A Stochastic Estimation Framework for Yearly Evolution of Worldwide Electricity Consumption
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We develop an autoregression process scheme that preserves an optimal degree of regression and prediction accuracy with minimum modeling error for the collected electricity data records.
- We analyze the experimental findings of the original dataset in conjunction with the forecasted datasets to demonstrate the importance and efficiency of the established scheme.
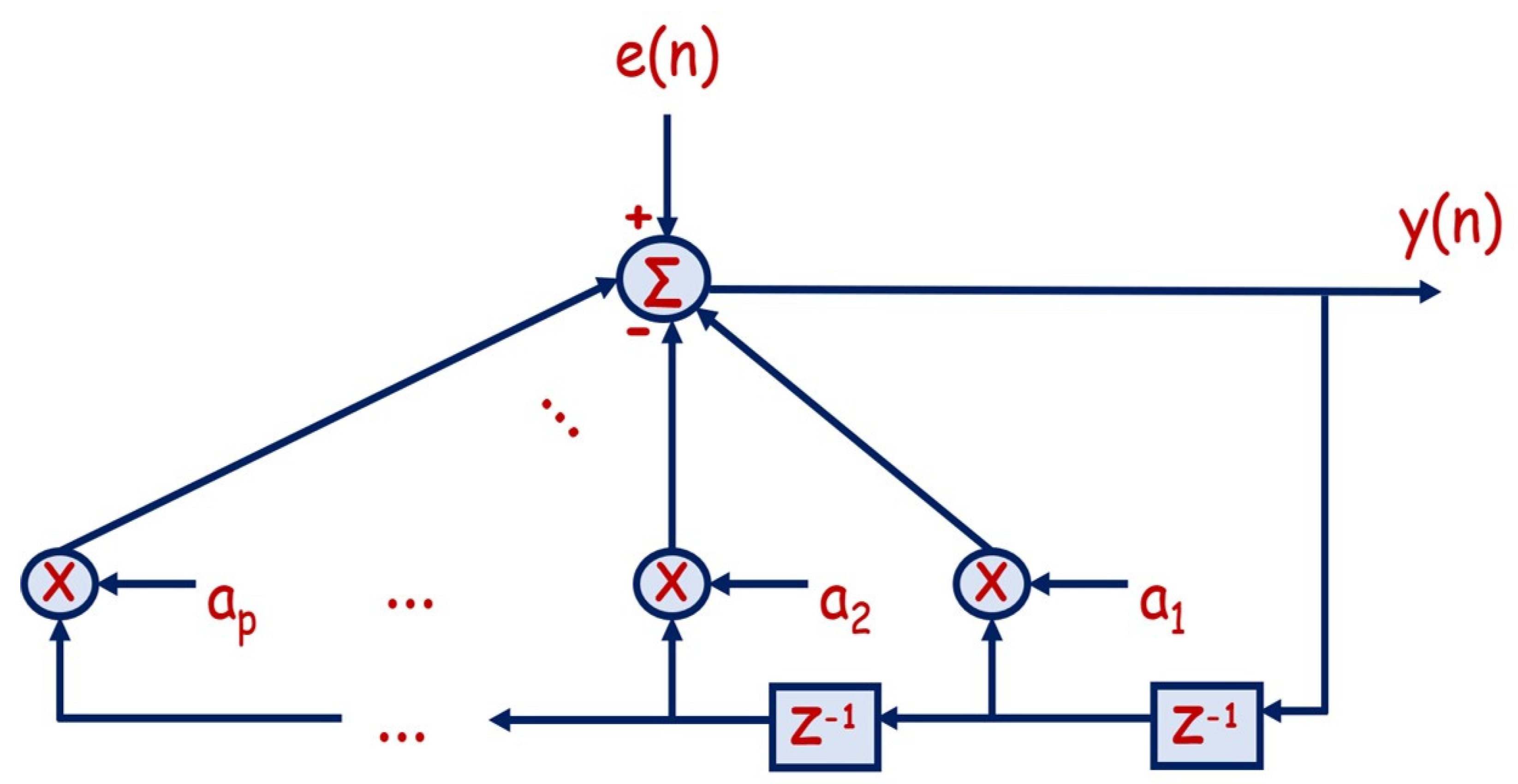
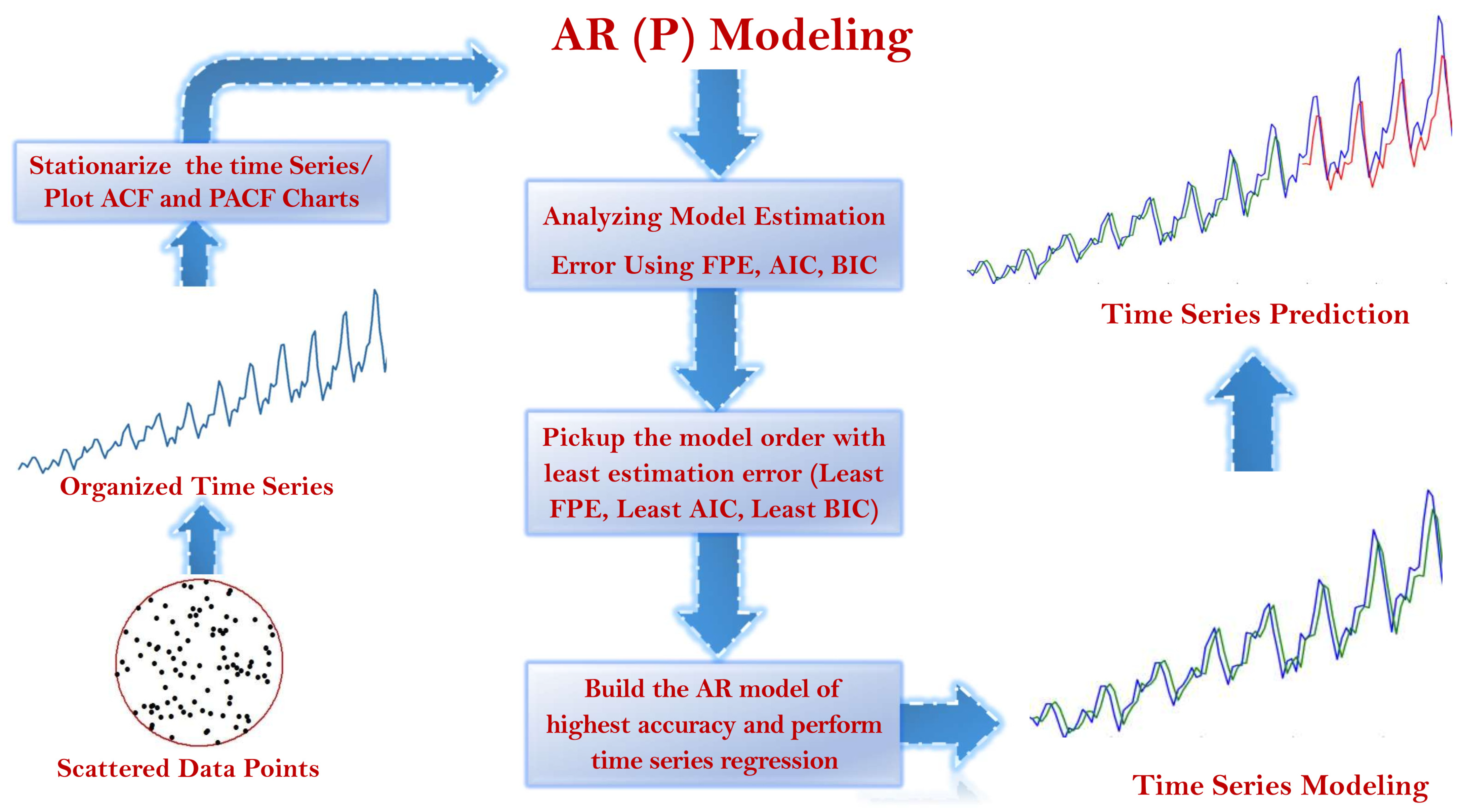
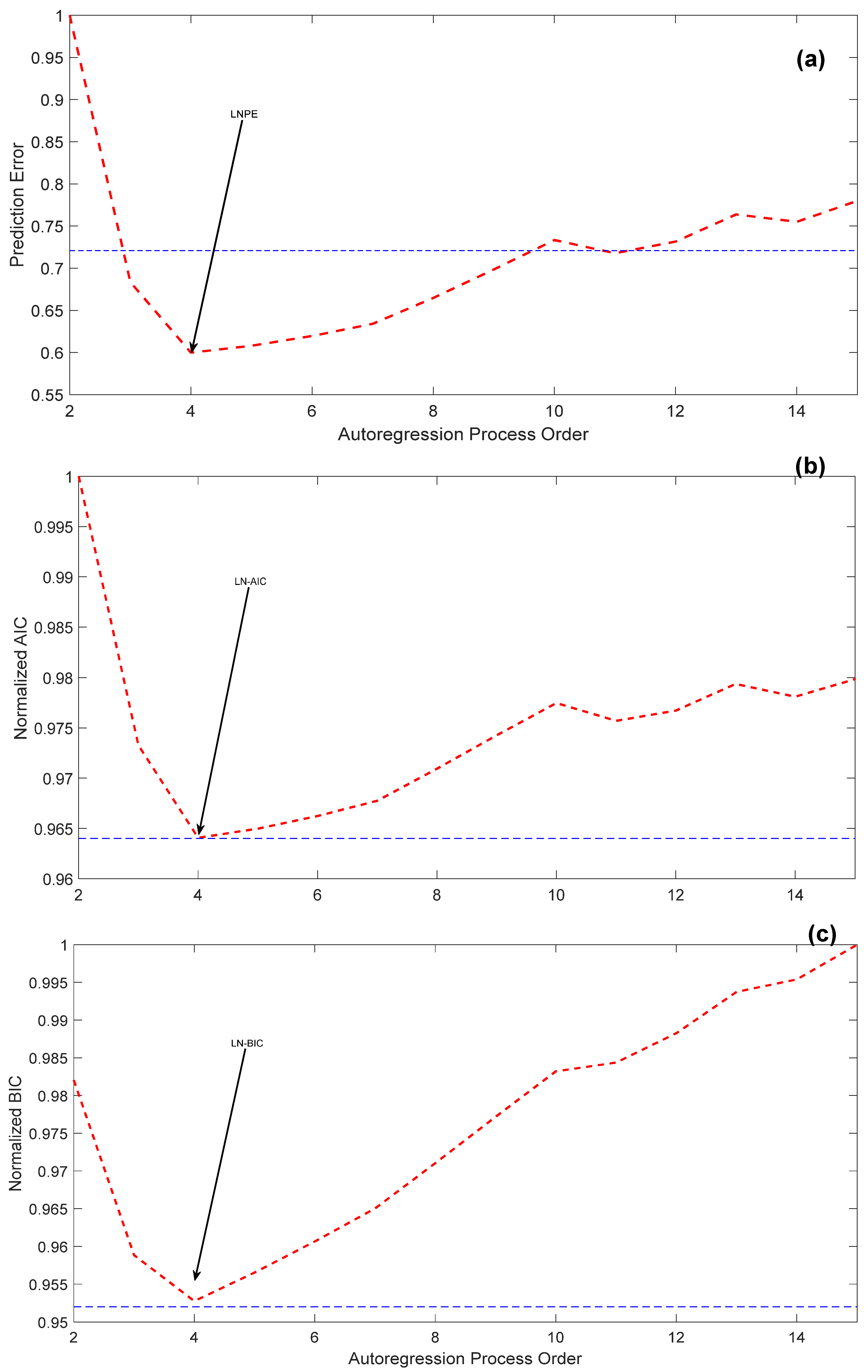
2. Autoregressive AR(p) Process Modeling
- The first-order AR process is obtained with one parameter according to the following formula:
- The second-order AR process is obtained with two parameters according to the following formula:
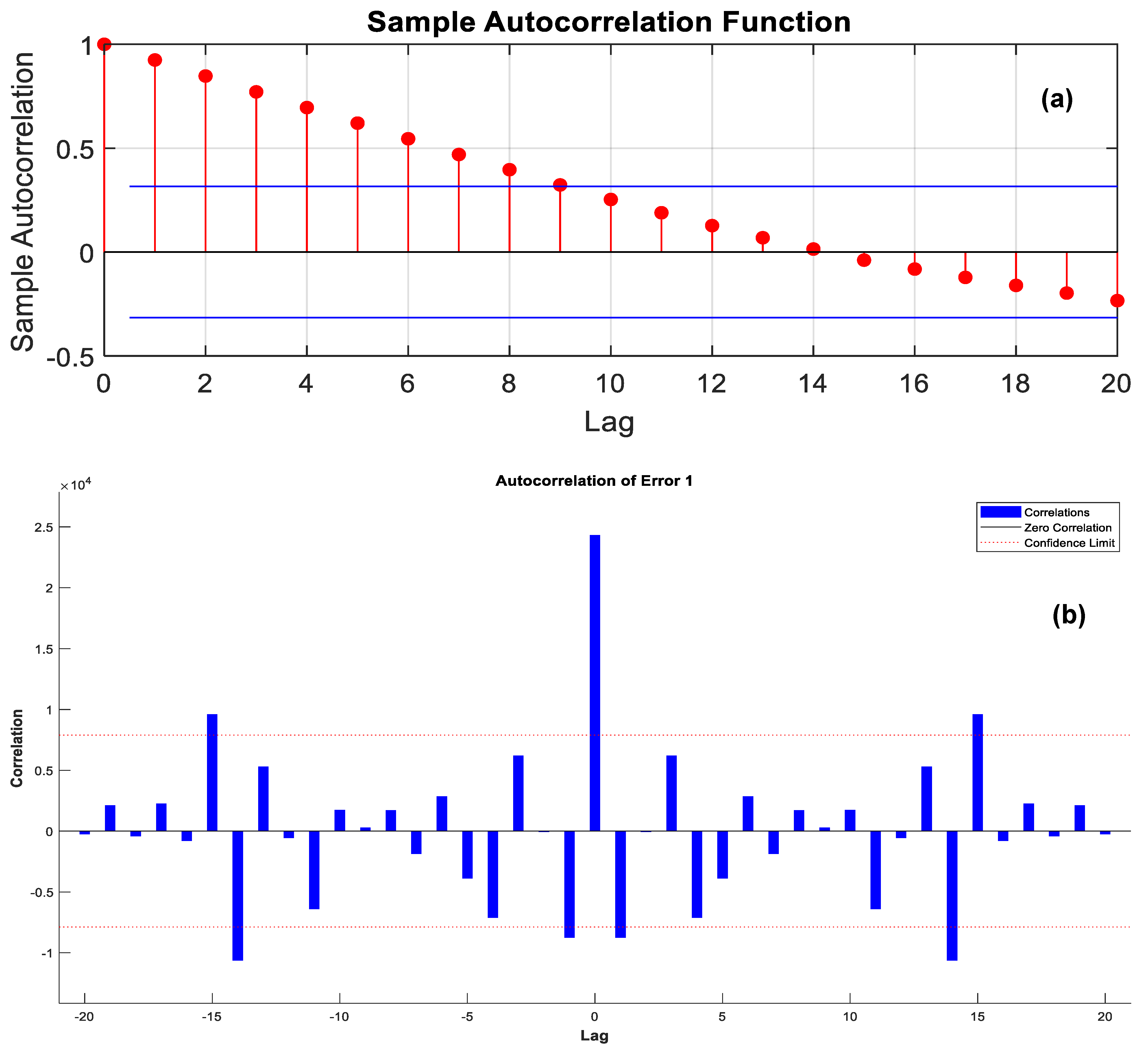
- The pth order AR process is obtained with parameters according to the following formula:where y(n) is the original dataset, is the estimated dataset, and e(n) is the accumulative autoregression error. Actually, to maintain the best autoregression process for dataset interpolation and extrapolation/estimation, the optimum autoregression order needs to be reached, which can be attained only when the accumulative autoregression/perdition error is minimized. Consequently, solving the computational minimization problem for the accumulative autoregression error can lead to computing the parameters for the autoregression process using autocorrelation function (ACF) Ryy(k) as follows:
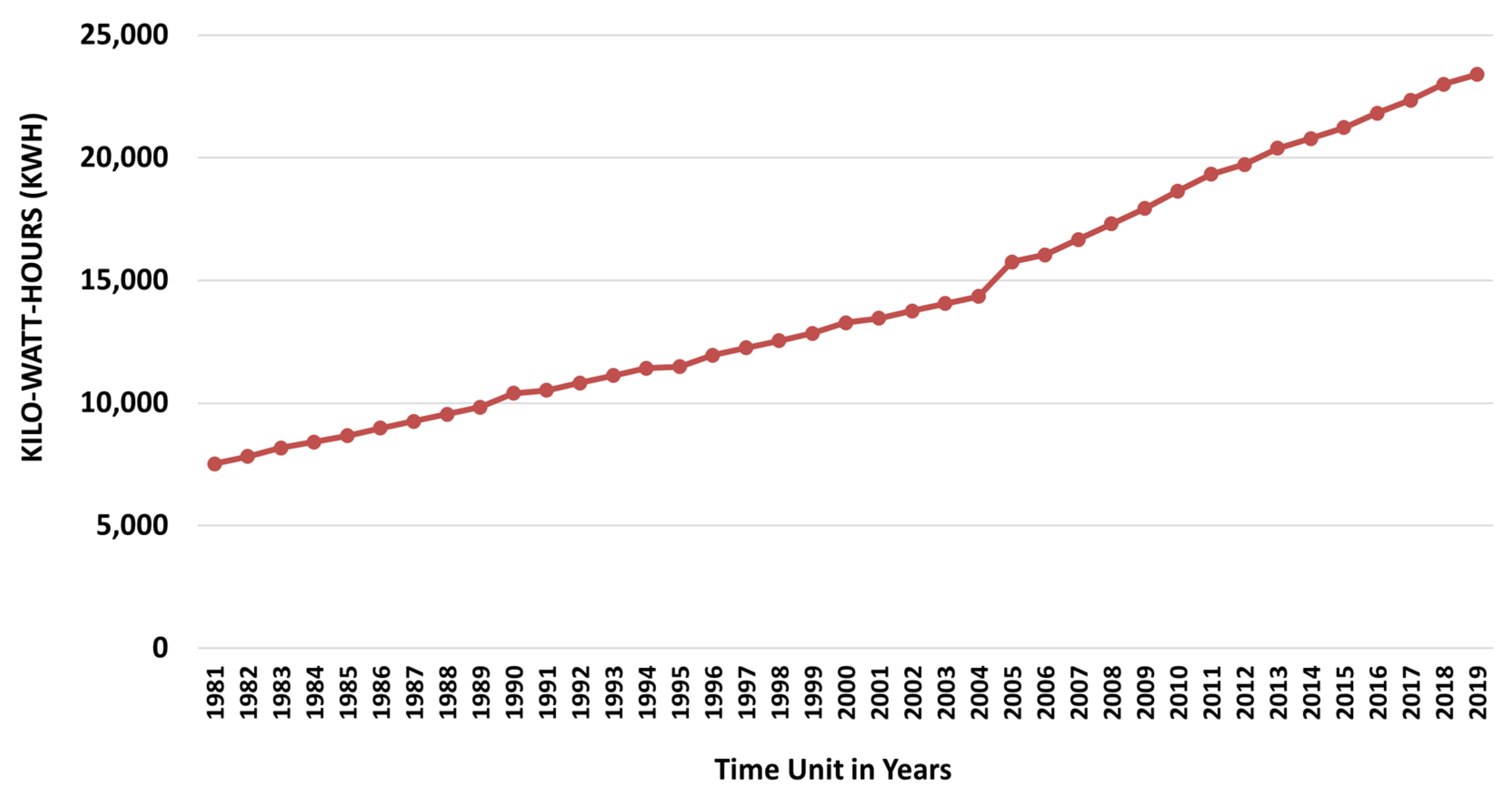
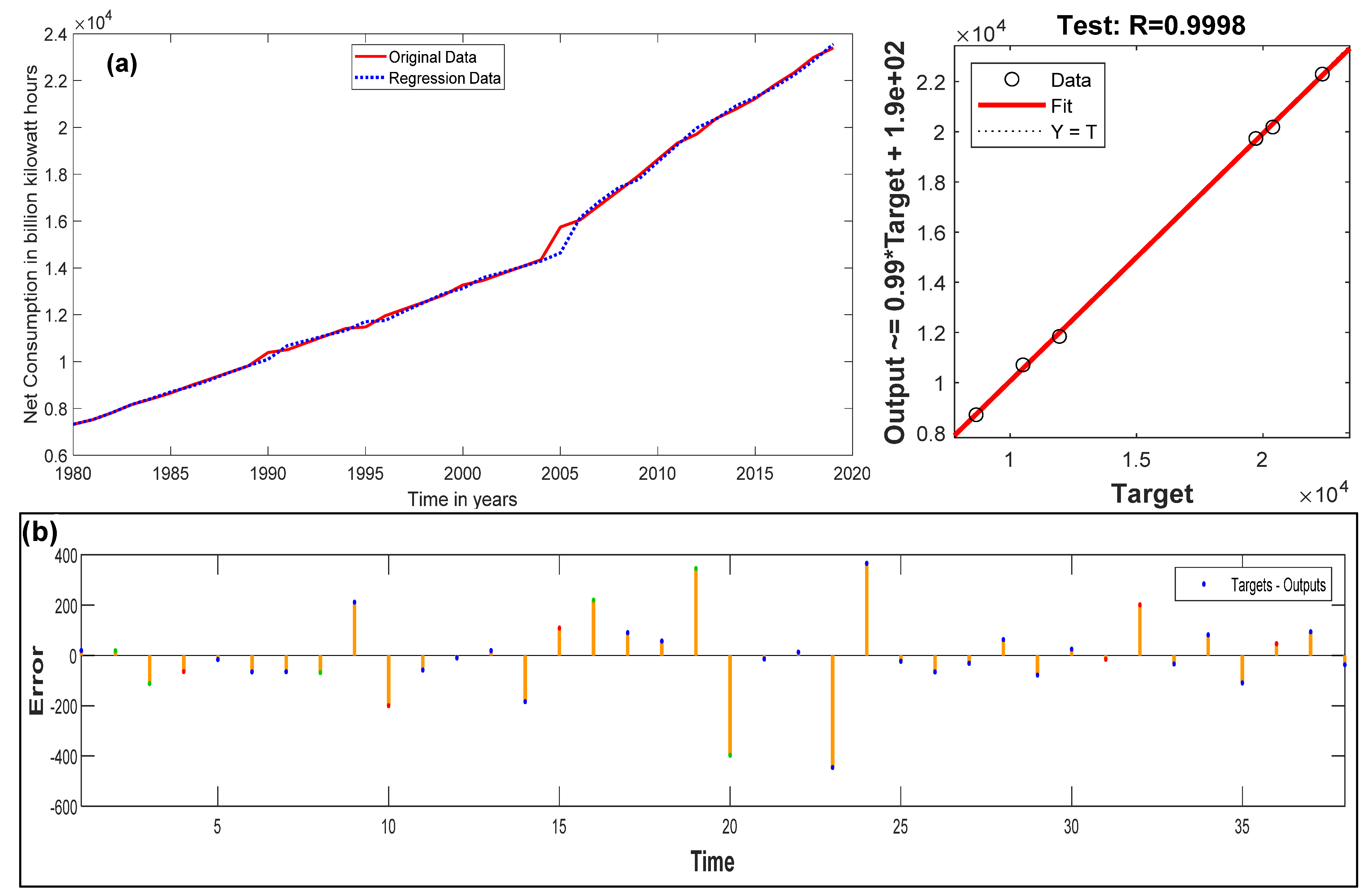
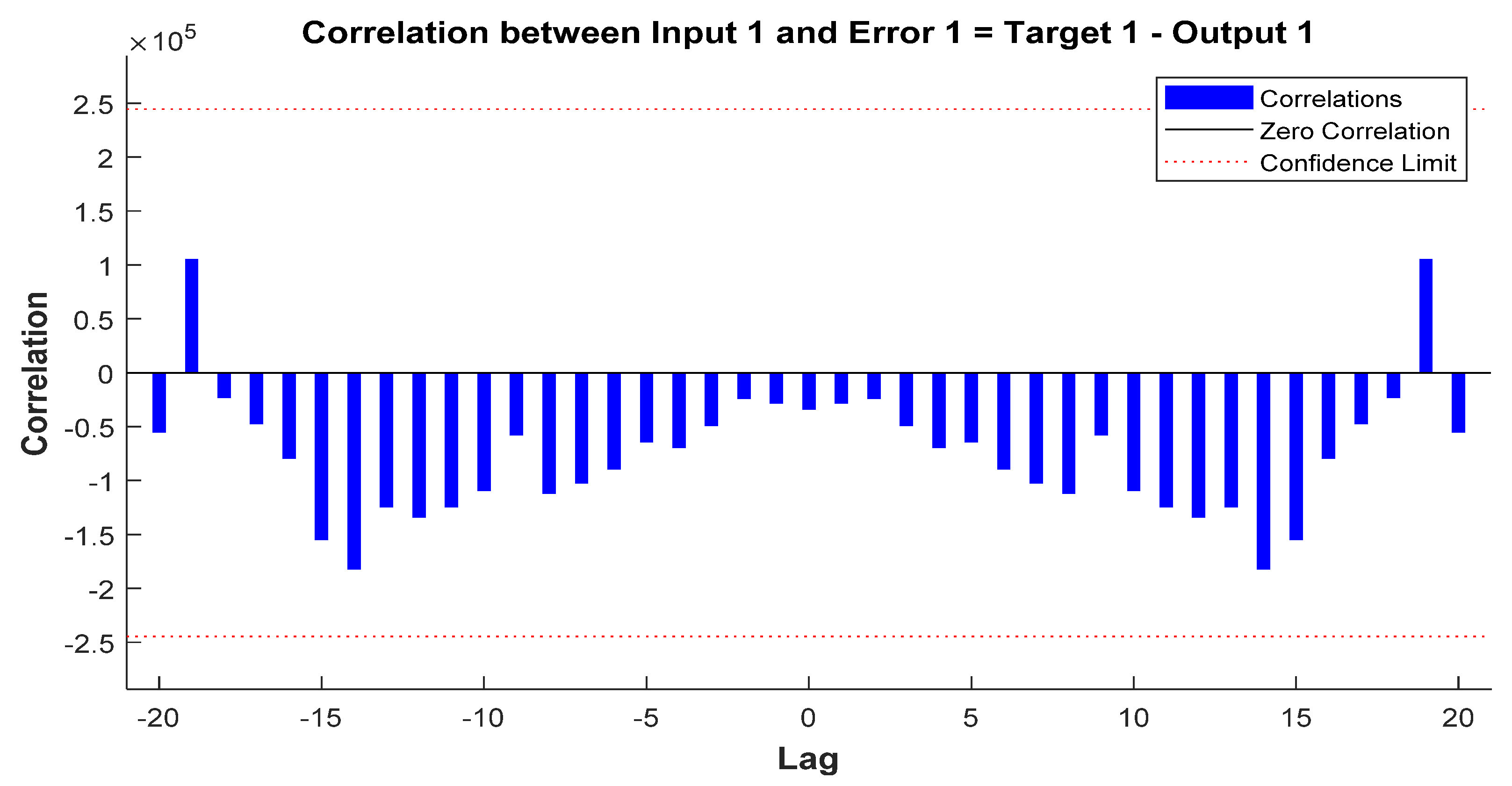
3. Electricity Consumption Estimation Schemes
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.Y. Global Energy Internet; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency-IEA. Electricity Information: Overview; Statistics Report; International Energy Agency-IEA: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen, N. Electricity consumption worldwide in 2017, by select country (in terawatt hours). Statista 2020, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen, N. Net consumption of electricity worldwide from 1980 to 2017(in billion kilowatt hours). Statista 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Enerdata. Global Energy Statistical Yearbook 2020: Electricity Domestic Consumption. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. Global Energy Development: The Reality and Challenges. In Global Energy Interconnection; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; Smadi, M.A. Parametric prediction study of global energy-related carbon dioxide emissions. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–13 June 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Korolkiewicz, M.; Agrawal, M.; Boland, J. Forecasting solar radiation on an hourly time scale using a Coupled AutoRegressive and Dynamical System (CARDS) model. Sol. Energy 2013, 87, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; Mao, Q.; al Nasr, K. Forecasting the Number of Monthly Active Facebook and Twitter Worldwide Users Using ARMA Model. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 15, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydia, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Selvakumar, A.I.; Kumar, G.E.P. Linear and non-linear autoregressive models for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; Tawalbeh, L. Autoregressive Modeling and Prediction of Annual Worldwide Cybercrimes for Cloud Environments. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Irbid, Jordan, 11–13 June 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, A.; Rajabioun, T.; Ioannou, P.A. Traffic Flow Prediction for Road Transportation Networks with Limited Traffic Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; Al Nasr, K. Supervised Regression Study for Electron Microscopy Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 2661–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, L.G.B.; Cuéllar, M.P.; Calvo-Flores, M.D.; Jiménez, M.D.C.P. An Application of Non-Linear Autoregressive Neural Networks to Predict Energy Consumption in Public Buildings. Energies 2016, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; al Nasr, K. Forecasting Model for the Annual Growth of Cryogenic Electron Microscopy Data. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12029, pp. 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nogales, F.; Contreras, J.; Conejo, A.; Espinola, R. Forecasting next-day electricity prices by time series models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 17, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.; Franca, P.M.; Lyra, C. Two-level network design with intermediate facilities: An application to electrical distribution systems. Omega 2011, 39, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutun, S.; Chou, C.-A.; Canıyılmaz, E. A new forecasting framework for volatile behavior in net electricity consumption: A case study in Turkey. Energy 2015, 93, 2406–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoos, A.; Hemmati, M.; Abdoos, A.A. Short term load forecasting using a hybrid in-telligent method. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 76, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-C. Electricity consumption prediction using a neural-network-based grey forecasting approach. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2017, 68, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Al-Haija, Q.; Tarayrah, M.; Enshasy, H.M. Time-Series Model for Forecasting Short-term Future Additions of Renewable Energy to Worldwide Capacity. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2020 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry: Way Towards a Sustain-able Economy (ICDABI), Sakheer, Bahrain, 26–27 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Hsu, L.C. Using genetic algorithms grey theory to forecast high technology industrial output. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 195, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, D.; Liu, J.; Qin, X. A Grey Prediction Approach to Forecasting Energy Demand in China. Energy Sources Part A Recov. Util. Environ. Eff. 2010, 32, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Tong, L.I. Forecasting energy consumption using a grey model improved by incorporating genetic programming. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.J.; Ma, Y.D.; Song, Z.L.; Ying, J. Forecasting the Energy Consumption of China by the Grey Prediction Model. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2012, 7, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.C.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, W.C. Forecasting short-term electricity consumption using the adaptive grey-based approach—An Asian case. Omega 2012, 40, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.G.; Manolakis, D.K. Digital Signal Processing. In Pearson, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 100131873741. Available online: https://www.pearson.com/us/higher-education/program/Proakis-Digital-Signal-Processing-4th-Edition/PGM258227.html (accessed on 22 March 2019).
- Gray, R.M. Toeplitz and Circulant Matrices: A Review. Found. Trends Commun. Inf. Theory 2005, 2, 155–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasr, K.; Abu-Al-Haija, Q. Forecasting the Growth of Structures from NMR and X-Ray Crystallography Experiments Released Per Year. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 19, 2040004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palachy, S. Detecting stationarity in time series data. Medium Towards Data Sci. 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, J. Probabilistic Model Selection with AIC, BIC, and MDL; in Probability; Machine Learning Mastery: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Niedwiecki, M.; Cioek, M. Akaike’s final prediction error criterion revisited. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 July 2017. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Al-Haija, Q. A Stochastic Estimation Framework for Yearly Evolution of Worldwide Electricity Consumption. Forecasting 2021, 3, 256-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast3020016
Abu Al-Haija Q. A Stochastic Estimation Framework for Yearly Evolution of Worldwide Electricity Consumption. Forecasting. 2021; 3(2):256-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast3020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Al-Haija, Qasem. 2021. "A Stochastic Estimation Framework for Yearly Evolution of Worldwide Electricity Consumption" Forecasting 3, no. 2: 256-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast3020016
APA StyleAbu Al-Haija, Q. (2021). A Stochastic Estimation Framework for Yearly Evolution of Worldwide Electricity Consumption. Forecasting, 3(2), 256-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast3020016





