Abstract
The concept of HBIM (Historic/Heritage Building Information Modeling) has attracted growing interest within research communities in recent years, as reflected in an expanding body of literature exploring its potential in data acquisition and modeling, historical evolution documentation, heritage management, and condition analysis. Yet, new challenges arise in extended HBIM capabilities by integration and interoperability with other technologies and environments for comprehensive heritage assessment. In this context, this paper presents a scoping review, based on the PRISMA protocol, of 60 publications from the Scopus database that document research frameworks and applications of IDPs (integrated digital platforms), where HBIM is combined with different systems to enhance data richness, functionality, and analytical evaluation, as well as to exchange, interpret, and use information effectively. The results show three major thematic areas, namely multi-scale analyses based on HBIM and GIS (geographic information systems); multi-source data repositories development; and sensor networks integration with advanced IoT (Internet of Things) systems. The overview outlines how these frameworks foster the development of interoperable, multi-layered, and data-driven ecosystems, advancing HBIM to an operational component in heritage management and enabling predictive diagnostics and real-time monitoring, while current limitations in semantic consistency, automation, and scalability still hinder full implementation.
1. Introduction
Since its initial introduction in 2009 by Murphy et al. [1] as a novel system for modeling historic structures derived from reality-based survey data, incorporating construction and material specifics behind the target surface, the concept of HBIM (Historic/Heritage Building Information Modeling) has garnered increasing attention within research communities. This phenomenon is evidenced by an expanding corpus of literature exploring its potential in a variety of fields, including data acquisition and modeling [2,3,4], historical evolution documentation [5,6], heritage management [7], and condition analysis [8,9,10].
Indeed, taking into account that the decision-making process for the assessment and conservation of architectural heritage relies on a multidisciplinary and multitemporal data foundation, including historical, diagnostic, and analytical information, HBIM offers significant opportunities in terms of data management, longevity, and accessibility, while fostering collaboration among stakeholders from diverse sectors within the industry throughout the long-lasting life cycle of the cultural asset [11].
A number of reviews have been published on HBIM in recent years. It is evident that a proportion of the aforementioned studies are more focused on the survey and digitization phases. These cover general approaches and case studies for data capturing and processing, as well as the modeling of object libraries and metadata handling [12]. Available software tools are also examined, including 3D models, visualizers, and analyzers based on academic and industrial references [13].
Some others provide a comprehensive outlook on the advancements, patterns, and emerging technologies for preserving and maintaining historic buildings. A systematic review of 59 studies from 2013 to 2023 was conducted with the objective of investigating the capacity of HBIM to document, analyze, and manage heritage structures [11]. A further systematic review of 1049 papers from 2010 to 2023 was undertaken to trace the evolution of HBIM from its origins and early applications to its current state and future prospects [14]. A bibliometric analysis of 433 documents published between 2008 and 2023 was conducted with the aim of analyzing the interrelationship between BIM and complementary technologies. The analysis synthesized the main trends of BIM adoption in heritage buildings and characterized the field of knowledge of BIM adoption. An overview of approximately 60 typical articles related to HBIM in combination with other modeling technologies was also conducted, with a focus on the research trends before and during the 2010s [15].
A number of studies have been conducted that offer in-depth analyses of specific aspects of HBIM case studies. These include information types and storage [16], open software tools and setup, parametric modeling, semantic features, data exchange, and cloud accessibility [17]. Other studies have focused on specific application domains, such as archaeology [18] and post-disaster reconstructions [19].
It is evident that a number of these reviews have had a direct bearing on the rationale underpinning this study, as it is built upon their concluding remarks and future outlooks. The necessity to integrate HBIM models and approaches with other working environments in an interoperable digital system is emphasized, with the objective of developing more comprehensive and versatile platforms. The utilization of such platforms has the potential to facilitate the enhancement and augmentation of the capabilities of the HBIM approach, thereby addressing and supplementing its existing limitations. These limitations pertain to the accurate representation of irregular geometries and decorated surfaces, the relationship with the environmental context, the management of experimental and real-time diagnostic data, the mapping of material alterations and pathologies, the organization of archival and bibliographic sources, and the establishment of connections with specialized fields of analysis, including material science and technology, artistic and archaeological studies, and mechanical performance.
For instance, Yang et al. [15] observe that data integration and exchange with reality-based modeling, computer graphics, ontology, and GIS can extend HBIM capabilities. These include enabling precise parametric modeling of complex structures, improving semantic segmentation, facilitating better management and analysis of spatial and semantic data, and aiding in structural assessments for conservation efforts. Nevertheless, they conclude that integration still faces challenges to enhance interoperability and reduce information loss among different platforms.
In a similar vein, Ávila et al. [14] posit that to achieve the full potential of HBIM, advancements in data interoperability, standardized protocols, extension to urban-scale applications, and real-time structural analysis are imperative. Penjor et al. [11] and Puerto et al. [20] advocate for the integration of sensors in heritage structures using the Internet of Things (IoT) as a future research direction. This innovation would enable real-time data collection and transmission to AI-based systems and facilitate the early detection of potential anomalies and the automation of mitigation responses.
In consideration of the interoperability of HBIM with other tools, Penjor et al. [11] propose the development of novel plugins or the enhancement of existing ones to optimize the effectiveness of HBIM processes, encompassing error detection, validation, and data processing. Lovell et al. [16] assert that the proprietary nature of BIM software hinders interoperability and data loss, and they propose a visual programming language (VPL) as a solution. Diara et al. [17] emphasize open-source software and codes as a means to achieve full HBIM flexibility and adaptation.
In addition to these premises, the present review was conceived with the objective of investigating the state of the art on HBIM-related IDPs (integrated digital platforms). In this context, issues of interoperability and integration between HBIM models and other environments, technologies, and tools are addressed and, where possible, resolved, with a view to supporting the knowledge, management, and assessment of architectural heritage. The investigation focuses on digital solutions that integrate HBIM with various systems to enhance data richness, functionality, and analytical evaluation. The objective is to facilitate effective exchange, interpretation, and utilization of information without compromising its semantics or necessitating extensive revisions.
To this end, based on the research methodological framework—which includes the formulation of research questions and the process of selecting and analyzing relevant contributions (Section 2)—an overview of thematic areas, fields of application, and technologies employed is provided (Section 3), leading to final considerations on research gaps and future perspectives (Section 4).
2. Materials and Methods
The present review was deliberately structured as a scoping review rather than a systematic review [21], in line with its exploratory aims and the heterogeneity of the literature on HBIM-related integrated digital platforms (IDPs). Scoping reviews are designed to map the extent and characteristics of existing research, offering an overview of study volume and focus while identifying knowledge gaps and clarifying key concepts—without assessing study quality or conducting quantitative synthesis.
Conversely, systematic reviews methodically address specific inquiries through critical appraisal and frequently incorporate meta-analysis to inform evidence-based practice or policy. The methodology employed is consistent with the principles of scoping reviews, prioritizing thematic exploration and comprehensive coverage over evaluative synthesis.
Accordingly, the scope of this review was initially defined through the formulation of broad research questions (RQs), serving as a preliminary step toward the identification, selection, organization, synthesis, and discussion of the literature:
RQ1: What are the main thematic areas in which HBIM-related IDPs are developed?
RQ2: What are the main application fields and purposes in which HBIM-related IDPs are applied?
RQ3: What are the frameworks/tools/technologies enabling HBIM-related IDPs?
Consequently, the review was conducted in accordance with the widely recognized methodology outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [22]. The subsequent subsections provide a more detailed exposition of the process steps (Figure 1).
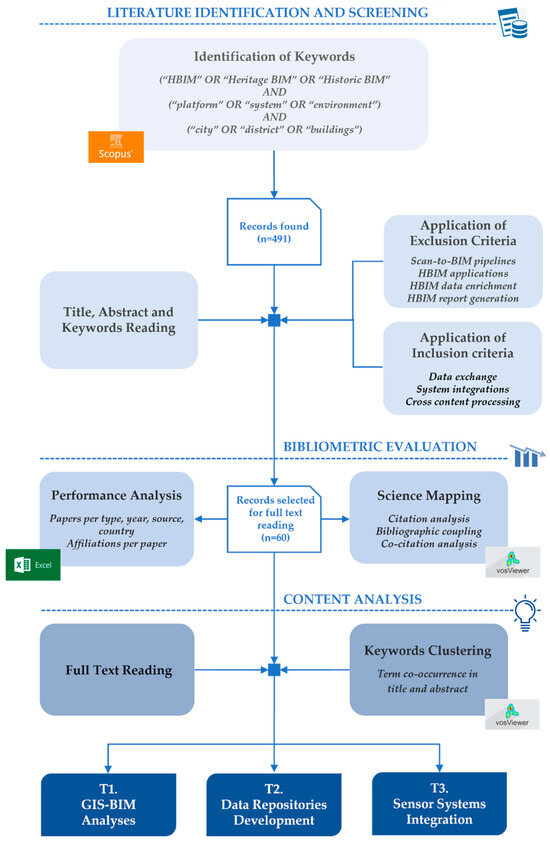
Figure 1.
Review methodology.
2.1. Literature Identification and Screening
The initial phase of the review involved conducting a literature search using the Scopus database, which was last accessed in December 2024. The decision to employ a unified database was made with the objective of enhancing the replicability of the study. This approach was adopted by the majority of the aforementioned reviews [14,15,16,19,20]. Scopus is renowned for its comprehensive coverage of scientific journals and its sophisticated indexing system, which facilitates access to recent publications [23].
These qualities have led to its frequent use as the sole source not only in some of the above-mentioned reviews [16,19,20] but also more broadly in recent reviews addressing the state of digital and emerging technologies in the AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) sector [23,24,25,26]. The search strategy employed Boolean operators to combine three sets of keywords related to (i) technology (“HBIM” OR “Heritage BIM” OR “Historic BIM”); (ii) target (“platform” OR “system” OR “environment”); and (iii) context (“city” OR “district” OR “buildings”).
The temporal limitation of the search to the last decade was necessitated by the rapid advancements in this field. The corpus included journal articles, conference proceedings, reviews, and book chapters written in English and with open access. No restrictions were applied regarding research fields, countries, or sources, acknowledging the inherently multidisciplinary nature of the topic and ensuring the broadest possible inclusion of studies. The search yielded a total of 438 papers. The subsequent phase of the review entailed the screening of abstracts and keywords with the objective of identifying relevant literature. During this stage, papers were excluded if they lacked any demonstrated or anticipated integration/interoperability between HBIM and external tools. In particular, studies were omitted when they described workflows or demonstrations in which data were processed solely upstream or downstream of HBIM (serving only input/output purposes), or when HBIM applications were restricted to narrow, discipline-specific tasks without interfacing with other systems. More specifically, the following topics were excluded:
- Modeling methodologies based on semi-automatic or automatic processes from photogrammetric or laser scanning data (e.g., SCAN-to-BIM), or based on generative geometry techniques, when these were not embedded within integrated workflows that connect HBIM to other data or systems;
- Ontologies, libraries, and HBIM-specific procedures (e.g., CIDOC CRM, IfcOWL, HiCO, ArCo, CityGML) that were addressed exclusively from a theoretical standpoint, without adequate evidence of implementation strategies, validation efforts, or contextualization within operative workflows or heritage-related use cases;
- Integration of documentary, experimental, and analytical data (e.g., FEM analyses or energy simulation tools within HBIM), when lacking methodological clarity regarding data alignment, workflow integration, or the interoperability between platforms;
- Visualization or reporting implementations (e.g., 3D models, digital dashboards) when these were not part of a broader interoperable framework or did not support collaborative or analytical functionalities beyond mere representation.
Conversely, the inclusion criteria comprised proofs of concept, frameworks, testbeds, and case studies that substantiate HBIM integration with external software environments, specifically demonstrating the following:
- Data exchange (e.g., standardized communication protocols such as IFC, XML, JSON), facilitating interoperability and synchronized data transfer across heterogeneous platforms within validated workflows;
- System integration (e.g., end-to-end workflows or collaborative interfaces linking databases, analytical tools, and visualization platforms), enabling interconnected software environments without modifying core software logic, thereby supporting multidisciplinary coordination and centralized heritage data management;
- Cross-content processing (e.g., computational methods such as semantic enrichment, machine learning, or automated transformation scripts), implementing data analysis and transformation across HBIM and allied systems to improve analytical precision, operational efficiency, or workflow automation in heritage-related contexts.
At the end of the second phase, 60 papers were selected for full-text reading and analysis.
2.2. Bibliometric Evaluation
As articulated in [27], bibliometric evaluation encompasses both performance analysis and science mapping. Performance analysis is concerned with the evaluation of contributions made by research entities, including authors, countries, and journals, within a given field of study. The study provides insights into the distribution of research output and the impact of contributions. Conversely, science mapping is a method of examining the intellectual relationships between research entities. It explores connections such as citations, co-citations, bibliographic coupling, co-words, and co-authorships. This approach facilitates the identification of interconnections between publications, thereby highlighting potential clusters that emphasize the interconnectedness across diverse subject areas, technologies, and applications.
The performance analysis in this review was based on the classification of papers according to the following criteria: type (Figure 2), source (Figure 3), year (Figure 4), country (Figure 5), countries contributing to a single paper (Figure 6), number of institutions/departments contributing to a single paper (Figure 7), and number of papers involving authors from non-academic fields, such as enterprises and public bodies. The classification by country and number of institutions/departments considered all co-author affiliations.
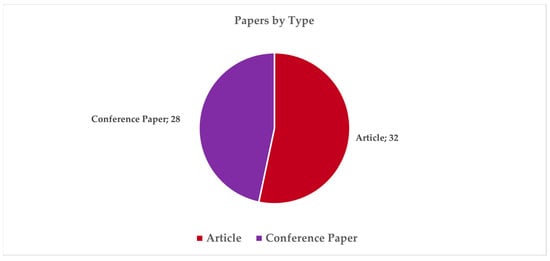
Figure 2.
Distribution of papers by type.
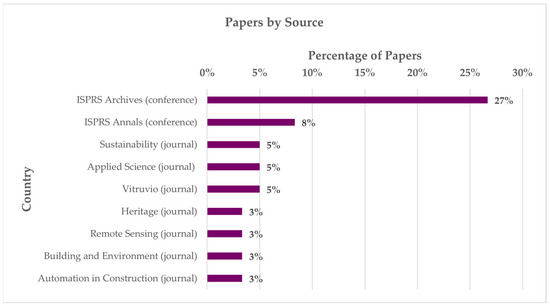
Figure 3.
Distribution of papers by source (only sources with at least 2 papers—3% of the total).
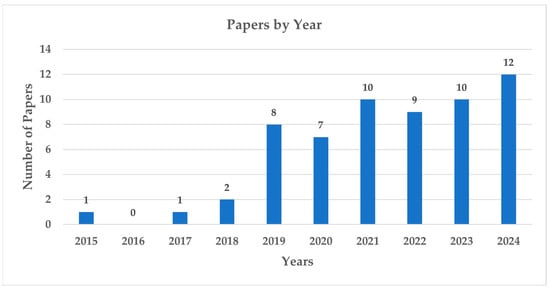
Figure 4.
Distribution of papers by year.
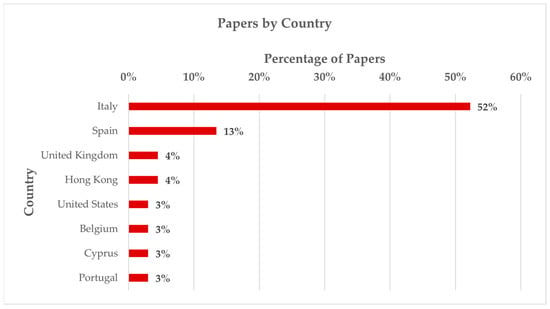
Figure 5.
Distribution of papers by country (only countries with more than 2% of papers are included)—countries not displayed: Morocco, China, Macau, Japan, Australia, Polonia, Georgia, Egypt, Taiwan.
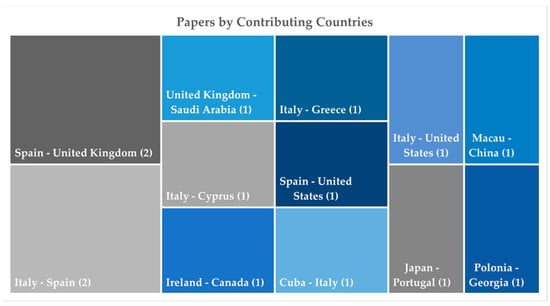
Figure 6.
Papers by contributing countries.
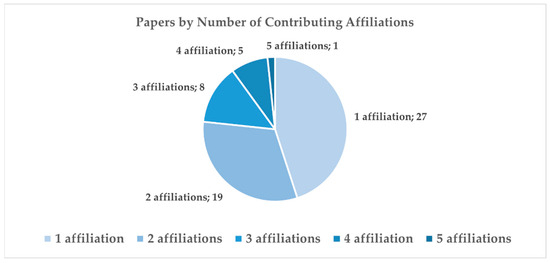
Figure 7.
Distribution of selected papers for full reading by number of affiliations (university departments, enterprises, research institutes, public bodies).
The overall results from the performance analysis reveal a balanced distribution between journal articles and conference papers (Figure 2), the latter mainly within ISPRS congresses, with a few papers from IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Building Simulation Conference Proceedings, Energy Procedia, Procedia Structural Integrity. This is representative of studies with different levels of maturity, and it indicates, combined with the trend of increasing scientific production over the past decade (Figure 4), that the topic is of recent development and rapidly rising.
The majority of articles can be found in the ISPRS Archives and Annals, which are dedicated to the technical and procedural aspects of surveying, modeling, and the application of digital and informational tools. This is in contrast to other journals that are more focused on built and cultural heritage (CH), such as Heritage and Vitruvio (Figure 3). Italy maintains a dominant position in scientific production, followed by Spain and the United Kingdom and Hong Kong (Figure 5), confirming a strong and sustained commitment to digital technologies and architectural heritage in Europe, where the significant presence of historic and monumental buildings has traditionally made research into innovative methods and approaches to knowledge and conservation a central focus.
Nevertheless, the research demonstrates a solid profile of international collaboration, with about 25% of papers involving institutions from at least two countries (Figure 6), and it shows a strong interdisciplinary collaboration, with 34 papers including researchers from different affiliations (Figure 7). Furthermore, the complexity and technological transfer potential of the research are underscored by a notable presence, approximately 15%, of papers (nine out of 60) including authors from outside the academic domain (Garibaldi Fragasso srl, Italy; B.Re.D srl, Italy; Office of Public Works, Ireland; Ove Arup and Partners, Hong Kong; Iperboole srl, Italy; GEOLAMBERT Company, Morocco; Grupo Empresarial GEOCUBA, Cuba; AESEI srl, Italy; FULL, the Future Urban Legacy Lab, Italy).
The analysis was supported by VOSViewer 1.6.20 for the science mapping. Initially, the citation analysis of the documents (Figure 8) was conducted. This emphasizes the significance of the authors, and consequently the research groups and institutions, whose studies on the topic have the most substantial impact in terms of scientific dissemination within the dataset. The analysis also considers the correlation between the number of citations and the year of publication.
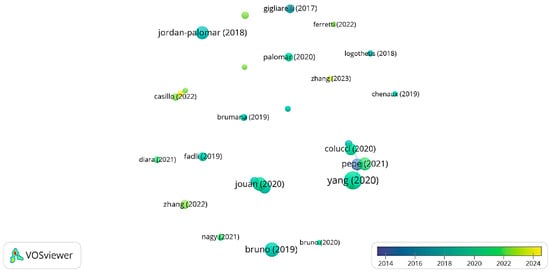
Figure 8.
Citation analysis of documents (minimum 15 citations, 23 items)—elaboration by VOSViewer 1.6.20.
Moreover, the bibliographic coupling (Figure 9), which measures the similarity between two documents based on the number of shared references, and the co-citation analysis of documents (Figure 10), which examines how frequently two documents are cited together by other references, were assessed. They help reveal how research areas develop, aggregate, and consolidate over time through networks of indirect collaboration, and which of the landmark papers are for the research field.
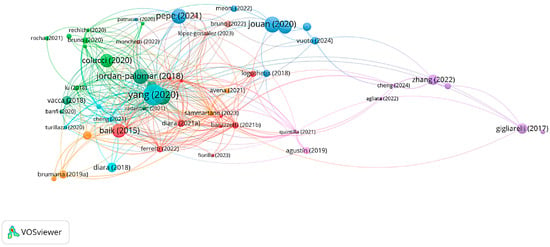
Figure 9.
Bibliographic coupling of documents (minimum 3 cited documents, 60 items)—elaboration by VOSViewer 1.6.20.
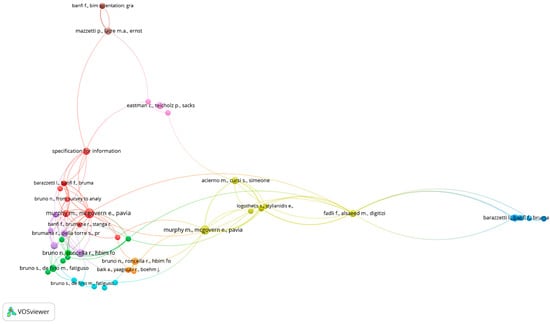
Figure 10.
Co-citation analysis of documents (minimum 2 cited documents, 54 items)—elaboration by VOSViewer 1.6.20.
Finally, the science mapping included the analysis of word co-occurrence in titles and abstracts (Figure 11) in order to identify thematic clusters from conceptual aggregation of terms. This proved to be a particularly useful resource in terms of providing a framework for the subsequent presentation and discussion.
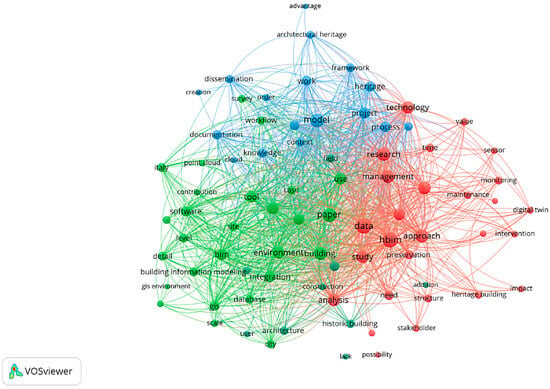
Figure 11.
Term co-occurrence in titles and abstracts (minimum 6 occurrences, 84 terms)—elaboration by VOSViewer 1.6.20.
The results of the science mapping show the presence of numerous researchers and research groups actively working on the topic and recognized by the scientific community. In particular, the citation analysis (Figure 8) highlights 23 authors whose works selected for this review have been cited at least 15 times. Among these, the following stand out with over 70 citations: Yang, X. (University of Connecticut, Storrs, United States); Bruno, N. (University of Parma, Italy); Jouan, P. (University of Liege, France); Pepe, M. (University of G. d’Annunzio Chieti and Pescara, Italy); Jordan-Palomar, I. (Polytechnic University of Valencia, Spain); Baik, A. (King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia); and Colucci, E. (Polytechnic University of Turin, Italy), with specializations mainly in remote sensing, cartography, surveying, Building Information Modeling, and architectural engineering.
A substantial aggregation of authors and their respective works on the subject can be ascertained through bibliographic coupling (see Figure 9) and co-citation analysis (cf. Figure 10) with regard to referenced literature and joint citations by scholars. This finding serves to substantiate the notion of a meticulously delineated, unified, and cooperative research domain, wherein the preponderance of contributions finds itself in close alignment with the prevailing themes, and a discernible compendium of foundational works exists to orient the research trajectory. The observation that peripheral contributions are limited could be indicative of the exploration of subjects that lie outside the primary themes of the field. However, this could also be indicative of reduced diversification or a paucity of alternative approaches within the field.
Finally, the term analysis was conducted to identify significant and recurring themes within the titles and abstracts of the collected literature (Figure 11). In detail, 84 terms with a minimum of six occurrences were examined, leading to the identification of three clusters.
The first cluster (green), including specific words such as “integration, gis, gis environment, database, scale, level, city, and construction”, refers to the connection of information systems across different dimensions, from the territorial to the building domain, for applications involving both the urban and architectural context.
The second cluster (red), including specific words such as “sensor, monitoring, maintenance, structure, time, and analysis”, refers to the use of measurement devices for detecting and observing building-related parameters over a period, aiming at performance assessment and control.
The third cluster (blue), including specific words such as “documentation, dissemination, knowledge, model, framework, and process”, concerns the combination of methods and records for managing information through data collection, organization, and sharing.
3. Results and Discussion
This section is structured to provide an overview of the content analysis of the selected 60 articles, discussing them in close correlation with the research questions RQ1, RQ2, and RQ3 outlined in Section 2.
3.1. RQ1: What Are the Main Thematic Areas in Which HBIM-Related IDPs Are Developed?
A thorough examination of the articles, in conjunction with the clustering methodology proposed by the co-occurrence analysis of terms (see Figure 11), has led to the identification of three primary thematic domains within the realm of HBIM-related IDPs. The initial theme (T1) pertains to multi-scale analyses facilitated by HBIM and GIS, encompassing 24 papers that concentrate on the integration of spatial data across various scales. The second theme (T2) pertains to the development of multi-source data repositories, as evidenced by 27 papers that underscore the structuring, management, and interconnection of heterogeneous data sources. The third theme (T3) addresses the integration and management of sensor systems, with 14 papers exploring the use of real-time data and monitoring technologies within HBIM workflows.
It is important to highlight that some papers can be attributed to more than one thematic area. Furthermore, in seven papers, the development of XR (extended reality) models based on HBIM is addressed either complementarily or predominantly. This aspect is not included as an independent thematic area, particularly because there are no interoperability features between the model and its XR implementation. However, in instances where such a reference is not explicitly made in the discourse pertaining to questions Q2 and Q3, these papers provide support to the discussion of limitations and potential future developments, offering distinct and relevant insights with respect to the objective of this review.
3.1.1. RQ1 in T1: Multi-Scale Analyses Through HBIM-GIS Integration
In greater detail, of the three thematic areas, HBIM-GIS integration (T1) has emerged as a key methodological framework within the digital humanities and built heritage domains. This fusion supports a range of IDPs that address the increasingly complex needs of conservation, risk assessment, and urban heritage management across multiple spatial scales. These systems have evolved beyond their original function as mere documentation tools to become operational instruments that encompass a wide range of applications, from territorial planning to architectural interventions at the level of design. They provide a robust, interoperable infrastructure for the management of historical environments.
As shown in Table 1, a growing body of literature demonstrates that HBIM-related IDPs have found application in several intersecting domains. Conservation and restoration remain foundational, where HBIM provides detailed semantic models that support documentation, diagnostic interpretation, and long-term planning. These models are often enriched with material properties, historical stratification, and condition assessments, while GIS contributes the environmental, cadastral, and infrastructural context necessary for interpreting heritage assets within their broader urban or territorial settings. In this sense, integration facilitates the shift from isolated architectural studies to holistic heritage management strategies.

Table 1.
Overview of key contributions to T1: multi-scale analyses through HBIM-GIS integration.
Risk assessment represents another major domain of application, particularly in relation to seismic, hydrogeological, and fire hazards. In these contexts, GIS-based terrain and environmental data are coupled with HBIM-derived architectural vulnerability models, allowing for predictive simulations and risk mapping that inform conservation priorities and emergency preparedness. The integration is especially effective in post-disaster contexts, where UAV-derived photogrammetry and point clouds are processed into HBIM environments that are georeferenced and semantically annotated, allowing for damage assessment and simulation of intervention scenarios.
Structural monitoring and analysis also benefit from T1 convergence, where the geometric precision of HBIM supports computational methods such as Thrust Network Analysis (TNA) or macro-element modeling. When connected to GIS datasets—such as seismic zones, excavation layers, or terrain models—these simulations can inform decisions about structural stability, retrofitting, and long-term maintenance planning, particularly in archaeological and post-seismic scenarios.
Urban heritage planning represents an additional field in which GIS-HBIM frameworks are increasingly deployed. Here, the ability to integrate multi-scale data—ranging from LoD0 topography to LoD5 construction detail—enables municipalities and researchers to evaluate heritage assets in relation to accessibility, environmental risks, and urban morphology. This spatial intelligence informs urban development strategies that are compatible with conservation goals, fostering more sustainable and context-aware planning practices.
Recent advancements have also highlighted the importance of semantic and temporal modeling within HBIM-related IDPs. Initiatives that incorporate CIDOC-CRM ontologies, semantic graphs, and stratigraphic data are reshaping the manner in which historical transformations are recorded and queried. The integration of metadata pertaining to material alterations, ownership transitions, and construction phases within these models facilitates diachronic analysis, thereby enabling researchers to trace the evolution of buildings and sites over time.
Furthermore, immersive and participatory visualization has emerged as a growing application domain. Projects integrating T1 with AR/VR platforms, as well as AI-based behavioral tracking, are expanding the scope of heritage engagement to include educational and touristic experiences. These platforms facilitate interactive exploration of heritage environments whilst concurrently collecting data on visitor behavior. This, in turn, can inform both spatial planning and conservation strategies. Across all these thematic areas, the convergence of GIS and HBIM is increasingly supported by integrated platforms and tools such as CHIMERA, Virtual Historic Dublin, and the Altinum open-source system. These environments illustrate how structured workflows, multi-scale hierarchies, and semantic enrichment can facilitate layered analyses that respect both territorial overviews and detailed architectural complexity.
3.1.2. RQ1 in T2: Development of Multi-Source Data Repositories in HBIM
In relation to the development of multi-source data repositories (T2), this theme is concerned with the analysis and definition of integrative digital environments that are capable of aggregating, storing, and managing information of diverse types (spatial, geometric, semantic, historical, and contextual) within a single system. In contradistinction to a rudimentary database, such a repository proffers an interactive, frequently bespoke interface that facilitates the interrogation and analysis of said data. These platforms thus become a digital container for heterogeneous outputs, historical and archival records, diagnostic reports, three-dimensional models, and point-cloud datasets, enabling the management and analysis of time-displaced documents and guaranteeing a systematic, organized approach.
The adoption of open and interoperable methodologies is pivotal in ensuring enhanced accessibility and data sharing, thereby supporting specialists and researchers and contributing to the establishment of a digital ecosystem for the integrated management of cultural heritage (CH). A critical attribute of these platforms is their capacity to function within a collaborative, web-accessible environment that transcends the constraints imposed by software installed locally on users’ devices. Consequently, data sharing and querying occur in a centralized context, thereby simplifying collaborative workflows and promoting greater efficiency in information management.
Recent studies have confirmed an increasing specialization of HBIM platforms geared towards cultural heritage management, encompassing both commercial and ad hoc solutions. These solutions are often developed through open-source technologies and structured in accordance with internationally recognized classification standards.
In Table 2, the scalar relationship between application domains, frameworks/tools/technologies, and reference authors clearly demonstrates that scientific interest is common to multiple areas, each addressed through different methodologies and instruments in varying contexts and scenarios. The subsequent section provides a detailed analysis of purpose-built research products, commercial solutions, and hybrid experiments, the combined use of ad hoc and commercial tools.

Table 2.
Overview of key contributions to T2 development: development of multi-source data repositories in HBIM.
3.1.3. RQ1 in T3: Integration and Management of Sensor Systems Within HBIM
In conclusion, the integration and management of sensor systems within HBIM-based IDPs (T3) has emerged as a highly effective strategy for the intelligent and sustainable management of CH. A comparative analysis of the selected 14 studies demonstrates how this technological synergy facilitates continuous, real-time monitoring of a wide range of environmental and structural parameters, enhancing the precision of conservation interventions and optimizing the overall preservation and upkeep of historic buildings.
The integration of in situ sensor data into HBIM models enables continuous monitoring and preventive maintenance of environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels, while simultaneously enabling the simulation of structural responses to various conditions. In addition, the use of cloud-based IDPs plays a crucial role in streamlining management processes by enabling interoperability among information models, sensor networks, and analytical tools. These platforms not only optimize climate control, structural stability assessments, and energy efficiency but also enable dynamic management of visitor flows, ensuring both the preservation and accessibility of CH sites.
Table 3 provides a detailed overview of the fields of application, frameworks, tools, and technologies analyzed in the selected studies, offering a comprehensive and comparative summary of the cutting-edge solutions driving the integration of HBIM and IoT systems within CH management.

Table 3.
Overview of key contributions of T3: integration and management of sensor systems within HBIM.
3.2. RQ2: What Are the Main Application Fields and Purposes in Which HBIM-Related IDPs Are Applied?
3.2.1. RQ2 in T1
With reference to T1, HBIM-GIS integration has evolved into a cornerstone methodology for managing built heritage across scales. As previously mentioned, these frameworks are being increasingly deployed in domains such as hazard modeling, architectural documentation, structural diagnostics, environmental risk assessment, and immersive digital engagement. The overarching objective is to enable multi-layered, data-driven decision-making in both preventive conservation and urban heritage planning.
In culturally significant settings, Baik et al. [42] offer a notable example through the Jeddah Historical BIM project, which integrates detailed digital models of the Nasif Historical House with geospatial urban datasets. Their introduction of the Hijazi Architectural Objects Library (HAOL), a parametric catalog tailored to Islamic architectural elements, demonstrates how culturally embedded design components can enhance both documentation and restoration planning. Barazzetti et al. [31] build upon this paradigm by focusing on multi-scale georeferencing and diagnostic data fusion in the fortified architecture of Sondrio.
Using UAV photogrammetry, GNSS, and thermographic imaging, they develop an integrated digital environment that supports semantic queries, condition mapping, and interactive visualization. This approach facilitates dynamic conservation workflows, with a strong emphasis on temporal monitoring. Bruno et al. [76] offer a more systematic response to challenges in semantic consistency and data exchange through the CHIMERA platform—a multi-temporal web-based system that structures data across five spatial levels, from territorial to architectural. Although effective in 4D analysis and stakeholder engagement, the platform still relies on external tools for modeling and suffers from data loss in BIM-to-GIS conversion.
As reported in Table 1, numerous studies have expanded these methodologies to encompass environmental and seismic risks. Agliata et al. [59] are an exemplary case study in this regard, as they have employed a spatially segmented modeling strategy in the Cervinara districts to calculate susceptibility indices for floods and landslides. The methodology employed integrates elevation models derived from UAV surveys with digital building models that are enriched with structural and environmental indicators. This enables the execution of risk assessments that are nuanced and grounded in physical and contextual parameters. Avena et al. [29] expand upon this line of inquiry in post-seismic Norcia, utilizing UAV and TLS-derived HBIM models enhanced with semantic damage classification. In a similar vein, Colucci et al. [30] have employed a T1 framework in the context of the San Lorenzo Church, addressing challenges pertaining to Level of Detail (LoD) conversion and semantic consistency across software platforms.
In a technically refined application, D’Urso et al. [36] integrate building modeling with geospatial analysis and Thrust Network Analysis to evaluate the structural integrity of historical monuments in Aquinum. The framework utilized by the aforementioned researchers integrates digital reconstructions with excavation data and seismic overlays, thereby facilitating proactive conservation measures. However, it should be noted that the framework is not equipped with real-time diagnostic feedback capabilities. At a broader scale, Sammartano et al. [28] propose macro-element modeling as a technique for component-level seismic risk analysis. Their case study on the Sant’Andrea Church in Campi di Norcia demonstrates how UAV and laser-scanned data can be combined within a semantic model to inform vulnerability indices and intervention priorities.
Addressing the issue of fire risk, Qiao et al. [77] developed an automated digital system that combines fire resistance metadata with spatial accessibility layers. The model has been applied to the Mandarin’s House in Macau, where it has been used to simulate fire propagation using proximity and flammability metrics. This has enabled evidence-based mitigation planning. Colucci et al. [32] make a significant contribution to urban-scale preventive planning through the implementation of a web-based GIS-HBIM platform for the Sacri Monti. The integration of TLS, UAV, and mobile mapping across LoD0–LoD5 facilitates multi-stakeholder maintenance scheduling. Nevertheless, the acquisition of real-time data and the automation of processes involving semantics continue to represent significant challenges.
In the domain of archaeological heritage, Delpozzo et al. [35] propose an open-source environment for the site of Altinum, integrating stratigraphic interpretation and reconstruction hypotheses within a georeferenced 3D modeling framework. The “as-reconstructed BIM” concept facilitates the incorporation of uncertainty and interpretive layers; however, manual conversion processes continue to impede scalability.
Recent advancements underscore the mounting significance of digital twins in the realm of heritage conservation. Rechichi [33] and Radanovic et al. [34] conceptualize these as dynamic, data-enriched systems that extend HBIM functionality through integration with IoT sensors and GIS layers. These twins move beyond static documentation by enabling real-time monitoring and predictive conservation. The Precacore project [37] is a case in point, in that it has embedded HBIM and GIS within a Cesium-based platform, augmented by AR/VR technologies such as Unity 3D and Microsoft Hololens for educational and touristic use. In a similar manner, CHIMERA incorporates environmental sensor streams into HBIM models, thereby supporting predictive maintenance protocols. Adding behavioral dimensions, García-Valldecabres et al. [38] integrate AI-based visitor flow tracking with HBIM-GIS systems to enhance both conservation oversight and tourism management. Temporal modeling is further refined by Galeazzo et al. [45], who propose a diachronic semantic system for the Venetian Lagoon. The application of CIDOC-CRM ontologies and Blazegraph for the integration of stratigraphic and archival data into HBIM models facilitates historical reasoning over time. However, the process of exporting these enriched models into lightweight formats, such as 3D Tiles, has been shown to result in metadata loss. This finding underscores the persistent challenge between conceptual richness and technical interoperability.
3.2.2. RQ2 in T2
With regard to T2, the analysis of the contributions related to data repositories highlights a strong multidisciplinary orientation and a convergence towards the use of digital tools and innovative methodologies for the management and valorization of the architectural and cultural heritage, in different application fields and with different aims, as demonstrated in Table 2.
The critical analysis of the scientific contributions collated has facilitated the identification and execution of an in-depth examination of the contents of each contribution. This examination has resulted in the emergence of recurring thematic fields and application purposes, reflecting heterogeneous yet convergent approaches, tools, and objectives. This process resulted in the delineation of four primary domains of application, which function as a unifying interpretative framework for the entire corpus analyzed.
The fields identified are the following: (i) recording and collation of technical, historical, and archival investigations; (ii) informative management and semantic enhancement; (iii) monitoring, management, and support for decisions; and (iv) digital visualization and dissemination. They not only represent the prevailing aims of the contributions but also highlight the different phases of the architectural and CH life cycle. Each field is associated with specific technological configurations: platforms developed ad hoc for specific needs, established commercial environments for operational applications, and hybrid configurations experimenting with advanced interoperability.
Among the main application fields that have emerged, one of the most relevant is undoubtedly that of the recording and collation of technical, historical, and archival investigations. These approaches are oriented towards the preservation of material and immaterial memory, as demonstrated by the work of Agustín et al. [46] and Quintilla et al. [78], who develop an HBIM inventory for the Aragonese heritage, and Fadli et al. [47], who proposes the Q-HBIM platform for the classification of traditional architecture in Qatar. In this direction are also the contributions of Brumana et al. [48], who develop a European semantic hub for the documentation of historical vaults, and Russo et al. [50], who propose an integrated methodology for the modeling, historical, and structural analysis of Silberkuhl thin-shell structures.
A further area of application concerns informative management and semantic enhancement, which is considered strategic in the construction of interoperable and updatable information environments. The contributions by Diara et al. [51] and Diara et al. [52] trace a design evolution culminating in the open-source ARK-BIM platform, specifically designed for the archaeological context, capable of integrating semantic data and supporting sharing in cloud environments [53]. In parallel, Palomar et al. [54] developed BIMlegacy, a collaborative platform for data synchronization in HBIM models, while Radanovic et al. [34] proposed a multilevel platform that combines geometric accuracy and semantic richness, including advanced functionalities.
T1 in the context of semantic enrichment is further explored by Barazzetti et al. [31] and Baik et al. [42], who develop platforms capable of handling multi-scale and multi-source data for CH sites. Logothetis et al. [55] present a cloud-based open-source BIM system for managing large BIM datasets, promoting collaboration and data accessibility across platforms for heritage and construction projects. In their contributions, Brumana et al. [48,49] and Turillazzi et al. [56] pioneered the definition of research products based on heritage-related ontologies, with the objective of facilitating urban regeneration. Their work laid the foundation for the integration of CH data, the facilitation of participatory planning, and the promotion of informed decision-making. Building on these foundations, Cheng et al. [57] introduced an ontology framework for timber architecture, with the aim of promoting structured knowledge management. In a similar vein, Brumana et al. [58] proposed an HBIM classification to ensure data quality and traceability.
Numerous contributions also focus on predictive maintenance and preventive management, recognizing the importance of monitoring, management, and support for decisions. Agliata et al. [59] propose a method for assessing the hydro-meteorological vulnerability of the built environment; Nagy et al. [60] integrate HBIM with IoT sensors for real-time energy monitoring; Hernández Peña et al. [61] develop a GIS-HBIM model for pathological diagnosis and conservation support. In this context, Meseguer et al. [44] explore the concept of digital twin as a tool for interdisciplinary coordination and decision support. Rechichi et al. [33] explore the spatial management of CH, while Picone et al. [62] adopt a universal design approach for the accessibility of the archaeological site of Pompeii.
Furthermore, increasing attention is being paid to the use and enhancement of heritage through immersive technologies. Banfi et al. [63] integrate HBIM and virtual reality for the management of sites exposed to hydraulic risks; Harmouche et al. [64] propose an XR platform with Beacons for the valorization of Islamic heritage in museums. Rocha et al. [65] promote the use of online HBIM platforms to expand access to CH, while Barrile et al. [37] implement an integrated system based on GIS, HBIM, and mixed reality for the management and dissemination of ancient villages.
The four identified domains reflect the increasing articulation of HBIM platforms, which are oriented to support different purposes and levels of insight. The domain referring to information management and semantic enrichment is the one with the largest number of associated authors, highlighting the growing interest in the semantic enhancement of the HBIM model in the conservation and management of CH. This is followed by domain 1 dedicated to the collection and storage of historical and technical survey data and domain 3 referring to the use of the repository for decision support, demonstrating a more technical–operational use of HBIM platforms. Domain 4, which pertains to digital visualization and dissemination, exhibits a comparatively modest yet discernible concentration of contributions, frequently concentrating on sophisticated communication and interaction experiences.
3.2.3. RQ2 in T3
Finally, with regard to T3 on sensor systems integration and management, Table 3 demonstrates four key areas in which these technologies are making a significant impact: structural diagnostics, preventive conservation, air quality management and energy efficiency, and, finally, heritage enhancement and accessibility. The fields in question demonstrate the manner in which the amalgamation of real-time data with advanced simulations is effecting a transformation in the manner in which we manage and care for historic buildings. This development renders quotidian operations more efficient, whilst concomitantly enabling more intelligent and sustainable interventions. In this sense, digital innovation plays a pivotal role in the safeguarding and enhancement of CH, thereby paving the way for a more thoughtful and forward-looking approach to its preservation.
The field of structural diagnostics represents a strategic area in which digital platforms and sensors play a critical role. In order to assess the structural behavior of a historic residential building based on the thermal contribution of heating systems, it is possible to integrate HBIM models into computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. It is evident that through the continuous monitoring of internal environmental parameters, the position and power of heating devices can be optimized. This, in turn, can lead to a significant reduction in structural deformations. Consequently, this contributes to the preventive conservation of the asset [70].
The integration of vibration sensors, extensometers, and crack sensors [71], as well as strain gauges and crack monitoring devices [69], into HBIM models enables real-time monitoring of the mechanical behavior of structures under both static and dynamic conditions. This approach facilitates the development of digital twin models oriented towards predictive conservation, supporting maintenance strategies based on objective data.
Information gathered from sensors allows for the early detection of critical issues related to external stresses, structural deformations, or seismic events, promoting timely and targeted interventions for the consolidation and protection of historic structures. In this direction, the use of operational modal analysis (OMA) and accelerometric processing techniques has demonstrated the effectiveness of continuous monitoring for assessing structural conditions and verifying the absence of damage following interventions or induced vibrations [67].
The theme of preventive conservation builds upon diagnostic applications, opening new avenues for the monitoring and maintenance of built heritage. IDPs are employed to automate risk detection, monitor the effectiveness of interventions, and support sustainable conservation strategies. In this context, semantically enriched HBIM models, integrated with real-time IoT data, enable predictive management that considers not only structural performance but also the cultural and identity-related attributes of the asset. Interoperable semantic structures allow the association of material elements with degradation processes, making this information accessible even to non-specialist stakeholders [74,75].
Addressing the potential conflict between the conservation requirements of a building and the risks associated with its public use, IDPs have facilitated the development of integrated approaches to enhance the efficiency of maintenance and conservation processes for historic structures. Through environmental monitoring and simulations based on real-time data, it becomes possible to define strategies that safeguard heritage assets without compromising their accessibility [72]. IDPs also prove effective in the design of adaptive ventilation systems for subterranean sites, using digital twin approaches. By leveraging real-time data from an in situ sensor network alongside CFD simulations conducted on an HBIM model tailored to the complexity of underground environments, efficient ventilation systems can be developed to reduce relative humidity levels in these sensitive spaces [73].
Another key area of application concerns energy management and optimization, where IDPs are used to enhance indoor air quality in historic buildings, supporting the design and control of adaptive HVAC systems. The integration of data from on-site IoT sensors with HBIM models enables significant improvements in indoor comfort while simultaneously reducing energy consumption [68]. Additionally, the inclusion of natural light sensors allows for the maximization of solar energy use, decreasing reliance on artificial lighting and helping preserve the architectural and visual integrity of heritage buildings [69].
In this context, various methodological approaches have been proposed—spanning from data acquisition to implementation and interpretation within IDPs—that demonstrate how the combination of HBIM and smart sensor systems can facilitate more effective heritage management. The development of IDPs capable of managing and visualizing heterogeneous real-time data from environmental and motion sensors plays a central role in this process [60]. Parameters such as climate, lighting, insulation, and retrofitting strategies [58] are emerging as key factors for improving energy efficiency and contributing to the long-term sustainability of the built heritage.
The adoption of cloud-based solutions further supports continuous monitoring and remote control of environmental parameters. Within this domain, studies have highlighted how microclimatic conditions—such as temperature, humidity, and air quality—not only affect thermal–hygrometric comfort but also have a direct impact on the long-term conservation of historic structures [66,67].
The enhancement of built heritage and the management of accessibility flows represent another significant area of application for IDPs. These platforms can support the design of sustainable visitor routes by leveraging data gathered from optical sensors capable of monitoring visitor movements and optimizing their operational management. Such an approach provides local authorities with an integrated perspective of heritage assets—ranging from individual buildings to broader urban spaces—thus promoting innovative practices for more efficient and intelligent heritage protection [38].
3.3. RQ3: What Are the Frameworks/Tools/Technologies Enabling HBIM-Related IDPs?
3.3.1. RQ3 in T1
From a theoretical standpoint, T1 is anchored in key principles such as semantic interoperability, spatial hierarchy, and multi-scale data structuring within IDPs. These principles are operationalized through the alignment of Levels of Detail (LoDs) in GIS with Levels of Development (LODs) in BIM, allowing for scalable modeling strategies that span from territorial representations (e.g., LoD0 city terrain) to detailed architectural components (LoD4/LOD500) [29,79]. This hierarchical logic facilitates both top-down planning and bottom-up conservation analyses within unified frameworks. The capacity for interoperability between platforms is contingent upon the implementation of open data standards, most notably CityGML for GIS and IFC for BIM.
Despite their inherent limitations, these standards serve as a foundational layer for the semantic exchange across systems [31,76]. Significant endeavors in the direction of integrated workflows have been made, with notable contributions including the CHIMERA platform [76]. This platform has been developed to facilitate stakeholder navigation and version control across multiple scales and temporal interfaces. Another significant development is the HAOL Library [42], which has been designed to serve as a culturally specific parametric repository. This repository is intended to support HBIM generation in the Jeddah context. Carrasco et al. [79] propose an illustrative methodology, delineating a structured three-phase pipeline. This pipeline comprises LiDAR-based terrain modeling, building footprint extraction, and city-scale 3D modeling. These processes are implemented via platforms such as Revit, ArcGIS Pro, and SketchUp. Their comparative evaluation of tool-specific performance across LoD1–LoD4 highlights the need for harmonized, yet flexible, workflows adaptable to both urban planning and architectural restoration.
As shown in Table 1, several technical limitations are evident across the case studies. The utilization of high-resolution modeling at advanced LoDs (LoD3–LoD5) remains a labor-intensive process, which limits the potential for broader scalability. Semantic degradation during data translation, particularly between IFC and CityGML or GeoPackage formats, frequently results in the loss of crucial metadata, including building interior details and ownership relationships [30,80].
Furthermore, while tools such as Autodesk InfraWorks or QGIS support GIS-HBIM pipelines, critical processes such as semantic enrichment, damage classification, and temporal data structuring remain semi-automated or manual. Evidence of this can be seen in initiatives such as the Virtual Historic Dublin project [81], which combines PostGIS, SketchUp, and CityGML to enable semantic querying across LoD1–LoD4. Similarly, Galeazzo et al. [45] adopt Blazegraph and CIDOC-CRM ontologies to embed diachronic knowledge into 3D models.
Across the board, automation has been identified as a persistent bottleneck. Workflows involving semantic alignment, data segmentation, and real-time integration (e.g., from IoT sensors) remain underdeveloped in both proprietary and open-source ecosystems. It is evident that even advanced platforms, including CHIMERA, Precacore, and various digital twin systems, offer innovative features such as environmental monitoring and behavioral analytics [33,34,38].
However, these platforms are often constrained by external software dependencies and high computational demands, which can limit accessibility, particularly for small or resource-constrained heritage institutions [44]. Another technical gap concerns the integration of remote sensing data, including Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery, for long-term heritage monitoring. As demonstrated by Tzima et al. [39], while machine learning algorithms have the capacity to enhance deformation detection, the integration of such dynamic datasets into BIM environments is limited by software incompatibilities. This generally necessitates the creation of bespoke workflows for data fusion. Such workflows are not only computationally intensive but also difficult to replicate or standardize across projects (Figure 12).
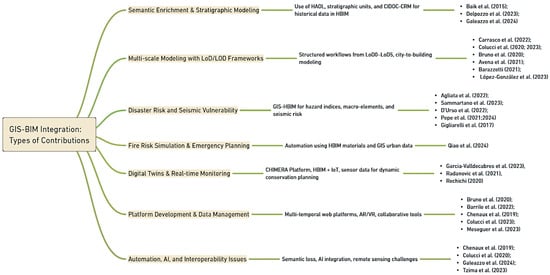
Figure 12.
Typologies of contributions in T1.
3.3.2. RQ3 in T2
Concerning the T2 development, the analysis of frameworks, tools, and technologies enabling HBIM-related IDPs highlights a close relationship between application domains and technology choices. The needs for cataloguing, semantic enrichment, monitoring, and accessibility are directly reflected in the architecture of the platforms, the formats used, and the data management systems.
This additional definition thus allows the complete reading of Table 2 of the contributions examined, thus highlighting the most recurrent strategies and emerging trends in the construction of HBIM-related IDPs.
The increasing and continuous development of digital tools and processes allows for customized and purpose-built solutions, enabling the platform to be adapted to specific needs while guaranteeing greater flexibility and interoperability, as in the case of Diara et al. [53] and Diara et al. [52], who present the ARK-BIM platform, a cloud-based solution specifically designed for the archaeological sector, which exploits web and open-source technologies to foster data accessibility and sharing.
Palomar et al. [54] present BIMlegacy, a purpose-built cloud platform for technical and non-technical users, designed with the objective of unifying and synchronizing information related to architectural heritage in a single Common Data Environment (CDE). The platform is accessible via WAN and has web interfaces designed for archaeologists, archivists, historians, and heritage managers.
PetroBIM is a tool developed for management and consultation by Quintilla et al. [78]. The Petrobim platform is designed to manage the information and documentation generated by the different technicians involved in a conservation intervention and project.
Rechichi et al. [33] propose an integrated BIM+GIS system, but with a purpose-built product (CHIMERA) that allows it to operate on multi-scale data, combining 3D information, maps, and images.
The repository concept, understood as an advanced platform for managing, storing, and systematizing heterogeneous data, finds a solid application in the context of the integration between Building Information Modeling (BIM) and GIS, as described in the contributions of Baik et al. [42] and Barazzetti et al. [31]. The former introduces Jeddah Historical Building Information Modeling (JHBIM), to preserve CH sites, while the latter introduces HBIM-GIS as a three-dimensional georeferenced digital environment aimed at collecting, structuring, and visualizing multi-scale and multi-temporal information related to historical assets and archaeological sites, using Autodesk InfraWorks. Similarly, Barrile et al. [37] study a proposal to unify HBIM (IFC—Industry Foundation Classes) and GIS (CityGML) formats in order to overcome interoperability limitations and guarantee dynamic and structured access to data.
By using advanced tools such as GeoServer, PostgreSQL/PostGIS, and HBIM modeling software, the platform developed by Hernández Peña et al. [61] allows to store, visualize, and navigate between complex data in an interactive way.
Banfi et al. [63] turn the repository into an advanced knowledge management system that can support the conservation, maintenance, and enhancement of CH.
Picone et al. [62], within the CHEAC project, describe the use of the IFC-certified usBIM.platform, developed by ACCA Software, and specifically adapted to the safe management and use of the archaeological site of Pompeii according to universal design principles. It is therefore a commercial solution, adapted to the needs of the project through specific customizations and integrations, as in the case of Agliata et al. [59] with the creation of an HBIM model of the area and the structuring of a GIS database through usBIM. GIS aims to create a repository of data and information on specific buildings and components in order to obtain susceptibility indices by combining data with different aggregation formulas.
Meseguer et al. [44] aim to develop the experimental GDHeritage platform to respond to the specific needs of architectural heritage management, combining open-source tools and customized solutions. The reasons for choosing such a construction allowed the integration of HBIM, GIS, and documentary databases and the accessibility for non-BIM expert users, such as historians and cultural institutions.
Regarding commercial products, Cheng et al. [57] highlight the role of Autodesk A360 as a collaborative environment for visualizing and managing 3D models, highlighting the need for the use of commercial products to enjoy the reliability and international standards that commercial platforms guarantee.
Radanovic et al. [34], on the other hand, propose a multilevel platform with high-fidelity visualization and access to integrated parametric, mesh, and point cloud models, while maintaining HBIM semantics. This is not a pre-existing commercial product but rather a customized system that leverages existing technologies (such as Unity, IFC, and Potree) to create a flexible and highly specialized infrastructure.
As posited by Logothetis et al. [55], the amalgamation and integration of open-source tools such as BIMserver, Nextcloud, and FreeCAD into a unified solution facilitates the creation of an interactive and accessible platform, thereby establishing a malleable environment that can be tailored to suit project requirements. In a similar vein, Harmouche et al. [64] concentrate on the integration and collaborative utilization of HBIM, XR, and Beacons for cultural mediation and the establishment of an immersive and interactive digital repository.
If Nagy et al. [60] develop the HBIM platform as an open-source, web-accessible cloud infrastructure designed for continuous monitoring of the energy performance of historic buildings using IoT sensors, Banfi et al. [63], making initial use of Autodesk Forge, succeed in overcoming the limitations of proprietary platforms through open-source languages (C++, PostgreSQL, Apache Kafka), creating a customized scalable platform, compatible with both cloud and on-premise environments in order to describe a cloud system for managing sites subject to hydraulic risk, integrating data from HBIM models, sensors, and VR apps.
The definition of databases in repositories is based on the adoption of international standards, which are essential to ensure interoperability and integration between heterogeneous systems. Cheng et al. [57] illustrate how CIDOC-CRM, together with IFC standards, enables semantic and structured data management, making it possible to link geometric and historical information. Similarly, Brumana et al. [58] and Turillazzi et al. [56] highlight the importance of standardizing levels of representation and relationships between objects, in order to support a coherent and easily exchangeable data flow between different actors.
Banfi et al. [63] make use of the IFC format to transfer data from Revit to cloud environments, as well as using JSON for real-time communication. Brumana et al. [48] propose the integration of structured vocabularies (Getty Vocabulary) and ontologies (CIDOC-CRM), with the aim of somaticizing data and facilitating search and reuse. Meseguer et al. [44] combine a relational database system with automatic field synchronization, enabling cohesive management of 2D, 3D, and metadata by BIM and non-BIM users.
The adoption of the IFC standard (particularly IFC4) is common. Palomar et al. [54] use an SQL Server database with API connection to Revit, ensuring semantic data matching. Radanovic et al. [34] adopt PostgreSQL, combined with spatially aligned IFC and OBJ files visualized in Unity. ShapeDiver is also used as an IFC-compliant AR/VR visualizer.
The adoption of open and interoperable standards remains a consistent priority. Logothetis et al. [55] adopt the IFC format, both in the 2 × 3 version and the more recent IFC4, to ensure compatibility between software, and Russo et al. [50] propose an ad hoc solution designed specifically for industrial heritage research. The decision to use open formats such as IFC4 guarantees scalability and integration with other architectural and engineering heritage management systems.
The analysis of contributions and Table 2 indicates a clear prevalence of ad hoc developed platforms in the domains of recording and collation of technical, historical, and archival investigations, as well as in the domain of informative management and semantic enhancement. These platforms have been developed in response to specific needs related to the survey, representation, and preservation of the historical memory of buildings. In this context, the utilization of commercial tools and hybrid experiments is constrained, frequently superseded by interoperability requirements.
The utilization of hybrid configurations is on the rise in the domain of monitoring and decision support, in conjunction with the employment of ad hoc platforms, where a greater variety of solutions is evident. Hybrid technologies represent the prevailing paradigm in the domain of digital visualization and dissemination, allowing the exploration of immersive and interactive ways of using heritage, both for cultural valorization and public communication.
The analysis reveals significant heterogeneity in the data used, reflecting the interdisciplinary and integrative nature of HBIM processes. The most recurring data categories include historical archival information, HBIM models, point clouds, meshes and textures, and multimedia content, indicating a complex and layered approach to heritage representation.
To complete the analysis, a summary matrix is proposed below that brings together in comparative form the contributions examined for T2, relating to the authors, the type of data integrated in the platforms, and the application domain of reference (Figure 13). This structure makes it possible to highlight the operational and information choices made in the different studies, highlighting the variety of data processed and the structure of the platforms, according to the specific application objectives.
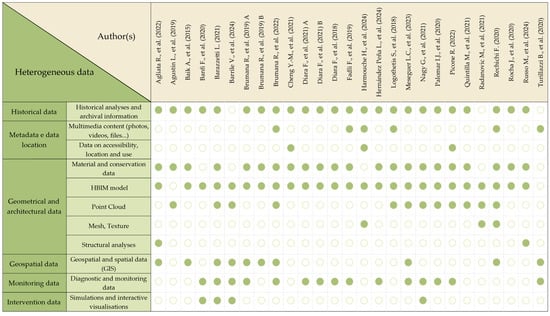
Figure 13.
Overview of heterogeneous data analyzed for each author in T2.
3.3.3. RQ3 in T3
Concerning T3, a wide range of frameworks, tools, and technologies have been employed in the development of IDPs, aiming to integrate HBIM models with intelligent IoT sensor infrastructures within highly interoperable digital architectures.
From the perspective of three-dimensional modeling, Autodesk Revit emerges as the most widely adopted HBIM environment, often enhanced through advanced tools such as Dynamo for model-optimized parameterization [41] and pyRevit, which extends functionality through custom automation [67]. Nevertheless, other parametric modeling tools are also employed within HBIM contexts, such as Graphisoft ArchiCAD [66], integrated with environmental data and sensor surveys in an interoperable digital environment. In this case, the combined use of CloudCompare for point cloud segmentation and Google Drive as a Common Data Environment (CDE) supports interdisciplinary cooperation and collaborative data management.
Software such as ANSYS is used for the geometric simplification of models in preparation for fluid dynamic simulations, which are particularly relevant in underground environments or spaces with specific microclimatic requirements [68,73]. Among the most common CFD tools are ANSYS Fluent, Autodesk CFD, and OpenStudio. These solutions are recurrently adopted across several studies [38,60,68,70,72].
From an informatic infrastructure standpoint, cloud-based platforms are playing an increasingly central role in workflow optimization and data management. Solutions such as Tridify, which allows parametric manipulation and interrogation of IFC models directly from the browser, facilitate the integration of HBIM and IoT systems for thermal and structural performance analysis [68,70,73]. The use of such cloud-based digital platforms enables the implementation of intelligent digital twins capable of collecting, storing, and visualizing heterogeneous data in real time from environmental and motion sensors. In this regard, the integration of HOMeBIM liveAPP—a multi-user, cloud-based platform developed for the real-time management of environmental sensor data—has been proposed to optimize indoor comfort, energy efficiency, and operational costs [58].
Regarding data management, numerous studies make use of MySQL—an open-source database management system known for its scalability and versatility in handling large data volumes [41,60,68,70,73]. These databases are often integrated with visualization dashboards such as Grafana, InfluxDB, or Datacake, which enable real-time supervision of environmental parameters and the activation of alerts for the automatic adoption of corrective measures [69].
In terms of environmental monitoring, the most frequently measured parameters with IoT sensors include temperature and relative humidity, along with CO2 concentration, key indicators to assess indoor air quality [41,60,67] and occupancy levels [60,72,73]. Monitoring of pollutants such as SO2 and NO2, which are potentially harmful to both occupants and the property itself, has also been reported [68]. Other recorded parameters include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), light levels (LUX), and motion sensor data (PIR), which are important for establishing links between environmental conditions and energy-saving strategies [60]. Some studies go further, implementing optical sensors for monitoring tourist flows and artificial intelligence systems such as the YOLOv3 model, trained on the COCO dataset, for real-time visual analysis [38].
Regarding structural monitoring, the integration of sensors into HBIM platforms is crucial for assessing the structural integrity of historic buildings. The use of accelerometers, linear potentiometers and electrical piezometers allows accurate detection of vibrations, displacements, and deformations, supporting advanced dynamic analyses such as operational modal analysis (OMA) [67] and probabilistic modeling with Bayesian model updating (BMU) [71].
The integration of these data into HBIM models—through dedicated digital tools, such as the H2BIM add-in developed with pyRevit—facilitates predictive and sustainable maintenance strategies, contributing to more effective long-term structural risk management and conservation planning. Finally, several studies have moved towards the development of customized IDP solutions, such as the use of proprietary HBIM platforms [60], or the integration of HBIM models and optical sensor data within ArcGIS Pro, leveraging artificial intelligence tools from the open-source CVLIB library for the automatic detection of people in images, aimed at managing and monitoring tourist flows [38].
Figure 14 summarizes the conducted analysis, comparing the sensor parameters and IoT sensor models explicitly declared by the authors in their respective studies, and providing a comparative overview of the solutions adopted for environmental and structural monitoring.
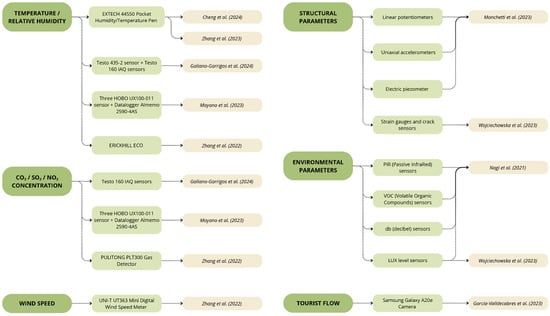
Figure 14.
Sensor parameters, types, and models identified through the analysis of T3.
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
All papers under the themes T1, T2, and T3 collectively represent a paradigm shift in the digital management of cultural heritage. These approaches transcend traditional documentation methods by enabling dynamic, stratified, and real-time interactions with complex built environments. The multi-scalar interoperability between territorial, urban, and architectural datasets fosters a layered analytical framework, while structured repositories increasingly function as active, interoperable platforms for continuous knowledge updating and decision support.
Concurrently, the incorporation of IoT sensor systems facilitates real-time environmental monitoring and predictive diagnostics, reconfiguring HBIM models as operational instruments rather than static archives. Despite these advances, critical barriers persist—including semantic fragmentation, platform dependency, and limited automation—which constrain scalability and the seamless integration of heterogeneous data sources and pave the way for future scientific and industrial efforts.
These frameworks bridge territorial analysis and architectural detail, enabling semantically enriched, dynamic models that enhance conservation, risk assessment, and documentation activities. However, several persistent challenges continue to limit their full operational potential.
A critical bottleneck remains the issue of data fragmentation across technical, semantic, and infrastructural dimensions. Heritage datasets are often dispersed among heterogeneous schemas, incompatible formats, and discipline-specific environments, leading to interoperability challenges between platforms based on IFC and those utilizing CityGML, GeoPackage, or 3D Tiles standards. This misalignment frequently results in semantic loss during data translation, particularly at higher LoD3–LoD5, where the preservation of fine-grained attributes is essential for structural, material, and historical analyses [71].
The current reliance on manual conversions, customized workflows, and external toolchains significantly undermines the continuity and scalability of digital heritage frameworks. Although automation processes have improved for basic operations such as terrain modeling and preliminary semantic structuring, critical tasks—such as damage classification, interior segmentation, and temporal stratification—remain largely manual and resource-intensive. As a result, scaling these frameworks to multi-site or territorial applications remains computationally demanding and operationally inefficient [82].
Real-time data integration, especially from IoT devices and remote sensing platforms, continues to face significant barriers due to semantic mismatches and computational overheads. While emerging digital twin environments offer promising avenues for dynamic conservation management, their deployment is constrained by the dependency on proprietary ecosystems, high infrastructural demands, and the immaturity of open-source alternatives capable of supporting semantic and real-time interoperability [82].
The integration of sensors is a pivotal aspect for the advancement of heritage monitoring. The development of real-time dynamic models capable of predictive analytics through machine learning techniques offers a transformative potential for HBIM frameworks, shifting them from static documentation repositories to active components in diagnostics, risk forecasting, and preventive conservation [82]. However, the integration of diverse sensor data within HBIM environments necessitates the establishment of shared protocols for optimal sensor placement, potentially supported by CFD simulations, and the development of adaptive control strategies for heritage-sensitive systems such as HVAC.
From a repository perspective, there has been an evolution towards the development of dynamic, interconnected digital knowledge systems. Instead of merely serving as passive archives, future repositories must evolve to function as digital anamnesis tools, capable of reconstructing and connecting complex knowledge across time and supporting documentation, analysis, and predictive decision-making processes [82]. Nevertheless, unresolved issues related to data ownership, intellectual property, and cybersecurity continue to pose considerable challenges, especially in collaborative and web-based infrastructures.
It is imperative to place greater emphasis on semantic enrichment strategies, particularly the incorporation of historical metadata, previous conservation interventions, and high-granularity environmental datasets. Such enhancements will facilitate a more profound and integrated comprehension of CH systems and promote a more extensive interdisciplinary approach to heritage management.
Scalability and replicability remain central challenges. Solutions must be adaptable to different heritage typologies, including hypogeal structures, open-air archaeological parks, and museum environments with high visitor fluxes. The standardization of data workflows, protocols for automation, and semantic interoperability will be essential for ensuring that IDPs are transferable across contexts [46,63,64,78,83,84,85].
Finally, significant progress has been made in importing HBIM datasets into XR environments for AR/VR-based visualization. These tools not only enhance accessibility but also offer new paradigms for participatory engagement and immersive learning. Nonetheless, critical issues persist, including the need for bidirectional data exchange, the mitigation of computational loads during real-time rendering, the implementation of robust updating systems for model sustainability, and the rigorous management of data quality and source verification. Without addressing these challenges, the long-term utility and credibility of XR-based heritage interaction platforms will remain limited.
The future trajectory of digital heritage management will be defined by its capacity to establish adaptive, scalable, and interdisciplinary ecosystems, capable of effectively addressing the increasing complexity inherent in cultural heritage conservation within a data-driven paradigm. In this context, the evolution of integrated frameworks must converge toward the realization of intelligent, modular, and genuinely interoperable systems, enabling the seamless integration of real-time environmental monitoring, semantic knowledge modeling, and predictive analytical methodologies. In this regard, the use of artificial intelligence (AI)—particularly through image recognition and data analytics—offers significant prospects [86]. Alongside the integration of HBIM with other information systems, it enhances the potential to leverage large and diverse datasets for the development of analytical models aimed at prediction and decision support, particularly in the context of condition assessment [87,88], continuous monitoring [89], and preventive conservation [90]. Achieving such a vision will necessitate not only sustained technological advancement but also the consolidation of interdisciplinary collaboration, the implementation of rigorous standards for data stewardship, and a firm adherence to principles of sustainability and ethical responsibility in the management of cultural assets in an increasingly digitalized environment.
Author Contributions
These authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
This research was granted by Next Generation UE—NRRP “Tech4You Project” funds assigned to Basilicata University Spoke 4 (PP4.2.1—“Materials, Architecture and Design: Open Knowledge and innovative digital tools for Cultural Heritage” (Scientific Coordinator: Antonella Guida)) and the relative Cascade Project: “ENVITAGE. sensor integration and data enrichment platform for ENVIronmental control of built heritage” (Scientific Coordinator: Mariella De Fino).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CIDOC-CRM | Conceptual Reference Model |
| CH | Cultural heritage |
| GIS | Geographic information systems |
| HBIM | Historic/Heritage Building Information Modeling |
| IDPs | Integrated digital platforms |
| IFC | Industry Foundation Classes |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LoDs | Levels of Detail |
| LODs | Levels of Development |
| TNA | Thrust Network Analysis |
| XR | Extended reality |
References
- Murphy, M.; McGovern, E.; Pavia, S. Historic Building Information Modelling (HBIM). Struct. Surv. 2009, 27, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, F.; Gaglio, F.; Martino, M.; De Falco, A. A HBIM Pipeline for the Conservation of Large-Scale Architectural Heritage: The City Walls of Pisa. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldo, M.; Agustin-Hernandez, L.; Verdoscia, C.; Tavolare, R. A Scan-To-Bim Workflow Proposal for Cultural Heritage. Automatic Point Cloud Segmentation and Parametric-Adaptive Modelling of Vaulted Systems. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, J.; León, J.; Nieto-Julián, J.E.; Bruno, S. Semantic Interpretation of Architectural and Archaeological Geometries: Point Cloud Segmentation for HBIM Parameterisation. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currà, E.; D’amico, A.; Angelosanti, M. HBIM between Antiquity and Industrial Archaeology: Former Segrè Papermill and Sanctuary of Hercules in Tivoli. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Antonella, M.; Fabio, F.; Dell’Osso, G.R. The Role of 4D Historic Building Information Modelling and Management in the Analysis of Constructive Evolution and Decay Condition within the Refurbishment Process. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 15, 1250–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan-Palomar, I.; Tzortzopoulos, P.; García-Valldecabres, J.; Pellicer, E. Protocol to Manage Heritage-Building Interventions Using Heritage Building Information Modelling (HBIM). Sustainability 2018, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Julián, E.; Bruno, S.; Moyano, J. An Efficient Process for the Management of the Deterioration and Conservation of Architectural Heritage: The HBIM Project of the Duomo of Molfetta (Italy). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massafra, A.; Davide, P.; Gulli, R. Reverse Engineering Workflows for the Structural Assessment of Historical Buildings. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2025, 19, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; de Fino, M. Decision-Making for Historic Building Diagnosis by Logical Inference in HBIM Approach: The Case of Onsite Inspection of Timber Elements. SCIRES-IT 2021, 11, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penjor, T.; Banihashemi, S.; Hajirasouli, A.; Golzad, H. Heritage Building Information Modeling (HBIM) for Heritage Conservation: Framework of Challenges, Gaps, and Existing Limitations of HBIM. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2024, 35, e00366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocobelli, D.P.; Boehm, J.; Bryan, P.; Still, J.; Grau-Bové, J. BIM for Heritage Science: A Review. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.J.; Lerones, P.M.; Llamas, J.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Zalama, E. A Review of Heritage Building Information Modeling (H-BIM). Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.; Blanca-Hoyos, Á.; Puertas, E.; Gallego, R. HBIM: Background, Current Trends, and Future Prospects. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Koehl, M.; Macher, H.; Murtiyoso, A.; Landes, T. Review of Built Heritage Modelling: Integration of HBIM and Other Information Techniques. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 46, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, L.J.; Davies, R.J.; Hunt, D.V.L. The Application of Historic Building Information Modelling (HBIM) to Cultural Heritage: A Review. Heritage 2023, 6, 6691–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F. HBIM Open Source: A Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scianna, A.; Gaglio, G.F.; La Guardia, M. HBIM Data Management in Historical and Archaeological Buildings. Archeol. Calc. 2021, 31, 231–252. [Google Scholar]
- Baarimah, A.O.; Alaloul, W.S.; Liew, M.S.; Kartika, W.; Al-Sharafi, M.A.; Musarat, M.A.; Alawag, A.M.; Qureshi, A.H. A Bibliometric Analysis and Review of Building Information Modelling for Post-Disaster Reconstruction. Sustainability 2022, 14, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, A.; Castañeda, K.; Sánchez, O.; Peña, C.A.; Gutiérrez, L.; Sáenz, P. Building Information Modeling and Complementary Technologies in Heritage Buildings: A Bibliometric Analysis. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.J.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic Review or Scoping Review? Guidance for Authors When Choosing between a Systematic or Scoping Review Approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Pomares, J.C. Digital Technologies in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction (Aec) Industry—A Bibliometric—Qualitative Literature Review of Research Activities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovsky, J.; Labonnote, N.; Vigren, O. Digital Technologies in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction. Autom. Constr. 2024, 158, 105212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusaed, A.; Yitmen, I.; Almssad, A. Reviewing and Integrating AEC Practices into Industry 6.0: Strategies for Smart and Sustainable Future-Built Environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Adabre, M.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ameyaw, E.E. Artificial Intelligence in the AEC Industry: Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Research Activities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartano, G.; Avena, M.; Fillia, E.; Spanò, A. Integrated HBIM-GIS Models for Multi-Scale Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Historical Buildings. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena, M.; Colucci, E.; Sammartano, G.; Spanò, A. HBIM Modelling for an Historical Urban Centre. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, E.; de Ruvo, V.; Lingua, A.; Matrone, F.; Rizzo, G. HBIM-GIS Integration: From IFC to CityGML Standard for Damaged Cultural Heritage in a Multiscale 3D GIS. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzetti, L. Integration Between Building Information Modeling And Geographic Information System for Historic Buildings And Sites: Historic-Bim-Gis. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 8, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, E.; Iacono, E.; Matrone, F.; Ventura, G.M. The Development of a 2d/3d Bim-Gis Web Platform for Planned Maintenance of Built and Cultural Heritage: The Main10ance Project. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechichi, F. Chimera: A BIM+GIS System for Cultural Heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radanovic, M.; Khoshelham, K.; Fraser, C. A Platform for Multilayered Documentation of Cultural Heritage. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpozzo, E.; Balletti, C. Bridging the Gap: An Open-Source Gis+bim System for Archaeological Data.The Case Study of Altinum, Italy. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.G.; Aldrighettoni, J. Geodatabase, Metric Reconstruction and a GIS Platform of Historical-Archaeological Sites in Aquino. Acta IMEKO 2024, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Genovese, E. Gis-like Environments and Hbim Integration for Ancient Villages Management and Dissemination. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 48, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Valldecabres, J.L.; Liu, J.; Willkens, D.S.; Escudero, P.A.; Lopez-Gonzalez, C.; Cortes Meseguer, L.; Orozco Carpio, P.R. Development of a Virtual Itinerary with Hbim and Gis. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzima, M.S.; Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Artopoulos, G.; Fokaides, P.; Chrysostomou, C. An Application of Machine Learning Algorithms by Synergetic Use of SAR and Optical Data for Monitoring Historic Clusters in Cypriot Cities. Energies 2023, 16, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliarelli, E.; Calcerano, F.; Cessari, L. Heritage Bim, Numerical Simulation and Decision Support Systems: An Integrated Approach for Historical Buildings Retrofit. Energy Procedia 2017, 133, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, C.; García-Valldecabres, J. The Integration of HBIM-SIG in the Development of a Virtual Itinerary in a Historical Centre. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, A.; Yaagoubi, R.; Boehm, J. Integration of Jeddah Historical Bim and 3D GIS for Documentation and Restoration of Historical Monument. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Costantino, D.; Alfio, V.S.; Restuccia, A.G.; Papalino, N.M. Scan to BIM for the Digital Management and Representation in 3D GIS Environment of Cultural Heritage Site. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 50, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, L.C.; Valldecabres, J.G. Digital Twins. HBIM Information Repositories to Centralize Knowledge and Interdisciplinary Management of Architectural Heritage. Vitruvio 2023, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeazzo, L.; Grillo, R.; Spinaci, G. A Geospatial and Time-Based Reconstruction of the Venetian Lagoon in a 3D Web Semantic Infrastructure. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2024, 3643, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Agustín, L.; Quintilla, M. Virtual Reconstruction In Bim Technology And Digital Inventories Of Heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadli, F.; AlSaeed, M. Digitizing Vanishing Architectural Heritage; The Design and Development of Qatar Historic Buildings Information Modeling [Q-HBIM] Platform. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Condoleo, P.; Grimoldi, A.; Previtali, M. Towards a Semantic Based Hub Platform of Vaulted Systems: Hbim Meets a Geodb. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Ioannides, M.; Previtali, M. Holistic Heritage Building Information Modelling (Hhbim): From Nodes to Hub Networking, Vocabularies and Repositories. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Cocco, P.L.; Giannetti, I. Analysis of the Form, Construction, and Structural Conception of Silberkuhl Shells through Construction History and Advanced HBIM. Structures 2024, 68, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. Open Source Hbim for Cultural Heritage: A Project Proposal. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F.; Cavallero, F. From Excavation Data to HBIM Environment and Cloud Sharing: The Case Study of Domus Regia, Sacraria Martis et Opis (Roman Forum, Rome-Italy). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 46, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. Ark-Bim: Open-Source Cloud-Based Hbim Platform for Archaeology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, I.J.; García Valldecabres, J.L.; Tzortzopoulos, P.; Pellicer, E. An Online Platform to Unify and Synchronise Heritage Architecture Information. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, S.; Karachaliou, E.; Valari, E.; Stylianidis, E. Open Source Cloud-Based Technologies for BIM. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turillazzi, B.; Leoni, G.; Gaspari, J.; Iadanza, E.; My, M.; Massari, M.; Boulanger, S.O.M.; Djalali, A. Heritage-Led Ontologies: Digital Platform for Supporting the Regeneration of Cultural and Historical Sites. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 249, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-L.; Mou, C.-C. Ontology-Based Hbim for Historic Buildings with Traditional Woodwork in Taiwan. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2021, 27, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumana, R.; Stanga, C.; Banfi, F. Models and Scales for Quality Control: Toward the Definition of Specifications (GOA-LOG) for the Generation and Re-Use of HBIM Object Libraries in a Common Data Environment. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 14, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliata, R.; Bortone, A.; Mollo, L. The Impact of the Aggregation Formula on Indicator-Based Method for the Assessment of Building Susceptibility to Hydro-Meteorological Hazards. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 72, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Ashraf, F. HBIM Platform & Smart Sensing as a Tool for Monitoring and Visualizing Energy Performance of Heritage Buildings. Dev. Built Environ. 2021, 8, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Peña, L.; Merlo, A.; Remond Noa, R.; Arencibia Iglesias, S.R.; Ricardo Desdín, S.E. Proposal Of A Model (Hbim-Gis) For The Pathological Diagnosis Of Architectural Heritage|Propuesta De Un Modelo Hbim-Sig Para El Diagnóstico De Patologías En El Patrimonio Arquitectónico. Loggia Arquit. Restaur. 2024, 37, 134–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, R. Universal Design and Interoperable Digital Platforms Between Conservation and New Fruition Opportunities. The Case Study of Arianna’s Domus in Pompeii. In Transforming our World through Universal Design for Human Development; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 297, ISBN 9781643683041. [Google Scholar]
- Banfi, F.; Previtali, M.; Brumana, R. Towards the Development of a Cloud-Based BIM Platform and VR Apps for Complex Heritage Sites Subject to the Risk of Flood and Water Level Changes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 949, 012105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmouche, H.; Hajji, R.; El Barhoumi, N.; Sardi, N.; Bouramdane, A. Integration of Hbim, Xr and Beacons for Cultural Mediation of Historical Heritage: The Case of “al-Quaraouiyine Mosque” in Fes. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 48, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Tomé, A. Multidisciplinarity and Accessibility in Heritage Representation in HBIM Casa de Santa Maria (Cascais)—A Case Study. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2021, 23, e00203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, J.; Fernández-Alconchel, M.; Nieto-Julián, J.E.; Marín-García, D.; Bruno, S. Integration of Dynamic Information on Energy Parameters in Hbim Models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meoni, A.; Vittori, F.; Piselli, C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Pisello, A.L.; Ubertini, F. Integration of Structural Performance and Human-Centric Comfort Monitoring in Historical Building Information Modeling. Autom. Constr. 2022, 138, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chan, C.C.C.; Kwok, H.H.L.; Cheng, J.C.P. Multi-Indicator Adaptive HVAC Control System for Low-Energy Indoor Air Quality Management of Heritage Building Preservation. Build. Environ. 2023, 246, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, G.; Bednarz, Ł.J.; Dolińska, N.; Opałka, P.; Krupa, M.; Imnadze, N. Intelligent Monitoring System for Integrated Management of Historical Buildings. Buildings 2024, 14, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Zhang, J.; Kwok, H.H.L.; Tong, J.C.K. Thermal Performance Improvement for Residential Heritage Building Preservation Based on Digital Twins. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchetti, S.; Bartoli, G.; Betti, M.; Facchini, L.; Rougier, E.; Zini, G. The Research Project “CHARMING PISTOIA”: An Integrated HBIM Project for Preservation and Maintenance of Heritage Structures. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2022, 44, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano-Garrigós, A.; López-González, C.; García-Valldecabres, J.; Pérez-Carramiñana, C.; Emmitt, S. The Influence of Visitors on Heritage Conservation: The Case of the Church of San Juan Del Hospital, Valencia, Spain. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kwok, H.H.L.; Luo, H.; Tong, J.C.K.; Cheng, J.C.P. Automatic Relative Humidity Optimization in Underground Heritage Sites through Ventilation System Based on Digital Twins. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, P.; Hallot, P. Digital Twin: Research Framework to Support Preventive Conservation Policies. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, P.; Hallot, P. Digital Twin: A Hbim-Based Methodology To Support Preventive Conservation Of Historic Assets Through Heritage Significance Awareness. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, N.; Rechichi, F.; Achille, C.; Zerbi, A.; Roncella, R.; Fassi, F. Integration of Historical GIS Data in a HBIM System. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Lam, C.C.; Wong, M.O.; Xu, Y. A Framework of Integrating HBIM and GIS for Automated Fire Risk Assessment of Heritage Buildings. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Lille, France, 3–5 June 2024; pp. 714–721. [Google Scholar]
- Quintilla, M.; Agustín, L. 3D Survey and Virtual Reconstruction of Heritage. The Case Study of the City Council and Lonja of Alcañiz. Vitruvio 2021, 6, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.A.; Lombillo, I.; Sánchez-Espeso, J. Methodology for the Generation of 3D City Models and Integration of HBIM Models in GIS: Case Studies. Vitruvio 2022, 7, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Palumbo, D.; Dewedar, A.K.H.; Spacone, E. Toward to Combination of GIS-HBIM Models for Multiscale Representation and Management of Historic Center. Heritage 2024, 7, 6966–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenaux, A.; Murphy, M.; Pavia, S.; Fai, S.; Molnar, T.; Cahill, J.; Lenihan, S.; Corns, A. A Review Of 3d GIS for Use in Creating Virtual Historic Dublin. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewczyński, B.; Szot, J. BIM Goals and Uses in the Management, Maintenance, and Preservation of Historic Buildings: An Open Access Perspective. Implementation Characteristics of HBIM for Improved Documentation and Lifecycle Management. Npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafeiro, J.; Tomé, A.; Nazário, M. Immersive Learning for Lost Architectural Heritage: Interweaving the Past and Present, Physical and Digital in the Monastery of Madre de Deus. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, U.; Quattrini, R.; D’alessio, M. A Comprehensive HBIM to XR Framework for Museum Management and User Experience in Ducal Palace at Urbino. Heritage 2022, 5, 1551–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Scioti, A.; Pierucci, A.; Rubino, R.; Di Noia, T.; Fatiguso, F. VERBUM—Virtual Enhanced Reality For Building Modelling (Virtual Technical Tour In Digital Twins For Building Conservation). J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2022, 27, 20–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lim, Y.L.; Li, W. Systematic Review: A Bibliometric Analysis of Building Technology and Its Potential Applications to Artificial Intelligence in the Field of Cultural Heritage Conservation from 2013 to 2023. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, V.; Bruno, S.; Fatiguso, F.; Nieto-Julián, E. Decay Assessment in Historic Buildings with Texture-Based Classification Techniques: From Digital Survey to HBIM. In REHABEND 2024 Construction Pathology, Rehabilitation Technology and Heritage Management (10th REHABEND Congress); Boffill, Y., Lombillo, I., Blanco, H., Eds.; University of Cantabria—Building Technology R&D Group: Santander, Spain, 2024; pp. 2448–2456. [Google Scholar]
- D’Auria, S.; Franzese, A.; Nicolella, M.; D’Agostino, P. Integration of HBIM and Machine Learning Processes for Cultural Heritage Maintenance. In Protection of Historical Constructions; Mazzolani, F.M., Landolfo, R., Faggiano, B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Laohaviraphap, N.; Waroonkun, T. Integrating Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things in Cultural Heritage Preservation: A Systematic Review of Risk Management and Environmental Monitoring Strategies. Buildings 2024, 14, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, F.M.; Santagati, C. An AI-Based DSS for Preventive Conservation of Museum Collections in Historic Buildings. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 35, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).