Abstract
Early identification of acute gout is crucial, enabling healthcare professionals to implement targeted interventions for rapid pain relief and preventing disease progression, ensuring improved long-term joint function. In this study, we comprehensively explored the potential early detection of gout flares (GFs) based on nurses’ chief complaint notes in the Emergency Department (ED). Addressing the challenge of identifying GFs prospectively during an ED visit, where documentation is typically minimal, our research focused on employing alternative Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to enhance detection accuracy. We investigated GF detection algorithms using both sparse representations by traditional NLP methods and dense encodings by medical domain-specific Large Language Models (LLMs), distinguishing between generative and discriminative models. Three methods were used to alleviate the issue of severe data imbalances, including oversampling, class weights, and focal loss. Extensive empirical studies were performed on the Gout Emergency Department Chief Complaint Corpora. Sparse text representations like tf-idf proved to produce strong performances, achieving F1 scores higher than 0.75. The best deep learning models were RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc and BioGPT, which had the best F1 scores for each dataset, with a 0.8 on the 2019 dataset and a 0.85 F1 score on the 2020 dataset, respectively. We concluded that although discriminative LLMs performed better for this classification task when compared to generative LLMs, a combination of using generative models as feature extractors and employing a support vector machine for classification yielded promising results comparable to those obtained with discriminative models.
1. Introduction
1.1. Gout as a Global Health Burden
Gout is a painful form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe joint inflammation, which is believed to be caused by the formation and accumulation of needle-shaped crystals in and around the joints. According to the National Institute of Health of the USA, there are four stages of gout development [1]. It is typically triggered by high levels of uric acid in the blood, called asymptomatic hyperuricemia. After that, the second stage of development is gout flares, i.e., periodic attacks of intense pain and swelling in the joints, which is the most recognizable stage of gout. This is followed by intercritical gout (the time between gout attacks without symptoms) and tophi (a later stage of the building up of crystals that may cause permanent joint damage). Early identification of gout flares (GFs) is one of the critical approaches to preventing the development of chronic gout and irreversible damage to patients.
Gout has become a significant health concern globally. A recent report on the global, regional, and national prevalence of gout estimated that, as of 2019, about 53 million people worldwide suffer from gout, a significant 63.44% increase from 22 million globally in 1990 [2]. In the USA, more than nine million people suffer from gout [3], which is the most prevalent type of inflammatory arthritis among men, affecting over 5% of them. The burden of gout in young populations (under 40) was estimated to have increased drastically from 38.71 to 45.94 per 100,000 population during 1990–2019, and a consistent trend was observed globally among countries of all sociodemographic index quantiles [4]. In addition to the painful experience, physical disability, and lowered quality of life [5], gout has also been implied to have links to other conditions or complications, for example, with the heart [6], such as hypertension, myocardial infarction (heart attack), congestive heart failure, etc.
1.2. Early Detection of Gout at Emergency Department
According to the U.S. National Emergency Department Sample (NEDS), gout accounts for more than 200,000 visits to the Emergency Department (ED) every year, making up 0.2% of all ED visits and costing more than $280 million in annual charges [7]. It is important to improve the continuity of care for gout patients, especially after an ED visit. Often, gout flares (GFs) treated in the ED lack optimal follow-up care, necessitating the development of methods for identifying and referring patients with GFs at an early stage during an ED visit [8]. While retrospective studies have leveraged natural language processing (NLP) for GF detection, the prospective identification of patients in real time ED settings presents a unique challenge, especially within the constraints of Emergency Department environments.
Despite the success of NLP techniques in healthcare [9], NLP-based Gout Flare Early Detection (GFED) is in severe lack of study. Only a few were identified, like Zheng et al. [10] which, however, worked on Electronic Medical Records. The problem of early warning of acute GFs becomes more challenging in the ED setting where the chief complaints of patients are only taken by nurses in an extremely succinct format. It is of paramount challenge to develop an effective GFED algorithm using such limited amount of information. The current study tries to address this critical gap by advancing the methodologies proposed by Osborne et al. [8]. Our study builds upon the groundwork laid by Osborne et al., who annotated two corpora of ED chief complaint notes for GFs and paves the way for our exploration of effective text representation methods and state-of-the-art medical/clinical Large Language Models (LLMs).
1.3. Rationale for Using Large Language Models
Large language models, such as BERT [11] (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), GPT [12] (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), and their variants, have demonstrated remarkable success in a wide range of natural language processing tasks. The use of large language models in text classification offers several compelling reasons:
Contextual understanding: Large language models leverage deep learning techniques to encode contextual information and relationships between words in a sentence. This contextual understanding allows them to capture subtle nuances and semantics, which is especially relevant in the medical domain where precise interpretation of clinical text is vital.
Transfer learning: Pre-training on vast corpora of textual data enables large language models to learn general language patterns. This pre-trained knowledge can be fine-tuned on domain-specific datasets, making them adaptable and effective for text classification tasks in the medical field with relatively limited labelled data.
These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry by enhancing medical decision-making, patient care, and biomedical research. Some tasks in NLP could be automated using LLMs, such as text classification [13,14], keyword extraction [15,16], machine translation [17], and text summarization [18]. Furthermore, NLP and LLMs can assist in the early detection and diagnosis of diseases by sifting through vast datasets to identify patterns, symptoms, and risk factors.
1.4. Gaps and Limitations of Current Literature
While some studies have compared a single generative LLM (GPT) with discriminative LLMs, a comprehensive comparison between multiple domain-specific generative LLMs and discriminative LLMs for disease detection is lacking. Such comparisons are essential to determine the performance disparities between different LLM types and guide the selection of the most suitable model for our specific medical intent and classification task.
In light of these gaps, our research aims to bridge these deficiencies in the current literature. We specifically focus on GFED by leveraging domain-specific generative LLMs as feature extractors. Additionally, our study includes comparative analyses of multiple domain-specific generative LLMs and discriminative LLMs to gain comprehensive insights into their performance on this particular medical classification task.
1.5. Our Contributions
In this paper, we make three contributions to the task of gout flare detection from nurse chief complaints. First, we compare the performance of domain-specific discriminative and generative models that are fine-tuned for the task. Second, we propose an alternative approach that uses domain-specific generative LLMs as feature extractors and a support vector machine as classifier. Third, we benchmark our methods against a baseline that uses sparse text representation (tf-idf). Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of using LLMs, such as RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc, BioELECTRA, and BioGPT, for processing medical text and detecting GFs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
We utilized the dataset of ED Chief Complaints (abbreviated as CC hereafter) notes, which were annotated by Osborne et al. for the presence of GFs [19]. Each CC text in the dataset was annotated to determine its indication of a GF, a non-GF, or remained unknown in terms of the status of GF. Following this, a manual chart review was conducted by a rheumatologist and a post-doctoral fellow to ascertain the GF status for a small portion of the ED counters. These served as the gold standard annotations of the real GF status. More details about dataset creation and dataset statistics can be found in Osborne et al.’s original paper [8].
The corpora contain two datasets for the year 2019 and 2020, namely GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS and GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS, respectively. Table 1 shows the annotation statistics of the two datasets. In our experiments, we used the human-annotated samples using chart review, as did Osborne et al. This means we used the two rows in Table 1 with an asterisk, where the “Review” column contains “Chart”. Table 2 shows some exemplars of annotations taken from Osborne et al.’s paper, where the “Predicted” and “Actual” columns are labels annotated by using CC texts alone and by using complete chart review, respectively. As ED nurses use large amounts of medical abbreviations when taking CC notes, we provided brief explanations for the CC notes to facilitate understanding.

Table 1.
Annotation Statistics of the Gout Flare Chief Complaint Datasets (from Osborne et al. [8]).

Table 2.
Examples of Chief Complaint Notes for Gout Flare (from Osborne et al. [8]).
2.2. Feature Extraction
In the feature engineering approach, we extracted the n-grams (n = 1, 2, 3) and tested different combinations of n-grams. CC texts were converted into sparse representations using tf-idf (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) [20] as initial feature values. A linear support vector machine (Linear SVM) was trained for classification. All implementations were done using the scikit-learn library (https://scikit-learn.org/, accessed on 29 February 2024).
It was challenging to extract more advanced syntactic or semantic features due to the noisiness of CC texts. As can be observed from Table 2, CC texts are extremely succinct, often containing a sequence of medical terms or abbreviations which record the facts reported by patients. Such CCs are not meaningful sentences for us to extract features from using the syntactic analysis results. Semantic analysis tools are either immature or non-existent in this particular area. However, we could still observe good performances from fine-tuning a machine learning model using the right sparse feature representation of CC texts.
2.3. Large Language Models
We employed several LLMs tailored for the medical domain with the hope to discern nuances in GF-related CCs, relying on their ability to capture intricate patterns within medical texts. All LLMs belong to the Transformers family [21], as we hoped that the multi-headed self-attention mechanism of the Transformers architecture could allow for learning meaningful associations between certain CC words to indicate the existence of GFs.
2.3.1. Discriminative Models
We strategically incorporated three robust discriminative LLMs renowned for their discriminative power—RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc [22], BioELECTRA [23], and BioBART [24]. These are the domain-specific versions of the RoBERTa [25], Electra [26], and BART [27] models, respectively. Although BART was a language model pretrained in a sequence-to-sequence fashion, it can be used equally well and in the same way as a discriminative model [27]. As such, we treated it as one representative of the discriminative category. The details of the discriminative LLMs are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Description of Discriminative LLMs Implemented.
2.3.2. Generative Models
In the realm of generative LLMs, we strategically chose BioGPT [29], BioMedLM (https://github.com/stanford-crfm/BioMedLM, accessed on 29 February 2024, by Stanford University and MosaicML), and PMC_LLaMA_7B [30] for their renowned scale and exceptional performance in natural language processing tasks. BioGPT and PMC_LLaMA_7B are the domain-specific versions of the GPT-2 [31] and LLaMA [32,33] models, respectively, while BioMedLM is a bespoke LLM pretrained for medical applications. These models represent the forefront of generative language understanding, and their comprehensive specifications, training data, and architectural features are elucidated in Table 4.

Table 4.
Description of Generative LLMs Implemented.
2.4. Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning was implemented to improve the models’ ability to understand and capture the nuances in the texts. For the discriminative models, full fine-tuning was implemented, but for the generative models, due to the size of the models and hardware constraints, full fine-tuning was not possible.
2.4.1. Fine-Tuning of Discriminative LLMs
All three discriminative LLMs use a bidirectional encoder as BERT [11]. The encoder part of these models was used to encode each CC text, and the “[CLS]” token was used as the dense representation. For RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc and BioELECTRA, a further feature transformation was applied. Essentially, the classification head was a Multiple Layer Perceptron (MLP), the hidden layer of which made a nonlinear transformation (of the same size). On the contrary, BioBART used a linear classification head following the tradition of BART usage.
In the fine-tuning process, the following hyperparameters were used: learning rate = 1 × 10−5, epoch number = 10, batch size = 14, early stopping patience = 3. The AdamW optimiser was used for training [36].
2.4.2. Fine-Tuning of Generative LLMs
Similarly, generative LLMs were used for encoding CC texts, and the “Extract” tokens (for all three models, as they all belong to the GPT family) were used to extract the dense representation, which was then sent to a linear classification head. Due to their large sizes, the generative LLMs were not fully fine-tuned. Instead, we used LoRA (Low Rank Adaptation) [37] to efficiently adapt the LLMs to specific tasks by only modifying a small portion of the whole parameter space.
The main idea behind LoRA is to exploit the low-rank structure of the model’s weight matrices during task adaptation, resulting in reduced memory usage and computational complexity [37]. The idea was inspired by Aghajanyan et al.’s finding that pre-trained language models have a low “intrinsic dimension,” meaning that they can still lean efficiently when their weight matrices are randomly projected to a smaller subspace [38].
Figure 1 illustrates the idea of low rank adaptation for efficient training. More precisely, LoRA hypothesizes that updates to model’s weight matrix, , can be represented by a low-rank decomposition, which is given by , where , and represents weight updates. During training (i.e., fine-tuning), is frozen while and contain the trainable parameters.
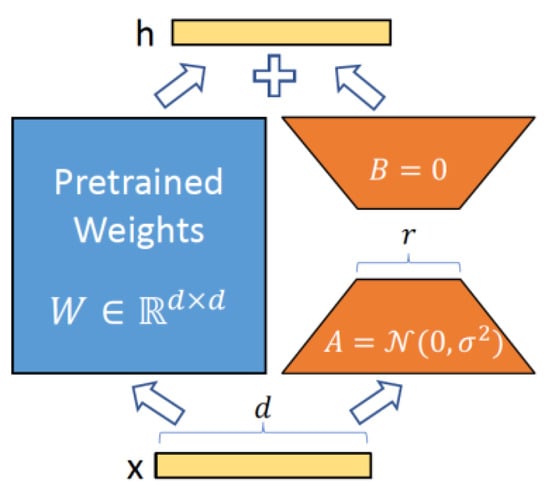
Figure 1.
Parametrization of LoRA. Only A and B are trained. (from the original LoRA paper [37]).
In our fine-tuning process, we applied the following LoRA parameters:
- The rank () of and was set to 8.
- The LoRA regularization coefficient α was set to 16.
- To prevent overfitting and enhancing model generalisation, we applied a LoRA dropout rate of 0.1.
- A learning rate of 3 × 10−4 was used, enabling efficient convergence during training.
2.5. Classification
In the feature engineering approach, a linear SVM (Support Vector Machine) for classification was trained. We opted for a SVM because it has been empirically proven to be a strong classifier across a wide range of applications in biomedical informatics [39] and bioinformatics [40]. When fine-tuning discriminative LLMs, either an MLP or a linear classifier was applied. Similarly, a linear layer was used for classification with generative LLMs. In the experiments, we also tested using generative LLMs only as the feature extractor and trained a SVM for classification. In this alternative approach, which required significantly less computational resources, generative LLMs were frozen, used to encode CC texts, and the hidden states of the “Extract” token were extracted as dense representation. A linear SVM was then trained in a similar way as in the feature engineering approach. This was to demonstrate the LLMs’ native ability to understand and represent medical texts for the downstream task.
2.6. Optimisation
Figure 2 summarises the whole pipeline of the learning task and the optimisation strategies that were employed to improve performance. We detail them one by one in the following subsections.
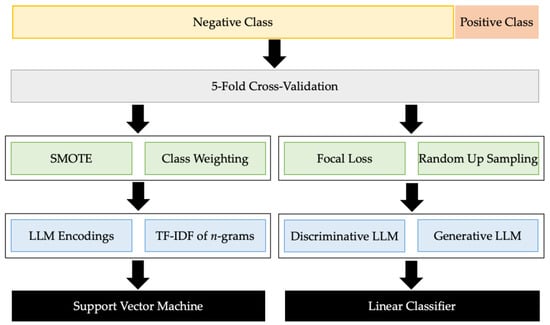
Figure 2.
The Learning Pipeline of Early Detection of Gout Flare from Chief Complaints.
2.6.1. Class Weights
We also observed severe data imbalances in the corpora. The data imbalance ratio of GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS is (70 + 9)/118 = 0.6695, while the imbalance ratio of GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS is (25 + 7)/232 = 0.1379. Our first method to handle data imbalance was class weights [41], which were set according to the relative sizes of each class as in Equation (1),
where is the weight for the j-th class, is the total number of classes, is the total number of samples, and is the number of samples of the j-th class [42].
2.6.2. Oversampling
However, the class weighting alone in Equation (1) could not well handle the severe data imbalance in the GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS, which is 5 times more imbalanced than GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS. Although the discriminative LLMs performed strongly in our experiments, they were extremely sensitive to this severe data imbalance. Therefore, we performed random over-sampling on the GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS. The positive samples in the training split, including GF-POS and GF-UNK combined, were randomly duplicated to match the size of GF-NEG.
The second approach we used to oversample the minority class was the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) [43]. SMOTE generates synthetic examples of the minority class by interpolating the feature space of the existing minority samples, thereby balancing the class distribution. This approach was only implemented in the method where we used the LLMs as feature extractors and classified with an SVM.
2.6.3. Focal Loss
In the context of our classification tasks with severely skewed data distribution, the choice of a suitable loss function also played a pivotal role in training and optimizing our models. Treating loss function as an additional “hyperparameter”, we employed two distinct loss functions per dataset and model requirement, namely cross-entropy loss and focal loss [44], to effectively guide the training process and address specific challenges posed by our datasets.
In instances where class imbalance persisted even after oversampling the training data, such as in the case of GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS, we employed focal loss as an alternative to cross-entropy to combat class imbalance, which is defined in Equation (2).
where is the posterior probability of each target (here ), is the scaling parameter, is the focusing parameter, and is the modulating factor of the original cross-entropy loss [44]. When using focal loss, was simply calculated by the class weighting in Equation (1).
3. Results
In this section, we meticulously analyse and compare the performances of all methods. The performance of each model was evaluated using standard metrics, including precision (a.k.a. Positive Predictive Value or PPV), recall (a.k.a. Sensitivity), and macro F1 score (a trade-off between precision and recall, averaged over the F1 scores for all classes). We compared our results with the original algorithm proposed by Osborne et al. [8], ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the advancements achieved.
3.1. Fine-Tuned LLM
This subcategory encompasses the results obtained by directly employing LLMs for CC classification. Table 5 shows the results, where the best performances in each metric were highlighted in bold. RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc outperformed the other four models in the 2019 dataset in terms of precision, recall, and F1 score, followed by BioBART and BioELECTRA who exhibited similar performance, while BioGPT and BioMedLM had the lowest performance among the five models.

Table 5.
Performances of Gout Flare Detection using Fine-Tuned LLMs.
On the 2020 dataset, the best model was by far BioGPT, outperforming the other LLM competitors by large margins. Good performances were obtained due to oversampling, which improved the results from 0.67 to 0.85 in terms of F1 score. However, it is unclear whether this suggests that BioGPT might be able to handle the data imbalance better. Nevertheless, it seems that large language models are sensitive to data size (unfortunately small in our application setting) and data imbalance (unfortunately severe data imbalance in GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS). In addition, oversampling seems to be an effective way to boost the performance of generative LLMs for this task.
BioMedLM did not achieve good performances on either dataset. It seems that it is not always “the bigger, the better” for domain-specific language models. The poor performance was possibly due to the limitations of the LoRA adaptor, which made it harder to fully adapt the large model to the special domain of gout flare CC texts, compared to BioGPT which was fully fine-tuned and adapted better. Indeed, choosing the “right” language model suitable for the downstream task is challenging.
3.2. Frozen LLMs as Feature Extractors
In this subcategory, we used LLMs to embed CC texts to dense feature vectors and used a SVM for classification. Table 6 shows the results. A SVM with BioGPT embeddings had the best performance on both datasets. It achieved an F1 score of 0.67 on GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS and 0.71 on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS. This indicates that this algorithm can effectively extract the relevant features from CC texts and classify them accurately.

Table 6.
Performances of Gout Flare Detection using LLM Embeddings.
It can be also observed that the SVM with BioMedLM embeddings and the SVM with PMC_Llama_7B embeddings have similar performance, but lower than the SVM with BioGPT embeddings. This may partially explain BioGPT’s good performance on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS. Again, bigger models do not always lead to better performance. On the other hand, while counterintuitive, the results are encouraging because healthcare institutions may invest less on smaller models to achieve competitive results in certain clinical applications. This has more impact on small organizations such as local general practices or community health centres, which are limited in computational resources.
3.3. Sparse Text Representation
This group of experiments involved the traditional feature engineering approach based on the tf-idf of n-gram features. Table 7 shows the results, where the baselines (discussed in the following paragraph) were lightly shaded. The best-performing settings were C = 0.15 (for SVM) and n = (1, 2) (meaning the combination of unigrams and bigrams) on GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS and C = 1.5 and n = (1, 2) on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS. The performances of the SVM could be deemed as promising. Though not beating the best-performing fine-tuned LLMs, the performances were stronger than other competitors, and more stable across datasets than other competitors, implying its better generalisability and better robustness, which echoes the findings in [40].

Table 7.
Performances of Gout Flare Detection using Sparse Text Representations.
In this section we have also included the results from the original publication of Osborne et al. [8], which are shaded. NAÏVE-GF predicts every mention of “gout” in CC texts as GF. SIMPLE-GF relies on the patient’s past medical history (PMH) (detectible by a compiled PMH gazetteer) and reported locations of potential GFs (based on a compiled location-gazetteer). If “gout” appears to the left of past medical history, or both a location keyword anywhere and “gout” appears in past medical history, then a GF alarm is triggered. BERT-GF is a fine-tuned BERT model for GF identification. See [8] for details of these baselines.
3.4. Comparative Analysis
Table 8 compares the results acquired from this study with the results obtained from the paper by Osborne et al. RoBERTa was the best-performing model on the GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS dataset, followed by BioELECTRA, showcasing the superiority of discriminative LLMs in classification tasks. The SVM with BioGPT embedding and tf-idf also performed well in relation to the other models. In the GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS dataset, the best was BioGPT which outperformed all the discriminative LLMs. This model responded very well to the fine-tuning and oversampling. This result was still outperformed by the SVM with tf-idf features. All our models outperformed the models used in the study by Osborne et al. (in grey) in both datasets. Overall, RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc, BioGPT, and tf-idf on n-grams were more robust models across datasets, particularly the latter. In addition, BioGPT was a more robust feature extractor when model parameters were frozen. Finally, this indicates a promising future direction in which to employ the strengths of different classifiers to achieve better recall while at the meantime keeping a better balance for precision.

Table 8.
Comparing the Performances of All Gout Flare Detection Methods.
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential and Limitations
The best performance on these datasets was achieved by the fine-tuned RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc on GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS and the fine-tuned BioGPT on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS (after handling class imbalance), outperforming other machine learning counterparts. This suggests that RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc and BioGPT can somehow capture the semantic features of CC texts and distinguish between GFs and non-flares in certain circumstances. However, the results also show that there is still a large gap between the performance of LLMs and the desired accuracy for GF detection. Meanwhile, large models seem to be more sensitive to or less robust to data imbalance and data size (recall that the number of positive cases in GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS is much smaller than in GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS).
Furthermore, the results also indicate that some models have a bias towards the negative class, which may affect their ability to predict the positive label. Therefore, more research is needed to address these challenges and improve the performance of LLMs for GF detection. One of the main challenges is the nature of the dataset. All the chief complaints contain the keyword “gout” (indicated by the 100% recall of the NAÏVE-GF baseline in Table 7 and Table 8) and most of them did not contain any clear indicator of gout flare. This makes it difficult for the models to learn the subtle differences between gout flares and non-flares. Upon analysing the ”Predicted” column of our test set (which contains the prediction of the human annotators based solely on the CC), we found that this is a challenging problem even for professional rheumatologists, which achieved less than 50% accuracy in our test set, if considering GF-UNK (unable to determine) as a failure in prediction.
Although the performance on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS was not as good as GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS, it was still an improvement compared to the baseline. We acknowledge that the dataset is challenging due to its data imbalance and small size, which contributed to the performance decline. Our approaches to tackling the data imbalance did improve the performance, but future work is still required to tackle this issue. One potential direction is the use of semi-supervised learning or weakly-supervised learning to utilize implicit knowledge from the large pool of unannotated data (i.e., not annotated by full chart review), which is left for our future work, if it proves difficult to encourage the medical community to share more high-quality annotated data.
4.2. Generalisability
A prominent phenomenon we observe is that the fine-tuned LLMs did not generalize well across datasets, in the sense that the best-performing model on one dataset (either 2019 or 2020) has a significant performance discrepancy on the other, which is especially obvious for the two best-performing deep learning models, RoBERTa-large-PM-M3-Voc and BioGPT. It is hard to conclude the causes for this. First of all, even in the natural language processing domains, the study of the capabilities and limitations of different types of LLMs is still an open domain with more hypotheses and debates than conclusions and consensus.
There is also possibility that the two models are good at capturing some specific patterns in one dataset but not the other. Indeed, the texts of the two datasets may have some different patterns that are worth digging deeper into (although this is beyond the scope of the current paper). This can be partially justified by some initial generalisation experiments we performed. We trained a SVM classifier using tf-df n-gram features using the optimised setting selected by five-fold cross-validation (see Section 3.3) on GOUT-CC-2019-CORPUS and found the test performance on GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS was only 0.46 F1; conversely, the generalisation performance was only 0.59. The most stable SVM classifier that was trained on one dataset did not generalize well to the other, and it looked that GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS had more challenges.
As stated before, the encouraging news is that SVMs seem to bring good performance and more stability [40], including SVMs trained using LLM embeddings as dense feature vectors. On the other hand, deep learning methods may be more sensitive to data volume, data size, and data imbalance, especially in the size of minority classes. This is especially obvious in GOUT-CC-2020-CORPUS where the imbalance ratio is close to 1:10. Therefore, random up-sampling was adopted. It is, however, unclear whether this sampling-based rebalancing strategy led to the performance discrepancy. On the contrary, SMOTEing using LLM embeddings seems to be more stable. However, the results in general also imply the possibility of using ensemble learning for training a more robust classifier because most baseline methods achieved reasonable performance [45].
Finally, we noticed that the 2020 dataset also included a huge number of unannotated CC texts. There is thus potential for us to apply semi-supervised learning [46] or weakly-supervised learning techniques [47]. More robust performance and better generalizability might be achieved by eliciting implicit knowledge from unannotated CC texts through learning from weakly-assigned pseudo-labels. Most of the discussions above, indeed, are part of future directions the authors would like to explore in more depth.
4.3. Ethical Issues
There are some potential ethical issues needing discussion. First of all, the dataset was compiled and shared by the authors of the original paper on PhysioNet [19]. The creation and publication of the dataset conformed to the national ethical requirements of the USA. The dataset is anonymised, and there is no information in the dataset that can be used to re-identify patients.
The method discussed in this study has by now proved its potential in “identifying” a large portion of patients who were indeed diagnosed with a gout flare after a complete chart review (and other diagnosis methods). This is encouraging because human annotators failed to make decisions for 127 out of 264 cases of the 2020 dataset. We also “evaluated” human performance on the remaining 137 cases, which was around 0.7755, similar to our SVM algorithms. Generally, we believe that the algorithms do not aim to replace ED doctors but to complement them. As such, the ultimate aim is to set alarms to as many patients at high risk of gout flare as possible while maintaining reasonably good precision.
4.4. Future Directions
We have discussed in detail about potential future directions in Section 4.2 when discussing ways of improving classifier generalizability. This section includes some further discussions from a few additional angles.
Full fine-tuning and distributed computing: While parameter-efficient fine-tuning, specifically LoRA, was applied in this study due to hardware constraints and the models’ size, pursuing full fine-tuning would enhance the results of the models. Implementing distributed computing is necessary to apply full fine-tuning. Due to the very large size of the models, this process requires distributing the model load across different GPUs to perform the calculations. This strategy would enable more comprehensive fine-tuning, potentially leading to an increase in model performance.
Enhanced dataset quality and size: With such a limited number of samples, the models cannot be properly trained, validated, and tested. To address this, more samples or whole new datasets must be acquired to test the models effectively.
Ensemble learning for enhanced embeddings: A promising route is the utilization of deep learning models to create an ensemble that enhances embeddings before their application in text classification. This strategy could potentially enhance the information captured by the embeddings, thereby leading to improved classification outcomes.
Task-specific continuous pre-training: Another possible direction is to use unsupervised learning to continuously pre-train the LLMs on the task-specific data, i.e., the chief complaint texts. This could help the models to adapt to the domain and the vocabulary, and to tackle the particular writing styles of CC notes in this task.
5. Conclusions
Overall, this study highlights the potential of generative LLMs for classification tasks, achieving results comparable to discriminative models. Additionally, the models also have shown potential as feature extractors for classification tasks, even without fine-tuning, due to their ability to understand contextual information and produce rich contextual embeddings. Despite the results between the two types of models being comparable, the computational requirements to perform the same task are much greater when using the generative LLMs employed in this study. Similar or superior results can be obtained using much smaller discriminative models. Still, this research highlights the importance of using the domain-specific variants of the models when the text contains specialized and out-of-word vocabulary. Our results are important because they demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of using generative LLMs for gout flare detection from chief complaints, which is a novel and challenging task that can benefit both clinical practice and research. Furthermore, our approaches can potentially improve the quality of care for gout patients, a large portion of whom could now receive proper and in-time follow-up after an ED visit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.J. and A.D.; methodology, X.J., L.L.O., A.N.B., P.K. and A.D.; software, L.L.O., A.N.B., P.K. and X.J.; validation, L.L.O. and X.J.; investigation, L.L.O., A.N.B., P.K. and X.J.; resources, X.J.; data curation, L.L.O.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L.O. and X.J.; writing—review and editing, L.L.O., X.J. and A.D.; supervision, X.J. and A.D.; project administration, X.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The APC was waived.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset the current paper used is a public dataset, which is available through PhysioNet at https://doi.org/10.13026/96v3-dw72 accessed on 29 February 2024.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- National Institute of Health. Gout (Health Topic). Available online: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/gout (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- He, Q.; Mok, T.N.; Sin, T.H.; Yin, J.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Ming, W.K.; Feng, B. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Gout From 1990 to 2019: Age-Period-Cohort Analysis With Future Burden Prediction. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2023, 9, e45943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Yokose, C.; Rai, S.K.; Pillinger, M.H.; Choi, H.K. Contemporary Prevalence of Gout and Hyperuricemia in the United States and Decadal Trends: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, C.; Ma, B.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Han, C.; Liu, T.; Li, Y. Global, regional and national burdens of gout in the young population from 1990 to 2019: A populationbased study. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.D.; Terkeltaub, R.; Khanna, D.; Singh, J.; Sarkin, A.; Shieh, M.; Kavanaugh, A.; Lee, S.J. Gout disease specific quality of life and the association with gout characteristics. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2010, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Cross, M.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Hoy, D.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Mansournia, M.A.; et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Years Lived With Disability Due to Gout and Its Attributable Risk Factors for 195 Countries and Territories 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Yu, S. Time Trends, Predictors, and Outcome of Emergency Department Use for Gout: A Nationwide US Study. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.D.; Booth, J.S.; O’Leary, T.; Mudano, A.; Rosas, G.; Foster, P.J.; Saag, K.G.; Danila, M.I. Identification of Gout Flares in Chief Complaint Text Using Natural Language Processing. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2020, 2020, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hossain, E.; Rana, R.; Higgins, N.; Soar, J.; Barua, P.D.; Pisani, A.R. Natural Language Processing in Electronic Health Records in relation to healthcare decision-making: A systematic review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Rashid, N.; Wu, Y.L.; Koblick, R.; Lin, A.T.; Levy, G.D.; Cheetham, T.C. Using Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning to Identify Gout Flares From Electronic Clinical Notes. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, (NAACL-HLT’2019), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M.F., Lin, H., Eds.; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 1877–1901. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2020/hash/1457c0d6bfcb4967418bfb8ac142f64a-Abstract.html (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Xu, B.; Gil-Jardiné, C.; Thiessard, F.; Tellier, E.; Avalos, M.; Lagarde, E. Pre-training A Neural Language Model Improves The Sample Efficiency of an Emergency Room Classification Model. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third International FLAIRS Conference (FLAIRS-33), North Miami Beach, FL, USA, 17–20 May 2020; Available online: https://aaai.org/papers/264-flairs-2020-18444/ (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Veladas, R.; Yang, H.; Quaresma, P.; Gonçalves, T.; Vieira, R.; Sousa Pinto, C.; Martins, J.P.; Oliveira, J.; Cortes Ferreira, M. Aiding Clinical Triage with Text Classification. In Progress in Artificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Marreiros, G., Melo, F.S., Lau, N., Lopes Cardoso, H., Reis, L.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12981, pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Yu, G. Automatic Keyphrase Extraction from Scientific Chinese Medical Abstracts Based on Character-Level Sequence Labeling. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2021, 6, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Bert-Based Chinese Medical Keyphrase Extraction Model Enhanced with External Features. In Towards Open and Trustworthy Digital Societies, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ke, H.R., Lee, C.S., Sugiyama, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 13133, pp. 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Erofeev, G.; Sorokina, I.; Gladkoff, S.; Nenadic, G. Investigating Massive Multilingual Pre-Trained Machine Translation Models for Clinical Domain via Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 5th Clinical Natural Language Processing Workshop (ClinicalNLP’2019), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 7 June 2019; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Sun, Z.; Idnay, B.; Nestor, J.G.; Soroush, A.; Elias, P.A.; Xu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Durrett, G.; Rousseau, J.F.; et al. Evaluating Large Language Models on Medical Evidence Summarization. npj Digit. Med. 2003, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, J.D.; O’Leary, T.; Mudano, A.; Booth, J.; Rosas, G.; Peramsetty, G.S.; Knighton, A.; Foster, J.; Saag, K.; Danila, M.I. Gout Emergency Department Chief Complaint Corpora, version 1.0; PhysioNet: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.D.; Raghavan, P.; Schütze, H. Introduction to Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30, pp. 5998–6008. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Lewis, P.; Ott, M.; Du, J.; Stoyanov, V. Pretrained Language Models for Biomedical and Clinical Tasks: Understanding and Extending the State-of-the-Art. In Proceedings of the 3rd Clinical Natural Language Processing Workshop (ClinicalNLP’2020), Online, 19 November 2020; pp. 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakarajan, K.R.; Kundumani, B.; Sankarasubbu, M. BioELECTRA: Pretrained Biomedical Text Encoder using Discriminators. In Proceedings of the 20th Workshop on Biomedical Language Processing (BioNLP’2021), Online, 16 August 2021; pp. 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Gan, R.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Yu, S. BioBART: Pretraining and Evaluation of A Biomedical Generative Language Model. In Proceedings of the 21st Workshop on Biomedical Language Processing (BioNLP’2022), Dublin, Ireland, 6 May 2022; pp. 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Clark, K.; Luong, M.T.; Le, Q.V.; Manning, C.D. ELECTRA: Pre-training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather Than Generators. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR’2020), Online, 27–30 April 2020; Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=r1xMH1BtvB (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL’2020), Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.W.H.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Anthony Celi, L.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Sun, L.; Xia, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhang, S.; Poon, H.; Liu, T.Y. BioGPT: Generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lin, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W. PMC-LLaMA: Towards Building Open-source Language Models for Medicine. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.10415. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.14454 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.0928. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2307.09288 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Gao, L.; Biderman, S.; Black, S.; Golding, L.; Hoppe, T.; Foster, C.; Phang, J.; He, H.; Thite, A.; Nabeshima, N.; et al. The Pile: An 800GB Dataset of Diverse Text for Language Modeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.00027. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00027 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Lo, K.; Wang, L.L.; Neumann, M.; Kinney, R.; Weld, D. S2ORC: The Semantic Scholar Open Research Corpus. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL’2020), Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 4969–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR’2019), New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019; Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Bkg6RiCqY7 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR’2021), Online, 3–7 May 2021; Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=nZeVKeeFYf9 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Aghajanyan, A.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Gupta, S. Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (ACL-IJCNLP’2020), Online, 1–6 August 2020; pp. 7319–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messem, A.V. Support vector machines: A robust prediction method with applications in bioinformatics. Handb. Stat. 2020, 43, 391–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyran, K.A.; Kawulok, J.; Kawulok, M.; Stawarz, M.; Michalak, M.; Pietrowska, M.; Widłak, P.; Polańska, J. Support Vector Machines in Biomedical and Biometrical Applications. In Emerging Paradigms in Machine Learning. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Ramanna, S., Jain, L., Howlett, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cheng, X. Weighting Methods for Rare Event Identification from Imbalanced Datasets. Front. Big Data 2021, 4, 715320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K. How to Improve Class Imbalance using Class Weights in Machine Learning? Analytics Vidhya. Available online: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2020/10/improve-class-imbalance-class-weights (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdennour, G.B.; Gasmi, K.; Ejbali, R. Ensemble Learning Model for Medical Text Classification. In Web Information Systems Engineering—WISE 2023; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Zhang, F., Wang, H., Barhamgi, M., Chen, L., Zhou, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.M.; Berton, L. A review of semi-supervised learning for text classification. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 9401–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sohn, S.; Liu, S.; Shen, F.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, E.J.; Amin, S.; Liu, H. A clinical text classification paradigm using weak supervision and deep representation. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).