Cumulative Median Estimation for Sufficient Dimension Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sliced Inverse Regression (SIR)
2.2. Sliced Inverse Median (SIME)
2.3. Cumulative Mean Estimation (CUME)
3. Cumulative Median Estimation
Estimation Procedure
- (1)
- Standardise data to find , where is the sample mean of and is an estimate of the covariance matrix of .
- (2)
- Sort Y and then for each value of y, find the cumulative L1 median
- (3)
- Using the ’s from the previous step, estimate the candidate matrix bywhere is the range of Y, the proportion of points used to find .
- (4)
- Calculate the eigenvectors , which correspond to the largest eigenvalues of , and estimate with .
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Simulated Datasets
- (1)
- Model 1:
- (2)
- Model 2:
- (3)
- Model 3:
- (4)
- Model 4:
- (5)
- Model 5:
- (Outl a): is from multivariate standard normal.
- (Outl b): is from multivariate standard Cauchy.
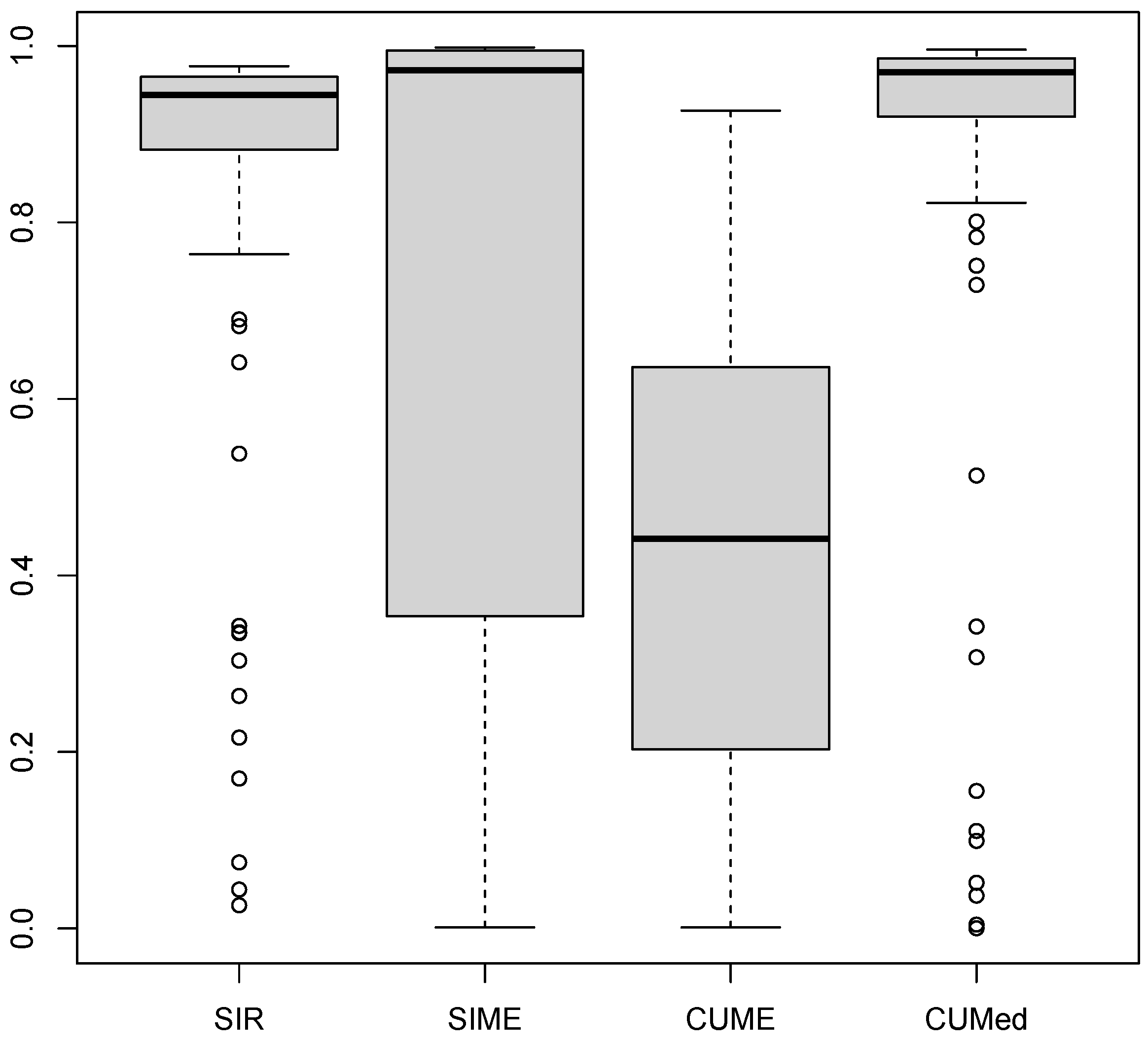
4.2. Real Data—Concrete Data
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, X.; Li, B.; Cook, R.D. Successive direction extraction for estimating the central subspace in a multiple-index regression. J. Multivar. Anal. 2008, 99, 1733–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Sufficient Dimension Reduction. Methods and Applications with R; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.-C. Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction (with discussion). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1991, 86, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.D.; Weisberg, S. Discussion of ‘’Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction”. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1991, 86, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, S. On directional regression for dimension reduction. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2007, 102, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiou, A.; Tian, L. Using slice inverse mean difference for sufficient dimension reduction. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2015, 106, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, L.P.; Zhu, L.X.; Feng, Z.H. Dimension Reduction in Regression through Cumulative Slicing Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2010, 105, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, L. Robust inverse regression for dimension reduction. J. Multivar. Anal. 2015, 134, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, E. Robust Dimension Reduction using Sliced Inverse Median Regression. Stat. Pap. 2018, 61, 1799–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babos, S.; Artemiou, A. Sliced inverse median difference regression. Stat. Methods Appl. 2020, 29, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.D. Regression Graphics: Ideas for Studying Regressions through Graphics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Croux, C.; Todorov, V.; Ruckstuhl, A.; Salibian-Barrera, M.; Verbeke, T.; Koller, M.; Conceicao, E.L.T.; di Palma, M.A. robustbase: Basic Robust Statistics R Package Version 0.93-3. 2018. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=robustbase (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Olive, D.J. Robust Multivariate Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Olive, D.J. Robust Statistics. 2020. Available online: http://parker.ad.siu.edu/Olive/robbook.htm (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Cerioli, A.; Farcomeni, A.; Riani, M. Strong consistency and robustness of the Forward Search estimator of multivariate location and scatter. J. Multivar. Anal. 2014, 126, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, I.-C. Modeling of strength of high performance concrete using artificial neural networks. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiou, A. Using adaptively weighted large margin classifiers for robust sufficient dimension reduction. Statistics 2019, 53, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xia, Y. Sliced regression for dimension reduction. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 103, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.; Xia, Y. An adaptive composite quantile approach to dimension reduction. Ann. Stat. 2014, 42, 1657–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | p | outl | SIR | SIME | CUME | CUMed |
| a | 0.997 (0.002) | 0.998 (0.002) | 0.989 (0.010) | 0.976 (0.018) | ||
| 5 | b | 0.647 (0.250) | 0.436 (0.331) | 0.479 (0.328) | 0.600 (0.173) | |
| 1 | a | 0.993 (0.004) | 0.996 (0.002) | 0.978 (0.013) | 0.949 (0.034) | |
| 10 | b | 0.520 (0.227) | 0.279 (0.356) | 0.217 (0.247) | 0.572 (0.185) | |
| a | 0.985 (0.006) | 0.992 (0.003) | 0.943 (0.025) | 0.891 (0.043) | ||
| 20 | b | 0.437 (0.249) | 0.080 (0.152) | 0.082 (0.146) | 0.515 (0.203) | |
| a | 0.962 (0.037) | 0.981 (0.014) | 0.961 (0.034) | 0.803 (0.151) | ||
| 5 | b | 0.543 (0.204) | 0.650 (0.183) | 0.493 (0.247) | 0.572 (0.139) | |
| 2 | a | 0.911 (0.039) | 0.960 (0.020) | 0.902 (0.043) | 0.638 (0.130) | |
| 10 | b | 0.329 (0.213) | 0.555 (0.133) | 0.283 (0.229) | 0.483 (0.079) | |
| a | 0.828 (0.045) | 0.910 (0.034) | 0.790 (0.063) | 0.490 (0.056) | ||
| 20 | b | 0.282 (0.183) | 0.456 (0.110) | 0.124 (0.157) | 0.399 (0.100) | |
| a | 0.998 (0.002) | 0.997 (0.002) | 0.988 (0.009) | 0.975 (0.019) | ||
| 5 | b | 0.603 (0.397) | 0.478 (0.420) | 0.405 (0.377) | 0.957 (0.076) | |
| 3 | a | 0.994 (0.003) | 0.996 (0.002) | 0.975 (0.018) | 0.951 (0.029) | |
| 10 | b | 0.563 (0.375) | 0.229 (0.361) | 0.147 (0.251) | 0.835 (0.241) | |
| a | 0.986 (0.006) | 0.993 (0.003) | 0.946 (0.027) | 0.886 (0.044) | ||
| 20 | b | 0.362 (0.354) | 0.057 (0.162) | 0.059 (0.141) | 0.774 (0.211) | |
| a | 0.906 (0.070) | 0.949 (0.030) | 0.888 (0.088) | 0.855 (0.104) | ||
| 5 | b | 0.669 (0.342) | 0.488 (0.436) | 0.357 (0.349) | 0.921 (0.174) | |
| 4 | a | 0.820 (0.090) | 0.880 (0.054) | 0.780 (0.098) | 0.691 (0.135) | |
| 10 | b | 0.539 (0.385) | 0.181 (0.298) | 0.158 (0.248) | 0.824 (0.265) | |
| a | 0.630 (0.133) | 0.791 (0.085) | 0.595 (0.127) | 0.491 (0.158) | ||
| 20 | b | 0.417 (0.368) | 0.031 (0.097) | 0.052 (0.129) | 0.751 (0.238) | |
| a | 0.935 (0.048) | 0.967 (0.019) | 0.918 (0.059) | 0.869 (0.095) | ||
| 5 | b | 0.176 (0.250) | 0.166 (0.304) | 0.259 (0.349) | 0.318 (0.337) | |
| 5 | a | 0.871 (0.076) | 0.929 (0.034) | 0.844 (0.078) | 0.741 (0.123) | |
| 10 | b | 0.136 (0.238) | 0.060 (0.151) | 0.111 (0.236) | 0.172 (0.240) | |
| a | 0.743 (0.101) | 0.871 (0.036) | 0.700 (0.100) | 0.542 (0.136) | ||
| 20 | b | 0.035 (0.074) | 0.023 (0.064) | 0.038 (0.117) | 0.066 (0.155) | |
| Median | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | outl | L1 Median | Oja |
| 1 | a | 0.955 (0.023) | 0.947 (0.044) |
| b | 0.598 (0.242) | 0.133 (0.194) | |
| 2 | a | 0.636 (0.128) | 0.586 (0.117) |
| b | 0.484 (0.063) | 0.212 (0.208) | |
| 3 | a | 0.946 (0.024) | 0.904 (0.099) |
| b | 0.835 (0.283) | 0.190 (0.354) | |
| 4 | a | 0.684 (0.169) | 0.507 (0.249) |
| b | 0.851 (0.199) | 0.249 (0.107) | |
| 5 | a | 0.754 (0.128) | 0.583 (0.285) |
| b | 0.122 (0.224) | 0.108 (0.273) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babos, S.; Artemiou, A. Cumulative Median Estimation for Sufficient Dimension Reduction. Stats 2021, 4, 138-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4010011
Babos S, Artemiou A. Cumulative Median Estimation for Sufficient Dimension Reduction. Stats. 2021; 4(1):138-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabos, Stephen, and Andreas Artemiou. 2021. "Cumulative Median Estimation for Sufficient Dimension Reduction" Stats 4, no. 1: 138-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4010011
APA StyleBabos, S., & Artemiou, A. (2021). Cumulative Median Estimation for Sufficient Dimension Reduction. Stats, 4(1), 138-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats4010011






