Benford’s Law for Telemetry Data of Wildlife
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistics
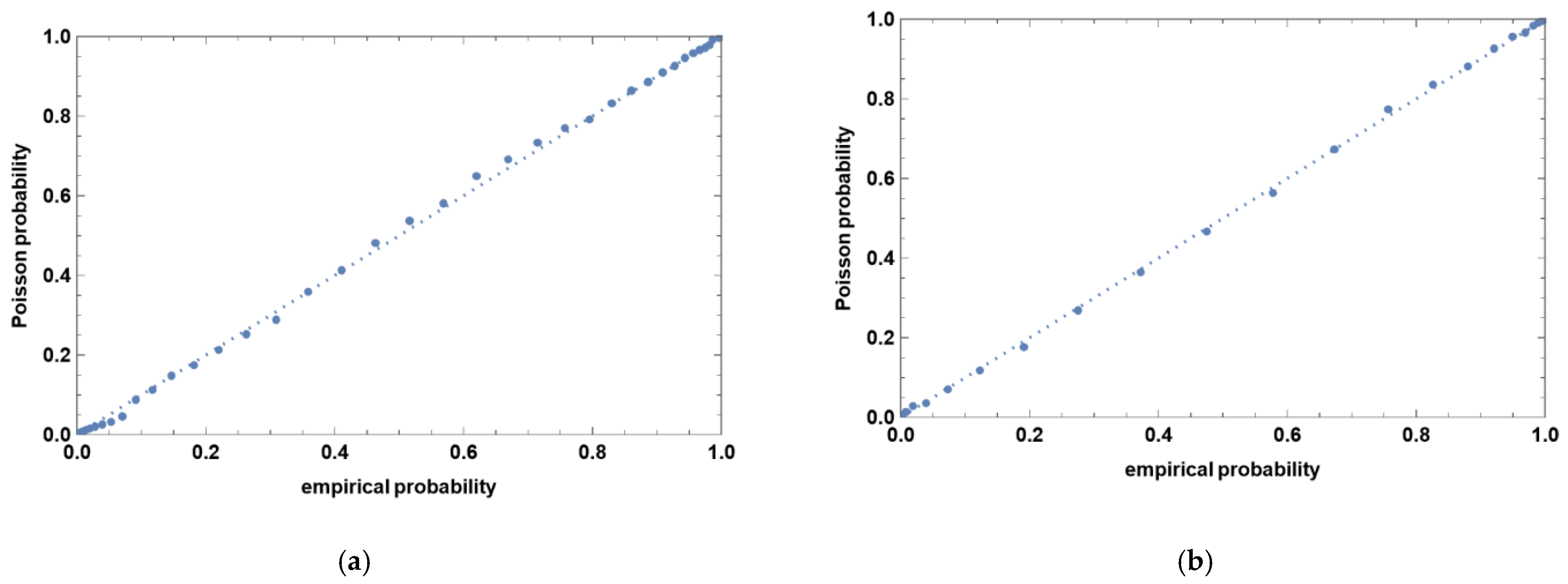
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newcomb, S. Note on the frequency of use of different digits in natural numbers. Am. J. Math. 1881, 4, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benford, F.A. The law of anomalous numbers. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1938, 78, 551–572. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, T.P.; Berger, A. Benford Online Bibliography. Available online: www.benfordonline.net/ (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Nigrini, M.J. Forensic Analytics: Methods and Techniques for Forensic Accounting Investigations; Wile: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Varian, H.R. Benford’s Law. Am. Stat. 1970, 26, 65–66. [Google Scholar]
- Carslaw, C.A.P.N. Anomalies in Income Numbers: Evidence of Goal Oriented Behavior. Account. Rev. 1988, 63, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Nigrini, M.J. Taxpayer compliance application of Benford’s law. J. Am. Tax. Assoc. 1996, 18, 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Akinadewo, I.S.; Akinkoye, E.Y. Tax Evasion Detection in Nigeria: Analysis of the Specific Forensic Accounting Techniques Used. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2020, 11, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Beber, B.; Scacco, A. What the Numbers Say: A Digit-Based Test for Election Fraud. Political Anal. 2012, 20, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyse, M.; George, S.L.; Evans, S.; Geller, N.L.; Edler, L.; Hutton, J. The Role of Biostatistics in the Prevention, Detection and Treatment of Fraud in Clinical Trials. Stat. Med. 1999, 18, 3435–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindls, R.; Hronová, S. Benford’s Law and Possibilities for Its Use in Governmental Statistics. Statistika 2015, 95, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Ma, B.Q. Empirical mantissa distributions of pulsars. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 33, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, J.C. Regularities and symmetries in atomic structure and spectra. High Energy Density Phys. 2013, 9, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arita, M. Scale-freeness and biological networks. J. Biochem. 2005, 138, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanario, J.M.; Coslado, M.A. Benford’s law and citations, articles and impact factor of scientific journals. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margellou, A.G.; Pomonis, P.J. Benford’s law, Zipf’s law and the pore properties in solids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 292, 109735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsburg, D. Digit Preference in the Bible. Chance 1997, 10, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Camponovo, M.; Moreno, J.; Idrovo, A.J.; Páez, M.; Achkar, M. Monitoring the Paraguayan epidemiological dengue surveillance system using Benford’s law. Biomédica 2016, 36, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambridge, M.; Jackson, A. National COVID numbers—Benford’s law looks for errors. Nature 2020, 581, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.P. The significant-digit phenomenon. Am. Math. Mon. 1995, 102, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.P. A statistical derivation of the significant-digit law. Stat. Sci. A Rev. J. Inst. Math. Stat. 1995, 10, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Hill, T.P. An Introduction to Benford’s Law; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, H.A.; Leuenberger, C. Benford’s law for exponential random variables. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2003, 63, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, D.; Lemons, N.; Peter, W. First Digit Oscillations. Stats 2021, 4, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietronero, L.; Tosatti, E.; Tosatti, V.; Vespignanic, A. Explaining the uneven distribution of numbers in nature: The laws of Benford and Zipf. Phys. A 2001, 293, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W. The promises and pitfalls of Benford’s law. Significance 2016, 13, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.M.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; da Luz, M.G.E.; Raposo, E.P.; Stanley, H.E. Optimizing the success of random searches. Nature 1999, 401, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårell, A.; Ball, J.; Hofgaard, A. Foraging and movement paths of female reindeer: Insights from fractal analysis, correlated random walks, and Lévy flights. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürger, K. Lévy Processes and Benford’s Law. In Benford’s Law: Theory and Applications; Miller, S.J., Ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 135–173. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, A.M.; Phillips, R.A.; Watkins, N.W.; Freeman, M.P.; Murphy, E.J.; Afanasyev, V.; Buldyrev, S.V.; da Luz, M.G.E.; Raposo, E.P.; Stanley, H.E.; et al. Revisiting Lévy flight search patterns of wandering albatrosses, bumblebees and deer. Nature 2007, 449, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Bunimovich, L.A.; Hill, T.P. One-dimensional dynamical systems and Benford’s law. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 2004, 357, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brähler, G.; Bensmann, M.; Jakobi, H.R. Das Benfordsche Gesetz und Seine Anwendbarkeit bei der Digitalen Prüfung von Fahrtenbüchern; Ilmenauer Schriften zur Betriebswirtschaftslehre; Technische Universität: Ilmenau, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sambridge, M.; Tkalčić, H.; Jackson, A. Benford’s Law in the natural sciences. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L22301–L22306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesberger, P.; Hackländer, K. Integrales Rotwildmanagement: Strategievernetzung Zwischen Forst-, Land-, Jagd- und Tourismuswirtschaft; FFG Project Number 848464; Final Project Report; BOKU: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pröger, L. Anwendbarkeit des Benford-Gesetzes auf Bewegungsdaten von Wildtieren. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Mathematics, Department of Integrative Biology and Biodiversity Research, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Defense. Its definition and relationships with local geodetic systems. In World Geodetic System 1984; Technical Report; DoD: Rockville, MD, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram Research Inc. Mathematica; Version 12.3; Wolfram Research Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lindley, D.V. A Statistical Paradox. Biometrika 1957, 44, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossovsky, A.E. On the Mistaken Use of the Chi-Square Test in Benford’s Law. Stats 2021, 4, 419–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrini, M.J. Audit Sampling Using Benford’s Law: A Review of the Literature with Some New Perspectives. J. Emerg. Technol. Account. 2017, 14, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druică, E.; Oancea, B.; Vâlsan, C. Benford’s law and the limits of digit analysis. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2018, 31, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueti, R.; Lupi, C. Some New Tests of Conformity with Benford’s Law. Stats 2021, 4, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, P.J.; Götze, F.; van Zwet, W.R. Resampling Fewer Than n Observations: Gains, Losses, and Remedies for Losses. Stat. Sin. 1997, 7, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, F. Contingency table involving small numbers and the χ2 test. Suppl. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1934, 1, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.; Cleveland, W.; Kleiner, B.; Tukey, P. Graphical Methods for Data Analysis; Chapman & Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, R.B.; Stephens, M.A. Goodness-of-Fit.-Techniques; Taylor & Francis (Informa): London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Clopper, C.; Pearson, E.S. The use of confidence or fiducial limits illustrated in the case of the binomial. Biometrika 1934, 26, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joenssen, D.W. Testing for Benford’s Law: A Monte Carlo Comparison of Methods; Working Paper; No. 2545243; SSRN: Rochester, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Digit: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed: | 21,473 | 13,461 | 9516 | 7669 | 5941 | 4691 | 3976 | 3576 | 3090 |
| Theoretical: | 22,093.5 | 12,923.8 | 9169.6 | 7112.5 | 5811.4 | 4913.4 | 4256.2 | 3754.2 | 3358.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pröger, L.; Griesberger, P.; Hackländer, K.; Brunner, N.; Kühleitner, M. Benford’s Law for Telemetry Data of Wildlife. Stats 2021, 4, 943-949. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4040055
Pröger L, Griesberger P, Hackländer K, Brunner N, Kühleitner M. Benford’s Law for Telemetry Data of Wildlife. Stats. 2021; 4(4):943-949. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4040055
Chicago/Turabian StylePröger, Lasse, Paul Griesberger, Klaus Hackländer, Norbert Brunner, and Manfred Kühleitner. 2021. "Benford’s Law for Telemetry Data of Wildlife" Stats 4, no. 4: 943-949. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4040055
APA StylePröger, L., Griesberger, P., Hackländer, K., Brunner, N., & Kühleitner, M. (2021). Benford’s Law for Telemetry Data of Wildlife. Stats, 4(4), 943-949. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4040055







