenly synthesized AgNP suspension could also be employed in an initial attempt to develop latent fingermarks on aluminum foil surfaces. The application of AgNPs synthesized through a chemical routine for the development of latent fingermarks on porous surfaces has been demonstrated to be effective [44]. The ridge detail presented in Figure 5 suggests that AgNPs should also be studied for the treatment of metallic surfaces, potentially having a broader applicability than porous substrates. Nevertheless, to optimize the efficacy of this approach for latent fingermark detection, it remains crucial to undertake further investigations and ascertain the ideal conditions.
Considering the limitations observed, more research is needed to obtain a reagent that would combine the development and mass spectrometry analysis of latent fingermarks deposited on a certain object. To enable chemical investigation of this type of evidence in real case scenarios, distinct types of surfaces and objects (which would directly interfere in signal acquisition) must be considered. While Lauzon et al. [39] suggested a procedure that allows the compatibility of fingermark silver-assisted LDI MS with conventional forensic procedures, a less expensive alternative to the silver sputtering method for sample preparation may be favored by our approach. The main challenge lies in transporting the evidence sample to the mass spectrometer target plate.
5. Conclusions
The development of new eco-friendly and easily scaled-up methods for large-scale synthesis of fingermark reagents are desired by experts in the field. In the present study, a suspension of AgNPs obtained through green synthesis using a plant extract showed to be a promising alternative for chemical analysis suitable for the detection of endogenous or exogenous compounds in latent fingermarks. Also, the detection of some endogenous lipids and salts were favored by this approach rather than using the conventional matrix-based MALDI approach. Further research should focus on exploring fingermarks treated with the greenly synthesized AgNPs through imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) and on transporting the sample to the target plate, making this application feasible for the forensic fingerprint community.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.B., C.C.B., M.H.S.R. and L.P.S.; methodology, R.M.B., C.C.B., M.H.S.R. and L.P.S.; formal analysis, R.M.B., C.C.B. and M.H.S.R.; investigation, R.M.B., C.C.B., M.H.S.R. and L.P.S.; resources, L.P.S.; data curation, R.M.B. and L.P.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.B., C.C.B. and L.P.S.; writing—review and editing, R.M.B., C.C.B., M.H.S.R. and L.P.S.; supervision, L.P.S.; project administration, L.P.S.; funding acquisition, L.P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Brazilian agencies Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES no. 23038.019088/2009-58), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq no. 311825/2021-4, 307853/2018-7, 408857/2016-1, 306413/2014-0, and 563802/2010-3), Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal (FAPDF no.193.001.392/2016), Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (Embrapa no. 10.20.03.009.00.00, 23.17.00.069.00.02, 13.17.00.037.00.00, 21.14.03.001.03.05, 13.14.03.010.00.02, 12.16.04.010.00.06, 22.16.05.016.00.04, and 11.13.06.001.06.03), and Universidade de Brasília (UnB). The APC was waived.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Project was approved by the Ethics Committee in Human Research of the Medicine Faculty of the University of Brasilia (n. 65610716.5.0000.5558).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are unavailable, due to intellectual property subjects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dilag, J.; Kobus, H.J.; Ellis, A.V. Nanotechnology as a new tool for fingermark detection: A review. Curr. Nanosci. 2011, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; McDonagh, A.M.; Maynard, P.; Roux, C. Metal-containing nanoparticles and nano-structured particles in fingermark detection. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 179, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moret, S.; Bécue, A.; Champod, C. Functionalised silicon oxide nanoparticles for fingermark detection. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 259, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Review of some interesting surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of noble metal nanoparticles and their applications to biosystems. Plasmonics 2007, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G. When small is different: Some recent advances in concepts and applications of Nanoscale Phenomena. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becue, A.; Champod, C.; Margot, P. Use of gold nanoparticles as molecular intermediates for the detection of fingermarks. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 168, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sametband, M.; Shweky, I.; Banin, U.; Mandler, D.; Almog, J. Application of nanoparticles for the enhancement of latent fingerprints. Chem. Commun. 2007, 11, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girod, A.; Ramotowski, R.; Weyermann, C. Composition of fingermark residue: A qualitative and quantitative review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 22, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan-Sandquist, K.; LeBeau, M.A.; Miller, M.L. Chemical analysis of pharmaceuticals and explosives in fingermarks using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 235, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, F.; Hudson, K.; Seviour, J. Detection of drugs and their metabolites in dusted latent fingermarks by mass spectrometry. Analyst 2009, 134, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becue, A. Emerging fields in fingermark (meta) detection–a critical review. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7983–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theaker, B.J.; Hudson, K.E.; Rowell, F.J. Doped hydrophobic silica nano-and micro-particles as novel agents for developing latent fingerprints. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 174, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, S.; Bécue, A.; Champod, C. Nanoparticles for fingermark detection: An insight into the reaction mechanism. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 425502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewski, A. Hybrid organic–inorganic silica based particles for latent fingermarks development: A review. Synth. Met. 2016, 222, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, E.; Pillay, K. A novel approach of fluorescent porous graphite carbon nitride based silica gel powder for latent fingerprint detection. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, J.; Rowell, F. Separation of fingerprint constituents using magnetic silica nanoparticles and direct on-particle SALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.; Chua, M.J.; Gu, F.; Rowell, F.; Ma, J. Environmental nicotine contamination in latent fingermarks from smoker contacts and passive smoking. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 200, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.M.; Clemente, M.C.; Martins, G.A.; Silva, L.P. Application of mesocellular siliceous foams (MCF) for surface-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI-MS) analysis of fingermarks. Sci. Justice 2018, 58, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, F.; Song, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, L. One step to detect the latent fingermarks with gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2009, 80, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Hunty, M.; Moret, S.; Chadwick, S.; Lennard, C.; Spindler, X.; Roux, C. Understanding physical developer (PD): Part II–is PD targeting eccrine constituents? Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Hunty, M.; Moret, S.; Chadwick, S.; Lennard, C.; Spindler, X.; Roux, C. An effective physical developer (PD) method for use in Australian laboratories. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 50, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlgrave, S.; Andress, M.; Ramotowski, R. Comparison of different physical developer working solutions—Part I: Longevity studies*. J. Forensic Identif. 2011, 61, 621–639. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, M.; Subapriya, M.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. Bio-Med. Sci. 2011, 1, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Nizioł, J.; Ruman, T. Surface-transfer mass spectrometry imaging on a monoisotopic silver nanoparticle enhanced target. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12070–12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizioł, J.; Rode, W.; Laskowska, B.; Ruman, T. Novel monoisotopic 109AgNPET for laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizioł, J.; Rode, W.; Zieliński, Z.; Ruman, T. Matrix-free laser desorption–ionization with silver nanoparticle-enhanced steel targets. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 335, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prysiazhnyi, V.; Dycka, F.; Kratochvil, J.; Stranak, V.; Popok, V.N. Effect of Ag nanoparticle size on ion formation in nanoparticle assisted LDI MS. Appl. Nano 2020, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekuła, J.; Nizioł, J.; Rode, W.; Ruman, T. Silver nanostructures in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry imaging. Analyst 2015, 140, 6195–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvith, V.S.; Philip, D. Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using biosynthesized gold and silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithara, R.; Selvakumar, P.; Arun, C.; Anandan, S.; Sivashanmugam, P. Economical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Acalypha hispida and its application in the detection of Mn(II) ions. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.J.; Finub, J.S.; Narayanan, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Piper longum leaf extracts and its cytotoxic activity against Hep-2 cell line. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 91, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Park, I.; Seung-Hyun, K.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, N.; Mazumder, J.A.; Sardar, M. Biotechnological applications of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Curr. Res. 2017, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatto, C.C.; Silva, L.P. Higher temperatures speed up the growth and control the size and optoelectrical properties of silver nanoparticles greenly synthesized by cashew nutshells. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 58, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Bakr, O.M.; Stellacci, F. A study of the surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles by the discrete dipole approximation method: Effect of shape, size, structure, and assembly. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Preet, S. Comparative assessment of green and chemically synthesized glutathione capped silver nanoparticles for antioxidant, mosquito larvicidal and eco-toxicological activities. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, N.; Shevchenko, D.; Bergquist, J. Approaches for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds with laser desorption/ionization techniques and mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauzon, N.; Dufresne, M.; Chauhan, V.; Chaurand, P. Development of laser desorption imaging mass spectrometry methods to investigate the molecular composition of latent fingermarks. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Fournelle, F.; Chaurand, P. Silver spray deposition for AgLDI imaging MS of cholesterol and other olefins on thin tissue sections. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, R.; Bleay, S.; Wolstenholme, R.; Clench, M.R.; Francese, S. Towards the integration of matrix assisted laser desorption ionisation mass spectrometry imaging into the current fingermark examination workflow. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 232, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francese, S.; Bradshaw, R.; Ferguson, L.S.; Wolstenholme, R.; Clench, M.R.; Bleay, S. Beyond the ridge pattern: Multi-informative analysis of latent fingermarks by MALDI mass spectrometry. Analyst 2013, 138, 4215–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon, N.; Dufresne, M.; Beaudoin, A.; Chaurand, P. Forensic analysis of latent fingermarks by silver-assisted LDI imaging MS on nonconductive surfaces. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 52, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Prasad, L.; Lukose, S.; Agarwal, P. Latent fingerprint development by using silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate—A comparative study. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).