Abstract
The paper discusses issues that surround decisions in risk and reliability, with a major emphasis on quantitative methods. We start with a brief history of quantitative methods in risk and reliability from the 17th century onwards. Then, we look at the principal concepts and methods in decision theory. Finally, we give several examples of their application to a wide variety of risk and reliability problems: software testing, preventive maintenance, portfolio selection, adversarial testing, and the defend-attack problem. These illustrate how the general framework of game and decision theory plays a relevant part in risk and reliability.
1. Introduction
Decision (and game) theory is becoming more relevant to addressing reliability and risk issues under uncertainty. A recent contribution was made by Ríos Insua et al. [1]. For many applications, quantifying risk and reliability measures is a means to an end; to be useful, those values must be used to derive optimal policies to minimise risk, to decide on maintenance strategies, or to make some other decision. The methods of decision theory provide coherent mathematical approaches to doing this. When decisions are made in an environment where there are competing players, game theory is the relevant mathematical approach; examples include adversarial commercial situations or minimising risks from criminal or terrorist threats.
In this paper, we address these topics with illustrative examples taken mainly (but not exclusively) from our work. Some of them are worked out analytically, while others require numerical computations; however, the reasoning behind each example is explained, and the reader is referred to the relevant references for a complete discussion. The target of the paper is twofold. On one hand, it is addressed to people who have no or limited knowledge about methods and models in decision theory applied to reliability and risk problems. On the other hand, this paper illustrate recent approaches, such as adversarial risk analysis, or possible uses of older but less known methods such as Bayesian robustness; therefore, this paper could also interest readers with more in-depth knowledge. There are so many methods, models, and application fields that could be used to achieve the above goals but they are limited to a few in this paper. The choice has fallen on a few topics in reliability (although also related to risk) and a particular risk, from finance. In reliability, we identified three relevant areas (software testing, maintenance, and acceptance sampling) while portfolio selection has been discussed in the context of financial risk. We were compelled to leave out many other works, for example, on natural disasters (flooding and earthquakes), or other papers of ours such as Ebert et al. [2] on queues at immigration control in airports and Trucco et al. [3] on human and organisational factors affecting safety in maritime transport. The examples chosen not only are representative of some areas in the field but also allow us to introduce approaches that could be of interest for readers such as influence diagrams, decision trees, Bayesian robustness, and adversarial risk analysis.
In Section 2, we give a historical account of how the development of risk and reliability methods is connected to the progress in probability theory and utility theory for normative decision making. In Section 3.1, we introduce the basic concept of utility-based decision-making. Decision problems are best framed with the help of graphical representations, so we consider decision trees and influence diagrams in Section 3.2. Examples of applications of decision trees for replacement in maintenance optimisation follow in Section 3.3. In Section 4, we include other application examples where a single decision maker deals with software testing, preventive maintenance, and portfolio selection. In Section 5, we examine problems in risk and reliability analysis that involve two or more actors with competing interests in the adversarial risk analysis framework. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. A Brief History of Quantitative Risk and Reliability
The section is not intended to provide a complete history of how risk and reliability became the object of quantitative study and then of interest in decision theory. Rather it mentions some works that have had an impact on this process. It shows how the current research in decision analysis, as applied to risk and reliability, is the result of centuries of work, which have grown independently until they have found common ground. More extensive illustrations can be found in papers about history of statistics such as Singpurwalla and Wilson [4].
The history of quantitative risk methods is tied closely to the history of probability theory, both of which have roots in insurance. Christiaan Huygens (1629–1695) was one of the earliest scientists to think mathematically about risk, motivated by problems in annuities widely due, at that time, to states and towns borrowing money. Huygens wrote up the solution, due to Fermat and Pascal, to a gambling problem called “The Problem of Points”, where the question is to determine the fair bet for a game where each player has an equal chance of winning and the bet is won as soon as either player wins the game a predetermined number of times. Huygens stated an axiom on the value of a fair game, which is considered the first approach to the notion of expectation. Huygens [5] is thus credited with publishing the first book on probability theory.
The idea of a fair price was linked to probability by Jacob Bernoulli (1654–1705) in a book [6] published posthumously by his nephew Nicholas as the first substantial treatment of probability. Jacob Bernoulli changed the focus from expected values, which were tediously calculated by a recursive approach, towards probabilities using his Law of Large Numbers. Expected value then became a derived concept, and the calculation of probabilities was direct and faster as it did not require the recursion that Huygens used. The connection between fair prices and probability is the basis for insurance pricing and came about during a period of rapid development of the insurance market, driven by the growth of maritime commerce in the 17th and 18th centuries. Soon after the publication of Bernoulli’s work, corporations began to engage in insurance. They were first chartered in England in 1720, and in 1735, the first insurance company in the American colonies was founded at Charleston, S.C. Therefore, by 1750, the idea of probability used in risk quantification, such as probability distributions, expected values, and fair price, and mortality were in use in insurance.
Later in the 18th century, a notable name is that of Thomas Bayes (1702–1761) and his famous essay on inverse probability [7,8]. Decision theory makes extensive use of Bayes’s Law as a way to express the uncertainty about factors that affect the consequence of a decision from expert opinion and data. Another important aspect of decision theory is the idea of utility to quantify preferences of consequences of adverse events, an important component in the process of managing risks in a coherent manner. The idea of utility arose through Daniel Bernoulli in 1738 and utilitarian philosophers such as Bentham (1748–1832). Around this time, the industrial revolution meant that manufacturing and transport carried far graver risks than before, and we do see the first attempts at risk management through regulation. In the United Kingdom, the Factory Act of 1802 (named the “Health and Morals of Apprentices Act”) started a sequence of such acts that attempted to improve health and safety at work.
The foundations of modern utility theory, from which a prescription for normative decision making comes about that is the basis of decision theory, had to wait until the early 20th century with the work by Ramsey [9]. The mathematical basis of today’s quantitative risk analysis is indeed normative decision theory. The impetus for a formal approach to utility came from von Neumann and Morgenstern [10] with their interest in rational choice, game theory, and the modelling of preferences.
Although Pearson [11] names the exponential distribution for the first time, it was only in the 1950s that the field of statistical reliability emerged and we began to see some of the methods that are in common use today. Here, we see Weibull’s (1887–1961) advocacy of the Weibull distribution [12,13], the statistical analysis of failure data by Davis [14], the proposal of Epstein and Sobel [15] that the exponential distribution should be used as a basic tool for reliability analysis, and the approach of Kaplan and Meier [16] for estimating the survival function under censoring. We begin to see the idea of system reliability emerging at this time as well. Drenick [17] looked at the failure characteristics of a complex system with the replacement of failed units; then, Birnbaum et al. [18] investigated the structural representation of systems of components. Fault trees also appeared in this decade; see the work by Watson [19]. Much of this work is summarised in the two books of Barlow and Proschan [20,21].
The last fifty years have been marked by many developments and the quantity of publications in the literature is rather overwhelming. From a historical perspective, perhaps the most important trend is the availability of computation to facilitate more complex risk and reliability analyses. However, the fundamental link between quantitative risk and reliability methods to probability and decision making has remained.
3. Basic Concepts of Decision Theory and Graphical Methods to Describe Decision Problems
3.1. Basic Concepts
The final goal of a risk analysis and a reliability study is, in general, a decision that reduces the social, economic, environmental, etc. negative consequences (losses) for an individual or a group, or increases their utility. A plethora of work has been published on decision theory and decision analysis, and we refer to the works of Wald [22], DeGroot [23], Berger [24], and French and Ríos Insua [25] for a thorough illustration. We consider decision-making under uncertainty and we present a Bayesian approach through definitions, properties, and a simple example related to risk. There are many critical aspects in the stages of a decision process: problem structuring, belief modelling, preference modelling, optimisation, and sensitivity analysis. Here, we are interested in illustrating some aspects, mostly related to sensitivity, arising when considering belief and preference modelling. In a Bayesian framework, beliefs over possible states of nature are modelled through a (prior) probability distribution, which in the presence of additional information, is updated via Bayes’s theorem, whereas preferences over consequences are modelled using utility functions (or, more commonly in the statistical community, loss functions). The consequences are the result of actions chosen within a feasible set combined with states of nature, and the goal is to find an optimal action, namely the one maximising the expected utility. The assessment of beliefs and preferences is a difficult task, especially when there are several decision makers and/or experts. Sensitivity analysis (often called Bayesian robustness in this framework) deals with the uncertainty in specifying prior distributions and utility/loss functions; see the book by Ríos Insua and Ruggeri [26] for a thorough survey.
More formally, we assume that the decision maker has to choose among a set of feasible actions a. Prior beliefs on the state variable are assessed through a prior distribution with density , and they are updated, via Bayes’s theorem, into a posterior distribution, with density , where x is the result of an experiment with likelihood over a sample space X. A consequence is associated to each pair , and preferences over the consequences are modelled with a utility function , which we simply denote by . We associate with each action a its posterior expected utility:
According to the Maximum Expected Utility Principle, we look for the optimal action , which maximises .
However, the assessment of u and , and the choice of the model , are performed with limited knowledge and some degree of arbitrariness. Such uncertainty in the specification has an impact on the optimal action and its expected utility, the model output in our case. A thorough review of the literature on how to handle such issues is provided in the book by Ríos Insua and Ruggeri [26]. Here, we present a simple, no data example adapted from Ruggeri et al. [27], which should make clear the importance of investigating the consequences of assessing probabilities and utilities imprecisely.
A football team is interested in signing a new player on a one-year contract. Two players, a and b, are available, and the team expects to have a (utility) gain in signing one of them, which depends on the possibility of qualifying () or not () for the European Champions League the next year. The probability of qualification is . The team managers believe that the monetary consequence of signing a and not being qualified is equivalent to the one obtained with signing b and being qualified. The other two possible consequences are, in general, different. We could represent the consequences in Table 1:

Table 1.
Monetary consequences of signing players.
In the team, there is uncertainty, maybe due to different opinions among the managers, about both the probability of being qualified and the monetary consequences. As a result, ranges are obtained for all of them: , , , and , where utilities are in million euros. We consider (Table 2) the following four utility–probability pairs associated with the bounds on utilities and probabilities:

Table 2.
Expected utilities of signing players.
Since in all four cases, , the team managers might decide to hire a but such a choice would not necessarily be optimal, e.g., considering and , then it would be and , raising doubts about the preference of a over b.
Martin et al. [28] addressed the issue of the choice of actions when the priors and the utilities (losses in their work) are in the classes and , respectively, as is done here. They proposed to consider non-dominated actions, i.e., the actions such that there exists no other action such that , for all , , with strict inequality for one pair .
3.2. Graphical Representation of Decision Problems
3.2.1. Decision Trees
Decision problems can be represented graphically using decision trees, where decision nodes are typically represented by a rectangle; chance (or random) nodes are represented by a circle; and outcomes, which are functions of decision actions and uncertainties, lie at the terminal points of the branches of the tree. Figure 1 shows the decision tree representation of a single-period decision problem. In the tree, the decision node is denoted by and the chance node is denoted by . The branches of the decision node represent the different decision actions a whereas the branches of represent possible values of the random quantity , which is commonly referred to as the state of nature.
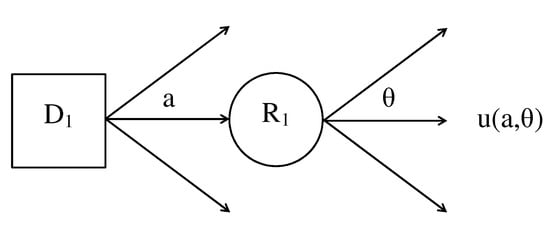
Figure 1.
Example of a single-period decision tree.
The decision tree is a chronological representation of the events in a decision problem. In Figure 1, first, a decision action a is taken at the decision node and then a possible value of the state of nature is observed at the chance node where uncertainty about is described by the probability distribution . Each combination of the pair implies an outcome or utility value at the terminal point of a specific path of the tree.
The solution to the single-period decision problem in Figure 1 is obtained by folding back the tree (see Lindley [29]) starting at the terminal nodes. This is done by working backwards, taking the expectation of at a random node such as ,
and by maximising with respect to action a at a decision node such as . The optimal action obtained at maximises the expected utility, as discussed in Section 3.1.
Later, we consider an example of a single-period decision tree that arises in the development of replacement strategies for components/systems in reliability analysis.
3.2.2. Influence Diagrams
An influence diagram (ID) is a graphical representation of a decision problem that contains the same information encoded by an equivalent decision tree. It is possible to convert an ID into a decision tree and vice versa. An ID is a directed acyclic graph containing three types of nodes: chance nodes that are represented by circles, decision nodes that are represented by squares, and deterministic nodes that are represented by squares with rounded edges. If an ID contains only chance nodes, then it is called a belief or Bayes network. A deterministic node is so-called because its value is a function of those taken by its parent nodes. A special type of deterministic node is a value node, which contains the value taken by utility as a function of its parent nodes. The advantage of an ID over decision tree is that the former provides a more compact and high-level representation of the decision problem because its size does not increase exponentially as additional decisions or uncertainties are added to an analysis. In fact, it displays the dependence among variables and the state of information under which decisions are made but it does not show the possible values associated with each decision or chance variable. Therefore, it is often the case that a problem is first represented as an ID and, afterwards, is converted to a decision tree for computation of the solution, which means finding the expected utility of all possible decisions, to be maximised over the decision space. The single-period replacement problem in Section 3.3.1 provides a simple example of the more compact representation of an ID, as shown in Figure 2, where there are no multiple arcs from the nodes. The decision node contains the value of , the chance node contains , the value node contains , the decision node influences the chance node, and the value node is influenced by both of them. The problem representation is completed by information on the conditional distributions of chance nodes given the parent nodes, that is, the conditional distribution of given for the specific example.
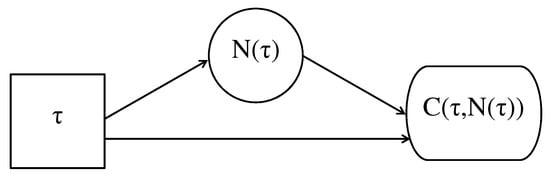
Figure 2.
Influence diagram (ID) representation of a single-period replacement problem.
The ID representation of the stopping problem tree in Section 3.3.2 is not a simplification because decision nodes in the multi-stage decision are binary, each stage is represented in the same way in a repetitive fashion, and the tree always has a terminal leaf after a stop branch.
In Figure 3, we show a simple example with a nonrepetitive structure adapted from Bedford and Cooke [30], which also shows that an ID enables the derivation of conditional independence relationships among nodes. The chance nodes in the ID are described as follows: fault can take values of yes or no, repair can take values of repairman is sent or repairman is not sent, and both primary alarm and secondary alarm can take values of alarm signals a fault or no signal. The decision node is self explanatory and the cost node can take two values if no secondary alarm is installed: one is the cost of sending a repairman after a false alarm; the second one adds the actual repair cost if a fault has really occurred. With the secondary alarm, the two previous cost values are increased by the installation cost. It is assumed that the alarms never fail to signal a fault, but false alarms can occur. Thus, unnecessary repairs can be reduced by installing a secondary alarm and by calling the repairman only if both alarms signal a fault. If the decision is not to install the secondary alarm, the value of its node is always alarm signals a fault. The repair node is in fact a deterministic node because its state is entirely known given the state of the alarms; however, it is regarded as a chance node with a degenerate distribution for later use. The problem description is completed by assigning probabilities to the following events: a fault occurs, the primary alarm signals a fault given that there is no fault, and the secondary alarm signals a fault given that there is no fault.
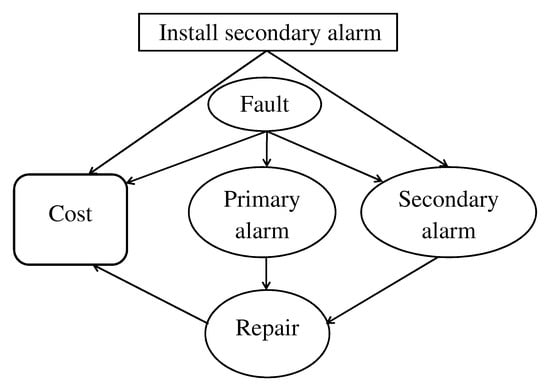
Figure 3.
ID representing the problem of installing a secondary alarm signalling a machine fault.
From the ID, we can find out conditional independence relationships using the global Markov property on any belief network determined by assigning a value to decision nodes. Suppose that the decision is to install a secondary alarm and to consider the repair node. Take the set of all its ancestors, which includes the two alarm nodes and the fault node (not the decision node because its value has been assigned) and remove all the remaining nodes (the cost node). Now moralise this subgraph by joining all unmarried parents using an undirected arc (the two alarm nodes in this case), and change all the directed arcs to undirected: the repair node is independent from the fault node given the pair of alarm nodes because all paths between them always go through the set of alarm nodes. With the same method, we can discover that the two alarm nodes are independent conditionally upon the fault node. The two moralised subgraphs are shown in Figure 4a,b.
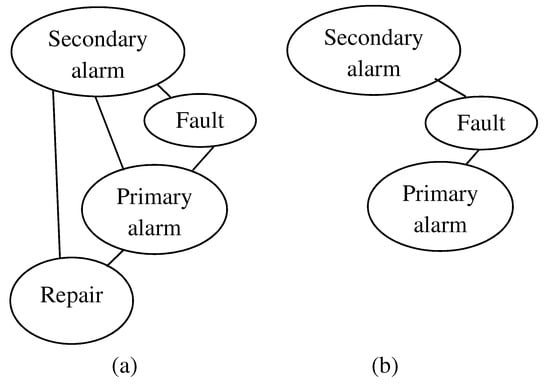
Figure 4.
Moral graphs for finding conditional independence relationships.
The decision tree structure for this problem is more complex. It starts with the decision node with two outgoing branches, each terminating with the fault node, from which two more branches come out and terminate with an alarm node. From this node, either four or two branches come out, depending on which subtree we are in. If we decide to install the secondary alarm, there are four branches, one for every pair of states for the two alarms. The terminal nodes are the costs associated with every path in the tree.
To complete this illustration, let be the probability of a fault and let p be the probability of a false alarm using any of the two alarms, which are assumed to be devices of the same type. Let also be the cost of sending a repairman, be the cost of an actual repair, and be the cost of a secondary alarm installation. Then, the costs of the decision of installing and not installing a secondary alarm are given by
respectively, where , , and F belong to and are random variables representing the state of the two alarms and the presence of a fault. The expected costs are easily derived using the conditional independence properties derived earlier, and it is found that it is convenient to install a secondary alarm if
Banks et al. [31] remarked that the graphical structure of an ID has the property that there is a directed path containing all decision nodes that specifies the order in which decisions are made by the decision maker. The authors pointed out also a drawback of IDs, i.e., their impossibility of representing problems in which there is no predetermined order for the decisions, for example, in medical diagnosis, where the decision about subsequent tests depends on the results of previous ones. In those cases, asymmetric decision trees are better graphical tools, but they might have too many branches as a consequence of having to consider as many subtrees as all possible test orders. The authors suggested, as a possible alternative, to consider multiple IDs, one for each possible test order, and to compare the solutions.
A simple introduction to IDs can be found in Bedford and Cooke [30], whereas a more advanced introduction is given by Banks et al. [31].
3.3. Single and Multi-Period Decisions
3.3.1. Single-Period Replacement Problem
Systems and components experience ageing or wear as a function of time and/or usage. For such systems, planned replacement strategies are used to prevent in-service failures that may be very costly relative to the cost associated with a planned replacement/repair. Mazzuchi and Soyer [32] proposed a Bayesian decision theoretic approach to develop optimal replacement strategies using age and block replacement protocols. In what follows, we consider a single-period block replacement problem under the assumption of minimal repair.
Typically, under the block replacement protocol, a planned replacement is made at time epochs , , …, irrespective of the age of the system and an in-service replacement is made whenever the system fails (the “good as new” scenario, since the replacement brings the reliability back to the initial one, assumed “good”). Another block replacement scenario was considered by Barlow and Hunter [33], where the system is minimally repaired upon failure but replaced at times , , …. This is known as block replacement with minimal repair where the item can be repaired so that its failure characteristics are restored to the state just prior to the failure (the “bad as old” scenario).
We let denote the cost of a planned replacement; be the cost of minimal repair, such that ; and be the number of failures in a time interval of length t. Then, in a planned replacement cycle of length , the cost per unit time is given by
The decision problem is to find such that the expected value of is minimised. The decision tree for the problem is shown in Figure 5, where the random represents , an unknown number of repairs in a replacement cycle of length .
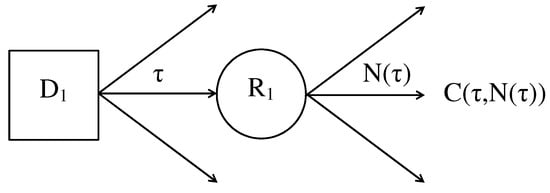
Figure 5.
Decision tree for a single-period replacement problem.
Following Barlow and Hunter [33], we model as a non-homogeneous Poisson process (NHPP) with intensity function . For a system subject to ageing or wear, a commonly used model is the power law form for the intensity function, that is,
where , and values of imply ageing over time. The mean value function for the NHPP is the cumulative intensity:
The common approach in the literature is to assume that and are given (or estimated based on past data) and to select the optimal replacement interval, , at the decision node of the tree by minimising
with respect to . For , it can be shown that the optimal interval is given by
Recent work in optimal replacement includes semiparametric policies considered by Merrick and Soyer [34], who considered block replacement for rail sections.
3.3.2. Multi-Period Stopping Problem
Decision trees are typically used in representing multi-period decision problems where a sequence of decisions are made and uncertainties are updated dynamically. Such problems arise in risk and reliability analysis in the context of the design of systems, life testing, optimal stopping, portfolio selection, etc. In this section, we present an example of an optimal stopping problem in software testing. The solution of sequential decision problems of this type relies on pre-posterior analysis and can become quite challenging to solve. These problems also arise in life testing; see, for example, van Dorp et al. [35], and Erkanli and Soyer [36].
Morali and Soyer [37] considered an optimal stopping problem in software testing and presented a Bayesian decision theoretic setup. In what follows, we use their notation and formulation of the multi-period problem. During the development phase, a new software goes through several stages of testing and, after each stage of testing, modifications are made to the software to fix the faults (or bugs). This process is known as debugging.
Let denote the life-length of the software during the ith stage of testing after the th modification made to it. Morali and Soyer [37] assumed that the failure rate during the ith stage of testing is constant and, thus, that is exponentially distributed with rate . The special feature of their model is that the failure rate changes from one testing stage to another as a result of corrections made to the software.
The authors assumed that, at the end of each stage, following modifications made to the software, a decision must be made whether to terminate the debugging process. Thus, after completion of i stages of testing, the decision of whether to stop testing is based on , where represents the available information prior to any testing. Morali and Soyer [37] considered a loss function that reflects the tradeoff between additional testing versus releasing an unreliable piece of software. More specifically, they defined the loss associated with stopping and releasing the software after the ith stage of testing stage as
where (·) represents the loss due to testing for one stage and (·) relates the loss associated with stopping and releasing the software. Note that, in this paper, we use both utilities and losses, choosing the notion more suitable for the topic at hand.
The stopping problem can be represented as a sequential decision problem as given by the m-stage decision tree in Figure 6 and can be solved using dynamic programming. The solution of the tree proceeds in the usual way by taking the expectation at random nodes and by minimising the expected loss at the decision nodes. At decision node i, the additional expected loss associated with the stop and the test decisions are given by the terms and , respectively, where
for , and the optimal decision at decision node i then is the one associated with .
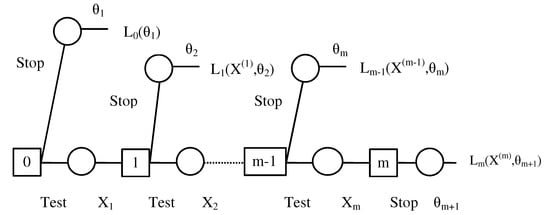
Figure 6.
Decision tree for an optimal stopping problem.
Multi-period decision problems also arise in the design of life tests such as accelerated life tests. Some of the recent work in this area include Zhang and Meeker [38,39], Meeker et al. [40], and Polson and Soyer [41].
4. Examples of Decision Problems
4.1. One-Stage Software Testing
Figure 1 showed the structure of the simplest decision problem, that of a single-period problem where a decision is made, a state of nature is revealed, and an outcome follows. There is no opportunity to learn from data about the state of nature , and therefore, one relies entirely on the prior .
Such a type of decision problem can be illustrated through its application to software testing. Here, we mention the paper by McDaid and Wilson [42] and the more recent book by Kenett et al. [43]. When developing software, bugs are often introduced and they cause it to fail, producing a result different from the specification. Developers are therefore interested in testing the software to discover and remove bugs before its release. Of course, they should be very careful to prevent the introduction of new bugs. There is an issue of the quality of testing and about the length of the test phase. There are conflicting aspects about costs: on one side, there could be excessive costs due to a very long test but, on the other side, early release might imply a less reliable software. There are other aspects such as the possible obsolescence of the software caused by a very delayed release, the loss of reputation due to a poor software, and the need to market the software before the release of similar ones by competitors. Therefore, it is important to determine an optimal release time, taking into account especially costs for testing and fixing software, with the latter strongly dependent on the number of bugs left in the software at its release. Such an optimal time could be easily found through a one-stage test.
In Figure 7, we present the decision tree for one-stage testing. In terms of the notation of this paper, the set of feasible actions are times a that one could test, , and the state of nature is the number of bugs discovered during and after testing, denoted and , respectively; hence, . The only deviation from Figure 1 is that is described by a probability model with parameters that are themselves unknown, and the prior distribution is directly specified on . However, the Partition Law of probability gives the prior on directly by integrating out :
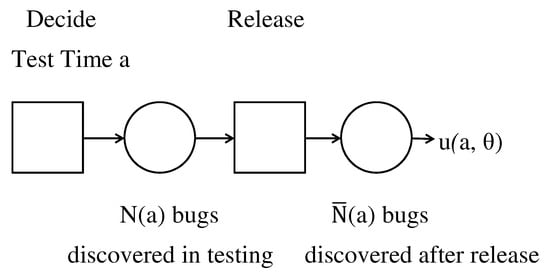
Figure 7.
The decision tree for single-stage testing.
Many models have been proposed for ; see, e.g., Singpurwalla and Wilson [44]). In this work a popular model of Goel and Okumoto [45] is used. The model assumes that is a Poisson process with mean function , for parameters and that represent the expected total number of bugs to be discovered eventually in the software (at ) and the rate of discovery, respectively. Thus, is Poisson distributed with an expected value . The motivation from this model comes from the fact that satisfies the differential equation:
so that the rate of bug discovery is proportional to , the expected number of bugs remaining to be discovered at time a.
Our knowledge about is quantified by the values of and . Expert opinion can be used to quantify this knowledge in the form of a probability distribution for and . In this approach, gamma distributions are used as they have a relatively simple form and can be defined to have an arbitrary positive mean and variance. The gamma distribution is defined by two parameters, a scale and a shape , and its density function has the form , where is the gamma function. The important thing to note here is that the mean and standard deviation are and , so that and can be uniquely determined if one has an opinion on the mean and standard deviation. McDaid and Wilson [42] described an elicitation process for these parameters that uses these relationships. Here, we assume that such an elicitation process has led to specifying a scale and a shape for and a scale and a shape for .
Given and , and are Poisson distributed. McDaid and Wilson [42] derived the unconditional prior and showed that the expected values are as follows:
With regard to utility function , the simple form for the utility of testing until time a and then releasing is as follows:
where A is the profit from releasing the software without any testing, C is the cost of fixing a bug discovered in testing, D is the cost of fixing a bug post-release, and F is the cost per unit time of testing, that includes both the testing costs as well as lost sales and market opportunity. In practice, D should be considerably larger than C.
Now, all the components of the decision problem have been specified. Solving the simple tree in Figure 7 involves taking the expectation with respect to the unknown states of nature and (making use of their expected values as in Equations (2) and (3)) and then maximising the resulting expected utility with respect to a to find the optimal testing time. Plugging Equations (2) and (3) into Equation (4) gives the expected utility of testing for a time a,
and the value of a that maximises this function, and therefore, the optimal time to test, is as follows:
This is not valid if , a case that we do not anticipate in practice and would imply that the optimal strategy is not to test and just repair all bugs post-release.
Figure 8 presents the expected utility and optimal testing time when the prior mean on is 100 (so that about 100 bugs are expected in the code), whereas the prior mean on is 0.01. For such a purpose, we take and . As a consequence, the two standard deviations coincide with the prior means, i.e., 100 and 0.01, respectively. The utility parameters are chosen as the following values: , , , and . The left plot shows as a function of a and identifies the optimal release time for an expected utility of 1333.6. The right plot shows how changes as a function of D, the cost of fixing a bug post-release; this shows how the testing time should increase as the relative cost of fixing bugs after testing rises.
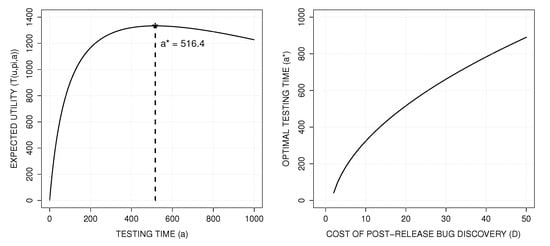
Figure 8.
Expected utility as a function of time (left) and optimal testing time as a function of post-release bug cost (right).
In this solution, the software is released regardless of the results of the testing. As a consequence, there is no opportunity to learn about its reliability from those results. In McDaid and Wilson [42], moving beyond this simplest case is also considered involving more than one stage of testing and in which learning about takes place.
A recent review of decision models for software testing including adversarial issues can be found in Ruggeri and Soyer [46].
4.2. Preventive Maintenance of Water Pumps
Christen et al. [47] analysed the operation data of a Worthington water pump, operating 24 h a day at the PEMEX Salamanca refinery in Guanajuato, Mexico. Data were recorded about operation hours before either maintenance or failure, whichever came first. The authors considered a random sign censoring model to describe the maintenance and failure processes and, based on a maximum expected utility approach, they proposed a maintenance policy that improved upon the existing one. Here, we take a different approach, further elaborating on the ideas about sensitivity issues in decision analysis introduced in Section 3.1.
There are observations, and they are presented in Table 3, split into 28 failure and 6 maintenance times.

Table 3.
Pump data: failure and maintenance times.
We consider independent and identically distributed exponential failure times with parameter , and we denote the observed times by , . The likelihood function is given by
based on the density at a failure time and the survival probability at a maintenance time.
We assume that interventions are made at fixed times, even when failures occur, and we consider two possible actions: {intervention after 10 h} and {intervention after 20 h}. We consider the following loss functions:
The integral component of the loss function is related to the cost incurred when the pump fails at time x and does not operate until an intervention occurs. We compare the two actions over a 20 h period so that we add the factor 2 in the first loss since failures can occur over two 10 h periods. The term C accounts for the cost of the extra intervention. A cost should multiply the integral part, but it is simpler to remove it and to consider the losses apart from a multiplicative constant.
If we consider a gamma distribution prior on , then we get a gamma distribution posterior , which we denote . It is possible to prove that, under such a distribution, the posterior expected losses are
Therefore, it holds that
We now suppose that there is uncertainty about both beliefs and preferences, namely on the prior distribution of and the value of C. In the former case, there could be different opinions on the expected failure time of the pump, given by ; in the latter case, there might be variability in the cost of the extra repair. The classes we entertain are very simplistic but useful for illustrative purpose. More sophisticated classes are presented in Ríos Insua and Ruggeri [26]. We consider the classes:
Given the likelihood (6), then the posterior distribution belongs to the class
If we take , , then the choice of or leads to opposite conclusions. In the former case, implies that the intervention after 10 h is the optimal action whereas the intervention after 20 h is the optimal decision in the latter case since we get . This is a typical situation in which the decision maker needs extra effort to specify beliefs and preferences or to honestly report that there is no clear-cut decision.
Bayesian analysis of repairable systems is considered in Pievatolo and Ruggeri [48], and minimal repair models for train systems are discussed in Pievatolo and Ruggeri [49]. Maintenance strategies for machine tools are presented in Merrick et al. [50], and maintenance practices for railroads are discussed in Merrick et al. [51]. Recent developments in maintenance optimisation can be found in Damien et al. [52] and Belyi et al. [53]. Degradation-based maintenance policies are considered in Zhang et al. [54].
4.3. Portfolio Selection
Markowitz [55] considered the single-period portfolio selection problem where an investor has to allocate a sum of money among K securities. A Bayesian decision theoretic setup to the problem was introduced by Winkler and Barry in [56], and the multi-period problem was discussed. In this section, we present a setup considered by Soyer and Tanyeri [57], who follow the formulation of Winkler and Barry [56].
We let denote the wealth of the investor at the end of time period t and denote the initial wealth of the investor. We define to be the return from security k during time period t and assume that there are no transaction costs. If is the amount invested in security k at the beginning of time period , then the wealth of the investor at the end of time period can be written as
Following Winkler and Barry [56], we assume that the investor’s objective is to maximise , the utility of wealth at the end of a finite time period T (with dependence on omitted). In the multi-period problem with a finite horizon T, the investor maximises the utility by sequentially choosing the decision variables and at different points in time based on the available information. That is, the optimal allocation is revised as the random quantities , are observed over time. The decision tree for the multi-period portfolio selection problem is shown in Figure 9, where the decision nodes at time periods are denoted by and the random (observation) nodes are denoted by .
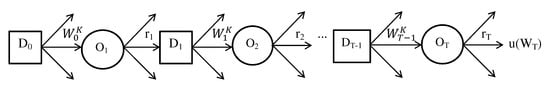
Figure 9.
Decision tree for the multi-period portfolio selection problem.
Given the initial wealth at , the investor determines ,,, the amounts invested in K securities. The random node denotes, for time period , the observed returns from K securities, . Given , the investor determines ,, at decision node , and this process is repeated at subsequent nodes. The solution of the problem involves dynamic programming formulation and backward induction by taking the expectation at random nodes and by maximising the expected utility at the decision nodes, as in Winkler and Barry [56].
As pointed out by Soyer and Tanyeri [57], at decision node , given the observed returns from the first periods, the decision variables are chosen by maximising , where denotes the expectation conditional on the returns from the first periods. We denote the expected utility corresponding to the optimal allocation by at time . Then, at decision node , the optimal allocation is obtained by maximising , where . Continuing in this manner at time 0, calculation of the optimal allocation for the first investment period involves implicit computation of expectations and maximisations at each time period. This can become quite cumbersome if the underlying parameters of the return distributions are unknown and a Bayesian approach is used for inference, as discussed in Winkler and Barry [56].
For the case of the single-period problem, that is, , one can obtain the solution analytically in some simple cases or use Monte Carlo-based methods. For example, if we consider a quadratic utility function for as
where , we can obtain an analytical solution for the optimal allocation at and if we assume that, at time period 1, the K dimensional return vector is normally distributed with mean vector and covariance matrix , denoted as where and are known, we can write
and, using the quadratic utility function, obtain
Then, it can be easily shown that the optimal allocation for investment period 1 is given by
where .
If we consider a two-period problem with a quadratic utility function for , that is, , then the dynamic programming solution can be obtained analytically under the assumption of independence of the return vectors. More specifically, if with and known and s independent, then we can show that the optimal allocations for investment periods 1 and 2 are given by
and
Furthermore, it can be shown by induction that, for the T period problem, the optimal allocations are given by
for .
When the parameters of the return vectors are not known, the solution of the dynamic program becomes quite cumbersome even when is independent. Winkler and Barry [56] considered the case of unknown mean vector for the two-period problem with quadratic utility function and noted that the solution can be obtained using numerical methods. More recently, Soyer and Tanyeri [57] considered two-period portfolio selection problems with stochastic volatility and illustrated Bayesian solutions using Monte Carlo-based methods.
5. Adversarial Issues in Reliability Analysis
5.1. Basic Concepts of Adversarial Decision Problems
The decision problems presented in the previous sections involved a single decision maker and were solved using decision analysis methods. There are problems in risk and reliability analysis that may involve two or more actors with competing interests. These problems with adversarial components can be set up as games that can be solved using game theory methods; see, for example, Luce and Raiffa [58]. Examples of adversarial situations in reliability analysis can be found in areas such as acceptance sampling (see Lindley and Singpurwalla [59]), life testing (see Lindley and Singpurwalla [60]), reliability demonstration (see Rufo et al. [61]), and warranty analysis (see Singpurwalla and Wilson [62]). A recent review of adversarial issues in reliability and survival analysis can be found in Singpurwalla et al. [63].
Lindley and Singpurwalla [59] considered an adversarial situation with two actors: a manufacturer M and a consumer C. The manufacturer M tries to sell a batch of items to C, who may either accept () or reject () the batch provided by M based on his utility function . The decision by C depends on the “evidence” provided by M to C based on a sample from an inspection or a life test that M may perform. The decision M faces is whether to offer a sample to C and, if so, the size of the sample based on his utility function . It is assumed that both M and C are expected utility maximisers.
Lindley and Singpurwalla [59] presented their setup in the context of acceptance sampling where M tries to convince C about the quality of his product implied by the unknown quantity . We can think of as the percent of defective items in the batch in the quality control setting or as the failure rate (or mean time to failure) in the life testing context considered by Lindley and Singpurwalla [60]. The outcome of the inspection/test is denoted by D.
Figure 10 shows the game tree associated with the problem. The decision node M in the game tree represents the manufacturer’s decision about n, the sample size, that is offered to the consumer. The decision implies that offering a sample to C is not beneficial to M, and in this case, the game is concluded. The random node D denotes the data, that is, the outcome of the inspection/test. In their development, the authors assume that both M and C agree about the probability model generating the data. Let denote the common probability model for the data-generating process. The decision node C represents the consumer’s decision to accept () or reject () the batch. Note that this decision is based on the observed sample data D, which is used by C for revising uncertainty about . C updates his prior to posterior distribution using . Lindley and Singpurwalla [59] specified the utility function of C as or . The utility function of M is specified as or , implying that M’s utility is a function of C’s decision as well as n and .
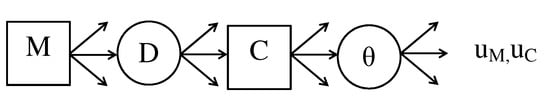
Figure 10.
Game tree for the adversarial life testing problem.
Lindley and Singpurwalla [59] developed a solution for the game tree assuming that M knows C’s decision criterion and the prior . Thus, for a given , M is able to infer if
at decision node C. The authors denote the sets of Ds implying the acceptance and rejection regions for C using and . Once the sets and are known, M chooses the optimal value of n at decision node M by maximising
where denotes M’s prior for . The authors developed the optimal strategy for M for Bernoulli, Poisson, and Gaussian sampling using numerical methods. An implementation of the proposed approach to the case of exponentially distributed life times is considered in Lindley and Singpurwalla [60]. More recently, Rufo et al. [61] extended the Lindley–Singpurwalla approach for life testing by introducing a Bayesian negotiation model.
The proposed framework by Lindley and Singpurwalla [59,60] for adversarial testing problems is based on the assumption that the manufacturer knows both the decision criterion for C as well as C’s prior for . In many cases, it may not be possible to obtain such information. The Bayesian approach to games involves a decision maker’s assessment of probabilities of the opponent’s actions. In their discussion of the Bayesian game theoretic approach, Kadane and Larkey [64] stated that
“…a decision maker has a subjective probability opinion with respect to all of the unknown contingencies affecting his payoffs. In particular in a simultaneous-move two-person game, the player whom we are advising is assumed to have an opinion about the major contingency faced, namely what the opposing player is likely to do”.
Furthermore, the authors point out that “infinite regress” is not a problem for the Bayesian decision maker since
“… all aspects of his opinion except his opinion about his opponent’s behaviour are irrelevant, and can be ignored in the analysis by integrating them out of the joint opinion”.
These and other criticisms of classical game theory have motivated the search for alternative solutions for decision problems with multiple actors. One such alternative is the adversarial risk analysis (ARA) approach recently proposed by Ríos Insua et al. [65]. ARA builds on the Kadane–Larkey approach by developing a model of the opponent’s strategies. This is done by incorporating uncertainty via subjective probabilities of the decision maker. As noted by Banks et al. [31], p. 1, the ARA model provides a probability distribution over the possible actions of the decision maker’s opponent and, using this, the optimal action is chosen by maximising the expected utility of the decision maker. We present the ARA formulation of Lindley–Singpurwalla’s adversarial life-testing problem in the next section.
5.2. Life Testing with Adversarial Modeling
Following Lindley and Singpurwalla [59,60], we consider the game tree of Figure 10 and analyse the manufacturer M’s decision process. The manufacturer/consumer game of Figure 10 is a sequential game similar to the “defend-attack” models discussed in Rios and Ríos Insua [66]. As before, we have the priors and and the utility functions ) and for M and C, respectively. denotes the consumer’s decision actions at decision node C.
The first step in the ARA solution is converting the game tree in Figure 10 to the decision tree of the manufacturer M shown in Figure 11. This is achieved by converting the decision node C to a random node for the manufacturer. Given the manufacturer’s decision n at node M and the outcome observed at random node D, the manufacturer needs to assess the probability of a consumer’s actions. These are the manufacturer’s subjective probabilities and we denote this discrete probability distribution by . The main issue is how to assess . This can be done directly as suggested in Kadane and Larkey [64] or by using the ARA approach, which takes into account the manufacturer’s perception of the consumer’s decision problem.
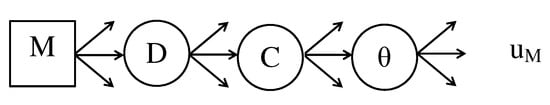
Figure 11.
Decision tree for the manufacturer.
The decision tree in Figure 12 represents the consumer’s decision problem as seen by the manufacturer. It is important to note that the consumer’s decision tree is obtained by converting the manufacturer’s decision node M to a random node. As before, the manufacturer analyses the consumer’s decision problem by assuming that he is an expected utility maximiser. The analysis of the tree is used to estimate . To achieve this, the manufacturer needs to specify , his probability distribution of the consumer’s prior , and utilities . Once is specified, we can estimate via Monte Carlo simulation. More specifically, we can simulate realisations of from , and for each realisation, we can solve the tree for given values of and obtain . In the final step, we use the manufacturer’s decision tree in Figure 11, where the probabilities are given by at the random node C. The optimal strategy for the manufacturer is computed by maximising expected utility.
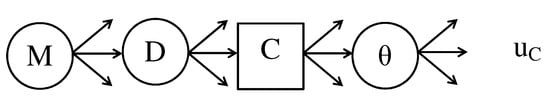
Figure 12.
Manufacturer’s perception of the consumer’s decision tree.
Implementation of the ARA approach may become complicated depending on the distributional assumptions and the form of the utility functions. In the Bernoulli sampling example of Lindley and Singpurwalla [59], the authors assumed a beta prior with parameters for the unknown proportion defective . The utility function of the consumer is specified as and , where . In the ARA setup, we can assume that the form of the probability distribution and the utility function are known but the respective coefficients are unknown. In other words, the manufacturer may know that the consumer’s prior distribution is a beta density with unknown parameters . Similarly, in the utility function , the coefficients , and are unknown. Thus, the manufacturer specifies his distribution , which is used in the solution of the consumer’s decision tree shown in Figure 12. The same approach can be used in specifying for Poisson and Gaussian sampling cases as well as the adversarial life-testing example discussed in Lindley and Singpurwalla [60]. The approach above is thoroug y illustrated in Gonzalez-Ortega et al. [67] and we refer the interested reader to it. Other implementation issues in ARA and its applications in risk analysis can be found in Banks et al. [31], Gonzalez-Ortega et al. [68], and Naveiro et al. [69].
5.3. Defend-Attack Problems in an Adversarial Setting
As pointed out in Section 5.2, the model employed for the specific life-testing problem belongs to the category of ARA defend-attack models. Ríos Insua et al. [70] provided a general description of the approach through the use of IDs. In this setting, there are two decision makers: the defender and the attacker. The attacker, after observing decision taken by the defender, selects an attack . After both parties have made their choice, there is a random outcome of the attack, with the conditional distribution depending on the choices. The actions and the outcome will produce utilities and for the defender and the attacker, respectively. This problem can be represented through a Multi-Agent Influence Diagram (MAID), in which some nodes are owned by the defender, some are owned by the attacker, and some are shared. The MAID, displayed in Figure 13 with one chance node, can be viewed as the superposition of two IDs, in which chance nodes are usually shared and assigned different (conditional) probability distributions by the two decision makers.
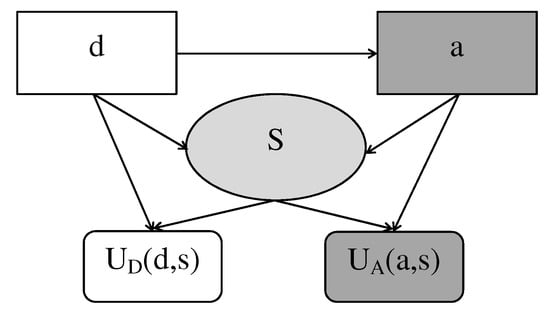
Figure 13.
Multi-Agent Influence Diagram (MAID) for the adversarial risk analysis (ARA) defend-attack model.
The defender must choose an action to maximise her expected utility without knowing the attacker’s action. Therefore she expresses her uncertainty by placing a probability distribution on the set , . The attacker’s utility itself is no concern for the defender; therefore, from her point of view, the ID of the defend-attack model becomes as represented in Figure 14.
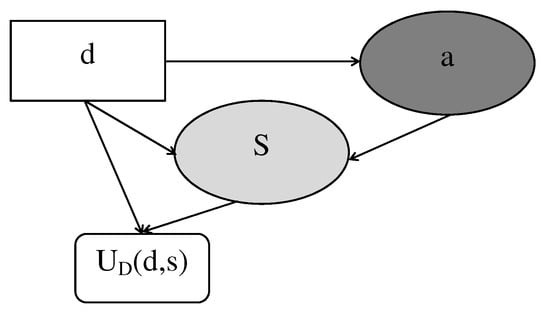
Figure 14.
Defender’s ID for the ARA defend-attack model.
The defender is now able to solve her ID: she computes her expected utility conditional on the attacker’s action first and then marginalises it with respect to . Letting denote the defender’s conditional distribution of the outcome, we obtain
and the best decision is the one that maximises .
In order to assess , the defender has to make a guess on the attacker’s utility and conditional distribution of the outcome, assuming he also is a utility maximiser, so that is a probability distribution of the best action chosen by him. The defender’s guess can be expressed as a probability distribution on the pair , so that the random optimal action of the attacker is , maximising
where the capitalised and emphasise that they are regarded as random quantities (and consequently also ). The defender’s distribution over can be considerably simplified using a parametric form. The cumulative distribution function of the defender over is now found as ; it is often approximated via Monte Carlo simulations of , as shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Approximation of . |
| for do |
| for to K do |
| sample |
| for do |
| compute |
| end for |
| find |
| end for |
| compute the empirical distribution function of |
| end for |
A worked-out case study in this framework is presented in Ríos Insua et al. [70] concerning a facility operator who wants to defend from a group of organised fare evaders (fare colluders).
6. Conclusions
In the paper, we presented many aspects of the use of decision theory methods in risk and reliability. Although advanced notions are introduced in the paper, we tried to present ideas and applications in a way useful for the learned readers and not only for researchers specialised on the topics so that they will be able to frame their problem in a rigorous and coherent way and to find pointers to specific analytic and computational techniques for their solution. The range of application areas that we included reflect our research interests, but the general principles of our work remain valid in other areas. Our experience also affected the approach (i.e., Bayesian) that we followed in the examples. Reliability has been one of the first applied areas in which Bayesian methods have been valued as very important due to the possible use of experts’ opinions about very reliable systems. The first comprehensive Bayesian book in reliability was by Martz and Waller [71] and was quite mathematical, and applications were scarce because of limitations in statistical and computing power in the 1980s. The most recent book by Hamada et al. [72] provides a different perspective, mostly due to the development of powerful computational methods, such as Markov Chain Monte Carlo, and increased interest in stochastic processes; it addresses many issues in reliability, including some that would fit very well with the scope of the current paper. In particular, Chapter 9 presents methods for planning the optimal collection of reliability data using genetic algorithms as computational tools. Chapter 10 discusses assurance testing to ensure that a reliability-related quantity of interest meets the given requirements; different risk criteria are considered to determine the plans. Accelerated life tests, mentioned in Chapter 7, offer opportunities to use decision analysis methods in an optimal way.
Two relevant books addressing both risk and reliability from a Bayesian viewpoint are the already cited one by Singpurwalla and Wilson [44] and one further by Singpurwalla [73]. The first book is about software testing, which was considered in Section 4. The second book is a must-read since it provides a rigourous and extensive illustration of decision theory applied to reliability, survival analysis, econometrics, and finance.
As mentioned earlier, risk is a notion related not only to reliability and finance but also to many other applied fields. A few examples are Varis and Kuikka [74] about environmental and natural resources management, Veneziano et al. [75] on seismic design of building, and Palomo et al. [76] on project management under disruptive events. For a discussion of approaches different from ours, we recommend Bedford and Cooke [30], Ben-Haim [77], Borgonovo et al. [78], and de Almeida et al. [79]. These sources are also valuable for the references therein.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P., F.R., R.S. and S.W.; Formal analysis, A.P., F.R., R.S. and S.W.; Investigation, A.P., F.R., R.S. and S.W.; Methodology, A.P., F.R., R.S. and S.W.; Writing, A.P., F.R., R.S. and S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F.; Soyer, R.; Wilson, S.P. Advances in Bayesian decision making in reliability. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 282, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, A.; Wu, P.; Mengersen, K.; Mira, A.; Datta, R.; Ruggeri, F. Fast and Likelihood-Free Parameter Estimation for Dynamic Queueing Networks. J. R. Stat. Soc. C 2021.
- Trucco, P.; Cagno, E.; Ruggeri, F.; Grande, O. A Bayesian Belief Network Approach for modelling Human and Organisational Factors Risk Analysis: A Case Study in Maritime Industry. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singpurwalla, N.D.; Wilson, S.P. Mathematics of Risk and Reliability: A Select History. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Kenett, R., Longford, N., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huygens, C. Tractatus, de ratiociniis in aleæ ludo. In Excercitationum Mathematicarum. Libri Quinque; Schooten, F., Ed.; Johannis Elsevirii: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1657. [Google Scholar]
- Bernoulli, J. Ars Conjectandi; Thurnisiorum, Fratrum: Basel, Switzerland, 1713. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, G.A. Thomas Bayes’ essay towards solving a problem in the Doctrine of Chances. Biometrika 1958, 45, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayes, T. An essay towards solving a problem in the Doctrine of Chances. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1763, 53, 370–418, Reprinted in 1958; see Barnard (1958). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, F.P. Truth and probability. In The Foundations of Mathematics and Other Logical Essays; Braithwaite, R.B., Ed.; Kegan Paul: London, UK, 1931; pp. 156–198. [Google Scholar]
- von Neumann, J.; Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. Contributions to the mathematical theory of evolution II: Skew variation in homogeneous material. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 186, 343–414. [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, W. A Statistical Theory of the Strength of Materials; Generalstabens Litografiska Anstalts Förlag: Stockholm, Sweden, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.J. An analysis of some failure data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 113–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, B.; Sobel, M. Life testing. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1953, 48, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenick, R.F. The failure law of complex equipment. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1960, 8, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, Z.W.; Esary, J.D.; Saunders, S.C. Multi-component systems and structures and their reliability. Technometrics 1961, 3, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, H.A. Launch Control Safety Study; Section VII; Bell Labs: Murray Hill, NJ, USA, 1961; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, R.; Proschan, F. Mathematical Theory of Reliability; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, R.; Proschan, F. Statistical Theory of Reliability and Life Testing, 1st ed.; Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, A. Statistical Decision Functions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot, M.H. Optimal Statistical Decisions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.O. Statistical Decision Theory and Bayesian Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- French, S.; Ríos Insua, D. Statistical Decision Theory; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- íos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F. (Eds.) Robust Bayesian Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri, F.; Ríos Insua, D.; Martín, J. Robust Bayesian analysis. In Bayesian Thinking, Modeling and Computation. Handbook of Statistics; Dey, D., Rao, C.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 25, pp. 623–667. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, J.; Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F. Issues in Bayesian loss robustness. Sankhyā Indian J. Stat. Ser. A 1998, 60, 405–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lindley, D.V. Making Decisions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bedford, T.; Cooke, R. Probabilistic Risk Analysis: Foundations and Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, D.L.; Rios, J.; Ríos Insua, D. Adversarial Risk Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzuchi, T.A.; Soyer, R. A Bayesian perspective on some replacement strategies. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1996, 51, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, R.; Hunter, L. Optimum preventive maintenance policies. Oper. Res. 1960, 8, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, J.R.; Soyer, R. Semiparametric Bayesian optimal replacement policies: Application to railroad tracks. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 2017, 33, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dorp, J.R.; Mazzuchi, T.A.; Soyer, R. Sequential inference and decision making for single mission systems development. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1997, 62, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkanli, A.; Soyer, R. Simulation-based designs for accelerated life tests. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2000, 90, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morali, N.; Soyer, R. Optimal stopping rules for software testing. Nav. Res. Logist. 2003, 50, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meeker, W.Q. Bayesian life test planning for the Weibull distribution with given shape parameter. Metrika 2005, 61, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meeker, W.Q. Bayesian methods for planning accelerated life tests. Technometrics 2006, 48, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; King, C.; Zhang, Y.; Meeker, W.Q. Bayesian life test planning for log-location-scale family of distributions. J. Qual. Technol. 2015, 47, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, N.G.; Soyer, R. Augmented probability simulation for accelerated life test design. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 2017, 33, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaid, K.; Wilson, S.P. Deciding how long to test software. Statistician 2001, 50, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenett, R.; Ruggeri, F.; Faltin, F. (Eds.) Analytic Methods in Systems and Software Testing; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Singpurwalla, N.D.; Wilson, S.P. Statistical Methods in Software Reliability: Reliability and Risk; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, A.L.; Okumoto, K. Time-dependent error detection rate model for software reliability and other performance measures. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1979, R-28, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, F.; Soyer, R. Decision models for software testing. In Analytic Methods in Systems and Software Testing; Kenett, R.S., Ruggeri, F., Faltin, F.W., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2018; pp. 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Christen, J.A.; Ruggeri, F.; Villa, E. Utility based maintenance analysis using a random sign censoring model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pievatolo, A.; Ruggeri, F. Bayesian reliability analysis of complex repairable systems. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 2004, 20, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pievatolo, A.; Ruggeri, F. Bayesian modeling of train doors’ reliability. In Handbook of Applied Bayesian Analysis; O’Hagan, A., West, M., Eds.; Oxford Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Merrick, J.R.; Soyer, R.; Mazzuchi, T.A. A Bayesian semiparametric analysis of the reliability and maintenance of machine tools. Technometrics 2003, 45, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, J.R.; Soyer, R.; Mazzuchi, T.A. Are maintenance practices for railroad tracks effective? J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2005, 100, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damien, P.; Galenko, A.; Popova, E.; Hanson, T. Bayesian semiparametric analysis for a single item maintenance optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 182, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyi, D.; Popova, E.; Morton, D.; Damien, P. Bayesian failure-rate modeling and preventive maintenance optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gaudoin, O.; Xie, M. Degradation-based maintenance decision using stochastic filtering for systems under imperfect maintenance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 245, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, H. Portfolio selection. J. Financ. 1952, 7, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, R.L.; Barry, C.B. A Bayesian model for portfolio selection and revision. J. Financ. 1975, 30, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, R.; Tanyeri, K. Bayesian portfolio selection with multi-variate random variance models. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 171, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, R.D.; Raiffa, H. Games and Decisions: Introduction and Critical Surveys; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Lindley, D.V.; Singpurwalla, N.D. On the evidence needed to reach agreed action between adversaries, with application to acceptance sampling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1991, 86, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, D.V.; Singpurwalla, N.D. Adversarial life testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1993, 55, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufo, M.; Martín, J.; Pérez, C. Adversarial life testing: A Bayesian negotiation model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 131, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singpurwalla, N.D.; Wilson, S.P. The warranty problem: Its statistical and game-theoretic aspects. SIAM Rev. 1993, 35, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singpurwalla, N.D.; Arnold, B.C.; Gastwirth, J.L.; Gordon, A.S.; Ng, H.K.T. Adversarial and amiable inference in Medical Diagnosis, Reliability and Survival Analysis. Int. Stat. Rev. 2016, 84, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadane, J.B.; Larkey, P.D. Subjective probability and the theory of games. Manag. Sci. 1982, 28, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos Insua, D.; Rios, J.; Banks, D. Adversarial risk analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2009, 104, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.; Ríos Insua, D. Adversarial risk analysis: Applications to basic counterterrorism models. In Algorithmic Decision Theory, ADT 2009; Rossi, F., Tsoukias, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ortega, J.; Soyer, R.; Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F. An adversarial risk analysis framework for batch acceptance problem. Decis. Anal. 2021, 18, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ortega, J.; Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F.; Soyer, R. Hypothesis Testing in Presence of Adversaries. Am. Stat. 2021, 75, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveiro, R.; Redondo, A.; Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F. Adversarial classification: An adversarial risk analysis approach. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2019, 113, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos Insua, D.; Cano, J.; Pellot, M.; Ortega, R. From risk analysis to adversarial risk analysis. In Current Trends in Bayesian Methodology with Applications; Upadhyay, S.K., Singh, U., Dey, D.K., Loganathan, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 313–336. [Google Scholar]
- Martz, H.F.; Waller, R.A. Bayesian Reliability Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.S.; Wilson, A.G.; Reese, C.S.; Martz, H.F. Bayesian Reliability; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Singpurwalla, N.D. Reliability and Risk: A Bayesian Perspective; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Varis, O.; Kuikka, S. Learning Bayesian decision analysis by doing: Lessons from environmental and natural resources management. Ecol. Model. 1999, 119, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziano, D.; Agarwal, A.; Karaca, E. Decision making with epistemic uncertainty under safety constraints: An application to seismic design. Probabilist. Eng. Mech. 2009, 24, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.; Ríos Insua, D.; Ruggeri, F. Modeling External Risks in Project Management. Risk Anal. 2007, 27, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Haim, Y. Info-Gap Decision Theory: Decisions under Severe Uncertainty, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Borgonovo, E.; Cappelli, V.; Maccheroni, F.; Marinacci, M. Risk analysis and decision theory: A bridge. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.T.; Cavalcante, C.A.V.; Alencar, M.H.; Ferreira, R.J.P.; de Almeida-Filho, A.T.; Garcez, T.V. Multicriteria and Multiobjective Models for Risk, Reliability and Maintenance Decision Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).