Abstract
Background: Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a highly prevalent parasitic disease resulting from the hydatid cyst of Echinococcus granulosus. It is also described as a zoonotic disease and considered a neglected tropical infection. Aim: This study assessed the antiparasitic activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), against E. granulosus infection in BALB/c mice. Methods: The green synthesis of AgNPs was accomplished using Zizyphus spina-christi leaves. AgNPs were orally administered to BALB/c mice for acute short-term toxicity evaluation, in doses of 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, and 300 mg/kg, and observations for toxic signs were carried out at 24, 48 h, and 14 days, continuously. Moreover, a total of 20 mice divided into two groups were intraperitoneally administered with 1500 viable protoscoleces for secondary hydatidosis infection. Results: The results showed that AgNPs did not induce any adverse effects or signs and no death, in either group of mice. The histopathological findings in the liver, kidneys, and intestine of the mice administered with AgNPs revealed mild histological effects compared with the control ones. The treated-infected mice showed a change in the appearance of the liver hydatid cysts from hyaline to milky cloudy compared with the untreated infected mice. Conclusion: Biosynthesized AgNPs showed anti-hydatic effects and are suggested as anti-echinococcal cyst treatment.
1. Introduction
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a widely distributed parasitic disease resulting from the hydatid cyst caused by E. granulosus. It is also described as a zoonotic disease and referred to as hydatid disease or hydatidosis [1]. The World Health Organization classified it with neglected tropical infections [2]. The highest prevalence is recorded in sheep farming areas where many stray dogs consume infected animals’ organs. In Iraq, hydatidosis is considered hyper-endemic. It is also one of the country’s most significant helminthic infections with significant socioeconomic impacts due to the effect on both humans and their livestock [3]. Human CE is a prominent public health problem in the Kurdistan region of Iraq, with a recorded surgical incidence of 6.3 per 100,000 among Arbil residents [4]. The surgical operation remains the primary method of treatment; however, other techniques also have an essential role in CE control. Leakage of the cystic fluid is the primary cause for the recurrence of the infection during surgery. Therefore, killing the protoscoleces within the cyst during the surgical procedure is essential. All of the scolicidal agents have adverse effects [5]. Currently, hypertonic saline is commonly used as scolicidal agent but it produces severe adverse effects as hypertonic saline can cause hypernatremia, leading to convulsions, intracranial bleeding, necrosis, and myelinolysis [6].
The WHO recommended benzimidazole as a medication for human infection. This drug is known to possess parasitostatic rather than parasiticidal effects. Low water solubility and low absorption of benzimidazole may be responsible for its ineffectiveness as a treatment option. Furthermore, it has many severe side effects on CE patients’ lifespan and prognosis [7]. These facts underline the need for new drugs. Therefore, researchers have made several attempts to increase the compound’s solubility, absorption, and bioavailability.
Among these trials, one of the things that improved the drug’s efficiency was the addition of nanoparticles (NPs), which increases the intra-cystic permeability of the curing compound [7]. NPs have a wide range of applications, especially in medical fields, which gives significant signs of progress in the development of methods for improving drug ability, drug distribution, diminishing toxicity of medications, and allowing programmed nanomaterial production [8]. Silver NPs are significantly explored nanostructures for unconventional and enhanced biomedical applications, owing to their size-related attractive physicochemical characteristics and biological functionality, including their high antimicrobial activity and non-toxic nature. AgNPs are appropriate alternatives for drug delivery, wound dressing, and tissue scaffold, as well protective coating applications [9]. Other previous studies investigated the activity of green synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles from Penicillium aculeatum, against the protoscoleces of E. granulosus. The authors stated that these NPs could be a potential scolicidal agent in CE therapy [10,11]. More recently, Salih et al. concluded that the biosynthesized AgNPs from some plant extracts showed remarkable effects against E. granulosus, particularly Eucalyptus globulus extract [12]. Moreover, AgNPs could minimize the toxic effects of albendazole (ABZ), the drug of choice for hydatid cyst disease treatment. These toxic effects of albendazole may include necrosis and degeneration, steatosis, and raised serum hepatic enzymes. Therefore, coating ABZ on AgNPs could be a promising method to increase ABZ effectiveness against cystic echinococcosis [13,14].
Echinococcosis is a significant disease that infects both humans and many domesticated animals, causing significant socioeconomic effects, and as no adequate and safe drugs are available, innovative and more efficient treatments are urgently required to overcome this therapeutic deficit. This study aimed to investigate the effect of the green AgNPs against secondary hydatid cysts within experimentally infected mice. This was done as different concentrations of the produced AgNPs were orally administered into BALB/c mice, and the acute short-term toxicity was examined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sidr Plant Extract
Fresh and healthy leaves of the Z. spina-christi (sidr) plant were collected from a tree cultivated in Erbil. The plant’s leaves were immediately washed by running under tap water three times, and then they were washed using double-distilled water. An amount of 25 gm of plant leaves were cut into small pieces, mixed with 100 mL of double-distilled water, and heated on a heater at 90 °C for 40 min. The content was then cooled to room temperature and filtered by Whatman No.1 filter paper to collect the plant extract, which was then kept in the refrigerator at 4 °C [15].
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Green Silver Nanoparticles
Silver nitrate (AgNO3) (CAS Number: 7761–88-8) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (S6506-25G) Gillingham, UK. A concentration of 1 mM AgNO3 solution was prepared. Furthermore, 100 mL of the prepared AgNO3 solution was gradually added by burette to 10 mL of the prepared sidr plant extract at 80 °C for 1 h until the color of the mixture changed and a dark brown precipitate was produced. The reduction of AgNO3 to Ag was monitored by the UV-Vis spectrum. The optical absorptions of AgNPs were recorded using a double-beam UV-Visible spectrum of the reaction solution (Super Aquarius spectrophotometer) and analyzed from 300–850 nm wavelengths. The precipitate was centrifuged at 7000 rpm. Finally, AgNPs were annealed using a Bunsen burner for one hour to obtain the AgNPs powder. Then, for further purification of NPs, the burned NPs were washed in double-distilled water twice, being left for 30 min each time, and the supernatant was discarded. Finally, ethanol was added as the final step of purification (Figure 1). The morphology of the synthesized AgNPs was investigated by fast emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, Quanta 450). Moreover, the chemical composition of the material was measured by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The crystal structure of nanoparticles was studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using PAN-analytical X’ Pert PRO (Cu Kα = 1.5406 A°), with a scanning rate of 1°/min in the 2θ range from 20° to 80° [16].
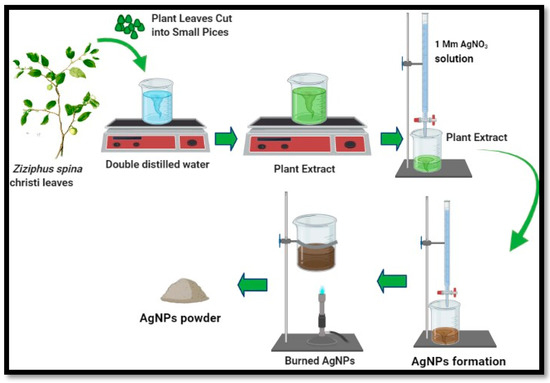
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Z. spina-christi (sidr) leaf extract: 100 mL of (1 mM) AgNO3 solution was added to 10 mL of the plant extract on a hotplate, then the color change was monitored.
2.3. Liver Samples Collection and Viability Test
The liver samples were collected from naturally infected sheep with hydatid cysts slaughtered in the abattoir of Soran City, Erbil province. The exposed surface of the cyst from the infected liver was sterilized with 70% ethanol. The hydatid fluid was aseptically aspirated. Next, the hydatid cysts were opened to remove the germinal layer and washed with normal saline to collect the protoscoleces, which are attached to the germinal layer. Then, the collected hydatid fluid was left for half an hour to allow the protoscoleces to settle down. Then, the supernatant was discarded and the protoscolices sediment was washed with sterile normal saline three times and left for 30 min each time. After that, the collected protoscolices were examined for viability and used immediately. The vitality of protoscoleces was assessed by viewing protoscoleces’ muscular movements under an optical microscope. Moreover, the protoscoleces’ viability was assessed by 0.1% aqueous eosin staining (0.1 g of eosin powder in 100 mL distilled water) [17,18]. A drop of the protoscolices sediment was smeared on a microscope glass slide, covered with cover glass, and examined by a light microscope. Unstained protoscolices were considered as viable, whereas red-stained protoscolices were recorded as dead. In this study, a sample with a viability of 97% or more was considered to be appropriate for the experiments.
2.4. In Vivo Toxicity of AgNPs
2.4.1. Experimental Animals
Healthy laboratory male and female BALB/c mice, about 6 weeks of age and 25–30 gm body weight, were purchased from Zakho University. The mice were inbred in the animal house of the Biology Department, Science Faculty, Soran University (Soran, Iraq). The mice were housed under the controlled condition of 20–25 °C with a 12 h dark/light cycle. Moreover, the mice were fed a standard diet and had access to clean water. All animals were handled under the guidelines of the ethics committee (issued from scientific research committee: Faculty of Science at Soran University: 1/1/277 on 9th of December 2019).
2.4.2. Acute (Short Term) Toxicity of AgNps Testing
For evaluating the toxicity of the AgNPs, in this experiment, a total of thirty BALB/c mice (21 female and 9 male), 25 ± 5 gm in body weight, and about 8 weeks old were used (Figure 2). The mice were supplied with the same amount of standard animal diet. They were randomly divided into five experimental groups, each with six mice per separate cage [19].
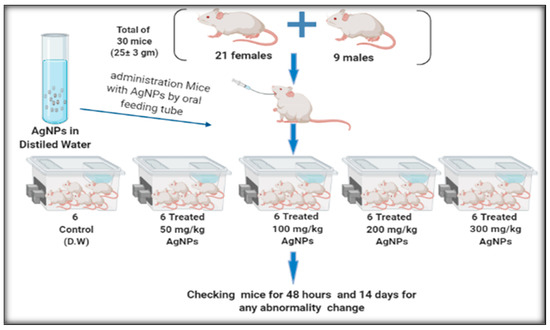
Figure 2.
The in vivo toxic effect of AgNPs using 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, and 300 mg/kg.
Group 1: Control group which were orally administered with sterilized distilled water.
Group 2: Experimental group which were orally administered with 50 mg/kg AgNPs diluted in distilled water.
Group 3: Experimental group which were orally administered with 100 mg/kg AgNPs diluted in distilled water.
Group 4: Experimental group which were orally administered with 200 mg/kg AgNPs diluted in distilled water.
Group 5: Experimental group which were orally administered with 300 mg/kg AgNPs diluted in distilled water.
The oral administration was performed with the aid of a feeding tube (a suitable intubation cannula). Daily observation of the treated animals was conducted for mortality or signs of intoxication, lethargy, behavioral changes, and food consumption for 14 days [20]. It is worth mentioning that doses were selected based on the previously published articles described by Maneewattanapinyo et al., 2011, and Adeyemi and Adewumi, 2014 [21,22].
2.5. In Vivo Effect of AgNps on Protoscoleces
2.5.1. Infection of BALB/c Mice with Secondary Hydatid Cysts
Forty healthy mice, 25 ± 5 gm in weight, and aged 6 weeks were used for secondary hydatid cyst infection. Each mouse was injected intraperitoneally with about 1500 protoscoleces [23]. All administrated mice were housed for six months to monitor the development of the secondary hydatid cysts.
2.5.2. Treatment of the Infected BALB/c Mice with AgNPs
The treatment experiment was performed on twenty infected mice with secondary hydatid cysts. The mice were divided into three groups, as shown below:
Group 1 (positive control group): Ten infected mice and none were treated with AgNPs.
Group 2 (treated group): Ten infected mice were treated with AgNPs.
Group 3 (negative control group): Five non-infected mice which were non-treated with AgNPs.
The treated mice were given 200 mg AgNPs/kg. The AgNPs, given to the treated group, were given orally and mixed with the standard animal diet every 2 days for 30 days. The controlled groups were given the same amount of the standard diet as was given to the treated groups but without AgNPs.
All mice were euthanized after 30 days, and internal organs and the peritoneal cavity were checked for the presence of the hydatid cyst infection. The cysts were removed from each mouse and collected in a Petri dish to evaluate their morphological change and to compare them with the normal controlled non-treated cyst. Furthermore, the size of the cysts was measured using a ruler [24]. Moreover, the weight of both the treated and controlled group mice was recorded, weekly, during the in vivo experiment.
2.6. Histological Preparation
Hydatid cysts from treated mice and non-treated controlled ones were isolated. In addition, the kidneys, liver, and intestines of the mice in the acute toxicity of AgNPs experiment were removed from the anaesthetized animal. The following steps were followed for tissue processing: the samples were immediately fixed in fixative 10% formalin for 24 h. Next, they were dehydrated using ethanol in ascending concentrations of 50%, 70%, 95%, and 100%. After that, the specimens were kept in 100% xylene for 10 min; this cleansing process was repeated twice, and then the specimens were infiltrated with melting paraffin wax. Finally, the samples were embedded in paraffin wax. Five-micron sections of the embedded specimens were prepared by rotary microtome, then floated in water in a water bath at 40 °C. Sections were mounted onto slides and stored at room temperature to allow for staining with hematoxylin and eosin stain (H and E) [25].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The results were analyzed using the Graph pad Prism software version 8 and the data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. A p-value of less than 0.05 (<0.05) was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Plant Extracts UV-Vis Spectrum
The UV-vis spectrum of the plant extract is shown in Figure 3A. The spectroscopic analysis of the extract showed two peaks at 266 nm (band I) and 320 nm (band II), and these correspond to the cinnamoyl and benzoyl with phenolic compounds. The peaks are associated with π to π* transition, which is related to the phytochemical constituents of the leaf extract. They can be considered as a source for the green synthesis of metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles.
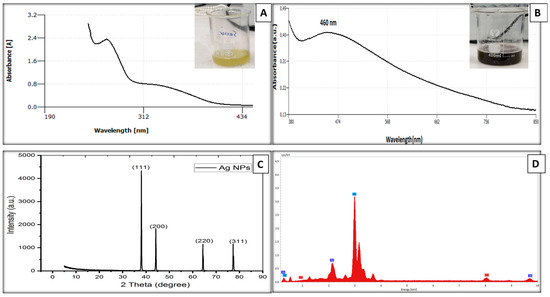
Figure 3.
(A) UV-Vis absorption spectrum of plant extract, (B) UV-Vis absorption spectrum of AgNPs, (C) XRD of the biosynthesized Ag NPs, and (D) EDX spectrum of green synthesized AgNPs.
3.1.2. Nanoparticles Characterization
In the present study, the green, environmentally friendly, and biologically synthesized AgNPs were successfully prepared from the leaf extracts of the sidr (Zizyphus spina-christi) plant. The visual inspection confirmed Ag nanoparticle formation as there was a color change of the mixture, which went from greenish-yellow to dark brown, as illustrated in Figure 3B.
The optical properties of AgNPs dispersed in water were recorded using double-beam UV-Visible spectra at room temperature in a quartz cuvette with a path length of 1 cm. All the samples exhibit strong UV absorption spectra with an absorption peak at 460 nm, as shown in Figure 3B, indicating AgNP fabrication. There were no other peaks observed which is a good indicator of purity of the crystalline structure of the AgNPs.
The XRD analysis of the synthesized AgNPs was conducted to confirm the crystalline nature and structure of the green synthesized AgNPs. Figure 3C shows the X-ray diffraction pattern of the prepared AgNPs; it demonstrates the face-centered cubic structure. From the XRD analysis, the dominant reflection peaks are 111, 200, and 220, corresponding with the scattering angles at 38.037°, 44.205°, and 64.344°, respectively. The obtained peaks are equivalent with the JCPDS: No. 36–1451 indicate that the AgNPs are pure crystalline. It can be noted that the narrow and high intensity of the peaks are good indicators of the quality and crystallinity feature of the growth material. Figure 3D illustrates the morphology and EDX analysis of AgNPs formed using the bioreduction technique. This assured the existence of the AgNPs. The other peaks besides the Ag one relate to the element of gold (Au); this peak was present as a gold coating was used to improve the quality of SEM images. Figure 4 presents the typical FE-SEM images of the AgNPs at different magnifications. The SEM micrographs demonstrate the identical distribution of the spherical-shaped AgNPs, with some agglomerations of nanoparticles, and that the average size ranged between 50–80 nm.
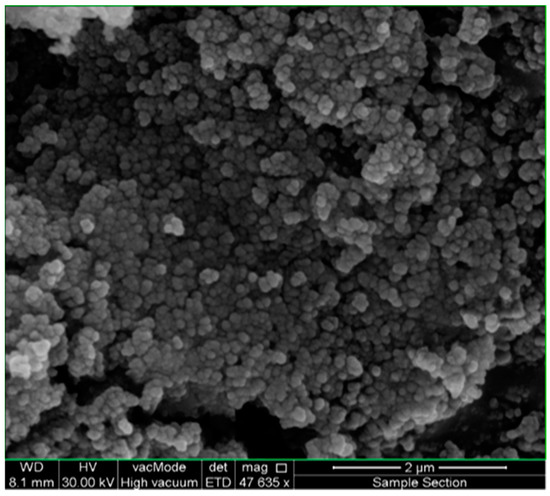
Figure 4.
Shows the typical FE-SEM images of the AgNPs synthesized using aqueous sidr plant extract. The synthesized AgNPs had spherical shapes, and the size of the particles was measured between 50–80 nm.
3.2. Viability of the Collected Protoscoleces
The collected protoscoleces from hydatid cysts showed muscular movements under the light microscope. Viable protoscoleces seemed to be colorless compared with dead ones that absorbed the stain and appeared red. The percentage of in vitro viability was 97%, which is appropriate for the subsequent experiments.
3.3. The Toxicity of Ag Nps
Acute (Short Term) Toxicity of AgNPs in BALB/c Mice
Different doses of AgNPs, including 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, and 300 mg/kg did not induce any adverse effects or signs in the mice as they were monitored for 2 days continuously. The mice were then kept and observed for the development of toxic signs for a further seven days with daily observations. Overall, no deaths were recorded during the seven days of observation in both the treated and control animals. Moreover, the experimented mice did not express any physiological behavior alterations within the 14 day period following the treatment. All treated and control groups of mice did not show any apparent changes in their general appearance or any difficulties in water or food intake, and they remained healthy with normal activities during the study period.
3.4. In Vivo Aspect of Echinococcosis
3.4.1. In Vivo Secondary Hydatid Cyst Infection
Following the intraperitoneal administration of BALB/c mice with 1500 viable protoscoleces, the outcome proved the formation of hydatid cysts within the liver and the peritoneal cavity of the injected mice after 6 months of infection (Figure 5).
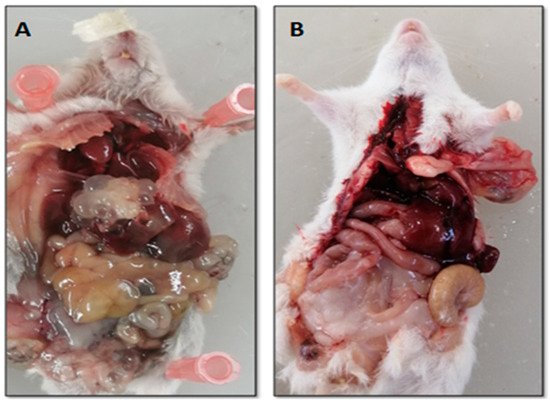
Figure 5.
Heavily infected liver with secondary hydatid cyst after six months post-infection (A), compared with liver of control non-infected mice (B).
3.4.2. In Vivo Efficiency of AgNPs
The Effect of AgNPs against Hydatid Cyst
After 30 days post-treatment, the collected hydatid cysts from all the mice that were anesthetized and sacrificed from both treated and controlled groups were isolated. The fluid from the hydatid cysts were aspirated: there were no protoscoleces. The hydatid cysts in all the mice from untreated group (group 1) were located in the peritoneal cavity. However, the hydatid cyst were also developed in the liver of four of the untreated mice (group 1). The results pointed out that nine out of the ten treated mice (group 2) developed cysts in the peritoneal cavity. However, the other mouse of the treated group with liver infection, exhibited more therapeutic effect by AgNPs than the other nine mice. The hydatid cysts present on the liver in the infected untreated group were transparent (Figure 6A) while the color of the cyst in the infected treated group changed, as it had a milky appearance (Figure 6B). On the other hand, after incorporating AgNPs into the mice’s diet, no significant noticeable differences were observed between the hydatid cyst developed intraperitoneally within treated and the untreated infected mice. However, in the treated mice, the hydatid cysts which formed in the intraperitoneal cavity seemed to be slightly cloudy in color, as shown in Figure 6D,E, compared with the transparent cysts of the infected untreated group, as illustrated in Figure 6C.
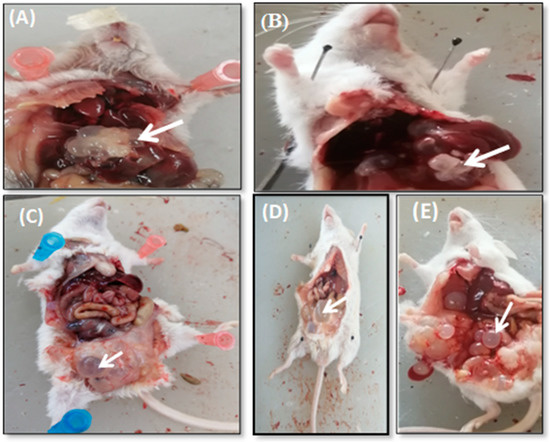
Figure 6.
Transparent hepatic hydatid cysts in infected untreated mouse (A) compared with the milky or cloudy appearance of the hepatic hydatid cysts in mouse treated with AgNPs for one month (B); (C) shows transparent hydatid cyst in the peritoneal cavity in infected untreated mice; (D,E) shows cloudy appearance of hydatid cysts in infected treated mice.
Effect of AgNPs on Mice Weight and Hydatid Cysts Size
The infected mice were weighed on the day that the AgNPs were administrated. When assessing through the naked eye, there was no marked decrease in the size of cysts between the infected treated groups compared with the infected control group. The smallest hydatid cyst size was detected in the infected control groups compared with the infected treated groups. The change in the hydatid cysts’ color was evident, but no apparent reduction in the cysts’ size was seen.
Figure 7 shows the hydatid cysts of both untreated control and treated mice by AgNPs. There was a slight reduction in the hydatid cyst size in the treated group compared with the control one. All the treated groups showed an apparent change in the color of the hydatid cysts but with no significant reduction in cyst size (Figure 8).
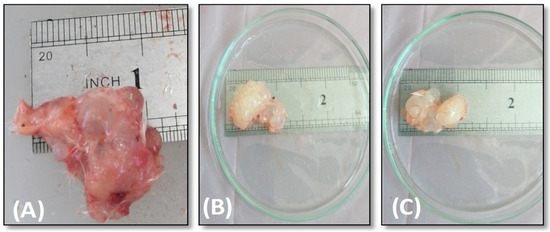
Figure 7.
Cysts’ size isolated from the infected mice; (A) control untreated; (B,C) treated mice.
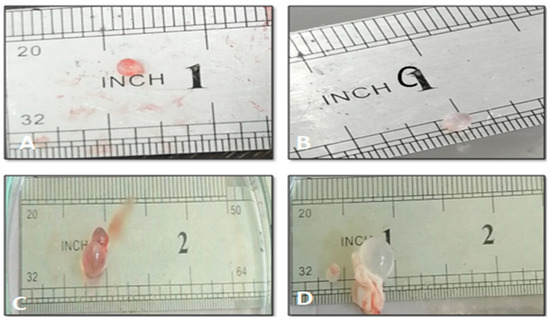
Figure 8.
Hydatid cysts isolated from the experimentally infected untreated mice (A,C), and infected treated mice (B,D).
In the present study, the infected untreated mice’s weights were compared with the weight of the infected treated groups and the mean of the different group weights decreased slightly. Still, depending on the ANOVA test, the mean differences were not significant (Figure 9). Thus, there were no statistically significant differences in the mice’s weights during the time of treatment (p > 0.05).
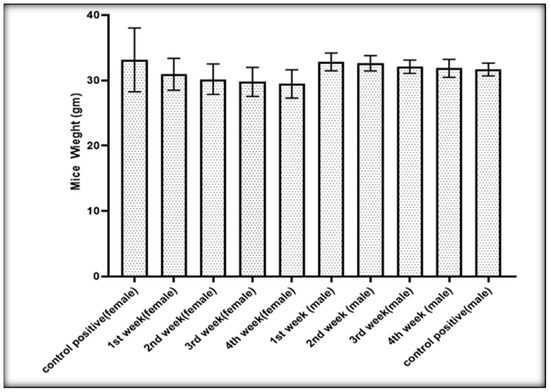
Figure 9.
Effect of AgNPs on the weight of the infected mice with hydatid cysts.
3.5. Histopathological Examinations
3.5.1. Hydatid Cysts from Treated and Untreated Infected Mice
The histological sections in Figure 10 show the effect of AgNPs on the hydatid cyst wall in those treated with 200 mg/kg and the untreated infected mice. The germinal and laminated layers’ typical structure is present in the control untreated hydatid cysts and is shown in Figure 10A–C. Their intact layers can be seen clearly. Cells of the germinal layer were equally distributed and arranged. In contrast, the effects of AgNPs in the treated groups can be seen. The laminated and germinal layers from the wall of the treated hydatid cysts showed rupture and destruction; the laminated layers were damaged and partially fragmented in many parts, indicative of a destructive effect mediated by these AgNPs, as shown in Figure 10D,G,H,J.
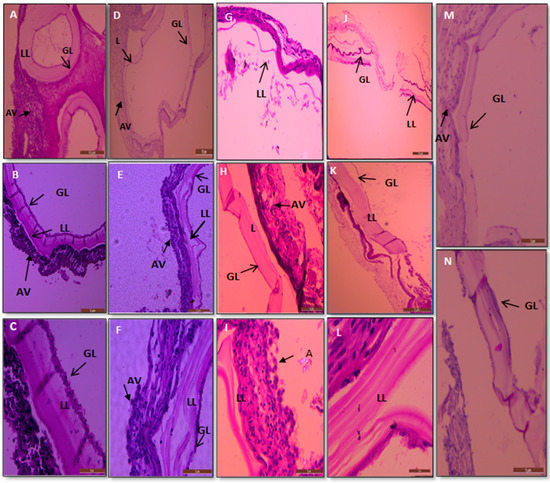
Figure 10.
Sections of cysts treated with 200 mg/kg AgNPs and untreated (control) infected mice. (A–C) Represent the control untreated mice hydatid cyst; the LL is tight and thick and GL is intact. (E,F,L) Show treated hydatid cysts from infected mice which were treated with AgNps, and LL became loose with vascular appearance. (D,K,I) Show that the LL is thinner and separated from the germinal layer. (G,J) Show the hydatid cysts layer destroyed. (H,M,N) Show the GL destructed and reduced cells. GL: germinal layer; LL: laminated layer; AV: adventitious layer. Stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bar = 2 μm & 10 μm.
Besides this, the laminated layer of the treated mice expressed increased numbers of vesicles and was looser (Figure 10E,F,L). The germinal layer had cellular damage and a reduction in the number of cells, some of which underwent degeneration, see Figure 10H,K,M,N. Moreover, the laminated layer structure is thin and loose, and there were reduced cell numbers in the germinal layer. The findings also revealed that the cyst wall was damaged, and vacuoles can be seen between the laminated and germinal layers (see Figure 10J,M).
3.5.2. The Histopathological Study of Acute Short-Term Toxicity of AgNPs
The histopathological effects of AgNPs were investigated in the treated mice (group 2) to detect the median lethal dose (LD50). The histological sections of the livers of control untreated mice revealed the typical structure of the hepatic tissue. Figure 11A,B illustrates that the liver consists of hepatic lobules in the section, each with a central vein. Each lobule has cords of hepatic cells that radiate from the central vein toward the periphery; among them are spaces called hepatic sinusoids.
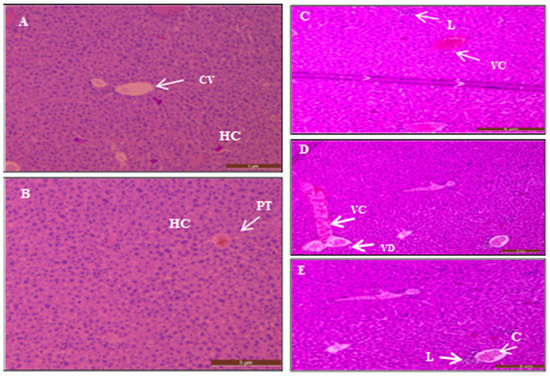
Figure 11.
Transverse sections in the liver of control untreated mice. Showing the central vein (CV), plates of hepatic cells (HC), and sinusoids (S) in (A) portal tract (PT) in (B) stained with H and E stain. (C) Shows vascular congestion (VC) and few scattered inflammatory cells (lymphocytes) (L) in a liver section of treated mice with 200 mg/kg AgNPs. (D) Illustrates liver section of treated mice with 300 mg/kg AgNPs which shows vascular congestion (VC) characterized by dilated blood vessels filled with RBCs. A few hydropic changes and vacuolar degeneration (VD) occurred as a reversible injury. (E) Portal tract dilated vein filled with RBCs (congestion) (C) and a few scattered inflammatory cells (Lymphocytes) (L). Stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bar = 5 μm.
In contrast, sections of the livers of treated mice showed several histopathological changes. Figure 11C illustrates vascular congestion and a few scattered inflammatory cells (lymphocytes) in a liver section of the mice treated with 200 mg/kg Ag. Figure 11D shows the liver section of mice given 300 mg/kg of AgNPs orally. The results show vascular congestion characterized by dilated blood vessels filled with RBCs, which indicate the initiation of the inflammation. In addition, vascular degeneration occurred as a reversible injury.
Figure 11E shows the portal tract vein dilation with congestion where the vein is filled with RBCs as an early stage of inflammation. Moreover, the accumulation of inflammatory cells such as lymphocytes is one remarkable histopathological change in the liver section of mice treated with 300 mg/kg AgNPs.
The kidney of the control mice showed the normal structure of glomeruli and nephrotic tubules (Figure 12A). In contrast, the kidneys of the mice which received oral administration of AgNPs exhibited several changes, including mild chronic inflammation with lymphocytes surrounded by edema signified by the white color (Figure 12B).
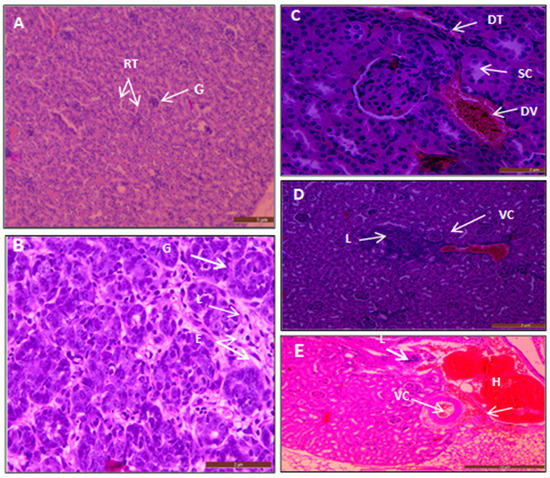
Figure 12.
Sections of kidney mice. (A) Kidney of control mouse reveals normal glomeruli (G) and normal renal tubules (RT). (B) Kidney of mouse administered with an oral dose of 300 mg/kg AgNPs reveals mild chronic inflammation with lymphocytes (L) surrounded by edema (E) (white in color). (C) Section from mice treated with 300 mg/kg represents a prominent dilated blood vessel (DV) filled with RBCs. It shows dilated tubules (DT) with swelling of cells (SC) as reversible injury and hydropic changes occurred. (D) Kidney of mice treated with 200 mg/kg shows vascular congestion (VC), dilated blood vessels filled with RBCs and lymphocytes (L) (chronic inflammatory cells infiltration). Moreover, lymphocytes with vascular congestion are seen in (E) as it shows kidney of mice treated with 300 mg/kg; it also demonstrated a hemorrhage (bleeding) (H). Stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bar= 5 μm for (A), 2 μm for (B–D), and 10 μm for (E).
Moreover, the histological sections of the kidneys of mice treated with 300 mg/kg Ag NPs revealed a prominent dilated blood vessel filled with RBCs. Moreover, it exhibited dilated tubules with swelling of cells as there was reversible injury and hydropic change (Figure 12C). Furthermore, the section of kidneys of mice treated with 200 mg/kg showed vascular congestion, dilated blood vessels filled with RBCs and lymphocytes (chronic inflammatory cells infiltration) as shown in Figure 12D. Hemorrhage was detected in sections of kidneys of mice treated with 300 mg/kg, and vascular congestion with a mild thickening in the wall of the blood vessel (Figure 12E).
In terms of the histological sections of the small intestine, the section from the control animals showed the normal structure with the mucosal layer which has the intestinal villi as finger-like structures and the crypts of Lieberkunn. Then, the submucosal layer was followed by the muscularis propria and the outermost serosa as in (Figure 13A).
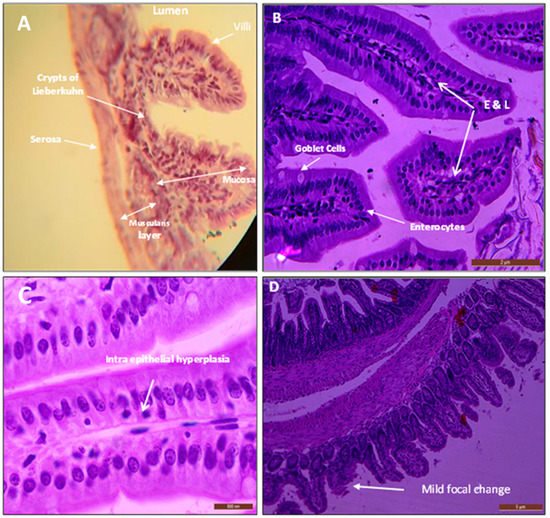
Figure 13.
(A) Normal intestinal mucosa shows the mucosa lined with columnar epithelium, the submucosa, muscularis properia, and finally serosa. With simple columnar absorptive cells (enterocytes) and goblet cells in (B) intestines of mice treated with 300 mg/kg revealed mild focal edema (E) and a few scattered chronic inflammatory cells lymphocytes (L). (C) Sections of the intestine show intraepithelial or intra-glandular lymphocytes (chronic inflammatory cells). (D) Focal mild broadening and atrophic changes as mild destruction occurred in the surface of villi (mild focal change). Stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bars for (A,D) 5 μm, 500 μm for (C), and 2 μm for (B).
Regarding the mice treated with AgNPs, no remarkable alteration was observed in their intestinal histological sections. Mice treated with 300 mg/kg revealed mild focal edema, few scattered chronic inflammatory cells (lymphocytes), as in Figure 13B. Additionally, intraepithelial or intra-glandular lymphocytes (chronic inflammatory cells) were observed in some sections as in Figure 13C. Moreover, mild focal broadening and atrophic changes were observed as mild destruction in the surface of villi (mild focal change) were exhibited in the intestine of a mouse treated with AgNPs (Figure 13D).
4. Discussion
As a treatment approach, benzimidazole is the only synthetic chemical drug licensed by the WHO for human treatment. These compounds are known as parasitostatic rather than parasiticidal agents. Additionally, benzimidazole’s failure to cure has been attributed mainly to its low aqueous solubility and low drug absorption level, and besides that, it also has several adverse effects [5,7]. Therefore, new therapeutic alternatives are urgently needed.
In this study, green synthesized AgNPs were used as a treatment. As a result of the medical applications, nanoparticles of many metals, such as Au, Ag, Pt, and ZnO, were widely tested. The green generated NPs are more stable and vastly diverse in morphology and size than those made by other organisms [26]. The use of different NPs has been investigated in many published studies and has shown several beneficial impacts against cystic hydatid disease [27]. Moreover, Choi et al. [28] confirmed that the AgNPs were well dispersed in water and showed no agglomeration or morphological variations, whereas ABZ is poorly water-soluble [29]. Previously published reviews focused on the studies related to the effects of different NPs against echinococcosis. They concluded that a wide range of organic and inorganic NPs were highly efficacious against CE, indicating that nanoparticles could be considered as an alternative and complementary resource for CE treatment [30,31]. Our previous work confirmed the significant effect of AgNPs and ZnONPs against protoscoleces in an in vitro model [32,33].
In the present study, AgNPs were produced using leaf extracts of Z. spina-christi. The visual inspection proved the formation of AgNPs. The color changed from greenish-yellow to intense dark brown, confirming the production of AgNPs. The presence of electron-rich functional groups in the plant is proposed to be accountable for AgNPs’ formation. It is suggested that the plant materials serve as a reducing and stabilizing agent for AgNP production. The extracts’ phytochemical composition includes phenolic content, cardiac glycosides, polyphenols, saponins, and tannins [34,35,36]. The rate of reduction was increased by leaving the mixture for 24 h. These findings were supported by the results previously recorded [37,38].
The UV-Vis spectroscopy technique is broadly performed for the structural categorization of NPs. The reduction of AgNO3 to AgNPs is checked by using the double-beam UV-Vis spectrum. The samples showed UV absorption spectra with a peak at 460 nm owing to the surface plasmon resonance. During the biosynthesis of AgNPs, the color change of the mixture is the primary sign that appears and is due to the surface plasmon resonance proving the release of AgNPs. The obtained results of the AgNPs had a perfect agreement with the previously reported literature. Arreche et al. generated AgNPs that have a surface plasmon peak at 460 nm [39]. On the other hand, in a previous study, the surface plasmon resonance band of AgNPs was documented in the range of 452–465 nm [40].
Furthermore, the present findings of EDX, X-ray diffraction, and SEM imaging confirmed the green synthesis of AgNPs by the plant extract.
The effect of AgNPs is due to small particles in the nanometer range that increase the permeability of Ag+ ions into microbial cells, resulting in cell death. Moreover, the presence of capping agents increases their biocidal efficacy [41]. The toxic effect of AgNPs has been explained in some studies. Rahimi et al. described the scolicidal impact of AgNPs as a probable electrostatic interaction between Ag-NPs (electrically positive) and the parasite (electrically negative) associated with organic complexes on its surface [11]. Naseri et al. explained the electrostatic interaction between protoscoleces (electrically negative) and PLGA-PEG (electrically positive), associated with copolymer complexes on its surface, which can account for the more scolicidal outcome of ABZs-loaded PLGA-PEG [42]. Regarding the mechanism of action of silver NPs, Nassef et al. also stated that they interfere with the cell membrane, resulting in the creation of pores through which the cellular contents leak out. Furthermore, they increase the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which destroy mitochondrial membranes and trigger apoptosis [13].
Ibrahim concluded that the biocidal properties of AgNPs against microorganisms are based on three main mechanisms. Firstly, AgNPs bind to the negatively charged cell surface, causing changes in the physical and chemical properties of cell membranes and cell walls, as well as disrupting essential functions such as permeability, osmoregulation, electron transport, and respiration. Secondly, by penetrating the cell and interacting with DNA, proteins, and other phosphorus- and sulfur-containing cell constituents, AgNPs can cause even more damage to cells. Thirdly, AgNPs emit silver ions, resulting in an increased biocidal effect that varies in size and dosage. Furthermore, multiple mechanisms were proposed to explain the cells’ death due to their interaction with Ag+. The Ag+ ions can interact with the proteins’ disulfide bonds. The microorganisms are unable to survive as a result of this interaction. Proton motive power, forming complexes with DNA and RNA, and splitting the cells’ mitochondrial membranes are the other proposed mechanisms [37].
Nanotoxicology has emerged as a new discipline to study the adverse effects of nanoparticles since nano-sized particles are comparatively more toxic than other sized particles. Many researchers focused on the toxicological aspects of nanomaterials before their implementation. In addition, different sizes and shapes of AgNPs have different toxicities [43]; AgNPs which are 20 nm in size are more toxic than AgNPs of 50 nm [44]. Among several different metal NPs, the synthesized AgNPs were reported as a non-toxic substance with good antimicrobial efficacies against viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Moreover, it was evaluated as a suitable carrier of various therapeutic drugs [9]. Therefore, this study was planned to evaluate the toxicity and therapeutic effects of the green synthesized AgNPs against E. granulosus infection in an experimental mice model.
In addition, our previous work on the in vitro hemolytic ability of AgNPs on the human RBCs revealed that the percentage of hemolysis slightly increased as the concentration of AgNPs increased [32]. This can be related to the formation of AgCl by binding the Ag+ ions with free chloride ions, reduced surface area owing to particle aggregation, and the appearance of a protein corona on particles [45]. It has been reported that AgNPs can cause hemolysis via altering erythrocytes membrane integrity and surface features. Moreover, reduced availability of Ag+ could stimulate the death of erythrocytes in vitro, and this is probably related to reactive oxygen species [46].
On the other hand, AgNPs are safe and have anti-inflammatory properties when used to treat ulcerative colitis [47]. Similarly, during their research on the effectiveness of AgNPs against Giardia lamblia in laboratory rats, Said et al. observed the accumulation of silver and discovered the safe limits of accumulated AgNPs within various organs [48].
The in vivo acute short time toxicity of selected AgNP concentrations for evaluating the lethal dose was performed in this study. The findings of this study for acute short time toxicity at various doses showed that the inoculated mice exhibited no mortality after gavages. Moreover, no anorexia and no adverse signs in the general appearance or behavior of the mice were noticed even after 7 or 14 days, as daily observations were made.
These findings agree with the study of Adeyemi and Adewumi, who did not report the occurrence of death or significant decrease in food consumption and body weight as a result of the treatment with AgNPs when they investigated the effect of AgNPs in Wistar rats orally exposed to 100 mg, 1000 mg, and 5000 mg/kg of AgNPs daily for 7, 14, and 21 days, but some biochemical parameters showed significant alteration such as AST, ALT, and ALP [22]. Furthermore, treating rats with a 5000 mg/kg dose of AgNPs caused dullness. However, the study of Maneewattanapinyo et al. suggested that colloidal AgNPs could be relatively safe when administered orally, ocularly, and topically to the animal models for short periods of time. Oral administration of AgNPs at 5000 mg/kg produced neither mortality nor acute toxic signs throughout the observation period. In the hematological analysis and blood chemistry analysis, there was a non-significant difference between mice treated with AgNPs and controls. There was neither any gross lesion nor histopathological changes observed in the various organs. As a result, it was indicated that the LD50 of colloidal AgNPs is more than 5000 mg/kg body weight [21].
The results from the acute toxicity evaluation indicated that mice exposed to AgNPs by oral administration exhibited no noticeable toxic or adverse health effects. Only mild histopathological changes were observed. The liver and the kidneys of the mice administered with 300 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg showed vascular congestion characterized by dilated blood vessels filled with RBCs, indicating the initiation of inflammation. In addition, infiltration by inflammatory cells, especially lymphocytes, was observed. Moreover, the kidney tissues of the treated animals exhibited edema, dilated tubules with swelling of cells as reversible injury hydropic change, and hemorrhage (bleeding). Similarly, Kim et al. studied the AgNPs (60 nm) orally administered to rats at a much larger dose of 1000 mg/kg [49]. These researchers reported non-significant changes in body weight relative to the doses of silver nanoparticles during the experiment. Their findings also indicated slight liver damage upon exposure to more than 300 mg of silver nanoparticles. The same results were also documented by Xue et al., who observed edema and loss of cytoplasm in liver cells with the high-dose AgNPs treatment mice. However, contrastingly from the present study, there was no infiltration of inflammatory cells in liver cells in all mice [50].
The experimental therapeutic dose in the present study of 200 mg/kg was selected based on the results of a previous study where a lethal dose of AgNPs of >200 mg/kg was mentioned [50]. Compared with another study, mice injected with 214 mg/kg AgNPs died within 48 h after injection. These mice showed apparent symptoms of passive behavior, piloerection, labored breathing, impaired movement, arching of the back, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. None of the mice injected with 134, 84, and 52.5 mg/kg AgNPs died until day 14 [44].
Moreover, several biochemical parameters were determined in rat serum, kidney, liver, and heart. The analysis includes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). The dose at 100 mg/kg produced more significant alterations in the biochemical parameters than did the higher doses (1000 and 5000 mg/kg, respectively). The alteration in the level of enzymes may represent adaptive mechanisms by the animals trying to offset stress imposed by exposure to the AgNPs [22]. Therefore, these researchers mentioned the pronounced biochemical alterations noticed with the 100 mg/kg AgNPs might not be entirely consistent with the results of Maneewattanapinyo et al., in which colloidal AgNPs had a LD50 of >5000 mg/kg in mice. They pointed out that the histopathological sections of different organs in control and treated animals showed no unusual lesions that could be attributed to the effect of oral and dermal administration of AgNPs at all observation times [21].
In the present work, the histopathological effects were seen in the liver and kidney tissues mainly; this agrees with the study of Wen et al., who concluded that the liver and kidneys could be the most affected organs by acute intravenous injection of AgNPs [51]. The genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of AgNPs are influenced by some physicochemical features, including dispersion rate, concentration, surface charge, size, morphology, and surface functionalization [9,52].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that investigated the anti-hydatid activity of green biosynthesized AgNPs in vitro and in animal models together. Secondary cysts were developed in mice experimentally infected with protoscolices of E. granulosus. The present study used female and male BALB/c mice. Previous research confirmed that BALB/c mice are good experimental models for CE [53,54]. Moreover, recent studies have used BALB/c mice for the same purpose [55,56,57]. Other researchers used only female BALB/c mice [58,59] or only male BALB/c mice [60].
The intraperitoneal injection of mice with 1500 protoscoleces, in this study, resulted in the development of secondary hydatid cyst after six months in all the injected mice; this agrees with the results of Ismail et al. [61]. A previous study showed that the male BALB/c mice are more susceptible to infection with secondary hydatidosis by intraperitoneal administration of protoscoleces than activated oncospheres [54]. Moreover, the current finding is also similar to the results of Torabi et al. [62].
The protoscoleces were immediately used in this research after isolation from the cysts. However, Ismail and Saad concluded that the survival rate of protoscoleces in vitro is 5 days if kept at 4 °C. At this ideal temperature, protoscoleces can remain viable and intact for a long time [19].
In the in vivo study, the goal was to determine the ability of the AgNPs dispersion through the cyst membrane and to exhibit effects on the hydatid cyst wall. The chosen concentration of AgNPs in the current research for in vivo treatment of mice was 200 mg/kg. The reason for this was to reduce the toxicity effect. A short treatment course (30 days) was chosen for infected mice.
In this study, the treatment of mice infected with protoscoleces with AgNPs resulted in a change in the liver hydatid cyst color to milky white. While the cysts formed in the peritoneal infected group slightly changed in color from hyaline transparent, the general appearance of the cyst in the control infected but non-treated group was a turbid color. The present finding is similar to the results of Jelowdar et al., who investigated the effect of combined albendazole and praziquantel and their loaded solid lipid nanoparticles components in chemoprophylaxis of experimental hydatidosis in the mice. They stated that the cysts formed in the untreated mice were more hyaline when compared with the ABZ and PZQ types [58].
Furthermore, the cysts in the treated animals recorded in the present study were slightly smaller than those in the non-treated control group. The weight of infected treated mice was reduced, but this reduction was non-significant (>0.05) compared with that of the control non-treated group.
However, unlike most of the previous studies [13,57,58,63] in which the experimental animals were treated for more extended periods, the current treatment protocol was implemented for a brief time on the very well advanced cysts which may display less of a reaction to treatment. It may require a more extended period of treatment to cure the hydatid cyst in vivo completely. Pérez-Serrano et al. also found that BZD had a more significant protoscolicidal effect on young protoscoleces than those with cyst layers [64]. The thickness of the cyst layers tends to be the most critical factor influencing drug permeability; larger cysts have thicker layers, which serve as a dense barrier. Furthermore, for the elimination of hydatid cysts, the germinal layer should be destroyed. The germinal layer can contain viable protoscolices because embryonic or stem cells are present in the germinal layer and have the potential to develop new protoscolices or brood capsules [65]. Moazeni et al. also investigated the effect of aromatic water of Zataria multiflora on secondary hydatid cysts using scanning electron microscopy. The results confirmed the germinal layer destruction. Their findings proved that aromatic water of Z. multiflora (20 mL/L in drinking water for 8 months) could prevent the development of hydatid cyst in experimental mice [65].
The histological changes of the cysts were examined in this study. The histological sections revealed some changes in the metacestode germinal layer and the laminated layer demonstrated the degenerative effect of the Ag NPs on the parasite. The control hydatid cyst did not exhibit any histological alterations. This finding agrees with the previously studied effect of ABZs-loaded on (SLN) [24]. Similarly, Jelowdar et al. found that the weakened cyst walls were evident in the combination drugs in the treatment group. The germinal layer was severely damaged, the laminated layer was absent, and the microfibrillar pattern of the laminated layer was no more present in the group treated with ABZ and PZQ loaded SLNs [58]. The combination of all outcomes of damages, including color-changing and loss of the integrity of the germinal layer and laminated layer contributes to the loss of cyst viability, confirming the efficacy of AgNPs against CE.
This finding indicated that, even though AgNPs cause significant changes in the cyst’s layer, either the drug concentration or long-term therapy is insufficient to reduce the cyst’s mass. Generally, AgNPs had an impact on the laminated and germinal layers in the present research. The findings of in vivo hydatid cyst layer changes are similar to those recorded by Lv et al. who investigated the in vivo trials of combined Huaier aqueous extract + L-ABZ treatment for chemotherapy in mice against CE, started at six weeks post-inoculation. The combination treatment revealed a weakened cyst wall with structural discontinuity and breakage in the laminated and germinal layers, as well as vacuolation between the two layers. The immune response and promoting the protoscolex apoptosis could be involved [66]. Thus, the result obtained from the present study is in agreement with the previous investigation.
5. Conclusions
We have successfully achieved a single-step green chemistry method that utilizes leaf extracts of Z. spina-christi as a reductant and a capping or stabilizing agent in the creation of AgNPs. This method produces stable, spherical silver nanoparticles with a range of hydrodynamic diameters of 50–80 nm. The acute short-term toxicity of AgNPs in mice revealed no adverse effects or signs as they were closely monitored for 48 h and for two weeks with daily observations. A suitable dose was selected for CE treatment in mice for the first time. The obtained data demonstrated that AgNPs showed significant in vivo effects on the hydatid cyst layer in BALB/c mice. However the histopathological study showed mild effects of AgNPs within the liver, kidneys, and intestine of the treated animals compared with the control mice. The present findings will not only be helpful for the toxicological evaluation of AgNPs, but it will also shed some light on future toxicological assessments in humans, which are essential to evaluate the safe dosage to minimize human health-related problems. The green synthesized AgNPs could be considered as a new potential therapeutic option against E. granulosus infection; however, further studies should be conducted to evaluate its efficacy through other routes of administration. Despite the promising results, more studies are needed to explain the probable mechanism of action of Ag NPs against hydatid cysts.
Author Contributions
S.M.H. and B.H.S. designed the study; S.M.H., B.H.S. and P.J.J. performed the research method; S.M.H., P.J.J. and B.H.S. analyzed the data; M.H.A. planned and carried out the simulation; and S.M.H., B.H.S. and M.H.A. wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the scientific committee of Soran University (1/1/277 on 9th of December 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the scientific research center at Soran University and Sisaf for assistance with the data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kern, P.; Menezes da Silva, A.; Akhan, O.; Müllhaupt, B.; Vizcaychipi, K.A.; Budke, C.; Vuitton, D.A. The Echinococcoses: Diagnosis, Clinical Management and Burden of Disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 259–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Working to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: First WHO Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases: Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/70503 (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Benyan, A.K.; Mahdi, N.K.; Abdul-Amir, F.; Ubaid, O. Second reported case of multilocular hydatid disease in Iraq. Qatar Med. J. 2013, 2013, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.I.; Meerkhan, A.A.; Boufana, B.; Hama, A.A.; Ahmed, B.D.; Mero, W.M.S.; Orsten, S.; Interisano, M.; Pozio, E.; Casulli, A. Two haplotype clusters of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in northern Iraq (Kurdistan region) support the hypothesis of a parasite cradle in the Middle East. Acta Trop. 2017, 172, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, B.; Xing, G.; Lv, H.; Jiang, Y. Protoscolicidal effects of chenodeoxycholic acid on protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 167, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, A.; Baudin, F.; Matmar, M.; Archambeau, D.; Ozier, Y. Severe hypernatremia after hypertonic saline irrigation of hydatid cysts. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles-Lucas, M.; Casulli, A.; Cirilli, R.; Carmena, D. Progress in the pharmacological treatment of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis: Compounds and therapeutic targets. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Paralikar, P.; Gupta, I.; Medici, S.; Santos, C.A. Recent advances in use of silver nanoparticles as antimalarial agents. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Honary, S.; Ali Mohammadi, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Rahimi, M.T.; Alizadeh, A.; Naghibi, F.; Saravanan, M. Green chemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using Penicillium aculeatum and their scolicidal activity against hydatid cyst protoscolices of Echinococcus granulosus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 5800–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.T.; Ahmadpour, E.; Rahimi Esboei, B.; Spotin, A.; Koshki, M.H.K.; Alizadeh, A.; Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Mohammadi, M.A. Scolicidal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 19, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, T.A.; Hassan, K.T.; Majeed, S.R.; Ibraheem, I.J.; Hassan, O.M.; Obaid, A. In vitro scolicidal activity of synthesised silver nanoparticles from aqueous plant extract against Echinococcus granulosus. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassef, N.E.; Saad, A.E.; Harba, N.M.; Beshay, E.V.N.; Gouda, M.A.; Shendi, S.S.; Mohamed, A.S.E. Evaluation of the therapeutic efficacy of albendazole-loaded silver nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus infection in experimental mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2019, 43, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Al-Ali, S.J.; Swar, S.O. Nanoparticles as a new approach for treating hydatid cyst disease. In Veterinary Pathobiology and Public Health; Unique Scientific Publishers: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2021; pp. 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwani, E.M. Rapid biosynthesis method and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Zizyphus spina christi leaf extract and their antibacterial efficacy in therapeutic application. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwaniyi, O.O.; Adegoke, H.I.; Adesuji, E.T.; Alabi, A.B.; Bodede, S.O.; Labulo, A.H.; Oseghale, C.O. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Thevetia peruviana Juss and its antimicrobial activities. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, J.D.; Barrett, N.J. Procedures for testing the viability of human hydatid cysts following surgical removal, especially after chemotherapy. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1980, 74, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Gorony, S.h.M.; Khalid, K.M. Efficacy of cyperus rotundus rhizomes-tubers extracts against protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus. World J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 6, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ismail, E.; Saad, M. In Vivo and In Vitro Survival Rates of Protoscoleces Kept at Different Constant Temperature. Open J. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klassen, C.D.; Casarett, L.J.; Amdur, M.O. Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons; Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 1986; ISBN 9780023646508. Available online: https://www.abebooks.co.uk/servlet/SearchResults?isbn=9780023646508 (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Maneewattanapinyo, P.; Banlunara, W.; Thammacharoen, C.; Ekgasit, S.; Kaewamatawong, T. An evaluation of acute toxicity of colloidal silver nanoparticles. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Dewumi, I. Biochemical evaluation of silver nanoparticles in Wistar rats. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 196091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Serrano, J.; Denegri, G.; Casado, N.; Rodriguez-Caabiero, F. In vivo effect of oral albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide on development of secondary echinococcosis in mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia, S.; Moazeni, M.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Oryan, A. In vivo evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against hydatid cyst. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaoui, M.; Fiette, L. Histopathology procedures: From tissue sampling to histopathological evaluation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 691, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Rafiei, A.; Ramezani, Z.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Jelowdar, A.; Kahvaz, M.S. Evaluation of the Hydatid Cyst Membrane Permeability of Albendazole and Albendazole Sulfoxide-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2017, 12, e34723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Reipa, V.; Hitchins, V.M.; Goering, P.L.; Malinauskas, R.A. Physicochemical characterization and in V itro hemolysis evaluation of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawa, B.H. Advances in the use of nanoparticles as anti-cystic echinococcosis agents: A review article. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2018, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, A.E.; Alanazi, A.D.; Baharvand, P.; Sepahvand, M.; Mahmoudvand, H. High Potency of Organic and Inorganic Nanoparticles to Treat Cystic Echinococcosis: An Evidence-Based Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, P.J.; Shnawa, B.H.; Hamad, S.M. Silver Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis, Characterization, Blood Compatibility and Protoscolicidal Efficacy against Echinococcus granulosus. Pak. Vet. J. 2021, 41, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawa, B.H.; Hamad, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Kareem, P.A.; Ahmed, M.H. Scolicidal activity of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles by Mentha longifolia L. leaves against Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Emergent Mater. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalaka, M.; Daniyan, S.; Mann, A. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of two Ziziphus species (Ziziphus mauritiana L. and Ziziphus spinachristi L.) on some microbial pathogens. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 4, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, S.M.J.; Jaran, A.S.; Haddadin, M.S.Y. Evaluation of Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Three Leaf Extracts of Ziziphus spina-christi (Sedr) Grown in Jordan. J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2016, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mervat, E.-H.; Mohamed, A.A.; Salem, M.Z.; Abdelkareem, M.S.; Ali, H.M. Chemical composition, antioxidant capacity and antibacterial activity against some potato bacterial pathogens of fruit extracts from Phytolacca dioica and Ziziphus spina-christi grown in Egypt. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 233, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.M. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oves, M.; Aslam, M.; Rauf, M.A.; Qayyum, S.; Qari, H.A.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, M.Z.; Tabrez, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Ismail, I.M.I. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreche, R.A.; de Oca-Vásquez, G.M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Vázquez, P.G. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Extracts from Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Wastes. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faried, M.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Hajalilou, A.; Zamanian, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Abouzari-Lotf, E.; Hara, H.; Khairudinet, N.B.B.A.; Nordi, M.F.B.M. A green approach for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ultrasonic radiation’s times in sodium alginate media: Characterization and antibacterial evaluation. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 4941231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.A.; Seckler, M.M.; Ingle, A.P.; Gupta, I.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Silver nanoparticles: Therapeutical uses, toxicity, and safety issues. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Spotin, A.; Akbari, N.A.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Ahmadpour, E. Scolicidal and apoptotic activities of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide-loaded PLGA-PEG as a novel nanopolymeric particle against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4595–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardari, R.R.R.; Zarchi, S.R.; Talebi, A.; Nasri, S.; Imani, S.; Khordamehr, A.; Sheshde, S.A.R. Toxicological effects of silver nanoparticles in rats. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 5587–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhawass, E.A.; Mohallal, M.E.; Soliman, M.F.M. Acute toxicity of different sizes of silver nanoparticles intraperitoneally injected in BALB/c mice using two toxicological methods. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lai, W.; Cui, M.; Liang, L.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. An Evaluation of Blood Compatibility of Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, K.C.; Schechter, P.J. Effects of nanocrystalline silver (NPI 32101) in a rat model of ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2732–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, D.E.; Elsamad, L.M.; Gohar, Y.M. Validity of silver, chitosan, and curcumin nanoparticles as anti-Giardia agents. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; Rha, D.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.D.; Choi, B.S.; Lim, R.; Chang, H.K.; Chung, Y.H.; et al. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, M. Acute toxic effects and gender-related biokinetics of silver nanoparticles following an intravenous injection in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Dan, M.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, J.; Shao, A.; Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, L. Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticle in rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Silveira, C.P.; Durán, M.; Martinez, D.S.T. Silver nanoparticle protein corona and toxicity: A mini-review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-B.; Jones, M.K.; Li, J.; Mcmanus, D.P. Echinococcus granulosus: Pre-culture of protoscoleces in vitro significantly increases development and viability of secondary hydatid cysts in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2005, 110, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia, S.; Moazeni, M.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Alavi, A.M. Hydatid cyst formation in male BALB/c mice following the intraperitoneal injection of live protoscoleces and activated oncospheres: A comparative study. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 38, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Haniloo, A.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Faghihzadeh, S. Efficiency of flubendazole-loaded mPEG-PCL nanoparticles: A promising formulation against the protoscoleces and cysts of Echinococcus granulosus. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminpour, S.; Rafiei, A.; Jelowdar, A.; Kouchak, M. Evaluation of the Protoscolicidal Effects of Albendazole and Albendazole Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Iran J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navvabi, A.; Homaei, A.; Khademvatan, S.; Khadem Ansari, M.H.; Keshavarz, M. Combination of TiO2 nanoparticles and Echinometra mathaeis gonad extracts: In vitro and in vivo scolicidal activity against hydatid cysts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelowdar, A.; Rafiel, A.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Rashidi, I.; Rahdar, M. Efficacy of combined albendazol and praziquntel and their loaded solid lipid nanoparticles components in chemoprophylaxis of experimental hydatidosis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.M.; Moazeni, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Abedi, M.; Tamaddon, A.M. Evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulfoxide (ABZ-SO)-loaded chitosan-PLGA nanoparticles in the treatment of cystic echinococcosis in laboratory mice. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryamand, S.; Khademvatan, S.; Hazrati Tappeh, K.; Heshmatian, B.; Jelodar, A. In Vitro and in Vivo Scolicidal Activities of Holothuria leucospilota Extract and CeO2 Nanoparticles against Hydatid Cyst. Iran J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ismail, E.; Saad, M.; Elsadig, A. Effect of Albendazole and Mebendazole on Hydatid Cyst of Mice. Open J. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, N.; Dobakhti, F.; Faghihzadeh, S.; Haniloo, A. In vitro and in vivo effects of chitosan-praziquantel and chitosan-albendazole nanoparticles on Echinococcus granulosus Metacestodes. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.H.; Richards, K.S.; Morris, D.L. Rapid recovery of Echinococcus granulosus following ‘successful’ albendazole therapy in a gerbil model. J. Helminthol. 1989, 63, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Serrano, J.; Casado, N.; Guillermo Denegri Rodriguez-Caabeiro, F. The effects of albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide combination-therapy on Echinococcus granulosus in vitro. Int. J. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, M.; Larki, S.; Saharkhiz, M.J.; Oryan, A.; Ansary Lari, M.; Mootabi Alavi, A. In vivo study of the efficacy of the aromatic water of Zataria multiflora on hydatid cysts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6003–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, M.; Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, X. In vitro and in vivo treatments of Echinococcus granulosus with Huaier aqueous extract and albendazole liposome. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).